Parankylosauria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Parankylosauria is a group of basal
 During the Mesozoic era, the southern continents (
During the Mesozoic era, the southern continents (

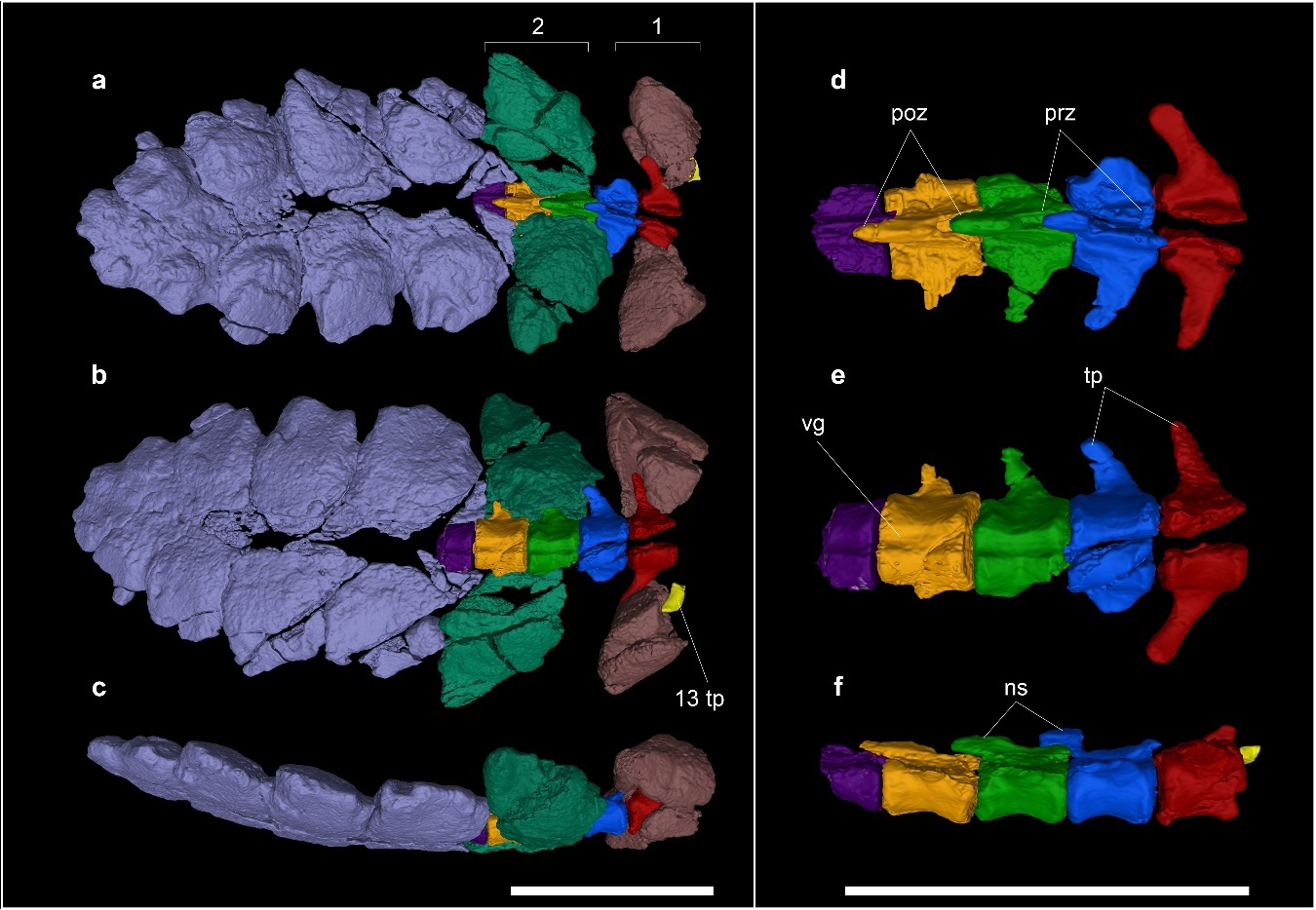
 Known members of Parankylosauria are all small animals, ranging from , and possessed proportionally large skulls. The most distinctive trait of the group is their macuahuitl, named after the mesoamerican weapon of the same name. This trait is similar to the
Known members of Parankylosauria are all small animals, ranging from , and possessed proportionally large skulls. The most distinctive trait of the group is their macuahuitl, named after the mesoamerican weapon of the same name. This trait is similar to the  Parankylosaurs, compared to the more well studied euankylosaurs, retain more traits seen in more primitive thyreophorans and stegosaurs. This is most applicable in the body, most distinctively seen in the possession of rather long and slender limbs. The skull, comparatively, is more similar to that of other ankylosaurs, thought to indicate the acquisition of advanced skull traits earlier in ankylosaur evolution. Also unlike euankylosaurs, it is thought, based on the preserved osteoderms of ''
Parankylosaurs, compared to the more well studied euankylosaurs, retain more traits seen in more primitive thyreophorans and stegosaurs. This is most applicable in the body, most distinctively seen in the possession of rather long and slender limbs. The skull, comparatively, is more similar to that of other ankylosaurs, thought to indicate the acquisition of advanced skull traits earlier in ankylosaur evolution. Also unlike euankylosaurs, it is thought, based on the preserved osteoderms of ''
 André Fonseca and colleagues in 2024 formally defined this clade in the ''
André Fonseca and colleagues in 2024 formally defined this clade in the ''
ankylosauria
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the clade Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs ...
n dinosaurs known from the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
. It is thought the group split from other ankylosaurs during the mid-Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
period, despite this being unpreserved in the fossil record.
History of research
 During the Mesozoic era, the southern continents (
During the Mesozoic era, the southern continents (South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, and Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
in addition to India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori language, Māori) or Tasmantis (from Tasman Sea), is an almost entirely submerged continent, submerged mass of continental crust in Oceania that subsided after breaking away from Gondwana 83� ...
) were unified into a supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
known as Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
. This was in contrast to the supercontinent of Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, with both originating from the breakup of Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 mi ...
. Gondwana itself gradually split apart over the course of the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
and Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
eras. Ankylosaurian dinosaurs from Laurasia have historically been far more extensively recorded and studied. Reports of the group in Gondwana date back to 1904, with a specimen from Australia and include referrals of ''Loricosaurus
''Loricosaurus'' (meaning "armour lizard") is a genus of sauropod represented by a single species. It is a titanosaurian that lived near the end of the Late Cretaceous period, approximately 71 million years ago in the early Maastrichtian. Found i ...
'', ''Lametasaurus
''Lametasaurus'' ( - meaning "Lameta lizard") named for the Lameta Formation, Jabalpur, India, is the generic name given to a possibly chimeric dinosaur species. The type species is ''L. indicus''.
History of discovery
Between October 1917 and 1 ...
'', and '' Brachypodosaurus'' to group among assorted fragmentary material. Much of this material including would later be shown to be misidentified and not belonging to ankylosaurs, including the named genera. The first definitive ankylosaur to be recognized from Gondwana was discovered in Australia in 1964 and later named in 1980 as ''Minmi paravertebra
''Minmi'' is a genus of small herbivorous ankylosaurian dinosaur that lived during the early Cretaceous Period of Australia, about 120 to 112 million years ago.
Discovery and species
In 1964, Dr Alan Bartholomai, a collaborator of the Queens ...
''. The possibility of a biogeographic
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
connection between South America and ankylosaurs in Australia was raised alongside discovery, though based on conjecture.
Ankylosaurs from Gondwana have remained very mysterious. Fossil material continues to be scant and southern taxa have been difficult to interpret in a phylogenetic context. Vertebrae of ''Antarctopelta
''Antarctopelta'' (; meaning 'Antarctic shield') is a genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur, a group of large, quadrupedal herbivores, that lived during the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous period on what is now James Ross Island, Antarctica ...
'' from Antarctica, for example, were so foreign compared to those of euankylosaurs that it was questioned if they might instead belong to a marine reptile
Marine reptiles are reptiles which have become secondarily adapted for an aquatic or semiaquatic life in a marine environment. Only about 100 of the 12,000 extant reptile species and subspecies are classed as marine reptiles, including mari ...
, which would make the genus based on a chimeric specimen. The discovery of the genus ''Stegouros'', published and named in 2021, helped to clear up the previous confusion. The type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wikt:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to ancho ...
of the genus preserved enough of the skeleton to make it clear that there was a previously unrecognized monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
grouping of these southern ankylosaur taxa. Thus the study naming the genus, by Sergio Soto-Acuña and colleagues, coined Parankylosauria based on the two aforementioned genera and ''Kunbarrasaurus
''Kunbarrasaurus'' (meaning "shield lizard") is an extinct genus of small ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Australia. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''K. ieversi''.
Discovery
In November 1989, at Marathon ...
''. The name, referencing its parent group, means "at the side of Ankylosauria".
The Parankylosauria may not have been the only Gondwanan ankylosaurians; ''Patagopelta
''Patagopelta'' (meaning "Patagonian shield") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (upper Campanian–lower Maastrichtian) Allen Formation of Argentina. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''P. ...
'' was described from Argentina in 2022, and has been found to be closely allied with North American nodosaurids in the subfamily Nodosaurinae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophyletic clade as the s ...
. This would suggest that in addition to the more ancient Parankylosauria, more derived euankylosaurians also inhabited South America, having migrated from North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
as part of a biotic interchange during the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campa ...
. However, more recent studies have suggested a parankylosaur affinity for ''Patagopelta''. In one of their analyses, Fonseca et al. (2024) recovered the enigmatic thyreophoran ''Jakapil'' as a basal ankylosaur, sister to both Parankylosauria and Euankylosauria. They noted that it took four steps in their analysis for ''Jakapil'' to fall within the Parankylosauria—a placement that should not be disregarded—though this is not the most parsimonious position.
Anatomy

thagomizer
A thagomizer () is the distinctive arrangement of spike-shaped osteoderms on the tails of some stegosaurian dinosaurs. These spikes are believed to have been a defensive measure against predators.
The arrangement of spikes originally had no dis ...
of stegosaurs and tail club
In zoology, a tail club is a bony mass at the end of the tail of some dinosaurs and of some mammals, most notably the Ankylosauridae, ankylosaurids and the glyptodonts, as well as meiolaniid turtles. It is thought that this was a form of defensive ...
s known in ankylosaurines
Ankylosaurinae is a subfamily of ankylosaurid dinosaurs, existing from the Early Cretaceous about 105 million years ago until the end of the Late Cretaceous, about 66 mya. Many genera are included in the clade, such as ''Ankylosaurus'', ''Pinacos ...
, though evolved independently from each. This was a structure at the end of the tail formed by a series of five pairs of robust osteoderms
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of Extant taxon, extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, Temnospondyli, ...
(bones in the skin) fused together, surrounding the sides of the tail and surrounding the entirety of it near the tip. This weapon is known directly in the genus ''Stegouros'', suspected based on indirect evidence in ''Antarctopelta'', and not confirmed in ''Kunbarrasaurus'', for which a complete tail is not known. In the former taxon the weapon is associated with dramatic shortening of the tail, made up of far fewer vertebrae than any other kind of thyreophora
Thyreophora ("shield bearers", often known simply as "armored dinosaurs") is a group of armored ornithischian dinosaurs that lived from the Early Jurassic until the end of the Cretaceous.
Thyreophorans are characterized by the presence of bod ...
n. As with many other members of this group, osteoderms would have covered much of the body of parankylosaurs, functioning as spiny armor.
 Parankylosaurs, compared to the more well studied euankylosaurs, retain more traits seen in more primitive thyreophorans and stegosaurs. This is most applicable in the body, most distinctively seen in the possession of rather long and slender limbs. The skull, comparatively, is more similar to that of other ankylosaurs, thought to indicate the acquisition of advanced skull traits earlier in ankylosaur evolution. Also unlike euankylosaurs, it is thought, based on the preserved osteoderms of ''
Parankylosaurs, compared to the more well studied euankylosaurs, retain more traits seen in more primitive thyreophorans and stegosaurs. This is most applicable in the body, most distinctively seen in the possession of rather long and slender limbs. The skull, comparatively, is more similar to that of other ankylosaurs, thought to indicate the acquisition of advanced skull traits earlier in ankylosaur evolution. Also unlike euankylosaurs, it is thought, based on the preserved osteoderms of ''Kunbarrasaurus
''Kunbarrasaurus'' (meaning "shield lizard") is an extinct genus of small ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Australia. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''K. ieversi''.
Discovery
In November 1989, at Marathon ...
'' and lack of flank osteoderms associated with other known genera, that parankylosaurs may not have had rather light coverings of dermal armor compared to their relatives. They possessed a pelvic shield, formed from a thin sheet of bone over the hip region, more reinforced than the superficial shielding of stegosaurs but not as overbuilt as those found in euankylosaurs.
Classification
 André Fonseca and colleagues in 2024 formally defined this clade in the ''
André Fonseca and colleagues in 2024 formally defined this clade in the ''PhyloCode
The ''International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'', known as the ''PhyloCode'' for short, is a formal set of rules governing phylogenetic nomenclature. Its current version is specifically designed to regulate the naming of clades, leaving the ...
'' as "the largest clade containing ''Stegouros elengassen
''Stegouros'' (, meaning "roofed tail") is an extinct genus of ankylosaurian dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Dorotea Formation of southern Chile. The genus contains a single species, ''Stegouros elengassen'', known from a semi-articulated, ...
'', but not ''Ankylosaurus magniventris
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of th ...
'' and ''Nodosaurus textilis
''Nodosaurus'' (meaning 'knobbed lizard') is a genus of herbivore, herbivorous nodosauridae, nodosaurid ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous, the fossils of which are found exclusively in the Frontier Formation in Wyoming.
Descripti ...
''". This definition ensures both ankylosaurids
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
and nodosaurids
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous Period (geology), periods in what is now Asia, Europe, North America, and possibly South America. While traditionally regarded as a monophylet ...
are excluded from Parankylosauria. The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an Phylogenetic tree, evolutionary tree because it does not s ...
is reproduced from the phylogenetic analysis
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
in the 2021 study by Sergio Soto-Acuña and colleagues:
In 2022, a study by Timothy G. Frauenfelder and colleagues on a new specimen (SAMA P40536) tentatively referred to ''Kunbarrasaurus
''Kunbarrasaurus'' (meaning "shield lizard") is an extinct genus of small ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Australia. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''K. ieversi''.
Discovery
In November 1989, at Marathon ...
'' tested their new specimen in the dataset of the 2021 study, finding a similar placement and composition of Parankylosauria, but also coded the specimen for an older phylogenetic dataset of a 2016 paper by Victoria Arbour
Victoria Megan Arbour is a Canadian evolutionary biologist and vertebrate palaeontologist at Royal BC Museum, where she is Curator of Palaeontology. An "expert on the armoured dinosaurs known as ankylosaurs", Arbour analyzes fossils and create ...
and Phil Currie
Philip John Currie (born March 13, 1949) is a Canadian palaeontologist and museum curator who helped found the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology in Drumheller, Alberta and is now a professor at the University of Alberta in Edmonton. In the ...
. The resulting analysis found ''Kunbarrasaurus
''Kunbarrasaurus'' (meaning "shield lizard") is an extinct genus of small ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Cretaceous of Australia. The genus contains a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''K. ieversi''.
Discovery
In November 1989, at Marathon ...
'' and the new specimen to nest together in a similar position on the tree to where Parankylosauria was found in the 2021 dataset, supporting that conclusion. The tree of the second dataset is reproduced below:
See also
*Timeline of ankylosaur research
This timeline of ankylosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the History of paleontology, history of paleontology focused on the ankylosaurs, quadrupedal herbivorous dinosaurs who were protected by a covering bony plates and spik ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from = Q109887677 Albian first appearances Dinosaur clades Cretaceous dinosaurs