Spacecraft Docking on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Docking and berthing of spacecraft is the joining of two space vehicles. This connection can be temporary, or partially permanent such as for space station modules.
''Docking'' specifically refers to joining of two separate free-flying space vehicles. ''Berthing'' refers to mating operations where a passive module/vehicle is placed into the mating interface of another space vehicle by using a
 Spacecraft docking capability depends on
Spacecraft docking capability depends on
File:Apollo-soyuz cropped.jpg, ASTP Docking Module
File:Space Shuttle docked to station - further cropped and rotated.jpg, Pressurized Mating Adapter
File:IDA attached to PMA.png, International Docking Adapter
File:1637984492234 Progress MS 17 undocking and Nauka nadir temporary docking adapter Removal 02.jpg, APAS to SSVP (SSVPA-GM) Docking Ring
 For the first fifty years of spaceflight, the main objective of most ''docking'' and ''berthing'' missions was to transfer crew, construct or resupply a space station, or to test for such a mission (e.g. the docking between Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188). Therefore, commonly at least one of the participating spacecraft was crewed, with a pressurized habitable volume (e.g. a space station or a lunar lander) being the target—the exceptions were a few fully uncrewed Soviet docking missions (e.g. the dockings of Kosmos 1443 and Progress 23 to an uncrewed
For the first fifty years of spaceflight, the main objective of most ''docking'' and ''berthing'' missions was to transfer crew, construct or resupply a space station, or to test for such a mission (e.g. the docking between Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188). Therefore, commonly at least one of the participating spacecraft was crewed, with a pressurized habitable volume (e.g. a space station or a lunar lander) being the target—the exceptions were a few fully uncrewed Soviet docking missions (e.g. the dockings of Kosmos 1443 and Progress 23 to an uncrewed
 Non-cooperative rendezvous and capture techniques have been theorized, and one mission has successfully been performed with uncrewed spacecraft in orbit.
A typical approach for solving this problem involves two phases. First,
Non-cooperative rendezvous and capture techniques have been theorized, and one mission has successfully been performed with uncrewed spacecraft in orbit.
A typical approach for solving this problem involves two phases. First,
 Docking has been discussed by NASA in regards to a Crewed Mars rover, such as with Mars habitat or ascent stage. The Martian surface vehicle (and surface habitats) would have a large rectangular docking hatch, approximately .
Docking has been discussed by NASA in regards to a Crewed Mars rover, such as with Mars habitat or ascent stage. The Martian surface vehicle (and surface habitats) would have a large rectangular docking hatch, approximately .
ISS undocking - Timelapse 01 - 20180328 034651 547.gif, Timelapse of undocking of a
robotic arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by join ...
. Because the modern process of un-berthing requires more crew labor and is time-consuming, berthing operations are unsuited for rapid crew evacuations in the event of an emergency.
History
Docking
 Spacecraft docking capability depends on
Spacecraft docking capability depends on space rendezvous
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions. Modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless ...
, the ability of two spacecraft to find each other and station-keep in the same orbit. This was first developed by the United States for Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was the second United States human spaceflight program to fly. Conducted after the first American crewed space program, Project Mercury, while the Apollo program was still in early development, Gemini was conceived in 1961 and ...
. It was planned for the crew of Gemini 6
Gemini 6A (officially Gemini VI-A) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed United States spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program.
The mission, flown by Wally Schirra and Thomas P. Stafford ...
to rendezvous and manually dock under the command of Wally Schirra
Walter Marty Schirra Jr. ( ; March 12, 1923 – May 3, 2007) was an American naval aviator (United States), naval aviator, test pilot, and NASA astronaut. In 1959, he became one of the Mercury Seven, original seven astronauts chosen for Pro ...
, with an uncrewed Agena Target Vehicle
The Agena Target Vehicle (; ATV), also known as Gemini-Agena Target Vehicle (GATV), was an uncrewed spacecraft used by NASA during its Gemini program to develop and practice orbital space rendezvous and docking techniques, and to perform large ...
in October 1965, but the Agena vehicle exploded during launch. On the revised mission Gemini 6A, Schirra successfully performed a rendezvous in December 1965 with the crewed Gemini 7
Gemini 7 (officially Gemini VII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was a 1965 crewed spaceflight in NASA's Gemini program. It was the fourth crewed Gemini flight, the twelfth crewed American spacef ...
, approaching to within , but there was no docking capability between two Gemini spacecraft. The first docking with an Agena was successfully performed under the command of Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aerospace engineering, aeronautical engineer who, in 1969, became the Apollo 11#Lunar surface operations, first person to walk on the Moon. He was al ...
on Gemini 8
Gemini 8 (officially Gemini VIII) With Gemini IV, NASA changed to Roman numerals for Gemini mission designations. was the sixth crewed spaceflight in NASA's Project Gemini, Gemini program. It was launched on March 16, 1966, and was the 14th crew ...
on March 16, 1966. Manual dockings were performed on three subsequent Gemini missions in 1966.
The Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
depended on lunar orbit rendezvous
Lunar orbit rendezvous (LOR) is a process for landing humans on the Moon and returning them to Earth. It was utilized for the Apollo program missions in the 1960s and 1970s. In a LOR mission, a main spacecraft and a lunar lander travel to lunar or ...
to achieve its objective of landing men on the Moon. This required first a transposition, docking, and extraction
Transposition, docking, and extraction (often abbreviated to transposition and docking) was a maneuver performed during Apollo lunar landing missions from 1969 to 1972, to withdraw the Apollo Lunar Module (LM) from its adapter housing which se ...
maneuver between the Apollo command and service module
The Apollo command and service module (CSM) was one of two principal components of the United States Apollo (spacecraft), Apollo spacecraft, used for the Apollo program, which landed astronauts on the Moon between 1969 and 1972. The CSM functi ...
(CSM) mother spacecraft and the Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed s ...
(LM) landing spacecraft, shortly after both craft were sent out of Earth orbit on a path to the Moon. Then after completing the lunar landing mission, two astronauts in the LM had to rendezvous and dock with the CSM in lunar orbit, in order to be able to return to Earth. The spacecraft were designed to permit intra-vehicular crew transfer through a tunnel between the nose of the Command Module and the roof of the Lunar Module. These maneuvers were first demonstrated in low Earth orbit
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an geocentric orbit, orbit around Earth with a orbital period, period of 128 minutes or less (making at least 11.25 orbits per day) and an orbital eccentricity, eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the artificial object ...
on March 7, 1969, on Apollo 9
Apollo 9 (March 3–13, 1969) was the third human spaceflight in NASA's Apollo program, which successfully tested systems and procedures critical to landing on the Moon. The three-man crew consisted of Commander James McDivitt, Command Modul ...
, then in lunar orbit in May 1969 on Apollo 10
Apollo 10 (May 18–26, 1969) was the fourth human spaceflight in the United States' Apollo program and the second to orbit the Moon. NASA, the mission's operator, described it as a "dress rehearsal" for the first Moon landing (Apollo 11, two ...
, then in six lunar landing missions, as well as on Apollo 13
Apollo 13 (April 1117, 1970) was the seventh crewed mission in the Apollo program, Apollo space program and would have been the third Moon landing. The craft was launched from Kennedy Space Center on April 11, 1970, but the landing was abort ...
where the LM was used as a rescue vehicle instead of making a lunar landing.
Unlike the United States, which used manual piloted docking throughout the Apollo, Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructe ...
, and Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
programs, the Soviet Union employed automated docking systems from the beginning of its docking attempts. The first such system, Igla, was successfully tested on October 30, 1967, when the two uncrewed Soyuz
Soyuz is a transliteration of the Cyrillic text Союз (Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, 'Union'). It can refer to any union, such as a trade union (''profsoyuz'') or the Soviet Union, Union of Soviet Socialist Republi ...
test vehicles Kosmos 186
Kosmos 186 ( meaning ''Cosmos 186'') and Kosmos 188 ( meaning ''Cosmos 188'') were two uncrewed Soviet Union spacecraft that incorporated a Soyuz programme descent module for landing scientific instruments and test objects.
Mission
Because ...
and Kosmos 188 docked automatically in orbit. This was the first successful Soviet docking. Proceeding to crewed docking attempts, the Soviet Union first achieved rendezvous of Soyuz 3
Soyuz 3 (, ''Union 3'') was a spaceflight mission launched by the Soviet Union on 26 October 1968. Flown by Georgy Beregovoy, the Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft completed 81 orbits over four days. The 47-year-old Beregovoy was a decorated World War ...
with the uncrewed Soyuz 2
Soyuz 2 (, Union 2) was an uncrewed spacecraft (capsule number 7K-OK-P No. 11)Soyuz-2 co ...
craft on October 25, 1968; docking was unsuccessfully attempted. The first crewed docking was achieved on January 16, 1969, between Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5. This early version of the Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
had no internal transfer tunnel, but two cosmonauts performed an extravehicular transfer from Soyuz 5 to Soyuz 4, landing in a different spacecraft than they had launched in.
In the 1970s, the Soviet Union upgraded the Soyuz spacecraft to add an internal transfer tunnel and used it to transport cosmonauts during the Salyut
The ''Salyut'' programme (, , meaning "salute" or "fireworks") was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissa ...
space station program with the first successful space station visit beginning on 7 June 1971, when Soyuz 11
Soyuz 11 () was the only crewed mission to board the world's first space station, Salyut 1. The crew, Georgy Dobrovolsky, Vladislav Volkov, and Viktor Patsayev, arrived at the space station on 7 June 1971, and departed on 29 June 1971. The ...
docked to Salyut 1
Salyut 1 (), also known as DOS-1 (Durable Orbital Station 1), was the world's first space station. It was launched into low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1971. The Salyut programme, ''Salyut'' program subsequently achieved five m ...
. The United States followed suit, docking its Apollo spacecraft to the Skylab
Skylab was the United States' first space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three trios of astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Skylab was constructe ...
space station in May 1973. In July 1975, the two nations cooperated in the Apollo-Soyuz Test Project, docking an Apollo spacecraft with a Soyuz using a specially designed docking module to accommodate the different docking systems and spacecraft atmospheres.
Beginning with Salyut 6
Salyut 6 () was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth station of the Salyut programme, and alternatively known DOS-5 as it was the fifth of the Durable Orbital Station series of civilian space stations. It was launched on 29 September 19 ...
in 1978, the Soviet Union began using the uncrewed Progress
Progress is movement towards a perceived refined, improved, or otherwise desired state. It is central to the philosophy of progressivism, which interprets progress as the set of advancements in technology, science, and social organization effic ...
cargo spacecraft to resupply its space stations in low earth orbit, greatly extending the length of crew stays. As an uncrewed spacecraft, Progress rendezvoused and docked with the space stations entirely automatically. In 1986, the Igla docking system was replaced with the updated Kurs system on Soyuz spacecraft. Progress spacecraft received the same upgrade several years later. The Kurs system is still used to dock to the Russian Orbital Segment
The Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) is the name given to the components of the International Space Station (ISS) constructed in Russia and operated by the Russian Roscosmos. The ROS handles Guidance, Navigation, and Control for the entire Station ...
of the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
.
Berthing
Berthing of spacecraft can be traced at least as far back as the berthing of payloads into the Space Shuttle payload bay. Such payloads could be either free-flying spacecraft captured for maintenance/return, or payloads temporarily exposed to the space environment at the end of theRemote Manipulator System
Canadarm or Canadarm1 (officially Shuttle Remote Manipulator System or SRMS, also SSRMS) is a series of robotic arms that were used on the Space Shuttle orbiters to deploy, manoeuvre, and capture payloads. After the Space Shuttle ''Columbia' ...
. Several different berthing mechanisms were used during the Space Shuttle era. Some of them were features of the Payload Bay (e.g., the Payload Retention Latch Assembly), while others were airborne support equipment (e.g., the Flight Support Structure used for HST servicing missions).
Hardware
Androgyny
Docking/berthing systems may be either androgynous ( ungendered) or non-androgynous ( gendered), indicating which parts of the system may mate together. Early systems for conjoining spacecraft were all non-androgynous docking system designs. Non-androgynous designs are a form of ''gender mating'' where each spacecraft to be joined has a unique design (male or female) and a specific role to play in the docking process. The roles cannot be reversed. Furthermore, two spacecraft of the same gender cannot be joined at all. Androgynous docking (and later androgynous berthing) by contrast has an identical interface on both spacecraft. In an androgynous interface, there is a single design which can connect to a duplicate of itself. This allows system-level redundancy (role reversing) as well as rescue and collaboration between any two spacecraft. It also provides more flexible mission design and reduces unique mission analysis and training.List of mechanisms/systems
Adapters
A docking or berthing adapter is a mechanical or electromechanical device that facilitates the connection of one type of docking or berthing interface to a different interface. Such interfaces may be docking/docking, docking/berthing, or berthing/berthing. Previously launched and planned to be launched adapters are listed below: * ASTP Docking Module: An airlock module that converted U.S. Probe and Drogue to APAS-75. Built byRockwell International
Rockwell International was a major American manufacturing conglomerate (company), conglomerate. It was involved in aircraft, the space industry, defense and commercial electronics, components in the automotive industry, printing presses, avioni ...
for the 1975 Apollo–Soyuz Test Project
Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international space mission, carried out jointly by the United States and the Soviet Union in July 1975. Millions of people around the world watched on television as an American Apollo spacecraft docked wit ...
mission.
* Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA): Converts an active Common Berthing Mechanism
The Common Mechanism (CBM) connects habitable elements in the US Orbital Segment (USOS) of the International Space Station (ISS). The CBM has two distinct sides that, once mated, form a cylindrical wiktionary:vestibule, vestibule between modules ...
to APAS-95
The terms Androgynous Peripheral Attach System (APAS), Androgynous Peripheral Assembly System (APAS) and Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS) are used interchangeably to describe a Russian family of spacecraft docking mechanisms, and are ...
. Three PMAs are attached to the ISS, PMA-1 and PMA-2 were launched in 1998 on STS-88
STS-88 was the first Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was flown by Space Shuttle Space Shuttle Endeavour, ''Endeavour'', and took the first American module, the Unity (ISS module), ''Unity'' node, to the station ...
, PMA-3 in late 2000 on STS-92
STS-92 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery''. STS-92 marked the 100th mission of the Space Shuttle and Discovery's 28th flight. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Flori ...
. PMA-1 is used to connect the Zarya control module with Unity node 1, Space Shuttles used PMA-2 and PMA-3 for docking.
* International Docking Adapter (IDA): Converts APAS-95
The terms Androgynous Peripheral Attach System (APAS), Androgynous Peripheral Assembly System (APAS) and Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS) are used interchangeably to describe a Russian family of spacecraft docking mechanisms, and are ...
to the International Docking System Standard. IDA-1 was planned to be launched on SpaceX CRS-7 until its launch failure, and attached to Node-2's forward PMA. IDA-2 was launched on SpaceX CRS-9
SpaceX CRS-9, also known as SpX-9, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station which launched on 18 July 2016. The mission was contracted by NASA and was operated by SpaceX using a Dragon capsule.
The cargo ...
and attached to Node-2's forward PMA. IDA-3, the replacement for IDA-1 launched on SpaceX CRS-18 and attached to Node-2's zenith PMA. The adapter is compatible with the International Docking System Standard (IDSS), which is an attempt by the ISS Multilateral Coordination Board to create a docking standard.
*SSPA-GM: Converts passive SSVP-M8000 (Hybrid Docking System) to passive SSVP-G4000. The docking ring initially used for Soyuz MS-18 and Progress MS-17 docking on Nauka until detached by Progress MS-17 for Prichal module arrived on ISS. It was made for the Nauka nadir and Prichal nadir ports of the International Space Station, where Soyuz and Progress spacecraft had to dock to a port designated for modules. Before removal of SSPA-GM, the docking ring is in diameter; that becomes after removal.
Docking of uncrewed spacecraft
 For the first fifty years of spaceflight, the main objective of most ''docking'' and ''berthing'' missions was to transfer crew, construct or resupply a space station, or to test for such a mission (e.g. the docking between Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188). Therefore, commonly at least one of the participating spacecraft was crewed, with a pressurized habitable volume (e.g. a space station or a lunar lander) being the target—the exceptions were a few fully uncrewed Soviet docking missions (e.g. the dockings of Kosmos 1443 and Progress 23 to an uncrewed
For the first fifty years of spaceflight, the main objective of most ''docking'' and ''berthing'' missions was to transfer crew, construct or resupply a space station, or to test for such a mission (e.g. the docking between Kosmos 186 and Kosmos 188). Therefore, commonly at least one of the participating spacecraft was crewed, with a pressurized habitable volume (e.g. a space station or a lunar lander) being the target—the exceptions were a few fully uncrewed Soviet docking missions (e.g. the dockings of Kosmos 1443 and Progress 23 to an uncrewed Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (), also known as DOS-6 (Durable Orbital Station 6) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Va ...
or Progress M1-5 to an uncrewed ''Mir
''Mir'' (, ; ) was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, first by the Soviet Union and later by the Russia, Russian Federation. ''Mir'' was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to ...
''). Another exception were a few missions of the crewed US Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
s, like berthings of the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
(HST) during the five HST servicing missions. The Japanese ETS-VII
The ETS-VII, or Engineering Test Satellite No. 7, was a satellite developed and launched by the National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). It is also known as KIKU-7. It was launched aboard an H-II rocket from Tanegashima Space Center, ...
mission (nicknamed ''Hikoboshi'' and ''Orihime'') in 1997 was designed to test uncrewed rendezvous and docking, but launched as one spacecraft which separated to join back together.
Changes to the crewed aspect began in 2015, as a number of economically driven commercial dockings of uncrewed spacecraft were planned. In 2011, two commercial spacecraft providers announced plans to provide autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defi ...
/ teleoperated uncrewed resupply spacecraft
Uncrewed spacecraft or robotic spacecraft are spacecraft without people on board. Uncrewed spacecraft may have varying levels of autonomy from human input, such as remote control, or remote guidance. They may also be autonomous, in which they ...
for servicing other uncrewed spacecraft. Notably, both of these servicing spacecraft were intending to dock with satellites that weren't designed for docking, nor for in-space servicing.
The early business model for these services was primarily in near-geosynchronous
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital ...
orbit, although large delta-v orbital maneuver
In spaceflight, an orbital maneuver (otherwise known as a burn) is the use of propulsion systems to change the orbit of a spacecraft.
For spacecraft far from Earth, an orbital maneuver is called a ''deep-space maneuver (DSM)''.
When a spacec ...
ing services were also envisioned.
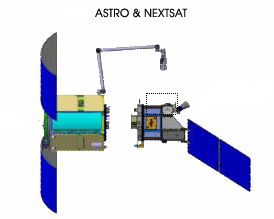
Building off of the 2007 Orbital Express
Orbital Express: ASTRO and NEXTSat
Orbital Express was a space mission managed by the United States Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) and a team led by engineers at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). The Orbital Express p ...
mission—a U.S. government
The Federal Government of the United States of America (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States.
The U.S. federal government is composed of three distinct branches: legislative, executi ...
-sponsored mission to test in-space satellite servicing with two vehicles designed from the ground up for on-orbit refueling and subsystem replacement—two companies announced plans for commercial satellite servicing missions that would require docking of two uncrewed vehicles.
* Space Infrastructure Servicing (SIS) is a spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
that was being developed by Canadian
Canadians () are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''C ...
aerospace firm MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates
MDA Space Ltd. is a Canadian space technology company headquartered in Brampton, Ontario, Canada, that provides geointelligence, robotics and space operations, and satellite systems.
History
MDA Space (formerly MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associat ...
(MDA)—maker of Canadarm
Canadarm or Canadarm1 (officially Shuttle Remote Manipulator System or SRMS, also SSRMS) is a series of robotic arms that were used on the Space Shuttle orbiters to deploy, manoeuvre, and capture payloads. After the Space Shuttle ''Columbia' ...
—to operate as a small-scale in-space refueling depot for communication satellites in geosynchronous orbit
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4 seconds (one sidereal day). The synchronization of rotation and orbital ...
. Intelsat
Intelsat S.A. (formerly Intel-Sat, Intelsat) is a Luxembourgish-American multinational satellite services provider with corporate headquarters in Luxembourg and administrative headquarters in Tysons, Virginia, United States. Originally formed ...
was a requirements
In engineering, a requirement is a condition that must be satisfied for the output of a work effort to be acceptable. It is an explicit, objective, clear and often quantitative description of a condition to be satisfied by a material, design, pro ...
and funding
Funding is the act of providing resources to finance a need, program, or project. While this is usually in the form of money, it can also take the form of effort or time from an organization or company. Generally, this word is used when a firm use ...
partner for the initial demonstration satellite, intended for launch in 2015.
* Mission Extension Vehicle
The Mission Extension Vehicle (MEV) is a spacecraft that extends the functional lifetime of another spacecraft through on-orbit satellite servicing. They are 2010s-design small-scale in-space satellite-refueling spacecraft first launched in 20 ...
(MEV) was a spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
being developed in 2011 by the U.S. firm ViviSat, a 50/50 joint venture of aerospace firms U.S. Space and ATK, to operate as a small-scale in-space satellite-refueling spacecraft.
MEV would dock but would not transfer fuel. Rather it would use " its own thrusters to supply attitude control
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle or satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, ...
for the target."
The SIS and MEV vehicles each planned to use a different docking technique.
SIS planned to utilize a ring attachment around the kick motor
while the Mission Extension Vehicle would use a somewhat more standard insert-a-probe-into-the-nozzle-of-the-kick-motor approach.
A prominent spacecraft that received a mechanism for uncrewed dockings is the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
(HST). In 2009 the STS-125
STS-125, or HST-SM4 (Hubble Space Telescope Servicing Mission 4), was the fifth and final Space Shuttle mission to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
The launch of the Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' occurred on May 11, 2009, at 2:01 pm EDT. Land ...
shuttle mission added the Soft-Capture Mechanism (SCM) at the aft bulkhead of the space telescope. The SCM is meant for unpressurized dockings and will be used at the end of Hubble's service lifetime to dock an uncrewed spacecraft to de-orbit Hubble. The SCM used was designed to be compatible to the NASA Docking System
The NASA Docking System is NASA's implementation of the International Docking System Standard (IDSS), an international spacecraft docking standard promulgated by the International Space Station Multilateral Coordination Board. NDS is a Docking an ...
(NDS) interface to reserve the possibility of a servicing mission.
The SCM will, compared to the system used during the five HST Servicing Missions to capture and berth the HST to the Space Shuttle,
significantly reduce the rendezvous and capture design complexities associated with such missions. The NDS bears some resemblance to the APAS-95 mechanism, but is not compatible with it.
Non-cooperative docking
Docking with a spacecraft (or other human made space object) that does not have an operable attitude control system might sometimes be desirable, either in order to salvage it, or to initiate a controlled de-orbit. Some theoretical techniques for docking with non-cooperative spacecraft have been proposed so far. Yet, with the sole exception of the Soyuz T-13 mission to salvage the crippledSalyut 7
Salyut 7 (), also known as DOS-6 (Durable Orbital Station 6) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Va ...
space station, , all spacecraft dockings in the first fifty years of spaceflight had been accomplished with vehicles where both spacecraft involved were under either piloted, autonomous or telerobotic attitude control
Spacecraft attitude control is the process of controlling the orientation of a spacecraft (vehicle or satellite) with respect to an inertial frame of reference or another entity such as the celestial sphere, certain fields, and nearby objects, ...
.
In 2007, however, a demonstration mission was flown that included an initial test
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film) ...
of a non-cooperative spacecraft captured by a controlled spacecraft with the use of a robotic arm.
Research and modeling work continues to support additional autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy is the capacity to make an informed, uncoerced decision. Autonomous organizations or institutions are independent or self-governing. Autonomy can also be defi ...
noncooperative capture missions in the coming years.
Salyut 7 space station salvage mission
Salyut 7
Salyut 7 (), also known as DOS-6 (Durable Orbital Station 6) was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Va ...
, the tenth space station of any kind launched, and Soyuz T-13 were docked in what author David S. F. Portree describes as "one of the most impressive feats of in-space repairs in history". Solar tracking failed and due to a telemetry fault the station did not report the failure to mission control while flying autonomously. Once the station ran out of electrical energy reserves it ceased communication abruptly in February 1985. Crew scheduling was interrupted to allow Soviet military commander Vladimir Dzhanibekov
Vladimir Aleksandrovich Dzhanibekov (, born 13 May 1942) is a retired Soviet Air Force Major General and a cosmonaut veteran of five orbital missions.
Biography
Dzhanibekov was born Vladimir Aleksandrovich Krysin () in the remote area of Iskand ...
and technical science flight engineer Viktor Savinykh to make emergency repairs.
All Soviet and Russian space stations were equipped with automatic rendezvous and docking systems, from the first space station Salyut 1 using the IGLA system, to the Russian Orbital Segment
The Russian Orbital Segment (ROS) is the name given to the components of the International Space Station (ISS) constructed in Russia and operated by the Russian Roscosmos. The ROS handles Guidance, Navigation, and Control for the entire Station ...
of the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
using the Kurs system. The Soyuz crew found the station was not broadcasting radar or telemetry for rendezvous, and after arrival and external inspection of the tumbling station, the crew judged proximity using handheld laser rangefinders.
Dzhanibekov piloted his ship to intercept the forward port of Salyut 7, matched the station's rotation and achieved soft dock with the station. After achieving hard dock they confirmed that the station's electrical system was dead. Prior to opening the hatch, Dzhanibekov and Savinykh sampled the condition of the station's atmosphere and found it satisfactory. Attired in winter fur-lined clothing, they entered the cold station to conduct repairs. Within a week sufficient systems were brought back online to allow robot cargo ships to dock with the station. Nearly two months went by before atmospheric conditions on the space station were normalized.
Uncrewed dockings of non-cooperative space objects
 Non-cooperative rendezvous and capture techniques have been theorized, and one mission has successfully been performed with uncrewed spacecraft in orbit.
A typical approach for solving this problem involves two phases. First,
Non-cooperative rendezvous and capture techniques have been theorized, and one mission has successfully been performed with uncrewed spacecraft in orbit.
A typical approach for solving this problem involves two phases. First, attitude
Attitude or Attitude may refer to:
Philosophy and psychology
* Attitude (psychology), a disposition or state of mind
** Attitude change
* Propositional attitude, a mental state held towards a proposition
Science and technology
* Orientation ...
and orbital changes are made to the "chaser" spacecraft until it has zero relative motion with the "target" spacecraft. Second, docking maneuvers commence that are similar to traditional cooperative spacecraft docking. A standardized docking interface on each spacecraft is assumed.
NASA has identified automated and autonomous rendezvous and docking — the ability of two spacecraft to rendezvous and dock "operating independently from human controllers and without other back-up, nd which requires technologyadvances in sensors, software, and realtime
Real-time, realtime, or real time may refer to:
Computing
* Real-time computing, hardware and software systems subject to a specified time constraint
* Real-time clock, a computer clock that keeps track of the current time
* Real-time Control Syst ...
on-orbit positioning and flight control, among other challenges" — as a critical technology to the "ultimate success of capabilities such as in-orbit propellant storage and refueling," and also for complex operations in assembling mission components for interplanetary destinations.
The Automated/Autonomous Rendezvous & Docking Vehicle (ARDV) is a proposed NASA Flagship Technology Demonstration (FTD) mission, for flight as early as 2014/2015. An important NASA objective on the proposed mission is to advance the technology and demonstrate automated rendezvous and docking. One mission element defined in the 2010 analysis was the development of a laser proximity operations sensor that could be used for non-cooperative vehicles at distances between and . Non-cooperative docking mechanisms were identified as critical mission elements to the success of such autonomous missions.
Grappling
Grappling is a fighting technique based on throws, trips, sweeps, clinch fighting, ground fighting and submission holds.
Grappling contests often involve takedowns and ground control, and may end when a contestant concedes defeat. Shou ...
and connecting to non-cooperative space objects was identified as a top technical challenge in the 2010 NASA Robotics, tele-robotics and autonomous systems roadmap.
Docking states
A docking/berthing connection is referred to as either "soft" or "hard". Typically, a spacecraft first initiates a ''soft dock'' by making contact and latching its docking connector with that of the target vehicle. Once the soft connection is secured, if both spacecraft are pressurized, they may proceed to a ''hard dock'' where the docking mechanisms form an airtight seal, enabling interior hatches to be safely opened so that crew and cargo can be transferred.Berthing spacecraft and modules
Docking and undocking describe spacecraft using a docking port, without assistance and under their own power. Berthing takes place when a spacecraft or unpowered module cannot use a docking port or requires assistance to use one. This assistance may come from a spacecraft, such as when theSpace Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable launch system, reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. ...
used its robotic arm to push ISS modules into their permanent berths. In a similar fashion the Poisk module was permanently berthed to a docking port after it was pushed into place by a modified Progress spacecraft which was then discarded. The Cygnus resupply spacecraft arriving at the ISS does not connect to a docking port, instead it is pulled into a berthing mechanism by the station's robotic arm and the station then closes the connection. The berthing mechanism is used only on the US segment of the ISS, the Russian segment of the ISS uses docking ports for permanent berths.
Mars surface docking
 Docking has been discussed by NASA in regards to a Crewed Mars rover, such as with Mars habitat or ascent stage. The Martian surface vehicle (and surface habitats) would have a large rectangular docking hatch, approximately .
Docking has been discussed by NASA in regards to a Crewed Mars rover, such as with Mars habitat or ascent stage. The Martian surface vehicle (and surface habitats) would have a large rectangular docking hatch, approximately .
Gallery
Soyuz spacecraft
Soyuz () is a series of spacecraft which has been in service since the 1960s, having made more than 140 flights. It was designed for the Soviet space program by the Korolev Design Bureau (now Energia). The Soyuz succeeded the Voskhod spacecraf ...
from the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United ...
References
{{Spacecraft Docking Systems Space rendezvous Spacecraft components