Patellar dislocation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A patellar dislocation is a knee injury in which the
 Patellar dislocations occur by:
* A direct impact that knocks the patella out of joint
* A twisting motion of the knee, or ankle
* A sudden lateral cut
Patellar dislocations occur by:
* A direct impact that knocks the patella out of joint
* A twisting motion of the knee, or ankle
* A sudden lateral cut
 To assess the knee, a clinician can perform the Patellar Aprehension Test by moving the patella back and forth while the people flexes the knee at approximately 30 degrees.
The people can do the ''patella tracking assessment'' by making a single leg squat and standing, or by lying on his or her back with knee extended from flexed position. A patella that slips laterally on early flexion is called the , and indicates imbalance between the VMO and lateral structures.
On
To assess the knee, a clinician can perform the Patellar Aprehension Test by moving the patella back and forth while the people flexes the knee at approximately 30 degrees.
The people can do the ''patella tracking assessment'' by making a single leg squat and standing, or by lying on his or her back with knee extended from flexed position. A patella that slips laterally on early flexion is called the , and indicates imbalance between the VMO and lateral structures.
On
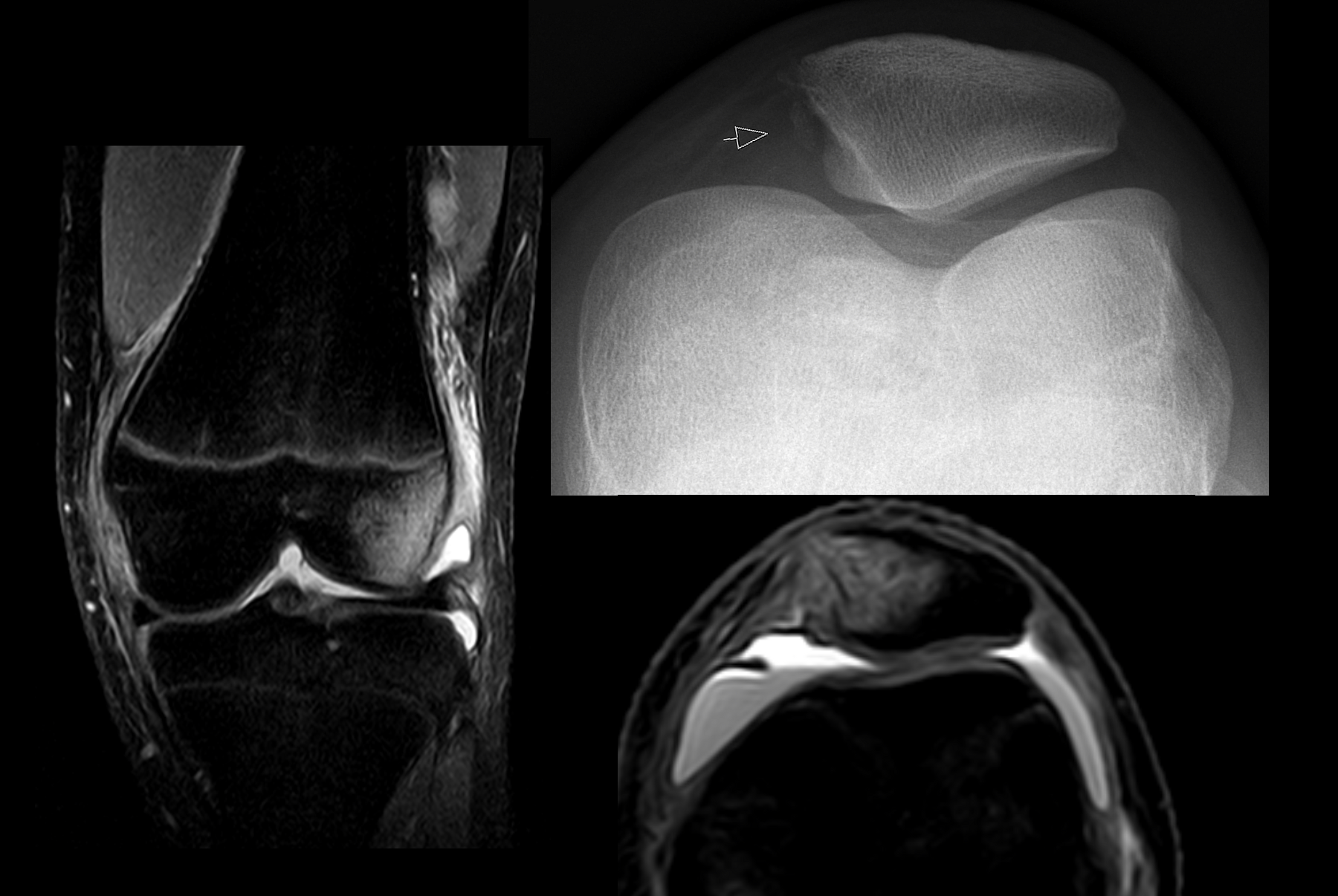
File:Lateral patellofemoral angle.jpg
File:Lateral and medial joint space of patella.jpg
 Two types of treatment options are typically available:
* Surgery
* Conservative treatment (rehabilitation and
Two types of treatment options are typically available:
* Surgery
* Conservative treatment (rehabilitation and
patella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as m ...
(kneecap) slips out of its normal position. Often the knee is partly bent, painful and swollen. The patella is also often felt and seen out of place. Complications may include a patella fracture or arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some ...
.
A patellar dislocation typically occurs when the knee is straight and the lower leg is bent outwards when twisting. Occasionally it occurs when the knee is bent and the patella is hit. Commonly associated sports include soccer, gymnastics
Gymnastics is a type of sport that includes physical exercises requiring balance, strength, flexibility, agility, coordination, dedication and endurance. The movements involved in gymnastics contribute to the development of the arms, legs, s ...
, and ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two o ...
. Dislocations nearly always occur away from the midline. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by X-rays
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ' ...
.
Reduction is generally done by pushing the patella towards the midline while straightening the knee. After reduction the leg is generally splinted in a straight position for a few weeks. This is then followed by physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patie ...
. Surgery after a first dislocation is generally of unclear benefit. Surgery may be indicated in those who have broken off a piece of bone within the joint or in which the patella has dislocated multiple times.
Patellar dislocations occur in about 6 per 100,000 people per year. They make up about 2% of knee injuries. It is most common in those 10 to 17 years old. Rates in males and females are similar. Recurrence after an initial dislocation occurs in about 30% of people.
Signs and symptoms
People often describe pain as being "inside the knee cap." The leg tends to flex even when relaxed. In some cases, the injured ligaments involved in patellar dislocation do not allow the leg to flex almost at all.Risk factors
A predisposing factor is tightness in the tensor fasciae latae muscle and iliotibial tract in combination with aquadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
imbalance between the vastus lateralis
The vastus lateralis (), also called the vastus externus, is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps femoris, a muscle in the thigh. Together with other muscles of the quadriceps group, it serves to extend the knee joint, moving the l ...
and vastus medialis muscles can play a large role, found, mainly, in women with higher level the physical activity. Moreover, women with patellofemoral pain may show increased Q-angle compared with women without patellofemoral pain.
Another cause of patellar symptoms is ''lateral patellar compression syndrome'', which can be caused from lack of balance or inflammation in the joints. The pathophysiology
Pathophysiology ( physiopathology) – a convergence of pathology with physiology – is the study of the disordered physiological processes that cause, result from, or are otherwise associated with a disease or injury. Pathology is t ...
of the kneecap is complex, and deals with the osseous soft tissue or abnormalities within the patellofemoral groove. The patellar symptoms cause knee extensor dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells ( microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopi ...
, and sensitive small variations affect the muscular mechanism that controls the joint movements.
24% of people whose patellas have dislocated have relatives who have experienced patellar dislocations.
Athletic population
Patellar dislocation occurs in sports that involve rotating the knee. Direct trauma to the knee can knock the patella out of joint.Anatomical factors
People who have larger Q angles tend to be more prone to having knee injuries such as dislocations, due to the central line of pull found in the quadriceps muscles that run from theanterior superior iliac spine
The anterior superior iliac spine ( abbreviated: ASIS) is a bony projection of the iliac bone, and an important landmark of surface anatomy. It refers to the anterior extremity of the iliac crest of the pelvis. It provides attachment for the in ...
to the center of the patella. The range of a normal Q angle for men ranges from <15 degrees and for females <20 degrees, putting females at a higher risk for this injury. An angle greater than 25 degrees between the patellar tendon and quadriceps muscle can predispose a person to patellar dislocation.
In patella alta, the patella sits higher on the knee than normal. Normal function of the VMO muscle stabilizes the patella. Decreased VMO function results in instability of the patella.
Forces
When there is too much tension on the patella, the ligaments will weaken and be susceptible to tearing ligaments or tendons due to shear force or torsion force, which then displaces the kneecap from its origination. Another cause that patellar dislocation can occur is when the trochlear groove that has been completely flattened is defined astrochlear
Trochlea (Latin for pulley) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a grooved structure reminiscent of a pulley's wheel.
Related to joints
Most commonly, trochleae bear the articular surface of saddle and other joints:
* Trochlea of humerus (part of t ...
dysplasia. Not having a groove because the trochlear bone has flattened out can cause the patella to slide because nothing is holding the patella in place.
Mechanism of injury
Anatomy of the knee
The patella is a triangular sesamoid bone that is embedded intendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
. It rests in the patellofemoral groove, an articular cartilage-lined hollow at the end of the thigh bone (femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
) where the thigh bone meets the shin bone (tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
). Several ligaments and tendons hold the patella in place and allow it to move up and down the patellofemoral groove when the leg bends. The top of the patella attaches to the quadriceps muscle via the quadriceps tendon
In human anatomy, the quadriceps tendon works with the Quadriceps muscle, quadriceps muscle to extend the leg. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the tuberosity of the tibia, shin via the patella (knee cap), where the quadriceps ten ...
, the middle to the vastus medialis obliquus and vastus lateralis
The vastus lateralis (), also called the vastus externus, is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps femoris, a muscle in the thigh. Together with other muscles of the quadriceps group, it serves to extend the knee joint, moving the l ...
muscles, and the bottom to the head of the tibia ( tibial tuberosity) via the patellar tendon
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when ...
, which is a continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon. The medial patellofemoral ligament attaches horizontally in the inner knee to the adductor magnus tendon and is the structure most often damaged during a patellar dislocation. Finally, the lateral collateral ligament and the medial collateral ligament
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), or tibial collateral ligament (TCL), is one of the four major ligaments of the knee. It is on the medial (inner) side of the knee joint in humans and other primates. Its primary function is to resist outwar ...
stabilize the patella on either side. Any of these structures can sustain damage during a patellar dislocation.
Diagnosis
 To assess the knee, a clinician can perform the Patellar Aprehension Test by moving the patella back and forth while the people flexes the knee at approximately 30 degrees.
The people can do the ''patella tracking assessment'' by making a single leg squat and standing, or by lying on his or her back with knee extended from flexed position. A patella that slips laterally on early flexion is called the , and indicates imbalance between the VMO and lateral structures.
On
To assess the knee, a clinician can perform the Patellar Aprehension Test by moving the patella back and forth while the people flexes the knee at approximately 30 degrees.
The people can do the ''patella tracking assessment'' by making a single leg squat and standing, or by lying on his or her back with knee extended from flexed position. A patella that slips laterally on early flexion is called the , and indicates imbalance between the VMO and lateral structures.
On X-ray
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ' ...
, with skyline projection
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by x-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images a ...
s, dislocations are readily diagnosed. In borderline cases of subluxation, the following measurements can be helpful:
* The ''lateral patellofemoral angle'', formed by:
:*A line connecting the most anterior points of the medial and lateral facets of the trochlea.
:*A tangent to the lateral facet of the patella.
:With the knee in 20° flexed, this angle should normally open laterally.
* The ''patellofemoral index'' is the ratio between the thickness of the medial joint space and the lateral joint space (L). With the knee 20° flexed, it should measure 1.6 or less.
Prevention
Thepatella
The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur (thigh bone) and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as m ...
is a floating sesamoid
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be prese ...
bone held in place by the quadriceps muscle tendon and patellar tendon ligament. Exercises should strengthen quadriceps muscles such as rectus femoris
The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius (deep to the rectus femoris), and the vastus lateralis. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle atta ...
, vastus intermedius, and vastus lateralis
The vastus lateralis (), also called the vastus externus, is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps femoris, a muscle in the thigh. Together with other muscles of the quadriceps group, it serves to extend the knee joint, moving the l ...
. However, tight and strong lateral quadriceps can be an underlying cause of patellar dislocation. If this is the case, it is advisable to strengthen the medial quadriceps, vastus medialis (VMO), and stretch the lateral muscles. Exercises to strengthen quadriceps muscles include, but are not limited to, squats and lunges. Adding extra external support around the knee by using devices such as knee rthoticsor athletic tape can help to prevent patellar dislocation and other knee-related injuries. External supports, such as knee braces and athletic tape
Athletic taping is the process of applying tape directly to the skin or over pre-wrap in order to maintain a stable position of bones and muscles during athletic activity. It is a procedure that uses athletic tape (pressure-sensitive tape similar ...
, work by providing movement in only the desired planes and help hinder movements that can cause abnormal movement and injuries. Women who wear high heels tend to develop short calf muscles and tendons. Exercises to stretch and strengthen calf muscles are recommended on a daily basis.
Treatment
 Two types of treatment options are typically available:
* Surgery
* Conservative treatment (rehabilitation and
Two types of treatment options are typically available:
* Surgery
* Conservative treatment (rehabilitation and physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patie ...
)
Surgery may impede normal growth of structures in the knee, so doctors generally do not recommend knee operations for young people who are still growing. There are also risks of complications, such as an adverse reaction to anesthesia or an infection.
When designing a rehabilitation program, clinicians consider associated injuries such as chipped bones or soft tissue tears. Clinicians take into account the person's age, activity level, and time needed to return to work and/or athletics. Doctors generally only recommend surgery when other structures in the knee have sustained severe damage, or specifically when there is:
* Concurrent osteochondral injury
* Continued gross instability
* Palpable disruption of the medial patellofemoral ligament and the vastus medialis obliquus
* High-level athletic demands coupled with mechanical risk factors and an initial injury mechanism not related to contact
Supplements like glucosamine
Glucosamine (C6H13NO5) is an amino sugar and a prominent precursor in the biochemical synthesis of glycosylated proteins and lipids. Glucosamine is part of the structure of two polysaccharides, chitosan and chitin. Glucosamine is one of the mos ...
and NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s can be used to minimize bothersome symptoms.
Rehabilitation
An effective rehabilitation program reduces the chances of re-injury and of other knee-related problems such as patellofemoral pain syndrome andosteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the ...
. Most patella dislocations are initially immobilized for the first 2–3 weeks to allow the stretched structures to heal. Rehabilitation focuses on maintaining strength and range of motion to reduce pain and maintain the health of the muscles and tissues around the knee joint. The objective of any good rehabilitation program is to reduce pain, swelling and stiffness as well as increase range of motion. A common rehabilitation plan is to strengthen both the hip abductors, hip external rotators and the quadricep muscles. Commonly used exercises include isometric quadricep sets, side lying clamshells, leg dips with internal tibial rotation, etc. The idea is that because the medial side is most often stretched by the more common lateral dislocation, medial strengthening will add more stabilizing support. With progression more intense range of motion exercises are incorporated.
Epidemiology
Rate in the United States are estimated 2.3 per 100,000 per year. Rates for ages 10–17 were found to be about 29 per 100,000 persons per year, while the adult population average for this type of injury ranged between 5.8 and 7.0 per 100,000 persons per year. The highest rates of patellar dislocation were found in the youngest age groups, while the rates declined with increasing ages. Females are more susceptible to patellar dislocation. Race is a significant factor for this injury, where Hispanics, African-Americans and Caucasians had slightly higher rates of patellar dislocation due to the types of athletic activity involved in:basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams, most commonly of five players each, opposing one another on a rectangular court, compete with the primary objective of shooting a basketball (approximately in diameter) through the defender's h ...
(18.2%), soccer (6.9%), and football (6.9%), according to Brian Waterman.
Lateral Patellar dislocation is common among the child population. Some studies suggest that the annual patellar dislocation rate in children is 43/100,000. The treatment of the skeletally immature is controversial due to the fact that they are so young and are still growing. Surgery is recommended by some experts in order to repair the medial structures early, while others recommend treating it non operatively with physical therapy. If re-dislocation occurs then reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament (MPFL) is the recommended surgical option.
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Patella Dislocation Sports medicine Dislocations, sprains and strains Patella Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate