|
Sabinov
Sabinov (, , ) is a small town located in the Prešov Region (north-eastern Slovakia), approximately 20 km from Prešov and 55 km from Košice. The population of Sabinov is 12,700. Etymology The name apparently comes from some shortened Slavic personal name, e.g. ''Soba'', ''Sobin'', ''Sobina'' (probably a short form of Soběslav). In Poland, there are documented personal names ''Soba'', ''Zoba'', ''Sobien'' (''Soben'' or ''Sobin''), ''Sobon'' (''Soboń'') and medieval village names ''Szebne'', ''Szobniow''. In the Czech Republic, ''Sobyn'', ''Sobień'', ''Soběn'' and medieval village names ''Sobyenow'', ''Sobíňov'', ''Soběnov''. The theory about the origin in a personal name is supported also by the common Slavic possessive suffix ''-ov'' preserved in later documents. The names ''Zob'', ''Zoba'', ''Zobas'' were used also in the Kingdom of Hungary in the 12th-13th century, but they may not be related to Soběslav and could be also of Hungarian origin. As legend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabinov District
Sabinov District (''okres Sabinov'') is a district in the Prešov Region of eastern Slovakia. It lies on the highlands of Šarišská vrchovina. The district had been established in 1923 and from 1996 exists in its present borders. Food, pharmaceutical and clothing industry and located foremost in its towns and Šarišské Michaľany. In the district are three recreational centers, mainly used during winter and skiing season. Overall, the district suffers from the high unemployment rate. In Sabinov district are 43 municipalities, in two of them are towns. Municipalities * Bajerovce * Bodovce * Brezovica * Brezovička * Červená Voda * Červenica pri Sabinove * Daletice * Drienica * Dubovica * Ďačov * Hanigovce * Hubošovce * Jakovany * Jakubova Voľa * Jakubovany * Jarovnice * Kamenica * Krásna Lúka * Krivany * Lipany * Lúčka *Ľutina Ľutina is a village and municipality in Sabinov District in the Prešov Region of north-eastern Slovakia. Etymology The name comes fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities And Towns In Slovakia
This is an alphabetical list of the 2,891 (singular , "municipality") in Slovakia. They are grouped into 79 Districts of Slovakia, districts (, singular ), in turn grouped into 8 Regions of Slovakia, regions (, singular ); articles on individual districts and regions list their municipalities. The average area of Slovak municipalities is about and an average population of about 1,888 people. * Ábelová * Abovce * Abrahám * Abrahámovce, Bardejov District * Abrahámovce, Kežmarok District * Abramová * Abranovce * Adamovské Kochanovce * Adidovce * Alekšince * Andovce * Andrejová * Ardanovce * Ardovo * Arnutovce * Báb, Nitra District, Báb * Babie * Babín * Babiná * Babindol * Babinec, Slovakia, Babinec * Bacúch * Bacúrov * Báč * Bačka, Slovakia, Bačka * Bačkov, Trebišov District, Bačkov * Bačkovík * Baďan * Bádice * Badín * Báhoň * Bajany * Bajč * Bajerov * Bajerovce * Bajka * Bajtava * Baka, Slovakia, Baka * Balá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
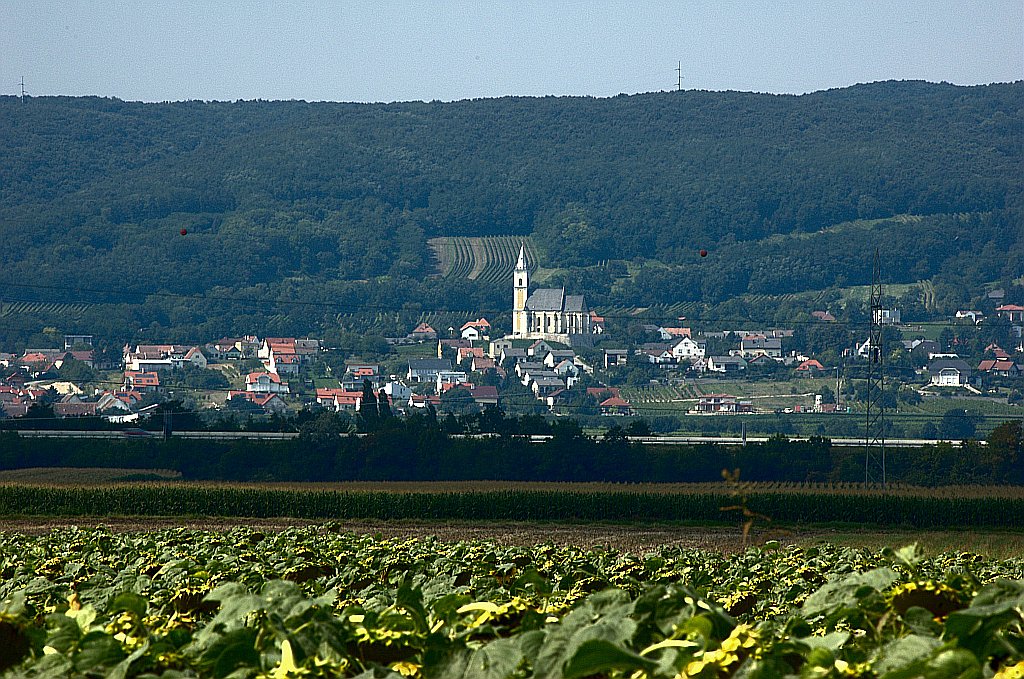
Kamenica, Sabinov District
Kamenica () is a village and municipality in Sabinov District in the Prešov Region of north-eastern Slovakia. History The Castle Kamenica first developed out of the castle of the same name that was built on a nearby hillock in the early 13th century in order to protect a major Polish trading route that had its terminus in Košice to the south. In 1436, the castle garrison rebelled and was quickly brought back under control, but not long after the Hussites had control of both castle and village. The castle was refurbished in the Renaissance style in the beginning of the 16th century. In 1556 imperial troops besieged under command of Simon Forgacs, captured and seven days later, on the order of Emperor Ferdinand I, turned the castle into the ruin that can be seen today. After the sack of the castle the surrounding villages including Kamenica dwindled in size. Later, stones from the castle were used to build a brewery in Lúčka in 1816. The Village The village itself was fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prešov
Prešov () is a city in eastern Slovakia. It is the seat of administrative Prešov Region () and Šariš. With a population of approximately 85,000 for the city, and in total more than 100,000 with the urban area, it is the second-largest city in eastern Slovakia and the List of cities and towns in Slovakia, third-largest city in all of Slovakia, after the nearby city of Košice. It belongs to the :sk:Košicko-prešovská aglomerácia, Košice-Prešov agglomeration and is the natural cultural, economic, transport and administrative center of the Prešov Region. It lends its name to the Eperjes-Tokaj Hill-Chain which was considered as the geographic entity on the first map of Hungary from 1528. There are many tourist attractions in Prešov such as castles (e.g. Šariš Castle), pools and the old town. Etymology The first written mention is from 1247 (). Several authors derived the name from Hungarian language, Hungarian (strawberry). Other alternative names of the city include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Slovakia
The districts of Slovakia are administrative units known as in the Slovak language. It is a second-tier territorial administrative unit, below a Region () in standing, and superior to a municipality (). Each district contains at least several municipalities. The cities of Bratislava and Košice are the only cities in Slovakia divided into internal urban districts, with five in Bratislava, and four in Košice. These urban districts are then further divided into smaller boroughs (which serve a function analogous to municipalities in typical districts). All other districts are larger in size and also include rural areas, and rural as well as urban municipalities. Each of these more typical districts has an urban centre serving as the seat of the district, usually the largest town (or the only town) of a given district. Rural municipalities are not legally allowed to become district seats. Map of current Slovak districts Characteristics Several districts form a "region" (). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prešov Region
The Prešov Region (, ; ), also Priashiv Region (, ), is one of the eight Slovak administrative regions and consists of 13 districts (okresy) and 666 municipalities, 23 of which have town status. The region was established in 1996 and is the most populous of all the regions in Slovakia. Its administrative center is the city of Prešov. Geography It is located in the north-eastern Slovakia and has an area of 8,975 km2. The region has a predominantly mountainous landscape. The subdivisions of Tatras – High Tatras and Belianske Tatras lie almost entirely in the region and include the highest point of Slovakia – Gerlachovský štít (2,654 ASL). Other mountain ranges and highlands in the region are Šarišská vrchovina, Čergov, Ondavská vrchovina, Slanské vrchy, Pieniny, Levoča Hills, Laborecká vrchovina, Bukovské vrchy, Vihorlat Mountains and Eastern Slovak Lowland. The basins in Prešov Region are Podtatranská kotlina, Hornádska kotlina and Košic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Car Registration Plates
Vehicles registered in Slovakia were generally assigned to one of the districts (''okres'') and from 1997 until 2022, the license plate coding () generally consisted of seven characters and takes the form XX-NNNLL, where XX was a two letter code corresponding to the district, NNN was a three digit number and LL were two additional letters (assigned alphabetically). From January 2023, a new state-wide numbering scheme was introduced, preserving the same layout, but replacing the initial two-letter district code with arbitrary letters of the alphabet (assigned alphabetically, starting with AA). Other changes include new font and a smaller coat of arms. Appearance There are three design varieties that are in valid use. * Between 1 April 1997 and 30 April 2004, the plates contained the Coat of Arms of Slovakia in the top left corner and the country code SK in the bottom left. The two district identifiers were separated from the serials by a dash. * On 1 May 2004, Slovakia joined t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zipser Germans
The Zipser Germans, Zipser Saxons, or, simply, just Zipsers (, , , ) are a German-speaking (more specifically Zipser German-speaking as native dialect) sub-ethnic group in Central- Eastern Europe and national minority in both Slovakia and Romania (there are also Zipser German settlements in the Zakarpattia Oblast, in the historical region of Carpathian Ruthenia, present-day western Ukraine). Along with the Sudeten Germans (), the Zipser Germans were one of the two most important ethnic German groups in the former Czechoslovakia. An occasional variation of their name as 'Tzipsers' can also be found in academic articles. Former Slovak President Rudolf Schuster is partly Zipser German and grew up in Medzev (). The Zipser Germans were previously native to the Szepes County (; , ) of Upper Hungary—today mostly north-eastern Slovakia—as that region was settled by colonists from present-day central Germany (and other parts of contemporary Germany) during the High Middle Ages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Royal Town
A royal free city, or free royal city (Latin: ''libera regia civitas''), was the official term for the most important cities in the Kingdom of Hungary from the late 12th centuryBácskai Vera – Nagy Lajos: Piackörzetek, piacközpontok és városok Magyarországon 1828-ban. Budapest, 1984. to the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. The cities were granted certain privileges by the King of Hungary to prevent their control by the Hungarian nobility, hence "royal", and exercised some self-government in relation to their internal affairs and so were "free". From the late 14th century, the elected envoys of the royal free cities participated in the sessions of the Hungarian Diet and so they became part of the legislature. This list also includes cities in the Kingdom of Croatia and the Banate of Bosnia, which were part of the Lands of the Hungarian Crown. The term "royal free city" in the kingdom's languages is as follows: * * * * * * * They had a status similar to the free imperial cit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Košice
Košice is the largest city in eastern Slovakia. It is situated on the river Hornád at the eastern reaches of the Slovak Ore Mountains, near the border with Hungary. With a population of approximately 230,000, Košice is the second-largest city in Slovakia, after the capital Bratislava. Being the economic and cultural centre of eastern Slovakia, Košice is the seat of the Košice Region and Košice Self-governing Region, it belongs to the :sk:Košicko-prešovská aglomerácia, Košice-Prešov agglomeration, and is home to the Constitutional Court of Slovakia, Slovak Constitutional Court, three universities, various dioceses, and many museums, galleries, and theatres. In 2013, Košice was the European Capital of Culture, together with Marseille, France. Košice is an important industrial centre of Slovakia, and the U. S. Steel Košice, s.r.o., U.S. Steel Košice steel mill is the largest employer in the city. The town has extensive railway connections and an Košice Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentapolitana
Pentapolitana (or rarely Pentapolis) was a league of towns in the Middle Ages of the five most important Hungarian royal free cities (Latin: ''libera regiae civitas'', Hungarian: ''szabad királyi város'', German: ''Königliche Freistadt''; Slovak: ''slobodné kráľovské mesto'') of the Kingdom of Hungary; Kassa (today Košice), Bártfa (Bardejov), Lőcse (Levoča), Eperjes (Prešov), and Kisszeben ( Sabinov). The cities are currently in eastern Slovakia. The first meeting of the representatives of the towns in question took place in 1412. The actual alliance arose between 1440 and 1445. The main role of the Pentapolitana was to control and to develop trade as there were important ancient trade routes in the region of the north-eastern part of the Kingdom of Hungary, present-day eastern Slovakia. The leading town of the Pentapolitana was Košice. In 1549, i.e. during the Reformation The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanians
Romanians (, ; dated Endonym and exonym, exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation native to Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. Sharing a Culture of Romania, common culture and Cultural heritage, ancestry, they speak the Romanian language and live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2021 Romanian census found that 89.3% of Romania's citizens identified themselves as ethnic Romanians. In one interpretation of the 1989 census results in Moldova, the majority of Moldovans were counted as ethnic Romanians as well.''Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook By'' David Levinson (author), David Levinson, Published 1998 – Greenwood Publishing Group.At the time of the 1989 census, Moldova's total population was 4,335,400. The largest nationality in the republic, ethnic Romanians, numbered 2,795,000 persons, accounting for 64.5 percent of the population. Source U.S. Library of Congres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |