|
Orbit (dynamics)
In mathematics, specifically in the study of dynamical systems, an orbit is a collection of points related by the evolution function of the dynamical system. It can be understood as the subset of phase space covered by the trajectory of the dynamical system under a particular set of initial conditions, as the system evolves. As a phase space trajectory is uniquely determined for any given set of phase space coordinates, it is not possible for different orbits to intersect in phase space, therefore the set of all orbits of a dynamical system is a partition of the phase space. Understanding the properties of orbits by using topological methods is one of the objectives of the modern theory of dynamical systems. For discrete-time dynamical systems, the orbits are sequences; for real dynamical systems, the orbits are curves; and for holomorphic dynamical systems, the orbits are Riemann surfaces. Definition Given a dynamical system (''T'', ''M'', Φ) with ''T'' a group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Number
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like Number (sports), jersey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space
The phase space of a physical system is the set of all possible physical states of the system when described by a given parameterization. Each possible state corresponds uniquely to a point in the phase space. For mechanical systems, the phase space usually consists of all possible values of the position and momentum parameters. It is the direct product of direct space and reciprocal space. The concept of phase space was developed in the late 19th century by Ludwig Boltzmann, Henri Poincaré, and Josiah Willard Gibbs. Principles In a phase space, every degree of freedom or parameter of the system is represented as an axis of a multidimensional space; a one-dimensional system is called a phase line, while a two-dimensional system is called a phase plane. For every possible state of the system or allowed combination of values of the system's parameters, a point is included in the multidimensional space. The system's evolving state over time traces a path (a phase-spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Space Method
Phase or phases may refer to: Science *State of matter, or phase, one of the distinct forms in which matter can exist *Phase (matter), a region of space throughout which all physical properties are essentially uniform *Phase space, a mathematical space in which each possible state of a physical system is represented by a point also referred to as a "microscopic state" **Phase space formulation, a formulation of quantum mechanics in phase space *Phase (waves), the position of a point in time (an instant) on a waveform cycle **Instantaneous phase, generalization for both cyclic and non-cyclic phenomena *AC phase, the phase offset between alternating current electric power in multiple conducting wires **Single-phase electric power, distribution of AC electric power in a system where the voltages of the supply vary in unison **Three-phase electric power, a common method of AC electric power generation, transmission, and distribution *Phase problem, the loss of information (the phase) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wandering Set
In dynamical systems and ergodic theory, the concept of a wandering set formalizes a certain idea of movement and mixing. When a dynamical system has a wandering set of non-zero measure, then the system is a dissipative system. This is the opposite of a conservative system, to which the Poincaré recurrence theorem applies. Intuitively, the connection between wandering sets and dissipation is easily understood: if a portion of the phase space "wanders away" during normal time-evolution of the system, and is never visited again, then the system is dissipative. The language of wandering sets can be used to give a precise, mathematical definition to the concept of a dissipative system. The notion of wandering sets in phase space was introduced by Birkhoff in 1927. Wandering points A common, discrete-time definition of wandering sets starts with a map f:X\to X of a topological space ''X''. A point x\in X is said to be a wandering point if there is a neighbourhood ''U'' of ''x'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Equilibrium Point
In the study of dynamical systems, a hyperbolic equilibrium point or hyperbolic fixed point is a fixed point that does not have any center manifolds. Near a hyperbolic point the orbits of a two-dimensional, non-dissipative system resemble hyperbolas. This fails to hold in general. Strogatz notes that "hyperbolic is an unfortunate name—it sounds like it should mean 'saddle point'—but it has become standard." Several properties hold about a neighborhood of a hyperbolic point, notably * A stable manifold and an unstable manifold exist, * Shadowing occurs, * The dynamics on the invariant set can be represented via symbolic dynamics, * A natural measure can be defined, * The system is structurally stable. Maps If T \colon \mathbb^ \to \mathbb^ is a ''C''1 map and ''p'' is a fixed point then ''p'' is said to be a hyperbolic fixed point when the Jacobian matrix \operatorname T (p) has no eigenvalues on the complex unit circle. One example of a map whose only fixed point is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitive Dependence On Initial Conditions
In chaos theory, the butterfly effect is the sensitive dependence on initial conditions in which a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state. The term is closely associated with the work of the mathematician and meteorologist Edward Norton Lorenz. He noted that the butterfly effect is derived from the example of the details of a tornado (the exact time of formation, the exact path taken) being influenced by minor perturbations such as a distant butterfly flapping its wings several weeks earlier. Lorenz originally used a seagull causing a storm but was persuaded to make it more poetic with the use of a butterfly and tornado by 1972. He discovered the effect when he observed runs of his weather model with initial condition data that were rounded in a seemingly inconsequential manner. He noted that the weather model would fail to reproduce the results of runs with the unrounded initial condition data. A very sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Theory
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of Scientific method, scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and Deterministic system, deterministic Scientific law, laws of dynamical systems that are highly sensitive to initial conditions. These were once thought to have completely random states of disorder and irregularities. Chaos theory states that within the apparent randomness of chaotic complex systems, there are underlying patterns, interconnection, constant feedback loops, repetition, self-similarity, fractals and self-organization. The butterfly effect, an underlying principle of chaos, describes how a small change in one state of a deterministic nonlinear system can result in large differences in a later state (meaning there is sensitive dependence on initial conditions). A metaphor for this behavior is that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can cause or prevent a tornado in Texas. Text was copied from this source, which is avai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limit (mathematics)
In mathematics, a limit is the value that a function (or sequence) approaches as the argument (or index) approaches some value. Limits of functions are essential to calculus and mathematical analysis, and are used to define continuity, derivatives, and integrals. The concept of a limit of a sequence is further generalized to the concept of a limit of a topological net, and is closely related to limit and direct limit in category theory. The limit inferior and limit superior provide generalizations of the concept of a limit which are particularly relevant when the limit at a point may not exist. Notation In formulas, a limit of a function is usually written as : \lim_ f(x) = L, and is read as "the limit of of as approaches equals ". This means that the value of the function can be made arbitrarily close to , by choosing sufficiently close to . Alternatively, the fact that a function approaches the limit as approaches is sometimes denoted by a right arrow (→ or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
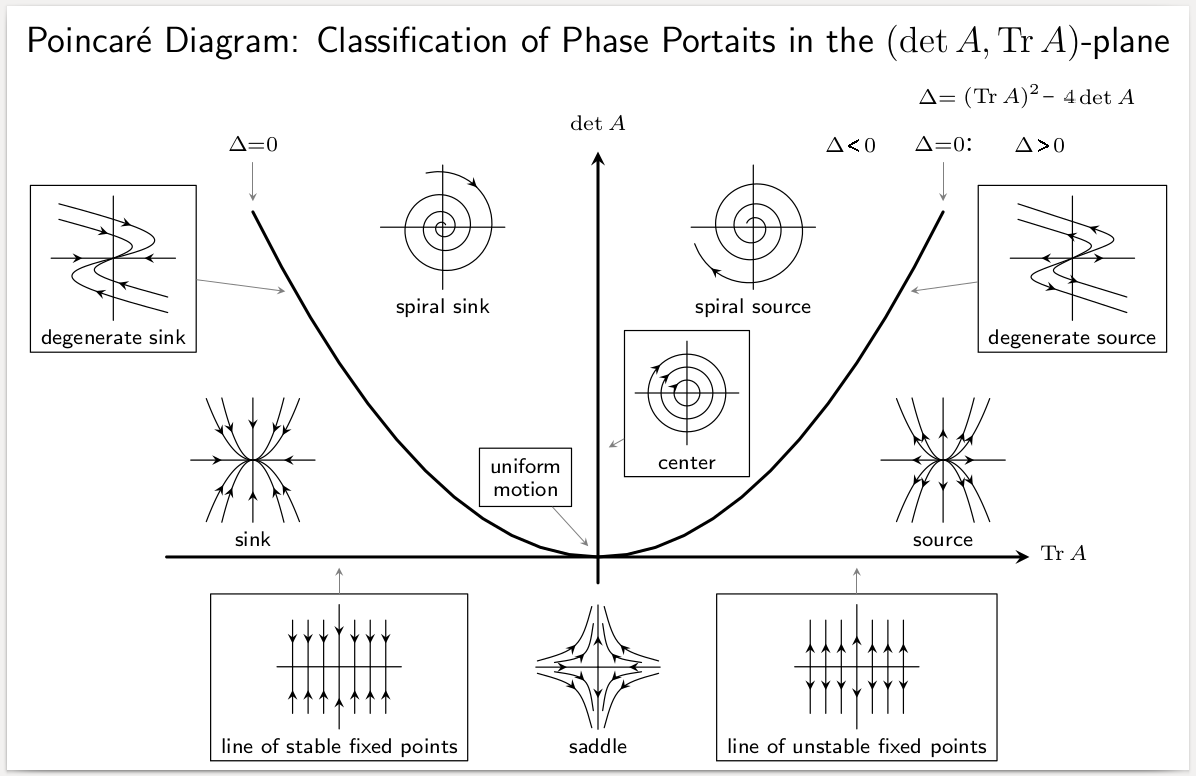
Equilibrium Point
In mathematics, specifically in differential equations, an equilibrium point is a constant solution to a differential equation. Formal definition The point \tilde\in \mathbb^n is an equilibrium point for the differential equation :\frac = \mathbf(t,\mathbf) if \mathbf(t,\tilde)=\mathbf for all t. Similarly, the point \tilde\in \mathbb^n is an equilibrium point (or fixed point) for the difference equation :\mathbf_ = \mathbf(k,\mathbf_k) if \mathbf(k,\tilde)= \tilde for k=0,1,2,\ldots. Equilibria can be classified by looking at the signs of the eigenvalues of the linearization of the equations about the equilibria. That is to say, by evaluating the Jacobian matrix at each of the equilibrium points of the system, and then finding the resulting eigenvalues, the equilibria can be categorized. Then the behavior of the system in the neighborhood of each equilibrium point can be qualitatively determined, (or even quantitatively determined, in some instances), by finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Point (mathematics)
In mathematics, a fixed point (sometimes shortened to fixpoint), also known as an invariant point, is a value that does not change under a given transformation (mathematics), transformation. Specifically, for function (mathematics), functions, a fixed point is an element that is mapped to itself by the function. Any set of fixed points of a transformation is also an invariant set. Fixed point of a function Formally, is a fixed point of a function if belongs to both the domain of a function, domain and the codomain of , and . In particular, cannot have any fixed point if its domain is disjoint from its codomain. If is defined on the real numbers, it corresponds, in graphical terms, to a curve in the Euclidean plane, and each fixed-point corresponds to an intersection of the curve with the line , cf. picture. For example, if is defined on the real numbers by f(x) = x^2 - 3 x + 4, then 2 is a fixed point of , because . Not all functions have fixed points: for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attractor
In the mathematical field of dynamical systems, an attractor is a set of states toward which a system tends to evolve, for a wide variety of starting conditions of the system. System values that get close enough to the attractor values remain close even if slightly disturbed. In finite-dimensional systems, the evolving variable may be represented algebraically as an ''n''-dimensional vector. The attractor is a region in ''n''-dimensional space. In physical systems, the ''n'' dimensions may be, for example, two or three positional coordinates for each of one or more physical entities; in economic systems, they may be separate variables such as the inflation rate and the unemployment rate. If the evolving variable is two- or three-dimensional, the attractor of the dynamic process can be represented geometrically in two or three dimensions, (as for example in the three-dimensional case depicted to the right). An attractor can be a point, a finite set of points, a curve, a mani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |