|
SpaceX CRS-9
SpaceX CRS-9, also known as SpX-9, was a Commercial Resupply Service mission to the International Space Station which launched on 18 July 2016. The mission was contracted by NASA and was operated by SpaceX using a Dragon capsule. The cargo was successfully carried aboard SpaceX's Falcon 9 Flight 27. Launch and operations history A July 2014 NASA Flight Planning Integration Panel (FPIP) presentation had this mission scheduled no earlier than (NET) 7 December 2015. By December 2014, the launch had been pushed back to NET 9 December 2015. Following the failure of SpaceX CRS-7 on 28 June 2015, the launch date was left open and, in September 2015, was moved to NET 21 March 2016. The flight was later pushed to 24 June, 27 June, 16 July, and finally 18 July 2016, as the crewed mission Soyuz MS-01 took the 24 June slot. CRS-9 launched on 18 July 2016 at 04:44 UTC from Cape Canaveral SLC-40 aboard a Falcon 9 launch vehicle. After 9 minutes and 37 seconds the Dragon spacecr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Resupply Services
Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) are a series of flights awarded by NASA for the delivery of cargo and supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) on commercially operated spacecraft. The first phase of CRS contracts (CRS-1) were signed in 2008 and awarded $1.6 billion to SpaceX for twelve SpaceX Dragon 1, Dragon 1 and $1.9 billion to Orbital Sciences for eight Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus flights, covering deliveries to 2016. The first operational resupply missions were flown by SpaceX in 2012 (SpaceX CRS-1, CRS SpX-1) and Orbital in 2014 (Cygnus CRS Orb-1, CRS Orb-1). In 2015, NASA extended CRS-1 to twenty flights for SpaceX and twelve flights for Orbital ATK. A second phase of contracts (CRS-2) was solicited in 2014. CRS-2 contracts were awarded in January 2016 to Orbital ATK's continued use of Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus, Sierra Nevada Corporation's new Dream Chaser, and SpaceX's new SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon 2, for cargo transport flights beginning in 2019 and expec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
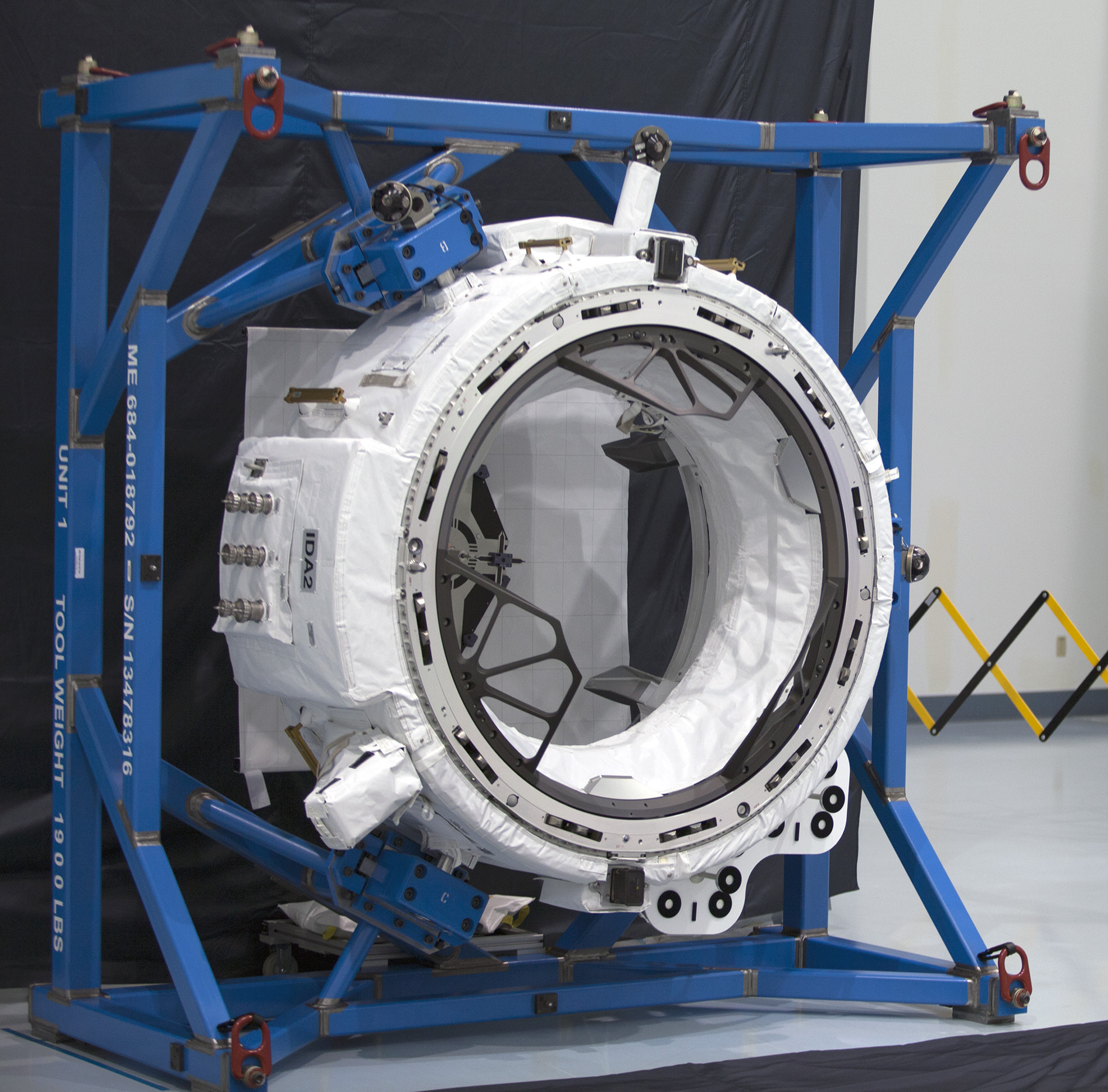
International Docking Adapter
The International Docking Adapter (IDA) is a spacecraft docking system adapter developed to convert APAS-95 to support docking with spacecraft that implement the International Docking System Standard. The IDA uses NASA Docking System (NDS) hardware. An IDA was permanently installed on each of the International Space Station's (ISS) two open Pressurized Mating Adapters (PMAs), both of which are connected to the ''Harmony'' module. History Prior to IDA several different docking adapters were designed to fill a similar role but were never implemented. APAS to LIDS Adaptor System The APAS to LIDS Adaptor System (ATLAS) was announced in 2008. It would have been placed on the open PMAs and converted APAS-95 to the Low Impact Docking System (LIDS). ATLAS was planned to be launched on Orion's first two missions to the International Space Station. Orion's missions to the ISS were later canceled altogether and its role as a crew transporter was replaced by the Commercial Crew Program ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth List of governors of California, governor of and then-incumbent List of United States senators from California, United States senator representing California) and his wife, Jane Stanford, Jane, in memory of their only child, Leland Stanford Jr., Leland Jr. The university admitted its first students in 1891, opening as a Mixed-sex education, coeducational and non-denominational institution. It struggled financially after Leland died in 1893 and again after much of the campus was damaged by the 1906 San Francisco earthquake. Following World War II, university Provost (education), provost Frederick Terman inspired an entrepreneurship, entrepreneurial culture to build a self-sufficient local industry (later Silicon Valley). In 1951, Stanfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Levitation
Magnetic levitation (maglev) or magnetic suspension is a method by which an object is levitation (physics), suspended with no support other than magnetic fields. Lorentz force, Magnetic force is used to counteract the effects of the gravitational force and any other forces. The two primary issues involved in magnetic levitation are ''lifting forces'': providing an upward force sufficient to counteract gravity, and ''stability'': ensuring that the system does not spontaneously slide or flip into a configuration where the lift is neutralized. Magnetic levitation is used for maglev trains, levitation melting, contactless melting, magnetic bearings, and for product display purposes. Lift Magnetic materials and systems are able to attract or repel each other with a force dependent on the magnetic field and the area of the magnets. For example, the simplest example of lift would be a simple dipole magnet positioned in the magnetic fields of another dipole magnet, oriented with like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature Regulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature as its own body temperature, thus avoiding the need for internal thermoregulation. The internal thermoregulation process is one aspect of homeostasis: a state of dynamic stability in an organism's internal conditions, maintained far from thermal equilibrium with its environment (the study of such processes in zoology has been called physiological ecology). If the body is unable to maintain a normal temperature and it increases significantly above normal, a condition known as hyperthermia occurs. Humans may also experience lethal hyperthermia when the wet bulb temperature is sustained above for six hours. Work in 2022 established by experiment that a wet-bulb temperature exceeding 30.55°C caused uncompensable heat stress in young, heal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is the process of determining the nucleic acid sequence – the order of nucleotides in DNA. It includes any method or technology that is used to determine the order of the four bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The advent of rapid DNA sequencing methods has greatly accelerated biological and medical research and discovery. Knowledge of DNA sequences has become indispensable for basic biological research, Genographic Project, DNA Genographic Projects and in numerous applied fields such as medical diagnosis, biotechnology, forensic biology, virology and biological systematics. Comparing healthy and mutated DNA sequences can diagnose different diseases including various cancers, characterize antibody repertoire, and can be used to guide patient treatment. Having a quick way to sequence DNA allows for faster and more individualized medical care to be administered, and for more organisms to be identified and cataloged. The rapid advancements in DNA seque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Capsule
A space capsule is a spacecraft designed to transport cargo, scientific experiments, and/or astronauts to and from space. Capsules are distinguished from other spacecraft by the ability to survive reentry and return a payload to the Earth's surface from orbit or sub-orbit, and are distinguished from other types of recoverable spacecraft by their blunt shape, not having wings and often containing little fuel other than what is necessary for a safe return. Capsule-based human spaceflight, crewed spacecraft such as Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz or Orion (spacecraft), Orion are often supported by a service or adapter module, and sometimes augmented with an extra module for extended space operations. Capsules make up the majority of crewed spacecraft designs, although one crewed spaceplane, the Space Shuttle, has flown in orbit. Current examples of crewed space capsules include Soyuz spacecraft, Soyuz, Shenzhou spacecraft, Shenzhou, and SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon 2. Examples of new crew capsu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same orbit, but certain schemes are commonly used in astronomy and orbital mechanics. A real orbit and its elements change over time due to gravitational Perturbation (astronomy), perturbations by other objects and the effects of general relativity. A Kepler orbit is an idealized, mathematical approximation of the orbit at a particular time. When viewed from an inertial frame, two orbiting bodies trace out distinct trajectories. Each of these trajectories has its Focus (geometry), focus at the common center of mass. When viewed from a non-inertial frame centered on one of the bodies, only the trajectory of the opposite body is apparent; Keplerian elements describe these non-inertial trajectories. An orbit has two sets of Keplerian elements depe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS) is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, supports astronauts working in space, services instruments and other payloads attached to the ISS, and is used for external maintenance. Astronauts receive specialized training to perform these functions with the various systems of the MSS. The MSS is composed of three components: * the Space Station Remote Manipulator System (SSRMS), known as Canadarm2. * the Mobile Remote Servicer Base System (MBS). * the Dextre, Special Purpose Dexterous Manipulator (SPDM, also known as "Dextre" or "Canada hand"). The system can move along rails on the Integrated Truss Structure on top of the US-provided Mobile Transporter cart, which hosts the MRS Base System. The system's control software was written in the Ada (programming language), Ada 95 programming ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 40
Space Launch Complex 40 (SLC-40), sometimes referred to as "Slick Forty," is one of two launch pad, launch pads located at the Integrate-Transfer-Launch Complex in Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida. It initially opened as Launch Complex 40 (LC-40) and was used by the United States Air Force alongside the neighboring Cape Canaveral Space Launch Complex 41, Space Launch Complex 41 for the Titan (rocket family), Titan III program. It initially saw use by the Titan IIIC throughout the 1960s and 1970s, before getting retrofitted for the Titan 34D during the 1980s. In the 1990s, Martin Marietta and the Air Force upgraded it to launch the Commercial Titan III, but the rocket's lack of success caused the pad to be used by the Titan IV throughout the decade and into the 2000s. Following the Titan family's retirement, the SLC-40 lease was given to SpaceX in 2007 for use by their new rocket, the Falcon 9. Since the early 2010s, the pad has transformed into a high-volume launch site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with four launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 36, 40, 41 and 46). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. uncrewed lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |