|
Gurdaspur District (British Punjab)
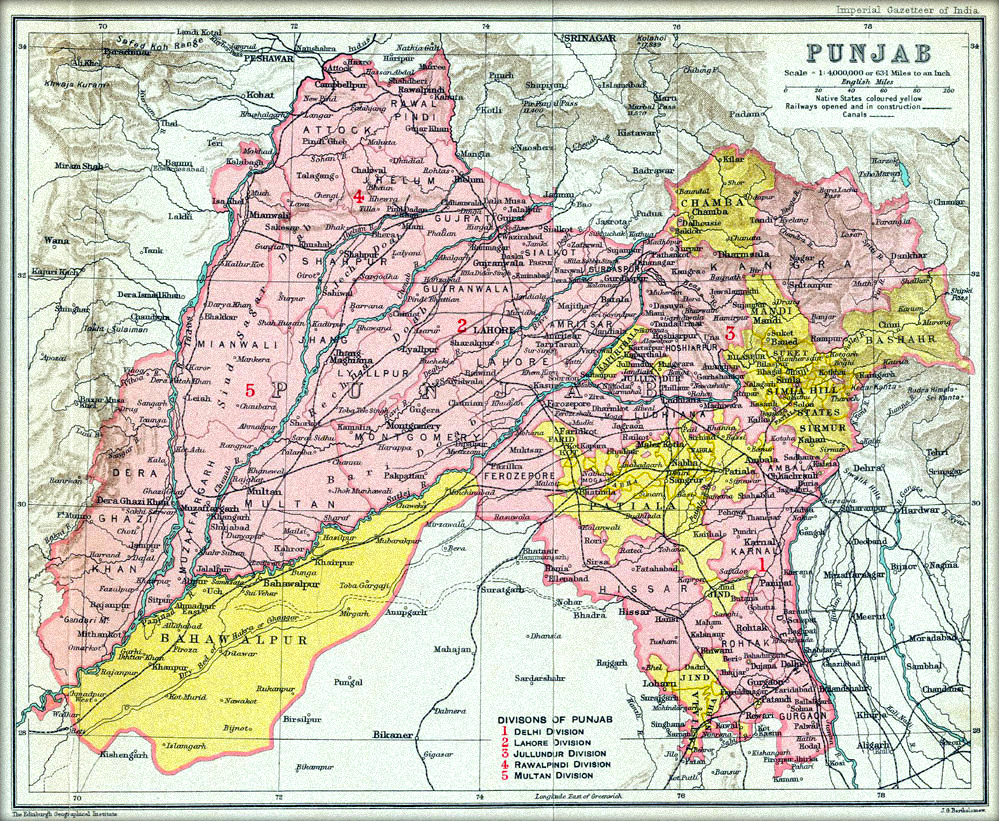
Gurdaspur District was a district in the Lahore Division of the Punjab Province of British India with its headquarters at Gurdaspur. It lay between 31°35' and 32°30′ N. and 74° 52′ and 75° 56′ E., with an area of 1,889 square miles. It was bounded north by the Jammu province of Kashmir; on the west by Sialkot District; on the south-west by Amritsar District; on the south-east and east by the Beas River, which separated it from the Kapurthala State and Hoshiarpur District, and also by Kangra District; and on the north-east by the Chamba State. Geography The District occupied the flat-land area of the Bari Doab, together with a triangular wedge of territory west of the Ravi River. It included the hill stations of Dalhousie and Bakloh, two isolated pieces of hill territory acquired from the Chamba State, together with a strip of territory on which the cart road ran connecting these outlying stations with the main body of the district. The Pathankot Tehsil (teh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent, * * lasting from 1858 to 1947. * * It is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or direct rule in India. * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom, which were collectively called ''Presidencies and provinces of British India, British India'', and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British British paramountcy, paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jammu And Kashmir (princely State)
Jammu and Kashmir, also known as Kashmir and Jammu, was a princely state in a subsidiary alliance with the Company rule in India, British East India Company from 1846 to 1858 and under the ''Suzerainty#British_paramountcy, paramountcy'' (or tutelage) of the The Crown, British Crown, from 1858 until the Partition of India in 1947, when it became a Kashmir#Kashmir_dispute, disputed territory, now administered by three countries: China, India, and Pakistan. Quote: "Kashmir, region of the northwestern Indian subcontinent. It is bounded by the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang to the northeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east (both parts of China), by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south, by Pakistan to the west, and by Afghanistan to the northwest. The northern and western portions are administered by Pakistan and comprise three areas: Azad Kashmir, Gilgit, and Baltistan, ... The southern and southeastern portions constitute the Indian state of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluk, or taluka () is a local unit of administrative division in India and Pakistan. It is a subdistrict of the area within a Zila (country subdivision), district including the designated populated place that serves as its administrative centre, with possible additional towns, and usually a number of village#South Asia, villages. The terms in India have replaced earlier terms, such as ''pargana'' (''pergunnah'') and ''thana''. In List of mandals in Andhra Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh and List of mandals in Telangana, Telangana, a newer unit called mandal (circle) has come to replace the tehsil system. A mandal is generally smaller than a tehsil, and is meant for facilitating local self-government in the panchayati raj in India, panchayat system. In West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, community development blocks (CDBs) are the empowered grassroots administrative unit, replacing tehsils. Tehsil office is primarily tasked with land revenue administration, be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cart Road
Cart Road is a census town in the Kurseong CD block in the Kurseong subdivision of the Darjeeling district in the state of West Bengal, India. Geography Location Cart Road is located at . Area overview The map alongside shows the eastern portion of the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region and a small portion of the terai region in its eastern and southern fringes, all of it in the Darjeeling district. In the Darjeeling Sadar subdivision 61.00% of the total population lives in the rural areas and 39.00% of the population lives in the urban areas. In the Kurseong subdivision 58.41% of the total population lives in the rural areas and 41.59% lives in the urban areas. There are 78 tea gardens/ estates (the figure varies slightly according to different sources), in the district, producing and largely exporting Darjeeling tea. It engages a large proportion of the population directly/ indirectly. Some tea gardens were identified in the 2011 census as census towns or villages. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakloh
Bakloh (or Bukloh (archaic spelling)) is a cantonment town. It is a hill station, 4584 feet above sea level, in Chamba district in the state of Himachal Pradesh, India. History Bakloh and Balun, Dalhousie Cantonment, along with a sliver of territory to connect the two cantonments, was acquired in 1866 from the Raja of Chamba for a sum of rupees 5000. firstly Bakloh was meant for a 'Goorkha Cantonment' for the ''4th Goorkha Regiment'', raised at Pithoragarh uttar Pradesh in 1857. Balun, the cantonment in Dalhousie, was for British troops. Bakloh remained the ''home'' and the Regimental Center and Depot, of the 4th Gorkha Rifles, known as the 4th Prince of Wales Own Gurkha Rifles, for 82 years, from 1866 to 1948. 2/4 Gorkha Rifles was raised in Bakloh on 22 April 1886; 3/4 Gorkha Rifles on 15 November 1940; and 4/4 Gorkha Rifles on 15 March 1941. In 1934, the 5 km long cart track from Bakloh to Tannu Hatti, on the Dalhousie road, was converted into a motor-able road. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalhousie, India
Dalhousie () is a hill station, near town of Chamba in Chamba district in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. It is situated on five hills and has an elevation of above sea level. Etymology Dalhousie Town was named after The Earl of Dalhousie, who was the British Governor-General in India while establishing this place as a summer retreat. Climate Dalhousie has a humid subtropical climate. Late summer and early spring see torrential rainfall due to monsoonal influence. The city sees over 90 frost Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor that deposits onto a freezing surface. Frost forms when the air contains more water vapor than it can normally hold at a specific temperature. The process is simila ... days per year and 20-30 snowy days. The average night temperature during the season is around , while the maximum is close to . See also *'' Lootera'', 2013 film shot in Dalhousie *'' Almost Pyaar with DJ Mohabbat'', 2023 film s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravi River
The Ravi River is a transboundary river in South Asia, flowing through northwestern India and eastern Pakistan, and is one of five major rivers of the Punjab region. Under the Indus Waters Treaty of 1960, the waters of the Ravi and two other rivers of the Punjab (Sutlej and Beas River) were allocated to India. Subsequently, the Indus Basin Project was developed in Pakistan, which transfers waters from western rivers of the Indus system to replenish the portion of the Ravi River lying in that country. Many inter-basin water transfers, irrigation, hydropower and multipurpose projects have been built in India. History According to ancient history traced to Vedas, the Ravi River was known as (). The Ravi was known as Purushni or Irawati to Indians in Vedic times and as Hydraotes () and Hyarotis (Ὑαρῶτις) to the Ancient Greeks. Part of the Battle of the Ten Kings was fought on a river, which according to Yaska (Nirukta 9.26) refers to the Ravi river at Punjab. Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bari Doab
''Doab'' () is a term used in South Asia Quote: "Originally and chiefly in South Asia: (the name of) a strip or narrow tract of land between two rivers; spec. (with) the area between the rivers Ganges and Jumna in northern India." for the tract Quote: "confluence, land between two rivers, used in India of the tongue of land between the Ganges and Jumna, and of similar tracts in the Punjab, etc., lit. ‘two waters’ " of land lying between two confluence, confluent rivers. It is similar to an interfluve. Quote: " a tract of land between two rivers : interfluve" In the ''Oxford Hindi-English Dictionary'', R. S. McGregor refers to its Persian origin in defining it as ''do-āb'' (, literally "two [bodies of] water") "a region lying between and reaching to the confluence of two rivers." Khadir, bangar, barani, nali and bagar Since North India and Pakistan are coursed by a multiplicity of Himalayan rivers that divide the plains into ''doabs'' (i.e. regions between two rivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamba State
Chamba State was one of the oldest princely states in present-day Republic of India, having been founded during the late 6th century. It was part of the States of the Punjab Hills of the Punjab Province (British India), Punjab Province in British Raj, India from 1859 to 1947. Its last ruler signed the instrument of accession to the Dominion of India, Indian Union of 15 April 1948. History According to tradition, the ancient name of Chamba was Champa, and its predecessor state was known as Brahmpur. This site later became Bharmour around 550 AD when Raja Maru Verman came from Kalpagram to the Chamba Hills. Around 920 CE, the capital was shifted from Bharmour to present day Chamba Town. The rulers of Chamba State patronized artists of the Pahari painting style. Between 1809 and 1846 Chamba was tributary to Sikh Empire & come under its The Kangra hills province of lahore durbar. In 1821, Chamba annexed Bhadrawah State. After the First Anglo-Sikh War, the British gained a large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangra District
Kangra district is the most populous district of Himachal Pradesh, India. Dharamshala is the administrative headquarters of the district. History Kangra is known for having one of the oldest serving Royal Dynasty in the world, the Katoch of the Kangra State. In 1758, Raja Ghamand Chand was appointed ''nazim'' or governor of Jullundur Doab under the Afghans. Ghamand Chand was a brave and strong ruler who restored the prestige of Kangra. As he was unable to capture Kangra Fort, he built another fort at Tira Sujanpur on the left bank of the Beas, almost opposite to Alampur on a hill overlooking the town. He died in 1774 and was succeeded by his son, Tegh Chand, who died too soon in 1775. Ghamand Chand's grandson, Raja Sansar Chand (r. 1775–1823) established the supremacy of Kangra over all the surrounding hill states. During his reign, Kangra became a major centre for the arts and several palaces were built. In 1805, the neighbouring hill states rebelled, with the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoshiarpur District
Hoshiarpur district is a district of Punjab, India, Punjab state in northern India. Hoshiarpur, one of the oldest districts of Punjab, is located in the North-east part of the Punjab state and shares common boundaries with Gurdaspur district in the north-west, Jalandhar district and Kapurthala district in south-west, Kangra district and Una district of Himachal Pradesh in the north-east. Hoshiarpur district comprises 4 sub-divisions, 10 community development blocks, 9 urban local bodies and 1417 villages. The district has an area of 3365 km2. and a population of 1,586,625 persons as per census 2011. Hoshiarpur, along with the districts of Nawanshehar, Kapurthala and parts of Jalandhar, represents one of the cultural regions of Punjab called Doaba or the Bist Doab - the tract of land between two rivers, namely Beas and Sutlej. The area, along with the Shivalik foothills on the right side of Chandigarh-Pathankot road in Hoshiarpur, is sub mountainous. This part of the district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapurthala State
Kapurthala State, was a kingdom and later princely state of the Punjab Province (1849–1947), Punjab Province of British India. Ruled by Ahluwalia Sikh rulers, spread across . According to the 1901 census the state had a population of 314,341 and contained two towns and 167 villages.Kapurthala state ''The Imperial Gazetteer of India'', 1909, v. 14, p. 408. In 1930, Kapurthala became part of the Punjab States Agency and acceded to the Dominion of India, Union of India in 1947. In colonial India, Kapurthala State was known for its composite nationalism, communal harmony, with its Sikh ruler Jagatjit Singh building the Moorish Mosque, Kapurthala, Moorish Mosque for his Muslim subjects. At the time of the Indian independence movement, the ruler of the Kapurthala S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |