The history of Slovakia spans from prehistoric settlements to the modern
Slovak Republic
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's ...
. Situated in
Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
, the region’s earliest evidence of human habitation dates to the
Palaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
era, with significant
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
and
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
cultures. By the
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
,
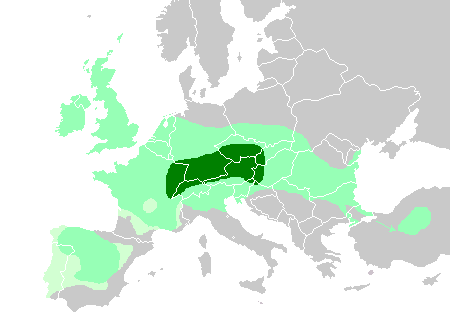
Celtic tribes
This is a list of ancient Celts, Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a la ...
like the
Boii
The Boii (Latin language, Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; ) were a Celts, Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (present-day Northern Italy), Pannonia (present-day Austria and Hungary), present-day Ba ...
established settlements, later displaced by
Germanic and
Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
migrations. The Slavs arrived in the 5th–6th centuries, forming the basis of Slavic states like
Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
(9th century), which adopted Christianity through
Cyrillo-Methodian missionary activity.
Following Great Moravia’s collapse, the territory became part of the
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
, enduring
Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire, the Mongol Empire (1206–1368), which by 1260 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
and later
Ottoman Wars
A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in ...
that split Hungary into three parts. Much of present-day territory of Slovakia resisted Ottoman conquest and became a province of the
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. The 19th century saw the rise of
Slovak nationalism
Slovak nationalism is an ethnic nationalist ideology that asserts that the Slovaks are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of the Slovaks.
History
Modern Slovak nationalism first arose in the 19th century in response to Magyarization of ...
, fueled by figures like
Ľudovít Štúr
Ľudovít Štúr (; 28 October 1815 – 12 January 1856), also known as Ľudovít Velislav Štúr, was a Slovak revolutionary, politician, and writer. As a leader of the Slovak nationalism, Slovak national revival in the 19th century and the c ...
, who codified modern
Slovak, and movements advocating autonomy within
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
.
Slovakia joined the Czechs to form
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
after
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, though tensions between Czechs and Slovaks persisted. During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Slovakia became a Nazi-aligned puppet state under
Jozef Tiso
Jozef Gašpar Tiso (, ; 13 October 1887 – 18 April 1947) was a Slovaks, Slovak politician and Catholic priest who served as president of the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), First Slovak Republic, a client state of Nazi Germany during World War ...
. Post-war, it was reintegrated into Czechoslovakia, which fell under
Communist rule in 1948. The
Prague Spring
The Prague Spring (; ) was a period of liberalization, political liberalization and mass protest in
the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic. It began on 5 January 1968, when reformist Alexander Dubček was elected Secretary (title), First Secre ...
of 1968 briefly liberalized politics until the
Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia
On 20–21 August 1968, the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic was jointly invaded by four fellow Warsaw Pact countries: the Soviet Union, the Polish People's Republic, the People's Republic of Bulgaria, and the Hungarian People's Republic. The ...
. After the
Velvet Revolution
The Velvet Revolution () or Gentle Revolution () was a non-violent transition of power in what was then Czechoslovakia, occurring from 17 November to 28 November 1989. Popular demonstrations against the one-party government of the Communist Pa ...
of 1989, Slovakia peacefully transitioned to democracy, culminating in its
independence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of ...
on 1 January 1993. Since then, it has developed a modern
market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production, and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a mark ...
and joined
NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
and the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
in 2004.
Prehistory
Discovery of ancient tools made by the
Clactonian technique near
Nové Mesto nad Váhom
Nové Mesto nad Váhom (; ; ) is a town in the Trenčín Region of Slovakia.
Geography
District town located at the northern edge of the Danubian Hills at the foothills of the northern end of the White Carpathians, on the Váh river. Other moun ...
attests that Slovakia's territory was inhabited in the
Palaeolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
. Other prehistoric discoveries include the
Middle Palaeolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle P ...
stone tools found near
Bojnice
Bojnice (; ) is a historical town in east Slovakia located on the Nitra (river), Nitra river, near the city of Prievidza. The town is situated just below the Bojnice Castle. It has a population of around 5,000.
Bojnice is best known for its popul ...
, and a
Neanderthal
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinction, extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle Pleistocene, Middle to Late Plei ...
discovery at a site near
Gánovce. The
Gravettian
The Gravettian is an archaeological industry of the European Upper Paleolithic that succeeded the Aurignacian circa 33,000 years BP. It is archaeologically the last European culture many consider unified, and had mostly disappeared by ...
culture was present principally in the river valleys of
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
,
Hron
The Hron (; ; ; ) is a long left tributary of the Danube[P ...]
,
Ipeľ
The Ipeľ (Slovak language, Slovak; ) or Ipoly (Hungarian language, Hungarian) (German language, German: ''Eipel'', archaic Slovak: ''Jupoľ'', Latin language, Latin: ''Bolia'') is a long river in Slovakia and Hungary, a tributary of the Danube ...
,
Váh
The Váh (; , ; ; Wag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich (''in Geograph ...
and as far as the city of
Žilina
Žilina (; ; ; ; Names of European cities in different languages: U-Z#Z, names in other languages) is a city in north-western Slovakia, around from the capital Bratislava, close to both the Czech and Polish borders. It is the List of cities ...
, and near the foot of the
Vihorlat,
Inovec, and
Tribeč
Tribeč () is a crystalline mountain range in western Slovakia, in the Inner Western Carpathians located in the Nitra Region. It is surrounded by the Danubian Lowland, Pohronský Inovec, Vtáčnik Mountains and the Upper Nitra Basin. Beech trees ...
mountains, as well as in the
Myjava
Myjava (; historically also Miava, , ) is a town in Trenčín Region, Slovakia.
Geography
It is located in the Myjava Hills at the foothills of the White Carpathians and nearby the Little Carpathians. The river Myjava flows through the town. It ...
Mountains. The best known artifact is the
Venus of Moravany
The Venus of Moravany () is a small prehistoric Venus figurine discovered in Slovakia in the early 20th century.
It was ploughed up in 1930 by farmer Štefan Hulman-Petrech near the village of Moravany nad Váhom in Slovakia.
It is made of mamm ...
from
Moravany nad Váhom
Moravany nad Váhom () is a village and municipality in Piešťany District in the Trnava Region of western Slovakia.
History
In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1348.
A small female figurine called the Venus of Moravany ...
.
Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
habitation was found in
Želiezovce
Želiezovce (, until 1895: ; ) is a town in Slovakia in the Nitra Region in the Levice District, near the Hron river.
Districts
* Jarok (Želiezovce), Jarok ()
* Karolína (Želiezovce), Karolína
* Mikula (Želiezovce), Mikula (1967 establis ...
,
Gemer, and the Bukové hory massif, the
Domica
The Domica cave is a karst cave situated on the south-western border of the ''Silicka planina Plateau'' south-east of Plesivec in the Rožňava District of the Košice Region in southern Slovakia. In combination with the Baradla cave, it makes ...
cave, and at
. The
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
was marked by the
Unetice,
Mad'arovce,
Tumulus
A tumulus (: tumuli) is a mound of Soil, earth and Rock (geology), stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds, mounds, howes, or in Siberia and Central Asia as ''kurgans'', and may be found through ...
,
Čaka
Čaka () is a village and municipality in the Levice District in the Nitra Region of south-west Slovakia.
History
In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1287.
Geography
The village lies at an altitude of 188 metres and covers ...
,
Velatice, and
Lusatian cultures, followed by the Calenderberg culture and the
Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallst ...
in the early
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
.
Antiquity

The
Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
were the first population in the territory of present-day Slovakia who can be identified on the basis of written sources. The first
Celtic groups came from the West around . Settlements of the
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a Iron Age Europe, European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman Republic, Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age ...
indicate that the Celts colonized the lowlands along the river
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
and its tributaries. The local population was either subjected by the Celts or withdrew to the mountainous northern territory. New Celtic groups arrived from Northern Italy during the . The Celts initially lived in tiny huts in sizewhich either formed small villages or were scattered across the countryside.
Some of the small hill forts which were built in the developed into important local economic and administrative centers. For example, the hill fort at Zemplín was a center of iron-working; glass works were unearthed at
Liptovská Mara
Liptovská Mara () is a reservoir in northern Slovakia, on the Váh river near Liptovský Mikuláš, in the Liptov region. The dam is named after one of the inundated villages.
It was built in 1965–1975. The area of the reservoir is 22 km ...
; and local coins were struck at Bratislava and Liptovská Mara. Coins from Bratislava bore inscriptions like
Biatec
Biatec was the name of a person, presumably a king, who appeared on the Celtic coins minted by the Boii in Bratislava (the capital of Slovakia) in the 1st century BC. The word Biatec (or Biatex) is also used as the name of those coins. In the li ...
and Nonnos. The fort at Liptovská Mara was also an important center of the cult of the bearers of the
Púchov culture
The Púchov culture was an archaeological culture named after site of Púchov-Skalka in Slovakia. Its probable bearer was the Celtic Cotini and/or Anartes tribes. It existed in northern and central Slovakia (although it also plausibly spread to ...
of the Northern Carpathians.
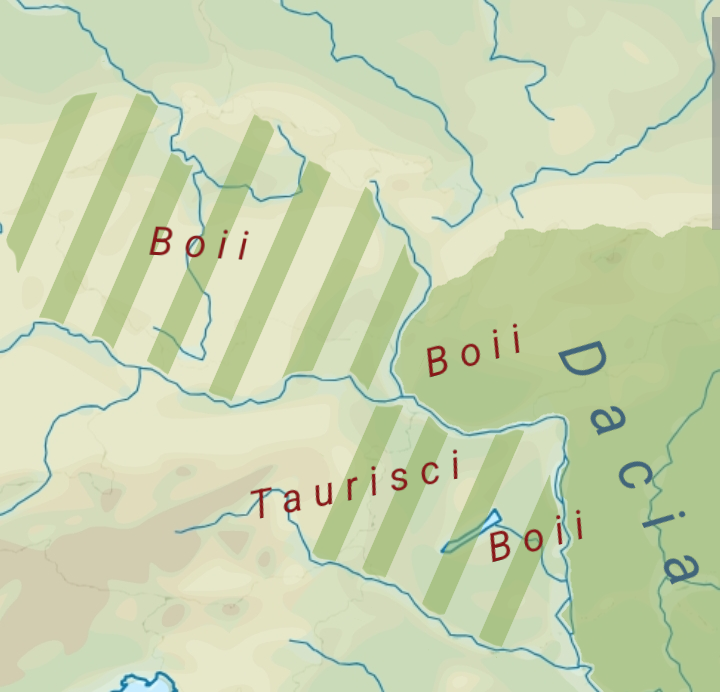
Burebista
Burebista () was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area located between the Danube, Tisza, and Dniester rivers, ...
, King of the
Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
, invaded the Middle Danube region and subjugated the majority of the local
Celtic tribes
This is a list of ancient Celts, Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a la ...
(the
Boii
The Boii (Latin language, Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; ) were a Celts, Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (present-day Northern Italy), Pannonia (present-day Austria and Hungary), present-day Ba ...
and the
Taurisci
The Taurisci were a federation of Celtic tribes who dwelt in today's Carinthia and northern Slovenia (Carniola) before the coming of the Romans (c. 200 BC). According to Pliny the Elder, they are the same as the people known as the Norici.
Et ...
) around . Burebista's empire collapsed after he died about 16 years later. Archaeological sites yielding painted ceramics and other artefacts of Dacian provenance suggest that Dacian groups settled among the local Celts in the region of the rivers
Bodrog
The Bodrog is a river in eastern Slovakia and north-eastern Hungary. It is a tributary of the river Tisza. The Bodrog is formed by the confluence of the rivers Ondava and Latorica near Zemplín in eastern Slovakia. It crosses the Slovak–Hu ...
,
Hron
The Hron (; ; ; ) is a long left tributary of the Danube[P ...]
and
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
. The spread of the "Púchov culture", associated with the Celtic
Cotini The Cotini, sometimes spelled Gotini (because it is found in some manuscript copies of Tacitus), were a Gaulish tribe living during Roman times in the mountains approximately near the modern borders of the Czech Republic, Poland, and Slovakia.
The ...
, shows that the bearers of that culture started a northward expansion during the same period.
The
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
and the
Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts ...
launched their first invasions against the territories along the Middle Danube in the last decade of the . Roman legions crossed the Danube near Bratislava under the command of
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
to fight against the Germanic
Quadi
The Quadi were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people during the Roman era, who were prominent in Greek and Roman records from about 20 AD to about 400 AD. By about 20 AD they had a kingdom centred in the area of present-day western Slovakia, north ...
in , but the local tribes' rebellion in Pannonia forced the Romans to return. Taking advantage of internal strifes, the Romans settled a group of Quadi in the lowlands along the Danube between the rivers
Morava and
Váh
The Váh (; , ; ; Wag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich (''in Geograph ...
in 21, making
Vannius
Vannius (flourished in 1st century AD) was the king of the Germanic tribe Quadi.
According to The Annals of Tacitus, Vannius came to power following the defeat of the Marcomannic King Catualda by the Hermunduri King Vibilius, establishing the ...
their king. The Germans lived in rectangular houses, rather than square ones, and cremated their dead, placing the ashes in an urn.
Although the Danube formed the frontier between the Roman Empire and the "
Barbaricum
Barbaricum (from the , "foreign", "barbarian") is a geographical name used by historical and archaeological experts to refer to the vast area of barbarian-occupied territory that lay, in Roman times, beyond the frontiers or '' limes'' of the Rom ...
", the Romans built small outposts along the left bank of the Danube, for instance, at
Iža
Iža (, Hungarian pronunciation:) is a village in south-western Slovakia.
Geography
The village lies at an altitude of and covers an area of . It is situated in the Komárno District of Slovakia's Nitra Region, very close to the town of Komá ...
and
Devín
Devín (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia, located in the Bratislava IV district. Originally a separate village at the confluence of the Danube and Morava rivers, Devín maintained its rural character and today, it is on ...
. During the same period, the Germanic tribes were expanding to the north along the rivers Hron,
Ipeľ
The Ipeľ (Slovak language, Slovak; ) or Ipoly (Hungarian language, Hungarian) (German language, German: ''Eipel'', archaic Slovak: ''Jupoľ'', Latin language, Latin: ''Bolia'') is a long river in Slovakia and Hungary, a tributary of the Danube ...
and Nitra. Roman troops crossed the Danube several times during the
Marcomannic Wars
The Marcomannic Wars () were a series of wars lasting from about AD 166 until 180. These wars pitted the Roman Empire against principally the Germanic peoples, Germanic Marcomanni and Quadi and the Sarmatian Iazyges; there were related conflicts ...
between 160 and 180. Emperor
Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors ...
accomplished the first chapter of his ''
Meditations
''Meditations'' () is a series of personal writings by Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor from 161–180 AD, recording his private notes to himself and ideas on Stoic philosophy. Composition
Marcus Aurelius wrote the 12 books of the ''Meditations'' i ...
'' during a campaign against the Quadi in the region of the Hron River in 172. The "
Miracle of the Rain"a storm which saved an exhausted Roman armyoccurred in the land north of the Danube in 173; Christian authors attributed it to a Christian soldier's prayer. Roman troops crossed the Danube for the last time in 374, during Emperor
Valentinian I
Valentinian I (; 32117 November 375), also known as Valentinian the Great, was Roman emperor from 364 to 375. He ruled the Western Roman Empire, Western half of the empire, while his brother Valens ruled the Byzantine Empire, East. During his re ...
's campaign against the Quadi who had allied with the
Sarmatians
The Sarmatians (; ; Latin: ) were a large confederation of Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Iranian Eurasian nomads, equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic–Caspian steppe, Pontic steppe from about the 5th century BCE to the 4t ...
and invaded the Roman province of
Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
.
Medieval history
New migrations

In the 4th century AD, the Roman Empire could no longer resist the attacks by the neighboring peoples. The empire's frontier started to collapse along the Danube in the 370s. The development of the
Hunnic Empire
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was pa ...
in the
Eurasian Steppes
The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan, Siberia, Euro ...
forced large groups of Germanic peoples, including the Quadi and the
Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who were first reported in the written records as inhabitants of what is now Poland, during the period of the Roman Empire. Much later, in the fifth century, a group of Vandals led by kings established Vand ...
, to leave their homelands by the Middle Danube and along the upper course of the river
Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa (see below) is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. It was once called "the most Hungarian river" because it used to flow entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national bo ...
in the early . Their lands were occupied by the
Heruli
The Heruli (also Eluri, Eruli, Herules, Herulians) were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity, known from records in the third to sixth centuries AD.
The best recorded group of Heruli established a kingdom north of the Middle Danu ...
,
Sciri
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones".
The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on the ...
,
Rugii
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians (), were one of the smaller Germanic peoples of Late Antiquity who are best known for their short-lived 5th-century kingdom upon the Roman frontier, near present-day Krems an der Donau in Austria. This kingdom, like t ...
and other Germanic peoples. However, the
Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorphologic ...
was dominated by the nomadic
Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
from the early and the Germanic peoples became subjects to
Attila the Hun
Attila ( or ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in early 453. He was also the leader of an empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Gepids, among others, in Central and East ...
.
Disputes among Attila's sons caused the disintegration of his empire shortly after his death in 453. The Germanic peoples either regained their independence or left the Carpathian Basin (like the Heruli and the Sciri, respectively). Warriors' graves from the next century yielded large number of swords, spears, arrow heads, axes and other weapons. Other archaeological finds, including a glass
beaker from
Zohor
Zohor is a village and municipality in western Slovakia in Malacky District in the Bratislava Region.
History
The village was first mentioned in 1314 as ''Sahur''.
Sport
FC Zohor are a football team that play at the Štadión FC Zohor on Poži ...
, shows that the local inhabitants had close contacts with the
Frankish Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lomba ...
and
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a subregion#Europe, subregion of northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also ...
.
Arrival of the Slavs
Regarding the early history of Slavs, Slavic texts or a record written by a Slav dating from before the late 9th century are not known. The foreign sources (mostly Greek and Latin) about Slavs are very inconsistent. According to a scholarly theory, the first Slavic groups settled in the eastern region of present-day Slovakia already in the . The 6th-century Byzantine historian
Jordanes
Jordanes (; Greek language, Greek: Ιορδάνης), also written as Jordanis or Jornandes, was a 6th-century Eastern Roman bureaucrat, claimed to be of Goths, Gothic descent, who became a historian later in life.
He wrote two works, one on R ...
wrote that the funeral feast at Attila's burial was called ''strava''. Scholars who identify that word as a
Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
expression say that Jordanes' report proves that Slavs inhabited the Carpathian Basin in the middle of the . However, according to a concurrent scholarly theory, ''strava'' may have been a
Hunnic term, because no primary source mentioned that the Slavs were present in Attila's court.
Settlements which represented a new
archaeological horizon
In archaeology, the general meaning of horizon is a distinctive type of sediment, artefact, style, or other cultural trait that is found across a large geographical area from a limited time period. The term derives from similar ones in geology, h ...
the so-called "
Prague-Korchak cultural horizon
The Prague-Korchak culture was an archaeological culture attributed to the Early Slavs. The other contemporary main Early Slavic culture was the Prague-Penkovka culture situated further south, with which it makes up the "Prague-type pottery" gr ...
"appeared along the northernmost fringes of the Carpathian Mountains around 500. Similar settlements, which are dated to the second half of the , were also excavated in the region of the confluence of the Danube and the Morava. "Prague-Korchak" settlements consisted of about 10 semi-sunken huts, each with a stone oven in a corner. The local inhabitants used handmade pottery and cremated the dead. Most historians associate the spread of the "Prague-Korchak" settlements with the expansion of the early Slavs.
According to historian Gabriel Fusek, written sources also evidence the presence of Slavs in the Central Europe in the first half of the . The 6th-century Byzantine historian,
Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea (; ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; ; – 565) was a prominent Late antiquity, late antique Byzantine Greeks, Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Justinian I, Empe ...
, wrote of a group of the Heruli who had "passed through the territory of all of the
Sclavenes
The ' (in Latin) or ' ( various forms in Greek) were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled in the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became one of the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early By ...
", or Slavs, during their migration towards the northern "
Thule
Thule ( ; also spelled as ''Thylē'') is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. First written of by the Greek explorer Pytheas of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, France) in about 320 BC, i ...
". Procopius's report implies that the Slavs inhabited the region of the river Morava, but its credibility is suspect. Procopius also wrote of an exiled
Longobard
The Lombards () or Longobards () were a Germanic people who conquered most of the Italian Peninsula between 568 and 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 and 796) t ...
prince, Hildigis, who first fled to the "Sclaveni" and then to the
Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the G ...
, "taking with him not only those of the Longobards who had followed him, but also many of the Sclaveni" in the 540s. According to a scholarly theory, Hildigis most probably mustered his Slavic warriors in the region of the Middle Danube.
The Germanic Longobards were expanding towards the Middle Danube in the early . Archaeological research shows that Longobard expansion bypassed virtually the entire territory of Slovakia and they settled only in the most north-western part of the country (
Záhorie , the Romanian village of Dumbrava, called Erdőhát in Hungarian, Pestişu Mic
Záhorie () is a region in western Slovakia between the Little Carpathians to the east and the Morava River to the west. Although not an administrative region, it is ...
). Unlike neighbouring Moravia, Slovakia (except of
Záhorie , the Romanian village of Dumbrava, called Erdőhát in Hungarian, Pestişu Mic
Záhorie () is a region in western Slovakia between the Little Carpathians to the east and the Morava River to the west. Although not an administrative region, it is ...
) did not belong to any German empire in this time. The Longobards and the local Slavs remained separated by the natural border formed by
Little
Little is a synonym for small size and may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Little'' (album), 1990 debut album of Vic Chesnutt
* ''Little'' (film), 2019 American comedy film
*The Littles, a series of children's novels by American author John P ...
and
White Carpathians
The White Carpathians (; ; ) are a mountain range on the border of the Czech Republic and Slovakia, part of the Carpathians.
They are part of the macroregion of Slovak-Moravian Carpathians, stretching from the Váh river and the Little Carpat ...
, respected by both sides according to
Ján Steinhübel. He also writes that the Slavs, who remained "an independent third party" in strained Longobard-Gepid relations, were not interested in conflicts with their Germanic neighbours, but made raids in the faraway Byzantine Empire.
Avar Khaganate

The Longobards left the Carpathian Basin for Northern Italy after the invasion of the territory by the
Avars in 568. The Avars were a group of nomadic warriors of mixed origin. They conquered the Carpathian Basin, subjugated the local peoples and launched plundering expeditions against the neighboring powers during the next decades. By the time of the Avars' arrival, the Slavs had settled in most lands that now form Slovakia, according to historian Stanislav Kirschbaum. Further migration waves strengthened the local Slavic population because new Slavic groups, pressed by the Avars, crossed the Eastern Carpathians, seceding from the Slavs who continued their expansion to the Balkan Peninsula. Dialects of Slovak still reflect that the Slavs came from different directions already in the Early Middle Ages, according to a widely accepted scholarly theory. Czech and Slovak share some features with the
South Slavic languages
The South Slavic languages are one of three branches of the Slavic languages. There are approximately 30 million speakers, mainly in the Balkans. These are separated geographically from speakers of the other two Slavic branches (West Slavic la ...
, distinguishing them from the other
West Slavic languages
The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group. They include Polish, Czech, Slovak, Kashubian, Silesian, Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian. The languages have traditionally been spoken across a mostly continuous re ...
. According to archaeologist P. M. Barford, these features suggest that the Carpathian Mountains and the
Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ), also known as the Sudeten Mountains or Sudetic Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince of the Bohemian Massif province in Central Europe, shared by the Czech Republic, Poland and Germany. They consist mainly of mountain rang ...
separated the ancestors of the
Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
and the
Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia ...
from the Slavs living to the north of those mountains. Especially the dialects of Central Slovakia, which "stand out from the continuous chain between the western and eastern dialects", preserved South Slavic features.
The 7th-century Frankish ''
Chronicle of Fredegar
The ''Chronicle of Fredegar'' is the conventional title used for a 7th-century Frankish chronicle that was probably written in Burgundy. The author is unknown and the attribution to Fredegar dates only from the 16th century.
The chronicle begi ...
'' wrote that the Avars employed the Slavs, or Wends, as ''"Befulci"'', showing that the Slavs formed special military units in the
Avar Khaganate
The Pannonian Avars ( ) were an alliance of several groups of Eurasian nomads of various origins. The peoples were also known as the Obri in the chronicles of the Rus' people, Rus, the Abaroi or Varchonitai (), or Pseudo-Avars in Byzantine Empi ...
. According to the same chronicle, the Wends rose up in rebellion against their Avar masters and elected a Frankish merchant,
Samo
Samo (–) was the founder and sole ruler of the first recorded political union of Slavs, Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire ("realm", "kingdom", or "tribal union"), ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to Fredegarius, the only ...
, their king "in the fortieth year of
Clothar's reign", that is in 623 or 624. Modern historians agree that the Avars' defeat during the
siege of Constantinople in 626 enabled Samo to consolidate his rule. He routed the invading army of
Dagobert I
Dagobert I (; 603/605 – 19 January 639) was King of the Franks. He ruled Austrasia (623–634) and Neustria and Burgundy (629–639). He has been described as the last king of the Merovingian dynasty to wield real royal power, after which the ...
,
King of the Franks
The Franks, Germanic peoples that invaded the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, were first led by individuals called dux, dukes and monarch, reguli. The earliest group of Franks that rose to prominence was the Salian Franks, Salian Mero ...
, in the
Battle of Wogastisburg
According to the contemporary ''Chronicle of Fredegar'', the Battle of Wogastisburg (also called the siege of Wogastisburg) took place between Slavs (''Sclav, cognomento Winidi'') under King Samo and Franks under King Dagobert I in 631 or 632. Th ...
in 631 or 632. The realm of Samo, who ruled for 35 years, collapsed soon after his death. Its exact borders cannot be determined, but it must have been located near the confluence of the Danube and the Morava rivers. Historian Richard Marsina puts its centre to
Lower Austria
Lower Austria ( , , abbreviated LA or NÖ) is one of the nine states of Austria, located in the northeastern corner of the country. Major cities are Amstetten, Lower Austria, Amstetten, Krems an der Donau, Wiener Neustadt and Sankt Pölten, which ...
.
A new horizon of mostly hand-made potterythe so-called "Devínska Nová Ves pottery"appeared between the Middle Danube and the Carpathians before the end of the . Large inhumation cemeteries yielding such pottery were unearthed at Bratislava,
Holiare
Holiare, until 1948 ''Gelér'' (, Hungarian pronunciation:) is a village and municipality in the Komárno District in the Nitra Region of south-west Slovakia.
Geography
The village lies at an altitude of 112 metres and covers an area of 9.885& ...
,
Nové Zámky
Nové Zámky (; ) is a town in Nové Zámky District in the Nitra Region of southwestern Slovakia.
Geography
The town is located on the Danubian Lowland, on the Nitra River, at an altitude of 119 metres. It is located around 100 km fr ...
and other places, suggesting that cemeteries were located near stable settlements. For instance, the cemetery at
Devínska Nová Ves
Devínska Nová Ves (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia. Its western borders are formed by the Morava River, which also forms the national border between Slovakia and Austria.
Devínska Nová Ves is notable mainly for its ...
, which contained about a thousand inhumation graves and thirty cremations, was used up until the end of the .
In the 670s, the new population of the "griffin and tendril"
archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
appeared in the Pannonian Basin expelling
Kuber
Kuber (also Kouber or Kuver) was a Bulgar leader who, according to the '' Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', liberated a mixed Bulgar and Byzantine Christian population in the 670s, whose ancestors had been transferred from the Eastern Roman Empi ...
's
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic peoples, Turkic Nomad, semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between the 5th and 7th centu ...
south out of
Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous province of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians ...
(the westernmost part of
Kubrat
Kubrat (; ) was the ruler of the Onogur–Bulgars, credited with establishing the confederation of Old Great Bulgaria in 632. His name derived from the Turkic words ''qobrat'' — "to gather", or ''qurt'', i.e. "wolf".
Origin
In the '' Nomi ...
's
Onoguria). Shortly afterwards the new Avar-Slav alliance could expand their territories even also over the
Vienna Basin
The Vienna Basin (, , , Hungarian: ''Bécsi-medence'') is a geologically young tectonic burial basin and sedimentary basin in the seam area between the Alps, the Carpathians and the Pannonian Plain. Although it topographically separates the Al ...
. The political and cultural development in Slovakia continued in two separate lines. Lowland areas in the southern Slovakia got under the direct military control of the Avars. The Avars held strategic centers in
Devín
Devín (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia, located in the Bratislava IV district. Originally a separate village at the confluence of the Danube and Morava rivers, Devín maintained its rural character and today, it is on ...
and
Komárno
Komárno (, , ), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom'', ''Öregkomárom'', ''Észak-Komárom'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian, is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old ...
which belonged to the most important centers of the khaganate. The Avars from Devín controlled Moravia and from Komárno they controlled southern Slovakia. In this time, the Avars already began to adopt a more settled lifestyle. The new period introduced Slavo-Avaric symbiosis and multi-ethnic Slavo-Avaric culture. The Slavs in southern Slovakia adopted new burial rite (inhumation), jewelry, fashion and used also common cemeteries with the Avars. Large Slavo-Avaric cemeteries can be found in
Devínska Nová Ves
Devínska Nová Ves (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia. Its western borders are formed by the Morava River, which also forms the national border between Slovakia and Austria.
Devínska Nová Ves is notable mainly for its ...
and
Záhorská Bystrica
Záhorská Bystrica (, ) is a city borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia. It is located in the northern part of the city, lying on the foothills of the Pezinok Carpathians, part of the Little Carpathians mountain range. It is part of the ...
near
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
and similar cemeteries, the proof of direct Avar power, south of the line
Devín
Devín (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia, located in the Bratislava IV district. Originally a separate village at the confluence of the Danube and Morava rivers, Devín maintained its rural character and today, it is on ...
-
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
-
Levice
Levice (; , Hungarian pronunciation: ; ) is a town in western Slovakia. The town lies on the left bank of the lower Hron river. The Old Church Slavonic, Old Slavic name of the town was ''Leva'', which means "the Left One".
The town is located i ...
-
Želovce-
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest cit ...
-
Šebastovce
Šebastovce () is a borough (city ward) of Košice, Slovakia. Located in the Košice IV district, it lies at an altitude of roughly above sea level, and borders the boroughs of Barca and Poľov. Šebastovce has a mostly rural character, with a ...
. North of this line, the Slavs preserved previous burial rite (cremation, sometimes tumuli). Natural increase of the population together with immigration from the south led to the settlement also in mountain areas.
In the 8th century, the Slavs increased their agricultural productivity (usage of iron plow) along with further development of crafts. Higher productivity initiated changes in the Slavic society, released a part of human resources previously required for farming and allowed to form groups of professional warriors. The Slavs began to build heavily fortified settlements (''hradisko'' - large
grad) protected by strong walls (8–10 m) and trenches (width 4–7 m, depth 2–3.5 m). Among the oldest belong
Pobedim
Pobedim () is a village and municipality in Nové Mesto nad Váhom District in the Trenčín Region of western Slovakia. A Slavic hill fort from the pre-Great Moravian period has been uncovered in the locality Hradištia. The hill fort belongs to ...
,
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
-Martinský Vrch,
Majcichov,
Spišské Tomášovce
Spišské Tomášovce (; ) is a village and municipality in the Spišská Nová Ves District in the Košice Region of central-eastern Slovakia.
History
In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1229.
Geography
The village lies at ...
and
Divinka
Divinka () is a village and municipality in Žilina District in the Žilina Region of northern Slovakia.
History
The modern village of Divinka consists of two parts, which were originally two separate villages: Divinka (former Malá Divina) and L ...
. The neighborhood with Avars raised unification process and probably also formation of local military alliances. The archaeological findings from this period (such as an exquisite noble tomb in
Blatnica) support the formation of a
Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
upper class on the territory that later became the nucleus of Great Moravia.
A series of
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
-
Avar wars (788–803) led to the political fall of the
khaganate
A khanate ( ) or khaganate refers to historic polity, polities ruled by a Khan (title), khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. Khanates were typically nomadic Mongol and Turkic peoples, Turkic or Tatars, Tatar societies located on the Eurasian Steppe, ...
.
In 805, the Slavs attacked again. Their offensive aimed mainly on the centers of Avar power -
Devín
Devín (, , ) is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia, located in the Bratislava IV district. Originally a separate village at the confluence of the Danube and Morava rivers, Devín maintained its rural character and today, it is on ...
and
Komárno
Komárno (, , ), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom'', ''Öregkomárom'', ''Észak-Komárom'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian, is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old ...
. The Avars were not able to resist attack and they were expelled to the right bank of
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
. The Slavs from Slovakia probably participated also in further conflicts between small Slavic dukes and remaining Avar
tarkhan
Tarkhan (, or ; ; zh, c=達干/達爾罕/答剌罕; ; ; alternative spellings ''Tarkan'', ''Tarkhaan'', ''Tarqan'', ''Tarchan'', ''Turxan'', ''Tarcan'', ''Turgan, Tárkány, Tarján, Tarxan'') is an ancient Central Asian title used by various ...
s.
Principality of Nitra
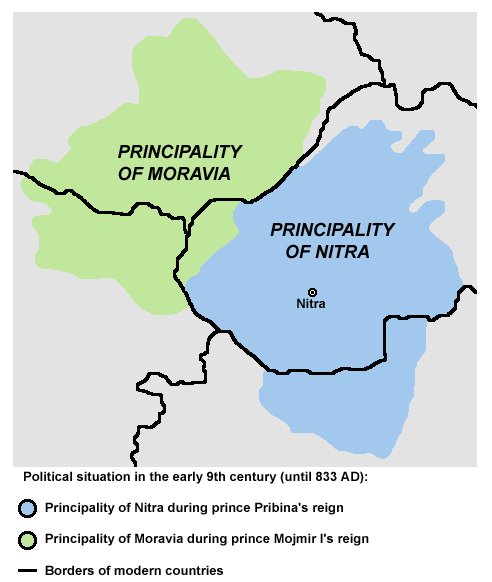
The ''
Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum
The ''Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum'' ("The Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians") is a Latin history written in Salzburg in the 870s. It describes the life and career of Salzburg's founding saint Rupert (d. 710), notably his ...
'', written around 870, narrates that
Moimir, the leader of the
Moravians
Moravians ( or Colloquialism, colloquially , outdated ) are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group from the Moravia region of the Czech Republic, who speak the Moravian dialects of Czech language, Czech or Czech language#Common Czech, Common ...
, expelled one
Pribina
Pribina (c. 800861) was a Slavs, Slavic prince whose adventurous career, recorded in the ''Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum, Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians'' (a historical work written in 870), illustrates the political ...
, forcing him to cross (or come up) the Danube and join
Radbod, who was the head of the
March of Pannonia
March is the third month of the year in both the Julian and Gregorian calendars. Its length is 31 days. In the Northern Hemisphere, the meteorological beginning of spring occurs on the first day of March. The March equinox on the 20 or 21 ...
in the
Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–887) was a Franks, Frankish-dominated empire in Western and Central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as List of Frankish kings, kings of the Franks since ...
from around 830. Radbod presented Pribina to King
Louis the German
Louis the German (German language, German: ''Ludwig der Deutsche''; c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany (German language, German: ''Ludwig II. von Deutschland''), was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 8 ...
who ordered that Pribina be instructed in the Christian faith and baptised. Three of the eleven extant copies of the ''Conversio'' also contain an out of context statement which says that Adalram, who was
Archbishop of Salzburg
The Archdiocese of Salzburg (; ) is a Latin Church, Latin rite archdiocese of the Catholic Church centered in Salzburg, Austria. It is also the principal diocese of the ecclesiastical province of Salzburg. The archdiocese is one of two Austrian ...
between 821 and 836, had once consecrated a church on Pribina's "estate at a place over the Danube called Nitrava". According to a widely accepted scholarly theory, "Nitrava" was identical with Nitra in present-day Slovakia and the forced unification of Pribina's
Principality of Nitra
The Principality of Nitra (; ), also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements that developed in the 9th century around Nitra, in present-day Slovakia. Its history remains uncertain because of a ...
with Mojmir's Moravia gave rise to the development a new state "
Great Moravia
Great Moravia (; , ''Meghálī Moravía''; ; ; , ), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Repub ...
".
Between 800 and 832, a group of Slavic forthills in Slovakia quickly arose and disappeared. Archaeological research confirmed the fall of several important central forthills approximately around the time when Pribina was expelled, e.g.
Pobedim
Pobedim () is a village and municipality in Nové Mesto nad Váhom District in the Trenčín Region of western Slovakia. A Slavic hill fort from the pre-Great Moravian period has been uncovered in the locality Hradištia. The hill fort belongs to ...
or
Čingov. The lack of written sources does not allow to finally conclude if these events were caused by internal changes or by Moravian expansion. Pribina could be a ruler of an independent entity (the
Principality of Nitra
The Principality of Nitra (; ), also known as the Duchy of Nitra, was a West Slavic polity encompassing a group of settlements that developed in the 9th century around Nitra, in present-day Slovakia. Its history remains uncertain because of a ...
) or in the case that Moravian expansion preceded his expulsion, he was a member of "Moravian" aristocracy.
Other historians write that
Pribina's Nitrava cannot be identified with Nitra. Charles Bowlus says that a letter, written by
Theotmar,
Archbishop of Salzburg
The Archdiocese of Salzburg (; ) is a Latin Church, Latin rite archdiocese of the Catholic Church centered in Salzburg, Austria. It is also the principal diocese of the ecclesiastical province of Salzburg. The archdiocese is one of two Austrian ...
and his
suffragan bishop
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations.
In the Catholic Church, a suffragan bishop leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led b ...
s in about 900, strongly suggests that Nitra was only conquered by
Svatopluk I of Moravia
Svatopluk I or Svätopluk I, also known as Svatopluk the Great, was a ruler of Great Moravia, which attained its maximum territorial expansion during his reign (870–871, 871–894).
Svatopluk's career started in the 860s, when he govern ...
only in the 870s. However, according to Třeštík, this information can be explained as a reasonable mistake of the Frankish bishops who knew that the territory was in the past a separate "regnum" different from Moravia and because it was ruled by
Svatopluk I
Svatopluk I or Svätopluk I, also known as Svatopluk the Great, was a ruler of Great Moravia, which attained its maximum territorial expansion during his reign (870–871, 871–894).
Svatopluk's career started in the 860s, when he govern ...
, they incorrectly assumed that he also conquered it. According to archaeologist Béla Miklós Szőke, no source substantiates either the theory that Pribina was the head of an independent polity or the identification of Nitrava with Nitra.
Richard Marsina writes that the Slovak nation emerged in that principality during Pribina's reign. Regarding the 9th century, the archaeological researches successfully established a distinction between "9th-century Slavic-Moravian" and "steppe" burial horizons in Slovakia.
Great Moravia

Moravia emerged along the borders of the Avars' territory. Great Moravia arose around 830 when
Mojmír I
Mojmir I, Moimir I or Moymir I (Latin: ''Moimarus'', ''Moymarus''; Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmír I.'') was the first known ruler of the Moravian Slavs (820s/830s–846) and eponym of the House of Mojmir. In modern scholarship, the creation of ...
unified the Slavic tribes settled north of the Danube and extended the Moravian supremacy over them.
When Mojmír I endeavoured to secede from the supremacy of the king of
East Francia
East Francia (Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire created in 843 and ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was established through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the for ...
in 846, King
Louis the German
Louis the German (German language, German: ''Ludwig der Deutsche''; c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany (German language, German: ''Ludwig II. von Deutschland''), was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 8 ...
deposed him and assisted Mojmír's nephew,
Rastislav (846–870) in acquiring the throne.
The new monarch pursued an independent policy: after stopping a Frankish attack in 855, he also sought to weaken influence of Frankish priests preaching in his realm. Rastislav asked the
Byzantine Emperor
The foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, which Fall of Constantinople, fell to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised s ...
Michael III
Michael III (; 9/10 January 840 – 24 September 867), also known as Michael the Drunkard, was Byzantine emperor from 842 to 867. Michael III was the third and traditionally last member of the Amorian dynasty, Amorian (or Phrygian) dynasty. He ...
to send teachers who would interpret Christianity in the Slavic vernacular. Upon Rastislav's request, two brothers, Byzantine officials and missionaries
Saints Cyril and Methodius
Cyril (; born Constantine, 826–869) and Methodius (; born Michael, 815–885) were brothers, Byzantine Christian theologians and missionaries. For their work evangelizing the Slavs, they are known as the "Apostles to the Slavs".
They are ...
came in 863.
Cyril
Cyril (also Cyrillus or Cyryl) is a masculine given name. It is derived from the Greek language, Greek name (''Kýrillos''), meaning 'lordly, masterful', which in turn derives from Greek (''kýrios'') 'lord'. There are various variant forms of t ...
developed the
first Slavic alphabet and translated the Gospel into
Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic ( ) is the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language and the oldest extant written Slavonic language attested in literary sources. It belongs to the South Slavic languages, South Slavic subgroup of the ...
. Rastislav was also preoccupied with the security and administration of his state. Numerous fortified castles built throughout the country are dated to his reign and some of them (''e.g.'', ''Dowina'' -
Devín Castle
Devín Castle ( or , , ) is a castle in Devín, which is a borough of Bratislava, the capital of Slovakia.
Description
The site has been settled since the Neolithic Age and fortified since the Bronze and Iron Age and later by Celts and Roman ...
)
are also mentioned in connection with Rastislav by Frankish chronicles.
[."]
During Rastislav's reign, the Principality of Nitra was given to his nephew Svätopluk as an appanage. The rebellious prince allied himself with the Franks and overthrew his uncle in 870. Similarly to his predecessor, Svätopluk I (871–894) assumed the title of the king (''rex''). During his reign, the Great Moravian Empire reached its greatest territorial extent, when not only present-day Moravia and Slovakia but also present-day northern and central Hungary, Lower Austria, Bohemia, Silesia, Lusatia, southern Poland and northern Serbia belonged to the empire, but the exact borders of his domains are still disputed by modern authors.
Svätopluk also withstood attacks of the seminomadic
Hungarian tribes
and the
Bulgarian Empire Bulgarian Empire may refer to:
* First Bulgarian Empire
The First Bulgarian Empire (; was a medieval state that existed in Southeastern Europe between the 7th and 11th centuries AD. It was founded in 680–681 after part of the Bulgars, led b ...
, although sometimes it was he who hired the Hungarians when waging war against East Francia.
In 880,
Pope John VIII
Pope John VIII (; died 16 December 882) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 14 December 872 to his death. He is often considered one of the most able popes of the 9th century.
John devoted much of his papacy to attempting ...
set up an independent ecclesiastical province in Great Moravia with Archbishop
Methodius as its head. He also named the German cleric
Wiching
Wiching or Viching"Wiching", '' :sk:Encyklopédia Slovenska'' () was the first bishop of Nitra, in present-day Slovakia.
Life
He served between 880 and 891 AD. Wiching was originally a Benedictine monk from Swabia. After 874, he served Svat ...
the Bishop of Nitra.
After the death of King Svätopluk in 894, his sons
Mojmír II (894–906?) and
Svatopluk II succeeded him as the King of Great Moravia and the Prince of Nitra respectively. However, they started to quarrel for domination of the whole empire. Weakened by an internal conflict as well as by constant warfare with Eastern Francia, Great Moravia lost most of its peripheral territories.
In the meantime, the Hungarian tribes, having suffered a defeat from the nomadic
Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks, , Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: , , , , , , ka, პაჭანიკი, , , ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Pečenezi, separator=/, Печенези, also known as Pecheneg Turks were a semi-nomadic Turkic peopl ...
, left their territories east of the Carpathian Mountains, invaded the Pannonian Basin and started to occupy the territory gradually around 896. Their armies' advance may have been promoted by continuous wars among the countries of the region whose rulers still hired them occasionally to intervene in their struggles.
Both Mojmír II and Svätopluk II probably died in battles with the Hungarians between 904 and 907 because their names are not mentioned in written sources after 906. In
three battles (4–5 July and 9 August 907) near
Brezalauspurc (now Bratislava), the Hungarians routed
Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
n armies. Historians traditionally put this year as the date of the breakup of the Great Moravian Empire.
Great Moravia left behind a lasting legacy in Central and Eastern Europe. The
Glagolitic script
The Glagolitic script ( , , ''glagolitsa'') is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It is generally agreed that it was created in the 9th century for the purpose of translating liturgical texts into Old Church Slavonic by Saint Cyril, a monk fro ...
and its successor
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ) is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking countries in Southeastern Europe, Ea ...
were disseminated to other Slavic countries, charting a new path in their cultural development. The administrative system of Great Moravia may have influenced the development of the administration of the
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
.
High Middle Ages
Settlement of Hungarians in the 10th century

From 895 to 902,
the Hungarians progressively imposed their authority on the
Pannonian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, with the term Carpathian Basin being sometimes preferred in Hungarian literature, is a large sedimentary basin situated in southeastern Central Europe. After the Treaty of Trianon following World War I, the geomorpholog ...
. Although some contemporary sources mention that Great Moravia disappeared without trace and its inhabitants left, archaeological research and
toponyms
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper nam ...
suggest the continuity of Slavic population in the river valleys of the
Inner Western Carpathians
Divisions of the Carpathians are a categorization of the Carpathian mountains system.
Below is a detailed overview of the major subdivisions and ranges of the Carpathian Mountains. The Carpathians are a "subsystem" of a bigger Alps-Himalaya S ...
.
The oldest Hungarian graves in Slovakia are dated to the end of the 9th and the beginning of the 10th century (
Medzibordožie region, Eastern Slovakia). These findings document only a relatively short stay, without direct continuation in the settlement.
Further findings elsewhere, in the most southern parts of Slovakia, are dated to 920-925 and consist mainly of graves of warrior type (isolated graves and smaller groups). Between 930 and 940, larger groups of Magyars began to migrate to the southern parts of today's Slovakia, but did not cross the line
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
,
Hlohovec
Hlohovec (, Hungarian ''Galgóc''), is a town in southwestern Slovakia, with a population of 21,508.
Name
The name comes from ''*Glogovec'', the Old Slavic name for a place densely overgrown by hawthorn. The Hungarian form ''Galgóc'' was ado ...
,
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
,
Levice
Levice (; , Hungarian pronunciation: ; ) is a town in western Slovakia. The town lies on the left bank of the lower Hron river. The Old Church Slavonic, Old Slavic name of the town was ''Leva'', which means "the Left One".
The town is located i ...
,
Lučenec
Lučenec (; ; ; ; Lelkes György (1992), Magyar helységnév-azonosító szótár, Balassi Kiadó, Budapest, 508 p.) is a town in the Banská Bystrica Region of south-central Slovakia. Historically, it was part, and in the 18th century the capital ...
,
Rimavská Sobota
Rimavská Sobota (; , ) is a town in southern Slovakia, in the Banská Bystrica Region, on the Rimava river. It has approximately 24,000 inhabitants. The town is a historical capital of Gömör és Kishont County (from 1850 to 1922).
Geography ...
. The territory affected by this early migration covers about 15% of today's Slovakia (7,500 km
2). Hungarian settlements from these first two waves are not documented in the most fertile regions of
Trnava Board,
Považie north of
Hlohovec
Hlohovec (, Hungarian ''Galgóc''), is a town in southwestern Slovakia, with a population of 21,508.
Name
The name comes from ''*Glogovec'', the Old Slavic name for a place densely overgrown by hawthorn. The Hungarian form ''Galgóc'' was ado ...
,
Ponitrie north of
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
and the
Eastern Slovak Lowland
The East(ern) Slovak Lowland ( Slovak: ''Východoslovenská nížina'') is the name of a part of the Great Hungarian Plain (Slovak: ''Veľká dunajská kotlina'') situated in Slovakia.
In terms of geomorphology, it forms one unit together with t ...
.
The initial confrontation did not have a permanent character, and during the 10th century both populations coexisted. In southern Slovakia, the Hungarians frequently founded their villages close to the older Slavic settlements as they changed their nomadic lifestyle and settled; they occasionally joined them and used the same cemeteries. In the 11th century, the differences between Slavic and Magyar graves disappeared. The archaeological research has also significantly changed the view on the settlement of the northern parts of the country.
In addition to the southern parts and river valleys of
Nitra (river)
The Nitra ( Slovak: Nitra, , ) is a river in western Slovakia. It flows into the Váh river in Komoča. Its source is in the Malá Fatra (Lesser Fatra) mountains north of Prievidza. The river Nitra passes through the towns of Bojnice, Topoľč ...
and
Váh
The Váh (; , ; ; Wag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich (''in Geograph ...
, a relative high population density is notable particularly for the
Spiš
Spiš ( ; or ; ) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (more specifically encompassing 14 former Slovak villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one ...
region with the
Poprad river
The Poprad (, ) is a river in northern Slovakia and southern Poland, and a tributary of the Dunajec River near Stary Sącz, Poland. It has a length of 170 kilometres (63 km of which are within the Polish borders) and a basin area of 2,0 ...
valley and the
Turiec Basin
The Turiec Basin (; ; ; ) is located in the northern part of central Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the ...
.
Liptov
Liptov () is a historical and geographical region in central Slovakia with around 140,000 inhabitants. The area is also known by the German name ''Liptau'', the Hungarian ''Liptó'', the Latin name ''Liptovium'' and the Polish ''Liptów''.
Etym ...
and the
Zvolen Basin
Zvolen (; ; ) is a city in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina River (Slovakia), Slatina rivers. It is famous for several historical and cultural attractions. It is surrounded by Poľana Protected Landscape Area, Po� ...
s,
Žilina Basin
Žilina (; ; ; ; Names of European cities in different languages: U-Z#Z, names in other languages) is a city in north-western Slovakia, around from the capital Bratislava, close to both the Czech and Polish borders. It is the List of cities ...
, Central
Orava and northern
Šariš
Šariš is the traditional name of a region situated in northeastern Slovakia. It encompasses the territory of the former (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) Sáros county.
History
Šariš county was created in the 13th century from th ...
were rather sparsely populated.
After the fall of the state, some non-landholding noblemen joined the Hungarian forces and participated in their raids in other parts of Europe. The chroniclers of the early history of the Kingdom of Hungary recorded that the prominent noble families of the kingdom descended either from leaders of the Hungarian tribes or from immigrants, and they did not connect any of them to Great Moravia. Archeological evidence proves that to the north of the line mentioned above, not only did the older settlement structures survive, but so also did the territorial administration led by native magnates.
The Great Moravian or potential Great Moravian origin of the clan
Hunt-Pázmán (''Hont-Pázmány'') has been advanced by some modern scholars.
The territory of the present-day Slovakia became progressively integrated into the developing state (the future
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
) in the early 10th century. The ''
Gesta Hungarorum
''Gesta Hungarorum'', or ''The Deeds of the Hungarians'', is the earliest book about Kingdom of Hungary, Hungarian history which has survived for posterity. Its genre is not chronicle, but ''gesta'', meaning "deeds" or "acts", which is a medie ...
'' ("Deeds of the Hungarians") mentions that Huba, head of one of the seven Hungarian tribes, received possessions around
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
and the
Žitava River Žitava may refer to:
*Žitava (river), a river in Slovakia
*a part of the municipality Radvaň nad Dunajom
*Zittau, Žitava being the Slavic name of the town in Germany
See also
*Peace of Žitava
The Peace of Zsitvatorok (or Treaty of Sitvatorok ...
; while according to the ''
Gesta Hunnorum et Hungarorum
The ''Gesta Hunnorum et Hungarorum'Reader's encyclopedia of Eastern European literature'', 1993, Robert B. Pynsent, Sonia I. Kanikova, p. 529. (Latin: "Deeds of the Huns and Hungarians") is a medieval chronicle written mainly by Simon of K� ...
'' ("Deeds of the Huns and Hungarians") another tribal leader,
Lél, settled down around
Hlohovec
Hlohovec (, Hungarian ''Galgóc''), is a town in southwestern Slovakia, with a population of 21,508.
Name
The name comes from ''*Glogovec'', the Old Slavic name for a place densely overgrown by hawthorn. The Hungarian form ''Galgóc'' was ado ...
() and following the Hungarian victory over the Moravians, he usually stayed around Nitra. Modern authors also claim that the north-western parts of the Pannonian Basin were occupied by one of the Hungarian tribes.
''Tercia pars regni'' or Principality of Nitra (11th century)

The development of the future Kingdom of Hungary started during the reign of Grand Prince
Géza Géza () is a Hungarian given name and may refer to any of the following:
As regnal or forename
* Géza, Grand Prince of the Hungarians
* Géza I of Hungary, King of Hungary
* Géza II of Hungary, King of Hungary
* Géza, son of Géza II of Hungar ...
(before 972–997) who expanded his rule over the territories of present-day Slovakia west of the River
Garam /
Hron
The Hron (; ; ; ) is a long left tributary of the Danube[P ...]
. Although, he was baptised in or after 972, he never became a convinced Christian – in contrast to his son,
Stephen
Stephen or Steven is an English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is w ...
who followed him in 997. Some authors claim that following his marriage with
Giselle of Bavaria
Gisela of Hungary (or Gisele, Gizella and of Bavaria; 985 – 7 May 1065) was the first queen consort of Hungary by marriage to Stephen I of Hungary, and the sister of Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor. She has been beatified by the Catholic Church.
...
, Stephen received the "Duchy of Nitra" in appanage from his father.
When Géza died, a member of the Árpád dynasty, the pagan
Koppány
Koppány, also called Cupan was a Hungarian lord in the late 10th century and leader of pagans opposing the Christianization of Hungary. As the duke of Somogy, he laid claim to the throne based on the traditional idea of seniority, but was defea ...
claimed the succession, but Stephen defeated him with the assistance of his wife's German retinue. A Slovak folk song mentions that ''Štefan kral'' (''i.e.'', King Stephen) could only overcome his pagan opponent with the assistance of Slovak warriors around
Bíňa
Bíňa () is a municipality and village in the Nové Zámky District in the Nitra Region of south-west Slovakia.
Geography
The village lies at an elevation of 132 metres (433 ft) and covers an area of 23.501 km² (9.074 mi²).
Hi ...
(). According to István Bóna the Slovak song may be a translation of a Hungarian folk song, because in 1664, none of the inhabitants of Bíňa was Slovak. Following his victory, Stephen received a crown from
Pope Silvester II
Pope Sylvester II (; – 12 May 1003), originally known as Gerbert of Aurillac, was a scholar and teacher who served as the bishop of Rome and ruled the Papal States from 999 to his death. He endorsed and promoted study of Moorish and Greco-Roma ...
and he was crowned as the first
King of Hungary
The King of Hungary () was the Monarchy, ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Magyarország apostoli királya'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 ...
in 1000 or 1001.
The Kingdom of Hungary integrated elements of the former Great Moravian state organization.
On the other hand, historians have not reached a consensus on this subject; ''e.g.'', it is still being debated whether the formation of the
basic unit of the administration (''vármegye'') in the kingdom followed foreign ( Frankish, Bulgarian, Moravian or Ottonian) patterns or it was an internal innovation.
Stephen
Stephen or Steven is an English given name, first name. It is particularly significant to Christianity, Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is w ...
(1000/1001–1038) established at least eight counties ''("vármegye")'' on the territories of present-day Slovakia:
Abov
Abov (Hungarian: ''Abaúj'') is historically the Slovak name of Abaúj County in the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it is an informal designation of the part of that county situated in Slovakia, as well as the official name of one of Slovakia's touri ...
(),
Boršod (),
Esztergom
Esztergom (; ; or ; , known by Names of European cities in different languages: E–H#E, alternative names) is a city with county rights in northern Hungary, northwest of the capital Budapest. It lies in Komárom-Esztergom County, on the righ ...
,
Hont,
Komárno
Komárno (, , ), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom'', ''Öregkomárom'', ''Észak-Komárom'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian, is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old ...
(),
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
(),
Tekov
Tekov ungarian: ''Bars''is the traditional name of a region situated in southern and central Slovakia. Its territory encompasses the former Bars county, existing in the Kingdom of Hungary from the 11th century until 1918, though it is now admin ...
() and
Zemplín () were probably founded by him. The scarcely populated northern and north-eastern territories of today Slovakia became the kings' private forests. King Stephen also set up several dioceses in his kingdom; in the 11th century, present-day Slovakia's territories were divided between the
Archdiocese of Esztergom
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associated ...
(established around 1000) and its suffragan, the
Diocese of Eger (founded between 1006 and 1009).
Around 1015, Duke
Bolesław I of Poland
Bolesław or Boleslav may refer to:
People
* Bolesław (given name) (also ''Boleslav'' or ''Boleslaus''), including a list of people with this name
Geography
* Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
* Bolesław, Olkusz Coun ...
took some territories of present-day Slovakia east of the River
Morava, with Hungarian King Stephen recapturing these territories in 1018.
Following King Stephen's death, his kingdom got involved in internal conflicts among the claimants for his crown and
Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry III (, 28 October 1016 – 5 October 1056), called the Black () or the Pious, was Holy Roman Emperor from 1046 until his death in 1056. A member of the Salian dynasty, he was the eldest son of Conrad II and Gisela of Swabia.
Henry was rais ...
also intervened in the struggles. In 1042, the Emperor Henry captured some parts of today Slovakia east of the River Hron and granted them to King Stephen's cousin,
Béla
Béla may refer to:
* Béla (crater), an elongated lunar crater
* Béla (given name), a common Hungarian male given name
See also
* Bela (disambiguation)
* Belá (disambiguation)
* Bělá (disambiguation) Bělá may refer to:
Places in the Cze ...
, but following the withdrawal of the Emperor's armies, King
Samuel Aba
Samuel Aba (; before 990 or 1009 – 5 July 1044) reigned as King of Hungary between 1041 and 1044. He was born to a prominent family with extensive domains in the region of the Mátra Hills. Based on reports in the ''Gesta Hungarorum'' and ...
's troops recaptured the territories.
In 1048, King
Andrew I of Hungary
Andrew I the White or the Catholic ( or ; 1015 – before 6 December 1060) was King of Hungary from 1046 to 1060. He descended from a younger branch of the Árpád dynasty. After he spent fifteen years in exile, an extensive revolt by the paga ...
conceded
one-third of his kingdom (''Tercia pars regni'') in appanage to his brother, Duke Béla. The duke's domains were centered around Nitra and
Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
(in Romanian: ''Biharea'' in present-day
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
). During the following 60 years, the ''Tercia pars regni'' were governed separately by members of the Árpád dynasty (''i.e.'', by the Dukes
Géza Géza () is a Hungarian given name and may refer to any of the following:
As regnal or forename
* Géza, Grand Prince of the Hungarians
* Géza I of Hungary, King of Hungary
* Géza II of Hungary, King of Hungary
* Géza, son of Géza II of Hungar ...
,
Ladislaus
Ladislaus ( or according to the case) is a masculine given name of Slavic origin.
It may refer to:
* Ladislaus of Hungary (disambiguation)
* Ladislaus I (disambiguation)
* Ladislaus II (disambiguation)
* Ladislaus III (disambiguation)
* La ...
,
Lampert and
Álmos
Álmos (), also Almos or Almus ( 820 – 895), was—according to the uniform account of Hungarian chronicles—the first head of the "loose federation" of the Hungarian tribes from around 850. Whether he was the Sacred king, sacred ruler (''k ...
). The dukes accepted the kings' supremacy, but some of them (Béla, Géza and Álmos) rebelled against the king in order to acquire the crown and allied themselves with the rulers of the neighbouring countries (''e.g.'', the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
,
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
).
The history of the ''Tercia pars regni'' ended in 1107, when King
Coloman of Hungary
Coloman the Learned, also the Book-Lover or the Bookish (; ; ; 10703February 1116), was King of Hungary from 1095 and King of Croatia from 1097 until his death. Because Coloman and his younger brother Álmos were underage when their father Gé ...
occupied its territories taking advantage of the pilgrimage of Duke Álmos (his brother) to the Holy Land. Although, Duke Álmos, when returned to the kingdom, tried to reoccupy his former duchy with the military assistance of
Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry V (; probably 11 August 1081 or 1086 – 23 May 1125) was King of Germany (from 1099 to 1125) and Holy Roman Emperor (from 1111 to 1125), as the fourth and last ruler of the Salian dynasty. He was made co-ruler by his father, Henry IV, i ...
, but he failed and was obliged to accept the ''
status quo
is a Latin phrase meaning the existing state of affairs, particularly with regard to social, economic, legal, environmental, political, religious, scientific or military issues. In the sociological sense, the ''status quo'' refers to the curren ...
''.
Mongol invasion (1241–1242)

In 1241, the
Mongols
Mongols are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, China ( Inner Mongolia and other 11 autonomous territories), as well as the republics of Buryatia and Kalmykia in Russia. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family o ...
invaded and devastated the north-western parts of the kingdom. In April 1241, the Mongolian army crossed the border with
Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
near
Hrozenkov.
Trenčín Castle
The Trenčín Castle (, ) is a castle above the town of Trenčín in western Slovakia.
History
The history of the castle goes back to the age of the Roman Empire, testified by the inscription telling about the victory of the II. Roman legion at ' ...
resisted the attack, but nearby places were plundered and some of them have never been restored. Mongols turned to the south and devastated regions along rivers
Váh
The Váh (; , ; ; Wag
w Słowniku geograficznym Królestwa Polskiego i innych krajów słowiańskich (''in Geograph ...
and
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
. Only the strong castles, ''e.g.'',
Trenčín
Trenčín (, also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a List of towns in Slovakia, city in western Slovakia of the central Váh River valley near the Czech Republic, Czech border, around from Bratislava. It has a populati ...
,
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
,
Fiľakovo
Fiľakovo (; , , ) is a town in the Banská Bystrica Region of south-central Slovakia. Historically it was located in Nógrád County (former), Nógrád County, as part of the Nógrád, Novohrad, "Newcastle" region.
Geography
It is located in the ...
() and fortified towns could resist attack. A part of the unprotected population escaped to the mountains and rough terrain where they built hill forts and camps. Most affected areas were the southwest Slovakia, Lower
Pohronie to
Zvolen
Zvolen (; ; ) is a city in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers. It is famous for several historical and cultural attractions. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the ...
and
Zemplín. It is estimated that at least a third of population died from famine and epidemics.
Following the withdrawal of the Mongol army,
Frederick II, Duke of Austria
Frederick II (; 25 April 1211 – 15 June 1246), known as Frederick the Quarrelsome (''Friedrich der Streitbare''), was Duke of Austria and Styria from 1230 until his death. He was the fifth and last Austrian duke from the House of Babenberg, sin ...
invaded the country. In July 1242 his army reached
Hlohovec
Hlohovec (, Hungarian ''Galgóc''), is a town in southwestern Slovakia, with a population of 21,508.
Name
The name comes from ''*Glogovec'', the Old Slavic name for a place densely overgrown by hawthorn. The Hungarian form ''Galgóc'' was ado ...
but the Hungarian army, mainly thank to troops from Trenčín and Nitra counties repelled the attack.
Bohumír (Bogomer), the
župa
A župa, or zhupa, is a historical type of administrative division in Southeast Europe and Central Europe, that originated in medieval South Slavs, South Slavic culture, commonly translated as "county" or "parish". It was mentioned for the first t ...
n of Trenčín who played an important role in the suppression of Austrian units, later led the army send to help
Bolesław V the Chaste
Bolesław V the Chaste (; 21 June 1226 – 7 December 1279) was Duke of Sandomierz in Lesser Poland from 1232 and High Duke of Poland from 1243 until his death, as the last male representative of the Lesser Polish branch of Piasts.
Birth and n ...
(son-in-law of the Hungarian king) attacked by
Konrad I of Masovia
Konrad I of Masovia (ca. 1187/88 – 31 August 1247), from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243.
Life
Konrad w ...
. The army consisted mainly of soldiers from the ethnic Slovak counties.
Development of counties and towns
The royal administration of the territory was developing gradually during the 11th-13th centuries: new counties were established with the partition of existing ones or central counties of the kingdom expanded their territory northward today's
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
(, ),
Trenčín
Trenčín (, also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a List of towns in Slovakia, city in western Slovakia of the central Váh River valley near the Czech Republic, Czech border, around from Bratislava. It has a populati ...
, Gemer-Malohont () and
Novohrad Novohrad may refer to:
* Nógrád County (former)
Nógrád (Hungarian language, Hungarian; , or ', ) was an administrative county (') of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now divided between Hungary and Slovakia. The name ' is still used ...
(), while the kings' private forests were organised into "forest counties" around
Zvolen
Zvolen (; ; ) is a city in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers. It is famous for several historical and cultural attractions. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the ...
and
Šariš
Šariš is the traditional name of a region situated in northeastern Slovakia. It encompasses the territory of the former (Comitatus (Kingdom of Hungary), comitatus) Sáros county.
History
Šariš county was created in the 13th century from th ...
Castle (). Following the occupation of his brother's duchy, King Coloman set up (or re-established) the third bishopric in present-day Slovakia.
Some of the towns in present-day Slovakia were granted special privileges already prior to the Mongol invasion:
Trnava
Trnava (, , ; , also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, to the northeast of Bratislava, on the Trnávka river. It is the capital of the Trnava Region and the Trnava District. It is the seat o ...
(1238),
Starý Tekov
Starý Tekov (, also ''Altbarsch, Altbersenberg, (Alt-)Bersenburg'', in earlier times also ''Berschenberg'', Alt ''Berschenburg'', ) is a village and municipality in the Levice District in the Nitra Region of Slovakia.
History
In historical recor ...
(1240),
Zvolen
Zvolen (; ; ) is a city in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers. It is famous for several historical and cultural attractions. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the ...
and
Krupina
Krupina (, ) is a town in southern central Slovakia. It is part of the Banská Bystrica Region and has approximately 8,000 inhabitants.
Etymology
The name is probably derived from Slavic root ''krup''. Proto-Slavic: ''krǫpъ'', ''krǫpъjь'' � ...
(before 1241). Following the withdrawal of the Mongol troops (1242), several castles were built or strengthened (''e.g.'',
Komárno
Komárno (, , ), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom'', ''Öregkomárom'', ''Észak-Komárom'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian, is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old ...
,
Beckov
Beckov (, ) is a village and municipality in the Nové Mesto nad Váhom District in the Trenčín Region of western Slovakia.
History
In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1208. ''Mihály de genere Bána'', royal equerry, who ...
() and
Zvolen
Zvolen (; ; ) is a city in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers. It is famous for several historical and cultural attractions. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the ...
) on the order of King Béla IV. In addition to a relatively developed network of castles, agglomerations of an urban character became more important. Medieval towns should serve both to economic and defensive purposes.
The territory of present-day Slovakia was rich in raw materials like gold, silver, copper, iron and salt and therefore the mining industry developed gradually in the region. The development of the mining industry and commerce strengthened the position of some settlements and they received privileges from the kings.
The list of towns with the earliest charters contains
Spišské Vlachy
Spiśské Vlachy (, , ''Wlachy'' or ''Wallendorf'', Latin: ''Villa Latina'') is a town in eastern Slovakia. It is in the Spiš region (''Szepes'' in Hungarian or ''Zips'' in German). It is now administratively in the district of Spišská Nová V ...
(1243),
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest cit ...
(before 1248),
Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra (river), Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of ...
(1248),
Banská Štiavnica
Banská Štiavnica (; ; , ) is a town in central Slovakia, in the middle of an immense caldera created by the collapse of an ancient volcano. For its size, the caldera is known as the Štiavnica Mountains. Banská Štiavnica has a population of ...
(1255),
Nemecká Ľupča
Nemecká (; ) is a village and municipality in Brezno District, in the Banská Bystrica Region of central Slovakia. The name, which can be translated as "German village", suggests villagers, or part of them, being of Carpathian Germans, German ori ...
(1263),
Komárno
Komárno (, , ), colloquially also called ''Révkomárom'', ''Öregkomárom'', ''Észak-Komárom'' in Hungarian language, Hungarian, is a town in Slovakia at the confluence of the Danube and the Váh rivers. Historically it was formed by the "old ...
(1269),
Gelnica
Gelnica (, ) is a town in the Košice Region of Eastern Slovakia. It has a population of 6,076.
Names
The name comes from the name of the river Hnilec derived from Slavic word ''hnilý'' (rotten). The initial ''g'' in the German form ''Göllnit ...
(before 1270),
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
(1291) and
Prešov
Prešov () is a city in eastern Slovakia. It is the seat of administrative Prešov Region () and Šariš. With a population of approximately 85,000 for the city, and in total more than 100,000 with the urban area, it is the second-largest city i ...
,
Veľký Šariš
Veľký Šariš is a small town near Prešov in eastern Slovakia. The town is known as the site of the largest brewery in Slovakia – Šariš Brewery.
Etymology
The etymology of the name is uncertain. Hungarian historians and linguists prefer t ...
and
Sabinov
Sabinov (, , ) is a small town located in the Prešov Region (north-eastern Slovakia), approximately 20 km from Prešov and 55 km from Košice. The population of Sabinov is 12,700.
Etymology
The name apparently comes from some shortened ...
(all in 1299). The
Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
in
Spiš
Spiš ( ; or ; ) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (more specifically encompassing 14 former Slovak villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one ...
() were granted a collective charter (1271) by King
Stephen V of Hungary
Stephen V (, , ; before 18 October 1239 – 6 August 1272) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1270 and 1272, and Duke of Styria from 1258 to 1260. He was the oldest son of King Béla IV and Maria Laskarina. King Béla ...
.
The colonisation of the northern parts of the Kingdom of Hungary continued during the period;
Walloon,
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany, the country of the Germans and German things
**Germania (Roman era)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizenship in Germany, see also Ge ...
,
Hungarian and
Slavic
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Slav ...
"guests" (''hospes'', as they are called in contemporary documents) arrived to the scarcely populated lands and settled down there. The contemporary documents mention that settlers from
Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
and
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
arrived to the western parts of present-day Slovakia, while on the northern and eastern parts,
Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
* Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin ...
and
Ruthenian "guests" settled down.
German guests had an important but not exclusive role in the development of towns. Smaller groups of Germans were present already prior the Mongol invasion, but their immigration took a significant rate in the 13th-14th century. In that time, there already existed settlements with a relatively highly developed economy in the territory of present-day Slovakia, but Germans who came from economically and administrative more advanced regions introduced new forms of production and management, new legal system and culture. The German guests settled in Upper and Lower
Spiš
Spiš ( ; or ; ) is a region in north-eastern Slovakia, with a very small area in south-eastern Poland (more specifically encompassing 14 former Slovak villages). Spiš is an informal designation of the territory, but it is also the name of one ...
, mining towns in Central Slovakia, their wide surroundings and many localities in Western Slovakia: Bratislava,
Trnava
Trnava (, , ; , also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, to the northeast of Bratislava, on the Trnávka river. It is the capital of the Trnava Region and the Trnava District. It is the seat o ...
and wine-growing towns in
Malé Karpaty
The Little Carpathians (also: ''Lesser Carpathians'', ; ; ) are a low mountain range, about 100 km long, and part of the Carpathian Mountains. The mountains are situated in Western Slovakia, covering the area from Bratislava to Nové Mesto ...
.
In the Middle Ages, present-day Slovakia belonged to the most urbanized regions of the Kingdom of Hungary and it was an important cultural and economic base. According to the decree of the King Vladislaus II Jagiello (1498) six of the ten most important towns in the kingdom were located in the present-day Slovakia:
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest cit ...
,
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
,
Bardejov
Bardejov (; , , , , ) is a town in North-Eastern Slovakia. It is situated in the Šariš region on a floodplain terrace of the Topľa River, in the hills of the Beskids, Beskyd Mountains. It exhibits numerous cultural monuments in its completely i ...
,
Prešov
Prešov () is a city in eastern Slovakia. It is the seat of administrative Prešov Region () and Šariš. With a population of approximately 85,000 for the city, and in total more than 100,000 with the urban area, it is the second-largest city i ...
,
Trnava
Trnava (, , ; , also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, to the northeast of Bratislava, on the Trnávka river. It is the capital of the Trnava Region and the Trnava District. It is the seat o ...
and
Levoča
Levoča (; ; )
is the principal town of Levoča District in the Prešov Region of eastern Slovakia, with a population of 14,256. The town has a historic center with a well-preserved town wall, a Gothic architecture, Gothic church with the talle ...
. In 1514, more than half of the royal towns and free mining towns of the kingdom were located in Slovakia. At the end of the Middle Ages, about two hundred other settlements had an urban character from a functional point of view. The first written mention prior 1500 is available for 2.476 settlements. The mining towns in Slovakia significantly contributed to the economy of the Kingdom of Hungary. Around the middle of the 14th century,
Kremnica
Kremnica (; , ) is a town in central Slovakia. It has around 5,300 inhabitants. The well-preserved medieval town built above important gold mines is the site of the oldest still-working mint in the world.
Name
The name is derived from Slovak '' ...
alone produced 400 kg of gold per year.
Banská Štiavnica
Banská Štiavnica (; ; , ) is a town in central Slovakia, in the middle of an immense caldera created by the collapse of an ancient volcano. For its size, the caldera is known as the Štiavnica Mountains. Banská Štiavnica has a population of ...
and
Banská Bystrica
Banská Bystrica (, also known by other #Etymology, alternative names) is a city in central Slovakia, located on the Hron River in a long and wide valley encircled by the mountain chains of the Low Tatras, the Greater Fatra, Veľká Fatra, and t ...
produced a substantial proportion of silver of the whole kingdom. During the second half of the 14th century, the Kingdom of Hungary produced cca 25% of Europe's total output.
The towns formed unions and associations to defend their privileges and common interests. The most important unions were the Community of Saxons of Spiš () (later reduced and known as the province of twenty-four Spiš towns), the Lower Hungarian Mining Towns (mining towns in Central Slovakia), Pentapolis (alliance of free royal towns in present-day Eastern Slovakia) and the Upper Hungarian Mining Towns (mining towns in eastern Slovakia including two mining towns in present-day Hungary).
The inhabitants of the privileged towns were mainly of German origin, followed by Slovaks and smaller number of Hungarians. Royal privileges prove that several families of the developing local nobility (''e.g.'', the Zathureczky, Pominorszky and Viszocsányi families) were of Slavic origin. The presence of
Jew
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, religion, and community are highly inte ...
s in several towns (''e.g.'', in Bratislava,
Pezinok
Pezinok (; in the local dialect ''Pezinek''; ; ; ) is a town in southwestern Slovakia. It is roughly northeast of Bratislava and, as of December 2023, had a population of 24,443.
Pezinok lies near the Little Carpathians and thrives mainly on vi ...
) is also documented at least from the 13th century; the Jews' special status was confirmed by a charter of King
Béla IV of Hungary
Béla IV (1206 – 3 May 1270) was King of Hungary and King of Croatia, Croatia between 1235 and 1270, and Duke of Styria from 1254 to 1258. As the oldest son of Andrew II of Hungary, King Andrew II, he was crowned upon the initiative of a group ...
in 1251, but decisions of local
synods
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word ''synod'' comes from the Ancient Greek () ; the term is analogous with the Latin word . Originally, ...
limited the participation of Jews (''i.e.'', they could not hold offices and they could not own lands). The
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, living in the region of Nitra, also faced similar limitations; they disappeared (perhaps converted to Christianity) by the end of the 13th century.
Period of the oligarchs (1290–1321)

The last decades of the 13th century were characterized by discords within the royal family and among the several groups of the aristocracy. The decay of the royal power and the rise of some powerful aristocrats gave rise to the transformation of the administrative system: the counties that had been the basic units of the royal administration (
"royal counties") transformed gradually into autonomous administrative units of the local nobility (
"noble counties"); however, the local nobility was not able to stop the rise of oligarchs.
Following the Mongol invasion of the kingdom, a competition started among the landowners: each of them endeavored to build a castle with or without the permission of the king. The competition started a process of differentiation among the noble families, because the nobles who were able to build a castle could also expand their influence over the neighbouring landowners. The conflicts among the members of the royal family also strengthened the power of the aristocrats (who sometimes received whole counties from the kings) and resulted in the formation of around eight huge territories (domains) in the kingdom, governed by powerful aristocrats in the 1290s.

In present-day Slovakia, most of the castles were owned by two powerful aristocrats (
Amade Aba
Amadeus Aba or Amade Aba (; ; ? – 5 September 1311) was a Hungarian oligarch in the Kingdom of Hungary who ruled ''de facto'' independently the northern and north-eastern counties of the kingdom (today parts of Hungary, Slovakia and Ukrai ...
and
Matthew III Csák
Máté Csák or Matthew III Csák (between 1260 and 1265 – 18 March 1321; , ), also Máté Csák of Trencsén (, ), was a Hungarian oligarch who ruled ''de facto'' independently the north-western counties of Medieval Hungary (today roughly th ...
) or their followers. Following the extinction of the Árpád dynasty (1301), both of them pretended to follow one of the claimants for the throne, but, in practice, they governed their territories independently. Amade Aba governed the eastern parts of present-day Slovakia from his seat in
Gönc
Gönc ( Slovak: ''Gynec'') is a town in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county in Northern Hungary, 55 kilometers from county capital Miskolc. It is the northernmost town of Hungary and the second smallest town of the county.
History
Gönc has been in ...
. He was killed by Charles Robert of Anjou's assassins at the south gate in
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest cit ...
in 1311.
Matthew III Csák was the ''de facto'' ruler of the western territories of present-day Slovakia, from his seat at
Trenčín
Trenčín (, also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a List of towns in Slovakia, city in western Slovakia of the central Váh River valley near the Czech Republic, Czech border, around from Bratislava. It has a populati ...
. He allied himself with the murdered Amade Aba's sons against Košice, but King
Charles I of Hungary
Charles I, also known as Charles Robert (; ; ; 128816 July 1342), was King of Hungary and Croatia in the union with Hungary, Croatia from 1308 to his death. He was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou and the only son of Charles Martel of A ...
, who had managed to acquire the throne against his opponents, gave military assistance to the town and the royal armies defeated him at the
Battle of Rozgony / Rozhanovce in 1312. However, the north-western counties remained in his power until his death in 1321 when the royal armies occupied his former castles without resistance.
Pressburg (Bratislava) county was ''de facto'' ruled by the
Dukes of Austria
From 976 until 1246, the Margraviate of Austria and its successor, the Duchy of Austria, was ruled by the House of Babenberg. At that time, those states were part of the Holy Roman Empire. From 1246 until 1918, the duchy and its successor, the Ar ...
from 1301 to 1328 when King
Charles I of Hungary
Charles I, also known as Charles Robert (; ; ; 128816 July 1342), was King of Hungary and Croatia in the union with Hungary, Croatia from 1308 to his death. He was a member of the Capetian House of Anjou and the only son of Charles Martel of A ...
reoccupied it.
Late Middle Ages (14th–15th centuries)
King Charles I strengthened the central power in the kingdom following a 20-year-long period of struggles against his opponents and the oligarchs. He concluded commercial
agreements
Agreement may refer to:
Agreements between people and organizations
* Gentlemen's agreement, not enforceable by law
* Trade agreement, between countries
* Consensus (disambiguation), a decision-making process
* Contract, enforceable in a court of ...
with Kings
John of Bohemia
John of Bohemia, also called the Blind or of Luxembourg (; ; ; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of Poland. He is well known for having died while fighting ...
and
Casimir III of Poland
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king fr ...
in 1335 which increased the trade on the commercial routes leading from Košice to
Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
and from
Žilina
Žilina (; ; ; ; Names of European cities in different languages: U-Z#Z, names in other languages) is a city in north-western Slovakia, around from the capital Bratislava, close to both the Czech and Polish borders. It is the List of cities ...
(hu.
Zsolna) to
Brno
Brno ( , ; ) is a Statutory city (Czech Republic), city in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic. Located at the confluence of the Svitava (river), Svitava and Svratka (river), Svratka rivers, Brno has about 403,000 inhabitants, making ...
.
The king confirmed the privileges of the 24 "
Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
" towns in Spiš, strengthened the special rights of
Prešov
Prešov () is a city in eastern Slovakia. It is the seat of administrative Prešov Region () and Šariš. With a population of approximately 85,000 for the city, and in total more than 100,000 with the urban area, it is the second-largest city i ...
and granted town privileges to
Smolník (hu.
Szomolnok ) The towns of present-day Slovakia were still dominated by its German citizens. However, the ''
Privilegium pro Slavis
The ''Privilegium pro Slavis'' ("Privilege for the Slavs") is a privilege granted to the Slovaks in Žilina. (; ), Kingdom of Hungary, by the King Louis I during his visit there in 1381. According to this privilege, Slovaks and Germans each occup ...
'', dated to 1381, attests notably to
nation-building
Nation-building is constructing or structuring a national identity using the power of the state. Nation-building aims at the unification of the people within the state so that it remains politically stable and viable. According to Harris Mylonas, ...
in the wealthy towns: King
Louis I Louis I may refer to:
Cardinals
* Louis I, Cardinal of Guise (1527–1578)
Counts
* Ludwig I, Count of Württemberg (c. 1098–1158)
* Louis I of Blois (1172–1205)
* Louis I of Flanders (1304–1346)
* Louis I of Châtillon (died 13 ...
gave the Slavs half of the seats in the municipal council of Žilina. Many of the towns (''e.g.'', Banská Bystrica, Bratislava, Košice, Kremnica and Trnava) received the status of "
free royal cities" ''(liberæ regiæ civitates)'' and they were entitled to send deputies to the assemblies of the
Estates of the Kingdom from 1441.
In the first half of the 14th century, the population of the regions of the former "forest counties" increased and their territories formed new counties such as Orava, Liptov,
Turiec
Turiec is a region in central Slovakia, one of the 21 official tourism regions. The region is not an administrative division today, but between the late 11th century and 1920 it was the Turóc County in the Kingdom of Hungary.
Etymology
The re ...
,
Zvolen
Zvolen (; ; ) is a city in central Slovakia, situated on the confluence of Hron and Slatina rivers. It is famous for several historical and cultural attractions. It is surrounded by Poľana mountain from the East, by Kremnické vrchy from the ...
in the northern parts of present-day Slovakia. In the region of Spiš, some elements of the population received special privileges: the 24 "Saxon" towns formed an autonomous community, independent of
Spiš county
Szepes (; , , ) was an administrative county of the Kingdom of Hungary, called Scepusium before the late 19th century. Its territory today lies in northeastern Slovakia, with a very small area in southeastern Poland. For the current region, see S ...
, and the "nobles with ten lances" were organised into a special autonomous administrative unit ("seat"). In 1412, King
Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it ''Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
mortgaged 13 of the "Saxon" towns to King
Władysław II of Poland so they ''de facto'' belonged to Poland until 1769.
From the 1320s, most of the lands of present-day Slovakia were owned by the kings, but
prelate
A prelate () is a high-ranking member of the Minister (Christianity), Christian clergy who is an Ordinary (church officer), ordinary or who ranks in precedence with ordinaries. The word derives from the Latin , the past participle of , which me ...
s and aristocratic families (''e.g.'', the
Drugeth
The House of Drugeth was a powerful noble family (of French origin) of the Kingdom of Hungary in the 14th to 17th centuries whose possessions were located in the northeastern parts of the kingdom. The ancestors of the family left Apulia (Southern ...
,
Szentgyörgyi
The Szentgyörgyi, also Szentgyörgyi és Bazini, was a noble family of the Kingdom of Hungary in the 13th to 16th centuries. The ancestor of the family, Thomas descended from the ''gens'' ("clan") Hont-Pázmány and he was the head ''(ispán)'' o ...
and
Szécsényi families) also hold properties on the territory.
In December 1385, the future King Sigismund, who was Queen Mary of Hungary's
prince consort
A prince consort is the husband of a monarch who is not a monarch in his own right. In recognition of his status, a prince consort may be given a formal title, such as ''prince''. Most monarchies do not allow the husband of a queen regnant to be ...
at that time, mortgaged the territories of present-day Slovakia west of the Váh River to his cousins, the
Jobst Jobst is a given name and surname.
Given name
People with given name Jobst include:
* Jobst of Moravia
* Jobst Oetzmann
* Jobst Brandt
* Jobst Fricke
* Jobst Wagner
* Jobst Nikolaus I, Count of Hohenzollern
* Jobst II, Count of Hoya
* Jobst Harr ...
and
Prokop of Moravia
Prokop of Moravia, or Prokop of Luxembourg (; ; c. 1358 – 24 September 1405), a member of the House of Luxembourg, was junior Margrave of Moravia from 1375 until his death in 1405 and the provincial governor of the kingdom.
Biography
Prokop ...
; and the former held his territories until 1389, while the latter could maintain his rule over some of the territories until 1405. King Sigismund (1387–1437) granted vast territories to his followers (''e.g.'', to the members of the
Cillei,
Rozgonyi and
Perényi Perényi may refer to:
* Béla Perényi, Hungarian chess player
*Eleanor Perenyi, American gardener and garden writer
*Péter Perényi, Comes of Temesvár
*Péter Perényi (1502–1548), Voivode of Transylvania
*Miklós Perényi
Miklós Perényi ...
families) during his reign; one of his principal advisers, the Polish
Stibor of Stiboricz
Stibor of Stiboricz of Ostoja coat of arms, Ostoja (also written in English as Scibor or Czibor; , , , ; c. 1348 – February 1414) was an aristocrat of Polish people, Polish origin in the Kingdom of Hungary. He was a close friend of King Sig ...
styled himself "Lord of the whole Váh" referring to his 15 castles around the river.
Following the death of King
Albert
Albert may refer to:
Companies
* Albert Computers, Inc., a computer manufacturer in the 1980s
* Albert Czech Republic, a supermarket chain in the Czech Republic
* Albert Heijn, a supermarket chain in the Netherlands
* Albert Market, a street mar ...
(1439), civil war broke out among the followers of the claimants for the throne. The Dowager Queen
Elisabeth hired Czech
mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rath ...
led by Jan Jiskra who captured several towns on the territory of present-day Slovakia (''e.g.'', Kremnica,
Levoča
Levoča (; ; )
is the principal town of Levoča District in the Prešov Region of eastern Slovakia, with a population of 14,256. The town has a historic center with a well-preserved town wall, a Gothic architecture, Gothic church with the talle ...
and
Bardejov
Bardejov (; , , , , ) is a town in North-Eastern Slovakia. It is situated in the Šariš region on a floodplain terrace of the Topľa River, in the hills of the Beskids, Beskyd Mountains. It exhibits numerous cultural monuments in its completely i ...
) and maintained most of them until 1462 when he surrendered to King Matthias Corvinus of Hungary, Matthias Corvinus.
Modern era
Early modern period
Habsburg and Ottoman administration
The Ottoman Empire conquered the central part of the Kingdom of Hungary, and set up several Ottoman provinces there (see Budin Eyalet, Eğri Eyalet, Uyvar Eyalet).
Transylvania became an Principality of Transylvania (1571–1711), Ottoman protectorate vassal and a base which gave birth to all the anti-Habsburg revolts led by the nobility of the Kingdom of Hungary during the period 1604 to 1711.
The remaining part of the former Kingdom of Hungary, which included much of present-day territory of Slovakia (except for the southern central regions), northwestern present-day Hungary, northern Croatia and present-day Burgenland, resisted Ottoman conquest and subsequently became a province of the
Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
. It remained to be known as the Kingdom of Hungary, but it is referred to by some modern historians as the "Royal Hungary".
Ferdinand I, prince of Austria was elected king of Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary. After the conquest of Buda in 1541 by the Ottomans, ''Pressburg'' (the modern-day capital of Slovakia,
Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
) became, for the period between 1536 and 1784/1848 the capital and the coronation city of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary.
From 1526 to 1830, nineteen Habsburg sovereigns went through coronation ceremonies as Kings and Queens of the Kingdom of Hungary in St. Martin's Concathedral, St. Martin's Cathedral.
After the Ottoman invasion, the territories that had been administered by the Kingdom of Hungary became, for almost two centuries, the principal battleground of the Turkish wars. The region suffered due to the wars against the Ottoman expansion. A lot of loss of life and property occurred during the wars and the region also practically lost all of its natural riches, especially gold and silver, which went to pay for the costly and difficult combats of an endemic war. In addition, the double taxation of some areas was a common practice, which further worsened the living standards of the declining population of local settlements.

During Ottoman administration, parts of the territory of present-day Slovakia were included into Ottoman provinces known as the Budin Eyalet, Eğri Eyalet and Uyvar Eyalet. Uyvar Eyalet had its administrative center in the territory of present-day Slovakia, in the town of Nové Zámky, Uyvar (Slovak: Nové Zámky). In the second half of the 17th century, Ottoman authority was expanded to eastern part of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary, where a vassal Ottoman principality led by prince Imre Thököly was established.
After the ousting of the Ottomans from Budin (which later became Budapest) in 1686, it became the capital of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary. Despite living under Hungarian, Habsburg and Ottoman administration for several centuries, the Slovak people succeeded in keeping their language and their culture.
Late modern period
Slovak National Movement
During the 18th century the Slovak National Movement emerged, partially inspired by the broader Pan-slavism, Pan-Slavic movement with the aim of fostering a sense of national identity among the Slovak people. Advanced mainly by Slovak religious leaders, the movement grew during the 19th century. At the same time, the movement was divided along the confessional lines and various groups had different views on everything from quotidian strategy to linguistics. Moreover, the Hungarian control remained strict after 1867 and the movement was constrained by the official policy of magyarization.
The first codification of standard Slovak by Anton Bernolák in the 1780s was based on the dialect from western Slovakia. It was supported by mainly Roman Catholicism, Roman Catholic intellectuals, with the center in
Trnava
Trnava (, , ; , also known by other #Names and etymology, alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, to the northeast of Bratislava, on the Trnávka river. It is the capital of the Trnava Region and the Trnava District. It is the seat o ...
. The Lutheran intellectuals continued to use a Slovakized form of Czech. Especially Ján Kollár and Pavel Jozef Šafárik were adherents of Pan-Slavic concepts that stressed the unity of all Slavic peoples. They considered
Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia ...
and
Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
members of a single nation and they attempted to draw the languages closer together.
In the 1840s, the Protestants split as
Ľudovít Štúr
Ľudovít Štúr (; 28 October 1815 – 12 January 1856), also known as Ľudovít Velislav Štúr, was a Slovak revolutionary, politician, and writer. As a leader of the Slovak nationalism, Slovak national revival in the 19th century and the c ...
developed a standard language based on the dialect from central Slovakia. His followers stressed the separate identity of the Slovak nation and uniqueness of its language. Štúr's version was finally approved by both the Catholics and the Lutherans in 1847 and, after several reforms, it remains standard
Slovak.

Hungarian Revolution of 1848
In the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, Slovak nationalist leaders took the side of the Austrians in order to promote their separation from the Kingdom of Hungary within the Austrian monarchy. The Slovak National Council (1848–1849), Slovak National Council even organized an uprising from Vienna with the aim of equalizing Slovaks and gaining autonomy in the Habsburg monarchy, called the Slovak Uprising of 1848–49, Slovak Uprising. In September, 1848, the Slovak National Council managed to organize a short-lived administration of the captured territories. However, the Slovak troops were later disbanded by the Vienna Imperial Court. On the other hand, thousands of volunteers from the current territory of Slovakia, among them a great number of Slovaks, fought in the Hungarian Army.
After the defeat of the Hungarian Revolution, the Hungarian political elite was oppressed by the Austrian authorities and many participants of the Revolution were executed, imprisoned, or forced to emigrate. In 1850, the Kingdom of Hungary was divided into five military districts or provinces, two of which had administrative centers in the territory of present-day Slovakia: the Military District of Pressburg (Bratislava) and the Military District of Košice.
The Austrian authorities abolished both provinces in 1860. The Slovak political elite made use of the period of neo-absolutism of the Vienna court and the weakness of the traditional Hungarian elite to promote their national goals. Turz-Sankt Martin (Martin, Slovakia, Martin / Túrócszentmárton) became the foremost center of the Slovak National Movement with foundation of the nationwide cultural association Matica slovenská (1863), the Slovak National Museum, and the Slovak National Party (historical party), Slovak National Party (1871).
Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867
The heyday of the movement came to a sudden end after 1867, when the Habsburg domains in central Europe underwent a Ausgleich, constitutional transformation into the dual monarchy of
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
as a result of the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867. The territory of present-day Slovakia was included in the Hungarian part of the dual monarchy, dominated by the Hungarian political elite which distrusted the Slovak elite due to its Pan-Slavism, separatism and its recent stand against the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. Matica was accused of Pan-Slavic separatism and was dissolved by the authorities in 1875; and other Slovak institutions (including schools) shared the same fate.
New signs of national and political life appeared only at the very end of the 19th century. Slovaks became aware that they needed to ally themselves with others in their struggle. One result of this awareness, the Congress of Oppressed Peoples of the Kingdom of Hungary, held in Budapest in 1895, alarmed the government. In their struggle Slovaks received a great deal of help from the Czechs. In 1896, the concept of Czecho-Slovak Mutuality was established in Prague to strengthen Czecho-Slovak cooperation and support the secession of Slovaks from the Kingdom of Hungary.
At the beginning of the 20th century, growing democratization of political and social life threatened to overwhelm the monarchy. The call for universal suffrage became the main rallying cry. In the Kingdom of Hungary, only 5 percent of inhabitants could vote. Slovaks saw in the trend towards representative democracy a possibility of easing ethnic oppression and a breakthrough into renewed political activity.
The Slovak political camp, at the beginning of the century, split into different factions. The leaders of the Slovak National Party, based in Martin, expected the international situation to change in the Slovaks' favor, and they set great store by Russia. The Roman Catholic faction of Slovak politicians led by Father Andrej Hlinka focused on small undertakings among the Slovak public and, shortly before the war, established a political party named the Slovak People's Party. The liberal intelligentsia rallying around the journal ''Hlas'' ("Voice"), followed a similar political path, but attached more importance to Czecho-Slovak cooperation. An independent Slovak Social Democratic Party of the Kingdom of Hungary, Social Democratic Party emerged in 1905.

The Slovaks achieved some results. One of the greatest of these was the election success in 1906, when, despite continued oppression, seven Slovaks managed to get seats in the Assembly. This success alarmed the government, and increased what was regarded by Slovaks as its oppressive measures. Magyarization achieved its climax with a new education act known as the Apponyi Act, named after education minister Count Albert Apponyi. The new act stipulated that the teaching of Hungarian must be included as a subject in the curriculum of non-state-owned four years elementary schools in the framework of compulsory schooling, as a condition for those schools to receive state financing. Non-government organizations such as the Upper Hungary Magyar Educational Society supported Magyarization at a local level.
Ethnic tension intensified when 15 Slovaks were killed during a riot on the occasion of the consecration of a new church at Černová / Csernova near Rózsahegy / Ružomberok (see Černová tragedy). The local inhabitants wanted the popular priest and nationalist politician Andrej Hlinka to consecrate their new church. Hlinka contributed significantly to the construction of the church, but his bishop Alexander Párvy suspended him from his office and from exercising all clerical functions because of Hlinka's involvement in the national movement. This resulted in a wave of solidarity with Hlinka across all today's Slovakia. The villagers tried to achieve a compromise solution and to cancel the suspensions or to postpone consecration until the Holy See decided about the Hlinka case. Párvy refused to consent, and appointed ethnic Slovak dean Martin Pazúrik for the task. Pazúrik, as well as Hlinka, were active in the election campaign but supported Hungarian and Magyarone politicians and continuously adopted an anti-Slovak attitude. The church had to be consecrated by force, with police assistance. Given where the event occurred, all 15 local gendarmes who participated in the subsequent tragedy were of Slovak origin. In the stress situation, the gendarmes shot dead 15 protesters among a crowd of about 300–400 villagers who tried to avoid the priests' convoy to enter their village. All this added to Slovak estrangement from and resistance to Hungarian rule, and the incident raised international attention on violation of national rights of non-Hungarian minorities.
Before the outbreak of World War I, the idea of Slovak autonomy became part of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, Archduke Franz Ferdinand's plan of federalization of the monarchy, developed with help of the Slovak journalist and politician Milan Hodža. This last realistic attempt to tie Slovakia to Austria-Hungary was abandoned because of the Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, Archduke's assassination, which in turn triggered World War I.
Czechoslovakia
= Formation of Czechoslovakia
=
After the outbreak of
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
the Slovak cause took firmer shape in resistance and in determination to leave the Dual Monarchy and to form an independent republic with the Czechs. The decision originated amongst people of Slovak descent in foreign countries. Slovaks in the United States of America, an especially numerous group, formed a sizable organization. These, and other organizations in Russia and in neutral countries, backed the idea of a Czecho-Slovak republic. Slovaks strongly supported this move.
The most important Slovak representative at this time, Milan Rastislav Štefánik, a French citizen of Slovak origin, served as a French general and as leading representative of the Czecho-Slovak National Council based in Paris. He made a decisive contribution to the success of the Czecho-Slovak cause. Political representatives at home, including representatives of all political persuasions, after some hesitation, gave their support to the activities of Tomáš Masaryk, Masaryk, Edvard Beneš, Beneš and Štefánik.
During the war the Hungarian authorities increased harassment of Slovaks, which hindered the nationalist campaign among the inhabitants of the Slovak lands. Despite stringent censorship, news of moves abroad towards the establishment of a Czech-Slovak state got through to Slovakia and met with much satisfaction.
During
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
(1914–1918) Czechs, Slovaks, and other national groups of Austria-Hungary gained much support from Czechs and Slovaks living abroad in campaigning for an independent state. In the turbulent final year of the war, sporadic protest actions took place in Slovakia; politicians held a secret meeting at Liptószentmiklós / Liptovský Mikuláš on 1 May 1918.
= First Czechoslovak Republic (1918–1938)
=
At the end of the war Austria-Hungary dissolved. The Prague National Committee proclaimed an independent republic of
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
on 28 October, and, two days later, the Slovak National Council (1918), Slovak National Council at Martin, Slovakia, Martin acceded to the Prague proclamation. The new republic was to include the Czech lands (
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
and
Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
), a small part of Silesia, Slovakia, and Subcarpathian Ruthenia. The new state set up a parliamentary democratic government and established a capital in the Czech city of Prague.
As a result of the counter-attack of the Hungarian Red Army in May–June, 1919, Czech troops were ousted from central and eastern parts of present Slovakia, where a puppet short-lived Slovak Soviet Republic with its capital in
Prešov
Prešov () is a city in eastern Slovakia. It is the seat of administrative Prešov Region () and Šariš. With a population of approximately 85,000 for the city, and in total more than 100,000 with the urban area, it is the second-largest city i ...
was established. However, the Hungarian army stopped its offensive and later the troops were withdrawn on the Entente's diplomatic intervention.

In the Treaty of Trianon signed in 1920, the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference set the southern border of Czechoslovakia further south from the Slovak-Hungarian language border due to strategic and economic reasons. Consequently, some fully or mostly Hungarian-populated areas were also included into Czechoslovakia. According to the 1910 census, which had been manipulated by the ruling Hungarian bureaucracy,
population of the present territory of Slovakia numbered 2,914,143 people, including 1,688,413 (57.9%) speakers of
Slovak, 881,320 (30.2%) speakers of Hungarian language, Hungarian, 198,405 (6.8%) speakers of German, 103,387 (3.5%) speakers of Rusyn language, Ruthenian and 42,618 (1.6%) speakers of other languages.
In addition, in Subcarpathian Ruthenia, which was also included into Czechoslovakia in this time period, the 1910 manipulated Hungarian census recorded 605,942 people, including 330,010 (54.5%) speakers of Rusyn language, Ruthenian, 185,433 (30.6%) speakers of Hungarian, 64,257 (10.6%) speakers of German, 11,668 (1.9%) speakers of Romanian language, Romanian, 6,346 (1%) speakers of
Slovak/Czech language, Czech, and 8,228 (1.4%) speakers of other languages. The Czechoslovak census of 1930 recorded in Slovakia 3,254,189 people, including 2,224,983 (68.4%)
Slovaks
The Slovaks ( (historical Sloveni ), singular: ''Slovák'' (historical: ''Sloven'' ), feminine: ''Slovenka'' , plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history ...
, 585,434 (17.6%) Hungarians, 154,821 (4.5%) Germans, 120,926 (3.7%)
Czechs
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavs, West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common Bohemia ...
, 95,359 (2.8%) Rusyns and 72,666 (3%) others.
[
Slovaks, whom the Czechs outnumbered in the Czechoslovak state, differed in many important ways from their Czech neighbors. Slovakia had a more agrarian and less developed economy than the Czech lands, and the majority of Slovaks practised Catholicism while fewer Czechs adhered to established religions. The Slovak people had generally less education and less experience with self-government than the Czechs. These disparities, compounded by centralized governmental control from Prague, produced discontent with the structure of the new state among the Slovaks.
Although Czechoslovakia, alone among the east-central European countries, remained a parliamentary democracy from 1918 to 1938, it continued to face minority problems, the most important of which concerned the country's large German population. A significant part of the new Slovak political establishment sought autonomy for Slovakia. The movement toward autonomy built up gradually from the 1920s until it culminated in independence in 1939.]Jozef Tiso
Jozef Gašpar Tiso (, ; 13 October 1887 – 18 April 1947) was a Slovaks, Slovak politician and Catholic priest who served as president of the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), First Slovak Republic, a client state of Nazi Germany during World War ...
in calls for equality between Czechs and Slovaks and for greater autonomy for Slovakia.
=Towards autonomy of Slovakia (1938–1939)
=
 In September 1938, France, Italy, United Kingdom and Nazi Germany concluded the Munich Agreement, which forced Czechoslovakia to cede the predominantly German region known as the Sudetenland to Germany. In November, by the First Vienna Award, Italy and Germany compelled Czechoslovakia (later Slovakia) to cede primarily Hungarian-inhabited Southern Slovakia to Hungary. They did this in spite of pro-German official declarations of Czech and Slovak leaders made in October. The Autonomous Land of Slovakia was established within the Second Czechoslovak Republic.
On 14 March 1939, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic (''Slovenská republika'') declared its independence and became a nominally independent state in Central Europe under Nazi Germany, Nazi German control of foreign policy and, increasingly, also some aspects of domestic policy.
In September 1938, France, Italy, United Kingdom and Nazi Germany concluded the Munich Agreement, which forced Czechoslovakia to cede the predominantly German region known as the Sudetenland to Germany. In November, by the First Vienna Award, Italy and Germany compelled Czechoslovakia (later Slovakia) to cede primarily Hungarian-inhabited Southern Slovakia to Hungary. They did this in spite of pro-German official declarations of Czech and Slovak leaders made in October. The Autonomous Land of Slovakia was established within the Second Czechoslovak Republic.
On 14 March 1939, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic (''Slovenská republika'') declared its independence and became a nominally independent state in Central Europe under Nazi Germany, Nazi German control of foreign policy and, increasingly, also some aspects of domestic policy. Jozef Tiso
Jozef Gašpar Tiso (, ; 13 October 1887 – 18 April 1947) was a Slovaks, Slovak politician and Catholic priest who served as president of the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), First Slovak Republic, a client state of Nazi Germany during World War ...
became Prime Minister and later President of the new state.
On 15 March, Nazi Germany invaded what remained of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
, and Silesia after the Munich agreement. The Germans established a protectorate over them which was known as the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. On the same day, Carpatho-Ukraine declared its independence. But Hungary immediately invaded and annexed the Republic of Carpatho-Ukraine. On 23 March, Hungary then occupied some additional disputed parts of territory of the present-day Eastern-Slovakia. This caused the brief Slovak-Hungarian War.
World War II
 The nominally independent Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic went through the early years of the war in relative peace. As an Axis Powers, Axis ally, the country took part in the Slovak invasion of Poland, wars against Poland and the Soviet Union. Although its contribution was symbolic in the German war efforts, the number of troops involved (approx. 45,000 in the Soviet campaign) was rather significant in proportion to the population (2.6 million in 1940).
Soon after independence, under the authoritarian government of Jozef Tiso, a series of measures aimed against the 90,000 Jews in the country were initiated. The Hlinka Guard began to attack Jews, and the "Jewish Code" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the Nuremberg Laws, the Code required that Jews wear a yellow armband, and they were banned from intermarriage and from many jobs. More than 64.000 Jews lost their livelihood. Between March and October 1942, the state deported approximately 57,000 Jews to the German-occupied part of Poland, where almost all of them were killed in Extermination camps. The Slovak Parliament accepted a bill that retroactively legalized the deportation in May 1942. The deportation of the remaining Jewish population was stopped when the government "resolved" the social problem caused by its own policy. However, 12,600 more Jews were deported by the German forces occupying Slovakia after the Slovak National Uprising in 1944. Around a half of them were killed in concentration camps. Other Jews were rounded up and massacred in the country by Slovak collaborators under German command, at Kremnička and Nemecká massacres, Kremnička and Nemecká. Some 10,000 Slovak Jews survived in Slovakia.
On 29 August 1944, 60,000 Slovak troops and 18,000 partisans, organized by various underground groups and the Czechoslovak government-in-exile, rose up against the Nazis. The insurrection later became known as the Slovak National Uprising. Slovakia was devastated by the fierce German counter-offensive and occupation, but the guerrilla warfare continued even after the end of organized resistance. Although ultimately quelled by the German forces, the uprising was an important historical reference point for the Slovak people. It allowed them to end the war as a nation which had contributed to the Allied victory.
Later in 1944 the Soviet attacks intensified. The Red Army, helped by Romanian troops, gradually routed out the German army from Slovak territory. On 4 April 1945, Soviet troops marched into the capital city of the Slovak Republic, Bratislava.
The nominally independent Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic went through the early years of the war in relative peace. As an Axis Powers, Axis ally, the country took part in the Slovak invasion of Poland, wars against Poland and the Soviet Union. Although its contribution was symbolic in the German war efforts, the number of troops involved (approx. 45,000 in the Soviet campaign) was rather significant in proportion to the population (2.6 million in 1940).
Soon after independence, under the authoritarian government of Jozef Tiso, a series of measures aimed against the 90,000 Jews in the country were initiated. The Hlinka Guard began to attack Jews, and the "Jewish Code" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the Nuremberg Laws, the Code required that Jews wear a yellow armband, and they were banned from intermarriage and from many jobs. More than 64.000 Jews lost their livelihood. Between March and October 1942, the state deported approximately 57,000 Jews to the German-occupied part of Poland, where almost all of them were killed in Extermination camps. The Slovak Parliament accepted a bill that retroactively legalized the deportation in May 1942. The deportation of the remaining Jewish population was stopped when the government "resolved" the social problem caused by its own policy. However, 12,600 more Jews were deported by the German forces occupying Slovakia after the Slovak National Uprising in 1944. Around a half of them were killed in concentration camps. Other Jews were rounded up and massacred in the country by Slovak collaborators under German command, at Kremnička and Nemecká massacres, Kremnička and Nemecká. Some 10,000 Slovak Jews survived in Slovakia.
On 29 August 1944, 60,000 Slovak troops and 18,000 partisans, organized by various underground groups and the Czechoslovak government-in-exile, rose up against the Nazis. The insurrection later became known as the Slovak National Uprising. Slovakia was devastated by the fierce German counter-offensive and occupation, but the guerrilla warfare continued even after the end of organized resistance. Although ultimately quelled by the German forces, the uprising was an important historical reference point for the Slovak people. It allowed them to end the war as a nation which had contributed to the Allied victory.
Later in 1944 the Soviet attacks intensified. The Red Army, helped by Romanian troops, gradually routed out the German army from Slovak territory. On 4 April 1945, Soviet troops marched into the capital city of the Slovak Republic, Bratislava.
Czechoslovakia after World War II
The victorious Powers restored Czechoslovakia in 1945 in the wake of World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, albeit without Carpathian Ruthenia, which Prague ceded to the Soviet Union. The Beneš decrees, adopted as a result of the events of the war, led to disenfranchisement and persecution of the Hungarian minority in southern Slovakia. The local Carpathian Germans, German minority was Flight and expulsion of Germans (1944–1950), expelled, with only the population of some villages such as Chmeľnica evading expulsion but suffering discrimination against use of their language.
The Czechs and Slovaks held elections in 1946. In Slovakia, the Democratic Party won the elections (62%), but the Czechoslovak Communist Party won in the Czech part of the republic, thus winning 38% of the total vote in Czechoslovakia, and eventually seized power in February 1948, making the country effectively a satellite state of the Soviet Union.
Strict Communist control characterized the next four decades, interrupted only briefly in the so-called Prague Spring
The Prague Spring (; ) was a period of liberalization, political liberalization and mass protest in
the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic. It began on 5 January 1968, when reformist Alexander Dubček was elected Secretary (title), First Secre ...
of 1968 after Alexander Dubček (a Slovak) became First Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia. Dubček proposed political, social, and economic reforms in his effort to make "socialism with a human face" a reality. Concern among other Warsaw Pact governments that Dubček had gone too far led to the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia, invasion and occupation of Czechoslovakia on 21 August 1968, by Soviet, Hungarian, Bulgarian, East German, and Polish troops. Another Slovak, Gustáv Husák, replaced Dubček as Communist Party leader in April 1969.
 The 1970s and 1980s became known as the period of "Normalization (Czechoslovakia), normalization", in which the apologists for the 1968 Soviet invasion prevented as best they could any opposition to their conservative régime. Political, social, and economic life stagnated. Because the reform movement had had its center in Prague, Slovakia experienced "normalization" less harshly than the Czech lands. In fact, the Slovak Republic saw comparatively high economic growth in the 1970s and 1980s relative to the Czech Republic (and mostly from 1994 till ).
The 1970s also saw the development of a dissident movement, especially in the Czech Republic. On 1 January 1977, more than 250 human rights activists signed a manifesto called Charter 77, which criticized the Czechoslovak government for failing to meet its human rights obligations.
The 1970s and 1980s became known as the period of "Normalization (Czechoslovakia), normalization", in which the apologists for the 1968 Soviet invasion prevented as best they could any opposition to their conservative régime. Political, social, and economic life stagnated. Because the reform movement had had its center in Prague, Slovakia experienced "normalization" less harshly than the Czech lands. In fact, the Slovak Republic saw comparatively high economic growth in the 1970s and 1980s relative to the Czech Republic (and mostly from 1994 till ).
The 1970s also saw the development of a dissident movement, especially in the Czech Republic. On 1 January 1977, more than 250 human rights activists signed a manifesto called Charter 77, which criticized the Czechoslovak government for failing to meet its human rights obligations.
Velvet Revolution (1989)
On 17 November 1989, a series of public protests known as the "Velvet Revolution
The Velvet Revolution () or Gentle Revolution () was a non-violent transition of power in what was then Czechoslovakia, occurring from 17 November to 28 November 1989. Popular demonstrations against the one-party government of the Communist Pa ...
" began and led to the downfall of Communist Party rule in Czechoslovakia. A transition government formed in December 1989, and the first free elections in Czechoslovakia since 1948 took place in June 1990. In 1992, negotiations on the new federal constitution deadlocked over the issue of Slovak autonomy. In the latter half of 1992, agreement emerged to dissolve Czechoslovakia peacefully. On 1 January 1993, the Czech Republic and the Slovak Republic each simultaneously and peacefully proclaimed their existence. Both states attained immediate recognition from the United States of America and from their European neighbors.
In the days following the "Velvet Revolution," Charter 77 and other groups united to become the Civic Forum, an umbrella group championing bureaucratic reform and civil liberties. Its leader, the playwright and former dissident Václav Havel won election as President of Czechoslovakia in December 1989. The Slovak counterpart of the Civic Forum, Public Against Violence, expressed the same ideals.
In the June 1990 elections, Civic Forum and Public Against Violence won landslide victories. Civic Forum and Public Against Violence found, however, that although they had successfully completed their primary objective – the overthrow of the communist régime – they proved less effective as governing parties. In the 1992 elections, a spectrum of new parties replaced both Civic Forum and Public Against Violence.
Contemporary period
Independent Slovakia
 In an Slovak parliamentary election, 1992, election held in June 1992, Václav Klaus's Civic Democratic Party won in Czechia on a platform of economic reform, and Vladimír Mečiar's Movement for a Democratic Slovakia (HZDS) emerged as the leading party in Slovakia, on a platform of Slovak autonomy. Mečiar and Klaus negotiated the Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, agreement to divide Czechoslovakia, and Mečiar's party – HZDS – ruled Slovakia for most of its first five years as an independent state, except for a 9-month period in 1994 after a vote of no-confidence, during which a reformist government under Prime Minister Jozef Moravčík operated.
The first president of newly independent Slovakia was Michal Kováč. The first prime minister, Mečiar, had served as the prime minister of the Slovak part of Czechoslovakia since 1992.
Rudolf Schuster won Slovak presidential election, 1999, the presidential election in May 1999. Mečiar's semi-authoritarian government allegedly breached democratic norms and the rule of law before its replacement after the parliamentary elections of 1998 by a coalition led by Mikuláš Dzurinda.
The first Dzurinda government made numerous political and economic reforms that enabled Slovakia to enter the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), close virtually all chapters in
In an Slovak parliamentary election, 1992, election held in June 1992, Václav Klaus's Civic Democratic Party won in Czechia on a platform of economic reform, and Vladimír Mečiar's Movement for a Democratic Slovakia (HZDS) emerged as the leading party in Slovakia, on a platform of Slovak autonomy. Mečiar and Klaus negotiated the Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, agreement to divide Czechoslovakia, and Mečiar's party – HZDS – ruled Slovakia for most of its first five years as an independent state, except for a 9-month period in 1994 after a vote of no-confidence, during which a reformist government under Prime Minister Jozef Moravčík operated.
The first president of newly independent Slovakia was Michal Kováč. The first prime minister, Mečiar, had served as the prime minister of the Slovak part of Czechoslovakia since 1992.
Rudolf Schuster won Slovak presidential election, 1999, the presidential election in May 1999. Mečiar's semi-authoritarian government allegedly breached democratic norms and the rule of law before its replacement after the parliamentary elections of 1998 by a coalition led by Mikuláš Dzurinda.
The first Dzurinda government made numerous political and economic reforms that enabled Slovakia to enter the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), close virtually all chapters in European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
(EU) negotiations, and make itself a strong candidate for accession to North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). However, the popularity of the governing parties declined sharply, and several new parties that earned relatively high levels of support in public opinion polls appeared on the political scene. Mečiar remained the leader (in opposition) of the HZDS, which continued to receive the support of 20% or more of the population during the first Dzurinda government.
In the September 2002 parliamentary election, a last-minute surge in support for Prime Minister Dzurinda's Slovak Democratic and Christian Union (SDKÚ) gave him a mandate for a second term. He formed a government with three other center-right parties: the Party of the Hungarian Coalition (SMK), the Christian Democratic Movement, Christian Democrats (KDH) and the Alliance of the New Citizen (ANO). The coalition won a narrow (three-seat) majority in the parliament. Dzurinda's Second Cabinet (2002–2006) announced strong NATO and EU integration and said they would continue the democratic and free market-oriented reforms begun by the first Dzurinda government.
The new coalition's main priorities were aimed at gaining NATO and EU invitations, attracting foreign investment, and reforming social services such as the health-care system. Vladimír Mečiar's Movement for a Democratic Slovakia, which received about 27% of the vote in 1998 (almost 900,000 votes), received only 19.5% (about 560,000 votes) in 2002 and again went into opposition, unable to find coalition partners. The opposition comprised the HZDS, Direction – Social Democracy, Smer (led by Robert Fico), and the Communist Party of Slovakia, Communists, who obtained about 6% of the popular vote.
Initially, Slovakia experienced more difficulty than the Czech Republic in developing a modern market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production, and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand. The major characteristic of a mark ...
. Slovakia Enlargement of NATO, joined NATO on 29 March 2004 and 2004 enlargement of the European Union, the EU on 1 May 2004. Slovakia was, on 10 October 2005, for the first time elected to a two-year term on the UN Security Council (for 2006–2007).
The next election took place on 17 June 2006, where the leftist Smer got 29.14% (around 670 000 votes) of the popular vote and formed a coalition with Slota's Slovak National Party and Mečiar's Movement for a Democratic Slovakia. Their opposition comprised the former ruling parties: the SDKÚ, the SMK and the KDH.
The Slovak parliamentary election, 2010, election in June 2010 was won by Smer with 34.8% but Fico was unable to form a government, so a coalition of SDKU, KDH, SaS and Most-Hid took over, with Iveta Radičová as the first woman prime minister. This government fell after the vote of the European Financial Stability Fund was connected with a no-confidence vote, as SaS argued, that Slovakia, should not bail out much richer countries.
Smer won the Slovak parliamentary election, 2012, election in 2012 with 44,42%. Fico formed Fico's Second Cabinet, his Second Cabinet. It was a single-party government claiming 83 of the 150 seats.
It officially supported the position of the EU during the Russo-Ukrainian War, Russian military invasion of Ukraine (2014–present) but sometimes doubted the efficacy of EU sanctions against Russia. In autumn 2015, during the European migrant crisis, the leaders of the four Visegrád Group states rejected the EU's proposal to reallocate 120,000 refugees.
The Slovak parliamentary election, 2016, election 2016 took place in March 2016; some days later Fico formed his Fico's Third Cabinet, Third Cabinet, composed of four parties.
Fico resigned as prime minister in March 2018 following the largest street protests in decades over the murder of Ján Kuciak, an investigative journalist who was investigating high-level political corruption linked to the organized crime. President Andrej Kiska appointed Peter Pellegrini to succeed Fico as prime minister.
In March 2019, Zuzana Čaputová was elected as the first female president of Slovakia. She was a member of the liberal Progressive Slovakia party, which had no seats in parliament.
After the 2020 Slovak parliamentary election, the Ordinary People and Independent Personalities won the election and Igor Matovič became the prime minister in March 2020. In April 2021, Eduard Heger was sworn in as prime minister two days after Matovič resigned. Heger was a close ally of Matovic and deputy head of his Ordinary People party. In May 2023, Heger resigned to be replaced by the Central Bank deputy governor, Ľudovít Ódor, as caretaker prime minister of a technocrat government.
In September 2023, populist left-wing Direction – Social Democracy, Smer-SSD, led by former prime minister Robert Fico, won 2023 Slovak parliamentary election, the general election, taking 79 seats in a 150-seat parliament with its allies, the centre-left Voice – Social Democracy, Hlas and nationalist Slovak National Party, SNS parties. The three parties agreed to form a coalition government. On 25 October 2023, Robert Fico became prime minister, announcing that the new government will stop Slovakia's military aid to Ukraine. At his first EU leaders meeting in Brussels, Fico said that Slovakia will not support further military aid for Ukraine nor support further Sanctions against Russia for the invasion of Ukraine, sanctions against Russia because of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. In April 2024, nationalist-left candidate Peter Pellegrini, a close ally of Fico, won 2024 Slovak presidential election, the presidential election.
At the beginning of 2025, Slovakia experienced the worst Cyberattack, cyber-attack in Slovak history on its land registry system, paralysed for days functioning of towns, municipalities and banks, by not being able to access land registry data. Minister of Agriculture, Richard Takáč, said that there is suspicion that the attack originated in Ukraine. In January 2025, large anti-government protests organised by a protest group Mier Ukrajine (Peace to Ukraine) broke out in Slovakia. On 31 January 2025, the prime minister of Slovakia Robert Fico together with Slovak Information Service showed photographs of Mamuka Mamulashvili, the leader of the Ukrainian military unit Georgian National Legion, with opposition activist Lucia Štasselová and online news commentator Martin Milan Šimečka, the father of opposition leader Michal Šimečka. Fico accused Šimečka and the government opposition of plotting a coup d'état in the country.
See also
* Communist Party of Czechoslovakia
* History of Bratislava
* History of Czechoslovakia
* History of the Czech Republic
* History of the Jews in Slovakia
* History of the Slovak language
* Politics of Slovakia
* Slovaks in Czechoslovakia (1918–1938)
Lists:
* List of presidents of Czechoslovakia
* List of prime ministers of Czechoslovakia
* List of presidents of Slovakia
* List of prime ministers of Slovakia
General:
* History of Europe
Notes
References
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Historiography
* Kirschbaum, Stanislav. ''A Guide to Historiography in Slovakia''. In: ''Canadian Slavonic Papers'' (1996) 38#3/4
online
Primary sources
* ''Procopius: History of the Wars (Books VI.16–VII.35.)'' (With an English Translation by H. B. Dewing) (2006). Harvard University Press. .
External links
History of Slovakia at the Slovak Ministry of Foreign Affairs website
History of Slovakia: Primary Documents
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20030817234636/http://www.slovak.sk/magazin_slovakia/496_Slovakia/history/history5.htm History of the Slovak national movement]
Concise Jewish History of Slovakia
Frontier of the Roman Empire in Slovakia
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Slovakia
History of Slovakia,
 The
The  In the 4th century AD, the Roman Empire could no longer resist the attacks by the neighboring peoples. The empire's frontier started to collapse along the Danube in the 370s. The development of the
In the 4th century AD, the Roman Empire could no longer resist the attacks by the neighboring peoples. The empire's frontier started to collapse along the Danube in the 370s. The development of the  The Longobards left the Carpathian Basin for Northern Italy after the invasion of the territory by the Avars in 568. The Avars were a group of nomadic warriors of mixed origin. They conquered the Carpathian Basin, subjugated the local peoples and launched plundering expeditions against the neighboring powers during the next decades. By the time of the Avars' arrival, the Slavs had settled in most lands that now form Slovakia, according to historian Stanislav Kirschbaum. Further migration waves strengthened the local Slavic population because new Slavic groups, pressed by the Avars, crossed the Eastern Carpathians, seceding from the Slavs who continued their expansion to the Balkan Peninsula. Dialects of Slovak still reflect that the Slavs came from different directions already in the Early Middle Ages, according to a widely accepted scholarly theory. Czech and Slovak share some features with the
The Longobards left the Carpathian Basin for Northern Italy after the invasion of the territory by the Avars in 568. The Avars were a group of nomadic warriors of mixed origin. They conquered the Carpathian Basin, subjugated the local peoples and launched plundering expeditions against the neighboring powers during the next decades. By the time of the Avars' arrival, the Slavs had settled in most lands that now form Slovakia, according to historian Stanislav Kirschbaum. Further migration waves strengthened the local Slavic population because new Slavic groups, pressed by the Avars, crossed the Eastern Carpathians, seceding from the Slavs who continued their expansion to the Balkan Peninsula. Dialects of Slovak still reflect that the Slavs came from different directions already in the Early Middle Ages, according to a widely accepted scholarly theory. Czech and Slovak share some features with the  The ''
The '' From 895 to 902, the Hungarians progressively imposed their authority on the
From 895 to 902, the Hungarians progressively imposed their authority on the  The development of the future Kingdom of Hungary started during the reign of Grand Prince
The development of the future Kingdom of Hungary started during the reign of Grand Prince  In 1241, the
In 1241, the  The last decades of the 13th century were characterized by discords within the royal family and among the several groups of the aristocracy. The decay of the royal power and the rise of some powerful aristocrats gave rise to the transformation of the administrative system: the counties that had been the basic units of the royal administration ( "royal counties") transformed gradually into autonomous administrative units of the local nobility ( "noble counties"); however, the local nobility was not able to stop the rise of oligarchs.
Following the Mongol invasion of the kingdom, a competition started among the landowners: each of them endeavored to build a castle with or without the permission of the king. The competition started a process of differentiation among the noble families, because the nobles who were able to build a castle could also expand their influence over the neighbouring landowners. The conflicts among the members of the royal family also strengthened the power of the aristocrats (who sometimes received whole counties from the kings) and resulted in the formation of around eight huge territories (domains) in the kingdom, governed by powerful aristocrats in the 1290s.
The last decades of the 13th century were characterized by discords within the royal family and among the several groups of the aristocracy. The decay of the royal power and the rise of some powerful aristocrats gave rise to the transformation of the administrative system: the counties that had been the basic units of the royal administration ( "royal counties") transformed gradually into autonomous administrative units of the local nobility ( "noble counties"); however, the local nobility was not able to stop the rise of oligarchs.
Following the Mongol invasion of the kingdom, a competition started among the landowners: each of them endeavored to build a castle with or without the permission of the king. The competition started a process of differentiation among the noble families, because the nobles who were able to build a castle could also expand their influence over the neighbouring landowners. The conflicts among the members of the royal family also strengthened the power of the aristocrats (who sometimes received whole counties from the kings) and resulted in the formation of around eight huge territories (domains) in the kingdom, governed by powerful aristocrats in the 1290s.
 During Ottoman administration, parts of the territory of present-day Slovakia were included into Ottoman provinces known as the Budin Eyalet, Eğri Eyalet and Uyvar Eyalet. Uyvar Eyalet had its administrative center in the territory of present-day Slovakia, in the town of Nové Zámky, Uyvar (Slovak: Nové Zámky). In the second half of the 17th century, Ottoman authority was expanded to eastern part of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary, where a vassal Ottoman principality led by prince Imre Thököly was established.
After the ousting of the Ottomans from Budin (which later became Budapest) in 1686, it became the capital of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary. Despite living under Hungarian, Habsburg and Ottoman administration for several centuries, the Slovak people succeeded in keeping their language and their culture.
During Ottoman administration, parts of the territory of present-day Slovakia were included into Ottoman provinces known as the Budin Eyalet, Eğri Eyalet and Uyvar Eyalet. Uyvar Eyalet had its administrative center in the territory of present-day Slovakia, in the town of Nové Zámky, Uyvar (Slovak: Nové Zámky). In the second half of the 17th century, Ottoman authority was expanded to eastern part of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary, where a vassal Ottoman principality led by prince Imre Thököly was established.
After the ousting of the Ottomans from Budin (which later became Budapest) in 1686, it became the capital of the Habsburg Kingdom of Hungary. Despite living under Hungarian, Habsburg and Ottoman administration for several centuries, the Slovak people succeeded in keeping their language and their culture.

 In the Treaty of Trianon signed in 1920, the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference set the southern border of Czechoslovakia further south from the Slovak-Hungarian language border due to strategic and economic reasons. Consequently, some fully or mostly Hungarian-populated areas were also included into Czechoslovakia. According to the 1910 census, which had been manipulated by the ruling Hungarian bureaucracy, population of the present territory of Slovakia numbered 2,914,143 people, including 1,688,413 (57.9%) speakers of Slovak, 881,320 (30.2%) speakers of Hungarian language, Hungarian, 198,405 (6.8%) speakers of German, 103,387 (3.5%) speakers of Rusyn language, Ruthenian and 42,618 (1.6%) speakers of other languages.
In addition, in Subcarpathian Ruthenia, which was also included into Czechoslovakia in this time period, the 1910 manipulated Hungarian census recorded 605,942 people, including 330,010 (54.5%) speakers of Rusyn language, Ruthenian, 185,433 (30.6%) speakers of Hungarian, 64,257 (10.6%) speakers of German, 11,668 (1.9%) speakers of Romanian language, Romanian, 6,346 (1%) speakers of Slovak/Czech language, Czech, and 8,228 (1.4%) speakers of other languages. The Czechoslovak census of 1930 recorded in Slovakia 3,254,189 people, including 2,224,983 (68.4%)
In the Treaty of Trianon signed in 1920, the Paris Peace Conference, 1919, Paris Peace Conference set the southern border of Czechoslovakia further south from the Slovak-Hungarian language border due to strategic and economic reasons. Consequently, some fully or mostly Hungarian-populated areas were also included into Czechoslovakia. According to the 1910 census, which had been manipulated by the ruling Hungarian bureaucracy, population of the present territory of Slovakia numbered 2,914,143 people, including 1,688,413 (57.9%) speakers of Slovak, 881,320 (30.2%) speakers of Hungarian language, Hungarian, 198,405 (6.8%) speakers of German, 103,387 (3.5%) speakers of Rusyn language, Ruthenian and 42,618 (1.6%) speakers of other languages.
In addition, in Subcarpathian Ruthenia, which was also included into Czechoslovakia in this time period, the 1910 manipulated Hungarian census recorded 605,942 people, including 330,010 (54.5%) speakers of Rusyn language, Ruthenian, 185,433 (30.6%) speakers of Hungarian, 64,257 (10.6%) speakers of German, 11,668 (1.9%) speakers of Romanian language, Romanian, 6,346 (1%) speakers of Slovak/Czech language, Czech, and 8,228 (1.4%) speakers of other languages. The Czechoslovak census of 1930 recorded in Slovakia 3,254,189 people, including 2,224,983 (68.4%)  In September 1938, France, Italy, United Kingdom and Nazi Germany concluded the Munich Agreement, which forced Czechoslovakia to cede the predominantly German region known as the Sudetenland to Germany. In November, by the First Vienna Award, Italy and Germany compelled Czechoslovakia (later Slovakia) to cede primarily Hungarian-inhabited Southern Slovakia to Hungary. They did this in spite of pro-German official declarations of Czech and Slovak leaders made in October. The Autonomous Land of Slovakia was established within the Second Czechoslovak Republic.
On 14 March 1939, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic (''Slovenská republika'') declared its independence and became a nominally independent state in Central Europe under Nazi Germany, Nazi German control of foreign policy and, increasingly, also some aspects of domestic policy.
In September 1938, France, Italy, United Kingdom and Nazi Germany concluded the Munich Agreement, which forced Czechoslovakia to cede the predominantly German region known as the Sudetenland to Germany. In November, by the First Vienna Award, Italy and Germany compelled Czechoslovakia (later Slovakia) to cede primarily Hungarian-inhabited Southern Slovakia to Hungary. They did this in spite of pro-German official declarations of Czech and Slovak leaders made in October. The Autonomous Land of Slovakia was established within the Second Czechoslovak Republic.
On 14 March 1939, the Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic (''Slovenská republika'') declared its independence and became a nominally independent state in Central Europe under Nazi Germany, Nazi German control of foreign policy and, increasingly, also some aspects of domestic policy.  The nominally independent Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic went through the early years of the war in relative peace. As an Axis Powers, Axis ally, the country took part in the Slovak invasion of Poland, wars against Poland and the Soviet Union. Although its contribution was symbolic in the German war efforts, the number of troops involved (approx. 45,000 in the Soviet campaign) was rather significant in proportion to the population (2.6 million in 1940).
Soon after independence, under the authoritarian government of Jozef Tiso, a series of measures aimed against the 90,000 Jews in the country were initiated. The Hlinka Guard began to attack Jews, and the "Jewish Code" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the Nuremberg Laws, the Code required that Jews wear a yellow armband, and they were banned from intermarriage and from many jobs. More than 64.000 Jews lost their livelihood. Between March and October 1942, the state deported approximately 57,000 Jews to the German-occupied part of Poland, where almost all of them were killed in Extermination camps. The Slovak Parliament accepted a bill that retroactively legalized the deportation in May 1942. The deportation of the remaining Jewish population was stopped when the government "resolved" the social problem caused by its own policy. However, 12,600 more Jews were deported by the German forces occupying Slovakia after the Slovak National Uprising in 1944. Around a half of them were killed in concentration camps. Other Jews were rounded up and massacred in the country by Slovak collaborators under German command, at Kremnička and Nemecká massacres, Kremnička and Nemecká. Some 10,000 Slovak Jews survived in Slovakia.
On 29 August 1944, 60,000 Slovak troops and 18,000 partisans, organized by various underground groups and the Czechoslovak government-in-exile, rose up against the Nazis. The insurrection later became known as the Slovak National Uprising. Slovakia was devastated by the fierce German counter-offensive and occupation, but the guerrilla warfare continued even after the end of organized resistance. Although ultimately quelled by the German forces, the uprising was an important historical reference point for the Slovak people. It allowed them to end the war as a nation which had contributed to the Allied victory.
Later in 1944 the Soviet attacks intensified. The Red Army, helped by Romanian troops, gradually routed out the German army from Slovak territory. On 4 April 1945, Soviet troops marched into the capital city of the Slovak Republic, Bratislava.
The nominally independent Slovak Republic (1939–1945), Slovak Republic went through the early years of the war in relative peace. As an Axis Powers, Axis ally, the country took part in the Slovak invasion of Poland, wars against Poland and the Soviet Union. Although its contribution was symbolic in the German war efforts, the number of troops involved (approx. 45,000 in the Soviet campaign) was rather significant in proportion to the population (2.6 million in 1940).
Soon after independence, under the authoritarian government of Jozef Tiso, a series of measures aimed against the 90,000 Jews in the country were initiated. The Hlinka Guard began to attack Jews, and the "Jewish Code" was passed in September 1941. Resembling the Nuremberg Laws, the Code required that Jews wear a yellow armband, and they were banned from intermarriage and from many jobs. More than 64.000 Jews lost their livelihood. Between March and October 1942, the state deported approximately 57,000 Jews to the German-occupied part of Poland, where almost all of them were killed in Extermination camps. The Slovak Parliament accepted a bill that retroactively legalized the deportation in May 1942. The deportation of the remaining Jewish population was stopped when the government "resolved" the social problem caused by its own policy. However, 12,600 more Jews were deported by the German forces occupying Slovakia after the Slovak National Uprising in 1944. Around a half of them were killed in concentration camps. Other Jews were rounded up and massacred in the country by Slovak collaborators under German command, at Kremnička and Nemecká massacres, Kremnička and Nemecká. Some 10,000 Slovak Jews survived in Slovakia.
On 29 August 1944, 60,000 Slovak troops and 18,000 partisans, organized by various underground groups and the Czechoslovak government-in-exile, rose up against the Nazis. The insurrection later became known as the Slovak National Uprising. Slovakia was devastated by the fierce German counter-offensive and occupation, but the guerrilla warfare continued even after the end of organized resistance. Although ultimately quelled by the German forces, the uprising was an important historical reference point for the Slovak people. It allowed them to end the war as a nation which had contributed to the Allied victory.
Later in 1944 the Soviet attacks intensified. The Red Army, helped by Romanian troops, gradually routed out the German army from Slovak territory. On 4 April 1945, Soviet troops marched into the capital city of the Slovak Republic, Bratislava.
 The 1970s and 1980s became known as the period of "Normalization (Czechoslovakia), normalization", in which the apologists for the 1968 Soviet invasion prevented as best they could any opposition to their conservative régime. Political, social, and economic life stagnated. Because the reform movement had had its center in Prague, Slovakia experienced "normalization" less harshly than the Czech lands. In fact, the Slovak Republic saw comparatively high economic growth in the 1970s and 1980s relative to the Czech Republic (and mostly from 1994 till ).
The 1970s also saw the development of a dissident movement, especially in the Czech Republic. On 1 January 1977, more than 250 human rights activists signed a manifesto called Charter 77, which criticized the Czechoslovak government for failing to meet its human rights obligations.
The 1970s and 1980s became known as the period of "Normalization (Czechoslovakia), normalization", in which the apologists for the 1968 Soviet invasion prevented as best they could any opposition to their conservative régime. Political, social, and economic life stagnated. Because the reform movement had had its center in Prague, Slovakia experienced "normalization" less harshly than the Czech lands. In fact, the Slovak Republic saw comparatively high economic growth in the 1970s and 1980s relative to the Czech Republic (and mostly from 1994 till ).
The 1970s also saw the development of a dissident movement, especially in the Czech Republic. On 1 January 1977, more than 250 human rights activists signed a manifesto called Charter 77, which criticized the Czechoslovak government for failing to meet its human rights obligations.
 In an Slovak parliamentary election, 1992, election held in June 1992, Václav Klaus's Civic Democratic Party won in Czechia on a platform of economic reform, and Vladimír Mečiar's Movement for a Democratic Slovakia (HZDS) emerged as the leading party in Slovakia, on a platform of Slovak autonomy. Mečiar and Klaus negotiated the Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, agreement to divide Czechoslovakia, and Mečiar's party – HZDS – ruled Slovakia for most of its first five years as an independent state, except for a 9-month period in 1994 after a vote of no-confidence, during which a reformist government under Prime Minister Jozef Moravčík operated.
The first president of newly independent Slovakia was Michal Kováč. The first prime minister, Mečiar, had served as the prime minister of the Slovak part of Czechoslovakia since 1992.
Rudolf Schuster won Slovak presidential election, 1999, the presidential election in May 1999. Mečiar's semi-authoritarian government allegedly breached democratic norms and the rule of law before its replacement after the parliamentary elections of 1998 by a coalition led by Mikuláš Dzurinda.
The first Dzurinda government made numerous political and economic reforms that enabled Slovakia to enter the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), close virtually all chapters in
In an Slovak parliamentary election, 1992, election held in June 1992, Václav Klaus's Civic Democratic Party won in Czechia on a platform of economic reform, and Vladimír Mečiar's Movement for a Democratic Slovakia (HZDS) emerged as the leading party in Slovakia, on a platform of Slovak autonomy. Mečiar and Klaus negotiated the Dissolution of Czechoslovakia, agreement to divide Czechoslovakia, and Mečiar's party – HZDS – ruled Slovakia for most of its first five years as an independent state, except for a 9-month period in 1994 after a vote of no-confidence, during which a reformist government under Prime Minister Jozef Moravčík operated.
The first president of newly independent Slovakia was Michal Kováč. The first prime minister, Mečiar, had served as the prime minister of the Slovak part of Czechoslovakia since 1992.
Rudolf Schuster won Slovak presidential election, 1999, the presidential election in May 1999. Mečiar's semi-authoritarian government allegedly breached democratic norms and the rule of law before its replacement after the parliamentary elections of 1998 by a coalition led by Mikuláš Dzurinda.
The first Dzurinda government made numerous political and economic reforms that enabled Slovakia to enter the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), close virtually all chapters in