|
Propionibacterium
''Propionibacterium'' is a gram-positive, anaerobic, rod-shaped genus of bacteria named for their unique metabolism: They are able to synthesize propionic acid by using unusual transcarboxylase enzymes. Its members are primarily facultative parasites and commensals of humans and other animals, living in and around the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and other areas of the skin. They are virtually ubiquitous and do not cause problems for most people, but propionibacteria have been implicated in acne and other skin conditions. One study found the ''Propionibacterium'' was the most prevalent human skin-associated genus of microorganisms. In ruminants, propionibacteria reduce nitrate to nontoxic nitrogen compounds. Members of the genus ''Propionibacterium'' are widely used in the production of vitamin B12, tetrapyrrole compounds, and propionic acid, as well as in the probiotics and cheese industries. The strain ''Propionibacterium freudenreichii'' subsp. ''shermanii'' is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionibacterium Acnes
''Cutibacterium acnes'' (''Propionibacterium acnes'') is the relatively slow-growing, typically aerotolerant anaerobic, gram-positive bacterium (rod) linked to the skin condition of acne; it can also cause chronic blepharitis and endophthalmitis, the latter particularly following intraocular surgery. Its genome has been sequenced and a study has shown several genes can generate enzymes for degrading skin and proteins that may be immunogenic (activating the immune system). The species is largely commensal and part of the skin flora present on most healthy adult humans' skin. It is usually just barely detectable on the skin of healthy preadolescents. It lives, among other things, primarily on fatty acids in sebum secreted by sebaceous glands in the follicles. It may also be found throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Originally identified as ''Bacillus acnes'', it was later named ''Propionibacterium acnes'' for its ability to generate propionic acid. In 2016, ''P. acnes'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionibacterium Freudenreichii
''Propionibacterium freudenreichii'' is a gram-positive, Motility, non-motile bacterium that plays an important role in the creation of Emmental cheese, and to some extent, Jarlsberg cheese, Leerdammer and Maasdam cheese. Its concentration in Swiss cheese (North America), Swiss-type cheeses is higher than in any other cheese. Propionibacteria are commonly found in milk and dairy products, though they have also been extracted from soil. ''P. freudenreichii'' has a circular chromosome about 2.5 Mb long. When Emmental cheese is being produced, ''P. freudenreichii'' ferments lactate to form acetate, propionate, and carbon dioxide: (3 C3H6O3 → 2 C2H5CO2 + C2H3O2 + CO2). The products of this fermentation (food), fermentation contribute to the nutty and sweet flavors of the cheese, and the carbon dioxide byproduct is responsible for forming the holes, or "Eyes (cheese), eyes" in the cheese. Cheesemakers control the size of the holes by changing the acidity, temperature, and curing time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionibacterium Acidifaciens
''Propionibacterium acidifaciens'' is a Gram-positive, anaerobic and pleomorphic bacterium from the genus of Propionibacterium which has been isolated from a human oral cavity in London in England England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It .... References Propionibacteriales Bacteria described in 2009 {{Propionibacterineae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
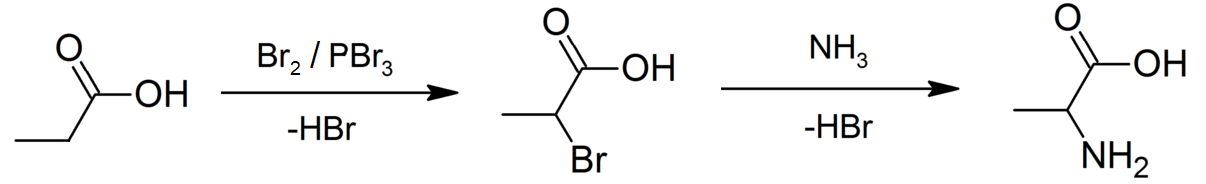
Propionic Acid
Propionic acid (, from the Greek language, Greek words πρῶτος : ''prōtos'', meaning "first", and πίων : ''píōn'', meaning "fat"; also known as propanoic acid) is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula . It is a liquid with a pungent and unpleasant smell somewhat resembling body odor. The anion as well as the Carboxylate salt, salts and esters of propionic acid are known as propionates or propanoates. About half of the world production of propionic acid is consumed as a preservative for both animal feed and food for human consumption. It is also useful as an intermediate in the production of other chemicals, especially polymers. History Propionic acid was first described in 1844 by Johann Gottlieb, who found it among the degradation products of sugar. Over the next few years, other chemists produced propionic acid by different means, none of them realizing they were producing the same substance. In 1847, French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas esta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
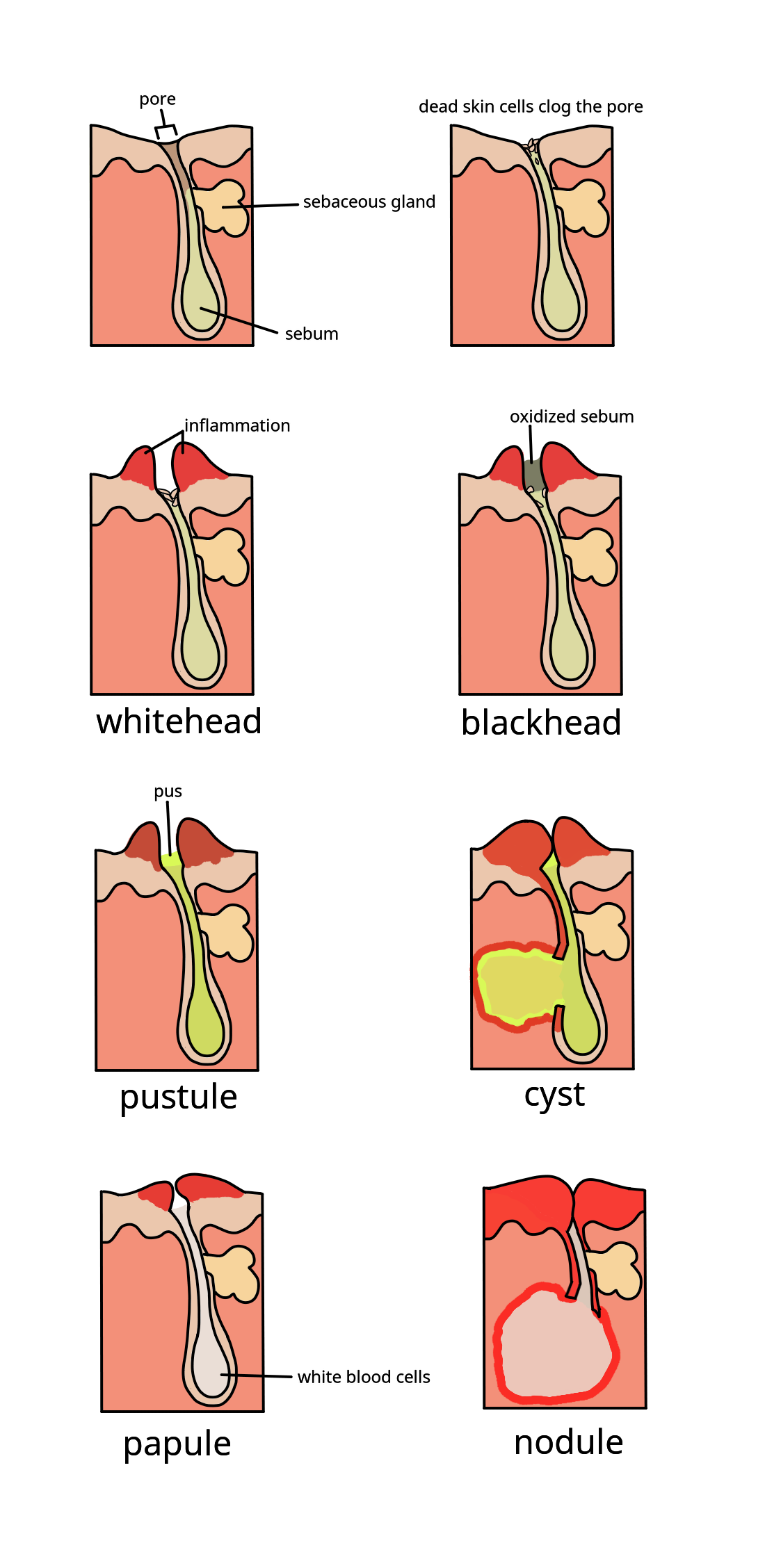
Acne
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight are associated with acne. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. One of eight B vitamins, it serves as a vital cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor in DNA synthesis and both fatty acid metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It plays an essential role in the nervous system by supporting myelinogenesis, myelin synthesis and is critical for the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. While animals require B12, plants do not, relying instead on alternative enzymatic pathways. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and is synthesized exclusively by certain archaea and bacteria. Natural food sources include meat, shellfish, liver, fish, poultry, Egg as food, eggs, and dairy products. It is also added to many breakfast cereals through food fortification and is available in dietary supplement and pharmaceutical forms. Supplements are commonly taken orally but may be administered via intramuscular injection to treat defic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
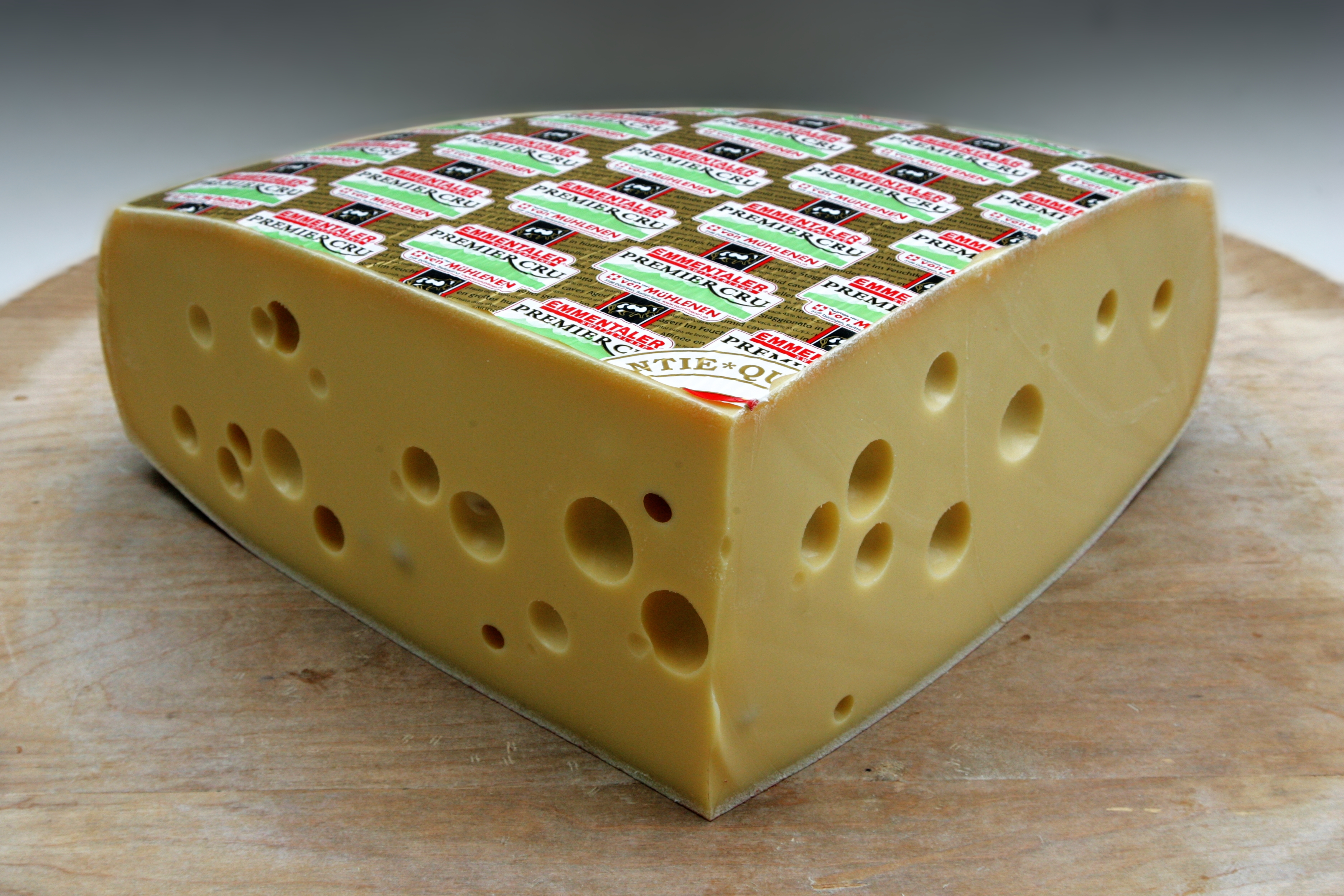
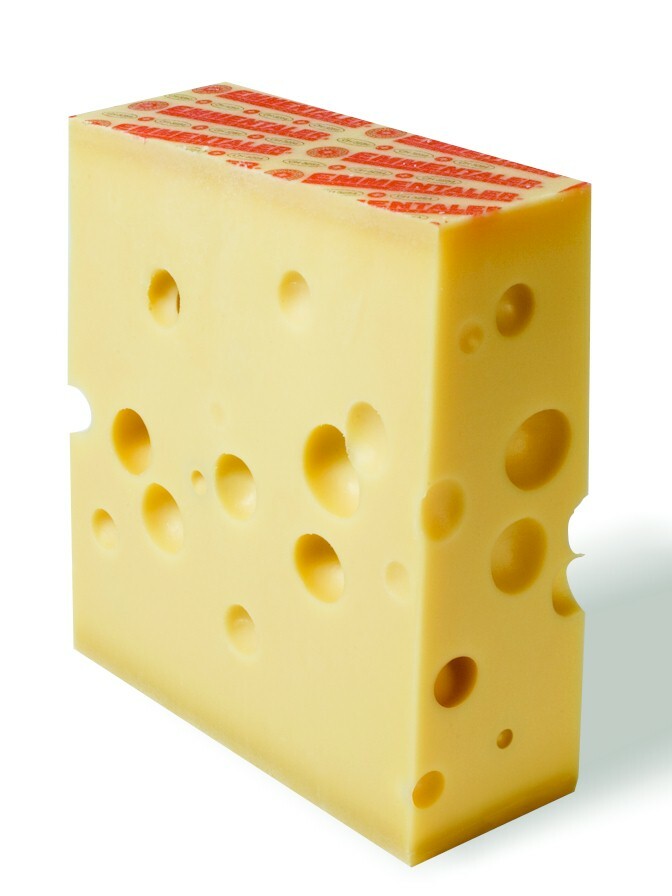
Eyes (cheese)
Eyes are the round holes that are a characteristic feature of Swiss-type cheese (e.g. Emmentaler cheese) and some Dutch-type cheeses. The eyes are formed by bubbles of carbon dioxide gas during the cheesemaking process. The gas is produced by various species of bacteria in the cheese. Swiss cheese In Swiss-type cheeses, the eyes form as a result of the activity of propionic acid bacteria (''propionibacteria''), notably ''Propionibacterium freudenreichii'' subsp. ''shermanii''.P.L.H. McSweeney, ''Biochemistry of Cheese Ripening: Introduction and Overview'', in: Fox, p. 349 These bacteria transform lactic acid into propionic acid and carbon dioxide, according to the formula: :3 lactate → 2 propionate + acetate + CO2 + H2O The CO2 so produced accumulates at weak points in the curd, where it forms the bubbles that become the cheese's eyes. Not all CO2 is so trapped: in an cheese, about 20 L of CO2 remain in the eyes, while 60 L remain dissolved in the cheese mass and 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comedones
A comedo (plural comedones) is a clogged hair follicle (pore) in the skin. Keratin (skin debris) combines with oil to block the follicle. A comedo can be open (blackhead) or closed by skin (whitehead) and occur with or without acne. The word ''comedo'' comes from Latin ''comedere'' 'to eat up' and was historically used to describe parasitic worms; in modern medical terminology, it is used to suggest the worm-like appearance of the expressed material. The chronic inflammatory condition that usually includes comedones, inflamed papules, and pustules ( pimples) is called acne. Infection causes inflammation and the development of pus. Whether a skin condition classifies as acne depends on the number of comedones and infection. Comedones should not be confused with sebaceous filaments. Comedo-type ductal carcinoma ''in situ'' (DCIS) is not related to the skin conditions discussed here. DCIS is a noninvasive form of breast cancer, but comedo-type DCIS may be more aggressive, so may b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmental Cheese
Emmental, Emmentaler, or Emmenthal is a yellow, medium-hard cheese that originated in the Emme Valley in Switzerland. It is classified as a Swiss-type cheese. History Emmental cheese originates from the Emme Valley in Switzerland. It has a savory but mild taste. While "Emmentaler" is registered as a geographical indication in Switzerland, a limited number of countries recognize the term as a geographical indication: similar cheeses of other origins, especially from France (as "Emmental"), the Netherlands, Bavaria, and Finland, are widely available and sold by that name. In some parts of the world, the names "Emmentaler" and " Swiss cheese" are used interchangeably for Emmental-style cheese. Production Three types of bacteria are needed to prepare Emmental: ''Streptococcus thermophilus'', '' Lactobacillus helveticus'', and ''Propionibacterium freudenreichii''. Historically, the eyes were a sign of imperfection, and until modern times, cheese makers would try to avoid them. No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facultative Parasite
A facultative parasite is an organism that may resort to parasitic activity, but does not absolutely rely on any host for completion of its life cycle. Examples of facultative parasitism occur among many species of fungi, such as family members of the genus '' Armillaria''. ''Armillaria'' species do parasitise living trees, but if the tree dies, whether as a consequence of the fungal infection or not, the fungus continues to eat the wood without further need for parasitic activity; some species even can ingest dead wood without any parasitic activity at all. As such, although they also are important ecological agents in the process of nutrient recycling by microbial decomposition, the fungi become pests in their role as destructive agents of wood rot. Similarly, green plants in genera such as ''Rhinanthus'' and '' Osyris'' can grow independently of any host, but they also act opportunistically as facultative root parasites of neighboring green plants. Among animals, facultati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |