|
Osteoderms
Osteoderms are bony deposits forming scales, plates, or other structures based in the dermis. Osteoderms are found in many groups of Extant taxon, extant and extinct reptiles and amphibians, including lizards, crocodilians, frogs, Temnospondyli, temnospondyls (extinct amphibians), various groups of dinosaurs (most notably ankylosaurs and stegosaurians), phytosaurs, aetosaurs, placodonts, and hupehsuchians (marine reptiles with possible ichthyosaur affinities). Osteoderms are uncommon in mammals, although they have occurred in many xenarthrans (armadillos and the extinct glyptodonts and Mylodontidae, mylodontid ground sloths). The heavy, bony osteoderms have evolved independently in many different lineages. The armadillo osteoderm is believed to develop in subcutaneous dermal tissues. These varied structures should be thought of as anatomical analogues, not homology (biology), homologues, and do not necessarily indicate monophyly. The structures are however derived from scute, sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetosaur
Aetosaurs () are heavily armored reptiles belonging to the extinct order (biology), order Aetosauria (; from Ancient Greek, Greek, (aetos, "eagle") and (, "lizard")). They were medium- to large-sized Omnivore, omnivorous or Herbivore, herbivorous pseudosuchians, part of the branch of archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. All known aetosaurs are restricted to the Late Triassic, and in some strata from this time they are among the most abundant fossil vertebrates. They have small heads, upturned snouts, erect limbs, and a body ornamented with four rows of plate-like osteoderms (bony scutes). Aetosaur fossil remains are known from Europe, North America, North and South America, parts of Africa, and India. Since their armoured plates are often preserved and are abundant in certain localities, aetosaurs serve as important Late Triassic tetrapod index fossils. Many aetosaurs had wide geographic ranges, but their Stratigraphy, stratigraphic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylodontidae
Mylodontidae is a family of extinct South American and North American ground sloths within the suborder Folivora of order Pilosa, living from around 23 million years ago (Mya) to 11,000 years ago. This family is most closely related to another family of extinct ground sloths, Scelidotheriidae, as well as to the extant arboreal two-toed sloths, family Choloepus, Choloepodidae; together these make up the superfamily Mylodontoidea. Phylogenetic analyses based on morphology uncovered the relationship between Mylodontidae and Scelidotheriidae; in fact, the latter was for a time considered a subfamily of mylodontids. However, molecular sequence comparisons were needed for the correct placement of Choloepodidae. These studies have been carried out using mitochondrial DNA sequences as well as with collagen amino acid sequences. The latter results indicate that Choloepodidae is closer to Mylodontidae than Scelidotheriidae is. The only other living sloth family, Bradypodidae (three-toed slot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Sloth
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. They varied widely in size with the largest, belonging to genera '' Lestodon'', ''Eremotherium'' and ''Megatherium'', being around the size of elephants. Ground sloths represent a paraphyletic group, as living tree sloths are thought to have evolved from ground sloth ancestors. The early evolution of ground sloths took place during the late Paleogene and Neogene of South America, while the continent was isolated. At their earliest appearance in the fossil record, they were already distinct at the family level. Sloths dispersed into the Greater Antilles during the Oligocene, and the presence of intervening islands between the American continents in the Miocene allowed a dispersal of some species into North America. They were hardy as evidenced by their high species diversity and their presence in a wide variety of environments, extending from the far south of Patagonia ( Cueva del Milodón ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scute
A scute () or scutum (Latin: ''scutum''; plural: ''scuta'' "Scutum (shield), shield") is a bony external plate or scale overlaid with horn, as on the shell of a turtle, the skin of crocodilians, and the feet of Bird anatomy#Scales, birds. The term is also used to describe the anterior portion of the mesothorax in insects as well as some arachnids (e.g., the family Ixodidae, the scale ticks). Properties Scutes are similar to scale (zoology), scales and serve the same function. Unlike the scales of lizards and snakes, which are formed from the Epidermis (skin), epidermis, scutes are formed in the lower vascular layer of the skin and the epidermal element is only the top surface . Forming in the living dermis, the scutes produce a Horn (anatomy), horny outer layer that is superficially similar to that of scales. Scutes will usually not overlap as snake scales (but see the pangolin). The outer keratin layer is shed piecemeal, and not in one continuous layer of skin as seen in snakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely semiaquatic group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian vertebrates composing the order (biology), order Anura (coming from the Ancient Greek , literally 'without tail'). Frog species with rough skin texture due to wart-like parotoid glands tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal and purely cosmetic, not from taxonomy (biology), taxonomy or evolutionary history. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest and associated wetlands. They account for around 88% of extant amphibian species, and are one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is known from the Early Triassic of Madagascar (250Myr, million years ago), but molecular clock, molecular clock dating suggests their divergent evolution, divergence from other amphibians may exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armadillo
Armadillos () are New World placental mammals in the order (biology), order Cingulata. They form part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of environments. Living armadillos are characterized by a leathery armour (anatomy), armor shell and long, sharp claws for digging. They have short legs, but can move quite quickly. The average length of an armadillo is about , including its tail. The giant armadillo grows up to and weighs up to , while the pink fairy armadillo has a length of only . When threatened by a predator, ''Tolypeutes'' species frequently roll up into a ball; they are the only species of armadillo capable of this. Recent genetic research has shown that the megafaunal glyptodonts (up to tall with maximum body masses of around 2 tonnes), which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gila Fg01
Gila may refer to: Animals * ''Gila'' (fish), a genus of cyprinid fish known as western chubs * Gila monster, a venomous lizard * Gila trout, a trout native to the Southwestern United States * Gila woodpecker, a species of woodpecker found in the Southwestern United States Places * Gila County, Arizona * Gila Mountains (Graham County), Arizona * Gila Mountains (Yuma County), Arizona * Gila River, a Colorado River tributary in New Mexico and Arizona * Gila, New Mexico, a census-designated place * Gila National Forest, New Mexico * Gila Wilderness, New Mexico, the world's first wilderness area * Gila Desert, the informal name of Sonoran Desert, United States and Mexico People * Gila (given name), a list of people * Eloy Gila (born 1988), Spanish footballer * Miguel Gila (1919–2001), Spanish actor * Nickname of Alberto Gilardino (born 1982), Italian football manager and former player * Gila (footballer), Portuguese football player and coach Virgílio José Pereira d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosauria is an order of large extinct marine reptiles sometimes referred to as "ichthyosaurs", although the term is also used for wider clades in which the order resides. Ichthyosaurians thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurians were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods, until they were replaced as the top aquatic predators by another marine reptilian group, the Plesiosauria, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armour (zoology)
Armor or armour in animals is a rigid cuticle or exoskeleton that provides exterior protection against attack by predators, formed as part of the body (rather than the behavioural utilization of external objects for protection) usually through the thickening and hardening of superficial tissues, outgrowths or skin secretions. It is often found in prey species that are too slow or clumsy to outrun predators, or those that would stand their ground and fight, thus needing to protect vital organs against claw, talon or bite injuries. Composition Armoured structures are usually composed of hardened mineral deposits, chitin, bone, or keratin. Species with armour Armour is evident in numerous animal species from both current and prehistoric times. Dinosaurs such as '' Ankylosaurus'', as well as other Thyreophora (armoured dinosaurs such as Ankylosauria and Stegosauria), grew thick plate-like armour on their bodies as well as offensive armour appendages such as the thagomizer or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
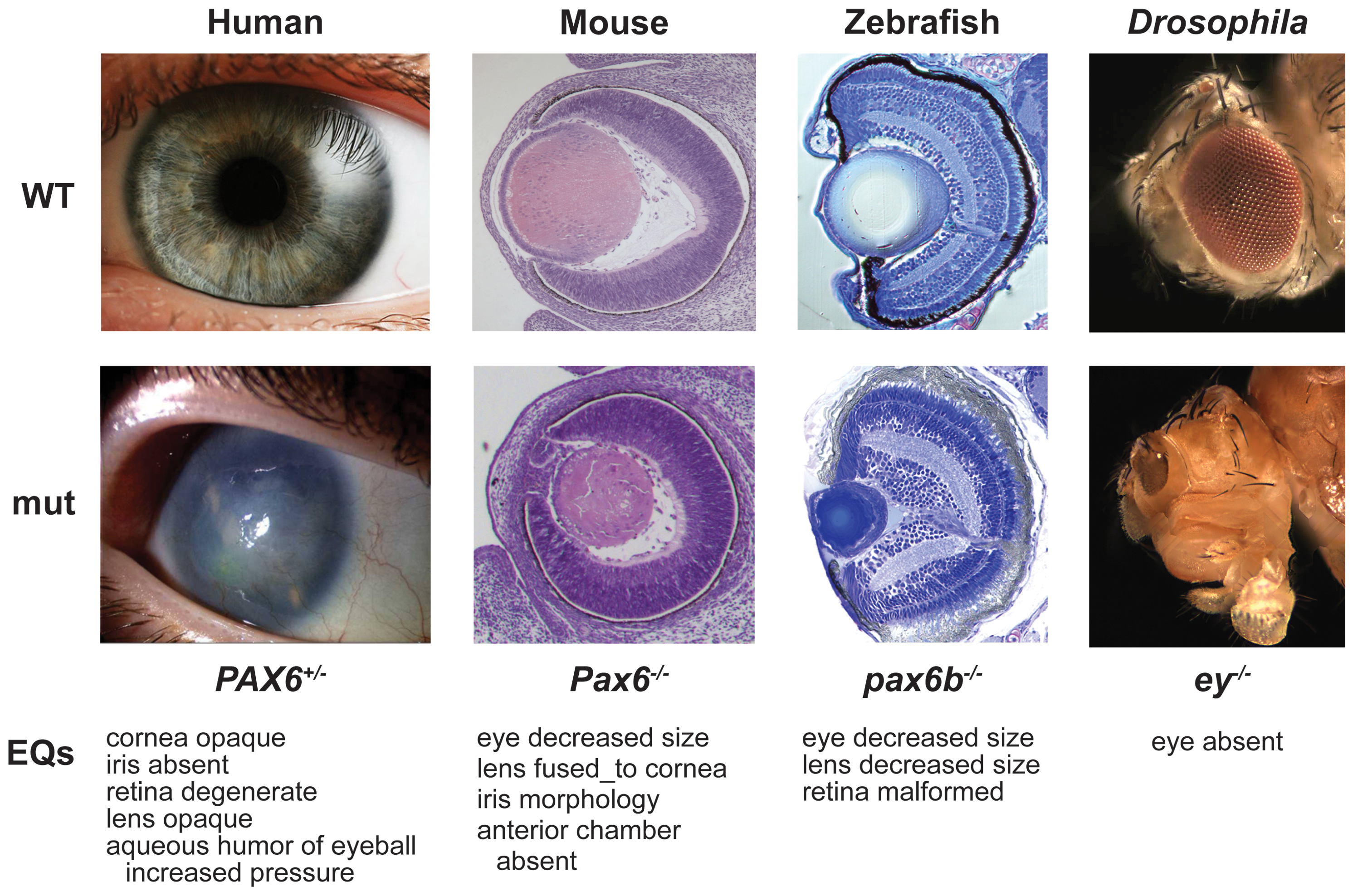
Deep Homology
In evolutionary developmental biology, the concept of deep homology is used to describe cases where growth and differentiation processes are governed by genetic mechanisms that are homologous and deeply conserved across a wide range of species. History In 1822, the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire dissected a crayfish, discovering that its body is organised like a vertebrate's, but inverted belly to back (dorsoventrally): Geoffroy's homology theory was denounced by the leading French zoologist of his day, Georges Cuvier, but in 1994, Geoffroy was shown to be correct. In 1915, Santiago Ramon y Cajal mapped the neural connections of the optic lobes of a fly, finding that these resembled those of vertebrates. In 1978, Edward B. Lewis helped to found evolutionary developmental biology, discovering that homeotic genes regulated embryonic development in fruit flies. In 1997, the term deep homology first appeared in a paper by Neil Shubin, Cliff Tabin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotes
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the Carboniferous period. Amniota is defined as the smallest crown clade containing humans, the Greek tortoise, and the Nile crocodile. Amniotes are distinguished from the other living tetrapod clade — the non-amniote lissamphibians (frogs/ toads, salamanders/ newts and caecilians) — by: the development of three extraembryonic membranes ( amnion for embryonic protection, chorion for gas exchange, and allantois for metabolic waste disposal or storage); thicker and keratinized skin; costal respiration (breathing by expanding/constricting the rib cage); the presence of adrenocortical and chromaffin tissues as a discrete pair of glands near their kidneys; more complex kidneys; the presence of an astragalus for better ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria: # the grouping contains its own most recent common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population), i.e. excludes non-descendants of that common ancestor # the grouping contains all the descendants of that common ancestor, without exception Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic'' grouping meets 1. but not 2., thus consisting of the descendants of a common ancestor, excepting one or more monophyletic subgroups. A ''polyphyletic'' grouping meets neither criterion, and instead serves to characterize convergent relationships of biological features rather than genetic relationships – for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, or aquatic insects. As such, these characteristic features of a polyphyletic grouping are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |