|
Enclosure (archaeology)
In archaeology, an enclosure is one of the most common types of archaeological site – It is any area of land separated from surrounding land by Earthworks (archaeology), earthworks, walls or fencing. Such a simple feature is found all over the world and during almost all archaeological periods. They may be few metres across or be large enough to encompass whole cities. Archaeological enclosures are typically representative of recurrent patterns of human activity throughout history through landscape. The absolute definition of archaeological enclosures has been debated over time. Some suggest that at a general level, enclosure (archaeologically) could be defined as the replacement of open-fields with privately owned-fields through walls, banks, and dividers. However, this definition has been criticised, as it appears many archaeological enclosures are not enclosed by a physical boundary. Enclosures served numerous practical purposes including being used to delineate settlement a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
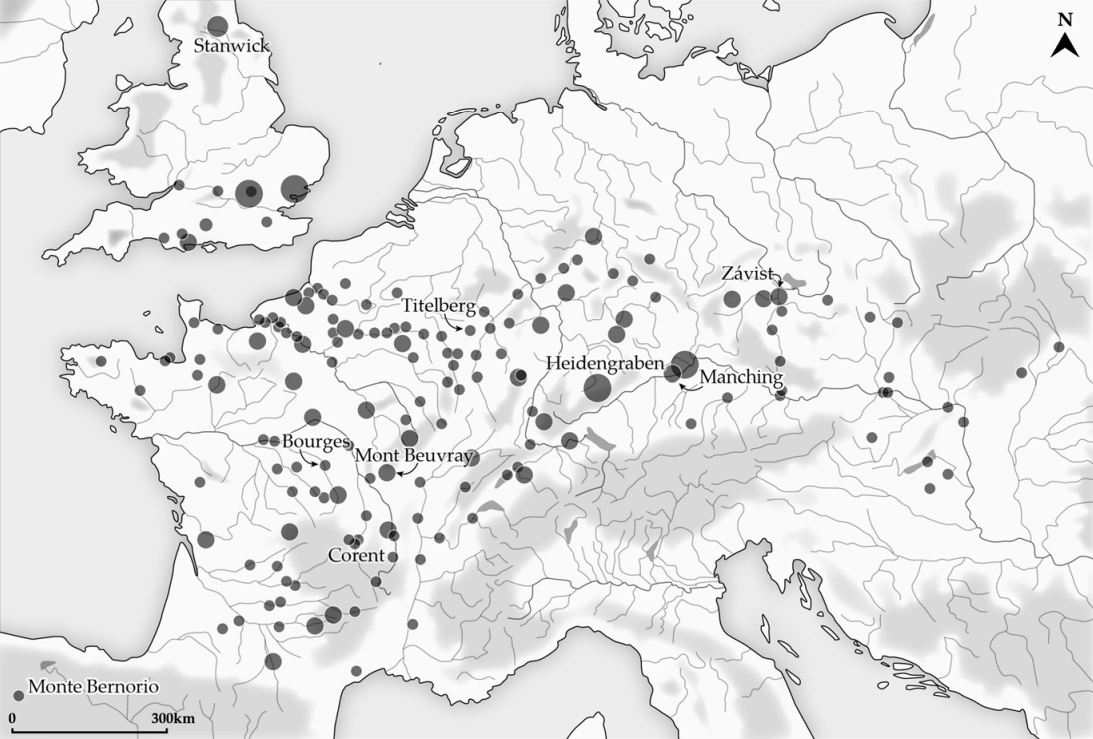
Oppida
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread across Europe, stretching from British Iron Age, Britain and Iberia in the west to the edge of the Great Hungarian Plain, Hungarian Plain in the east. These settlements continued to be used until the Romans conquered Southern and Western Europe. Many subsequently became Roman-era towns and cities, whilst others were abandoned. In regions north of the rivers Danube and Rhine, such as most of Germania, where the populations remained independent from Rome, ''oppida'' continued to be used into the 1st century AD. Definition is a Latin word meaning 'defended (fortified) administrative centre or town', originally used in reference to non-Roman towns as well as provincial towns under Roman control. The word is derived from the earlier Latin , 'encl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-penetrating Radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a geophysical method that uses radar pulses to image the subsurface. It is a non-intrusive method of surveying the sub-surface to investigate underground utilities such as concrete, asphalt, metals, pipes, cables or masonry. This nondestructive method uses electromagnetic radiation in the microwave band ( UHF/ VHF frequencies) of the radio spectrum, and detects the reflected signals from subsurface structures. GPR can have applications in a variety of media, including rock, soil, ice, fresh water, pavements and structures. In the right conditions, practitioners can use GPR to detect subsurface objects, changes in material properties, and voids and cracks. GPR uses high-frequency (usually polarized) radio waves, usually in the range 10 MHz to 2.6 GHz. A GPR transmitter and antenna emits electromagnetic energy into the ground. When the energy encounters a buried object or a boundary between materials having different permittivities, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. Lidar may operate in a fixed direction (e.g., vertical) or it may scan multiple directions, in a special combination of 3-D scanning and laser scanning. Lidar has terrestrial, airborne, and mobile applications. It is commonly used to make high-resolution maps, with applications in surveying, geodesy, geomatics, archaeology, geography, geology, geomorphology, seismology, forestry, atmospheric physics, laser guidance, airborne laser swathe mapping (ALSM), and Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter, laser altimetry. It is used to make digital 3D modeling, 3-D representations of areas on the Earth's surface and ocean bottom of the intertidal and near coastal zone by varying the wavelength of light. It has also been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraal
Kraal (also spelled ''craal'' or ''kraul'') is an Afrikaans and Dutch language, Dutch word, also used in South African English, for an pen (enclosure), enclosure for cattle or other livestock, located within a Southern African Human settlement, settlement or village surrounded by a fence of thorn-bush branches, a palisade, Earth structure, mud wall, or other fencing, roughly circular in form. It is similar to a ''Boma (enclosure), boma'' in eastern or central Africa. In Curaçao, another Dutch colony, the enclosure was called "koraal" which means coral and which in Papiamentu is translated "kura", a word still in use today for any enclosed terrain, like a garden. Etymology In the Afrikaans language a ''kraal'' is a term derived from the Portuguese language, Portuguese word , cognate with the Spanish-language , which entered into English separately. In Eastern and Central Africa, the equivalent word for a livestock enclosure is ''Boma (enclosure), boma'', but this has taken on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livestock Enclosure At Score - Geograph
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals which are raised for consumption, and sometimes used to refer solely to farmed ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, and goats. The breeding, maintenance, slaughter and general subjugation of livestock called ''animal husbandry'', is a part of modern agriculture and has been practiced in many cultures since humanity's transition to farming from hunter-gatherer lifestyles. Animal husbandry practices have varied widely across cultures and periods. It continues to play a major economic and cultural role in numerous communities. Livestock farming practices have largely shifted to intensive animal farming. Intensive animal farming increases the yield of the various commercial outputs, but also nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tel Jezreel
Tel Jezreel is an archaeological site in the eastern Jezreel Valley ( Harod Valley) in northern Israel. The ancient city of Jezreel () served as a main fortress of the Northern Kingdom of Israel under king Ahab in the 9th century BCE. Biblical references Prior to the division of the United Kingdom of Israel, the city was the hometown of Ahinoam, second wife of King David, Michal, Saul's daughter, being the first, Ahinoam being his second, and Abigail, widow of Nabal, being his third (). According to the First Book of Kings, the royal palace of King Ahab, "one of the most famous of the royal residences of the kings of Israel", was in Jezreel, adjacent to the vineyard of Naboth (). Ahab's capital remained in Samaria. According to , following the prophet Elijah's victory over the prophets of Ba'al at Mount Carmel, Elijah instructs Ahab to return home to Jezreel, where he would be reporting on events to Jezebel, his wife, but "the hand of the Lord was upon Elijah" and he rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Enclosure
In the study of the history of religions and anthropology, a sacred enclosure refers to any structure intended to separate two spaces: a sacred space and a profane space. Generally, it is a separation wall erected to mark the difference between the two spaces, acquiring significant symbolic meaning. Many human cultures have made use of sacred enclosures, found in Mesopotamia, as well as in pre-Columbian America, sub-Saharan Africa, such as in Notsé, or in Mediterranean cultures, such as Greece and Rome. The use of sacred enclosures is also a crucial aspect of the Abrahamic religions, as seen in the construction of the Temple of Jerusalem or pilgrimages such as the Hajj. In some cases, this separation is placed within a single sacred space, dividing it, as with enclosures separating people according to their gender in certain churches, mosques, and synagogues. The term refers to the structure that establishes, reinforces, or accentuates separations, but it is sometimes used m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chumash People
The Chumash are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of the central and southern coastal regions of California, in portions of what is now Kern County, California, Kern, San Luis Obispo County, California, San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara County, California, Santa Barbara, Ventura County, California, Ventura and Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles counties, extending from Morro Bay in the north to Malibu, California, Malibu in the south to Mt Pinos in the east. Their territory includes three of the Channel Islands (California), Channel Islands: Santa Cruz Island, Santa Cruz, Santa Rosa Island (California), Santa Rosa, and San Miguel Island, San Miguel; the smaller island of Anacapa Island, Anacapa was likely inhabited seasonally due to the lack of a consistent water source. Modern place names with Chumash origins include Malibu, California, Malibu, Nipomo, California, Nipomo, Lompoc, California, Lompoc, Ojai, California, Ojai, Pismo Beach, Point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysler Enclosure, Comprehensive From North
FCA US, LLC, doing business as Stellantis North America and known historically as Chrysler ( ), is one of the " Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotive company Stellantis. Stellantis North America sells vehicles worldwide under the Chrysler, Dodge, Jeep, and Ram Trucks nameplates. It also includes Mopar, its automotive parts and accessories division, and SRT, its performance automobile division. The division also distributes Alfa Romeo, Fiat, and Maserati vehicles in North America. The original Chrysler Corporation was founded in 1925 by Walter Chrysler from the remains of the Maxwell Motor Company. In 1998, it merged with Daimler-Benz, which renamed itself DaimlerChrysler but in 2007 sold off its Chrysler stake. The company operated as Chrysler LLC through 2009, then as Chrysler Group LLC. In 2014, it was acquired by Fiat S.p.A.; it subsequently operated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tor Enclosure
A tor enclosure is a type of prehistoric monument found in the southwestern part of Great Britain. These monuments emerged around 4000 BCE in the early Neolithic. Tor enclosures are large enclosures situated near natural rock outcrops, especially tors, on hilltops or the sides of hills. They consist of one or more roughly circular stone walls built around the tor. They are comparable to the causewayed enclosures found elsewhere in the British Isles and many are of similar Neolithic date although others are from later in prehistory. Examples The best known examples are Carn Brea in Cornwall, the first to be identified, following excavations in the early 1970s, and Helman Tor between Bodmin and Lostwithiel also in Cornwall. Other possible examples are: * Rough Tor on Bodmin Moor, Cornwall * Stowe's Hill, also on Bodmin Moor * Whittor on Dartmoor Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, South West England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |