Peptide Bond on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
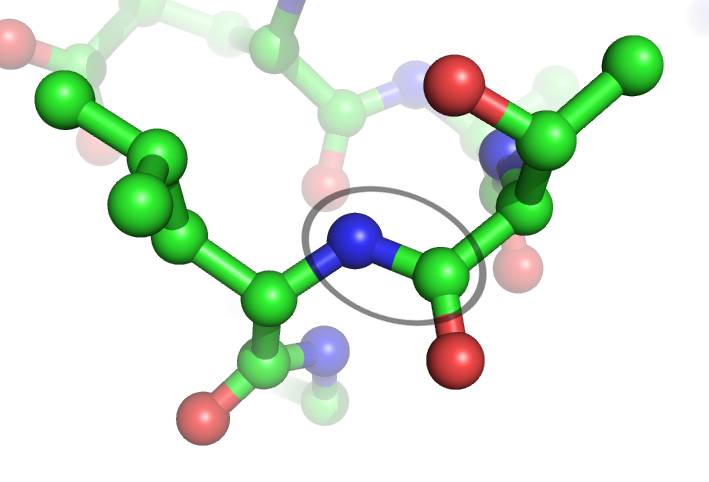 In
In
 When two amino acids form a '' dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of
When two amino acids form a '' dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of  The formation of the peptide bond consumes energy, which, in organisms, is derived from ATP. Peptides and
The formation of the peptide bond consumes energy, which, in organisms, is derived from ATP. Peptides and
 In
In organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain ...
, a peptide bond is an amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a chemical compound, compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl functional group, groups or hydrogen at ...
type of covalent
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
chemical bond
A chemical bond is the association of atoms or ions to form molecules, crystals, and other structures. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds or through the sharing of electrons a ...
linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
number two) of another, along a peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty am ...
or protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
chain.
It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids.
Synthesis
condensation reaction
In organic chemistry, a condensation reaction is a type of chemical reaction in which two molecules are combined to form a single molecule, usually with the loss of a small molecule such as water. If water is lost, the reaction is also known as a ...
. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a substituent, chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone chain, backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a mo ...
(C1) carboxylic acid
In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group () attached to an Substituent, R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as or , sometimes as with R referring to an organyl ...
moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide.
The amide bond is synthesized when the carboxyl group of one amino acid molecule reacts with the amino group of the other amino acid molecule, causing the release of a molecule of water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
(H2O), hence the process is a dehydration synthesis reaction.
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
s are chains of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s held together by peptide bonds (and sometimes by a few isopeptide bonds). Organisms use enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s to produce nonribosomal peptide
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacterium, bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be ma ...
s, and ribosome
Ribosomes () are molecular machine, macromolecular machines, found within all cell (biology), cells, that perform Translation (biology), biological protein synthesis (messenger RNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order s ...
s to produce proteins via reactions that differ in details from dehydration synthesis.
Some peptides, like alpha-amanitin, are called ribosomal peptides as they are made by ribosomes, but many are nonribosomal peptide
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacterium, bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be ma ...
s as they are synthesized by specialized enzymes rather than ribosomes. For example, the tripeptide glutathione is synthesized in two steps from free amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, by two enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s: glutamate–cysteine ligase (forms an isopeptide bond, which is not a peptide bond) and glutathione synthetase (forms a peptide bond).
Degradation
A peptide bond can be broken byhydrolysis
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution reaction, substitution, elimination reaction, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water ...
(the addition of water). The hydrolysis of peptide bonds in water releases 8–16 kJ/ mol (2–4 kcal/ mol) of Gibbs energy. This process is extremely slow, with the half life at 25 °C of between 350 and 600 years per bond.
In living organisms, the process is normally catalyzed by enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
s known as peptidases or protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalysis, catalyzes proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products ...
s, although there are reports of peptide bond hydrolysis caused by conformational strain as the peptide/protein folds into the native structure. This non-enzymatic process is thus not accelerated by transition state stabilization, but rather by ground-state destabilization.
Spectra
Thewavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves ...
of absorption for a peptide bond is 190–230 nm, which makes it particularly susceptible to UV radiation.
Cis/trans isomers of the peptide group
Significant delocalisation of thelone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair refers to a pair of valence electrons that are not shared with another atom in a covalent bondIUPAC ''Gold Book'' definition''lone (electron) pair''/ref> and is sometimes called an unshared pair or non-bonding pair. Lone ...
of electrons on the nitrogen atom gives the group a partial double-bond character. The partial double bond renders the amide group planar, occurring in either the cis or trans isomers. In the unfolded state of proteins, the peptide groups are free to isomerize and adopt both isomers; however, in the folded state, only a single isomer is adopted at each position (with rare exceptions). The trans form is preferred overwhelmingly in most peptide bonds (roughly 1000:1 ratio in trans:cis populations). However, X-Pro peptide groups tend to have a roughly 30:1 ratio, presumably because the symmetry between the Cα and Cδ atoms of proline makes the cis and trans isomers nearly equal in energy, as shown in the figure below.
The dihedral angle associated with the peptide group (defined by the four atoms Cα–C'–N–Cα) is denoted ; for the cis isomer ( synperiplanar conformation), and for the trans isomer ( antiperiplanar conformation). Amide groups can isomerize about the C'–N bond between the cis and trans forms, albeit slowly ( seconds at room temperature). The transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked w ...
s require that the partial double bond be broken, so that the activation energy is roughly 80 kJ/mol (20 kcal/mol). However, the activation energy can be lowered (and the isomerization catalyzed) by changes that favor the single-bonded form, such as placing the peptide group in a hydrophobic environment or donating a hydrogen bond to the nitrogen atom of an X-Pro peptide group. Both of these mechanisms for lowering the activation energy have been observed in ''peptidyl prolyl isomerases'' (PPIases), which are naturally occurring enzymes that catalyze the cis-trans isomerization of X-Pro peptide bonds.
Conformational protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after Protein biosynthesis, synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of Amino acid, amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered protein tertiary structure, t ...
is usually much faster (typically 10–100 ms) than cis-trans isomerization (10–100 s). A nonnative isomer of some peptide groups can disrupt the conformational folding significantly, either slowing it or preventing it from even occurring until the native isomer is reached. However, not all peptide groups have the same effect on folding; nonnative isomers of other peptide groups may not affect folding at all.
Chemical reactions
Due to its resonance stabilization, the peptide bond is relatively unreactive under physiological conditions, even less than similar compounds such asester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
s. Nevertheless, peptide bonds can undergo chemical reactions, usually through an attack of an electronegative atom on the carbonyl carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
, breaking the carbonyl double bond and forming a tetrahedral intermediate. This is the pathway followed in proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis o ...
and, more generally, in N–O acyl exchange reactions such as those of inteins. When the functional group attacking the peptide bond is a thiol, hydroxyl or amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
, the resulting molecule may be called a cyclol or, more specifically, a thiacyclol, an oxacyclol or an azacyclol, respectively.
See also
* The Proteolysis MapReferences
{{Authority control Protein structure Chemical bonding