Robert Burns Woodward on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Robert Burns Woodward (April 10, 1917 – July 8, 1979) was an American
Nobelprize.org Woodward's doctoral work involved investigations related to the synthesis of the female sex hormone
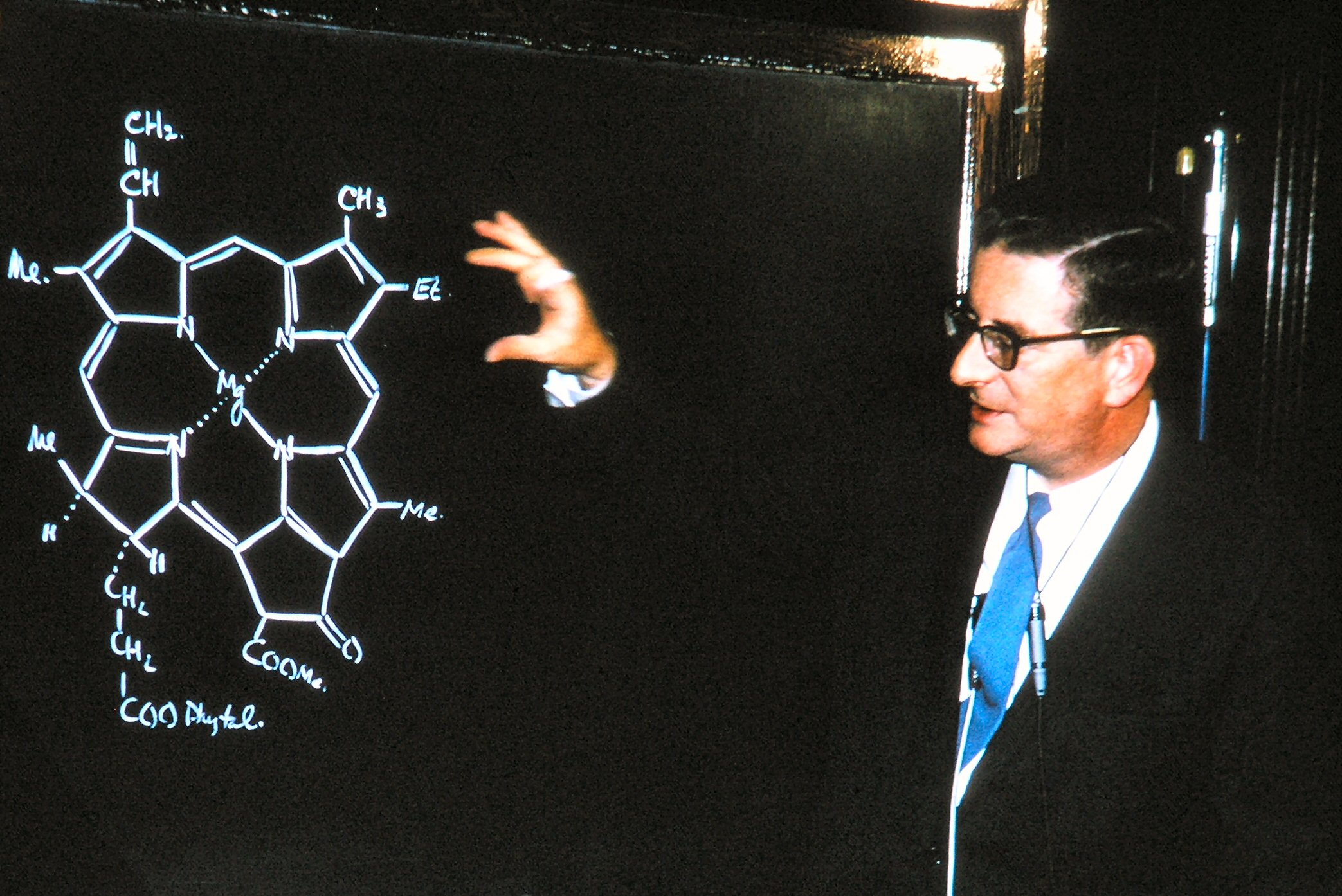 Culminating in the 1930s, the British chemists Christopher Ingold and Robert Robinson among others had investigated the mechanisms of organic reactions, and had come up with empirical rules which could predict reactivity of organic molecules. Woodward was perhaps the first synthetic organic chemist who used these ideas as a predictive framework in synthesis. Woodward's style was the inspiration for the work of hundreds of successive synthetic chemists who synthesized medicinally important and structurally complex natural products.
Culminating in the 1930s, the British chemists Christopher Ingold and Robert Robinson among others had investigated the mechanisms of organic reactions, and had come up with empirical rules which could predict reactivity of organic molecules. Woodward was perhaps the first synthetic organic chemist who used these ideas as a predictive framework in synthesis. Woodward's style was the inspiration for the work of hundreds of successive synthetic chemists who synthesized medicinally important and structurally complex natural products.
Robert M. Williams
(Colorado State), Harry Wasserman (Yale), Yoshito Kishi (Harvard), Stuart Schreiber (Harvard), William R. Roush ( Scripps-Florida), Steven A. Benner (UF), James D. Wuest (Montreal), Christopher S. Foote (UCLA), Kendall Houk (UCLA), porphyrin chemist Kevin M. Smith (LSU), Thomas R. Hoye (University of Minnesota), Ronald Breslow (Columbia University) and David Dolphin (UBC). Woodward had an encyclopedic knowledge of chemistry, and an extraordinary memory for detail. Probably the quality that most set him apart from his peers was his remarkable ability to tie together disparate threads of knowledge from the chemical literature and bring them to bear on a chemical problem.
link
His longest known lecture defined the unit of time known as the "Woodward", after which his other lectures were deemed to be so many "milli-Woodwards" long. In many of these, he eschewed the use of slides and drew structures by using multicolored chalk. Typically, to begin a lecture, Woodward would arrive and lay out two large white handkerchiefs on the countertop. Upon one would be four or five colors of chalk (new pieces), neatly sorted by color, in a long row. Upon the other handkerchief would be placed an equally impressive row of cigarettes. The previous cigarette would be used to light the next one. His Thursday seminars at Harvard often lasted well into the night. He had a fixation with blue, and many of his suits, his car, and even his parking space were coloured in blue. In one of his laboratories, his students hung a large black and white photograph of the master from the ceiling, complete with a large blue "tie" appended. There it hung for some years (early 1970s), until scorched in a minor laboratory fire. He detested exercise, could get along with only a few hours of sleep every night, was a heavy smoker, and enjoyed Scotch whisky and martinis.Robert Burns Woodward
.
Video podcast of Robert Burns Woodward talking about cephalosporinRobert Burns Woodward: Three Score Years and Then?
David Dolphin, '' Aldrichimica Acta'', 1977, ''10''(1), 3–9.
Robert Burns Woodward Patents
Notes from Robert Burns Woodward's Seminars
taken by Robert E. Kohler i
Science History Institute Digital Collections
* including the Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1965 ''Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Natural Products'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Woodward, Robert Burns 1917 births 1979 deaths 20th-century American chemists 20th-century American educators American Nobel laureates American science writers Foreign members of the Royal Society Harvard University faculty Massachusetts Institute of Technology alumni Wesleyan University people Nobel laureates in Chemistry National Medal of Science laureates American organic chemists Stereochemists People from Belmont, Massachusetts Recipients of the Copley Medal 20th-century American writers Time Person of the Year Members of the American Philosophical Society Quincy High School (Massachusetts) alumni
organic chemist
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
. He is considered by many to be the preeminent synthetic organic chemist of the twentieth century, having made many key contributions to the subject, especially in the synthesis of complex natural products and the determination of their molecular structure
Molecular geometry is the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that constitute a molecule. It includes the general shape of the molecule as well as bond lengths, bond angles, torsional angles and any other geometrical parameters that det ...
. He worked closely with Roald Hoffmann
Roald Hoffmann (born Roald Safran; July 18, 1937) is a Polish-American theoretical chemist who won the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He has also published plays and poetry. He is the Frank H. T. Rhodes Professor of Humane Letters Emeritus at C ...
on theoretical studies of chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, ...
s. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
in 1965.
Early life and education
Woodward was born inBoston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, on April 10, 1917. He was the son of Margaret Burns (an immigrant from Scotland who claimed to be a descendant of the poet, Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 1759 – 21 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the List of national poets, national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the be ...
) and her husband, Arthur Chester Woodward, himself the son of Roxbury apothecary, Harlow Elliot Woodward.
His father was one of the many victims of the 1918 influenza pandemic
The 1918–1920 flu pandemic, also known as the Great Influenza epidemic or by the common misnomer Spanish flu, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the Influenza A virus subtype H1N1, H1N1 subtype of the influenz ...
.
From a very early age, Woodward was attracted to and engaged in private study of chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
while he attended a public primary school, and then Quincy High School, in Quincy, Massachusetts
Quincy ( ) is a city in Norfolk County, Massachusetts, Norfolk County, Massachusetts, United States. It is the largest city in the county. Quincy is part of the Greater Boston area as one of Boston's immediate southern suburbs. Its population in ...
. By the time he entered high school, he had already managed to perform most of the experiments in Ludwig Gattermann's then widely used textbook of experimental organic chemistry. In 1928, Woodward contacted the Consul-General of the German consulate in Boston (Baron von Tippelskirch ), and through him, managed to obtain copies of a few original papers published in German journals. Later, in his Cope lecture, he recalled how he had been fascinated when, among these papers, he chanced upon Diels and Alder's original communication about the Diels–Alder reaction
In organic chemistry, the Diels–Alder reaction is a chemical reaction between a Conjugated system, conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the Diels–Alder reaction#The dienophile, dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexe ...
. Throughout his career, Woodward was to repeatedly and powerfully use and investigate this reaction, both in theoretical and experimental ways. In 1933, he entered the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a Private university, private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of moder ...
(MIT), but neglected his formal studies badly enough to be excluded at the end of the 1934 fall term. MIT readmitted him in the 1935 fall term, and by 1936 he had received the Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, B.S., B.Sc., SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree that is awarded for programs that generally last three to five years.
The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Scienc ...
degree. Only one year later, MIT awarded him the doctorate
A doctorate (from Latin ''doctor'', meaning "teacher") or doctoral degree is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities and some other educational institutions, derived from the ancient formalism '' licentia docendi'' ("licence to teach ...
, when his classmates were still graduating with their bachelor's degrees.The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1965 – Robert B. Woodward BiographyNobelprize.org Woodward's doctoral work involved investigations related to the synthesis of the female sex hormone
estrone
Estrone (E1), also spelled oestrone, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estriol. Estrone, as well as the other estrogens, are synthesized ...
. MIT required that graduate students have research advisors. Woodward's advisors were James Flack Norris and Avery Adrian Morton, although it is not clear whether he actually took any of their advice. After a short postdoctoral stint at the University of Illinois, he took a Junior Fellowship at Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
from 1937 to 1938, and remained at Harvard in various capacities for the rest of his life. In the 1960s, Woodward was named Donner Professor of Science, a title that freed him from teaching formal courses so that he could devote his entire time to research.
Research and career
Early work
The first major contribution of Woodward's career in the early 1940s was a series of papers describing the application ofultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
in the elucidation of the structure of natural products. Woodward collected together a large amount of empirical data, and then devised a series of rules later called the Woodward's rules, which could be applied to finding out the structures of new natural substances, as well as non-natural synthesized molecules. The expedient use of newly developed instrumental techniques was a characteristic Woodward exemplified throughout his career, and it marked a radical change from the extremely tedious and long chemical methods of structural elucidation that had been used until then.
In 1944, with his post doctoral researcher, William von Eggers Doering, Woodward reported the synthesis of the alkaloid
Alkaloids are a broad class of natural product, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids.
Alkaloids are produced by a large varie ...
quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
, used to treat malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
. Although the synthesis was publicized as a breakthrough in procuring the hard to get medicinal compound from Japanese occupied southeast Asia, in reality it was too long and tedious to adopt on a practical scale. Nevertheless, it was a landmark for chemical synthesis. Woodward's particular insight in this synthesis was to realize that the German chemist Paul Rabe had converted a precursor of quinine called quinotoxine to quinine in 1905. Hence, a synthesis of quinotoxine (which Woodward actually synthesized) would establish a route to synthesizing quinine. When Woodward accomplished this feat, organic synthesis was still largely a matter of trial and error, and nobody thought that such complex structures could actually be constructed. Woodward showed that organic synthesis could be made into a rational science, and that synthesis could be aided by well-established principles of reactivity and structure. This synthesis was the first one in a series of exceedingly complicated and elegant syntheses that he would undertake.
Later work and its impact
 Culminating in the 1930s, the British chemists Christopher Ingold and Robert Robinson among others had investigated the mechanisms of organic reactions, and had come up with empirical rules which could predict reactivity of organic molecules. Woodward was perhaps the first synthetic organic chemist who used these ideas as a predictive framework in synthesis. Woodward's style was the inspiration for the work of hundreds of successive synthetic chemists who synthesized medicinally important and structurally complex natural products.
Culminating in the 1930s, the British chemists Christopher Ingold and Robert Robinson among others had investigated the mechanisms of organic reactions, and had come up with empirical rules which could predict reactivity of organic molecules. Woodward was perhaps the first synthetic organic chemist who used these ideas as a predictive framework in synthesis. Woodward's style was the inspiration for the work of hundreds of successive synthetic chemists who synthesized medicinally important and structurally complex natural products.
Organic syntheses and Nobel Prize
During the late 1940s, Woodward synthesized many complex natural products includingquinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
, cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
, cortisone
Cortisone is a pregnene (21-carbon) steroid hormone. It is a naturally-occurring corticosteroid metabolite that is also used as a pharmaceutical prodrug. Cortisol is converted by the action of the enzyme corticosteroid 11-beta-dehydrogenase ...
, strychnine
Strychnine (, , American English, US chiefly ) is a highly toxicity, toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, ...
, lysergic acid, reserpine
Reserpine is a drug that is used for the treatment of hypertension, high blood pressure, usually in combination with a thiazide diuretic or vasodilator. Large clinical trials have shown that combined treatment with reserpine plus a thiazide diur ...
, chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words (, "pale green") and (, "leaf"). Chlorophyll allows plants to absorb energy ...
, cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus '' Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''.
Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibio ...
, and colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to prevent and treat gout, to treat familial Mediterranean fever and Behçet's disease, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction. The American College of Rheumatology recommends colchicine, nonstero ...
. With these, Woodward opened up a new era of synthesis, sometimes called the 'Woodwardian era' in which he showed that natural products could be synthesized by careful applications of the principles of physical organic chemistry
Physical organic chemistry, a term coined by Louis Hammett in 1940, refers to a discipline of organic chemistry that focuses on the relationship between chemical structures and chemical reaction, reactivity, in particular, applying experimental to ...
, and by meticulous planning.
Many of Woodward's syntheses were described as spectacular by his colleagues and before he did them, it was thought by some that it would be impossible to create these substances in the lab. Woodward's syntheses were also described as having an element of art in them, and since then, synthetic chemists have always looked for elegance as well as utility in synthesis. His work also involved the exhaustive use of the then newly developed techniques of infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functio ...
and later, nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near field) and respond by producing an electromagnetic signal with a ...
spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
. Another important feature of Woodward's syntheses was their attention to stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, studies the spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which are defined ...
or the particular configuration of molecules in three-dimensional space. Most natural products of medicinal importance are effective, for example as drugs, only when they possess a specific stereochemistry. This creates the demand for ' stereoselective synthesis', producing a compound with a defined stereochemistry. While today a typical synthetic route routinely involves such a procedure, Woodward was a pioneer in showing how, with exhaustive and rational planning, one could conduct reactions that were stereoselective. Many of his syntheses involved forcing a molecule into a certain configuration by installing rigid structural elements in it, another tactic that has become standard today. In this regard, especially his syntheses of reserpine and strychnine were landmarks.
During World War II, Woodward was an advisor to the War Production Board
The War Production Board (WPB) was an agency of the United States government that supervised war production during World War II. President Franklin D. Roosevelt established it in January 1942, with Executive Order 9024. The WPB replaced the Su ...
on the penicillin project. Although often given credit for proposing the beta-lactam structure of penicillin
Penicillins (P, PCN or PEN) are a group of beta-lactam antibiotic, β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from ''Penicillium'' Mold (fungus), moulds, principally ''Penicillium chrysogenum, P. chrysogenum'' and ''Penicillium rubens, P. ru ...
, it was actually first proposed by chemists at Merck and Edward Abraham
Sir Edward Penley Abraham, (10 June 1913 – 8 May 1999) was an English biochemist instrumental in the development of the first antibiotics penicillin and cephalosporin.
Early life and education
Abraham was born on 10 June 1913 at 47 South V ...
at Oxford and then investigated by other groups, as well (e.g., Shell). Woodward at first endorsed an incorrect tricyclic ( thiazolidine fused, amino bridged oxazinone) structure put forth by the penicillin group at Peoria. Subsequently, he put his imprimatur
An imprimatur (sometimes abbreviated as ''impr.'', from Latin, "let it be printed") is a declaration authorizing publication of a book. The term is also applied loosely to any mark of approval or endorsement. The imprimatur rule in the Catho ...
on the beta-lactam structure, all of this in opposition to the thiazolidine– oxazolone structure proposed by Robert Robinson, the then leading organic chemist of his generation. Ultimately, the beta-lactam structure was shown to be correct by Dorothy Hodgkin
Dorothy Mary Crowfoot Hodgkin (née Crowfoot; 12 May 1910 – 29 July 1994) was a Nobel Prize-winning English chemist who advanced the technique of X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of biomolecules, which became essential for ...
using X-ray crystallography
X-ray crystallography is the experimental science of determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to Diffraction, diffract in specific directions. By measuring th ...
in 1945.
Woodward also applied the technique of infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functio ...
and chemical degradation to determine the structures of complicated molecules. Notable among these structure determinations were santonic acid, strychnine, magnamycin and terramycin. In each one of these cases, Woodward again showed how rational facts and chemical principles, combined with chemical intuition, could be used to achieve the task.
In the early 1950s, Woodward, along with the British chemist Geoffrey Wilkinson
Sir Geoffrey Wilkinson FRS (14 July 1921 – 26 September 1996) was a Nobel laureate English chemist who pioneered inorganic chemistry and homogeneous transition metal catalysis.
Education and early life
Wilkinson was born at Springside, Todm ...
, then at Harvard, postulated a novel structure for ferrocene
Ferrocene is an organometallic chemistry, organometallic compound with the formula . The molecule is a Cyclopentadienyl complex, complex consisting of two Cyclopentadienyl anion, cyclopentadienyl rings sandwiching a central iron atom. It is an o ...
, a compound consisting of a combination of an organic molecule with iron. This marked the beginning of the field of transition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
organometallic chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and so ...
which grew into an industrially very significant field. Wilkinson won the Nobel Prize for this work in 1973, along with Ernst Otto Fischer. Some historians think that Woodward should have shared this prize along with Wilkinson. Remarkably, Woodward himself thought so, and voiced his thoughts in a letter sent to the Nobel Committee.
Woodward won the Nobel Prize in 1965 for his synthesis of complex organic molecules. He had been nominated a total of 111 times from 1946 to 1965. In his Nobel lecture, he described the total synthesis of the antibiotic cephalosporin, and claimed that he had pushed the synthesis schedule so that it would be completed around the time of the Nobel ceremony.
B12 synthesis and Woodward–Hoffmann rules
In the early 1960s, Woodward began work on what was the most complex natural product synthesized to date— vitamin B12. In a remarkable collaboration with his colleague Albert Eschenmoser in Zurich, a team of almost one hundred students and postdoctoral workers worked for many years on the synthesis of this molecule. The work was finally published in 1973, and it marked a landmark in the history of organic chemistry. The synthesis included almost a hundred steps, and involved the characteristic rigorous planning and analyses that had always characterised Woodward's work. This work, more than any other, convinced organic chemists that the synthesis of any complex substance was possible, given enough time and planning (see also palytoxin, synthesized by the research group of Yoshito Kishi, one of Woodward's postdoctoral students). As of 2019, no other total synthesis of Vitamin B12 has been published. That same year, based on observations that Woodward had made during the B12 synthesis, he andRoald Hoffmann
Roald Hoffmann (born Roald Safran; July 18, 1937) is a Polish-American theoretical chemist who won the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He has also published plays and poetry. He is the Frank H. T. Rhodes Professor of Humane Letters Emeritus at C ...
devised rules (now called the Woodward–Hoffmann rules
The Woodward–Hoffmann rules (or the pericyclic selection rules) are a set of rules devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann to rationalize or predict certain aspects of the stereochemistry and activation energy of Pericyclic reaction, ...
) for elucidating the stereochemistry
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, studies the spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which are defined ...
of the products of organic reactions. Woodward formulated his ideas (which were based on the symmetry
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is Invariant (mathematics), invariant und ...
properties of molecular orbital
In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding ...
s) based on his experiences as a synthetic organic chemist; he asked Hoffman to perform theoretical calculations to verify these ideas, which were done using Hoffmann's Extended Hückel method. The predictions of these rules, called the "Woodward–Hoffmann rules
The Woodward–Hoffmann rules (or the pericyclic selection rules) are a set of rules devised by Robert Burns Woodward and Roald Hoffmann to rationalize or predict certain aspects of the stereochemistry and activation energy of Pericyclic reaction, ...
" were verified by many experiments. Hoffmann shared the 1981 Nobel Prize for this work along with Kenichi Fukui, a Japanese chemist who had done similar work using a different approach; Woodward had died in 1979 and Nobel Prizes are not awarded posthumously.
Woodward Institute
While at Harvard, Woodward took on the directorship of the Woodward Research Institute, based atBasel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
, Switzerland, in 1963. He also became a trustee of his alma mater, MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ...
, from 1966 to 1971, and of the Weizmann Institute of Science
The Weizmann Institute of Science ( ''Machon Weizmann LeMada'') is a Public university, public research university in Rehovot, Israel, established in 1934, fourteen years before the State of Israel was founded. Unlike other List of Israeli uni ...
in Israel.
Death
Woodward died inCambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is a suburb in the Greater Boston metropolitan area, located directly across the Charles River from Boston. The city's population as of the 2020 United States census, ...
, from a heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom ...
in his sleep. At the time, he was working on the synthesis of an antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
, erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used ...
. A student of his said about him:
:''I owe a lot to R. B. Woodward. He showed me that one could attack difficult problems without a clear idea of their outcome, but with confidence that intelligence and effort would solve them. He showed me the beauty of modern organic chemistry, and the relevance to the field of detailed careful reasoning. He showed me that one does not need to specialize. Woodward made great contributions to the strategy of synthesis, to the deduction of difficult structures, to the invention of new chemistry, and to theoretical aspects as well. He taught his students by example the satisfaction that comes from total immersion in our science. I treasure the memory of my association with this remarkable chemist.''
Publications
During his lifetime Woodward authored or coauthored almost 200 publications, of which 85 are full papers, the remainder comprising preliminary communications, the text of lectures, and reviews. The pace of his scientific activity soon outstripped his capacity to publish all experimental details, and much of the work in which he participated was not published until a few years after his death. Woodward trained more than two hundred Ph.D. students and postdoctoral workers, many of whom later went on to distinguished careers. Some of his best-known students includRobert M. Williams
(Colorado State), Harry Wasserman (Yale), Yoshito Kishi (Harvard), Stuart Schreiber (Harvard), William R. Roush ( Scripps-Florida), Steven A. Benner (UF), James D. Wuest (Montreal), Christopher S. Foote (UCLA), Kendall Houk (UCLA), porphyrin chemist Kevin M. Smith (LSU), Thomas R. Hoye (University of Minnesota), Ronald Breslow (Columbia University) and David Dolphin (UBC). Woodward had an encyclopedic knowledge of chemistry, and an extraordinary memory for detail. Probably the quality that most set him apart from his peers was his remarkable ability to tie together disparate threads of knowledge from the chemical literature and bring them to bear on a chemical problem.
Honors and awards
For his work, Woodward received many awards, honors and honorary doctorates, including election to theAmerican Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (The Academy) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, and other ...
in 1948, the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
in 1953, the American Philosophical Society
The American Philosophical Society (APS) is an American scholarly organization and learned society founded in 1743 in Philadelphia that promotes knowledge in the humanities and natural sciences through research, professional meetings, publicat ...
in 1962, and membership in academies around the world. He was also a consultant to many companies such as Polaroid, Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Pharmaceutical industry, pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered at The Spiral (New York City), The Spiral in Manhattan, New York City. Founded in 184 ...
, and Merck. Other awards include:
* John Scott Medal
John Scott Award, created in 1816 as the John Scott Legacy Medal and Premium, is presented to men and women whose inventions improved the "comfort, welfare, and happiness of human kind" in a significant way. "...the John Scott Medal Fund, establish ...
, from the Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and a center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and wikt:statesman, statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin ...
and City of Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, 1945
* Leo Hendrik Baekeland Award, from the North Jersey Section of the American Chemical Society
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a scientific society based in the United States that supports scientific inquiry in the field of chemistry. Founded in 1876 at New York University, the ACS currently has more than 155,000 members at all ...
, 1955
* Elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1956
* Davy Medal
The Davy Medal is awarded by the Royal Society of London "for an outstandingly important recent discovery in any branch of chemistry". Named after Humphry Davy, the medal is awarded with a monetary gift, initially of £1000 (currently £2000). Re ...
, from the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
in 1959
* Roger Adams Medal, from the American Chemical Society in 1961
* Pius XI Gold Medal, from the Pontifical Academy of Sciences in 1969
* National Medal of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral science, behavior ...
from the United States in 1964 ("''For an imaginative new approach to the synthesis of complex organic molecules and, especially, for his brilliant syntheses of strychnine, reserphine, lysergic acid, and chlorophyll.''")
* Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outst ...
in 1965
* Willard Gibbs Award
The Willard Gibbs Award, presented by thChicago Sectionof the American Chemical Society, was established in 1910 by William A. Converse (1862–1940), a former Chairman and Secretary of the Chicago Section of the society and named for Professor Jo ...
from the Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
Section of the American Chemical Society in 1967
* Lavoisier Medal from the Société chimique de France in 1968
* The Order of the Rising Sun
The is a Japanese honors system, Japanese order, established in 1875 by Emperor Meiji. The Order was the first national decoration awarded by the Japanese government, created on 10 April 1875 by decree of the Council of State. The badge feat ...
, Second Class from the Emperor of Japan in 1970
* Hanbury Memorial Medal from The Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain in 1970
* Pierre Bruylants Medal from the University of Louvain in 1970
* AMA Scientific Achievement Award in 1971
* Cope Award from the American Chemical Society, shared with Roald Hoffmann
Roald Hoffmann (born Roald Safran; July 18, 1937) is a Polish-American theoretical chemist who won the 1981 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He has also published plays and poetry. He is the Frank H. T. Rhodes Professor of Humane Letters Emeritus at C ...
in 1973
* Copley Medal
The Copley Medal is the most prestigious award of the Royal Society of the United Kingdom, conferred "for sustained, outstanding achievements in any field of science". The award alternates between the physical sciences or mathematics and the bio ...
from the Royal Society, London in 1978
Honorary degrees
Woodward also received over twentyhonorary degrees
An honorary degree is an academic degree for which a university (or other degree-awarding institution) has waived all of the usual requirements. It is also known by the Latin phrases ''honoris causa'' ("for the sake of the honour") or ''ad hono ...
, including honorary doctorates from the following universities:
* Wesleyan University
Wesleyan University ( ) is a Private university, private liberal arts college, liberal arts university in Middletown, Connecticut, United States. It was founded in 1831 as a Men's colleges in the United States, men's college under the Methodi ...
in 1945;
* Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
in 1957;
* University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, wo ...
in 1964;
* Brandeis University
Brandeis University () is a Private university, private research university in Waltham, Massachusetts, United States. It is located within the Greater Boston area. Founded in 1948 as a nonsectarian, non-sectarian, coeducational university, Bra ...
in 1965;
* Technion Israel Institute of Technology in Haifa
Haifa ( ; , ; ) is the List of cities in Israel, third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropolitan area i ...
in 1966;
* University of Western Ontario
The University of Western Ontario (UWO; branded as Western University) is a Public university, public research university in London, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is located on of land, surrounded by residential neighbourhoods and the Thame ...
in Canada in 1968;
* University of Louvain in Belgium, 1970.
Personal life
Family
In 1938, he married Irja Pullman; they had two daughters: Siiri Anna (b. 1939) and Jean Kirsten (b. 1944). In 1946, he married Eudoxia Muller, an artist and technician whom he met at the Polaroid Corp. This marriage, which lasted until 1972, produced a daughter, and a son: Crystal Elisabeth (b. 1947), and Eric Richard Arthur (b. 1953).Idiosyncrasies
His lectures frequently lasted for three or four hours.''Remembering organic chemistry legend Robert Burns Woodward Famed chemist would have been 100 this year'' By Bethany Halford C&EN Volume 95 Issue 15 , pp. 28–34 Issue Date: April 10, 201link
His longest known lecture defined the unit of time known as the "Woodward", after which his other lectures were deemed to be so many "milli-Woodwards" long. In many of these, he eschewed the use of slides and drew structures by using multicolored chalk. Typically, to begin a lecture, Woodward would arrive and lay out two large white handkerchiefs on the countertop. Upon one would be four or five colors of chalk (new pieces), neatly sorted by color, in a long row. Upon the other handkerchief would be placed an equally impressive row of cigarettes. The previous cigarette would be used to light the next one. His Thursday seminars at Harvard often lasted well into the night. He had a fixation with blue, and many of his suits, his car, and even his parking space were coloured in blue. In one of his laboratories, his students hung a large black and white photograph of the master from the ceiling, complete with a large blue "tie" appended. There it hung for some years (early 1970s), until scorched in a minor laboratory fire. He detested exercise, could get along with only a few hours of sleep every night, was a heavy smoker, and enjoyed Scotch whisky and martinis.
.
References
Bibliography
* Robert Burns Woodward: Architect and Artist in the World of Molecules; Otto Theodor Benfey, Peter J. T. Morris, Chemical Heritage Foundation, April 2001. * Robert Burns Woodward and the Art of Organic Synthesis: To Accompany an Exhibit by the Beckman Center for the History of Chemistry (Publication / Beckman Center for the History of Chemistry); Mary E. Bowden; Chemical Heritage Foundation, March 1992 * * *Video podcast of Robert Burns Woodward talking about cephalosporin
David Dolphin, '' Aldrichimica Acta'', 1977, ''10''(1), 3–9.
Robert Burns Woodward Patents
External links
Notes from Robert Burns Woodward's Seminars
taken by Robert E. Kohler i
Science History Institute Digital Collections
* including the Nobel Lecture, December 11, 1965 ''Recent Advances in the Chemistry of Natural Products'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Woodward, Robert Burns 1917 births 1979 deaths 20th-century American chemists 20th-century American educators American Nobel laureates American science writers Foreign members of the Royal Society Harvard University faculty Massachusetts Institute of Technology alumni Wesleyan University people Nobel laureates in Chemistry National Medal of Science laureates American organic chemists Stereochemists People from Belmont, Massachusetts Recipients of the Copley Medal 20th-century American writers Time Person of the Year Members of the American Philosophical Society Quincy High School (Massachusetts) alumni