Skin flora on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Skin flora, also called skin microbiota, refers to microbiota (
Skin flora, also called skin microbiota, refers to microbiota (
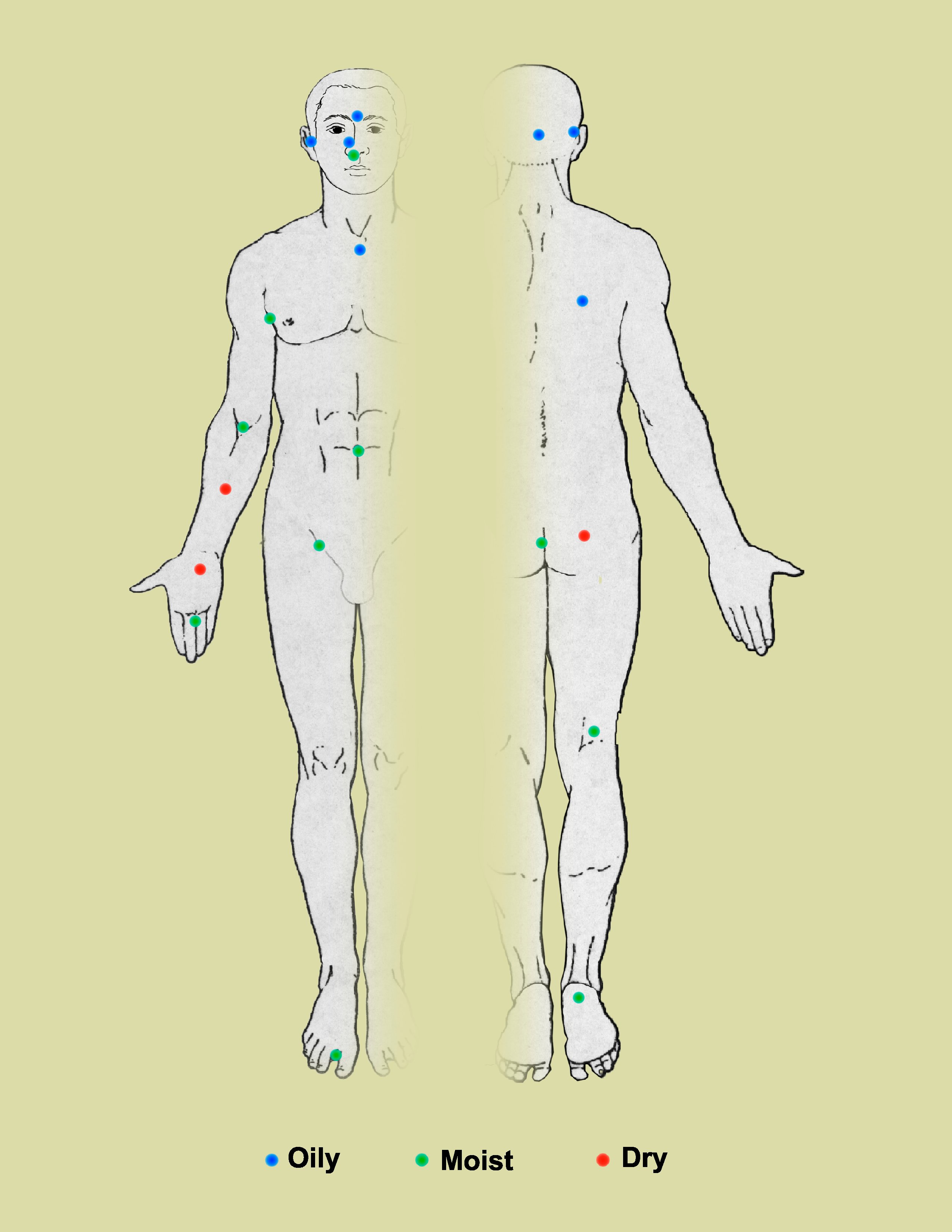 There are three main ecological areas: sebaceous, moist, and dry. ''
There are three main ecological areas: sebaceous, moist, and dry. ''
Cellulitis Skin Infection
Human microbiome project
Hygiene of the Skin: When Is Clean Too Clean?
{{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine Bacteriology Environmental microbiology Microbiology Microbiology terms
 Skin flora, also called skin microbiota, refers to microbiota (
Skin flora, also called skin microbiota, refers to microbiota (communities
A community is a Level of analysis, social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place (geography), place, set of Norm (social), norms, culture, religion, values, Convention (norm), customs, or Ide ...
of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s) that reside on the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
, typically human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anato ...
.
Many of them are bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
of which there are around 1,000 species upon human skin from nineteen phyla
Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
. Most are found in the superficial layers of the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermal layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
and the upper parts of hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwee ...
s.
Skin flora is usually non-pathogenic, and either commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
(are not harmful to their host) or mutualistic (offer a benefit). The benefits bacteria can offer include preventing transient pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
organisms from colonizing the skin surface, either by competing for nutrients, secreting chemicals against them, or stimulating the skin's immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
. However, resident microbes can cause skin disease
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major funct ...
s and enter the blood system, creating life-threatening diseases, particularly in immunosuppressed people.
A major non-human skin flora is '' Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis'', a chytrid
Chytridiomycota are a division of zoosporic organisms in the kingdom (biology), kingdom Fungi, informally known as chytrids. The name is derived from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "little pot", describing the structure containing unreleased zo ...
and non-hyphal zoosporic fungus that causes chytridiomycosis, an infectious disease thought to be responsible for the decline in amphibian populations.
Species variety
Bacteria
The estimate of the number of bacteria species present on skin has been radically changed by the use of16S ribosomal RNA
16S ribosomal RNA (or 16 S rRNA) is the RNA component of the 30S subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome ( SSU rRNA). It binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and provides most of the SSU structure.
The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S ...
to identify bacterial species present on skin samples direct from their genetic material. Previously such identification had depended upon microbiological culture
A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microorganism, microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational a ...
upon which many varieties of bacteria did not grow and so were hidden to science.
'' Staphylococcus epidermidis'' and ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' were thought from cultural based research to be dominant. However 16S ribosomal RNA research finds that while common, these species make up only 5% of skin bacteria. However, skin variety provides a rich and diverse habitat for bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
. Most come from four phyla: Actinomycetota
The Actinomycetota (or Actinobacteria) are a diverse phylum of Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great importance to land flora because of their contributions to soil systems. In soil t ...
(51.8%), Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Bacillota, such as '' Megasphaera'', ...
(24.4%), Pseudomonadota
Pseudomonadota (synonym "Proteobacteria") is a major phylum of gram-negative bacteria. Currently, they are considered the predominant phylum within the domain of bacteria. They are naturally found as pathogenic and free-living (non- parasitic) ...
(16.5%), and Bacteroidota
The phylum (biology), phylum Bacteroidota (synonym Bacteroidetes) is composed of three large classes of Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, nonsporeforming, anaerobic or aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria that are widely distributed in the envir ...
(6.3%).
 There are three main ecological areas: sebaceous, moist, and dry. ''
There are three main ecological areas: sebaceous, moist, and dry. ''Propionibacteria
''Propionibacterium'' is a Gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes.
Its members are pr ...
'' and ''Staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
'' species were the main species in sebaceous areas. In moist places on the body '' Corynebacteria'' together with ''Staphylococci'' dominate. In dry areas, there is a mixture of species but Betaproteobacteria
''Betaproteobacteria'' are a class of Gram-negative bacteria, and one of the six classes of the phylum '' Pseudomonadota'' (synonym Proteobacteria).
Metabolism
The ''Betaproteobacteria'' comprise over 75 genera and 400 species. Together, they ...
and Flavobacteriales
The order Flavobacteriales comprises several families of environmental bacteria.
Comparative genomics and molecular signatures
''Flavobacteriales'' is of one of the orders from the phylum ''Bacteroidota''. Comparative genomic studies have ident ...
are dominant. Ecologically, sebaceous areas had greater species richness than moist and dry ones. The areas with least similarity between people in species were the spaces between finger
A finger is a prominent digit (anatomy), digit on the forelimbs of most tetrapod vertebrate animals, especially those with prehensile extremities (i.e. hands) such as humans and other primates. Most tetrapods have five digits (dactyly, pentadact ...
s, the spaces between toes, axillae, and umbilical cord
In Placentalia, placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord i ...
stump. Most similarly were beside the nostril
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates ...
, nares (inside the nostril), and on the back.
:::
Fungal
A study of the area between toes in 100 young adults found 14 different genera of fungi. These includeyeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
s such as '' Candida albicans'', '' Rhodotorula rubra'', '' Torulopsis'' and '' Trichosporon cutaneum'', dermatophytes (skin living fungi) such as '' Microsporum gypseum'', and '' Trichophyton rubrum'' and nondermatophyte fungi (opportunistic fungi that can live in skin) such as '' Rhizopus stolonifer'', '' Trichosporon cutaneum'', ''Fusarium
''Fusarium'' (; ) is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the s ...
'', '' Scopulariopsis brevicaulis'', '' Curvularia'', ''Alternaria alternata
''Alternaria alternata'' is a fungus causing leaf spots, rots, and blights on many plant parts, and other diseases. It is an opportunistic pathogen on over 380 host species of plant.
It can also cause upper respiratory tract infections and a ...
'', '' Paecilomyces'', ''Aspergillus flavus
''Aspergillus flavus'' is a saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is best known for its colonization of cereal grains, legumes, and tree nuts. Postharvest rot typically develops during harvest, storage, and/or ...
'' and ''Penicillium
''Penicillium'' () is a genus of Ascomycota, ascomycetous fungus, fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Some members of th ...
'' species.
A study by the National Human Genome Research Institute
The National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) is an institute of the National Institutes of Health, located in Bethesda, Maryland.
NHGRI began as the Office of Human Genome Research in The Office of the Director in 1988. This Office transi ...
in Bethesda, Maryland
Bethesda () is an unincorporated, census-designated place in southern Montgomery County, Maryland, United States. Located just northwest of Washington, D.C., it is a major business and government center of the Washington metropolitan region ...
, researched the DNA of human skin fungi at 14 different locations on the body. These were the ear canal, between the eyebrows, the back of the head, behind the ear, the heel, toenails, between the toes, forearm, back, groin, nostrils, chest, palm, and the crook of the elbow. The study showed a large fungal diversity across the body, the richest habitat being the heel, which hosts about 80 species of fungi. By way of contrast, there are some 60 species in toenail clippings and 40 between the toes. Other rich areas are the palm, forearm and inside the elbow, with from 18 to 32 species. The head and the trunk hosted between 2 and 10 each.
Umbilical microbiome
The umbilicus, ornavel
The navel (clinically known as the umbilicus; : umbilici or umbilicuses; also known as the belly button or tummy button) is a protruding, flat, or hollowed area on the abdomen at the attachment site of the umbilical cord.
Structure
The u ...
, is an area of the body that is rarely exposed to UV light, soaps, or bodily secretions (the navel does not produce any secretions or oils) and because it is an almost undisturbed community of bacteria it is an excellent part of the skin microbiome to study. The navel, or umbilicus is a moist microbiome of the body (with high humidity and temperatures), that contains a large amount of bacteria, especially bacteria that favors moist conditions such as ''Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name ('' coryneform'' means "club-s ...
'' and ''Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
''.
The Belly Button Biodiversity Project began at North Carolina State University
North Carolina State University (NC State, North Carolina State, NC State University, or NCSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Raleigh, North Carolina, United States. Founded in 1887 and p ...
in early 2011 with two initial groups of 35 and 25 volunteers. Volunteers were given sterile cotton swabs and were asked to insert the cotton swabs into their navels, to turn the cotton swab around three times and then return the cotton swab to the researchers in a vial that contained a 0.5'' ''ml 10% phosphate saline buffer. Researchers at North Carolina State University, led by Jiri Hulcr, then grew the samples in a culture until the bacterial colonies were large enough to be photographed and then these pictures were posted on the Belly Button Biodiversity Project's website (volunteers were given sample numbers so that they could view their own samples online). These samples then were analyzed using 16S rDNA libraries so that strains that did not grow well in cultures could be identified.
The researchers at North Carolina State University discovered that while it was difficult to predict every strain of bacteria in the microbiome of the navel that they could predict which strains would be prevalent and which strains of bacteria would be quite rare in the microbiome. It was found that the navel microbiomes only contained a few prevalent types of bacteria (''Staphylococcus'', ''Corynebacterium'', Actinobacteria, Clostridiales, and Bacilli) and many different types of rare bacteria. Other types of rare organisms were discovered inside the navels of the volunteers including three types of Archaea, two of which were found in one volunteer who claimed not to have bathed or showered for many years.
''Staphylococcus'' and ''Corynebacterium'' were among the most common types of bacteria found in the navels of this project's volunteers and these types of bacteria have been found to be the most common types of bacteria found on the human skin in larger studies of the skin microbiome (of which the Belly Button Biodiversity Project is a part). (In these larger studies it has been found that females generally have more ''Staphylococcus'' living in their skin microbiomes (usually ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'') and that men have more ''Corynebacterium'' living in their skin microbiomes.)
According to the Belly Button Biodiversity Project at North Carolina State University, there are two types of microorganisms found in the navel and surrounding areas. Transient bacteria (bacteria that does not reproduce) forms the majority of the organisms found in the navel, and an estimated 1400 various strains were found in 95% of participants of the study.
The Belly Button Biodiversity Project is ongoing and has now taken swabs from over 500 people. The project was designed with the aim of countering that misconception that bacteria are always harmful to humans and that humans are at war with bacteria. In actuality, most strains of bacteria are harmless if not beneficial for the human body. Another of the project's goals is to foster public interest in microbiology. Working in concert with the Human Microbiome Project, the Belly Button Biodiversity Project also studies the connections between human microbiomes and the factors of age, sex, ethnicity, location and overall health.
Relationship to host
Skin microflora can becommensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
s, mutualistic or pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s. Often they can be all three depending upon the strength of the person's immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
. Research upon the immune system in the gut and lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory syste ...
has shown that microflora aids immunity development: however such research has only started upon whether this is the case with the skin. ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
'' is an example of a mutualistic bacterium that can turn into a pathogen and cause disease: if it gains entry into the circulatory system
In vertebrates, the circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the body. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart ...
it can result in infections in bone, joint, gastrointestinal, and respiratory systems. It can also cause dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
. However, ''P. aeruginosa'' produces antimicrobial substances such as pseudomonic acid (that are exploited commercially such as Mupirocin). This works against staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. ''P. aeruginosa'' also produces substances that inhibit the growth of fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one ...
species such as '' Candida krusei'', '' Candida albicans'', '' Torulopsis glabrata'', ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'' and '' Aspergillus fumigatus''. It can also inhibit the growth of ''Helicobacter pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits l ...
''. So important is its antimicrobial actions that it has been noted that "removing ''P. aeruginosa'' from the skin, through use of oral or topical antibiotics, may inversely allow for aberrant yeast colonization and infection."
Another aspect of bacteria is the generation of body odor
Body odor or body odour (BO) is present in all animals and its intensity can be influenced by many factors (behavioral patterns, survival strategies). Body odor has a strong genetic basis, but can also be strongly influenced by various factors, ...
. Sweat
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and Apocrine sweat gland, apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distribu ...
is odorless however several bacteria may consume it and create byproducts which may be considered putrid by humans (as in contrast to flies, for example, that may find them attractive/appealing).
Several examples are:
* ''Propionibacteria
''Propionibacterium'' is a Gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes.
Its members are pr ...
'' in adolescent and adult sebaceous glands can turn its amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s into propionic acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a ...
.
* '' Staphylococcus epidermidis'' creates body odor by breaking sweat into isovaleric acid (3-methyl butanoic acid).
* ''Bacillus subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'' (), known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacill ...
'' creates strong foot odor.
Skin defenses
Antimicrobial peptides
The skin createsantimicrobial peptides
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also called host defence peptides (HDPs) are part of the innate immune response found among all classes of life. Fundamental differences exist between Prokaryote, prokaryotic and eukaryota, eukaryotic cells that may ...
such as cathelicidin
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) is an antimicrobial peptide
encoded in the human by the ''CAMP'' gene. The active form is LL-37. In humans, ''CAMP'' encodes the peptide precursor CAP-18 (18 kDa), which is processed by proteinase 3-me ...
s that control the proliferation of skin microbes. Cathelicidins not only reduce microbe numbers directly but also cause the secretion of cytokine
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
release which induces inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and ...
, and reepithelialization. Conditions such as atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
have been linked to the suppression in cathelicidin production. In rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, en ...
abnormal processing of cathelicidin cause inflammation. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
has been linked to self-DNA created from cathelicidin peptides that causes autoinflammation. A major factor controlling cathelicidin is vitamin D3.
Acidity
The superficial layers of the skin are naturally acidic ( pH 4–4.5) due to lactic acid insweat
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and Apocrine sweat gland, apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distribu ...
and produced by skin bacteria. At this pH mutualistic flora such as ''Staphylococci
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
'', '' Micrococci'', ''Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name ('' coryneform'' means "club-s ...
'' and ''Propionibacteria
''Propionibacterium'' is a Gram-positive bacteria, gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes.
Its members are pr ...
'' grow but not transient bacteria such as Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
like ''Escherichia
''Escherichia'' ( ) is a genus of Gram-negative, non-Endospore, spore-forming, Facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Enterobacteriaceae. In those species which are inhabitants of the gastroin ...
'' and ''Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The 348 members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a ...
'' or Gram positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain i ...
ones such as ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
''. Another factor affecting the growth of pathological bacteria is that the antimicrobial substances secreted by the skin are enhanced in acidic conditions. In alkaline conditions, bacteria cease to be attached to the skin and are more readily shed. It has been observed that the skin also swells under alkaline conditions and opens up allowing bacterial movement to the surface.
Immune system
If activated, theimmune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
in the skin produces cell-mediated immunity against microbes such as dermatophytes (skin fungi). One reaction is to increase stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin language, Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis (skin), epidermis. Consisting of dead tissue, it protects underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress. It is ...
turnover and so shed the fungus from the skin surface. Skin fungi such as '' Trichophyton rubrum'' have evolved to create substances that limit the immune response to them. The shedding of skin is a general means to control the buildup of flora upon the skin surface.
Skin diseases
Microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s play a role in noninfectious skin disease
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major funct ...
s such as atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
, rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, en ...
, psoriasis
Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete b ...
, and acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
Damaged skin can cause nonpathogenic bacteria to become pathogenic
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ.
The term ...
. The diversity of species on the skin is related to later development of dermatitis.
Acne vulgaris
Acne vulgaris
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, ...
is a common skin condition characterised by excessive sebum production by the pilosebaceous unit
A sebaceous gland or oil gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in t ...
and inflammation of the skin. Affected areas are typically colonised by '' Cutibacterium acnes''; a member of the commensal
Commensalism is a long-term biological interaction (symbiosis) in which members of one species gain benefits while those of the other species neither benefit nor are harmed. This is in contrast with mutualism, in which both organisms benefit f ...
microbiota even in those without acne. High populations of ''C. acnes'' are linked to acne vulgaris although only certain strains are strongly associated with acne while others with healthy skin. The relative population of ''C. acnes'' is similar between those with acne and those without.
Current treatment includes topical and systemic antibacterial drugs which result in decreased ''C. acnes'' colonisation and/or activity. Potential probiotic treatment includes the use of '' Staphylococcus epidermidis'' to inhibit ''C. acnes'' growth. ''S. epidermidis'' produces succinic acid which has been shown to inhibit ''C. acnes'' growth. '' Lactobacillus plantarum'' has also been shown to act as an anti-inflammatory and improve antimicrobial properties of the skin when applied topically. It was also shown to be effective in reducing acne lesion size.
Atopic dermatitis
Individuals withatopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin. Atopic dermatitis is also often called simply eczema but the same term is also used to refer to dermatitis, the larger group of skin conditi ...
have shown an increase in populations of ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'' in both lesion
A lesion is any damage or abnormal change in the tissue of an organism, usually caused by injury or diseases. The term ''Lesion'' is derived from the Latin meaning "injury". Lesions may occur in both plants and animals.
Types
There is no de ...
al and nonlesional skin. Atopic dermatitis flares are associated with low bacterial diversity due to colonisation by ''S. aureus'' and following standard treatment
The standard treatment, also known as the standard of care, is the medical treatment that is normally provided to people with a given condition. In many scientific studies, the control group receives the standard treatment rather than a placebo w ...
, bacterial diversity has been seen to increase.
Current treatments include combinations of topical or systemic antibiotics, corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invol ...
, and diluted bleach baths. Potential probiotic treatments include using the commensal skin bacteria, ''S. epidermidis'', to inhibit ''S. aureus'' growth. During atopic dermatitis flares, population levels of ''S. epidermidis'' has been shown to increase as an attempt to control ''S. aureus populations''.
Low gut microbial diversity in babies has been associated with an increased risk of atopic dermatitis. Infants with atopic eczema have low levels of ''Bacteroides
''Bacteroides'' is a genus of Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacteria. ''Bacteroides'' species are non endospore–forming bacilli, and may be either motile or nonmotile, depending on the species. The DNA base composition is 40–48% GC. Un ...
'' and high levels of Bacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Bacillota, such as '' Megasphaera'', ...
. ''Bacteroides'' have anti-inflammatory properties which are essential against dermatitis. (See gut microbiota
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the g ...
)
Psoriasis vulgaris
Psoriasis vulgaris typically affects drier skin sites such as elbows and knees. Dry areas of the skin tend to have high microbial diversity and fewer populations than sebaceous sites. A study using swab sampling techniques show areas rich inBacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Bacillota, such as '' Megasphaera'', ...
(mainly ''Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a sing ...
'' and ''Staphylococcus
''Staphylococcus'', from Ancient Greek σταφυλή (''staphulḗ''), meaning "bunch of grapes", and (''kókkos''), meaning "kernel" or " Kermes", is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria in the family Staphylococcaceae from the order Bacillale ...
'') and Actinomycetota
The Actinomycetota (or Actinobacteria) are a diverse phylum of Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great importance to land flora because of their contributions to soil systems. In soil t ...
(mainly ''Corynebacterium
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name ('' coryneform'' means "club-s ...
'' and '' Propionibacterium'') are associated with psoriasis. While another study using biopsies associate increased levels of Bacillota and Actinomycetota with healthy skin. However most studies show that individuals affected by psoriasis have a lower microbial diversity in the affected areas.
Treatments for psoriasis include topical agents, phototherapy, and systemic agents. Current research on the skin microbiota's role in psoriasis is inconsistent therefore there are no potential probiotic treatments.
Rosacea
Rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, en ...
is typically connected to sebaceous sites of the skin. The skin mite
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods) of two large orders, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as eac ...
'' Demodex folliculorum'' produce lipases that allow them to use sebum as a source of food therefore they have a high affinity for sebaceous skin sites. Although it is a part of the commensal skin microbiota, patients affected with rosacea show an increase in ''D. folliculorum'' compared to healthy individuals, suggesting pathogenicity.
'' Bacillus oleronius'', a ''Demodex
''Demodex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of ''Demodex'' are known. Two species live on humans: ''Demodex folliculorum'' and ''Demodex brevis'', both frequently referred to as eyelash ...
'' associated microbe, is not typically found in the commensal skin microbiota but initiates inflammatory pathways whose starting mechanism is similar to rosacea patients. Populations of ''S. epidermidis'' have also been isolated from pustules of rosacea patients. However it is possible that they were moved by ''Demodex'' to areas that favour growth as ''Demodex'' has shown to transport bacteria around the face.
Current treatments include topical and oral antibiotics and laser therapy. As current research has yet to show a clear mechanism for ''Demodex'' influence in rosacea, there are no potential probiotic treatments.
Clinical
Infected devices
Skin microbes are a potential source of infected medical devices such ascatheters
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. Catheters are man ...
.
Hygiene
The human skin is host to numerous bacterial and fungal species, some of which are known to be harmful, some known to be beneficial and the vast majority unresearched. The use of bactericidal and fungicidal soaps will inevitably lead to bacterial and fungal populations which are resistant to the chemicals employed (seedrug resistance
Drug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a medication such as an antimicrobial or an antineoplastic in treating a disease or condition. The term is used in the context of resistance that pathogens or cancers have "acquired", that is ...
).
Contagion
Skin flora do not readily pass between people: 30 seconds of moderate friction and dry hand contact results in a transfer of only 0.07% of natural hand flora from naked with a greater percentage from gloves.Removal
The most effective (60–80% reduction) antimicrobial washing is withethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
, isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor.
Isopropyl alcohol, an organic polar molecule, is miscible in water, ethanol, an ...
, and n-propanol. Viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almo ...
are most affected by high (95%) concentrations of ethanol, while bacteria are more affected by n-propanol.
Unmedicated soaps are not very effective as illustrated by the following data. Health care workers washed their hands once in nonmedicated liquid soap for 30 seconds. The students/technicians for 20 times.
:::
An important use of hand washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap, soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to th ...
is to prevent the transmission of antibiotic resistant skin flora that cause hospital-acquired infection
A hospital-acquired infection, also known as a nosocomial infection (from the Greek , meaning "hospital"), is an infection that is acquired in a hospital or other health care, healthcare facility. To emphasize both hospital and nonhospital sett ...
s such as methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus''. While such flora have become antibiotic resistant due to antibiotics there is no evidence that recommended antiseptics or disinfectants selects for antibiotic-resistant organisms when used in hand washing. However, many strains of organisms are resistant to some of the substances used in antibacterial soaps such as triclosan
Triclosan (sometimes abbreviated as TCS) is an antibacterial and antifungal agent present in some consumer products, including toothpaste, soaps, detergents, toys, and surgical cleaning treatments. It is similar in its uses and mechanism of act ...
.
One study of bar soaps in dentist clinics found they all had their own flora and on average from two to five different genera of microorganisms with those used most more likely to have more species varieties. Another study of bar soaps in public toilets found even more flora. Another study found that very dry soaps are not colonized while all are that rest in pools of water. However, one experiment using soaps inoculated with ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
'' and ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
'' that washing with inoculated bar soap did not transmit these bacteria to participants hands.
Damaged skin
Washing skin repeatedly can damage the protective external layer and cause transepidermal loss of water. This can be seen in roughness characterized by scaling and dryness, itchiness,dermatitis
Dermatitis is a term used for different types of skin inflammation, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened ...
provoked by microorganisms and allergen
An allergen is an otherwise harmless substance that triggers an allergic reaction in sensitive individuals by stimulating an immune response.
In technical terms, an allergen is an antigen that is capable of stimulating a type-I hypersensitivi ...
s penetrating the corneal layer and redness. Wearing gloves can cause further problems since it produces a humid environment favoring the growth of microbes and also contains irritants such as latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latices are found in nature, but synthetic latices are common as well.
In nature, latex is found as a wikt:milky, milky fluid, which is present in 10% of all floweri ...
and talcum powder.
Hand washing can damage skin because the stratum corneum
The stratum corneum (Latin language, Latin for 'horny layer') is the outermost layer of the epidermis (skin), epidermis. Consisting of dead tissue, it protects underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress. It is ...
top layer of skin consists of 15 to 20 layers of keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
disks, corneocyte
Corneocytes are terminally differentiated keratinocytes and compose most of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis. They are regularly replaced through desquamation and renewal from lower epidermal layers and are essential fo ...
s, each of which is each surrounded by a thin film of skin lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s which can be removed by alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
s and detergent
A detergent is a surfactant or a mixture of surfactants with Cleanliness, cleansing properties when in Concentration, dilute Solution (chemistry), solutions. There are a large variety of detergents. A common family is the alkylbenzene sulfonate ...
s.
Damaged skin defined by extensive cracking of skin surface, widespread reddening or occasional bleeding has also been found to be more frequently colonized by '' Staphylococcus hominis'' and these were more likely to be methicillin
Methicillin ( USAN), also known as meticillin ( INN), is a narrow-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the penicillin class.
Methicillin was discovered in 1960.
Medical uses
Compared to other penicillins that face antimicrobial resistance ...
resistant. Though not related to greater antibiotic resistance, damaged skin was also more like to be colonized by ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'', gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
, '' Enterococci'' and '' Candida''.
Comparison with other flora
The skin flora is different from that of the gut which is predominantlyBacillota
The Bacillota (synonym Firmicutes) are a phylum of bacteria, most of which have Gram-positive cell wall structure. They have round cells, called cocci (singular coccus), or rod-like forms (bacillus). A few Bacillota, such as '' Megasphaera'', ...
and Bacteroidota
The phylum (biology), phylum Bacteroidota (synonym Bacteroidetes) is composed of three large classes of Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, nonsporeforming, anaerobic or aerobic, and rod-shaped bacteria that are widely distributed in the envir ...
. There is also low level of variation between people that is not found in gut studies. Both gut and skin flora however lack the diversity found in soil flora.
See also
* Bacterial disease *Body odor
Body odor or body odour (BO) is present in all animals and its intensity can be influenced by many factors (behavioral patterns, survival strategies). Body odor has a strong genetic basis, but can also be strongly influenced by various factors, ...
* Gut flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the g ...
* Human flora
* Human Microbiome Project
* Medical microbiology
* Microbial ecology
Microbial ecology (or environmental microbiology) is a discipline where the interaction of Microorganism, microorganisms and their environment are studied. Microorganisms are known to have important and harmful ecological relationships within t ...
* Microflora
* Oral microbiology
* Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
* Vaginal flora
References
External links
Cellulitis Skin Infection
Human microbiome project
Hygiene of the Skin: When Is Clean Too Clean?
{{Portal bar, Biology, Medicine Bacteriology Environmental microbiology Microbiology Microbiology terms
flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
Microbiomes