Religion In Quebec on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The demographics of Quebec constitutes a complex and sensitive issue, especially as it relates to the
The demographics of Quebec constitutes a complex and sensitive issue, especially as it relates to the
https://web.archive.org/web/20080501112831/http://www40.statcan.ca/l01/cst01/demo62f.ht
%
Only groups with 0.06 percent or more of respondents are shown.'' Ethnicity according to the older more general system of classification is shown below: ''Percentages are calculated as a proportion of the total number of respondents (7,125,580) and may total more than 100% due to dual responses
Only groups of more than 0.02% are shown''
 Although they represent today approximately 3% of the Quebec population, the indigenous peoples of Quebec have contributed a lot to Quebec society thanks to their ideals of respect for flora, fauna, nature and the environment as well as thanks to their values of hospitality, generosity and sharing. Economically, through the
Although they represent today approximately 3% of the Quebec population, the indigenous peoples of Quebec have contributed a lot to Quebec society thanks to their ideals of respect for flora, fauna, nature and the environment as well as thanks to their values of hospitality, generosity and sharing. Economically, through the
 In the
In the
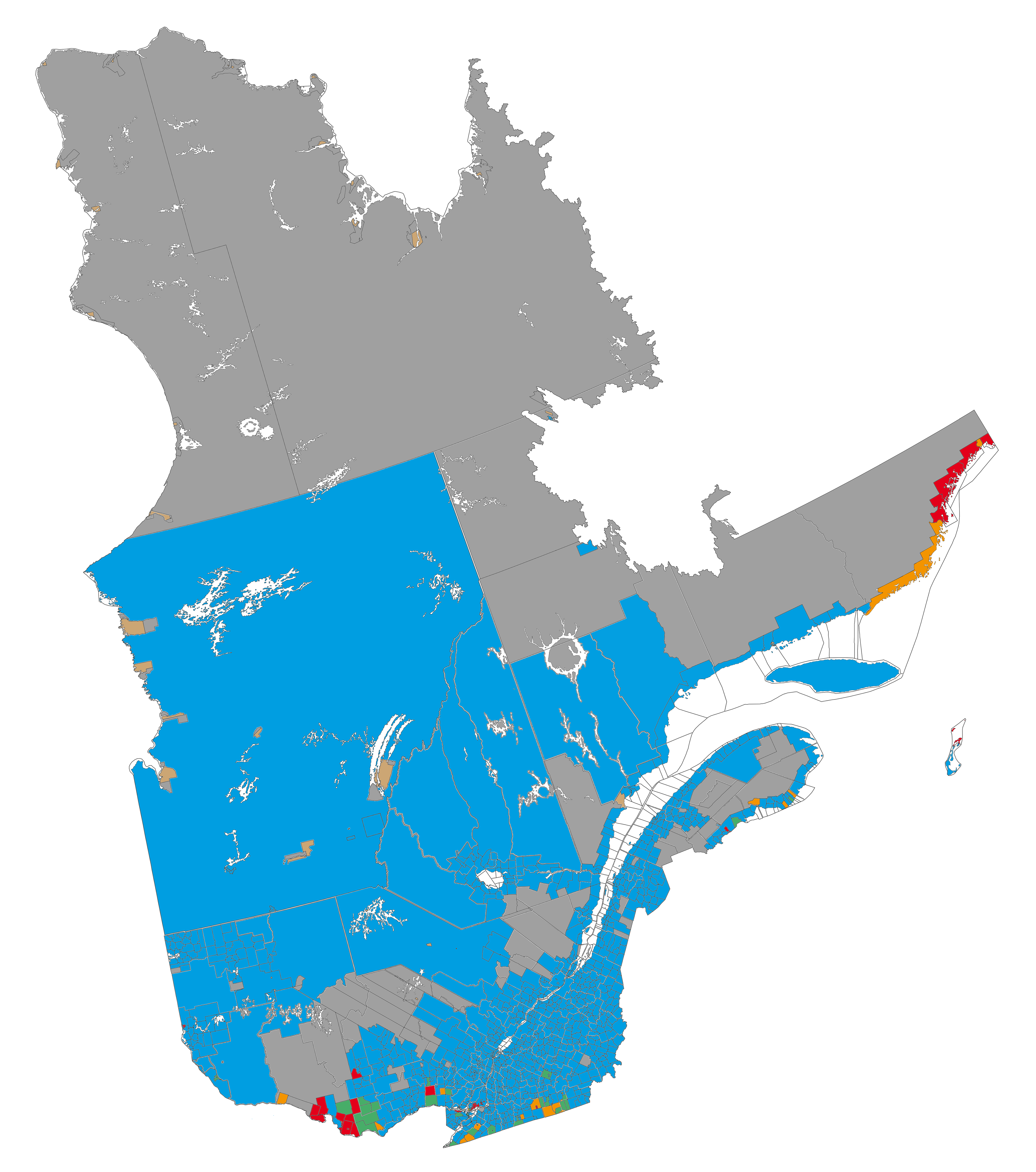 Quebec differs from other Canadian provinces in that
Quebec differs from other Canadian provinces in that
 Early on, colonists borrowed words from
Early on, colonists borrowed words from
 During the days of New France, there began to be an extremely pronounced demographic increase of anglophones versus francophones in North America, a trend which continues to this day. In 1700, for every 250,000 English-speakers, there was 16,500 French-speakers.
After the conquest of 1759, this reality became more brutal for Quebec, which now had to avoid assimilation by the British Empire's regime and survive culturally as well as linguistically.
Still today, as French's demographic weight on the continent and in Canada continues to decline, Quebec faces the threat of assimilation. Since 2011, the population with French as their mother tongue on the
During the days of New France, there began to be an extremely pronounced demographic increase of anglophones versus francophones in North America, a trend which continues to this day. In 1700, for every 250,000 English-speakers, there was 16,500 French-speakers.
After the conquest of 1759, this reality became more brutal for Quebec, which now had to avoid assimilation by the British Empire's regime and survive culturally as well as linguistically.
Still today, as French's demographic weight on the continent and in Canada continues to decline, Quebec faces the threat of assimilation. Since 2011, the population with French as their mother tongue on the
 *
*
''Interprovincial migrants, by age group and sex, Canada, provinces and territories, annual''.
/ref>
Institut de la statistique du QuébecStatistics CanadaPopulationData.net
{{People of Canada
 The demographics of Quebec constitutes a complex and sensitive issue, especially as it relates to the
The demographics of Quebec constitutes a complex and sensitive issue, especially as it relates to the national question
''National question'' is a term used for a variety of issues related to nationalism. It is seen especially often in socialist thought and doctrine.
In socialism
* ''Social Democracy and the National Question'' by Vladimir Medem in 1904
* ''S ...
. Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
is the only one of Canada's provinces
Canada has ten provinces and three territories that are sub-national administrative divisions under the jurisdiction of the Canadian Constitution. In the 1867 Canadian Confederation, three provinces of British North America—New Brunswick, No ...
to feature a Francophone
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
(French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
-speaking) majority, and where anglophones
The English-speaking world comprises the 88 countries and territories in which English is an official, administrative, or cultural language. In the early 2000s, between one and two billion people spoke English, making it the largest language ...
(English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
-speakers) constitute an officially recognized minority group. According to the 2011 census, French is spoken by more than 85.5% of the population while this number rises to 88% for children under 15 years old. According to the 2011 census, 95% of Quebec's people are able to conduct a conversation in French, with less than 5% of the population not able to speak French.
In 2025, Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
had estimated the province's population to be 9,111,629. In the 2021 census, Quebec's population was determined to be 8,501,833 living in 3,749,035 of its 4,050,164 total dwellings, a 4.1% change from its 2016 population of 8,164,361. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2016. Quebec accounts for a little under 23% of the Canadian population. Quebec's demographic weight in Canada has been gradually decreasing since 1971 when it was 28% of the population. In 2023, Quebec's three most populated regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
are Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
(2,109,525), Montérégie
Montérégie () is an administrative region in the southwest part of Quebec. It includes the cities of Boucherville, Brossard, Châteauguay, Longueuil, Saint-Hyacinthe, Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Salaberry-de-Valleyfield and Vaudreuil-Dorion.
...
(1,492,662) and Capitale-Nationale
Capitale-Nationale (; ) is one of the 17 administrative regions of Quebec. It is anchored by the provincial capital, Quebec City, and is largely coextensive with that city's metropolitan area. It has a land area of 18,684.78 km2. It reported ...
(793,001). Quebec's three least populated regions are Nord-du-Québec
Nord-du-Québec (; ) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.
Spread over nearly 14 degrees of latitude, north of the 49th parallel, the region covers on the Labrador Peninsula, making ...
(46,650), Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord (Region 09) (, ; ) is an List of regions of Quebec, administrative region of Quebec, on the Quebec-Labrador peninsula, Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, Canada.
The region runs along the St. Lawrence River and then the Gulf of St. Lawrence, ...
(89,914) and Gaspésie-Îles-de-la-Madeleine (92,059).
Quebec is home to "one of the world's most valuable founder populations". Founder population
In population genetics, the founder effect is the loss of genetic variation that occurs when a new population is established by a very small number of individuals from a larger population. It was first fully outlined by Ernst Mayr in 1942, using ...
s are very valuable to medical genetic research as they are pockets of low genetic variability which provide a useful research context for discovering gene-disease linkages. The Quebec founder population arose through the influx of people into Quebec from France in the 17th century to mid-18th century; a high proportion of the settlers either returned to France or died. Of the approximately 33,500 colonists who arrived to Canada, fewer than 10,000 remained. There were approximately 8,500 colonists who settled from France and had at least one child in the colony. About seven million Canadians (along with several million French Americans
French Americans or Franco-Americans () are citizens or nationals of the United States who identify themselves with having full or partial French or French-Canadian heritage, ethnicity and/or ancestral ties. They include French-Canadian ...
in the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
) are descendants of these original 8,500 colonists.
Vital statistics
While Quebec'sfertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
is higher than the Canadian average, it has been sharply decreasing in the past 15 years. At 1.38 children per woman in 2008, it is above the Canada-wide rate of 1.26, and is just above the historic low of 1.36 in 1987. This contrasts with its fertility rates before 1960, which were among the highest of any industrialized society. For example, between 1951 and 1961, the population grew nearly 30% with only small net migration (large number of international migrants had settled in Quebec in the preceding period but large numbers of Quebec residents had emigrated to other provinces as well as New England), a natural growth rate matched today only by some African countries.
Although Quebec is home to only 22.0% of the population of Canada, the number of international adoptions in Quebec is the highest of all provinces of Canada. In 2001, 42% of international adoptions in Canada were carried out in Quebec.
Population growth rate: 2.5% (2023)
Birth rate: 8.8‰ (2023)
Synthetic fertility index: 1.38 (2023)
Death rate: 7.0‰ (2023)
Permanent immigration rate: 6.0‰ (2003)
Infant mortality rate: 0.46% (2023)
Life expectancy: In 2002, life expectancy was 80.7 years for males and 84.1 years for females.
Urbanisation: In 2001, 80.4% of Quebecers lived in urban areas.
Marriages: In 2019, 22,250 marriage
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognised union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children (if any), and b ...
s were celebrated, about 600 less than in 2017 and 2018. These numbers illustrate a continuing trend where marriages are becoming less numerous; in 1970, the number of marriages hit a peak with more than 50,000 celebrations and the number has been slowly decreasing ever since. The average age for marriage is now 33.5 for men and 32.1 for women, an increase of 8.0 and 8.5 years respectively since 1970. 72% of marriages occur on a Saturday. Half of all marriages unite a man and woman with an age gap of 3 years or less. Though they are still uncommon, civil unions
A civil union (also known as a Civil partnership in the United Kingdom, civil partnership) is a legally recognized arrangement similar to marriage, primarily created to provide legal recognition for Same-sex relationship, same-sex couples. Civi ...
are becoming more and more popular.
Demographic growth: In 2019, Quebec registered the highest rate of population growth since 1972 (when quality data began to be recorded), with an increase of 110,000 people, mostly because of the arrival of a high number of non-permanent residents. The number of non-permanent residents has recently sky-rocketed from a little over 100,000 in 2014 to 260,000 in 2019. Quebec's population growth is usually middle-of-the-pack compared to other provinces and very high compared to other developed countries (ex. United States, France, Germany, etc.) because of the federal government of Canada's aggressive immigration policies. Since the 1970s, Quebec has always had more immigrants than emigrants. This can be attributed to international immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as Permanent residency, permanent residents. Commuting, Commuter ...
as the number of people moving to Quebec from another province is always lower than the other way around. As of 2019, most international immigrants come from China, India or France.
Education and work: In 2016, 3 out of 10 people in Quebec possessed a postsecondary
Tertiary education (higher education, or post-secondary education) is the educational level following the completion of secondary education.
The World Bank defines tertiary education as including universities, colleges, and vocational school ...
degree or diploma. While women were more likely to have a university degree (33% vs 26%) or college degree (21% vs 11%), men were more numerous in having received vocational training
Vocational education is education that prepares people for a Skilled worker, skilled craft. Vocational education can also be seen as that type of education given to an individual to prepare that individual to be gainfully employed or self em ...
. In Quebec, couples where both parents work are far more likely to have children than couples where only one parent works or none of them do.
Households: In Quebec, most people are owners of the property that they live in. The vast majority of couples with or without children are property owner
In property law, title is an intangible construct representing a bundle of rights in a piece of property in which a party may own either a legal interest or equitable interest. The rights in the bundle may be separated and held by different part ...
s. Most one-person households, however, are renter
Renting, also known as hiring or letting, is an agreement where a payment is made for the use of a good, service or property owned by another over a fixed period of time. To maintain such an agreement, a rental agreement (or lease) is sign ...
s. Single-parent homes are equally divided between being property owners or renters. From 1996 to 2016, the number of people per household has decreased from an average of 2.5 to 2.25. In 2016, the vast majority of low income households were one-person households. In 2016, 80% of both property owners and renters considered their housing to be "unaffordable".
Population centres
Age structure
Age structure: ''(2016 census)'' In 2016, Quebec's median age was 41.2 years old. According to Quebec'sage pyramid
A population pyramid (age structure diagram) or "age-sex pyramid" is a graphical illustration of the distribution of a population (typically that of a country or region of the world) by age groups and sex; it typically takes the shape of a pyramid ...
, the most numerous generation is the baby-boomers
Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the demographic cohort preceded by the Silent Generation and followed by Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964 during the mid-20th century baby boom that fol ...
that are between 54 and 74 years of age. There are a few other less pronounced peaks, namely in the 1980s, and the one around 2010. A noticeable crater can be observed around the year 2000 because of a record-low amount of births. In 2020, 20.8% of the population is less than 20 years old, 59.5% are aged between 20 and 64 years old, and 19.7% are 65 years old or older. In 2019, Quebec witnessed an increase in the number of births compared to the year before (84,200 vs 83,840) and had a replacement rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
of about 1.6 per woman. Replacement rates being below 2.1 something that is the norm in industrialised regions like Quebec. Quebec has a higher replacement rate than the Canadian average (1,47). Quebec's rate can also be both higher (ex. Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
(1.48), Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it share ...
(1.42), Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
(1.36), Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
(1.29), etc.) or lower (ex. United States (1.73), New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
(1.75), Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
(1.70), England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
(1.65), etc.) than other industrialised regions'. In Quebec, a lowered rate of giving birth has been mostly observed in people in their 20s. From 30 years of age and onwards, the rate is either increasing or stable. This demonstrates a trend towards wanting to form a family later in life. As of 2020, the average lifespan is 82.3 years. Between 2010 and 2019, there were between 1000 and 1600 deaths every week, with deaths being at their highest levels in January and their lowest levels in July. In 2021, the region's life expectancy increased after a decline amid the pandemic, reaching 83 years.
Population history
Population since 1824: ''Source:Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; ), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in ...
'https://web.archive.org/web/20080501112831/http://www40.statcan.ca/l01/cst01/demo62f.ht
%
Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
population
Ethnic origin
''Percentages are calculated as a proportion of the total number of respondents (7,435,905) and may total more than 100 percent due to dual responses.Only groups with 0.06 percent or more of respondents are shown.'' Ethnicity according to the older more general system of classification is shown below: ''Percentages are calculated as a proportion of the total number of respondents (7,125,580) and may total more than 100% due to dual responses
Only groups of more than 0.02% are shown''
Future projections
Visible minorities and Indigenous peoples
The 2021 census counted a total Indigenous population of 205,010 (2.5%) including 116,550First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
(1.4%), 61,010 Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
(0.7%), and 15,800 Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
(0.2%). The Indigenous population tends to be undercounted, as some Indian bands regularly refuse to participate in Canadian censuses for political reasons regarding the question of Indigenous sovereignty. In 2016, the Mohawk
Mohawk may refer to:
Related to Native Americans
*Mohawk people (Kanien’kehá:ka), an indigenous people of North America (Canada and New York)
*Mohawk language (Kanien’kéha), the language spoken by the Mohawk people
*Mohawk hairstyle, from a ...
reserves of Kahnawake
The Kahnawake Mohawk Territory (, in the Mohawk language, ''Kahnawáˀkye'' in Tuscarora) is a First Nations reserve of the Mohawks of Kahnawà:ke on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec, Canada, across from Montreal. Establi ...
and Doncaster 17 along with the Indian settlement An Indian settlement is a census subdivision outlined by the Canadian government Department of Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada for census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acqui ...
of Kanesatake
Kanesatake () is a Mohawk (''Kanien'kéha:ka'') settlement on the shore of the Lake of Two Mountains in southwestern Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Ottawa and St. Lawrence rivers and about west of Montreal. People who reside in ''Kan ...
and Lac-Rapide, a reserve of the Algonquins of Barriere Lake
Algonquins of Barriere Lake are an Algonquin people, Algonquin First Nations in Canada, First Nation in Quebec, Canada. They primarily live on the Indian reserve of Rapid Lake, Quebec, Rapid Lake in Outaouais. In 2017 the Band government, band had ...
, were not counted.'
Approximately 16% of the population of Quebec belongs to a visible minority
In Canada, a visible minority () is defined by the Government of Canada as "persons, other than aboriginal peoples, who are non-Caucasian in race or non-white in colour". The term is used primarily as a demographic category by Statistics Canada ...
group, as of the 2021 Canadian census. This is a lower percentage than that of British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
, Ontario, Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, t ...
, and Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
but higher than that of the remaining five provinces. Most visible minorities in Quebec live in or near Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
.
The indigenous peoples of Quebec have inhabited the region for several millennia. Each community possesses its own social structure, culture and territorial entity. In 2016, the indigenous population of Quebec numbered 182,885 people. However, because federal law only recognized children of indigenous fathers until the 1980s, the actual number may be higher.
All the ethnicities living primarily south of the 55th parallel are collectively referred to in Quebec as "Amerindians
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of ...
", "Indians", "First Nations" or, obsolete, "Redskins". The ten First Nations ethnic groups in Quebec are linked to two linguistic groups. The Algonquian family is made up of eight ethnic groups: the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
, the Algonquin
Algonquin or Algonquian—and the variation Algonki(a)n—may refer to:
Languages and peoples
*Algonquian languages, a large subfamily of Native American languages in a wide swath of eastern North America from Canada to Virginia
**Algonquin la ...
, the Attikamek
The Atikamekw are an Indigenous people in Canada. Their historic territory, ('Our Land'), is in the upper Saint-Maurice River valley of Quebec (about north of Montreal). One of the main communities is Manawan, about northeast of Montreal. ...
, the Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
, the Wolastoqiyik
The Wolastoqiyik, (, also known as the Maliseet or Malecite () are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the Indigenous people of the Wolastoq ( Saint John River) valley and its tributaries. Their terri ...
, the Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Bru ...
, the Innu
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to ...
and the Naskapi
The Naskapi (Nascapi, Naskapee, Nascapee) are an Indigenous people of the Subarctic native to the historical region St'aschinuw (ᒋᑦ ᐊᔅᒋᓄᐤ, meaning 'our Clusivity, nclusiveland'), which was located in present day northern Qu ...
s. These last two formed, until 1978, a single ethnic group: the Innu. The Iroquoian family is made up of the Huron-Wendat
The Huron-Wendat Nation (or Huron-Wendat First Nation) is an Iroquoian-speaking nation that was established in the 17th century. In the French language, used by most members of the First Nation, they are known as the . The French gave the nickn ...
and the Mohawks
The Mohawk, also known by their own name, (), are an Indigenous people of North America and the easternmost nation of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy (also known as the Five Nations or later the Six Nations).
Mohawk are an Iroquoi ...
. Only the Mohawks were part of the Iroquois Confederacy
The Iroquois ( ), also known as the Five Nations, and later as the Six Nations from 1722 onwards; alternatively referred to by the Endonym and exonym, endonym Haudenosaunee ( ; ) are an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Ind ...
(''Haudenosaunee''), along with five other Indigenous groups from New York State
New York, also called New York State, is a state in the northeastern United States. Bordered by New England to the east, Canada to the north, and Pennsylvania and New Jersey to the south, its territory extends into both the Atlantic Ocean and ...
and Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
. The eleventh indigenous ethnic group in Quebec, the Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
(or, obsolete, the Eskimo
''Eskimo'' () is a controversial Endonym and exonym, exonym that refers to two closely related Indigenous peoples: Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Canadian Inuit, and the Greenlandic Inuit) and the Yupik peoples, Yupik (or Sibe ...
s), belong to the Inuit–Aleut family. The Inuit live mainly in Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; ) is an area in Canada which comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homelan ...
, Nord-du-Québec
Nord-du-Québec (; ) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.
Spread over nearly 14 degrees of latitude, north of the 49th parallel, the region covers on the Labrador Peninsula, making ...
(Nouveau Quebec) and make up the majority of the population living north of the 55th parallel.
Of these indigenous peoples, so-called "nomadic" tribes exist, specifically the tribes of Algonquian cultures (eg: the Algonquins, the Cree and the Innu), as well as more "sedentary" ones, specifically the tribes of Iroquoian traditions (eg: the Iroquois and the Hurons-Wendat). The more sedentary groups are the ones who developed more complex forms of social organization. Traditionally, nomadic tribes follow the migration of herds of animals that serve as prey, such as bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
, moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
or seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
. The way of life of the Algonquian and Inuit tribes is dictated by the obligations of hunting and fishing. The traditions of the Iroquoian tribes, producers of the Three Sisters (corn
Maize (; ''Zea mays''), also known as corn in North American English, is a tall stout Poaceae, grass that produces cereal grain. It was domesticated by indigenous peoples of Mexico, indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 9,000 years ago ...
, beans
A bean is the seed of some plants in the legume family (Fabaceae) used as a vegetable for human consumption or animal feed. The seeds are often preserved through drying (a ''pulse''), but fresh beans are also sold. Dried beans are tradition ...
and squash
Squash most often refers to:
* Squash (sport), the high-speed racquet sport also known as squash racquets
* Squash (plant), the fruit of vines of the genus ''Cucurbita''
Squash may also refer to: Sports
* Squash (professional wrestling), an extr ...
), are instead developed around a matriarchal structure derived from the "long cabin" called a longhouse
A longhouse or long house is a type of long, proportionately narrow, single-room building for communal dwelling. It has been built in various parts of the world including Asia, Europe, and North America.
Many were built from lumber, timber and ...
which houses within it several families under the authority of one dean.
Relations with Québécois
 Although they represent today approximately 3% of the Quebec population, the indigenous peoples of Quebec have contributed a lot to Quebec society thanks to their ideals of respect for flora, fauna, nature and the environment as well as thanks to their values of hospitality, generosity and sharing. Economically, through the
Although they represent today approximately 3% of the Quebec population, the indigenous peoples of Quebec have contributed a lot to Quebec society thanks to their ideals of respect for flora, fauna, nature and the environment as well as thanks to their values of hospitality, generosity and sharing. Economically, through the fur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals h ...
and the development of relationships with settlers, including coureurs des bois
A coureur des bois (; ) or coureur de bois (; ) were independent entrepreneurial French Canadians, French Canadian traders who travelled in New France and the interior of North America, usually to trade with Indigenous peoples of the Americas, ...
, merchants, cartographers and Jesuit fathers. In addition to contributing to , indigenous peoples also contributed through their more advanced knowledge than settlers in the following areas: holistic medicine, the functioning of human biology, remedies for several diseases, curing scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease (state of malnutrition) resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, fatigue, and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum d ...
at settlers' arrival (its thought this was done with a cure made from fir
Firs are evergreen coniferous trees belonging to the genus ''Abies'' () in the family Pinaceae. There are approximately 48–65 extant species, found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Eurasia, and North Africa. The genu ...
, white cedar White cedar may refer to several different trees:
* Bignoniaceae
** '' Tabebuia heterophylla'' - native to Caribbean islands and also cultivated as an ornamental tree
* Cupressaceae:
** ''Chamaecyparis thyoides'' – Atlantic white cypress
** ''Cup ...
or ''anneda''), winter clothing ( tanning), architecture that insulates against the cold, means of faster transport on snow (snowshoe
Snowshoes are specialized outdoor gear for walking over snow. Their large footprint spreads the user's weight out and allows them to travel largely on top of rather than through snow. Adjustable bindings attach them to appropriate winter footw ...
s and dogsled
A dog sled or dog sleigh is a sled pulled by one or more sled dogs used to travel over ice and through snow, a practice known as mushing. Numerous types of sleds are used, depending on their function. They can be used for dog sled racing. Tradi ...
) and on water (canoe
A canoe is a lightweight, narrow watercraft, water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using paddles.
In British English, the term ' ...
s, kayaks
]
A kayak is a small, narrow human-powered watercraft typically propelled by means of a long, double-bladed paddle. The word ''kayak'' originates from the Inuktitut word '' qajaq'' (). In British English, the kayak is also considered to be ...
and rabaskas), ''l'acériculture'' (the process of making maple syrup
Maple syrup is a sweet syrup made from the sap of maple trees. In cold climates, these trees store starch in their trunks and roots before winter; the starch is then converted to sugar that rises in the sap in late winter and early spring. Ma ...
), sports (lacrosse
Lacrosse is a contact team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game w ...
and ice fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
Shelters
L ...
), moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
and caribou
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only represe ...
hunting, trapping
Animal trapping, or simply trapping or ginning, is the use of a device to remotely catch and often kill an animal. Animals may be trapped for a variety of purposes, including for meat, fur trade, fur/feathers, sport hunting, pest control, and w ...
, the territory and its components, watersheds and their watercourses and natural resources.
When Europeans arrived in America in the 16th century, the Algonquian-speaking peoples and the St. Lawrence Iroquoians made allies with the French colonists for the purpose of trade. The first connection was made with the arrival of Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
when he set foot in Gaspé and met Donnacona
Chief Donnacona (died 1539 in France) was the chief of the St. Lawrence Iroquois village of Stadacona, located at the present site of Quebec City, Quebec, Canada. French explorer Jacques Cartier, concluding his second voyage to what is now Can ...
, chief of the village of Stadacona
Stadacona was a 16th-century St. Lawrence Iroquoian village not far from where Quebec City was founded in 1608.
History
French explorer and navigator Jacques Cartier, while travelling and charting the Saint Lawrence River, reached the village ...
(Stadaconé, today, the city of Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
), in 1534. Moreover, the legend of the Kingdom of Saguenay
The Kingdom of Saguenay () was a mythical kingdom that French- Breton maritime explorer Jacques Cartier tried to reach in 1535, supposedly located inland of present-day Quebec, Canada. The indigenous people had told Cartier about a rich kingdom ...
prompted King Francis I
Francis I (; ; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis&nbs ...
to finance new trips to the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
.
Rights of indigenous people
 In the
In the Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by British King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The ...
, issued by King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until his death in 1820. The Acts of Union 1800 unified Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and ...
, the indigenous peoples were stated to have an indisputable right to their lands. However, quickly following the proclamation and after the peace treaties with New France and France concluded, the British Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
decided to institute territorial treaties which allowed British authorities to proceed with the total extinction of the land titles of the Indigenous groups.
Entirely under federal tutelage and direction, indigenous rights were enunciated in the Indian Act
The ''Indian Act'' () is a Canadian Act of Parliament that concerns registered Indians, their bands, and the system of Indian reserves. First passed in 1876 and still in force with amendments, it is the primary document that defines how t ...
and adopted at the end of the 19th century. This act confines First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
within the Indian reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve () or First Nations reserve () is defined by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty, that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band." ...
s created for them. The Indian Act is still in effect today.
In 1975, the Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
, Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
and the Quebec government agreed to an agreement called the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement
The James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement () is an Aboriginal land claim settlement, approved in 1975 by the Cree and Inuit of northern Quebec, and later slightly modified in 1978 by the Northeastern Quebec Agreement (), through which Quebec's ...
that would extended Indigenous rights beyond Indian reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve () or First Nations reserve () is defined by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty, that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band." ...
s, and to over two-thirds of Quebec's territory. Because this extension was enacted without the participation of the federal government
A federation (also called a federal state) is an entity characterized by a political union, union of partially federated state, self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a #Federal governments, federal government (federalism) ...
, the extended Indigenous rights only exist in Quebec. In 1978, the Naskapi
The Naskapi (Nascapi, Naskapee, Nascapee) are an Indigenous people of the Subarctic native to the historical region St'aschinuw (ᒋᑦ ᐊᔅᒋᓄᐤ, meaning 'our Clusivity, nclusiveland'), which was located in present day northern Qu ...
s joined the agreement when the Northeastern Quebec Agreement was signed. As a result, these three ethnic groups were able to break away from their subjugation to the Indian Act.
In recent times, discussions have been underway for several years with the Montagnais of the Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord (Region 09) (, ; ) is an List of regions of Quebec, administrative region of Quebec, on the Quebec-Labrador peninsula, Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, Canada.
The region runs along the St. Lawrence River and then the Gulf of St. Lawrence, ...
and Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean
Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean (, ) is a region in Quebec, Canada on the Labrador Peninsula. It contains the Saguenay Fjord, the estuary of the Saguenay River, stretching through much of the region. It is also known as Sagamie in French, from the fi ...
for the potential creation of a similar autonomy in two new distinct territories that would be called ''Innu Assi'' and ''Nitassinan''. Moreover, in January 2010, an agreement between Quebec City and Montagnais granted the Mashteuiatsh
Mashteuiatsh is a First Nations reserve in the Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean region of Quebec, Canada, about north from the centre of Roberval. It is the home to the Pekuakamiulnuatsh First Nation. It is located on a headland jutting out on the w ...
Band Council the ability to plan out development in the entire Ashuapmushuan Wildlife Reserve
The Ashuapmushuan Wildlife Reserve is a wildlife reserve in Quebec, Canada, in the watershed of the Ashuapmushuan River. It is mainly located in the region of Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean, between the municipality of La Doré and the city of Chibo ...
, which is located on the ''Nitassinan'' of the community of the Pekuakamiulnuatsh.
A few political institutions have also been created over time:
* The Assembly of First Nations Quebec-Labrador
The Assembly of First Nations Quebec-Labrador (, AFNQL) is a political organization representing the First Nations of Quebec and Labrador. It represents these First Nations to the ''Secrétariat aux affaires autochtones du Québec'' and to the m ...
* The Grand Council of the Crees
The Grand Council of the Crees (Eeyou Istchee) or the GCC(EI) (ᐄᔨᔨᐤ ᐊᔅᒌ in Cree), is the political body that represents the approximately 20,000 Cree people (who call themselves "Eeyou" or "Eenou" in the various dialects of East ...
* The Makivik Corporation
Makivvik (, ; ) (''formerly Makivik Corporation'') is the legal representative of Quebec's Inuit, established in 1978 under the terms of the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement, the agreement that established the institutions of Nunavik. As s ...
Indigenous lands
The following table shows the traditional territories of theFirst Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
and Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
peoples who live in Quebec, including the basins of the St. Lawrence Valley
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawren ...
and James Bay
James Bay (, ; ) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. It borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is politically part of Nunavut. Its largest island is Akimiski Island.
Numerous waterways of the ...
, as well as on the Labrador peninsula
The Labrador Peninsula, also called Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, is a large peninsula in eastern Canada. It is bounded by Hudson Bay to the west, the Hudson Strait to the north, the Labrador Sea to the east, Strait of Belle Isle and the Gulf of ...
.
Acadians
The subject ofAcadians in Quebec
The Acadians, Acadian community in Quebec is distributed across several regions and comprises individuals with diverse origins. A survey conducted by Léger revealed that over one million Quebecers have an Acadian surname. A study by the Universi ...
is an important one as more than a million people in Quebec are of Acadian
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern American region of Acadia, ...
ascent, with roughly 4.8 million possessing one or multiple Acadian ancestors in their genealogy tree. Furthermore, more than a million people wear a patronym
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (more specifically an avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor. It is the male equivalent of a matronymic.
Patronymics are used, ...
of Acadian origin. All of this is because a large number of Acadians had fled Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
to take refuge in Quebec during the Great Upheaval
The Expulsion of the Acadians was the forced removal of inhabitants of the North American region historically known as Acadia between 1755 and 1764 by Great Britain. It included the modern Canadian Maritime provinces of Nova Scotia, New Br ...
.
Quebec houses an Acadian community spread out across several regions. Nowadays, Acadians mainly live on the Magdalen Islands
The Magdalen Islands (, ) are a Canadian archipelago in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Since 2005, the 12-island archipelago is divided into two municipalities: the majority-francophone Municipality of Îles-de-la-Madeleine and the majority-angloph ...
and in Gaspesia, but about thirty other communities are present elsewhere in Quebec, mostly in the Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord (Region 09) (, ; ) is an List of regions of Quebec, administrative region of Quebec, on the Quebec-Labrador peninsula, Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, Canada.
The region runs along the St. Lawrence River and then the Gulf of St. Lawrence, ...
and Centre-du-Québec
Centre-du-Québec (, ''Central Quebec'') is a region of Quebec, Canada. The main centres are Drummondville, Victoriaville, and Bécancour. It has a land area of and a 2016 census population of 242,399 inhabitants.
Description
The Centre-du- ...
regions. An Acadian community in Quebec can be called a "Cadie" or "Petite Cadie", and some cities and villages use the demonym "Cadien".
The ''Festival Acadien des Îles-de-la-Madeleine'' is a festival which occurs every year in memory of the founders of the first villages on the Magdalen Islands
The Magdalen Islands (, ) are a Canadian archipelago in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Since 2005, the 12-island archipelago is divided into two municipalities: the majority-francophone Municipality of Îles-de-la-Madeleine and the majority-angloph ...
. The festival is held in Havre Aubert for about two weeks. There, Québécois and Acadians from all corners of Quebec and other neighbouring lands mingle to celebrate Acadian culture. The town of Bonaventure
Bonaventure ( ; ; ; born Giovanni di Fidanza; 1221 – 15 July 1274) was an Italian Catholic Franciscan bishop, Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal, Scholasticism, scholastic theologian and philosopher.
The seventh Minister General ( ...
, in Gaspesia, also houses the ''Musé Acadien du Québec'' which features permanent exhibitions on Acadians in Quebec, like ''Une Acadie québécoise'' and ''Secrets d'Acadiens, les coulisses de la rue Grand-Pré''. In 2002, on National Acadian Day
The National Acadian Day () is observed in parts of Canada each year on August 15, to celebrate Acadian culture. It was during the first National Convention of the Acadians held at Memramcook, New Brunswick, in 1881 that the Acadian leaders rece ...
, the '' Commission de la capitale nationale du Québec'' unveiled a monument to Acadians entitled "Towards the Light". The monument symbolizes and explains the predominant role that the Acadians and their descendants played in the history of Quebec. The Premier of Quebec, Bernard Landry
Bernard Landry (; March 9, 1937 – November 6, 2018) was a Canadian politician who served as the 28th premier of Quebec from 2001 to 2003. A member of the Parti Québécois (PQ), he led the party from 2001 to 2005, also serving as the leader ...
, declared at this unveiling that:
Languages
 Quebec differs from other Canadian provinces in that
Quebec differs from other Canadian provinces in that French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
is the only official
An official is someone who holds an office (function or Mandate (politics), mandate, regardless of whether it carries an actual Office, working space with it) in an organization or government and participates in the exercise of authority (eithe ...
and preponderant language, while English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
predominates in the rest of Canada
English Canada comprises that part of the population within Canada, whether of British origin or otherwise, that speaks English.
The term ''English Canada'' is also used for any of the following:
*Describing all the provinces of Canada ...
. French is the common language
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make co ...
, understood and spoken by 94.46% of the population. Quebec is the only Canadian province whose population is mainly Francophone
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
; 6,102,210 people (78.1% of the population) recorded it as their sole native language in the 2011 Census, and 6,249,085 (80.0%) recorded that they spoke it most often at home. Knowledge of French is widespread even among those who do not speak it natively; in 2011, about 94.4% of the total population reported being able to speak French, alone or in combination with other languages.
A considerable number of Quebec residents consider themselves to be bilingual
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. When the languages are just two, it is usually called bilingualism. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolin ...
in French and English. In Quebec, about 42.6% of the population (3,328,725 people) report knowing both languages; this is the highest proportion of bilinguals in any Canadian province. The federal electoral district of Lac-Saint-Louis
Lac-Saint-Louis () is a federal electoral district in Quebec, Canada, which has been represented in the House of Commons since 1997.
It is on the southwestern tip of the Island of Montreal, encompassing a small part of the city of Montreal. I ...
, located in the Bilingual Belt
The bilingual belt (French: ''la ceinture bilingue'') is a term for the portion of Canada where both French and English are regularly spoken.
The term was coined by Richard Joy in his 1967 book ''Languages in Conflict'', where he wrote, "The ...
, is the most bilingual area in the province with 72.8% of its residents claiming to know English and French, according to the 2011 census. In contrast, in the rest of Canada
English Canada comprises that part of the population within Canada, whether of British origin or otherwise, that speaks English.
The term ''English Canada'' is also used for any of the following:
*Describing all the provinces of Canada ...
, in 2006, only about 10.2 percent (2,430,990) of the population had a knowledge of both of the country's official languages.
The Quebec government defends the French language and the Francophonie
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
in the face of the mostly English-dominated rest of North America. The Gendron Commission report of 1968 established the foundations for the white book of the government of Quebec' linguistic policy. Dependent on commissions of inquiry, this policy statement is also accompanied the Charter of the French language
The ''Charter of the French Language'' (, ), also known as Bill 101 (, ), is a law in the Canadian province of Quebec defining French, the language of the majority of the population, as the official language of the provincial government. It is th ...
-or "Bill 101"- since 1977.
French
French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
is the official language of Quebec. Québécois French
Quebec French ( ), also known as Québécois French, is the predominant variety of the French language spoken in Canada. It is the dominant language of the province of Quebec, used in everyday communication, in education, the media, and governme ...
is the most widely used variant. The oversees the application of the linguistic policy on the territory jointly with the Superior Council of the French Language and the Commission de toponymie du Québec
The Commission de toponymie du Québec (, ''Toponymy Commission of Québec'') is the Government of Québec's public body responsible for cataloging, preserving, making official and publicizing Québec's place names and their origins according to th ...
. Their recommendations then become part of the debate on the standard for Quebec French and are represented in Le Grand Dictionnaire terminologique (GDT), the (BDL) and various other works. Through its linguistic recommendations, the GDT fights against the invasion of Frenglish into the French language. Since the 1970s, scientific research on the matter has been carried out by university organizations, including the Trésor de la langue française au Québec
The (''Treasury of the French language in Quebec'', TLFQ) is a project created in the 1970s with the primary objective of establishing a scientific infrastructure for research into the history of Quebec French and, also, its current usage. ...
(TLFQ) and the .
The French settlers who settled in New France came largely from the western and northern provinces of France. They generally spoke a variety of regional languages of the Oïl language family. Thus, creating the need for the colonists to "unify their ''patois
''Patois'' (, same or ) is speech or language that is considered nonstandard, although the term is not formally defined in linguistics. As such, ''patois'' can refer to pidgins, creoles, dialects or vernaculars, but not commonly to jargon or sl ...
''" ("unite their dialects") and creating Quebec French. Québécois French became the vernacular language
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken form of language, particularly when perceived as having lower social status or less prestige than standard language, which is more codified, institutionally promoted, literary, or formal. More n ...
of New France, and it remained as such until the British's conquest of New France.
 Early on, colonists borrowed words from
Early on, colonists borrowed words from Algonquin
Algonquin or Algonquian—and the variation Algonki(a)n—may refer to:
Languages and peoples
*Algonquian languages, a large subfamily of Native American languages in a wide swath of eastern North America from Canada to Virginia
**Algonquin la ...
, a language they frequently interacted with, often to name and describe new aspects of geography, temperature, fauna or flora not present in the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
. Then, Quebec French's evolution was affected by the French court
The Kingdom of France is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. It was one of the most powerful states in Europe from the High Middle Ages to 1848 during ...
due to the arrival of the King's daughters
The King's Daughters ( , or in the spelling of the era) were the approximately 800 young French people, French women who immigrated to New France between 1663 and 1673 as part of a program sponsored by King Louis XIV. The program was designed ...
. These 800 women were mostly orphaned girls that had been adopted by the state as part of a program sponsored by King Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the longest of any monar ...
, and been educated
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also fol ...
in convent
A convent is an enclosed community of monks, nuns, friars or religious sisters. Alternatively, ''convent'' means the building used by the community.
The term is particularly used in the Catholic Church, Lutheran churches, and the Anglican ...
s to become exemplary settlers and wives. Once their training was complete, between 1663 and 1673, they were sent to New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
and married among the colonists, instilling the ''King's French'' into the population in the process.
In his 1757 ''Memoir on the State of New France'', Bougainville writes:
The British conquest of 1759 turned the evolution of French in Quebec and North America upside down. By having ties severed with France, the French spoken in Quebec definitively separated from the French spoken in metropolitan France. Quebec French was then truly born, retaining the peculiarities of the old languages of Oïl (which were almost extinct in France at that point) and the ''King's French'', and being both influenced and threatened by the language of the new English conquerors. Quebec's French continued to evolve in its own direction, retaining some aspects the non-isolated rest of the French-speaking world lost, and, over time, new influences and remoteness formed the regional accents and different dialects of Quebec French.
Canada is estimated to be home to between 32 and 36 regional French accents, 17 of which can be found in Quebec. There are 11 accents exclusive to mainland Quebec; they are the regional accents of Gaspé (Gaspésien), Bas-Saint-Laurent
The Bas-Saint-Laurent (, 'Lower Saint-Lawrence) is an administrative region of Quebec located along the south shore of the lower Saint Lawrence River in Quebec. The river widens at this place, later becoming a bay that discharges into the Atlan ...
, Saguenay-Lac Saint-Jean
Lac Saint-Jean (, ) is a large, relatively shallow lake in south-central Quebec, Canada, in the Laurentian Highlands. It is situated north of the Saint Lawrence River, into which it drains via the Saguenay River. It covers an area of , and is ...
(Saguenéen), Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
-Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands ...
, Beauce Beauce may refer to:
* Beauce, France, a natural region in north-central France
* Beaucé, a commune in the Ille-et-Vilaine department, Brittany, France
* Beauce, Quebec
Beauce (; ) is a historical and traditional region of Quebec, Canada, lo ...
(Beauceron), the Eastern Townships
The Eastern Townships (, ) is a historical administrative region in southeastern Quebec, Canada. It lies between the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands, St. Lawrence Lowlands and the American border, and extends from Granby, Quebec, Granby in ...
, Mauricie-Haute-Mauricie ( Magoua), Greater Montreal
Greater Montreal (, ) is the most populous metropolitan area in Quebec and the second most populous in Canada after Greater Toronto. In 2015, Statistics Canada identified Montreal's Census Metropolitan Area (CMA) as with a population of 4,02 ...
, Eastern Montreal- Laval, Rouyn-Noranda
Rouyn-Noranda (; Canada 2021 Census, 2021 population 42,313) is a city on Osisko Lake in the Abitibi-Témiscamingue region of Quebec, Canada.
The city of Rouyn-Noranda is coextensive with a territory equivalent to a regional county municipalit ...
and Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord (Region 09) (, ; ) is an List of regions of Quebec, administrative region of Quebec, on the Quebec-Labrador peninsula, Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, Canada.
The region runs along the St. Lawrence River and then the Gulf of St. Lawrence, ...
. There are 4 accents off the mainland, 1 on the Isle-aux-Coudres
L'Isle-aux-Coudres (), is a municipality located on island aux Coudres, in the St. Lawrence River, in Charlevoix Regional County Municipality, Capitale-Nationale region, Quebec, Canada.
Variations of the official name are: La Baleine, L'Île-au ...
, and 3 on the Îles-de-la-Madeleine: the accents of ''Villages Medelinots'', ''Havre-aux-Maisons'', and ''Havre-Aubert''. Finally, there are 2 accents that cross provincial borders: the accents of Outaouais
Outaouais (, ; also commonly called The Outaouais) is a region of western Quebec, Canada. It includes the city of Gatineau, the municipality of Val-des-Monts, the municipality of Cantley, Quebec, Cantley and the Papineau Regional County Municipal ...
-Eastern Ontario
Eastern Ontario (census population 1,892,332 in 2021) () is a secondary region of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It occupies a wedge-shaped area bounded by the Ottawa River and Quebec to the northeast and east, the St. Lawr ...
(Outaouais) and Témiscouata- Madawaska (Brayon
Brayons (; ), also called Madawaskayens, are a Francophone people inhabiting the area in and around Madawaska County, New Brunswick, Canada, and some parts of northern Maine.
In French, Brayons are referred to by the masculine or the feminine ...
). There are also people in Quebec who will naturally speak using ''Standard Québécois'' or Joual
''Joual'' () is an accepted name for the linguistic features of Quebec French that are associated with the French-speaking working class in Montreal which has become a symbol of national identity for some. ''Joual'' has historically been stigma ...
, both of which are considered sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language ( non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, age group, or other social group.
Sociolects involve both passive acquisit ...
s rather than regional accents.
Fragility and protection of French
 During the days of New France, there began to be an extremely pronounced demographic increase of anglophones versus francophones in North America, a trend which continues to this day. In 1700, for every 250,000 English-speakers, there was 16,500 French-speakers.
After the conquest of 1759, this reality became more brutal for Quebec, which now had to avoid assimilation by the British Empire's regime and survive culturally as well as linguistically.
Still today, as French's demographic weight on the continent and in Canada continues to decline, Quebec faces the threat of assimilation. Since 2011, the population with French as their mother tongue on the
During the days of New France, there began to be an extremely pronounced demographic increase of anglophones versus francophones in North America, a trend which continues to this day. In 1700, for every 250,000 English-speakers, there was 16,500 French-speakers.
After the conquest of 1759, this reality became more brutal for Quebec, which now had to avoid assimilation by the British Empire's regime and survive culturally as well as linguistically.
Still today, as French's demographic weight on the continent and in Canada continues to decline, Quebec faces the threat of assimilation. Since 2011, the population with French as their mother tongue on the Island of Montreal
The Island of Montreal (, ) is an island in southwestern Quebec, Canada, which is the site of a number of municipalities, including most of the city of Montreal, and is the most populous island in Canada. It is the main island of the Hochelag ...
, Quebec's metropolis, has fallen below 50%, with only 49% of the population being francophone due to a sharp increase in the immigrant allophone
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is one of multiple possible spoken soundsor '' phones''used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, the voiceless plos ...
population (whose mother tongue is neither French nor English).
Efforts have been made to preserve the primacy of the French language in Quebec. Such efforts include: instating the Charter of the French language
The ''Charter of the French Language'' (, ), also known as Bill 101 (, ), is a law in the Canadian province of Quebec defining French, the language of the majority of the population, as the official language of the provincial government. It is th ...
, Quebec's participation in the Francophonie
The Francophonie or Francophone world is the whole body of people and organisations around the world who use the French language regularly for private or public purposes. The term was coined by Onésime Reclus in 1880 and became important a ...
since 1971, French immigration to Quebec, etc. Several institutions seek to protect and promote French such as the , the Superior Council of the French Language, the Commission de toponymie du Québec
The Commission de toponymie du Québec (, ''Toponymy Commission of Québec'') is the Government of Québec's public body responsible for cataloging, preserving, making official and publicizing Québec's place names and their origins according to th ...
, etc.
English
As of 2011,English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Culture, language and peoples
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
* ''English'', an Amish ter ...
is the mother tongue of nearly 650,000 Quebecers (8% of the population). Anglo-Quebecers constitute the second largest linguistic group in Quebec. In addition, in 2001, roughly 50,000 people (0.7% of the population) considered their mother tongue to be both French and English. According to the latest censuses of 2001, 2006, 2011 and 2016, the percentage of anglophones in the population has more or less stabilized, but in absolute numbers, they are constantly increasing. Allophones
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is one of multiple possible spoken soundsor '' phones''used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, the voiceless plosi ...
, on the other hand, are increasing sharply in absolute numbers as well as in percentage. According to the 2016 census, 49.1% of people living in Quebec say they can conduct a conversation in English (English as mother tongue or as a second language). As for French-English bilingualism, 44.5% of people in Quebec state that they are bilingual, that is to say, able to conduct a conversation in both French and English.
English made its first appearance in Quebec in 1760, when the British invaded and conquered ''Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
'' (New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
). Shortly afterwards, the first English and Scottish merchants came to settle in the cities of Québec City and Montreal. In 1784, United Empire Loyalists
United Empire Loyalist (UEL; or simply Loyalist) is an honorific title which was first given by Guy Carleton, 1st Baron Dorchester, the 1st Lord Dorchester, the governor of Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Quebec and Governor General, governor ...
flooded Quebec following their expulsion from the Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
during the United States' War of Independence. This dramatically increased the number of English speakers in Quebec. These Loyalists, avoiding the French-speaking and Catholic countryside, settled mainly in then underdeveloped regions, such as the Eastern Townships
The Eastern Townships (, ) is a historical administrative region in southeastern Quebec, Canada. It lies between the Great Lakes–St. Lawrence Lowlands, St. Lawrence Lowlands and the American border, and extends from Granby, Quebec, Granby in ...
and the Outaouais
Outaouais (, ; also commonly called The Outaouais) is a region of western Quebec, Canada. It includes the city of Gatineau, the municipality of Val-des-Monts, the municipality of Cantley, Quebec, Cantley and the Papineau Regional County Municipal ...
. The proclamation of the Act of Union of 1840 caused massive immigration from the British Isles to Quebec, which introduced Celtic language
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves ...
s for the first time, and was aimed at the linguistic assimilation of the French-speaking population, which had a considerable impact on French-language culture in Quebec. Today, Anglo-Quebecers reside mainly in Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and the Pontiac Pontiac most often refers to:
* Pontiac (Odawa leader) ( – 1769), Native American war chief
*Pontiac (automobile), a former General Motors brand
Pontiac may also refer to:
Places and jurisdictions Canada
* Pontiac, Quebec, a municipality
** Apo ...
region.
Anglophones in Quebec have several institutions and infrastructural systems. At the school level, anglophones in Quebec have several school boards grouped together into the ''Association des commissions scolaire anglophones du Québec''. In terms of media, anglophones own, among others, the ''Montreal Gazette
''The Gazette'', also known as the ''Montreal Gazette'', is a Canadian English-language broadsheet daily newspaper which is owned by Postmedia Network. It is published in Montreal, Quebec, Canada.
It is the only English-language daily newspape ...
'' in Montreal, and the '' Chronicle-Telegraph'' in Quebec City. Other organisations include the Quebec Writers' Federation
The Quebec Writers’ Federation (QWF) is a not-for-profit registered charitable organization representing and serving the English-language literary community in the province of Quebec, Canada.
QWF is a literary arts presenter, provides profession ...
, which is a group of English-speaking Quebec authors, and the Voice of English-speaking Quebec, which represents the interests of the English-speaking community in the Québec region
Image:Regions administratives du Quebec.png, 350px, The seventeen administrative regions of Quebec.
poly 213 415 206 223 305 215 304 232 246 230 255 266 251 283 263 289 280 302 291 307 307 315 308 294 318 301 333 299 429 281 432 292 403 311 388 ...
.
Other languages
The term "allophone
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is one of multiple possible spoken soundsor '' phones''used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, the voiceless plos ...
" is used to refer to people whose mother tongue is neither French nor English. We can distinguish two groups of allophones: people who speak indigenous languages, and those who speak so-called immigrant languages.
In the 2016 census, where one could note more than one language as their mother tongue, Quebec had 1,171,045 people (14.5% of the population) who reported a mother tongue that was neither French nor English, and 1,060,830 people (13.2% of the population) who did not declare French or English as a mother tongue at all. In this census, 47,025 (0.6% of the population) reported an aboriginal language as a mother tongue, while 1,124,020 (13.9% of the population) reported an immigrant language as a mother tongue.
Indigenous languages
Three families of aboriginal languages exist in Quebec, which encompass eleven languages. Each of these languages belong to and are spoken by members of a specific ethnic group. Sometimes, the language in question is spoken natively by all members of the group, sometimes they are spoken only by a few individuals. These languages are also sometimes sub-divided into different dialects in the indigenous communities. *
* Algonquian language family
The Algonquian languages ( ; also Algonkian) are a family of Indigenous languages of the Americas and most of the languages in the Algic language family are included in the group. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from t ...
** Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
(spoken by the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
s of Centre-du-Québec
Centre-du-Québec (, ''Central Quebec'') is a region of Quebec, Canada. The main centres are Drummondville, Victoriaville, and Bécancour. It has a land area of and a 2016 census population of 242,399 inhabitants.
Description
The Centre-du- ...
)
** Algonquin
Algonquin or Algonquian—and the variation Algonki(a)n—may refer to:
Languages and peoples
*Algonquian languages, a large subfamily of Native American languages in a wide swath of eastern North America from Canada to Virginia
**Algonquin la ...
(spoken by the Algonquins
The Algonquin people are an Indigenous people who now live in Eastern Canada and parts of the United States. They speak the Algonquin language, which is part of the Algonquian language family. Culturally and linguistically, they are closely ...
of the Outaouais
Outaouais (, ; also commonly called The Outaouais) is a region of western Quebec, Canada. It includes the city of Gatineau, the municipality of Val-des-Monts, the municipality of Cantley, Quebec, Cantley and the Papineau Regional County Municipal ...
)
** Maliseet-passamaquoddy (spoken by the Maliseet
The Wolastoqiyik, (, also known as the Maliseet or Malecite () are an Algonquian-speaking First Nation of the Wabanaki Confederacy. They are the Indigenous people of the Wolastoq ( Saint John River) valley and its tributaries. Their terri ...
of Bas-Saint-Laurent
The Bas-Saint-Laurent (, 'Lower Saint-Lawrence) is an administrative region of Quebec located along the south shore of the lower Saint Lawrence River in Quebec. The river widens at this place, later becoming a bay that discharges into the Atlan ...
)
** Mi'kmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Bru ...
(spoken by the Micmacs of Gaspésie and the Magdalen Islands
The Magdalen Islands (, ) are a Canadian archipelago in the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Since 2005, the 12-island archipelago is divided into two municipalities: the majority-francophone Municipality of Îles-de-la-Madeleine and the majority-angloph ...
)
** the linguistic continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated variet ...
of:
*** Atikamekw
The Atikamekw are an Indigenous people in Canada. Their historic territory, ('Our Land'), is in the upper Saint-Maurice River valley of Quebec (about north of Montreal). One of the main communities is Manawan, about northeast of Montreal. ...
(spoken by the Attikamek
The Atikamekw are an Indigenous people in Canada. Their historic territory, ('Our Land'), is in the upper Saint-Maurice River valley of Quebec (about north of Montreal). One of the main communities is Manawan, about northeast of Montreal. ...
s of Lanaudière
Lanaudière (, ) is one of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada, situated immediately to the northeast of Montreal. It has a total population ( 2016 Census) of 494,796 inhabitants, an increase of 4.9% over the 2011 census.
Geogr ...
and Mauricie
Mauricie () is a traditional and current administrative region of Quebec. La Mauricie National Park is contained within the region, making tourism in Mauricie popular. The region has a land area of 35,860.05 km2 (13,845.64 sq mi) and a popu ...
)
*** Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
(spoken by the Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
s of Nord-du-Québec
Nord-du-Québec (; ) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.
Spread over nearly 14 degrees of latitude, north of the 49th parallel, the region covers on the Labrador Peninsula, making ...
)
*** Innu-aimun
Innu-aimun or Montagnais is an Algonquian language spoken by over 10,000 Innu in Labrador and Quebec in Eastern Canada. It is a member of the Cree–Montagnais–Naskapi dialect continuum and is spoken in various dialects depending on the com ...
(spoken by the Innu-Montagnais of the Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord (Region 09) (, ; ) is an List of regions of Quebec, administrative region of Quebec, on the Quebec-Labrador peninsula, Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, Canada.
The region runs along the St. Lawrence River and then the Gulf of St. Lawrence, ...
and Saguenay-Lac-Saint-Jean)
*** Naskapi
The Naskapi (Nascapi, Naskapee, Nascapee) are an Indigenous people of the Subarctic native to the historical region St'aschinuw (ᒋᑦ ᐊᔅᒋᓄᐤ, meaning 'our Clusivity, nclusiveland'), which was located in present day northern Qu ...
(spoken by the Innu-Naskapi of the Côte-Nord
Côte-Nord (Region 09) (, ; ) is an List of regions of Quebec, administrative region of Quebec, on the Quebec-Labrador peninsula, Quebec-Labrador Peninsula, Canada.
The region runs along the St. Lawrence River and then the Gulf of St. Lawrence, ...
)
* Inuit-Aleut language family
** Nunavimmiutitut ( Inuktitut dialect spoken by the Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwe ...
of Nord-du-Québec
Nord-du-Québec (; ) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.
Spread over nearly 14 degrees of latitude, north of the 49th parallel, the region covers on the Labrador Peninsula, making ...
)
* Iroquoian language family
** Mohawk
Mohawk may refer to:
Related to Native Americans
*Mohawk people (Kanien’kehá:ka), an indigenous people of North America (Canada and New York)
*Mohawk language (Kanien’kéha), the language spoken by the Mohawk people
*Mohawk hairstyle, from a ...
, also known as "agnier" (spoken by the Iroquois-Mohawks of Montérégie
Montérégie () is an administrative region in the southwest part of Quebec. It includes the cities of Boucherville, Brossard, Châteauguay, Longueuil, Saint-Hyacinthe, Saint-Jean-sur-Richelieu, Salaberry-de-Valleyfield and Vaudreuil-Dorion.
...
and the Laurentides
The Laurentides (, ) is a region of Quebec. While it is often called the Laurentians in English, the region includes only part of the Laurentian Mountains. It has a total land area of and its population was 589,400 inhabitants as of the 2016 C ...
)
** Wendat
The Huron-Wendat Nation (or Huron-Wendat First Nation) is an Iroquoian-speaking nation that was established in the 17th century. In the French language, used by most members of the First Nation, they are known as the . The French gave the nickn ...
(spoken by the Huron-Wendat of the Capitale-Nationale
Capitale-Nationale (; ) is one of the 17 administrative regions of Quebec. It is anchored by the provincial capital, Quebec City, and is largely coextensive with that city's metropolitan area. It has a land area of 18,684.78 km2. It reported ...
)
In the 2016 census, 50,895 people in Quebec said they knew at least one indigenous language. Furthermore, 45,570 people declared having an aboriginal language as their mother tongue. For 38,995 of them, it was the language most frequently spoken at home. Additionally, 1,195 people who did not have an aboriginal language as their mother tongue reported using an aboriginal language most often at home.
In Quebec, most indigenous languages are currently transmitted quite well from one generation to the next with a mother tongue retention rate of 92%.
Immigrant languages
In the 2016 census, 1,124,020 people declared having an immigrant language as their mother tongue in Quebec. The most cited languages areArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
(2.5% of the total population), Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many countries in the Americas
**Spanish cuisine
**Spanish history
**Spanish culture
...
(1.9%), Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
(1.4%), Creole languages (mainly Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole (; , ; , ), or simply Creole (), is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language spoken by 10 to 12million people worldwide, and is one of the two official languages of Haiti (the other being French), where it ...
) (0.8%) and Mandarin
Mandarin or The Mandarin may refer to:
Language
* Mandarin Chinese, branch of Chinese originally spoken in northern parts of the country
** Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Mandarin, the official language of China
** Taiwanese Mandarin, Stand ...
(0.6%).
Both the number and proportion of allophones have been increasing in Quebec since the 1951 census.
In 2015, the vast majority (89%) of young allophone students in Quebec attended French-language schools.
Mother tongue language
Language spoken at home
Knowledge of languages
The question on knowledge of languages allows for multiple responses. The following figures are from the2021 Canadian Census
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canada, Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, whic ...
and the 2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial census. ...
, and lists languages that were selected by at least one per cent of respondents.
Religion
Religion, more precisely theRoman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, has long occupied a central and integral place in Quebec society since the arrival of the first French settlers in New France. However, since the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
and the Second Vatican Council
The Second Ecumenical Council of the Vatican, commonly known as the or , was the 21st and most recent ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. The council met each autumn from 1962 to 1965 in St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City for session ...
in the 1960s, there has been a real separation between state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
and religion, and society in general sees religion as a private matter.
From the beginning of ''Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
'', and throughout French-Canadian history, catholicism and the Catholic Church have played a preponderant role in the social and political development of Quebec.
The first mass in what would become Quebec was celebrated in 1535, by the priest accompanying Jacques Cartier
Jacques Cartier (; 31 December 14911 September 1557) was a French maritime explorer from Brittany. Jacques Cartier was the first Europeans, European to describe and map the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and the shores of the Saint Lawrence River, wh ...
on his voyage to the New World. Amerindians were evangelized by Catholic missionaries
Missionary work of the Catholic Church has often been undertaken outside the geographically defined parishes and dioceses by religious orders who have people and material resources to spare, and some of which specialized in missions. Eventually, p ...
before the founding of parishes
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
. In 1627, Cardinal Richelieu
Armand Jean du Plessis, 1st Duke of Richelieu (9 September 1585 – 4 December 1642), commonly known as Cardinal Richelieu, was a Catholic Church in France, French Catholic prelate and statesman who had an outsized influence in civil and religi ...
recited a royal proclamation
A proclamation (Lat. ''proclamare'', to make public by announcement) is an official declaration issued by a person of authority to make certain announcements known. Proclamations are currently used within the governing framework of some nations ...
by Louis XIII
Louis XIII (; sometimes called the Just; 27 September 1601 – 14 May 1643) was King of France from 1610 until his death in 1643 and King of Navarre (as Louis II) from 1610 to 1620, when the crown of Navarre was merged with the French crown.
...
which banished all non-Catholics, including Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
, from New France. In 1658, the apostolic vicariate
An apostolic vicariate is a territorial jurisdiction of the Catholic Church under a titular bishop centered in missionary regions and countries where dioceses or parishes have not yet been established. The status of apostolic vicariate is often ...
of Quebec was founded, followed by the Archdiocese of Quebec
The Archdiocese of Québec (; ) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Quebec, Canada. It is the oldest episcopal see in the New World north of Mexico and the primatial see of Canada. The Archdioce ...
in 1674. The archbishop of Quebec
The archbishop of Quebec is the head of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec, who is responsible for looking after its spiritual and administrative needs. As the archdiocese is the metropolitan bishop, metropolitan see of the ecclesiastical p ...
, who today is the primate
Primates is an order (biology), order of mammals, which is further divided into the Strepsirrhini, strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and Lorisidae, lorisids; and the Haplorhini, haplorhines, which include Tarsiiformes, tarsiers a ...
of the Catholic Church of Canada, was once part of the Sovereign Council of New France
The Sovereign Council of New France (, ), or simply Sovereign Council (), was a governing body in New France. It served as both Supreme Court for the colony of New France, as well as a policy-making body, though this latter role diminished over ti ...
.
The extraordinary power that the Catholic Church once had in Quebec is reflected in all areas of culture, from language to the fine arts, theater, literature and film. The golden age for ecclesiastics would come in the mid-nineteenth century (around 1840) as this was a period during which the Church, influenced by ultramontanism
Ultramontanism is a clerical political conception within the Catholic Church that places strong emphasis on the prerogatives and powers of the Pope. It contrasts with Gallicanism, the belief that popular civil authority—often represented b ...
, concretized its influence (see Clericalism in Quebec). The influence of the Church began to wane a hundred years later, when, after the Grande Noirceur
The Grande Noirceur (, English, Great Darkness) refers to the regime of conservative policies undertaken by the governing body of Quebec Premier Maurice Le Noblet Duplessis from 1936 to 1939 and from 1944 to 1959.
In today's historiography of ...
, Quebec society was profoundly transformed by the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
. Created in 1966, the deals with current issues concerning ethical and moral values (ex. gay marriage, euthanasia and abortion).
Several holy men and women from Quebec have been recognized for their venerable actions and canonized
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of sa ...
as saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the ...
s:
* Saint Brother André Bessette
André Bessette, C.S.C. (born Alfred; 9 August 1845 – 6 January 1937), commonly known as Brother André () and since his canonization as Saint André of Montreal, was a lay brother of the Congregation of Holy Cross and a significant figure of ...
canonized in 2010 by Pope Benedict XVI
Pope BenedictXVI (born Joseph Alois Ratzinger; 16 April 1927 – 31 December 2022) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 19 April 2005 until his resignation on 28 February 2013. Benedict's election as p ...
.
* Saint Kateri Tekakwitha
Kateri Tekakwitha ( in Mohawk), given the name Tekakwitha, baptized as Catherine ("Kateri" in Mohawk), and informally known as Lily of the Mohawks (1656 – April 17, 1680), is a Mohawk/ Algonquin Catholic saint and virgin. Born in the Mohawk v ...
canonized on October 21, 2012 by Pope Benedict XVI.
* Saint Mary of the Incarnation canonized in 2014 by Pope François
Pope Francis (born Jorge Mario Bergoglio; 17 December 1936 – 21 April 2025) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 13 March 2013 until Death and funeral of Pope Francis, his death in 2025. He was the fi ...
.
* Saint François de Laval
Francis-Xavier de Montmorency-Laval, commonly referred to as François de Laval (; 30 April 1623 – 6 May 1708), was a French Catholic prelate who served as Apostolic Vicar of New France from 1658 to 1674 and as Bishop of Quebec from its creat ...
canonized in 2014 by Pope François.
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, a practice consisting of reformed catholicism, has been present in Quebec for a long time. From the very beginning of ''Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
'', several Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
of the calvinist
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Protestantism, Continenta ...
religion were present in Quebec. Huguenots have been identified in almost all classes of society: settlers, fishermen, daughters of the king, etc. During the early French Regime, the number of protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
immigrants was estimated to be 1,450 people. In 1627, protestantism became no longer tolerated in New France. After Quebec was conquered by the British, the Protestant religion, more particularly of the Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
faith, became tolerated again. This was because British immigrants who came to certain regions of Quebec followed this religion.
The preceded Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
in Quebec.
While the first synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
was established in Montreal in 1777, Jews remained a negligible religious group in Quebec until the early 20th century when a wave of Jewish immigrants settled in Montreal. The Jewish community of today, established mainly on the island of Montreal, now numbers about 120,000 people. In 2010, this community was made up of 26.1% traditionalist Jews, 24.3% orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pag ...
, 15.2% conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
, 9% reconstructionist and reformist
Reformism is a political tendency advocating the reform of an existing system or institution – often a political or religious establishment – as opposed to its abolition and replacement via revolution.
Within the socialist movement, ref ...
, and 25.4% of Montreal Jews say they have no religious affiliation. In the 20th century, successive waves of immigrants from Africa, Asia, Greece, Ireland and Italy settled in Montreal, bringing their cultural and religious customs. Some religious communities, such as Eastern Christians
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations further east, south or north. The term does not describe a ...
, then established places of worship.
Religion and politics
Many aspects of life for French-speaking Quebeckers remained dominated by the Catholic Church in the decades following 1867. The Church operated many of the institutions of the province, including most French-language schools, hospitals, and charitable organizations. The leader of the Catholic Church in Quebec was the Bishop of Montreal, and from 1840 to 1876 this wasIgnace Bourget
Ignace Bourget (; October 30, 1799 – June 8, 1885) was a Canadian Roman Catholic priest who held the title of Bishop of Montreal from 1840 to 1876. Born in Lévis, Quebec, in 1799, Bourget entered the clergy at an early age, undertook several ...
, an opponent of liberalism. Bourget eventually succeeded in gaining more influence than the liberal, reformist Institut Canadien. At his most extreme, Bourget went so far as to deny a Church burial to Joseph Guibord, a member of the Institut, in 1874. A court decision forced Bourget to allow Guibord to be buried in a Catholic cemetery, but Bourget deconsecrated the burial plot of ground, and Guibord was buried under army protection. The conservative approach of the Catholic Church was the major force in Quebec society until the reforms of the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
during the 1960s. In 1876, Pierre-Alexis Tremblay
Pierre-Alexis "Pitre" Tremblay (December 27, 1827 – January 4, 1879) was a surveyor and Quebec political figure. He was a Liberal Member of Parliament from 1867 to 1875 and 1878 to 1879.
He was born in La Malbaie, Lower Canada, in 1827 an ...
was defeated in a federal by-election because of pressure from the Church on voters, but succeeded in getting his loss annulled with the help of a new federal law. He quickly lost the subsequent election. In 1877, the Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
sent representatives to force the Quebec Churchto minimize its interventions in the electoral process.
Lionel Groulx
Lionel Groulx (; 13 January 1878 – 23 May 1967) was a Canadian Roman Catholic priest, historian, professor, public intellectual and Quebec nationalist.
Biography
Early life and ordination
Lionel Groulx, né Joseph Adolphe Lyonel Groulx, ...
wanted to build a nationalistic French-Canadian identity, in purpose to protect the power of the Church and dissuade the public from popular-rule and secularist views. Groulx propagated French-Canadian nationalism and argued that maintaining a Roman Catholic Quebec was the only means to 'emancipate the nation against English power.' He believed the powers of the provincial government of Quebec could and should be used within Confederation, to bolster provincial autonomy (and thus Church power), and advocated it would benefit the French-Canadian nation economically, socially, culturally and linguistically. Groulx successfully promoted Québécois nationalism and the ultra-conservative Catholic social doctrine, to which the Church would maintain dominance in political and social life in Quebec. In the 1920s–1950s, this form of traditionalist Catholic nationalism became known as clerico-nationalism
Clerico-Nationalism was a right-wing ideology current in Quebec from the years after World War I until the end of the 1950s, from the premiership of Maurice Duplessis until the Quiet Revolution. Clerico-nationalism was a traditionalist, religio ...
.
In 1936, Maurice Duplessis
Maurice Le Noblet Duplessis, (; April 20, 1890 – September 7, 1959) byname "Le Chef" (, "The Boss"), was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 16th premier of Quebec. A Conservatism in Canada, conservative, Quebec nationalism, ...
hung a crucifix
A crucifix (from the Latin meaning '(one) fixed to a cross') is a cross with an image of Jesus on it, as distinct from a bare cross. The representation of Jesus himself on the cross is referred to in English as the (Latin for 'body'). The cru ...
in the National Assembly of Quebec
The National Assembly of Quebec (, ) is the Legislature, legislative body of the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec in Canada. Legislators are called MNAs (Members of the National Assembly; ). The lieutenant governor of Que ...
. It hung there for 83 years, until it was removed on 10 July 2019.
During the 1940s and 1950s Quebec Premier Maurice Duplessis
Maurice Le Noblet Duplessis, (; April 20, 1890 – September 7, 1959) byname "Le Chef" (, "The Boss"), was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 16th premier of Quebec. A Conservatism in Canada, conservative, Quebec nationalism, ...
party, the Union Nationale, often had the active support of the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
during political campaigns, using the slogan ''Le ciel est bleu; l'enfer est rouge'' ("Heaven is blue; hell is red"; red is the colour of the Liberal party, and blue was the colour of the Union Nationale).
Sharia law
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on scriptures of Islam, particularly the Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, inta ...
is explicitly banned in Quebec, upheld by a unanimous vote against it in 2005 by the National Assembly.
Churches
The oldestparish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
in North America is the Cathedral-Basilica of Notre-Dame de Québec
The Cathedral-Basilica of Notre-Dame de Québec ("Our Lady of Quebec City"), located at 16, rue de Buade, Quebec City, Quebec, is the primatial church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec. It is the oldest church in Canada and was the f ...
. Its construction began in 1647, when it was then known under the name ''Notre-Dame-de-la-Paix'', and it was finished in 1664. Its first mass was celebrated by Father Vimont on December 24, 1650. This church obtained the status of cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
in 1674, when François de Laval
Francis-Xavier de Montmorency-Laval, commonly referred to as François de Laval (; 30 April 1623 – 6 May 1708), was a French Catholic prelate who served as Apostolic Vicar of New France from 1658 to 1674 and as Bishop of Quebec from its creat ...
became archbishop of Quebec
The archbishop of Quebec is the head of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Quebec, who is responsible for looking after its spiritual and administrative needs. As the archdiocese is the metropolitan bishop, metropolitan see of the ecclesiastical p ...
, and then the status of minor basilica
Basilicas are Catholic church buildings that have a designation, conferring special privileges, given by the Pope. Basilicas are distinguished for ceremonial purposes from other churches. The building need not be a basilica in the architectura ...
in 1874. It was also rebuilt twice after the siege of Quebec in 1759 and the fire of 1922.
The most frequented place of worship in Quebec is the Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré
The Basilica of Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré () is a basilica set along the Saint Lawrence River in Quebec, Canada, east of Quebec City, and one of the six national shrines of Canada. It has been credited by the Catholic Church with many miracles of c ...
. This basilica welcomes millions of visitors each year, especially during the novena
A novena (from , "nine") is an ancient tradition of devotional praying in Christianity, consisting of private or public prayers repeated for nine successive days or weeks. The nine days between the Feast of the Ascension and Pentecost, when the ...
of Saint Anne
According to apocrypha, as well as Christianity, Christian and Islamic tradition, Saint Anne was the mother of Mary, mother of Jesus, Mary, the wife of Joachim and the maternal grandmother of Jesus. Mary's mother is not named in the Bible's Gosp ...
, on July 26. The Sainte-Anne-de-Beaupré basilica is recognized for its numerous miracles, which is why thousands of crutches can be found at its entrance.
Saint Joseph's Oratory
Saint Joseph's Oratory of Mount Royal ( French: ''Oratoire Saint-Joseph-du-Mont-Royal'') is a Roman Catholic minor basilica and national shrine located at 3800 Queen Mary Road in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood on Mount Royal's Westmount S ...
is the largest place of worship in the world dedicated to Saint Joseph
According to the canonical Gospels, Joseph (; ) was a 1st-century Jewish man of Nazareth who was married to Mary, the mother of Jesus, and was the legal father of Jesus.
Joseph is venerated as Saint Joseph in the Catholic Church, Eastern O ...
. Located beside Mount Royal
Mount Royal (, ) is a mountain in the city of Montreal, immediately west of Downtown Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The city's name is derived from the mountain's name.
The mountain is part of the Monteregian Hills situated between the Laurentian M ...
, it is known for its 283 steps, which pilgrims come to climb on their knees every year, reciting a prayer on each of the steps.
Many pilgrimages include places such as Saint Benedict Abbey, , Notre-Dame de Montréal Basilica
Notre-Dame Basilica of Montreal ( French: ''Basilique Notre-Dame de Montréal'') is a minor basilica of the Catholic Church in the historic Old Montreal district of Montreal in Quebec, Canada. It is located at 110 Notre-Dame Street West, at the ...
, Marie-Reine-du-Monde de Montréal Basilica-Cathedral, Saint-Michel Basilica-Cathedral
Saint-Michel Basilica-Cathedral () is a Roman Catholic minor basilica and cathedral dedicated to St. Michael located in Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada. The church is the seat of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Sherbrooke. The basilica was decreed on ...
, Saint-Patrick's Basilica, etc.
Another important place of worship in Quebec is the anglican Holy Trinity Cathedral, which was erected between 1800 and 1804. It was the first anglican cathedral built outside the British Isles.
In August 2019, the Minister of Culture
A culture minister or a heritage minister is a common cabinet position in governments. The culture minister is typically responsible for cultural policy, which often includes arts policy (direct and indirect support to artists and arts organiza ...
, Nathalie Roy
Nathalie Roy (born May 8, 1964) is a Canadian politician. She is a member of the National Assembly of Quebec for the riding of Montarville, first elected in the 2012 election. From 2018 to 2022 she served as minister of Culture and Communic ...
, announced the allocation of $15 million to preserve the cultural heritage that the churches of Quebec embody, and $5 million for the requalification of places of worship.
Migration
Immigration
The 2021 census reported thatimmigrants
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short- ...
(individuals born outside Canada) comprise 1,210,595 persons or 14.6 percent of the total population of Quebec.Recent immigration
The2021 Canadian census
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canada, Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, whic ...
counted a total of 202,740 people who immigrated to Quebec between 2016 and 2021.Interprovincial migration
Since it began being recorded in 1971 until 2018, each year Quebec has had negative interprovincial migration, and among the provinces it has experienced the largest net loss of people due to the effect. Between 1981 and 2017, Quebec lost 229,700 people below the age of 45 to interprovincial migration. Per capita, Quebec has lost significantly fewer people than other provinces. This is due to the large population of the province and the very low migration rate of francophone Quebeckers. However, Quebec receives much fewer than average in-migrants from other provinces. In Quebec,allophones
In phonology, an allophone (; from the Greek , , 'other' and , , 'voice, sound') is one of multiple possible spoken soundsor '' phones''used to pronounce a single phoneme in a particular language. For example, in English, the voiceless plosi ...
are more likely to migrate out of the province than average: between 1996 and 2001, over 19,170 migrated to other provinces; 18,810 of whom migrated to Ontario.
''Source: Statistics Canada''Statistics Canada, table 051-0012''Interprovincial migrants, by age group and sex, Canada, provinces and territories, annual''.
/ref>
See also
*Demographics of Canada
Statistics Canada conducts a country-wide census that collects demographic data every five years on the first and sixth year of each decade. The 2021 Canadian census enumerated a total population of 36,991,981, an increase of around 5.2 percent ...
*Demographic history of Quebec
This is a demographic history of Quebec chronicling the evolution of the non-indigenous population in Quebec.
Historical Census population
See also
*Demographics of Quebec
*History of Quebec
*Timeline of Quebec history
* the revenge of the ...
* Demolinguistics of Quebec
*Demographics of Montreal
The Demographics of Montreal concern population growth and structure for Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The information is analyzed by Statistics Canada and compiled every five years, with the most recent census having taken place in 2021.
Population ...
*'' Cahiers québécois de démographie'' academic journal
* Immigration to Quebec
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-ter ...
*Immigration to Canada
According to the 2021 Canadian census, immigrants in Canada number 8.3 million persons and make up approximately 23 percent of Canada's total population. This represents the eighth-largest Immigration, immigrant population in the world, whi ...
*Population of Canada by province and territory
Canada is divided into 10 provinces and three territories. The majority of Canada's population is concentrated in the areas close to the Canada–US border. Its four largest provinces by area (Ontario, Quebec, British Columbia, and Alberta) a ...
Notes
References
External links
Institut de la statistique du Québec
{{People of Canada
Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
Quebec society