Skanderna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the
 To the east, the Scandinavian Mountains proper bounds with mountains that are lower and less dissected and are known in Swedish as the (literally 'fore-fell'). Generally the do not surpass 1,000 m above sea level. As a geomorphic unit the extends across Sweden as a 650 km long and 40 to 80 km broad belt from Dalarna in the south to Norrbotten in the north. While lower than the Scandinavian Mountains proper, the ''
To the east, the Scandinavian Mountains proper bounds with mountains that are lower and less dissected and are known in Swedish as the (literally 'fore-fell'). Generally the do not surpass 1,000 m above sea level. As a geomorphic unit the extends across Sweden as a 650 km long and 40 to 80 km broad belt from Dalarna in the south to Norrbotten in the north. While lower than the Scandinavian Mountains proper, the ''
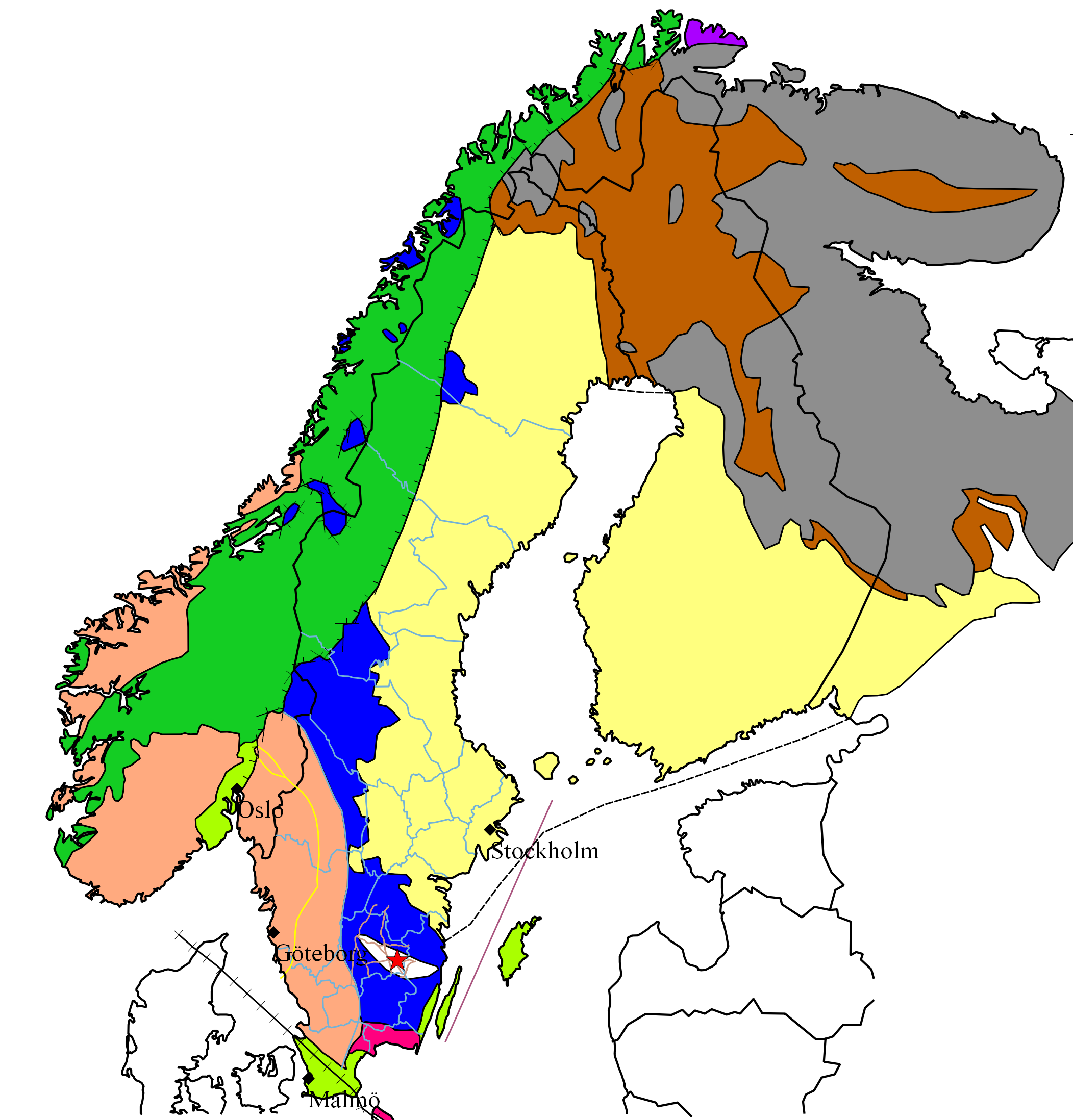 Most of the rocks of the Scandinavian Mountains are Caledonian, which means they were put in place by the Caledonian orogeny. Caledonian rocks overlie rocks of the much older Svecokarelian and Sveconorwegian provinces. The Caledonian rocks actually form large nappes ( sv, skollor) that have been thrust over the older rocks. Much of the Caledonian rocks have been eroded since they were put in place, meaning that they were once thicker and more contiguous. It is also implied from the erosion that the nappes of Caledonian rock once reached further east than they do today. The erosion has left remaining massifs of Caledonian rocks and windows of
Most of the rocks of the Scandinavian Mountains are Caledonian, which means they were put in place by the Caledonian orogeny. Caledonian rocks overlie rocks of the much older Svecokarelian and Sveconorwegian provinces. The Caledonian rocks actually form large nappes ( sv, skollor) that have been thrust over the older rocks. Much of the Caledonian rocks have been eroded since they were put in place, meaning that they were once thicker and more contiguous. It is also implied from the erosion that the nappes of Caledonian rock once reached further east than they do today. The erosion has left remaining massifs of Caledonian rocks and windows of
 The Cenozoic glaciations that affected
The Cenozoic glaciations that affected
Image:Galdh├ĖpiggenFromFannar├źki.jpg, Galdh├Ėpiggen seen from west, Norway's highest mountain
Image:Glittertind1999.jpg, Glittertind
Image:Falketind.jpg, Falketind in Jotunheimen
Image:Abisko alps.JPG, Landscape between
 # 1,324 m (4,344 ft) Halti (Lappi/Lapland and Norwegian Troms)
# 1,317 m (4,321 ft) Ridnitsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,280 m (4,200 ft) Kiedditsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,240 m (4,068 ft) Kovddoskaisi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,239 m (4,065 ft) Ruvdnaoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,180 m (3,871 ft) Loassonibba (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,150 m (3,773 ft) Urtasvaara (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,144 m (3,753 ft) Kahperusvaarat (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,130 m (3,707 ft) Aldorassa (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,100 m (3,608 ft) Kieddoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,324 m (4,344 ft) Halti (Lappi/Lapland and Norwegian Troms)
# 1,317 m (4,321 ft) Ridnitsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,280 m (4,200 ft) Kiedditsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,240 m (4,068 ft) Kovddoskaisi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,239 m (4,065 ft) Ruvdnaoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,180 m (3,871 ft) Loassonibba (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,150 m (3,773 ft) Urtasvaara (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,144 m (3,753 ft) Kahperusvaarat (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,130 m (3,707 ft) Aldorassa (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,100 m (3,608 ft) Kieddoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
 * Dovrefjell
* Jotunheimen
* Dovrefjell
* Jotunheimen
Scandinavian Peninsula
The Scandinavian Peninsula ( sv, Skandinaviska halv├Čn; no, Den skandinaviske halv├Ėy (Bokm├źl) or nn, Den skandinaviske halv├Ėya; fi, Skandinavian niemimaa) is a peninsula located in Northern Europe, which roughly comprises the mainlands ...
. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway
This list of Norwegian fjords shows many of the fjords in Norway. In total, there are about 1,190 fjords in Norway and the Svalbard islands. The sortable list includes the lengths and locations of those fjords.
Fjords
See also
* List of gla ...
, whereas to the northeast they gradually curve towards Finland. To the north they form the border between Norway and Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, reaching high at the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
. The mountain range just touches northwesternmost Finland but are scarcely more than hills at their northernmost extension at the North Cape ().
The mountains are relatively high for a range so young and are very steep in places; Galdh├Ėpiggen in South Norway is the highest peak in mainland Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54┬░N, or may be based on other g ...
, at ; Kebnekaise is the highest peak on the Swedish side, at , whereas the slope of Halti is the highest point in Finland, at , although the peak of Halti is situated in Norway.
The Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands
The Scandinavian montane birch forests and grasslands is defined by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) as a terrestrial tundra ecoregion in Norway, Sweden, and Finland.
Conservation value
The Scandinavian montane birch forests and grasslands is on ...
terrestrial ecoregion is closely associated with the mountain range.
Names in Scandinavia
Its names in the Scandinavian languages are, inSwedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, (encyclopedic and professional usage), ('the Fells', common in colloquial speech) or ('the Keel'), and in Norwegian , , ('the Keel') or ('the North Ridge', name coined in 2013). The names and are often preferentially used for the northern part, where the mountains form a narrow range near the border region of Norway and Sweden. In South Norway there is a broad scatter of mountain regions with individual names, such as Dovrefjell, Hardangervidda, Jotunheimen, and Rondane.
Orography
The mountain chain's highest summits are mostly concentrated in an area (of mean altitude of over 1,000 m) betweenStavanger
Stavanger (, , American English, US usually , ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Norway. It is the fourth largest city and third largest metropolitan area in Norway (through conurbation with neighboring Sandnes) and the a ...
and Trondheim in South Norway, with numerous peaks over 1,300 m and some peaks over 2,000 m. Around Trondheim Fjord
The Trondheim Fjord or Trondheimsfjorden (), an inlet of the Norwegian Sea, is Norway's third-longest fjord at long. It is located in the west-central part of the country in Tr├Ėndelag county, and it stretches from the municipality of ├śrla ...
, peaks decrease in altitude to about 400ŌĆō500 m rising again to heights in excess of 1,900 m further north in Swedish Lapland and nearby areas of Norway. The southern part of the mountain range contains the highest mountain of Northern Europe, Galdh├Ėpiggen at almost 2,500 m. This part of the mountain chain is also broader and contains a series of plateaux and gently undulating surfaces that hosts scattered inselbergs. The plateaux and undulating surfaces of the southern Scandinavian Mountains form a series of stepped surfaces. Geomorphologist Karna Lidmar-Bergstr├Čm and co-workers recognize five widespread stepped surfaces. In eastern Norway, some of the stepped surfaces merge into a single surface. Dovre and Jotunheimen are rises from the highest of the stepped surfaces. In south-western Norway, the plateaux and gently undulating surfaces are strongly dissected
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause ...
by fjords and valleys. The mountain chain is present in Sweden from northern Dalarna northwards; south of this point the Scandinavian Mountains lie completely within Norway. Most of the Scandinavian Mountains lack "alpine topography", and where present it does not relate to altitude. An example of this is the distribution of cirque
A (; from the Latin word ') is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from Scottish Gaelic , meaning a pot or cauldron) and (; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform ...
s in southern Norway that can be found both near sea level and at 2,000 m. Most cirques are found between 1,000 and 1,500 m.
 To the east, the Scandinavian Mountains proper bounds with mountains that are lower and less dissected and are known in Swedish as the (literally 'fore-fell'). Generally the do not surpass 1,000 m above sea level. As a geomorphic unit the extends across Sweden as a 650 km long and 40 to 80 km broad belt from Dalarna in the south to Norrbotten in the north. While lower than the Scandinavian Mountains proper, the ''
To the east, the Scandinavian Mountains proper bounds with mountains that are lower and less dissected and are known in Swedish as the (literally 'fore-fell'). Generally the do not surpass 1,000 m above sea level. As a geomorphic unit the extends across Sweden as a 650 km long and 40 to 80 km broad belt from Dalarna in the south to Norrbotten in the north. While lower than the Scandinavian Mountains proper, the ''Climate, permafrost and glaciers
The climate of the Nordic countries is maritime along the coast of Norway, and much more continental in Sweden in therain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
of the Scandinavian Mountains. The combination of a northerly location and moisture from the North Atlantic Ocean has caused the formation of many ice fields and glaciers. In the mountains, the air temperature decreases with increasing altitude, and patches of mountain permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 ┬░C (32 ┬░F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
in regions with a mean annual air temperature (MAAT) of -1.5 ┬░C will be found at wind exposed sites with little snow cover during winter. Higher up, widespread permafrost may be expected at altitudes with a MAAT of -3.5 ┬░C, continuous permafrost at altitudes with a MAAT of -6.0 ┬░C.
Within the EU-sponsored project PACE (Permafrost and Climate in Europe), a 100 m deep borehole was drilled in bedrock above Tarfala research station at an altitude of 1540 m above sea level. The stable ground temperature at a depth of 100 meters is still -2.75 ┬░C. The measured geothermal gradient in the drillhole of 1.17 ┬░C /100 m allows to extrapolate a permafrost thickness of 330 meters, a further proof that continuous permafrost exists in these altitudes and above, up to the top of Kebnekaise.
In the Scandinavian Mountains, the lower limit of widespread discontinuous permafrost drops from 1700 meters in the west of southern Norway to 1500 meters near the border with Sweden, and from 1600 m in northern Norway to 1100 m in northern, more continental Sweden ( Kebnekaise area). In contrast to the lower limit of permafrost, the mean glacier altitude (or glaciation limit) is related to the amount of precipitation. Thus the snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
, or glacier equilibrium line as the limit between the accumulation zone and ablation zone shows the opposite trend, from 1500 meters in the west ( Jostefonn) to 2100 meters in the east ( Jotunheimen).
Geology
Bedrock
 Most of the rocks of the Scandinavian Mountains are Caledonian, which means they were put in place by the Caledonian orogeny. Caledonian rocks overlie rocks of the much older Svecokarelian and Sveconorwegian provinces. The Caledonian rocks actually form large nappes ( sv, skollor) that have been thrust over the older rocks. Much of the Caledonian rocks have been eroded since they were put in place, meaning that they were once thicker and more contiguous. It is also implied from the erosion that the nappes of Caledonian rock once reached further east than they do today. The erosion has left remaining massifs of Caledonian rocks and windows of
Most of the rocks of the Scandinavian Mountains are Caledonian, which means they were put in place by the Caledonian orogeny. Caledonian rocks overlie rocks of the much older Svecokarelian and Sveconorwegian provinces. The Caledonian rocks actually form large nappes ( sv, skollor) that have been thrust over the older rocks. Much of the Caledonian rocks have been eroded since they were put in place, meaning that they were once thicker and more contiguous. It is also implied from the erosion that the nappes of Caledonian rock once reached further east than they do today. The erosion has left remaining massifs of Caledonian rocks and windows of Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pĻ×Æ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
rock.
While there are some disagreements, geologists generally recognize four units among the nappes: an uppermost, an upper, a middle and a lower unit. The lower unit is made up Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ...
( Vendian), Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ļ×Æ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
, Ordovician and Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
-aged sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles t ...
. Pieces of Precambrian shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of a ...
rocks are in some places also incorporated into the lower nappes.
It was during the Silurian and Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
periods that the Caledonian nappes were stacked upon the older rocks and upon themselves. This occurred in connection to the closure of the Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean (; ) was an ocean that existed in the late Neoproterozoic and early Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale (between 600 and 400 million years ago). The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleoco ...
as the ancient continents of Laurentia and Baltica collided. This collision produced a Himalayas-sized mountain range named the Caledonian Mountains
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that o ...
roughly over the same area as the present-day Scandinavian Mountains. The Caledonian Mountains began a post-orogenic collapse in the Devonian, implying tectonic extension and subsidence. Despite occurring in about the same area, the ancient Caledonian Mountains and the modern Scandinavian Mountains are unrelated.
Origin
The origin of today's mountain topography is debated by geologists. Geologically, the Scandinavian Mountains are an elevated, passive continental margin similar to the mountains and plateaux found on the opposite side of theNorth Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
in Eastern Greenland
Tunu, originally ├śstgr├Ėnland ("East Greenland"), was one of the three counties (''amter'') of Greenland until 31 December 2008. The county seat was at the main settlement, Tasiilaq. The county's population in 2005 was around 3,800.
The county ...
or in Australia's Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills, that runs rough ...
. The Scandinavian Mountains attained its height by tectonic processes different from orogeny, chiefly in the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
. A two-stage model of uplift has been proposed for the Scandinavian Mountains in South Norway. A first stage in the Mesozoic and a second stage starting from the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the ...
. The uplift of South Norway has elevated the westernmost extension of the sub-Cambrian peneplain
The sub-Cambrian peneplain is an ancient, extremely flat, erosion surface (peneplain) that has been exhumed and exposed by erosion from under Cambrian strata over large swathes of Fennoscandia. Eastward, where this peneplain dips below Cambrian an ...
which forms part of what is known as the Paleic surface in Norway. In South Norway, the Scandinavian Mountains had their main uplift phase later (Neogene
The Neogene ( ), informally Upper Tertiary or Late Tertiary, is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period Mya. ...
) than in northern Scandinavia which had its main phase of uplift in the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Pal├”ogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
. For example, the Hardangervidda uplifted from sea level to its present 1200ŌĆō1100 m in Early Pliocene times.
The various episodes of uplift of the Scandinavian Mountains were similar in orientation and tilted land surfaces to the east while allowing rivers to incise the landscape. Some of the tilted surfaces constitute the Muddus plains
The Muddus plains is a landscape type in northern Sweden characterized by its flat topography dotted with inselbergs. The topographic character of the Muddus plains was first described in detail by Walter Wr├źk in 1908. The Muddus plains are part ...
landscape of northern Sweden. The progressive tilt contributed to create the parallel drainage pattern of northern Sweden. Uplift is thought to have been accommodated by coast-parallel normal faults and not by fault-less doming. Therefore, the common labelling of the southern Scandinavian Mountains and the northern Scandinavian Mountains as two domes is misleading. There are divided opinions on the relation between the coastal plains of Norway, the strandflat
Strandflat ( no , strandflate) is a landform typical of the Norwegian coast consisting of a flattish erosion surface on the coast and near-coast seabed. In Norway, strandflats provide room for settlements and agriculture, constituting important ...
, and the uplift of the mountains.
Unlike orogenic mountains, there is no widely accepted geophysical model to explain elevated passive continental margins such as the Scandinavian Mountains. Various mechanisms of uplift have, however, been proposed over the years. A 2012 study argues that the Scandinavian Mountains and other elevated passive continental margins most likely share the same mechanism of uplift and that this mechanism is related to far-field stresses in Earth's lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
. The Scandinavian Mountains can according to this view be likened to a giant anticlinal Anticlinal may refer to:
*Anticline, in structural geology, an anticline is a fold that is convex up and has its oldest beds at its core.
*Anticlinal, in stereochemistry, a torsion angle between 90┬░ to 150┬░, and ŌĆō90┬░ to ŌĆō150┬░; see Alkane_st ...
lithospheric fold
Fold, folding or foldable may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Fold'' (album), the debut release by Australian rock band Epicure
*Fold (poker), in the game of poker, to discard one's hand and forfeit interest in the current pot
*Above ...
. Folding could have been caused by horizontal compression acting on a thin to thick crust transition zone (as are all passive margins).
Alternative lines of research have stressed the role of climate in inducing erosion that induces an isostatic compensation; fluvial and glacial erosion and incision during the Quaternary is thought to have contributed to the uplift of the mountain by forcing an isostatic response. The total amount of uplift produced by this mechanism could be as much as 500 m. Other geoscientists have implied diapir
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped RayleighŌĆōT ...
ism in the asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between ~ below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is not ...
as being the cause of uplift. One hypothesis states that the early uplift of the Scandinavian Mountains could be indebted to changes in the density of the lithosphere and asthenosphere caused by the Iceland plume when Greenland and Scandinavia rifted apart about 53 million years ago.
Quaternary geology
Many slopes and valleys are straight because they follow tectonic fractures that are more prone to erosion. Another result of tectonics in the relief is that slopes corresponding to footwalls of normal faults tend to be straight. There is evidence that thedrainage divide
A drainage divide, water divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a singl ...
between the Norwegian Sea and the south-east flowing rivers were once further west. Glacial erosion is thought to have contributed to the shift of the divide, which in some cases ought to have been in excess of 50 km. Much of the Scandinavian Mountains has been sculpted by glacial erosion. The mountain chain is dotted with glacial cirque
A (; from the Latin word ') is an amphitheatre-like valley formed by glacial erosion. Alternative names for this landform are corrie (from Scottish Gaelic , meaning a pot or cauldron) and (; ). A cirque may also be a similarly shaped landform ...
s usually separated from each other by pre-glacial paleosurface
In geology and geomorphology a paleosurface is a surface made by erosion of considerable antiquity. Paleosurfaces might be flat or uneven in some cases having considerable relief. Flat and large paleosurfaces ŌĆöthat is planation surfacesŌĆö have ...
s. Glacier erosion has been limited in these paleosurfaces which form usually plateaus between valleys. As such the paleosurfaces were subject of diverging and slow ice flow during the glaciations. In contrast valleys concentrated ice flow forming fast glaciers or ice streams
An ice stream is a region of fast-moving ice within an ice sheet. It is a type of glacier, a body of ice that moves under its own weight. They can move upwards of a year, and can be up to in width, and hundreds of kilometers in length. They t ...
. At some locations coalesced cirques form arêtes and pyramidal peaks. Glacial reshaping of valleys is more marked in the western part of the mountain chain where drowned glacier-shaped valleys constitute the fjords of Norway. In the eastern part of the mountain chain, glacial reshaping of valleys is weaker. Many mountain tops contain blockfield
A blockfieldWhittow, John (1984). ''Dictionary of Physical Geography''. London: Penguin, 1984, pp. 66 and 190. .
(also spelt block fieldLeser, Hartmut, ed. (2005). ''W├Črterbuch Allgemeine Geographie'', 13th ed., dtv, Munich, pp. 107 and 221. ...
s which escaped glacial erosion either by having been nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. ...
s in the glacial periods or by being protected from erosion under cold-based glacier ice. Karst
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
systems, with their characteristic caves and sinkholes, occur at various places in the Scandinavian Mountains, but are more common in the northern parts. Present-day karst systems might have long histories dating back to the Pleistocene or even earlier.
Much of the mountain range is mantled by deposits of glacial origin including till blankets, moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
s, drumlins and glaciofluvial material in the form of outwash plains and eskers. Bare rock surfaces are more common in the western side of the mountain range. Although the ages of these deposits and landforms vary, most of them were formed in connection to the Weichselian glaciation and the subsequent deglaciation Deglaciation is the transition from full glacial conditions during ice ages, to warm interglacials, characterized by global warming and sea level rise due to change in continental ice volume. Thus, it refers to the retreat of a glacier, an ice shee ...
.
 The Cenozoic glaciations that affected
The Cenozoic glaciations that affected Fennoscandia
__NOTOC__
Fennoscandia (Finnish language, Finnish, Swedish language, Swedish and no, Fennoskandia, nocat=1; russian: ążąĄąĮąĮąŠčüą║ą░ąĮą┤ąĖčÅ, Fennoskandiya) or the Fennoscandian Peninsula is the geographical peninsula in Europe, which includes ...
most likely began in the Scandinavian Mountains. It is estimated that during 50% of the last 2.75 million years the Scandinavian Mountains hosted mountain-centered ice caps and ice fields. The ice fields from which the Fennoscandian Ice Sheet grew out multiple times most likely resembled today's ice fields in Andean Patagonia. During the last glacial maximum
The Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent.
Ice sheets covered much of Northern North America, Northern Eur ...
(ca. 20 ka BP) all the Scandinavian Mountains were covered by the Fennoscandian Ice Sheet, which extended well beyond the mountains into Denmark, Germany, Poland and the former USSR. As the ice margin started to recede 22ŌĆō17 ka BP the ice sheet became increasingly concentrated in the Scandinavian Mountains. Recession of the ice margin led the ice sheet to be concentrated in two parts of the Scandinavian Mountains, one part in South Norway and another in northern Sweden and Norway. These two centres were for a time linked, so that the linkage constituted a major drainage barrier that formed various large ephemeral ice-dammed lakes. About 10 ka BP, the linkage had disappeared and so did the southern centre of the ice sheet a thousand years later. The northern centre remained a few hundred years more, and by 9,7 ka BP the eastern Sarek Mountains hosted the last remnant of the Fennoscandian Ice Sheet. As the ice sheet retreated to the Scandinavian Mountains it was dissimilar to the early mountain glaciation that gave origin to the ice sheet as the ice divide lagged behind as the ice mass concentrated in the west.
Highest mountains
Norway
Of the 10 highest mountain peaks in Scandinavia ( prominence greater than ), six are situated in Oppland, Norway. The other four are situated in Sogn og Fjordane, Norway. # Galdh├Ėpiggen ( Innlandet) # Glittertind (Innlandet) #Store Skagast├Ėlstind
Store Skagast├Ėlstind (also known as Storen) is the third highest peak in Norway. It is situated on the border between the municipality of Luster and ├ģrdal in Vestland county, Norway. The mountain is part of the Hurrungane range. The mountai ...
( Vestland)
# Store Styggedalstinden east (Vestland)
# Skarstind (Innlandet)
# Vesle Galdh├Ėpiggen (Innlandet)
# Surtningssue (Innlandet)
# Store Memurutinden
Store Memurutinden is the eighth-highest mountain in Norway. It is in Lom Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. The tall mountain is located on the Memurutindene mountains within Jotunheimen National Park. The mountain sits about south of ...
(Innlandet)
# Jervvasstind (Vestland)
# Sentraltind (Vestland)
Abisko National Park
Abisko National Park ( sv, Abisko nationalpark) is a National Park in Sweden, established in 1909.
Geography
Abisko is situated in the Swedish province of Lapland near the Norwegian border (distance approx. by railway), and belongs to Kir ...
and Kebnekaise
Sweden
There are 12 peaks inSweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
that reach above , or 13 depending on how the peaks are defined. Eight of them are located in Sarek National Park
Sarek National Park ( sv, Sareks nationalpark) is a national park in Jokkmokk Municipality, Lapland in northern Sweden. Established in 1909, the park is the oldest national park in Europe. It is adjacent to two other national parks, namely Stor ...
and the neighbouring national park Stora Sj├Čfallet
Stora Enso Oyj (from sv, Stora and fi, Enso ) is a manufacturer of pulp, paper and other forest products, headquartered in Helsinki, Finland. The majority of sales takes place in Europe, but there are also significant operations in Asia and S ...
. The other four peaks are located in the further north region of Kebnekaise. All mountain names are in Sami but with the more common Swedish spelling of it.
# Kebnekaise ( Lappland) ŌĆō Note: Altitude includes the peak glacier. If melting continues, Kebnekaise Nordtoppen, just 500 meters away, might become the highest point.
# Kebnekaise Nordtoppen (Lappland) ŌĆō the highest fixed point in Sweden.
# Sarektj├źkk├ź Stortoppen (Lappland)
# Kaskasatj├źkka
Kaskasatj├źkka is a mountain in Sweden with an elevation of Sea level#AMSL, above mean sea level (AMSL). Its peak is located about north of the mountain huts and Tarfala research station, research station in the Tarfala Valley.
References
...
(Lappland)
# Sarektj├źkk├ź Nordtoppen (Lappland)
# Kaskasapakte (Lappland)
# Sarektj├źkk├ź Sydtoppen (Lappland)
# Akka Stortoppen (Lappland)
# Akka Nordv├żsttoppen (Lappland)
# Sarektj├źkk├ź Buchttoppen (Lappland)
# P├źrtetj├źkka (Lappland)
# Palkatj├źkka (Lappland)
''Other popular mountains for skiers, climbers and hikers in Sweden''
* Sulitelma 1,860 m (Lappland)
* Helagsfj├żllet
Helagsfj├żllet, the mountain of Helags, is a mountain in H├żrjedalen, Sweden, and is part of the Scandinavian Mountains. The peak reaches 1,797 metres above sea level, which makes it the highest mountain in Sweden south of the Arctic Circle. Its g ...
1,796 m ( H├żrjedalen)
* Norra Storfj├żllet
Norra Storfj├żllet is a minor sub-range of the Scandinavian Mountains, located in the county of V├żsterbotten, in Lapland, Sweden. It is, for the most part, located within Vindelfj├żllen Nature Reserve. It reaches a maximum height of at the peak k ...
1,767 m (Lappland)
* Templet 1,728 m (J├żmtland
J├żmtland (; no, Jemtland or , ; Jamtish: ''Jamtlann''; la, Iemptia) is a historical province () in the centre of Sweden in northern Europe. It borders H├żrjedalen and Medelpad to the south, ├ģngermanland to the east, Lapland to the north a ...
)
* Lillsylen 1,704 m (J├żmtland)
* ├ģreskutan 1,420 m (J├żmtland)
* Storv├żttesh├źgna
Storv├żttesh├źgna (in Sami: ''Gealta'') is a peak of the L├źngfj├żllet massif in the southern part of the Scandinavian mountain range, near Gr├Čvelsj├Čn in Idre parish, ├älvdalen Municipality. It is the highest point in Dalarna and Svealand
...
1,204 m ( Dalarna)
* Nipfj├żllet 1,191 m (Dalarna)
* St├żdjan 1,131 m (Dalarna)
Finland
 # 1,324 m (4,344 ft) Halti (Lappi/Lapland and Norwegian Troms)
# 1,317 m (4,321 ft) Ridnitsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,280 m (4,200 ft) Kiedditsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,240 m (4,068 ft) Kovddoskaisi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,239 m (4,065 ft) Ruvdnaoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,180 m (3,871 ft) Loassonibba (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,150 m (3,773 ft) Urtasvaara (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,144 m (3,753 ft) Kahperusvaarat (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,130 m (3,707 ft) Aldorassa (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,100 m (3,608 ft) Kieddoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,324 m (4,344 ft) Halti (Lappi/Lapland and Norwegian Troms)
# 1,317 m (4,321 ft) Ridnitsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,280 m (4,200 ft) Kiedditsohkka (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,240 m (4,068 ft) Kovddoskaisi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,239 m (4,065 ft) Ruvdnaoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,180 m (3,871 ft) Loassonibba (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,150 m (3,773 ft) Urtasvaara (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,144 m (3,753 ft) Kahperusvaarat (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,130 m (3,707 ft) Aldorassa (Lappi/Lapland)
# 1,100 m (3,608 ft) Kieddoaivi (Lappi/Lapland)
See also
 * Dovrefjell
* Jotunheimen
* Dovrefjell
* Jotunheimen
Notes
References
External links
{{Authority control Mountain ranges of Europe Mountain ranges of Norway Mountain ranges of Finland Mountain ranges of Sweden Scandinavia