Punjab (; ; also
romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical,
cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, and
historical region
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
in South Asia. It is located in the
northwestern part of the
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, comprising areas of modern-day eastern
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and
northwestern India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Pakistan's major cities in Punjab are
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
,
Faisalabad
Faisalabad, formerly known as Lyallpur, is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, second-largest city and primary List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, industrial center of the Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan ...
,
Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, third-largest city in the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is a commercial and industrial hub, being the list of cities in P ...
,
Gujranwala
Gujranwala is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fourth most-populous city in the Pakistani province of Punjab. Located in northern-central Punjab's Rachna Doab, it serves as the headquarters of its Gujranwala District, epony ...
,
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
,
Sialkot
Sialkot (Punjabi language, Punjabi, ) is a city located in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the capital of the Sialkot District and the List of most populous cities in Pakistan, 12th most populous city in Pakistan. The boundaries of Sialkot are joined ...
, and
Bahawalpur
Bahawalpur (Urdu: ; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the 13th largest city of Pakistan and List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, 8th most populous city of Punjab. Bahawalpur is the capital of Bahawalpur Division.
Founded in ...
, while India’s are
Ludhiana
Ludhiana () is the most populous Cities in India, city in the Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab.164.100.161.224
http://164.100.161.224 › filesPDF
Ludhiana State: Punjab Business & Industrial Centre, Tier 2 1 ... The city has an estima ...
,
Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
,
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a city and union territory in northern India, serving as the shared capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. Situated near the foothills of the Shivalik range of Himalayas, it borders Haryana to the east and Punjab in the ...
,
Jalandhar
Jalandhar () is a city in the state of Punjab, India, Punjab in India. With a considerable population, it ranks as the List of cities in Punjab and Chandigarh by population, third most-populous city in the state and is the largest city in the ...
,
Patiala,
Mohali
Mohali, officially Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar or Ajitgarh, is a planned city in the Mohali district in Punjab, India, Punjab, India, which is an administrative and a commercial hub lying south-west of Chandigarh. It is the headquarters of the M ...
, and
Bathinda
Bathinda is a city and municipal corporation in Punjab, India. The city is the administrative headquarters of Bathinda district. It is located in northwestern India in the Malwa Region, west of the capital city of Chandigarh and is the fifth ...
.
Punjab grew out of the settlements along the five rivers, which served as an important route to the
Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
as early as the ancient
Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE ...
, dating back to ,
followed by
migrations of the
Indo-Aryan peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of peoples predominantly found in South Asia, who (traditionally) speak Indo-Aryan languages. Historically, Aryans were the Indo-Iranian speaking pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia int ...
. Agriculture has been the chief economic feature of the Punjab and formed the foundation of
Punjabi culture
Punjabi culture grew out of the settlements along the five rivers (the name ''Punjab'', is derived from two Persian words, ''Panj'' meaning "Five" and ''Âb'' meaning "Water") which served as an important route to the Near East as early as the an ...
.
The Punjab emerged as an important agricultural region, especially following the
Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, or the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period during which technology transfer initiatives resulted in a significant increase in crop yields. These changes in agriculture initially emerged in Developed country , devel ...
during the mid-1960s to the mid-1970s, and has been described as the "
breadbasket
The breadbasket of a country or of a region is an area which, because of the richness of the soil and/or advantageous climate, produces large quantities of wheat or other grain. Rice bowl is a similar term used to refer to Southeast Asia; Calif ...
of both India and Pakistan."
Punjab's history is a tapestry of conflict, marked by the rise of indigenous dynasties and empires. Following
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
's invasion in the 4th century BCE,
allied with Punjabi republics to establish the
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
.
Successive reigns of the
Indo-Greek Kingdom
The Indo-Greek Kingdom, also known as the Yavana Kingdom, was a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic-era Ancient Greece, Greek kingdom covering various parts of modern-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northwestern India.
The term "Indo-Greek Kingdom" ...
,
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
, and
Indo-Scythians
The Indo-Scythians, also known as Indo-Sakas, were a group of nomadic people of Iranic Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into the present-day regions of Afghanistan, Eastern Iran and the northwestern Indian subcontinent: p ...
followed, but were ultimately defeated by Eastern Punjab
Janapada
The Janapadas () () (c. 1100–600 BCE) were the realms, republics (ganapada) and kingdoms (sāmarājya) of the Vedic period in the Indian subcontinent. The Vedic period reaches from the late Bronze Age into the Iron Age: from about 1500 BCE to ...
s such as the
Yaudheya
Yaudheya (Brahmi script: 𑀬𑁅𑀥𑁂𑀬) or Yoddheya Gana (Yoddheya Republic) was an ancient military ganasangha (republic) based in the Eastern region of the Sapta Sindhu, in modern day Haryana. The word Yaudheya is a derivative of the w ...
,
Trigarta Kingdom
Trigarta (also known as Kangra and Jalandhara) was an ancient Indo-Aryan kingdom based in the region of modern day Punjab. The focal point of its administration was situated in Jalandhar. However at its zenith it encompassed the hill terri ...
,
Audumbaras
The Audumbras, or Audumbaras (Hindi;ओदुम्बर) were a north Indian tribal nation east of the Punjab, in the Western Himalaya region. They were the most important tribe of the Himachal, and lived in the lower hills between Sirmaur, C ...
,
Arjunayanas
Arjunayana, Arjunavana, Arjunavayana or Arjunayanaka was an ancient republican people located in Punjab or north-eastern Rajasthan. They emerged as a political power during the Shunga period (). In the Allahabad Pillar Inscription of Samudragupt ...
, and
Kuninda Kingdom.
In the 5th and 6th centuries CE, Punjab faced devastating Hunnic invasions, yet the
Vardhana dynasty
The Pushyabhuti dynasty (IAST: Puṣyabhūti), also known as the Vardhana dynasty, was the ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Thanesar in northern India during the 6th and 7th centuries. The dynasty reached its zenith under its last ruler Harsha ...
emerged triumphant, ruling over
Northern India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
. The 8th century CE witnessed the
Hindu Shahis
The Hindu Shahis, also referred to as the Kabul Shahis and Uḍi Śāhis, were a dynasty established between 843 CE and 1026 CE. They endured multiple waves of conquests for nearly two centuries and their core territory was described as having c ...
rise, known for defeating the
Saffarid dynasty
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conqu ...
and the
Samanid Empire
The Samanid Empire () was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, ruled by a dynasty of Iranian ''dehqan'' origin. The empire was centred in Khorasan and Transoxiana, at its greatest extent encompassing northeastern Iran and Central Asia, from 819 ...
. Concurrently, the
Tomara dynasty
The Tomaras of Delhi (also called Tomar dynasty in modern vernaculars due to schwa deletion) ruled parts of present-day Delhi and Haryana in India during 8th–12th century. Their rule over this region is attested to by multiple inscriptions ...
and
Katoch Dynasty
Katoch is a Chandravanshi Rajput clan. Their areas of residence are mainly in the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, and Uttarakhand, and the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. Traditionally resided in Kangra Fort, Trigarta Kingd ...
controlled eastern Punjab, resisting
Ghaznavid
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus to the Indus Va ...
invasions.
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
took hold in Western Punjab under Ghaznavid rule. The Delhi Sultanate then succeeded the Ghaznavids in which the
Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
and
Sayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451 for 37 years.See:
* M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill
* The Islamic frontier in the east: Expansion ...
Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
s are described as Punjabi origin.
The 15th century saw the emergence of the
Langah Sultanate
The Langah Sultanate was a late medieval sultanate based in the Punjab region in the western Indian subcontinent between the 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the lower Doab tract with Multan at its centre. The Langah Sult ...
in south Punjab, acclaimed for its victory over the
Lodi dynasty
The Lodi dynasty was an Afghan royal family that ruled Sultanate of Delhi from 1451 to 1526. It was the fifth and final dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, and was founded by Bahlul Lodi when he replaced the Sayyid dynasty.
Bahlul Lodi
Followin ...
.
After the
Mughal Empire's decline in the 18th century, Punjab experienced a period of anarchy. In 1799 CE, the
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
established its rule, undertaking conquests into
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
and
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire, colloquially known as the Afghan Empire, or the Saddozai Kingdom, was an Afghanistan, Afghan empire founded by the Durrani tribe of Pashtuns under Ahmad Shah Durrani in 1747, which spanned parts of Central Asia, the Iranian ...
held territories, shaping the diverse and complex history of Punjab.
The boundaries of the region are ill-defined and focus on historical accounts and thus the geographical definition of the term "Punjab" has changed over time. In the 16th century
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
the Punjab region was divided into three, with the
Lahore Subah
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is the second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and 27th largest in the world, with a population of over 14 million. Lahore is one of Pakistan ...
in the west, the Delhi
Subah
A ''Subah'' is a term for a province or state in several South Asian languages. It was introduced by the Mughal Empire to refer to its subdivisions or provinces; and was also adopted by other polities of the Indian subcontinent. The word is derive ...
in the east and the
Multan Subah
Multan is the fifth-most populous city in the Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the sixth-largest city in the country; and serves as the administrative headquarters of its eponymous divi ...
in the south. Under the
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
until the
Partition of India
The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, the Dominion of India, Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Paki ...
in 1947, the
Punjab Province encompassed the present Indian
states and union territories of
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
,
Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
,
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
,
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a city and union territory in northern India, serving as the shared capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. Situated near the foothills of the Shivalik range of Himalayas, it borders Haryana to the east and Punjab in the ...
, and
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, and the
Pakistani regions of
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
, and
Islamabad Capital Territory
The Islamabad Capital Territory is a federal territory of Pakistan, centred around Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan. It is located on the northern edge of the Pothohar Plateau, at the foot of the Margalla Hills, in the northwest of the ...
.
The predominant
ethnolinguistic group
An ethnolinguistic group (or ethno-linguistic group) is a group that is unified by both a common ethnicity and language. Most ethnic groups share a first language. However, "ethnolinguistic" is often used to emphasise that language is a major bas ...
of the Punjab region are the
Punjabi people
The Punjabis (Punjabi language, Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Pañjābī) are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region, comprising areas of northwestern India and eastern Paki ...
, who speak the
Indo-Aryan Punjabi language
Punjabi, sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It is one of the most widely spoken native languages in the world, with approximately 150 million native sp ...
.
Punjabi Muslims
Punjabi Muslims are Punjabis who are adherents of Islam. With a population of more than 112 million, they are the third-largest predominantly Islam-adhering Muslims, Muslim ethnicity in the world, after Arab Muslims, Arabs and Bengali Muslims, ...
are the majority in
West Punjab
West Punjab (; ) was a province in the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955. It was established from the western-half of British Punjab, following the independence of Pakistan. The province covered an area of 159,344 km sq (61523 sq mi), i ...
(Pakistan), while
Punjabi Sikhs
Punjabi Sikhs are ethnic Punjabis who adhere to Sikhism. They are the second-largest religious group amongst Punjabis after the Punjabi Muslims, who predominantly inhabit Pakistani Punjab. Punjabi Sikhs form the largest religious community i ...
are the majority in
East Punjab
East Punjab was a state of Dominion of India from 1947 until 1950. It consisted parts of the Punjab Province of British India that remained in India following the partition of the state between the new dominions of Pakistan and India by the ...
(India). Other religious groups include
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
,
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
,
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
,
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
,
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
, and
Ravidassia
Ravidassia or the Ravidas Panth is a religion based on the teachings of Ravidas, Guru Ravidas. It was considered a sect within Sikhism until 2009. However, some Ravidassias continue to maintain Sikh religious practices, including the reverence of ...
.
Etymology
The name Punjab is of
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
origin, with its two parts ( and ) being cognates of the
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
words and , of the same meaning.
The word ''pañjāb'' is thus calque of Indo-Aryan "pañca-áp" and means "The Land of Five Waters", referring to the rivers
Jhelum
Jhelum (; , ) is a city, located along the western bank of the Jhelum River, in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the 21st largest city in Punjab and 31st largest in Pakistan, by population. Located in northern Punjab, it serves as the capital of the ...
,
Chenab
The Chenab River is a major river in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, the Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul region of Himac ...
,
Ravi
Ravi may refer to:
People
* Ravi (name), including a list of people and characters with the name
* Ravi (composer) (1926–2012), Indian music director
* Ravi (Ivar Johansen) (born 1976), Norwegian musical artist
* Ravi (rapper) (born 1993), a Sou ...
,
Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
, and
Beas. All are
tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
of the
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
, the Sutlej being the largest. References to a land of five rivers may be found in the ''
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
'', in which one of the regions is named as ''Panchanada'' (). Earlier, the Punjab was known as
Sapta Sindhu
The Rigveda refers to a number of rivers located in the northwestern Indian subcontinent, from Gandhara to Kurukshetra.
Rigvedic geography
Identification of Rigvedic hydronyms has engaged multiple historians; it is the single most important way ...
in the
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
or ''Hapta Hendu'' in
Avesta
The Avesta (, Book Pahlavi: (), Persian language, Persian: ()) is the text corpus of Zoroastrian literature, religious literature of Zoroastrianism. All its texts are composed in the Avestan language and written in the Avestan alphabet. Mod ...
, translating into "The Land of Seven Rivers", with the other two being Indus and
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
. The ancient
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
referred to the region as ''Pentapotamía'' (), which has the same meaning as that of Punjab.
History

Ancient period
The Punjab region is noted as the site of one of the earliest urban societies, the
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE ...
which flourished from about and declined rapidly 1,000 years later, following the
Indo-Aryan migrations
The Indo-Aryan migrations were the migrations into the Indian subcontinent of Indo-Aryan peoples, an ethnolinguistic group that spoke Indo-Aryan languages. These are the predominant languages of today's Bangladesh, Maldives, Nepal, North India ...
that overran the region in waves between and .
Frequent intertribal wars stimulated the growth of larger groupings ruled by chieftains and kings, who ruled local kingdoms known as
Mahajanapadas
The Mahājanapadas were sixteen Realm, kingdoms and aristocracy, aristocratic republics that existed in ancient India from the sixth to fourth centuries BCE, during the History of India#Second urbanisation (c. 600 – 200 BCE), second urbanis ...
.
The rise of kingdoms and dynasties in the Punjab is chronicled in the ancient Hindu epics, particularly the
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
.
The epic battles described in the ''
Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
'' are chronicled as being fought in what is now the state of Haryana and historic Punjab. The
Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
s,
Kambojas
The Kambojas were a southeastern Iranian peoples, Iranian people who inhabited the northeastern most part of the territory populated by Iranian tribes, which bordered the Indian subcontinent, Indian lands. They only appear in Indo-Aryan langua ...
,
Trigartas
Trigarta (also known as Kangra and Jalandhara) was an ancient Indo-Aryan kingdom based in the region of modern day Punjab. The focal point of its administration was situated in Jalandhar. However at its zenith it encompassed the hill terri ...
,
Andhra
Andhra Pradesh (ISO: , , AP) is a state on the east coast of southern India. It is the seventh-largest state and the tenth-most populous in the country. Telugu is the most widely spoken language in the state, as well as its official lang ...
,
Pauravas
The Pauravas were an ancient tribe in the northern Indus valley, to which Raja Porus may have belonged.
Origins
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, due to the closeness of the names. ...
,
Bahlikas
The Bahlikas (; ''Bāhlika'') were the inhabitants of a location called Bahlika (, located in Bactria), mentioned in the Atharvaveda, Mahabharata, Ramayana, Puranas, Vartikka of Katyayana, Brhatsamhita, Amarkosha, and other ancient inscriptions ...
(
Bactrian settlers of the Punjab),
Yaudheya
Yaudheya (Brahmi script: 𑀬𑁅𑀥𑁂𑀬) or Yoddheya Gana (Yoddheya Republic) was an ancient military ganasangha (republic) based in the Eastern region of the Sapta Sindhu, in modern day Haryana. The word Yaudheya is a derivative of the w ...
s, and others sided with the
Kauravas
''Kaurava'' is a Sanskrit term which refers to descendants of Kuru, a legendary king of India who is the ancestor of many of the characters of the epic ''Mahabharata''. Usually, the term is used for the 100 sons of King Dhritarashtra and his ...
in the great battle fought at
Kurukshetra
Kurukshetra () is a city and administrative headquarters of Kurukshetra district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is also known as Dharmakshetra ("Realm of duty") and as the "Land of the Bhagavad Gita".
Legends
According to the Puranas ...
. According to Fauja Singh and L.M. Joshi: "There is no doubt that the Kambojas, Daradas, Kaikayas, Andhra, Pauravas, Yaudheyas, Malavas, Saindhavas, and Kurus had jointly contributed to the heroic tradition and composite culture of ancient Punjab."
Invasions of Alexander the Great (c. 4th century BCE)

The earliest known notable local king of this region was known as
King Porus
Porus or Poros ( ; 326–321 BC) was an ancient Indian king whose territory spanned the region between the Jhelum River (Hydaspes) and Chenab River (Acesines), in the Punjab region of what is now India and Pakistan. He is only mentioned in Gr ...
, who fought the famous
Battle of the Hydaspes
The Battle of the Hydaspes also known as Battle of Jhelum, or First Battle of Jhelum, was fought between the Macedonian Empire under Alexander the Great and the Pauravas under Porus in May of 326 BCE. It took place on the banks of the Hydas ...
against
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
. His kingdom spanned between rivers ''Hydaspes'' (
Jhelum
Jhelum (; , ) is a city, located along the western bank of the Jhelum River, in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the 21st largest city in Punjab and 31st largest in Pakistan, by population. Located in northern Punjab, it serves as the capital of the ...
) and ''Acesines'' (
Chenab
The Chenab River is a major river in India and Pakistan, and is one of the 5 major rivers of the Punjab region. It is formed by the union of two headwaters, the Chandra and Bhaga, which rise in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul region of Himac ...
);
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-si ...
had held the territory to contain almost 300 cities.
He (alongside
Abisares) had a hostile relationship with the Kingdom of
Taxila
Taxila or Takshashila () is a city in the Pothohar region of Punjab, Pakistan. Located in the Taxila Tehsil of Rawalpindi District, it lies approximately northwest of the Islamabad–Rawalpindi metropolitan area and is just south of the ...
which was ruled by his extended family.
When the armies of Alexander crossed the Indus in its eastward migration, probably in
Udabhandapura
Hund (Pashto: ), historically known as Udabhandapura (Udabhāṇḍa(pura) in Sanskrit), is a small village in Swabi District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is located on the right bank of the Indus River, approximately 15 km north of ...
, he was greeted by the ruler of Taxila,
Omphis.
Omphis had hoped to force both Porus and Abisares into submission leveraging the might of Alexander's forces and diplomatic missions were mounted, but while Abisares accepted the submission, Porus refused.
This led Alexander to seek for a face-off with Porus.
Thus began the Battle of the Hydaspes in 326 BCE; the exact site remains unknown.
The battle is thought to be resulted in a decisive
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
victory; however, A. B. Bosworth warns against an uncritical reading of Greek sources that were exaggerated.
Alexander later founded two cities—''
Nicaea
Nicaea (also spelled Nicæa or Nicea, ; ), also known as Nikaia (, Attic: , Koine: ), was an ancient Greek city in the north-western Anatolian region of Bithynia. It was the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and seve ...
'' at the site of victory and
''Bucephalous'' at the battle-ground, in memory of
his horse, who died soon after the battle.
Later,
tetradrachm
The tetradrachm () was a large silver coin that originated in Ancient Greece. It was nominally equivalent to four drachmae. Over time the tetradrachm effectively became the standard coin of the Antiquity, spreading well beyond the borders of the ...
s would be minted depicting Alexander on horseback, armed with a ''sarissa'' and attacking a pair of Indians on an elephant.
Porus refused to surrender and wandered about atop an elephant, until he was wounded and his force routed.
When asked by Alexander how he wished to be treated, Porus replied "Treat me as a king would treat another king". Despite the apparently one-sided results, Alexander was impressed by Porus and chose to not depose him.
Not only was his territory reinstated but also expanded with Alexander's forces annexing the territories of Glausaes, who ruled to the northeast of Porus' kingdom.
After Alexander's death in ,
Perdiccas
Perdiccas (, ''Perdikkas''; 355BC – 320BC) was a Macedonian general, successor of Alexander the Great, and the regent of Alexander's empire after his death. When Alexander was dying, he entrusted his signet ring to Perdiccas. Initially ...
became the regent of his empire, and after Perdiccas's murder in ,
Antipater
Antipater (; ; 400 BC319 BC) was a Macedonian general, regent and statesman under the successive kingships of Philip II of Macedon and his son, Alexander the Great. In the wake of the collapse of the Argead house, his son Cassander ...
became the new regent. According to
Diodorus
Diodorus Siculus or Diodorus of Sicily (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek historian from Sicily. He is known for writing the monumental universal history '' Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which survive intact, b ...
, Antipater recognized Porus's authority over the territories along the
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
. However,
Eudemus, who had served as Alexander's
satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median kingdom, Median and Achaemenid Empire, Persian (Achaemenid) Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic empi ...
in the Punjab region, treacherously killed Porus.
Mauryan Empire (c. 320–180 BCE)
, with the aid of
Kautilya
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
, had established his empire around . The early life of Chandragupta Maurya is not clear. Kautilya enrolled the young Chandragupta in the
university at Taxila to educate him in the arts, sciences, logic, mathematics, warfare, and administration.
Megasthenes
Megasthenes ( ; , died 290 BCE) was an ancient Greek historian, indologist, diplomat, ethnographer and explorer in the Hellenistic period. He described India in his book '' Indica'', which is now lost, but has been partially reconstructe ...
' account, as it has survived in Greek texts that quote him, states that Alexander the Great and Chandragupta met, which if true would mean his rule started earlier than . As Alexander never crossed the
Beas River, so his territory probably lay in the
Punjab region
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
. With the help of the small Janapadas of Punjab, he had gone on to conquer much of the North West Indian subcontinent.
He then defeated the Nanda rulers in
Pataliputra
Pataliputra (IAST: ), adjacent to modern-day Patna, Bihar, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Magadha ruler Ajatashatru in 490 BCE, as a small fort () near the Ganges river.. Udayin laid the foundation of the city of Pataliput ...
to capture the throne. Chandragupta Maurya fought Alexander's successor in the east,
Seleucus
Seleucus or Seleukos (Ancient Greek: Σέλευκος) was a Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian Greek name, possibly meaning "very bright" or “very white”. It is likely related to the ancient name Zaleucus (Ancient Greek language, Ancient ...
when the latter invaded. In a peace treaty, Seleucus ceded all territories west of the Indus and offered a marriage, including a portion of
Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian language, Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient Iranian peoples, Iranian civilization in Central Asia based in the area south of the Oxus River (modern Amu Darya) and north of the mountains of the Hindu Kush, an area ...
, while Chandragupta granted Seleucus 500 elephants. The chief of the Mauryan military was also always a
Yaudheya
Yaudheya (Brahmi script: 𑀬𑁅𑀥𑁂𑀬) or Yoddheya Gana (Yoddheya Republic) was an ancient military ganasangha (republic) based in the Eastern region of the Sapta Sindhu, in modern day Haryana. The word Yaudheya is a derivative of the w ...
n warrior according to the Bijaygadh Pillar inscription, which states that the Yaudheyas elected their own chief who also served as the general for the Mauryans.
The Mauryan military was also made up vastly of men from the Punjab Janapadas.
Chandragupta's rule was very well organised. The Mauryans had an autocratic and centralised administration system, aided by a council of ministers, and also a well-established espionage system. Much of Chandragupta's success is attributed to
Chanakya
Chanakya (ISO 15919, ISO: ', चाणक्य, ), according to legendary narratives preserved in various traditions dating from the 4th to 11th century CE, was a Brahmin who assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta Maurya, Chandragup ...
, the author of the ''
Arthashastra
''Kautilya's Arthashastra'' (, ; ) is an Ancient Indian Sanskrit treatise on statecraft, politics, economic policy and military strategy. The text is likely the work of several authors over centuries, starting as a compilation of ''Arthashas ...
.'' Much of the Mauryan rule had a strong bureaucracy that had regulated tax collection, trade and commerce, industrial activities, mining, statistics and data, maintenance of public places, and upkeep of temples.
Medieval period
Hindu Shahis (c. 820–1030 CE)
In the 9th century, the
Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis, also referred to as the Kabul Shahis and Uḍi Śāhis, were a dynasty established between 843 CE and 1026 CE. They endured multiple waves of conquests for nearly two centuries and their core territory was described as having c ...
dynasty originating from the region of
Oddiyana
(also: ''Uḍḍiyāna'', ''Uḍḍāyāna'', ''Udyāna'' or 'Oḍḍiyāna'), a small region in early medieval India, is ascribed importance in the development and dissemination of Vajrayāna Buddhism.‘Uḍḍiyāna and Kashmir’, pp 265-2 ...
, replaced the Taank kingdom, ruling Western Punjab along with eastern Afghanistan.
The tribe of the
Gakhars
The Gakhar () is a historical Punjabi tribe, originating in the Pothohar Plateau of Punjab, Pakistan. They predominantly adhere to Islam.
History
In the Muslim historiography, the Gakhars have been frequently confused with the Khokhars, who ...
/
Khokhars
Khokhar () is a historical Punjabi clan primarily native to the Salt Range of Pakistani Punjab. Khokhars are also found in the Indian states of Punjab and Haryana. Khokhars predominantly follow Islam, having converted to Islam from Hinduism a ...
, formed a large part of the Hindu Shahi army according to the Persian historian
Firishta
Firishta or Ferešte (), full name Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Astarabadi (), was a Persian historian, who later settled in India and served the Deccan Sultans as their court historian. He was born in 1570 and died between 1611 and 1623.
Life
F ...
. The most notable rulers of the empire were Lalliya, Bhimadeva and Jayapala who were accredited for military victories.
Lalliya had reclaimed the territory at and around Kabul between 879 and 901 CE after it had been lost under his predecessor to the
Saffarid dynasty
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conqu ...
. He was described as a fearsome Shahi. Two of his ministers reconstructed by Rahman as Toramana and Asata are said to of have taken advantage of
Amr al-Layth's preoccupation with rebellions in Khorasan, by successfully raiding
Ghazna
Ghazni (, ), historically known as Ghaznayn () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana (), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategica ...
around 900 CE.
After a defeat in Eastern Afghanistan suffered on the Shahi ally Lawik, Bhimadeva mounted a combined attack around 963 CE.
Abu Ishaq Ibrahim was expelled from Ghazna and Shahi-Lawik strongholds were restored in Kabul and adjacent areas. This victory appears to have been commemorated in the Hund Slab Inscription (HSI).
Turkic rule (c. 1030–1320 CE)
The
Turkic Ghaznavids
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''Ġaznaviyān'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus ...
in the tenth century overthrew the Hindu Shahis and consequently ruled for 157 years in Western Punjab, gradually declining as a power until the
Ghurid
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Tajik people, Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Emp ...
conquest of Lahore by
Muhammad of Ghor in 1186, deposing the last Ghaznavid ruler
Khusrau Malik
Abu'l-Muzaffar Khusrau Malik ibn Khusrau-Shah (), better known simply as Khusrau Malik (; also spelled Khosrow), was the last Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 1160 to 1186. He was the son and successor of Khusrau Shah (r. 1157–1160) ...
. Following the death of
Muhammad of Ghor in 1206 by Punjabi assassins near the Jhelum river, the Ghurid state fragmented and was replaced in northern India by the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. .
Tughlaq dynasty (c. 1320–1410 CE)
The Tughlaq dynasty's reign formally started in 1320 in
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of
Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq
Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq (), or Ghazi Malik (; died 1 February 1325) was the Sultan of Delhi from 1320 to 1325. He was the first sultan of the Tughluq dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate. During his reign, Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq founded the city of ...
after defeating
Khusrau Khan at the
Battle of Lahrawat.
During Ghazi Malik's reign, in 1321 he sent his eldest son Jauna Khan, later known as
Muhammad bin Tughlaq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 – 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his epithets, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February 1 ...
, to
Deogir
Daulatabad Fort, originally Deogiri Fort, is a historic fortified citadel located in Daulatabad village near Aurangabad, Maharashtra, India. It was the capital of the Yadavas (9th century – 14th century CE), for a brief time the capital of th ...
to plunder the Hindu kingdoms of Arangal and Tilang (now part of
Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
). His first attempt was a failure.
[William Lowe (Translator), , Volume 1, pages 296-301] Four months later, Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq sent large army reinforcements for his son asking him to attempt plundering Arangal and Tilang again. This time Jauna Khan succeeded and Arangal fell, it was renamed to Sultanpur, and all plundered wealth, state treasury and captives were transferred from the captured kingdom to the Delhi Sultanate.The Muslim aristocracy in Lukhnauti (Bengal) invited Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq to extend his coup and expand eastwards into Bengal by attacking
Shamsuddin Firoz Shah
Shamsuddin Firuz Shah (, , ''Shams Ad-Dīn Firūz Shāh''; reigned: 1301–1322) was the independent ruler of the Lakhnauti Kingdom. He ascended the throne with the title of ''Al-Sultan Al-Azam Shams Al-Duniya wa Al-Din Abu Al-Muzaffar Firuz Shah ...
, which he did over 1324–1325 CE,
after placing Delhi under control of his son Ulugh Khan, and then leading his army to Lukhnauti. Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq succeeded in this campaign.
After his father's death in 1325 CE, Muhammad bin Tughlaq assumed power and his rule saw the empire expand to most of the Indian subcontinent, its peak in terms of geographical reach.
[Muḥammad ibn Tughluq](_blank)
Encyclopædia Britannica He attacked and plundered
Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the ...
,
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
,
Lakhnauti,
Chittagong
Chittagong ( ), officially Chattogram, (, ) (, or ) is the second-largest city in Bangladesh. Home to the Port of Chittagong, it is the busiest port in Bangladesh and the Bay of Bengal. The city is also the business capital of Bangladesh. It ...
,
Mithila
Mithila may refer to:
Places
* Mithilā, a synonym for the ancient Videha state
** Mithilā (ancient city), the ancient capital city of Videha
* Mithila (region), a cultural region (historical and contemporary), now divided between India and Nepa ...
and many other regions in India. His distant campaigns were expensive, although each raid and attack on non-Muslim kingdoms brought new looted wealth and ransom payments from captured people. The extended empire was difficult to retain, and rebellions became commonplace all over the Indian subcontinent.
[Tarikh-I Firoz Shahi](_blank)
Ziauddin Barni, The History of India by its own Historians - The Muhammadan Period, Volume 3, Trubner London, pp. 235–240 Muhammad bin Tughlaq died in March 1351 while trying to chase and punish people for rebellion and their refusal to pay taxes in
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
and
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
.
[Vincent A Smith, , Chapter 2, pp. 242–248, Oxford University Press]
After Muhammad bin Tughlaq's death, the Tughlaq empire was in a state of disarray with many regions assuming independence; it was at this point that
Firuz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was ...
, Ghazi Malik's nephew, took reign. His father's name was Rajab (the younger brother of Ghazi Malik) who had the title ''
Sipahsalar
() or (; ), in Arabic rendered as () or (), was a title used in much of the Islamic world during the 10th–15th centuries, to denote the senior-most military commanders, but also as a generic general officer rank.
Islamic East and Persia
Th ...
''. His mother Naila was a Punjabi Bhatti princess (daughter of Rana Mal) from
Dipalpur
Dipalpur (), also spelt Depalpur, is a city in the Okara District of Pakistani province of Punjab that served as headquarters of Depalpur Tehsil, the largest Tehsil of Pakistan. It is situated 150 kilometres from the province capital Lahore on ...
and
Abohar
Abohar is a city and municipal corporation in the Fazilka district of the Indian state of Punjab, southeast of Fazilka city and northeast of Sri Ganganagar. It is near the India-Pakistan border. Abohar's population was 145,302 as of 2011. The ...
according to the historian
William Crooke
William Crooke (6 August 1848 – 25 October 1923) was a British orientalist and a key figure in the study and documentation of Anglo-Indian folklore. He was born in County Cork, Ireland, and was educated at Erasmus Smith's Tipperary Grammar S ...
. The southern states had drifted away from the Sultanate and there were rebellions in Gujarat and Sindh, while "Bengal asserted its independence." He led expeditions against Bengal in 1353 and 1358. He captured
Cuttack
Cuttack (, or officially Kataka in Odia language, Odia ), is the former capital, deputy capital and the 2nd largest city of the Indian state of Odisha. It is also the headquarters of the Cuttack district. The name of the city is an anglicised f ...
, desecrated the
Jagannath Temple, Puri
The Jagannath Temple is a Hindu temple dedicated to the god Jagannath, a form of Vishnu in Hinduism. It is located in Puri in the state of Odisha, situated on the eastern coast of India. As per temple records, King Indradyumna of Avanti bu ...
, and forced Raja Gajpati of Jajnagar in
Orissa
Odisha (), formerly Orissa ( the official name until 2011), is a state located in Eastern India. It is the eighth-largest state by area, and the eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the thir ...
to pay tribute. He also laid siege to the
Kangra Fort and forced Nagarkot to pay tribute. During this time, Tatar Khan of
Greater Khorasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
attacked Punjab, but he was defeated and his face slashed by the sword given by
Feroz Shah Tughlaq
Firuz Shah Tughlaq (1309 – 20 September 1388), also known as Firuz III, was Sultan of Delhi from 1351 until his death in 1388. He succeeded his cousin Muhammad bin Tughlaq following the latter's death at Thatta, Sindh. His father was Si ...
to Raja
Kailas Pal
Raja Kailas Pal Pathania (1353-1397 CE) was a Raja of the Nurpur kingdom, who succeeded Raja Jas Pal as the chief of the Pathania Clan of Rajputs. He is accorded credit for wounding and defeating Tatar Khan, a governor of Khorasan, who had invade ...
who ruled the Nagarkot region in Punjab.
Sayyid dynasty (c. 1410–1450 CE)
Khizr Khan
Khizr Khan (reigned 28 May 1414 – 20 May 1421) was the founder of the Sayyid dynasty, the fourth ruling dynasty of the Delhi sultanate, in northern India soon after the invasion of Timur and the fall of the Tughlaq dynasty.
Khizr Khan was Go ...
established the
Sayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451 for 37 years.See:
* M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill
* The Islamic frontier in the east: Expansion ...
, the fourth dynasty of the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. after the fall of the
Tughlaqs
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath a ...
.
Following
Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
's 1398 sack of
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
, he appointed
Khizr Khan
Khizr Khan (reigned 28 May 1414 – 20 May 1421) was the founder of the Sayyid dynasty, the fourth ruling dynasty of the Delhi sultanate, in northern India soon after the invasion of Timur and the fall of the Tughlaq dynasty.
Khizr Khan was Go ...
as deputy of
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
(
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
). He held Lahore, Dipalpur, Multan and Upper Sindh. Khizr Khan captured Delhi on 28 May 1414 thereby establishing the Sayyid dynasty. Khizr Khan did not take up the title of
sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
, but continued the fiction of his allegiance to Timur as ''Rayat-i-Ala''(vassal) of the
Timurids
The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate, Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, and parts of contem ...
- initially that of Timur, and later his son
Shah Rukh
Shah Rukh or Shahrukh Mirza (, ''Šāhrokh''; 20 August 1377 – 13 March 1447) was the ruler of the Timurid Empire between 1405 and 1447.
He was the son of the Central Asian conqueror Timur (Tamerlane), who founded the Timurid dynasty in 1370 ...
. After the accession of Khizr Khan, the Punjab,
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
and Sindh were reunited under the Delhi Sultanate, where he spent his time subduing rebellions. Punjab was the powerbase of Khizr Khan and his successors as the bulk of the Delhi army during their reigns came from
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
and
Dipalpur
Dipalpur (), also spelt Depalpur, is a city in the Okara District of Pakistani province of Punjab that served as headquarters of Depalpur Tehsil, the largest Tehsil of Pakistan. It is situated 150 kilometres from the province capital Lahore on ...
.
Khizr Khan was succeeded by his son
Mubarak Shah after his death on 20 May 1421. Mubarak Shah referred to himself as ''Muizz-ud-Din Mubarak Shah'' on his coins, removing the Timurid name with the name of the Caliph, and declared himself a Shah. He defeated the advancing
Hoshang Shah Ghori, ruler of
Malwa Sultanate
The Malwa Sultanate was a late medieval kingdom in the Malwa, Malwa region, covering the present day Indian states of Madhya Pradesh and south-eastern Rajasthan from 1401 to 1562. It was founded by Dilawar Khan, who following Timur's invasion ...
and forced him to pay heavy tribute early in his reign. Mubarak Shah also put down the rebellion of
Jasrath Khokhar
Jasrat Khan ( – ), also known as Jasrath, was a 15th-century Punjabi Muslim chieftain who ruled parts of Punjab from 1410 until his death in 1442. He had his capital at Sialkot.
A son of Shaikha, Jasrat fought against Tamerlane during his in ...
and managed to fend off multiple invasions by the Timurids of Kabul.
The last ruler of the Sayyids,
Ala-ud-Din, voluntarily abdicated the throne of the Delhi Sultanate in favour of
Bahlul Khan Lodi
Bahlul Khan Lodi (; died 12 July 1489) was the chief of the Afghan Lodi tribe. He was the founder of the Lodi dynasty from the Delhi Sultanate, upon the abdication of the last claimant from the previous Sayyid rule. Bahlul became Sultan of th ...
on 19 April 1451, and left for Badaun, where he died in 1478.
Langah Sultanate (c. 1450–1540 CE)
In 1445, Sultan Qutbudin, chief of ''Langah'' (a
Jat
The Jat people (, ), also spelt Jaat and Jatt, are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, many Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in l ...
Zamindar
A zamindar in the Indian subcontinent was an autonomous or semi-autonomous feudal lord of a ''zamindari'' (feudal estate). The term itself came into use during the Mughal Empire, when Persian was the official language; ''zamindar'' is the ...
tribe),
established the
Langah Sultanate
The Langah Sultanate was a late medieval sultanate based in the Punjab region in the western Indian subcontinent between the 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the lower Doab tract with Multan at its centre. The Langah Sult ...
in
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
after the fall of the
Sayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty was the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, with four rulers ruling from 1414 to 1451 for 37 years.See:
* M. Reza Pirbha, Reconsidering Islam in a South Asian Context, , Brill
* The Islamic frontier in the east: Expansion ...
. Husseyn Langah I (reigned 1456–1502) was the second ruler of Langah Sultanate. He undertook military campaigns in Punjab and captured
Chiniot
Chiniot ( Punjabi, Urdu: ) is a city and the administrative headquarters of Chiniot District in the province of Punjab, Pakistan. Located on the bank of the river Chenab, it is the 28th most populous city in Pakistan.
It is also known for ...
and
Shorkot
Shorkot (), (), is a city in Punjab (Pakistan) and serves as the capital of Shorkot Tehsil in Jhang District.
The city is renowned for the tombs of several prominent Sufism, Sufi saints, including Sultan Bahoo, Syed Akbar Ali Shah Gilani, Syed ...
from the Lodis. Shah Husayn successfully repulsed attempted invasion by the Lodis led by
Tatar Khan
Muhammad Tatar Khan (, ) was the Sultan of North Bengal during 1259-1268 CE after usurping the Governorship of Ijjauddin Balban Iuzbaki.
History
In 1258 CE, Tatar Khan defeated Izzuddin Balban, later building a tomb for his predecessor in 1 ...
and
Barbak Shah, as well as his daughter Zeerak Rumman.
Modern period
Mughal Empire (c. 1526–1761 CE)
The
Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of pre ...
came to power in the early 16th century and gradually expanded to control all of the Punjab from their capital at
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
. During the Mughal era,
Saadullah Khan, born into a family of Punjabi agriculturalists
belonging to the
Thaheem tribe from
Chiniot
Chiniot ( Punjabi, Urdu: ) is a city and the administrative headquarters of Chiniot District in the province of Punjab, Pakistan. Located on the bank of the river Chenab, it is the 28th most populous city in Pakistan.
It is also known for ...
remained
grand vizier
Grand vizier (; ; ) was the title of the effective head of government of many sovereign states in the Islamic world. It was first held by officials in the later Abbasid Caliphate. It was then held in the Ottoman Empire, the Mughal Empire, the Soko ...
(or Prime Minister) of the Mughal Empire in the period 1645–1656.
Other prominent Muslims from Punjab who rose to nobility during the Mughal Era include
Wazir Khan,
, and
Shahbaz Khan Kamboh
Shahrullah Kamboh (; 1529 – 11 November 1599), better known as Shahbaz Khan Kamboh (), was one of the leading generals of Mughal emperor Akbar. He participated in some of the most difficult expeditions of Akbar and annexed numerous territories ...
. The Mughal Empire ruled the region until it was severely weakened in the eighteenth century.
As Mughal power weakened, Afghan rulers took control of the region.
Contested by the
Marathas
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
and Afghans, the region was the center of the growing influence of the
misl
Major Indoor Soccer League has been the name of three different American professional indoor soccer leagues:
*Major Indoor Soccer League (1978–1992), known in its final two seasons as the Major Soccer League
*Major Indoor Soccer League (2001–2 ...
s, who expanded and established the Sikh Confederacy as the Mughals and Afghans weakened, ultimately ruling the Punjab,
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ; , ; abbr. KP or KPK), formerly known as the North West Frontier Province (NWFP), is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Northern Pakistan, northwestern region of the country, Khyber ...
, and territories north into the
Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
.
Sikh Empire (c. 1799–1849 CE)

In the 19th century, Maharajah
Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 – 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839.
Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia M ...
established the
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Ranjit Singh captured
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered in the
Second Anglo-Sikh War
The Second Anglo-Sikh War was a military conflict between the Sikh Empire and the East India Company which took place from 1848 to 1849. It resulted in the fall of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab region, Punjab and what sub ...
. It was forged on the foundations of the
Khalsa
The term ''Khalsa'' refers to both a community that follows Sikhism as its religion,[Khalsa: Sikhism< ...]
from a collection of autonomous
Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
''
misl
Major Indoor Soccer League has been the name of three different American professional indoor soccer leagues:
*Major Indoor Soccer League (1978–1992), known in its final two seasons as the Major Soccer League
*Major Indoor Soccer League (2001–2 ...
s''.
At its peak in the 19th century, the Empire extended from the
Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass (Urdu: درۂ خیبر; ) is a mountain pass in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, on the border with the Nangarhar Province of Afghanistan. It connects the town of Landi Kotal to the Valley of Peshawar at Jamrud by tr ...
in the west to western
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
in the east, and from
Mithankot
Mithankot ( Punjabi / ) also known as Kot Mithan, is a city in Rajanpur District in Punjab, Pakistan. Mithankot is located on the west bank of the Indus River, a short distance downstream from its junction with Panjnad River. Most of its inhabita ...
in the south to
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
in the north. It was divided into four provinces:
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
, in Punjab, which became the Sikh capital;
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
, also in Punjab;
Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
; and Kashmir from 1799 to 1849. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 3.5 million in 1831 (making it the
19th most populous country at the time),
Amarinder Singh
Amarinder Singh (born 11 March 1942) is an Indian politician, military historian, former royal and Indian Army veteran who served as the 15th Chief Minister of Punjab. His father, Yadavindra Singh, was the last Maharaja of the princely st ...
's The Last Sunset: The Rise and Fall of the Lahore Durbar it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to
be annexed by the
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
.
British Punjab (c. 1849–1947 CE)
The Sikh Empire ruled the Punjab until the British annexed it in 1849 following the
First
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
and
Second Anglo-Sikh War
The Second Anglo-Sikh War was a military conflict between the Sikh Empire and the East India Company which took place from 1848 to 1849. It resulted in the fall of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab region, Punjab and what sub ...
s. Most of the Punjabi homeland formed a province of British India, though a number of small
princely states retained local rulers who recognized British authority.
The Punjab with its rich farmlands became one of the most important colonial assets.
Lahore was a noted center of learning and culture, and
Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, third-largest city in the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is a commercial and industrial hub, being the list of cities in P ...
became an important military installation.
Most Punjabis supported the British during
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, providing men and resources to the war effort even though the Punjab remained a source of anti colonial activities.
Disturbances in the region increased as the war continued.
At the end of the war, high casualty rates, heavy taxation, inflation, and a widespread influenza epidemic disrupted Punjabi society.
In 1919, Colonel
Reginald Dyer
Colonel Reginald Edward Harry Dyer, (9 October 186423 July 1927) was a British military officer in the Bengal Army and later the newly constituted British Indian Army. His military career began in the regular British Army, but he soon transf ...
ordered troops under command to fire on a crowd of demonstrators, mostly Sikhs in
Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
. The
Jallianwala massacre fueled the
Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events in South Asia with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British colonial rule. It lasted until 1947, when the Indian Independence Act 1947 was passed.
The first nationalistic ...
.
Nationalists declared the independence of India from Lahore in 1930 but were quickly suppressed.
When the Second World War broke out, nationalism in British India had already divided into religious movements.
Many Sikhs and other minorities supported the Hindus, who promised a secular multicultural and multireligious society, and Muslim leaders in Lahore passed a resolution to work for a Muslim Pakistan, making the Punjab region a center of growing conflict between Indian and Pakistani nationalists.
At the end of the war, the British granted separate independence to India and Pakistan, setting off massive communal violence as Muslims fled to Pakistan and Hindu and Sikh Punjabis fled east to India.
The
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
had major political, cultural, philosophical, and literary consequences in the Punjab, including the establishment of a new system of education. During the
independence movement
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a ...
, many Punjabis played a significant role, including
Madan Lal Dhingra,
Sukhdev Thapar
Sukhdev Thapar (15 May 1907 – 23 March 1931) was an Indian freedom fighter who fought against the British government for Indian independence. He was a member of the '' Hindustan Socialist Republican Association'' (HSRA), and was executed al ...
,
Ajit Singh Sandhu,
Bhagat Singh
Bhagat Singh (27 September 1907 – 23 March 1931) was an Indian anti-colonial revolutionary who participated in the mistaken murder of a junior British police officer in December 1928 in what was intended to be retaliation for the deat ...
,
Udham Singh
Udham Singh (born Sher Singh; 26 December 1899 – 31 July 1940) was an Indian revolutionary belonging to Ghadar Party and HSRA, best known for assassinating Michael O'Dwyer, the former lieutenant governor of the Punjab in India, on 13 March ...
,
Kartar Singh Sarabha
Kartar Singh Sarabha (24 May 1896 — 16 November 1915) was a prominent Indian revolutionary and a key figure in the Ghadar Movement against the British Raj. Born in Sarabha village, Ludhiana, he went to the U.S. for studies but became deeply i ...
,
Bhai Parmanand
Bhai Parmanand (4 November 1876 – 8 December 1947) was an Indian nationalist and a prominent leader of the Ghadar Party and Hindu Mahasabha.
Early life
Parmanand was born on 4 November 1876 in Karyala (Punjab, Pakistan) to Bhai Tara Chand C ...
,
Choudhry Rahmat Ali
Choudhry Rahmat Ali (16 November 1897 – 3 February 1951) was a Muslim nationalist activist who is credited with coining the name "Pakistan" for a separate Muslim homeland in British India and is sometimes regarded as the originator of the Pa ...
, and
Lala Lajpat Rai
Lala Lajpat Rai (28 January 1865 — 17 November 1928) was an Indian revolutionary, politician, and author, popularly known as ''Punjab Kesari (Lion of Punjab).'' He was one of the three members of the Lal Bal Pal trio. He died of severe tra ...
. At the time of partition in 1947, the province was split into East and West Punjab.
East Punjab
East Punjab was a state of Dominion of India from 1947 until 1950. It consisted parts of the Punjab Province of British India that remained in India following the partition of the state between the new dominions of Pakistan and India by the ...
(48%) became part of India, while
West Punjab
West Punjab (; ) was a province in the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955. It was established from the western-half of British Punjab, following the independence of Pakistan. The province covered an area of 159,344 km sq (61523 sq mi), i ...
(52%) became part of Pakistan. The Punjab bore the brunt of the
civil unrest
Civil disorder, also known as civil disturbance, civil unrest, civil strife, or turmoil, are situations when law enforcement and security forces struggle to maintain public order or tranquility.
Causes
Any number of things may cause civil di ...
following
partition, with casualties estimated to be in the millions.
Another major consequence of partition was the sudden shift towards religious homogeneity occurred in all districts across Punjab owing to the new international border that cut through the province. This rapid demographic shift was primarily due to wide scale migration but also caused by large-scale
religious cleansing riots which were witnessed across the region at the time. According to historical demographer
Tim Dyson
Tim Dyson (born 1949) is a British demographer with a focus on India's population. He is currently Professor Emeritus of Population Studies at the London School of Economics. He was elected as a Fellow of the British Academy
The British Acade ...
, in the eastern regions of Punjab that ultimately became
Indian Punjab
Punjab () is a state in northwestern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the north and northeast, Haryana to the south and southeast, a ...
following independence, districts that were 66% Hindu in 1941 became 80% Hindu in 1951; those that were 20% Sikh became 50% Sikh in 1951. Conversely, in the western regions of Punjab that ultimately became
Pakistani Punjab
Punjab (, ) is a province of Pakistan. With a population of over 127 million, it is the most populous province in Pakistan and the second most populous subnational polity in the world. Located in the central-eastern region of the country, i ...
, all districts became almost exclusively Muslim by 1951.
Geography
The geographical definition of the term "Punjab" has changed over time. In the 16th century
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
it referred to a relatively smaller area between the
Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
and the
Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
rivers.
Sikh Empire

At its height in the first half of the 19th century, the Sikh Empire spanned a total of over .
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire, colloquially known as the Afghan Empire, or the Saddozai Kingdom, was an Afghanistan, Afghan empire founded by the Durrani tribe of Pashtuns under Ahmad Shah Durrani in 1747, which spanned parts of Central Asia, the Iranian ...
. The following modern-day political divisions made up the historical Punjab region during the Sikh Empire:
* Punjab region, to
Mithankot
Mithankot ( Punjabi / ) also known as Kot Mithan, is a city in Rajanpur District in Punjab, Pakistan. Mithankot is located on the west bank of the Indus River, a short distance downstream from its junction with Panjnad River. Most of its inhabita ...
in the south
**
Punjab, Pakistan
Punjab (, ) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. With a population of over 127 million, it is the Demographics of Pakistan, most populous province in Pakistan and the List of first-level administrative divisions by popu ...
, excluding
Bahawalpur State
**
Punjab, India
Punjab () is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states ...
, south to areas just across the
Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
river
**
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
, India, south to areas just across the
Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
river
**
Jammu Division
The Jammu division (; ) is a Divisions of India, revenue and administrative division of the Indian-administered Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir in the disputed Kashmir region.The application of the term "administered" to t ...
,
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir may refer to:
* Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), a region administered by India as a union territory since 2019
* Jammu and Kashmir (state), a region administered by India as a state from 1952 to 2019
* Jammu and Kashmir (prin ...
, India and Pakistan (1808–1846)
*
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
region, Pakistan/China
**
Kashmir Valley
The Kashmir Valley, also known as the Vale of Kashmir, is an intermontane valley in northern Jammu and Kashmir, a region in Indian-administered Kashmir.(a) (subscription required) Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcont ...
, India (1819–1846)
**
Gilgit
Gilgit (; Shina language, Shina: ; ) is a city in Pakistani-administered Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit–Baltistan in the disputed Kashmir region.The application of the term "administered" to the various regions of Kashmir and a mention of the Kas ...
,
Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan (1842–1846)
**
Ladakh
Ladakh () is a region administered by India as a union territory and constitutes an eastern portion of the larger Kashmir region that has been the subject of a Kashmir#Kashmir dispute, dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947 and India an ...
, India (1834–1846)
*
Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass (Urdu: درۂ خیبر; ) is a mountain pass in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, on the border with the Nangarhar Province of Afghanistan. It connects the town of Landi Kotal to the Valley of Peshawar at Jamrud by tr ...
, Pakistan/Afghanistan
**
Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
, Pakistan (taken in 1818, retaken in 1834)
**
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ; , ; abbr. KP or KPK), formerly known as the North West Frontier Province (NWFP), is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Northern Pakistan, northwestern region of the country, Khyber ...
and the
Federally Administered Tribal Areas
The Federally Administered Tribal Areas, commonly known as FATA, was a semi-autonomous tribal region in north-western Pakistan that existed from 1947 until being merged with the neighbouring province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in 2018 through the ...
, Pakistan (documented from
Hazara, taken in 1818, again in 1836 to
Bannu
Bannu (, ), also called Bani Gul or Bani (, ) is a city located on the Kurram River in southern Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is the capital of Bannu Division. Bannu's residents are primarily members of the Banuchi tribe and speak Banuch ...
)
* Parts of
Western Tibet, China (
briefly in 1841, to
Taklakot
Purang or Burang (,, zh, s=普兰镇), is a Towns of China, town which serves as the administrative center of Purang County, Ngari Prefecture of the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR), China. The town lies at an altitude of 3,900m (12,795 feet) in ...
)
After Ranjit Singh's death in 1839, the empire was severely weakened by internal divisions and political mismanagement. This opportunity was used by the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
to launch the
First
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
and
Second Anglo-Sikh War
The Second Anglo-Sikh War was a military conflict between the Sikh Empire and the East India Company which took place from 1848 to 1849. It resulted in the fall of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab region, Punjab and what sub ...
s. The country was finally annexed and dissolved at the end of the Second Anglo-Sikh War in 1849 into separate
princely states and the
province of Punjab. Eventually, a Lieutenant Governorship was formed in Lahore as a direct representative of
the Crown
The Crown is a political concept used in Commonwealth realms. Depending on the context used, it generally refers to the entirety of the State (polity), state (or in federal realms, the relevant level of government in that state), the executive ...
.
Punjab (British India)
In British India, until the
Partition of India
The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, the Dominion of India, Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Paki ...
in 1947, the
Punjab Province was geographically a triangular tract of country of which the
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
and its tributary the
Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
formed the two sides up to their confluence, the base of the triangle in the north being the
Lower Himalayan Range
The Lower Himalayan Range, also called the Lesser Himalayas and Mahabharat Lekh or Himachal, is one of the four parallel sub-ranges of the Himalayas. It has the Great Himalayas to the north and the Sivalik Hills to the south. It extends from t ...
between those two rivers. Moreover, the province as constituted under British rule also included a large tract outside these boundaries. Along the northern border, Himalayan ranges divided it from
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
and
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
. On the west it was separated from the
North-West Frontier Province
The North-West Frontier Province (NWFP; ) was a province of British India from 1901 to 1947, of the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955, and of the Pakistan, Islamic Republic of Pakistan from 1970 to 2010. It was established on 9 November ...
by the Indus, until it reached the border of
Dera Ghazi Khan District
Dera Ghazi Khan (, Punjabi language, Punjabi: ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district in Punjab, Pakistan. Its administrative capital is Dera Ghazi Khan.
The district lies to the west of the Indus River. The Sulaiman Mountains rise to a height ...
, which was divided from
Baluchistan
Balochistan ( ; , ), also spelled as Baluchistan or Baluchestan, is a historical region in West and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region of de ...
by the
Sulaiman Range
The Sulaiman Mountains, also known as Kōh-e Sulaymān, Kasē Ghrūna Da Suleiman Ghruna (Pashto: د كسې غرونه ، د سلیمان غرونه; "Mountains of Qaes/Kasi and Solomon") ( Balochi:; "Mountains of Solomon") are a north–south ex ...
. To the south lay
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
and
Rajputana
Rājputana (), meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the entire present-day States of India, Indian state of Rajasthan, parts of the neighboring states of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and adjo ...
, while on the east the rivers
Jumna and
Tons separated it from the
United Provinces.
In total Punjab had an area of approximately 357 000 km square about the same size as modern day Germany, being one of the largest provinces of the British Raj.
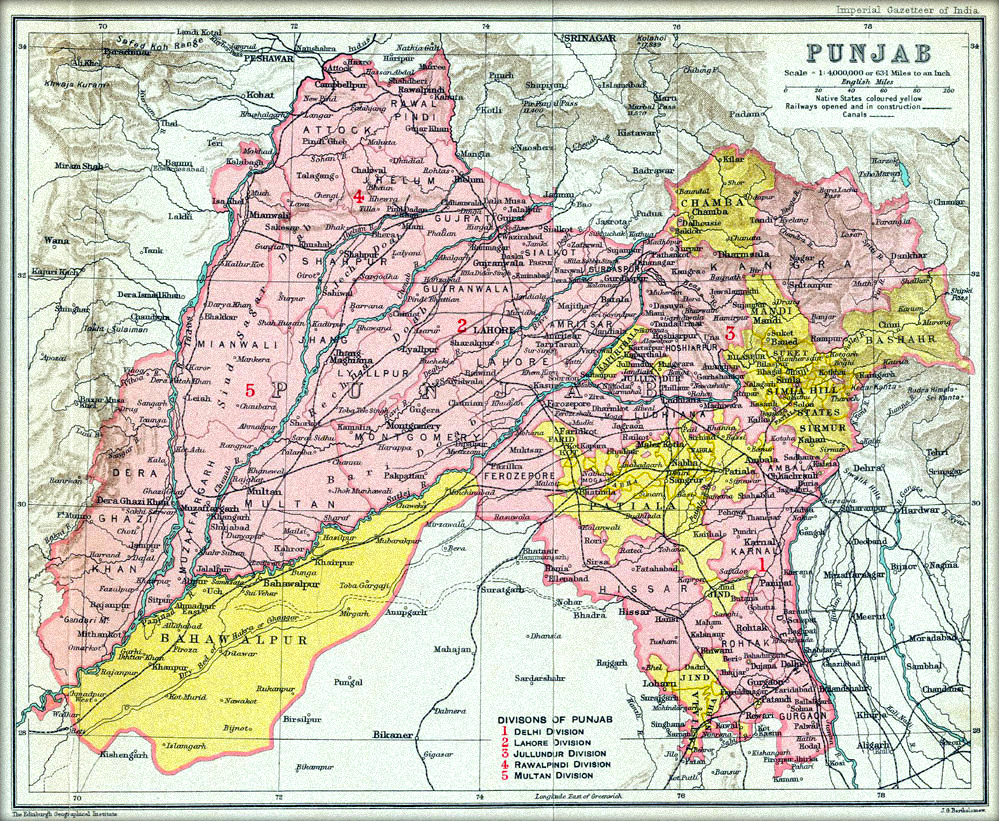
It encompassed the present day
Indian states
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 districts and smaller administrative divisions by the respe ...
of
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
, Haryana,
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a city and union territory in northern India, serving as the shared capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. Situated near the foothills of the Shivalik range of Himalayas, it borders Haryana to the east and Punjab in the ...
, Delhi, and some parts of
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
which were merged with Punjab by the British for administrative purposes (but excluding the former
princely states which were later combined into the
Patiala and East Punjab States Union
The Patiala and East Punjab States Union (PEPSU) was a States and union territories of India, state of India, uniting eight princely states between 1948 and 1956. The capital and principal city was Patiala. The state covered an area of 26,208 ...
) and the Pakistani regions of the
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
,
Islamabad Capital Territory
The Islamabad Capital Territory is a federal territory of Pakistan, centred around Islamabad, the capital of Pakistan. It is located on the northern edge of the Pothohar Plateau, at the foot of the Margalla Hills, in the northwest of the ...
and
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa
Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (; ; , ; abbr. KP or KPK), formerly known as the North West Frontier Province (NWFP), is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Northern Pakistan, northwestern region of the country, Khyber ...
.
In 1901 the frontier districts beyond the Indus were separated from Punjab and made into a new province: the
North-West Frontier Province
The North-West Frontier Province (NWFP; ) was a province of British India from 1901 to 1947, of the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955, and of the Pakistan, Islamic Republic of Pakistan from 1970 to 2010. It was established on 9 November ...
. Subsequently, Punjab was divided into four natural geographical divisions by colonial officials on the decadal census data:
# ''Indo-Gangetic Plain West geographical division'' (including
Hisar district
Hisar district is one of the 22 districts of Haryana, India. Hisar city serves as the district headquarters. Hisar district has four sub-divisions that is, Hisar, Barwala, Hansi and Narnaud, each headed by an SDM. The district is also part of ...
,
Loharu State
Loharu State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was part of the Punjab States Agency and was a nine-gun salute state.
Loharu State encompassed an area of , and was situated in the south-east corner ...
,
Rohtak district
Rohtak district is a district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is located in the southeast of the state and northwest of Delhi, bounded by Jind and Sonipat districts to the north, Jhajjar and Sonipat districts to the east, and Hissar, C ...
,
Dujana State,
Gurgaon district
Gurgaon district, officially known as Gurugram district, is one of the 22 districts of Haryana in northern India. The city of Gurgaon is the administrative headquarters of the district. The population is 1,514,432. It is one of the southern dist ...
,
Pataudi State
Pataudi State was a small princely state in India, established in 1804 by the East India Company rule in India.
The state formed a part of the Delhi Territory in the Ceded and Conquered Provinces. It was under the suzerainty of the Commission ...
, Delhi,
Karnal district
Karnal district is one of the 22 Districts of Haryana, districts of Haryana, a state in North India which constitutes the National Capital Region (NCR) of the country. The city of Karnal is a part of the National Capital Region (India), Nation ...
,
Jalandhar district
Jalandhar district is a district in Doaba region of the state of Punjab, India. The district headquarters is the city of Jalandhar.
Before the Partition of India, Jalandhar was also the headquarters of the Jalandhar Division, with constituent ...
,
Kapurthala State
Kapurthala State, was a kingdom and later princely state of the Punjab Province (1849–1947), Punjab Province of British India. Ruled by Ahluwalia Sikh rulers, spread across . According to the 1901 census the state had a population of 314,341 a ...
,
Ludhiana district
Ludhiana district is one of the 23 districts in the Indian state of Punjab. It is Punjab's largest district by both area and population. Ludhiana, the largest city in Punjab, is the district headquarters.
The main industries are bicycle parts ...
,
Malerkotla State
The State of Malerkotla or Maler Kotla was a princely state of Afghan origin in the Punjab region established in the medieval era and lasting to the era of British India. It has been described as being a princely enclave.
Its rulers belonged ...
,
Firozpur district
Firozpur district, also known as Ferozepur district, is one of the twenty-three districts in the state of Punjab, India. Firozpur district comprises an area of .
Firozpur (Ferozepur) is the capital city of the district. It is situated inside t ...
,
Faridkot State
Faridkot State was a self-governing princely state of Punjab ruled by Brar Jats outside British India during the British Raj period in the Indian sub-continent until Indian independence. The state was located in the south of the erstwhile Firoz ...
,
Patiala State
Patiala State was a kingdom and princely state in Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India, and one of the Phulkian States, that Instrument of Accession, acceded to the Dominion of India, Union of India upon Indian independence ...
,
Jind State
Jind State (also spelled Jhind State) was a princely state located in the Punjab and Haryana regions of north-western India. The state was in area and its annual income was Rs.3,000,000 in the 1940s. This state was founded and ruled by the Sidh ...
,
Nabha State
Nabha State, with its capital at Nabha, was one of the Phulkian princely states of Punjab (British India), Punjab during the British Raj in India. This state was ruled by the Sidhu clan belonging to the Sikhs, Sikh religion.
History
Orig ...
,
Lahore District
Lahore District () is a Districts of Punjab, Pakistan, district in Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan, consisting of the provincial capital, Lahore and surrounding areas. It is the most populous Districts of Pakistan, district of Pakistan, with ...
,
Amritsar district
Amritsar district is one of the twenty three districts that make up the Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab. Located in the Majha region of Punjab, the city of Amritsar is the headquarters of this district.
As of 2011, it is the second most ...
,
Gujranwala District
Gujranwala District (), is a Districts of Pakistan, district that is a part of the in Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan. Gujranwala District is bordered by the districts of Wazirabad District, Wazirabad, Sialkot District, Sialkot, Hafizabad Di ...
, and
Sheikhupura district
Sheikhupura District (;
), is a district located in Lahore Division of Punjab Province, Pakistan. Sheikhupura is the headquarters of Sheikhupura district. According to the 1998 census of Pakistan, the district had a population of 3,321,029 of ...
);
# ''Himalayan geographical division'' (including
Nahan State,
Simla District
Shimla district, known as Simla district until 1972, is one of the twelve districts of the state of Himachal Pradesh in northern India. Its headquarters is the state capital of Shimla. Neighbouring districts are Mandi and Kullu in the north, K ...
,
Simla Hill States
The Hill States of India were princely states lying in the northern border regions of the British Indian Empire. The historic terms ''Punjab Hills'' and ''Pahari Hills'' were used to describe the foothills of the Western Himalayan-range prior ...
,
Kangra district
Kangra district is the most populous district of Himachal Pradesh, India. Dharamshala is the administrative headquarters of the district.
History
Kangra is known for having one of the oldest serving Royal Dynasty in the world, the Katoch of ...
,
Mandi State
Mandi State was a princely state within (British India), with the town of Mandi, Himachal Pradesh, Mandi as its capital. The state of Mandi (the name means "market" in Hindi), which included two towns and 3,625 villages, was part of the States ...
,
Suket State
Suket State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The capital of the state was Pangna. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 15 April 1948. Formerly it belonged to the States of the ...
, and
Chamba State
Chamba State was one of the oldest princely states in present-day Republic of India, having been founded during the late 6th century. It was part of the States of the Punjab Hills of the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab Province in Br ...
);
# ''Sub-Himalayan geographical division'' (including
Ambala district
Ambala district is one of the 22 districts of Haryana state in the country of India with Ambala town serving as the administrative headquarters of the district. District Ambala lies on the North-Eastern edge of Haryana and borders Punjab and Hima ...
,
Kalsia State
Kalsia was a princely state in Punjab, British India, one of the former Cis-Sutlej states. It was founded by Gurbaksh Singh Kalsia in 1760. After India's independence, it was included in PEPSU and later in the Indian East Punjab after the St ...
,
Hoshiarpur district
Hoshiarpur district is a district of Punjab, India, Punjab state in northern India. Hoshiarpur, one of the oldest districts of Punjab, is located in the North-east part of the Punjab state and shares common boundaries with Gurdaspur district in ...
,
Gurdaspur District
Gurdaspur district is a district in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, India. Gurdaspur is the district headquarters. It internationally borders Narowal District of Pakistani Punjab, and the districts of Amritsar, Pathankot, Kapurthala ...
,
Sialkot District
Sialkot District ( Punjabi and ), is one of the districts of the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is located in the northeast of the province. The city of Sialkot is the capital of the district. The Sialkot Cantonment was established in 1852 ...
,
Gujrat District
Gujrat ( Punjabi, ) is a district of Gujrat Division in the Pakistani province of Punjab. The Gujrat District was created by the British Government in 1846. According to the 2023 Pakistani census the population of the Gujrat District is 3,219 ...
,
Jhelum District
Jhelum District () is a district, located partially on the Pothohar Plateau and in Indus Plain, in Punjab, Pakistan. Jhelum is one of the oldest districts of Punjab. It was established on 23 March 1849. Jhelum is known for providing many sold ...
,
Rawalpindi District
Rawalpindi District (Punjabi language, Punjabi and ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district located in the northernmost part of the Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab province of Pakistan. Parts of the district form part of the Islamabad Rawalpindi metropo ...
, and
Attock District
Attock District ( Punjabi/Urdu), known as Campbellpur District during British Raj, is a district, located on the Pothohar Plateau, in north western Punjab, Pakistan; created in April 1904. According to 2023 Pakistani census population of Att ...
;
# ''North-West Dry Area geographical division'' (including
Montgomery District
Montgomery District was an administrative district of the former Punjab Province of British India, in what is now Pakistan. Named after Sir Robert Montgomery, it lay in the Bari Doab, or the tract between the Sutlej and the Ravi rivers, extend ...
,
Shahpur District
Shahpur District, established in 1893 during the British Raj, existed in what is now Pakistan until 1960. From its inception until 1914, Shahpur served as the district headquarters. In 1914, the headquarters were relocated to Sargodha, althoug ...
,
Mianwali District
The Mianwali District () is a Districts of Pakistan, district located in the Sargodha Division of the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Mianwali District remained part of Rawalpindi Division until 1963, when Mianwali District beca ...
,
Lyallpur District
Faisalabad District (Lyallpur District until 1979) ( Punjabi and ) is one of the districts of Punjab, Pakistan. According to the 2023 census of Pakistan it had a population of 9,075,819, of which 3,691,999 were in Faisalabad City. It is the th ...
,
Jhang District
Jhang District (Punjabi language, Punjabi and ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district of Faisalabad Division, Faisalabad division in the Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab province, Pakistan. Jhang is the capital and administrative seat of the district.
...
,
Multan District
Multan District (), is a district in the province of Punjab, Pakistan. Its capital is the city of Multan. The district has a population of million (as of 2024) and an area of 3,720 square kilometres. The district consists of tehsils of Multa ...
,
Bahawalpur State,
Muzaffargarh District
Muzaffargarh District () is a district of the Punjab province of Pakistan. Its capital is Muzaffargarh city. It lies on the bank of the Chenab River.
History
Muzaffargarh () was founded by the Saddozai Nawab of Multan, Nawab Muzaffar Kha ...
, and
Dera Ghazi Khan District
Dera Ghazi Khan (, Punjabi language, Punjabi: ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district in Punjab, Pakistan. Its administrative capital is Dera Ghazi Khan.
The district lies to the west of the Indus River. The Sulaiman Mountains rise to a height ...
).
Partition of British Punjab
The struggle for Indian independence witnessed competing and conflicting interests in the Punjab. The landed elites of the Muslim, Hindu and Sikh communities had loyally collaborated with the British since annexation, supported the Unionist Party and were hostile to the Congress party–led independence movement.
[Pritam Singh, Federalism, Nationalism and Development: India and the Punjab Economy, Routledge, 19 February 2008, p.54] Amongst the peasantry and urban middle classes, the Hindus were the most active
National Congress supporters, the Sikhs flocked to the
Akali movement
The Akali movement (IPA: ; known in Punjabi as the Akali Morcha), also called the Gurdwara Reform Movement, was a campaign to bring reform in the gurdwaras (the Sikhism, Sikh places of worship) in India during the early 1920s. The movement led to ...
whilst the Muslims eventually supported the
Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties British India
*All-India Muslim League, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan
** Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organization above
**Unionist Muslim L ...
.
Since the partition of the sub-continent had been decided, special meetings of the Western and Eastern Section of the Legislative Assembly were held on 23 June 1947 to decide whether or not the Province of the Punjab be partitioned. After voting on both sides, partition was decided and the existing Punjab Legislative Assembly was also divided into
West Punjab
West Punjab (; ) was a province in the Dominion of Pakistan from 1947 to 1955. It was established from the western-half of British Punjab, following the independence of Pakistan. The province covered an area of 159,344 km sq (61523 sq mi), i ...
Legislative Assembly and the East Punjab Legislative Assembly. This last Assembly before independence, held its last sitting on 4 July 1947.
Major cities
Historically,
Lahore
Lahore ( ; ; ) is the capital and largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, second-largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and ...
has been the capital of the Punjab region and continues to be the most populous city in the region, with a population of 11 million for the city proper.
Faisalabad
Faisalabad, formerly known as Lyallpur, is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, second-largest city and primary List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, industrial center of the Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan ...
is the 2nd most populous city and largest industrial hub in this region. Other major cities are
Rawalpindi
Rawalpindi is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, third-largest city in the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab. It is a commercial and industrial hub, being the list of cities in P ...
,
Gujranwala
Gujranwala is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fourth most-populous city in the Pakistani province of Punjab. Located in northern-central Punjab's Rachna Doab, it serves as the headquarters of its Gujranwala District, epony ...
,
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
,
Ludhiana
Ludhiana () is the most populous Cities in India, city in the Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab.164.100.161.224
http://164.100.161.224 › filesPDF
Ludhiana State: Punjab Business & Industrial Centre, Tier 2 1 ... The city has an estima ...
,
Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
,
Jalandhar
Jalandhar () is a city in the state of Punjab, India, Punjab in India. With a considerable population, it ranks as the List of cities in Punjab and Chandigarh by population, third most-populous city in the state and is the largest city in the ...
, and
Chandigarh
Chandigarh is a city and union territory in northern India, serving as the shared capital of the states of Punjab and Haryana. Situated near the foothills of the Shivalik range of Himalayas, it borders Haryana to the east and Punjab in the ...
are the other cities in Punjab with a city-proper population of over a million.
Climate
The climate has significant impact on the economy of Punjab, particularly for agriculture in the region. Climate is not uniform over the whole region, as the areas adjacent to the Himalayas generally receive heavier rainfall than those at a distance.
There are three main seasons and two transitional periods. During the hot season, from mid-April to the end of June, the temperature may reach . The
monsoon season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
, from July to September, is a period of heavy rainfall, providing water for crops in addition to the supply from canals and
irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
systems. The transitional period after the monsoon season is cool and mild, leading to the winter season, when the temperature in January falls to at night and by day. During the transitional period from winter to the hot season, sudden
hailstorm
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
s and heavy showers may occur, causing damage to crops.
Western Punjab
Central Punjab
Eastern Punjab
Demographics
Languages

The major language is
Punjabi, which is written in India with the
Gurmukhi
Gurmukhī ( , Shahmukhi: ) is an abugida developed from the Laṇḍā scripts, standardized and used by the second Sikh guru, Guru Angad (1504–1552). Commonly regarded as a Sikh script, Gurmukhi is used in Punjab, India as the official scrip ...
script, and in Pakistan using the
Shahmukhi
Shahmukhi (, , , ) is the right-to-left abjad-based script developed from the Perso-Arabic alphabet used for the Punjabi language varieties, predominantly in Punjab, Pakistan. It is generally written in the Nastaʿlīq calligraphic hand, whic ...
script. The Punjabi language has official status and is widely used in education and administration in Indian Punjab, whereas in Pakistani Punjab these roles are instead fulfilled by the
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
language.
Several languages closely related to Punjabi are spoken in the various parts of the region.
Dogri,
Kangri
Kangri can mean:
*of, from, or related to the Kangra Valley or the Kangra district of himachal.
*Kangri language, the Indo-Aryan language of the valley
*Kanger
A kanger (; also known as kangri or kangid or kangir) is an earthen pot woven around ...
, and other
western Pahari
The Western Pahari languages are a range of languages and dialects of Northern Indo-Aryan languages spoken in the western parts of the Himalayan range, primarily in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. They are also spoken in Jammu and Jaunsar ...
dialects are spoken in the north-central and northeastern parts of the region, while
Bagri is spoken in south-central and southeastern sections. Meanwhile,
Saraiki is generally spoken across a wide belt covering the southwest, while in the northwest there are large pockets containing speakers of
Hindko
Hindko (, , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken by several million people of various ethnic backgrounds in northwestern Pakistan, primarily in the provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Police, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and northern Pun ...
and
Pothwari.
Religions
Background
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
is the oldest of the religions practised by Punjabi people, however, the term ''Hindu'' was also applied over a vast territory with much regional diversity.
The
historical Vedic religion
The historical Vedic religion, also called Vedism or Brahmanism, and sometimes ancient Hinduism or Vedic Hinduism, constituted the religious ideas and practices prevalent amongst some of the Indo-Aryan peoples of the northwest Indian subcontin ...
constituted the religious ideas and practices in the Punjab during the
Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
(), centered primarily in the worship of
Indra
Indra (; ) is the Hindu god of weather, considered the king of the Deva (Hinduism), Devas and Svarga in Hinduism. He is associated with the sky, lightning, weather, thunder, storms, rains, river flows, and war. volumes
Indra is the m ...
. The bulk of the
Rigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
was composed in the Punjab region between circa 1500 and 1200 BCE, while later Vedic scriptures were composed more eastwards, between the
Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
and
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
rivers. An ancient Indian law book called the
Manusmriti
The ''Manusmṛti'' (), also known as the ''Mānava-Dharmaśāstra'' or the Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitutions among the many ' of Hinduism.
Over fifty manuscripts of the ''Manusmriti'' are now known, but the earli ...
, developed by Brahmin Hindu priests, shaped Punjabi religious life from 200 BCE onward.
Later, the
spread of Buddhisim and Jainism in the Indian subcontinent saw the growth of
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
and
Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religions, Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its s ...
in the Punjab.
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
was introduced via southern Punjab in the 8th century, becoming the majority by the 16th century, via local conversion.
There was a small Jain community left in Punjab by the 16th century, while the Buddhist community had largely disappeared by the turn of the 10th century. The region became predominantly
Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
due to missionary
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
saints whose
dargah
A Sufi shrine or dargah ( ''dargâh'' or ''dargah'', Turkish: ''dergâh'', Hindustani: ''dargāh'' दरगाह درگاہ, ''dôrgah'') is a shrine or tomb built over the grave of a revered religious figure, often a Sufi saint or dervi ...
s dot the landscape of the Punjab region.
The rise of
Sikhism
Sikhism is an Indian religion and Indian philosophy, philosophy that originated in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent around the end of the 15th century CE. It is one of the most recently founded major religious groups, major religio ...
in the 1700s saw some Punjabis, both Hindu and Muslim, accepting the new Sikh faith.
A number of Punjabis during the
colonial period of India became Christians, with all of these religions characterizing the religious diversity now found in the Punjab region.
Colonial era
A number of Punjabis during the
colonial period of India became Christians, with all of these religions characterizing the religious diversity now found in the Punjab region.
Additionally during the colonial era, the practice of
religious syncretism
Religious syncretism is the blending of religious belief systems into a new system, or the incorporation of other beliefs into an existing religious tradition.
This can occur for many reasons, where religious traditions exist in proximity to each ...
among
Punjabi Muslims
Punjabi Muslims are Punjabis who are adherents of Islam. With a population of more than 112 million, they are the third-largest predominantly Islam-adhering Muslims, Muslim ethnicity in the world, after Arab Muslims, Arabs and Bengali Muslims, ...
and
Punjabi Hindus
Punjabi Hindus are adherents of Hinduism who identify ethnically, linguistically, culturally, and genealogically as Punjabis and are natives of the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. Punjabi Hindus are the third-largest religious ...
was noted and documented by officials in census reports:
The ''Indo−Gangetic Plain West geographical division'' included
Hisar district
Hisar district is one of the 22 districts of Haryana, India. Hisar city serves as the district headquarters. Hisar district has four sub-divisions that is, Hisar, Barwala, Hansi and Narnaud, each headed by an SDM. The district is also part of ...
,
Loharu State
Loharu State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. It was part of the Punjab States Agency and was a nine-gun salute state.
Loharu State encompassed an area of , and was situated in the south-east corner ...
,
Rohtak district
Rohtak district is a district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is located in the southeast of the state and northwest of Delhi, bounded by Jind and Sonipat districts to the north, Jhajjar and Sonipat districts to the east, and Hissar, C ...
,
Dujana State,
Gurgaon district
Gurgaon district, officially known as Gurugram district, is one of the 22 districts of Haryana in northern India. The city of Gurgaon is the administrative headquarters of the district. The population is 1,514,432. It is one of the southern dist ...
,
Pataudi State
Pataudi State was a small princely state in India, established in 1804 by the East India Company rule in India.
The state formed a part of the Delhi Territory in the Ceded and Conquered Provinces. It was under the suzerainty of the Commission ...
,
Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, but spread chiefly to the west, or beyond its Bank (geography ...
,
Karnal district
Karnal district is one of the 22 Districts of Haryana, districts of Haryana, a state in North India which constitutes the National Capital Region (NCR) of the country. The city of Karnal is a part of the National Capital Region (India), Nation ...
,
Jalandhar district
Jalandhar district is a district in Doaba region of the state of Punjab, India. The district headquarters is the city of Jalandhar.
Before the Partition of India, Jalandhar was also the headquarters of the Jalandhar Division, with constituent ...
,
Kapurthala State
Kapurthala State, was a kingdom and later princely state of the Punjab Province (1849–1947), Punjab Province of British India. Ruled by Ahluwalia Sikh rulers, spread across . According to the 1901 census the state had a population of 314,341 a ...
,
Ludhiana district
Ludhiana district is one of the 23 districts in the Indian state of Punjab. It is Punjab's largest district by both area and population. Ludhiana, the largest city in Punjab, is the district headquarters.
The main industries are bicycle parts ...
,
Malerkotla State
The State of Malerkotla or Maler Kotla was a princely state of Afghan origin in the Punjab region established in the medieval era and lasting to the era of British India. It has been described as being a princely enclave.
Its rulers belonged ...
,
Firozpur district
Firozpur district, also known as Ferozepur district, is one of the twenty-three districts in the state of Punjab, India. Firozpur district comprises an area of .
Firozpur (Ferozepur) is the capital city of the district. It is situated inside t ...
,
Faridkot State
Faridkot State was a self-governing princely state of Punjab ruled by Brar Jats outside British India during the British Raj period in the Indian sub-continent until Indian independence. The state was located in the south of the erstwhile Firoz ...
,
Patiala State
Patiala State was a kingdom and princely state in Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India, and one of the Phulkian States, that Instrument of Accession, acceded to the Dominion of India, Union of India upon Indian independence ...
,
Jind State
Jind State (also spelled Jhind State) was a princely state located in the Punjab and Haryana regions of north-western India. The state was in area and its annual income was Rs.3,000,000 in the 1940s. This state was founded and ruled by the Sidh ...
,
Nabha State
Nabha State, with its capital at Nabha, was one of the Phulkian princely states of Punjab (British India), Punjab during the British Raj in India. This state was ruled by the Sidhu clan belonging to the Sikhs, Sikh religion.
History
Orig ...
,
Lahore District
Lahore District () is a Districts of Punjab, Pakistan, district in Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan, consisting of the provincial capital, Lahore and surrounding areas. It is the most populous Districts of Pakistan, district of Pakistan, with ...
,
Amritsar district
Amritsar district is one of the twenty three districts that make up the Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab. Located in the Majha region of Punjab, the city of Amritsar is the headquarters of this district.
As of 2011, it is the second most ...
,
Gujranwala District
Gujranwala District (), is a Districts of Pakistan, district that is a part of the in Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab, Pakistan. Gujranwala District is bordered by the districts of Wazirabad District, Wazirabad, Sialkot District, Sialkot, Hafizabad Di ...
, and
Sheikhupura District
Sheikhupura District (;
), is a district located in Lahore Division of Punjab Province, Pakistan. Sheikhupura is the headquarters of Sheikhupura district. According to the 1998 census of Pakistan, the district had a population of 3,321,029 of ...
.
The ''Himalayan geographical division'' included
Sirmoor State
Sirmur (also spelled as Sirmor, Sirmaur, Sirmour, or Sirmoor) was a princely state of India, located in the region that is now the Sirmaur district of Himachal Pradesh. The state was also known as Nahan, after its main city, Nahan. The stat ...
,
Simla District
Shimla district, known as Simla district until 1972, is one of the twelve districts of the state of Himachal Pradesh in northern India. Its headquarters is the state capital of Shimla. Neighbouring districts are Mandi and Kullu in the north, K ...
,
Simla Hill States
The Hill States of India were princely states lying in the northern border regions of the British Indian Empire. The historic terms ''Punjab Hills'' and ''Pahari Hills'' were used to describe the foothills of the Western Himalayan-range prior ...
,
Bilaspur State
Bilaspur State or Kahlur State, sometimes Kahloor Riyasat, was a kingdom (697–1849) and later princely state (1849–1948) in the Punjab Province ruled by a separate branch of Chandravanshi Chandel rajput dynasty. Raja Bir Chand 697–73 ...
,
Kangra district
Kangra district is the most populous district of Himachal Pradesh, India. Dharamshala is the administrative headquarters of the district.
History
Kangra is known for having one of the oldest serving Royal Dynasty in the world, the Katoch of ...
,
Mandi State
Mandi State was a princely state within (British India), with the town of Mandi, Himachal Pradesh, Mandi as its capital. The state of Mandi (the name means "market" in Hindi), which included two towns and 3,625 villages, was part of the States ...
,
Suket State
Suket State was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. The capital of the state was Pangna. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 15 April 1948. Formerly it belonged to the States of the ...
, and
Chamba State
Chamba State was one of the oldest princely states in present-day Republic of India, having been founded during the late 6th century. It was part of the States of the Punjab Hills of the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab Province in Br ...
.
The ''Sub−Himalayan geographical division'' included
Ambala district
Ambala district is one of the 22 districts of Haryana state in the country of India with Ambala town serving as the administrative headquarters of the district. District Ambala lies on the North-Eastern edge of Haryana and borders Punjab and Hima ...
,
Kalsia State
Kalsia was a princely state in Punjab, British India, one of the former Cis-Sutlej states. It was founded by Gurbaksh Singh Kalsia in 1760. After India's independence, it was included in PEPSU and later in the Indian East Punjab after the St ...
,
Hoshiarpur district
Hoshiarpur district is a district of Punjab, India, Punjab state in northern India. Hoshiarpur, one of the oldest districts of Punjab, is located in the North-east part of the Punjab state and shares common boundaries with Gurdaspur district in ...
,
Gurdaspur district
Gurdaspur district is a district in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, India. Gurdaspur is the district headquarters. It internationally borders Narowal District of Pakistani Punjab, and the districts of Amritsar, Pathankot, Kapurthala ...
,
Sialkot District
Sialkot District ( Punjabi and ), is one of the districts of the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is located in the northeast of the province. The city of Sialkot is the capital of the district. The Sialkot Cantonment was established in 1852 ...
,
Gujrat District
Gujrat ( Punjabi, ) is a district of Gujrat Division in the Pakistani province of Punjab. The Gujrat District was created by the British Government in 1846. According to the 2023 Pakistani census the population of the Gujrat District is 3,219 ...
,
Jhelum District
Jhelum District () is a district, located partially on the Pothohar Plateau and in Indus Plain, in Punjab, Pakistan. Jhelum is one of the oldest districts of Punjab. It was established on 23 March 1849. Jhelum is known for providing many sold ...
,
Rawalpindi District
Rawalpindi District (Punjabi language, Punjabi and ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district located in the northernmost part of the Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab province of Pakistan. Parts of the district form part of the Islamabad Rawalpindi metropo ...
, and
Attock District
Attock District ( Punjabi/Urdu), known as Campbellpur District during British Raj, is a district, located on the Pothohar Plateau, in north western Punjab, Pakistan; created in April 1904. According to 2023 Pakistani census population of Att ...
.
The ''North−West Dry Area geographical division'' included
Montgomery District
Montgomery District was an administrative district of the former Punjab Province of British India, in what is now Pakistan. Named after Sir Robert Montgomery, it lay in the Bari Doab, or the tract between the Sutlej and the Ravi rivers, extend ...
,
Shahpur District
Shahpur District, established in 1893 during the British Raj, existed in what is now Pakistan until 1960. From its inception until 1914, Shahpur served as the district headquarters. In 1914, the headquarters were relocated to Sargodha, althoug ...
,
Mianwali District
The Mianwali District () is a Districts of Pakistan, district located in the Sargodha Division of the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Mianwali District remained part of Rawalpindi Division until 1963, when Mianwali District beca ...
,
Lyallpur District
Faisalabad District (Lyallpur District until 1979) ( Punjabi and ) is one of the districts of Punjab, Pakistan. According to the 2023 census of Pakistan it had a population of 9,075,819, of which 3,691,999 were in Faisalabad City. It is the th ...
,
Jhang District
Jhang District (Punjabi language, Punjabi and ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district of Faisalabad Division, Faisalabad division in the Punjab (Pakistan), Punjab province, Pakistan. Jhang is the capital and administrative seat of the district.
...
,
Multan District
Multan District (), is a district in the province of Punjab, Pakistan. Its capital is the city of Multan. The district has a population of million (as of 2024) and an area of 3,720 square kilometres. The district consists of tehsils of Multa ...
,
Bahawalpur State,
Muzaffargarh District
Muzaffargarh District () is a district of the Punjab province of Pakistan. Its capital is Muzaffargarh city. It lies on the bank of the Chenab River.
History
Muzaffargarh () was founded by the Saddozai Nawab of Multan, Nawab Muzaffar Kha ...
,
Dera Ghazi Khan District
Dera Ghazi Khan (, Punjabi language, Punjabi: ) is a Districts of Pakistan, district in Punjab, Pakistan. Its administrative capital is Dera Ghazi Khan.
The district lies to the west of the Indus River. The Sulaiman Mountains rise to a height ...
, and the Biloch Trans–Frontier Tract.
Post-partition
In the present-day, the vast majority of Pakistani Punjabis are Sunni Muslim by faith, but also include significant minority faiths, such as Shia Muslims, Ahmadi Muslims,
Hindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
,
Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
and Christians.
Sikhism, founded by
Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also known as ('Father Nanak'), was an Indian spiritual teacher, mystic and poet, who is regarded as the founder of Sikhism and is t ...
is the main religion practised in the post-1966 Indian Punjab state. About 57.7% of the population of Punjab state is
Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
, 38.5% is
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
, with the remaining population including
Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
,
Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, and
Jains
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion whose three main pillars are nonviolence (), asceticism (), and a rejection of all simplistic and one-sided views of truth and reality (). Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and ...
. Punjab state contains the holy Sikh cities of
Amritsar
Amritsar, also known as Ambarsar, is the second-List of cities in Punjab, India by population, largest city in the India, Indian state of Punjab, India, Punjab, after Ludhiana. Located in the Majha region, it is a major cultural, transportatio ...
,
Anandpur Sahib
Anandpur Sahib, also referred simply as Anandpur (), is a city in Rupnagar district (Ropar), on the edge of Shivalik Hills, in the Indian state of Punjab. Located near the Sutlej River, the city is one of the most sacred religious places in Si ...
,
Tarn Taran Sahib
Tarn Taran Sahib is a city in the Majha region of the state of Punjab, India. It is the district headquarters and hosts the municipal council of Tarn Taran district. Gurdwara Sri Tarn Taran Sahib, a prominent Sikh shrine, is located in the c ...
,
Fatehgarh Sahib
Fatehgarh Sahib () is a city and a sacred pilgrimage site of Sikhism in the north west Indian state of Punjab. It is the headquarters of Fatehgarh Sahib district, located about north of Sirhind. Fatehgarh Sahib is named after Fateh Singh, the ...
and
Chamkaur Sahib.
The Punjab was home to several
Sufi saints
Sufi saints or wali (, plural ʾawliyāʾ أولياء) played an instrumental and foregrounding role in spreading Islam throughout the world. In the traditional Islamic view, a saint is portrayed as someone "marked by pecialdivine favor ... ...
, and Sufism is
well established in the region. Also,
Kirpal Singh revered the Sikh Gurus as saints.
Tribes


The Punjab region is diverse. Historic census reports taken in the
colonial era Colonial period (a period in a country's history where it was subject to management by a colonial power) may refer to:
Continents
*European colonization of the Americas
* Colonisation of Africa
* Western imperialism in Asia
Countries
* Col ...
details the main
castes
A caste is a fixed social group into which an individual is born within a particular system of social stratification: a caste system. Within such a system, individuals are expected to marry exclusively within the same caste (endogamy), foll ...
are represented, alongside numerous subcastes and
tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide use of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. The definition is contested, in part due to conflict ...
(also known as ''
Jāti
''Jāti'' is the term traditionally used to describe a cohesive group of people in the Indian subcontinent, like a caste, sub-caste, clan, tribe, or a religious sect. Each Jāti typically has an association with an occupation, geography or trib ...
'' or ''
Barādarī''), formed parts of the various ethnic groups in the region, contemporarily known as
Punjabis
The Punjabis (Punjabi language, Punjabi: ; ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ; romanised as Pañjābī) are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group associated with the Punjab region, comprising areas of northwestern India and eastern Paki ...
,
Saraikis
The Saraikis () are an Indo-Aryan community native to central Pakistan, unified by their use of the Saraiki language and a shared regional identity that transcends tribal and ethnic affiliations.
Mostly inhabiting southern Punjab as well as mo ...
,
Haryanvis,
Hindkowans
Hindkowans, also known as the Hindki, is a contemporary designation for speakers of Indo-Aryan languages who live among the neighbouring Pashtuns, particularly the speakers of various Hindko dialects of Western Punjabi (Lahnda). The origins ...
,
Dogras
The Dogras, or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group living primarily in the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. They speak their native Dogri language. They live predominantly in the Duggar region of the Jammu Div ...
,
Paharis, and more.
Economy
The historical region of Punjab produces a relatively high proportion of the food output from India and Pakistan. The region has been used for extensive wheat farming. In addition, rice, cotton,
sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, fruit, and vegetables are also grown.
The agricultural output of the Punjab region in Pakistan contributes significantly to Pakistan's GDP. Both Indian and Pakistani Punjab is considered to have the best infrastructure of their respective countries. The Indian state of Punjab is currently the
16th richest state or the eighth richest large state of India. Pakistani Punjab produces 68% of Pakistan's foodgrain production. Its share of Pakistan's GDP has historically ranged from 51.8% to 54.7%.
Called "The Granary of India" or "The Bread Basket of India", Indian Punjab produces 1% of the
world's rice, 2% of its wheat, and 2% of its cotton.
In 2001, it was recorded that farmers made up 39% of Indian Punjab's workforce. In the Punjab region of Pakistan, 42.3% of the labour force is engaged in the agriculture sector.
Alternatively, Punjab is also adding to the economy with the increase in employment of Punjab youth in the
private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The private sector employs most of the workfo ...
. Government schemes such as 'Ghar Ghar Rozgar and Karobar Mission' have brought enhanced employability in the private sector. , more than 32,000 youths have been placed in different jobs and 12,000 have been skill-trained.
See also
*
Chak (village)
Chak, a Punjabi word, is the land revenue settlement/assessment circle marking a contiguous block of land. The word Chak comes from Chakar referring to a wheel in Punjabi, specifically a wheel associated with a water well. Historically th ...
*
Dhani (settlement type)
Dhani ( ') or Thok is a type of hamlet, the smallest conglomeration of houses, in the sandy Bagar region of the northwestern states of Rajasthan, Haryana and Punjab in India. Per the Census of India, 70% of Indians live in villages. 80% of the ...
*
Jallianwala Bagh
Jallianwala Bagh () is a historic garden and memorial of national importance close to the Golden Temple complex in Amritsar, Punjab, India, preserved in the memory of those wounded and killed in the Jallianwala Bagh Massacre that took place on t ...
*
Music of Punjab
The music of Punjab reflects the traditions of the Punjab, Punjab region associated with Punjabi language. Punjab is currently divided into two parts: Punjab, India, East Punjab, in India, and Punjab, Pakistan, West Punjab, the most populous pr ...
*
Panjab Digital Library
The Panjab Digital Library is a voluntary organization digitizing and preserving the cultural heritage of Panjab since 2003. With over 85 million digitized pages, it is the biggest resource of digital material on Panjab. There are many his ...
*
Punjabi cuisine
Punjabi cuisine is a culinary style originating in the Punjab, a region in the northern part of South Asia, which is now divided into an Punjab, India, Indian part to the east and a Punjab, Pakistan, Pakistani part to the west. This cuisine ha ...
*
Punjabi dance
Punjabi dances are an array of folk and religious dances of the Punjabi people indigenous to the Punjab region, straddling the border of India and Pakistan. The style of Punjabi dances ranges from very high energy to slow and reserved, and there ...
*
Sattagydia
Sattagydia (Old Persian: 𐎰𐎫𐎦𐎢𐏁 ''Thataguš'', country of the "hundred cows") was one of the easternmost regions of the Achaemenid Empire, part of its Seventh tax district according to Herodotus, along with Gandārae, Dadicae an ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* Condos, Mark. ''The Insecurity State: Punjab and the Making of Colonial Power in British India'' (2020
excerpt
*
*
uraishee 73''Punjabi Adab De Kahani'', Abdul Hafeez Quaraihee, Azeez Book Depot, Lahore, 1973.
*
hopra 77''Punjab as a Sovereign State'', Gulshan Lal Chopra, Al-Biruni, Lahore, 1977.
* Patwant Singh. 1999. ''The Sikhs''. New York: Doubleday. .
* ''The Evolution of Heroic Tradition in Ancient Panjab'', 1971, Buddha Parkash.
* ''Social and Political Movements in ancient Panjab'', Delhi, 1962, Buddha Parkash.
* ''History of Porus'', Patiala, Buddha Parkash.
* ''History of the Panjab'', Patiala, 1976, Fauja Singh, L.M. Joshi (Ed).
* ''The Legacy of the Punjab'', 1997, R.M. Chopra.
* ''The Rise Growth and Decline of Indo-Persian Literature'', R.M. Chopra, 2012, Iran Culture House, New Delhi. 2nd revised edition, published in 2013.
* Sims, Holly. "The State and Agricultural Productivity: Continuity versus Change in the Indian and Pakistani Punjabs." ''
Asian Survey
''Asian Survey: A Bimonthly Review of Contemporary Asian Affairs'' is a bimonthly academic journal of Asian studies published by the University of California Press on behalf of the Institute of East Asian Studies at the University of California, ...
'', 1 April 1986, Vol. 26(4), pp. 483–500.
External links
*
*
{{Authority control
Regions of India
Regions of Pakistan
Historical regions
Geography of South Asia
Historical Indian regions
Historical regions of Pakistan

 The earliest known notable local king of this region was known as
The earliest known notable local king of this region was known as  In the 19th century, Maharajah
In the 19th century, Maharajah  At its height in the first half of the 19th century, the Sikh Empire spanned a total of over .
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan
At its height in the first half of the 19th century, the Sikh Empire spanned a total of over .
The Punjab was a region straddling India and the Afghan  It encompassed the present day
It encompassed the present day 
 The Punjab region is diverse. Historic census reports taken in the
The Punjab region is diverse. Historic census reports taken in the