Ryukyu Kingdom on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ryukyu Kingdom was a kingdom in the
 Japanese products—silver, swords, fans,
Japanese products—silver, swords, fans,


 In 1655, tribute relations between Ryukyu and
In 1655, tribute relations between Ryukyu and
"The Ryukyus and Taiwan in the East Asian Seas: A Longue Durée Perspective"
''Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus''. 27 October 2006, translated and abridged from ''Academia Sinica Weekly'', No. 1084. 24 August 2006. At the same time, the appearance of independence was maintained for diplomatic reasons with Qing China until the
 * Foreign relations of the Ryukyu Kingdom
* Foreign relations of Imperial China
*
* Foreign relations of the Ryukyu Kingdom
* Foreign relations of Imperial China
*
Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan
Nara National Research Institute for Cultural Properties {{DEFAULTSORT:Ryukyu Kingdom Kingdom Former countries in East Asia Former countries in Japanese history Former kingdoms Island countries 1429 establishments in Asia 1879 disestablishments in Asia States and territories established in 1429 States and territories disestablished in 1879 Former monarchies of East Asia History of Okinawa Prefecture
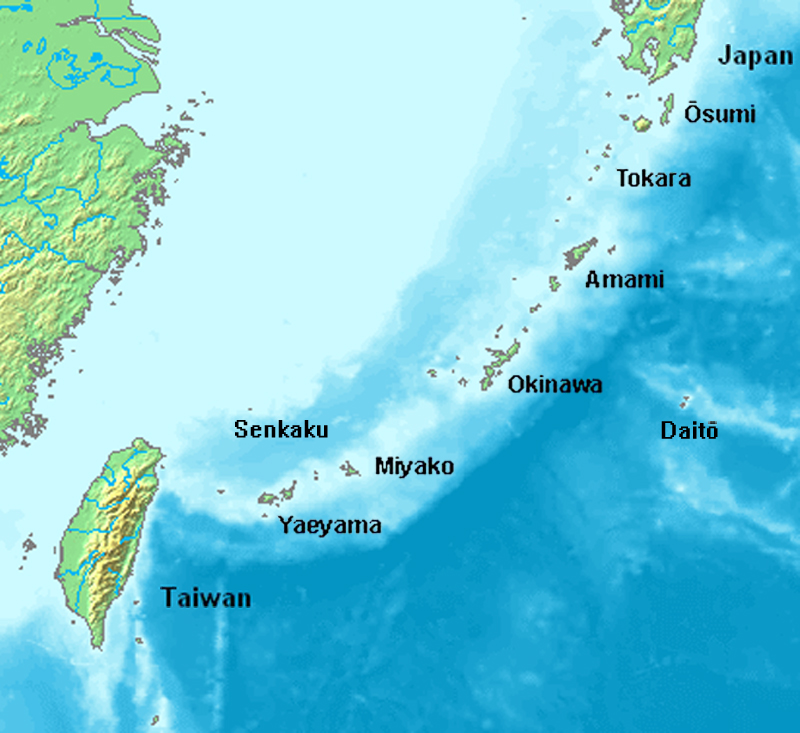
Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Geography of Taiwan, Taiwan: the Ryukyu Islands are divided into the Satsunan Islands (Ōsumi Islands, Ōsumi, Tokara Islands, Tokara and A ...
from 1429 to 1879. It was ruled as a tributary state
A tributary state is a pre-modern state in a particular type of subordinate relationship to a more powerful state which involved the sending of a regular token of submission, or tribute, to the superior power (the suzerain). This token often ...
of imperial Ming China by the Ryukyuan monarchy, who unified Okinawa Island
, officially , is the largest of the Okinawa Islands and the Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands of Japan in the Kyushu region. It is the smallest and least populated of the five Japanese archipelago, main islands of Japan. The island is ...
to end the Sanzan period, and extended the kingdom to the Amami Islands
The The name ''Amami-guntō'' was standardized on February 15, 2010. Prior to that, another name, ''Amami shotō'' (奄美諸島), was also used. is a Japanese archipelago in the Satsunan Islands, which is part of the Ryukyu Islands, and is sout ...
and Sakishima Islands
The (or 先島群島, ''Sakishima-guntō'') (Okinawan language, Okinawan: ''Sachishima'', Miyakoan language, Miyako: ''Saksїzїma'', Yaeyama language, Yaeyama: ''Sakїzїma'', Yonaguni language, Yonaguni: ''Satichima'') are an archipelago loca ...
. The Ryukyu Kingdom played a central role in the maritime trade networks of medieval East Asia and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
despite its small size. The Ryukyu Kingdom became a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back to ...
of the Satsuma Domain
The , briefly known as the , was a Han system, domain (''han'') of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan during the Edo period from 1600 to 1871.
The Satsuma Domain was based at Kagoshima Castle in Satsuma Province, the core of the modern city of ...
of Japan after the invasion of Ryukyu in 1609 but retained ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' (; ; ) describes practices that are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. The phrase is often used in contrast with '' de facto'' ('from fa ...
'' independence until it was transformed into the Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, and simultaneously a tributary state of the Qing Empire, until 1875, before being fully incorporated into Japan as the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islan ...
by the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
in 1872. The Ryukyu Kingdom was formally annexed and dissolved by Japan in 1879 to form Okinawa Prefecture
is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan. It consists of three main island groups—the Okinawa Islands, the Sakishima Islands, and the Daitō Islands—spread across a maritime zone approximately 1,000 kilometers east to west an ...
, and the Ryukyuan monarchy was integrated into the new Japanese nobility.
History
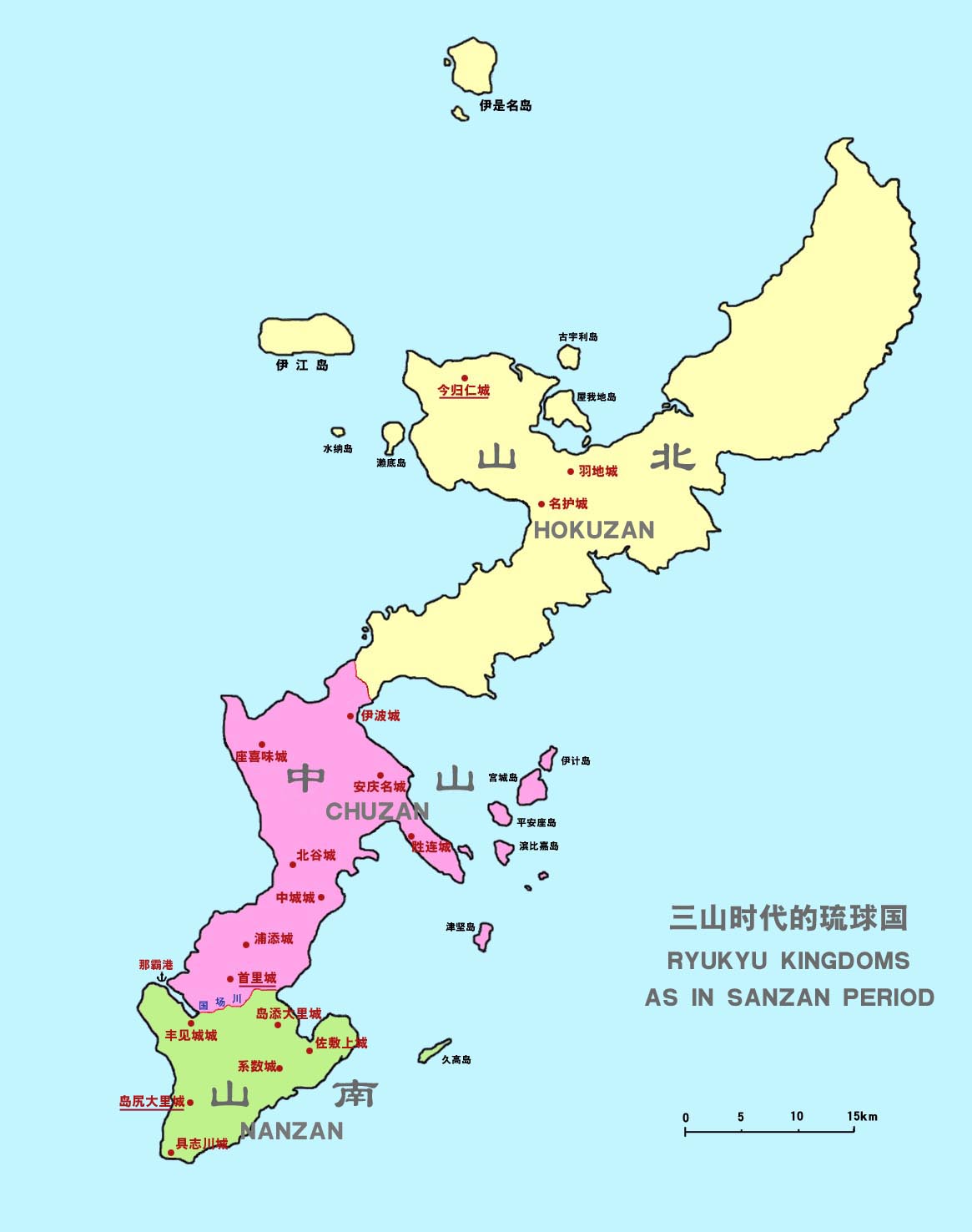
Origins of the Kingdom
In the 14th century small domains scattered onOkinawa Island
, officially , is the largest of the Okinawa Islands and the Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands of Japan in the Kyushu region. It is the smallest and least populated of the five Japanese archipelago, main islands of Japan. The island is ...
were unified into three principalities: , , and . This was known as the period. Hokuzan, which constituted much of the northern half of the island, was the largest in terms of land area and military strength but was economically the weakest of the three. Nanzan constituted the southern portion of the island. Chūzan lay in the center of the island and was economically the strongest. Its political capital at Shuri, Nanzan was adjacent to the major port of Naha
is the Cities of Japan, capital city of Okinawa Prefecture, the southernmost prefecture of Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city has an estimated population of 317,405 and a population density of 7,939 people per km2 (20,562 persons per sq. mi.). ...
, and Kume-mura, the center of traditional Chinese education. These sites and Chūzan as a whole would continue to form the center of the Ryukyu Kingdom until its abolition.
Many Chinese people moved to Ryukyu to serve the government or to engage in business during this period. At the request of the Ryukyuan King, the Ming Chinese sent thirty-six Chinese families from Fujian
Fujian is a provinces of China, province in East China, southeastern China. Fujian is bordered by Zhejiang to the north, Jiangxi to the west, Guangdong to the south, and the Taiwan Strait to the east. Its capital is Fuzhou and its largest prefe ...
to manage oceanic dealings in the kingdom in 1392, during the Hongwu Emperor
The Hongwu Emperor (21 October 1328– 24 June 1398), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizu of Ming, personal name Zhu Yuanzhang, courtesy name Guorui, was the List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, founding emperor of the Ming dyna ...
's reign. Many Ryukyuan officials were descended from these Chinese immigrants, being born in China or having Chinese grandfathers. They assisted the Ryukyuans in advancing their technology and diplomatic relations. On 30 January 1406, the Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor (2 May 1360 – 12 August 1424), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Chengzu of Ming, personal name Zhu Di, was the third List of emperors of the Ming dynasty, emperor of the Ming dynasty, reigning from 1402 to 142 ...
expressed horror when the Ryukyuans castrated some of their own children to become eunuchs to serve in the Ming imperial palace. Emperor Yongle said that the boys who were castrated were innocent and did not deserve castration, and he returned them to Ryukyu, and instructed the kingdom not to send eunuchs again.
These three principalities (tribal federations led by major chieftains) battled, and Chūzan emerged victorious. The Chūzan leaders were officially recognized by Ming dynasty China as the rightful kings over those of Nanzan and Hokuzan, thus lending great legitimacy to their claims. The ruler of Chūzan passed his throne to King Hashi; Hashi conquered Hokuzan in 1416 and Nanzan in 1429, uniting the island of Okinawa for the first time, and founded the first Shō dynasty. Hashi was granted the surname "Shō" ( zh, c=尚, p=Shàng, links=no) by the Ming emperor in 1421, becoming known as Shō Hashi
Shō Hashi (1372–1439) was a king of Chūzan, one of Sanzan period, three tributary states to China on the western Pacific island of Okinawa Island, Okinawa. He is traditionally described as the unifier of Okinawa and the founder of the Ryuky ...
( zh, c=尚巴志, p=Shàng Bāzhì, links=no).
Shō Hashi adopted the Chinese hierarchical court system, built Shuri Castle
is a Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyuan ''gusuku'' castle in Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Between 1429 and 1879, it was the palace of the Ryukyu Kingdom, before becoming largely neglected. In 1945, during the Battle of Okinawa, it was ...
and the town as his capital, and constructed Naha harbor. When in 1469 King Shō Toku, who was a grandson of Shō Hashi, died without a male heir, a palatine servant declared he was Toku's adopted son and gained Chinese investiture. This pretender, Shō En, began the Second Shō dynasty. Ryukyu's golden age occurred during the reign of Shō Shin
was a king of the Ryukyu Kingdom, the third ruler of the second Shō dynasty. Shō Shin's long reign has been described as "the Great Days of Chūzan", a period of great peace and relative prosperity. He was the son of Shō En, the founder of ...
, the second king of that dynasty, who reigned from 1478 to 1526.
The kingdom extended its authority over the southernmost islands in the Ryukyu archipelago by the end of the 15th century, and by 1571 the Amami Ōshima
, also known as Amami, is the largest island in the Amami Islands, Amami archipelago between Kyūshū and Okinawa Prefecture, Okinawa. It is one of the Satsunan Islands, all of which belong to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan.
The island, 712.35 ...
Islands, to the north near Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa and the other Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regio ...
, were incorporated into the kingdom as well. While the kingdom's political system was adopted and the authority of Shuri recognized, in the Amami Ōshima Islands, the kingdom's authority over the Sakishima Islands
The (or 先島群島, ''Sakishima-guntō'') (Okinawan language, Okinawan: ''Sachishima'', Miyakoan language, Miyako: ''Saksїzїma'', Yaeyama language, Yaeyama: ''Sakїzїma'', Yonaguni language, Yonaguni: ''Satichima'') are an archipelago loca ...
to the south remained for centuries at the level of a tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
-suzerain
A suzerain (, from Old French "above" + "supreme, chief") is a person, state (polity)">state or polity who has supremacy and dominant influence over the foreign policy and economic relations of another subordinate party or polity, but allows i ...
relationship.
Golden age of maritime trade
For nearly two hundred years the Ryukyu Kingdom would thrive as a key player in maritime trade withSoutheast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, Radius, radially arrayed compass directions (or Azimuth#In navigation, azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A ''compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, ...
and East Asia. Central to the kingdom's maritime activities was the continuation of the tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
relationship with Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
China, begun by Chūzan in 1372, and enjoyed by the three Okinawan kingdoms which followed it. China provided ships for Ryukyu's maritime trade activities, allowed a limited number of Ryukyuans to study at the Imperial Academy in Beijing, and formally recognized the authority of the King of Chūzan, allowing the kingdom to trade formally at Ming ports. Ryukyuan ships, often provided by China, traded at ports throughout the region, which included, among others, China, Đại Việt
Đại Việt (, ; literally Great Việt), was a Vietnamese monarchy in eastern Mainland Southeast Asia from the 10th century AD to the early 19th century, centered around the region of present-day Hanoi. Its early name, Đại Cồ Việt,(ch ...
(Vietnam), Japan, Java
Java is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea (a part of Pacific Ocean) to the north. With a population of 156.9 million people (including Madura) in mid 2024, proje ...
, Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political ce ...
, Malacca
Malacca (), officially the Historic State of Malacca (), is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state in Malaysia located in the Peninsular Malaysia#Other features, southern region of the Malay Peninsula, facing the Strait of Malacca ...
, Pattani, Palembang
Palembang (, Palembang: ''Pelémbang'', Mandarin: 巨港 (Jùgǎng), Hokkien: 舊港 (Kū-káng), Jawi: ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of South Sumatra. The city proper covers on both banks of the Musi River in the ea ...
, Siam, and Sumatra
Sumatra () is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the list of islands by area, sixth-largest island in the world at 482,286.55 km2 (182,812 mi. ...
.
 Japanese products—silver, swords, fans,
Japanese products—silver, swords, fans, lacquer
Lacquer is a type of hard and usually shiny coating or finish applied to materials such as wood or metal. It is most often made from resin extracted from trees and waxes and has been in use since antiquity.
Asian lacquerware, which may be c ...
ware, folding screens—and Chinese products—medicinal herbs, minted coins, glazed ceramics, brocades, textiles—were traded within the kingdom for Southeast Asian sappanwood, rhino
A rhinoceros ( ; ; ; : rhinoceros or rhinoceroses), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant taxon, extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates (perissodactyls) in the family (biology), famil ...
horn, tin, sugar, iron, ambergris, Indian ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
, and Arabian frankincense
Frankincense, also known as olibanum (), is an Aroma compound, aromatic resin used in incense and perfumes, obtained from trees of the genus ''Boswellia'' in the family (biology), family Burseraceae. The word is from Old French ('high-quality in ...
. Altogether, 150 voyages between the kingdom and Southeast Asia on Ryukyuan ships were recorded in the '' Rekidai Hōan'', an official record of diplomatic documents compiled by the kingdom, as having taken place between 1424 and the 1630s, with 61 of them bound for Siam, 10 for Malacca, 10 for Pattani, and 8 for Java, among others.
The Chinese policy of ''haijin
The Haijin () or sea ban were a series of related policies in China restricting private maritime trading during much of the Ming dynasty and early Qing dynasty. The sea ban was an anomaly in Chinese history as such restrictions were unknown durin ...
'' (, "sea bans"), limiting trade with China to tributary states and those with formal authorization, along with the accompanying preferential treatment of the Ming Court towards Ryukyu, allowed the kingdom to flourish and prosper for roughly 150 years. In the late 16th century, however, the kingdom's commercial prosperity fell into decline. The rise of the ''wokou
''Wokou'' ( zh, c=, p=Wōkòu; ; Hepburn romanization, Hepburn: ; ; literal Chinese translation: "dwarf bandits"), which translates to "Japanese pirates", were pirates who raided the coastlines of China and Korea from the 13th century to the 17 ...
'' threat among other factors led to the gradual loss of Chinese preferential treatment; the kingdom also suffered from increased maritime competition from Portuguese traders.
Japanese invasion and subordination
Around 1590,Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period, Sengoku and Azuchi-Momoyama periods and regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: ...
asked the Ryukyu Kingdom to aid in his campaign to conquer Korea. If successful, Hideyoshi intended to then move against China. As the Ryukyu Kingdom was a tributary state of the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
, the request was refused. The Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868.
The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars ...
that emerged following Hideyoshi's fall authorized the Shimazu family— feudal lords of the Satsuma domain (present-day Kagoshima Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,527,019 (1 February 2025) and has a geographic area of 9,187 Square kilometre, km2 (3,547 Square m ...
)—to send an expeditionary force to conquer the Ryukyus. The subsequent invasion
An invasion is a Offensive (military), military offensive of combatants of one geopolitics, geopolitical Legal entity, entity, usually in large numbers, entering territory (country subdivision), territory controlled by another similar entity, ...
took place in 1609, but Satsuma still allowed the Ryukyu Kingdom to find itself in a period of "dual subordination" to Japan and China, wherein Ryukyuan tributary relations were maintained with both the Tokugawa shogunate and the Chinese court.
Occupation occurred fairly quickly, with some fierce fighting, and King Shō Nei
was king of the Ryukyu Kingdom from 1589 to 1620. He reigned during the 1609 invasion of Ryukyu and was the first king of Ryukyu to be a vassal to the Shimazu clan of Satsuma, a Japanese feudal domain.
Shō Nei was the great-grandson of Sh� ...
was taken prisoner to Kagoshima and later to Edo (modern-day Tokyo). To avoid giving the Qing any reason for military action against Japan, the king was released two years later and the Ryukyu Kingdom regained a degree of autonomy. However, the Satsuma domain seized control over some territory of the Ryukyu Kingdom, notably the Amami-Ōshima island group, which was incorporated into the Satsuma domain and remains a part of Kagoshima Prefecture, not Okinawa Prefecture.
The kingdom was described by Hayashi Shihei in '' Sangoku Tsūran Zusetsu'', which was published in 1785.
Tributary relations

 In 1655, tribute relations between Ryukyu and
In 1655, tribute relations between Ryukyu and Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
(the China's dynasty that followed Ming after 1644) were formally approved by the shogunate. This was seen to be justified, in part, because of the desire to avoid giving Qing any reason for military action against Japan.
Since Ming China prohibited trade with Japan, the Satsuma domain, with the blessing of the Tokugawa shogunate, used the trade relations of the kingdom to continue to maintain trade relations with China. Considering that Japan had previously severed ties with most European countries except the Dutch, such trade relations proved especially crucial to both the Tokugawa shogunate and Satsuma domain, which would use its power and influence, gained in this way, to help overthrow the shogunate in the 1860s.
The Ryukyuan king was a vassal of the Satsuma ''daimyō'', after Shimazu's Ryukyu invasion in 1609, the Satsuma Clan established a governmental office's branch known as ''Zaibankaiya'' (在番仮屋) or ''Ufukaiya'' (大仮屋) at Shuri in 1628, and became the base of Ryukyu domination for 250 years, until 1872. The Satsuma Domain's residents can be roughly compared to a European resident in a protectorate. However, the kingdom was not considered as part of any '' han'' (fief): up until the formal annexation of the islands and abolition of the kingdom in 1879, the Ryukyus were not truly considered ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' (; ; ) describes practices that are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. The phrase is often used in contrast with '' de facto'' ('from fa ...
'' part of Edo Japan. Though technically under the control of Satsuma, Ryukyu was given a great degree of autonomy, to best serve the interests of the Satsuma ''daimyō'' and those of the shogunate, in trading with China. Ryukyu was a tributary state of China, and since Japan had no formal diplomatic relations with China, it was essential that China not realize that Ryukyu was controlled by Japan. Thus, Satsuma—and the shogunate—was obliged to be mostly hands-off in terms of not visibly or forcibly occupying Ryukyu or controlling the policies and laws there. The situation benefited all three parties involved—the Ryukyu royal government, the Satsuma ''daimyō'', and the shogunate—to make Ryukyu seem as much a distinctive and foreign country as possible. Japanese were prohibited from visiting Ryukyu without shogunal permission, and the Ryukyuans were forbidden from adopting Japanese names, clothes, or customs. They were even forbidden from divulging their knowledge of the Japanese language during their trips to Edo; the Shimazu family, ''daimyōs'' of Satsuma, gained great prestige by putting on a show of parading the King, officials, and other people of Ryukyu to and through Edo. As the only ''han'' to have a king and an entire kingdom as vassals, Satsuma gained significantly from Ryukyu's exoticness, reinforcing that it was an entirely separate kingdom.
According to statements by Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
imperial official Li Hongzhang in a meeting with Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was the 18th president of the United States, serving from 1869 to 1877. In 1865, as Commanding General of the United States Army, commanding general, Grant led the Uni ...
, China had a special relationship with the island and the Ryukyu had paid tribute to China for hundreds of years, and the Chinese reserved certain trade rights for them in an amicable and beneficial relationship. Japan ordered tributary relations to end in 1875 after the tribute mission of 1874 was perceived as a show of submission to China.
Annexation by the Japanese Empire
In 1872,Emperor Meiji
, posthumously honored as , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the List of emperors of Japan, traditional order of succession, reigning from 1867 until his death in 1912. His reign is associated with the Meiji Restoration of 1868, which ...
unilaterally declared that the kingdom was then Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, and simultaneously a tributary state of the Qing Empire, until 1875, before being fully incorporated into Japan as the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islan ...
.Lin, Man-houng"The Ryukyus and Taiwan in the East Asian Seas: A Longue Durée Perspective"
''Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus''. 27 October 2006, translated and abridged from ''Academia Sinica Weekly'', No. 1084. 24 August 2006. At the same time, the appearance of independence was maintained for diplomatic reasons with Qing China until the
Meiji government
The was the government that was formed by politicians of the Satsuma Domain and Chōshū Domain in the 1860s. The Meiji government was the early government of the Empire of Japan.
Politicians of the Meiji government were known as the Meiji ...
abolished the Ryukyu Kingdom when the islands were incorporated as Okinawa Prefecture
is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan. It consists of three main island groups—the Okinawa Islands, the Sakishima Islands, and the Daitō Islands—spread across a maritime zone approximately 1,000 kilometers east to west an ...
on 27 March 1879. The Amami-Ōshima island group which had been integrated into Satsuma Domain became a part of Kagoshima Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu and the Ryukyu Islands. Kagoshima Prefecture has a population of 1,527,019 (1 February 2025) and has a geographic area of 9,187 Square kilometre, km2 (3,547 Square m ...
.
The last king of Ryukyu was forced to relocate to Tokyo, and was given a compensating ''kazoku
The was the hereditary peerage of the Empire of Japan, which existed between 1869 and 1947. It was formed by merging the feudal lords (''Daimyo, daimyō'') and court nobles (''kuge'') into one system modelled after the British peerage. Distin ...
'' rank as Marquis Shō Tai.. Many royalist supporters fled to China. The king's death in 1901 diminished the historic connections with the former kingdom. With the abolition of the aristocracy after World War II, the Sho family continues to live in Tokyo.
Major events
* 1187 – Shunten becomes King of Okinawa, based atUrasoe Castle
is a Ryukyuan ''gusuku'' which served as the capital of the medieval Okinawan principality of Chūzan prior to the unification of the island into the Ryukyu Kingdom, and the moving of the capital to Shuri Castle, Shuri. In the 14th century, Ura ...
.
* 1272 – Envoys from the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
are expelled from Okinawa by King Eiso.
* 1276 – Mongols are violently driven off the island again.
* 1372 – The first Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of ...
envoy visits Okinawa, which had been divided into three kingdoms during the Sanzan period. Formal tributary relations with the Chinese Empire begin.
* 1389 – An envoy from Ryukyu visits the Goryeo
Goryeo (; ) was a Korean state founded in 918, during a time of national division called the Later Three Kingdoms period, that unified and ruled the Korea, Korean Peninsula until the establishment of Joseon in 1392. Goryeo achieved what has b ...
Kingdom, resulting in diplomatic ties between the two kingdoms.
* 1392 – An envoy from Ryukyu visits the Joseon
Joseon ( ; ; also romanized as ''Chosun''), officially Great Joseon (), was a dynastic kingdom of Korea that existed for 505 years. It was founded by Taejo of Joseon in July 1392 and replaced by the Korean Empire in October 1897. The kingdom w ...
Kingdom.
* 1416 – Chūzan, led by Shō Hashi
Shō Hashi (1372–1439) was a king of Chūzan, one of Sanzan period, three tributary states to China on the western Pacific island of Okinawa Island, Okinawa. He is traditionally described as the unifier of Okinawa and the founder of the Ryuky ...
, occupies Nakijin Castle, capital of Hokuzan. Hamashita, Takeshi. ''Okinawa Nyūmon'' (沖縄入門, "Introduction to Okinawa"). Tokyo: Chikuma Shobō, 2000, pp. 207–13.
* 1429 – Chūzan occupies Nanzan Castle, capital of Nanzan, unifying Okinawa Island
, officially , is the largest of the Okinawa Islands and the Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands of Japan in the Kyushu region. It is the smallest and least populated of the five Japanese archipelago, main islands of Japan. The island is ...
. Shō Hashi moves the capital to Shuri Castle
is a Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyuan ''gusuku'' castle in Shuri, Okinawa, Shuri, Okinawa Prefecture, Japan. Between 1429 and 1879, it was the palace of the Ryukyu Kingdom, before becoming largely neglected. In 1945, during the Battle of Okinawa, it was ...
(now part of modern-day Naha
is the Cities of Japan, capital city of Okinawa Prefecture, the southernmost prefecture of Japan. As of 1 June 2019, the city has an estimated population of 317,405 and a population density of 7,939 people per km2 (20,562 persons per sq. mi.). ...
).
* 1458 – Amawari's rebellion against the Kingdom.
* 1466 – Kikai Island invaded by Ryukyu.
* 1470 – Shō En (Kanemaru) establishes the Second Shō dynasty.
* 1477 – Shō Shin
was a king of the Ryukyu Kingdom, the third ruler of the second Shō dynasty. Shō Shin's long reign has been described as "the Great Days of Chūzan", a period of great peace and relative prosperity. He was the son of Shō En, the founder of ...
, whose rule is called the "Great Days of Chūzan", ascends to the throne. Golden age of the kingdom.
* 1500 – Sakishima Islands
The (or 先島群島, ''Sakishima-guntō'') (Okinawan language, Okinawan: ''Sachishima'', Miyakoan language, Miyako: ''Saksїzїma'', Yaeyama language, Yaeyama: ''Sakїzїma'', Yonaguni language, Yonaguni: ''Satichima'') are an archipelago loca ...
annexed by Ryukyu.
* 1609 – (5 April) ''Daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and no ...
'' (Lord) of Satsuma in southern Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa and the other Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Islands). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regio ...
invades the kingdom. King Shō Nei
was king of the Ryukyu Kingdom from 1589 to 1620. He reigned during the 1609 invasion of Ryukyu and was the first king of Ryukyu to be a vassal to the Shimazu clan of Satsuma, a Japanese feudal domain.
Shō Nei was the great-grandson of Sh� ...
is captured.
* 1611 – In accordance with the peace treaty, Satsuma annexes the Amami and Tokara Islands
The is an archipelago in the Nansei Islands, and are part of the Satsunan Islands, which is in turn part of the Ryukyu Archipelago. The chain consists of twelve small islands located between Yakushima and Amami-Oshima. The islands have a total ...
(Satsunan Islands
The is a geopolitical name for a group of islands that forms the northern part of the Ryukyu Islands. The whole island group belongs to Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan.
Major islands
* Satsunan Islands
** Ōsumi Islands with:
*** Tanegashima, Yak ...
); Kings of Ryukyu become vassals to the daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji era, Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and no ...
of the Satsuma Domain.
* 1623 – Completion of '' Omoro Sōshi''.
* 1650 – Completion of '' Chūzan Seikan''.
* 1724 – Completion of '' Chūzan Seifu''.
* 1745 – Completion of '' Kyūyō''.
* 1846 – Dr. Bernard Jean Bettelheim (d. 1870), a Hungarian Protestant missionary serving with the Loochoo Naval Mission
The Loochoo Naval Mission (1843–1861) was a Church of England mission society dedicated in the Christian outreach to outlying Ryukyu Islands. At the time, the islands were a sovereign nation but are now part of Japan.
The work of the mission was ...
, arrives in Ryukyu Kingdom. He establishes the first foreign hospital on the island at the Naminoue Gokoku-ji Temple.
* 1852 – Commodore Matthew C. Perry
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858) was a United States Navy officer who commanded ships in several wars, including the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War. He led the Perry Expedition that Bakumatsu, ended Japan' ...
of the US Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
visits the kingdom and establishes a coaling station in Naha.
* 1854 – Perry returns to Okinawa to sign the Loochoo Compact with the Ryukyuan government. Bettelheim leaves with Perry.
* 1866 – The last official mission from the Qing Empire
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
visits the kingdom.
* 1872 – Emperor Meiji
, posthumously honored as , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the List of emperors of Japan, traditional order of succession, reigning from 1867 until his death in 1912. His reign is associated with the Meiji Restoration of 1868, which ...
unilaterally declares King Shō Tai
was the final King of Ryukyu, initially as Second Shō dynasty, hereditary king of the Tributary system of China#Ryukyu Kingdom, Qing tributary Ryukyu Kingdom from 8 June 1848 until 10 October 1872 and finally as the Empire of Japan, Japanese a ...
as the "Domain Head of Ryukyu Domain
The was a short-lived domain of the Empire of Japan, lasting from 1872 to 1879, and simultaneously a tributary state of the Qing Empire, until 1875, before being fully incorporated into Japan as the current Okinawa Prefecture and other islan ...
".
* 1874 – The last tributary envoy to China is dispatched from Naha. / Kaiser Wilhelm I erects a " friendship monument" on Miyako Island. / Japan invades Taiwan on behalf of Ryukyu.
* 1879 – Japan abolishes Ryukyu Domain and declares the creation of Okinawa Prefecture
is the southernmost and westernmost prefecture of Japan. It consists of three main island groups—the Okinawa Islands, the Sakishima Islands, and the Daitō Islands—spread across a maritime zone approximately 1,000 kilometers east to west an ...
, formally annexing the islands. Shō Tai is forced to abdicate, but is granted the rank of within the Meiji peerage system.
Monarchy
Royal crest
Thefamily crest
A crest is a component of a heraldry, heraldic display, consisting of the device borne on top of the Helmet (heraldry), helm. Originating in the decorative sculptures worn by knights in tournament (medieval), tournaments and, to a lesser exten ...
of the Ryukyuan kings is called Mitsu-domoe and it is commonly used in Japan.
In Shinto
, also called Shintoism, is a religion originating in Japan. Classified as an East Asian religions, East Asian religion by Religious studies, scholars of religion, it is often regarded by its practitioners as Japan's indigenous religion and as ...
ism, Mitsu-domoe represents Emperor Ojin (Divine name Yahata). King Shō Toku worshshipped Yahata and adapted the crest. He has also built the Asato Hachiman Shrine.
It is also said to be a balance of three forces, symbolizing the balance of Kitayama, Nakayama, and Nanzan.
List of Ryukyuan kings
See also
 * Foreign relations of the Ryukyu Kingdom
* Foreign relations of Imperial China
*
* Foreign relations of the Ryukyu Kingdom
* Foreign relations of Imperial China
* Gusuku
often refers to castles or fortresses in the Ryukyu Islands that feature stone walls. However, the origin and essence of ''gusuku'' remain controversial. In the archaeology of Okinawa Prefecture, the ''Gusuku period'' refers to an archaeological ...
* History of the Ryukyu Islands
* History of Sakishima Islands
* Hua–Yi distinction
* Mudan Incident of 1871
* Military of the Ryukyu Kingdom
* Ryukyu independence movement
* Ryukyu Islands
The , also known as the or the , are a chain of Japanese islands that stretch southwest from Kyushu to Geography of Taiwan, Taiwan: the Ryukyu Islands are divided into the Satsunan Islands (Ōsumi Islands, Ōsumi, Tokara Islands, Tokara and A ...
* Ryukyuan missions to Edo
* Ryukyuan missions to Imperial China
* Ryukyuan missions to Joseon
** Joseon missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom
** Imperial Chinese missions to the Ryukyu Kingdom
* Tamaudun (intact royal tombs)
* Okinawan martial arts
* Names of Ryukyu
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
* * . * . * . * , 283 pp. * . * . * . * , 213 pp.External links
* * . *Comprehensive Database of Archaeological Site Reports in Japan
Nara National Research Institute for Cultural Properties {{DEFAULTSORT:Ryukyu Kingdom Kingdom Former countries in East Asia Former countries in Japanese history Former kingdoms Island countries 1429 establishments in Asia 1879 disestablishments in Asia States and territories established in 1429 States and territories disestablished in 1879 Former monarchies of East Asia History of Okinawa Prefecture