Ossifies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in

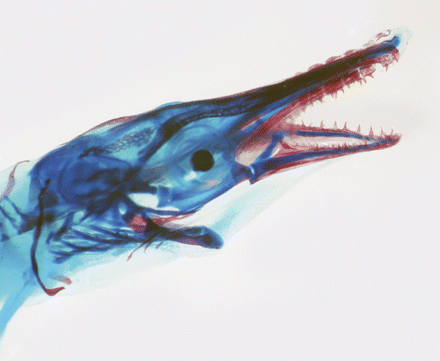 Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in
Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in
bone remodeling
300 px, Bone tissue is removed by osteoclasts, and then new bone tissue is formed by osteoblasts. Both processes utilize cytokine ( Insulin-like_growth_factor.html" ;"title="TGF-β, Insulin-like growth factor">IGF) signalling.
In osteology, bone ...
is the process of laying down new bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
material by cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a d ...
named osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for " bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts fu ...
s. It is synonymous with bone tissue
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provi ...
formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provi ...
: Intramembranous ossification
Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created.
Intramembranous ossification i ...
is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly ever ...
), while endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development and bone healing, bone repair of the mammalian skeleton, skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossificatio ...
involves cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
as a precursor.
In fracture healing
Bone healing, or fracture healing, is a proliferative physiological process in which the body facilitates the repair of a bone fracture.
Generally, bone fracture treatment consists of a doctor reducing (pushing) displaced bones back into place ...
, endochondral osteogenesis
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the p ...
is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s treated by plaster of Paris
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the ...
with metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
plates, screws
A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the screw head, head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety ...
, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis
Osteoblasts (from the Greek language, Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cell (biology), cells with a single Cell nucleus, nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the p ...
.
Heterotopic ossification
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is the process by which bone tissue forms Heterotopia (medicine), outside of the skeleton in muscles and soft tissue.
Symptoms
In traumatic heterotopic ossification (traumatic myositis ossificans), the patient may ...
is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provi ...
that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification
Calcification is the accumulation of calcium salts in a body tissue. It normally occurs in the formation of bone, but calcium can be deposited abnormally in soft tissue,Miller, J. D. Cardiovascular calcification: Orbicular origins. ''Nature M ...
is often confused with ossification. Calcification is synonymous with the formation of calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
-based salts and crystals within cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a d ...
and tissue. It is a process that occurs during ossification, but not necessarily ''vice versa''.
The exact mechanisms by which bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
development is triggered remains unclear, but growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for ...
s and cytokines
Cytokines () are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling.
Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes ...
appear to play a role.
Intramembranous ossification
Intramembranous ossification
Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome (excluding chondrichthyans such as sharks) skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created.
Intramembranous ossification i ...
forms the flat bone
Flat bones are bones whose principal function is either extensive protection or the provision of broad surfaces for muscular attachment. These bones are expanded into broad, flat plates,'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918). (See infobox) as in the cranium ...
s of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
, mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
and hip bone
The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the Ilium (bone) ...
.
Osteoblasts cluster together to create an ossification center. They then start secreting osteoid, an unmineralized collagen-proteoglycan matrix that has the ability to bind calcium. As calcium binds to the osteoid, the matrix hardens, and the osteoblasts become entrapped, transforming into osteocytes.
As osteoblasts continue to secrete osteoid
In histology, osteoid is the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue. Osteoblasts begin the process of forming bone tissue by secreting the osteoid as several specific proteins. The os ...
, it surrounds blood vessels, leading to the formation of trabecular (cancellous or spongy) bone. These blood vessels will eventually develop into red bone marrow. Mesenchymal cells on the bone surface form a membrane known as the periosteum. Osteoblasts secrete osteoid in parallel with the existing matrix, creating layers of compact (cortical) bone.
Endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development and bone healing, bone repair of the mammalian skeleton, skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossificatio ...
is the formation of long bones and other bones.
This requires a hyaline cartilage
Hyaline cartilage is the glass-like (hyaline) and translucent cartilage found on many joint surfaces. It is also most commonly found in the ribs, nose, larynx, and trachea. Hyaline cartilage is pearl-gray in color, with a firm consistency and has ...
precursor. There are two centers of ossification for endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development and bone healing, bone repair of the mammalian skeleton, skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossificatio ...
.
The primary center
In long bones, bone tissue first appears in the diaphysis
The diaphysis (: diaphyses) is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat).
It is a middle tubular part composed of compact bone which surrounds a centr ...
(middle of shaft). Chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, ) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word '' chondroblast'' is commonly used to describe an immatu ...
s multiply and form trebeculae. Cartilage is progressively eroded and replaced by hardened bone, extending towards the epiphysis
An epiphysis (; : epiphyses) is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from one or more secondary centers of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, inc ...
. A perichondrium
The perichondrium (from Greek and ) is a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage of developing bone. It consists of two separate layers: an outer fibrous layer and inner chondrogenic layer. The fibrous layer conta ...
layer surrounding the cartilage forms the periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. (At the joints of long bones the bone's outer surface is lined with "articular cartila ...
, which generates osteogenic cells that then go on to make a collar that encircles the outside of the bone and remodels the medullary cavity on the inside.
The nutrient artery enters via the nutrient foramen from a small opening in the diaphysis. It invades the primary center of ossification, bringing osteogenic cells (osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for " bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts fu ...
s on the outside, osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and bone remodeling, remodeling of bones of the vertebrate, vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests th ...
s on the inside.) The canal of the nutrient foramen is directed away from more active end of bone when one end grows more than the other. When bone grows at same rate at both ends, the nutrient artery is perpendicular to the bone.
Most other bones (e.g. vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
e) also have primary ossification centers, and bone is laid down in a similar manner.
Secondary centers
The secondary centers generally appear at the epiphysis
An epiphysis (; : epiphyses) is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from one or more secondary centers of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, inc ...
. Secondary ossification mostly occurs after birth (except for distal femur and proximal tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
which occurs during 9th month of fetal development). The epiphyseal arteries and osteogenic cells invade the epiphysis
An epiphysis (; : epiphyses) is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from one or more secondary centers of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, inc ...
, depositing osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and bone remodeling, remodeling of bones of the vertebrate, vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests th ...
s and osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for " bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts fu ...
s which erode the cartilage and build bone, respectively. This occurs at both ends of long bones but only one end of digits and ribs.

Evolution
 Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in
Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
. One hypothesis is that bone developed from tissues that evolved to store mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s. Specifically, calcium-based minerals were stored in cartilage and bone was an exaptation
Exaptation or co-option is a shift in the function of a trait during evolution. For example, a trait can evolve because it served one particular function, but subsequently it may come to serve another. Exaptations are common in both anatomy and be ...
development from this calcified cartilage. However, other possibilities include bony tissue evolving as an osmotic barrier
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of ...
, or as a protective structure.
See also
*Dystrophic calcification
Dystrophic calcification (DC) is the calcification occurring in degenerated or necrotic tissue, as in hyalinized scars, degenerated foci in leiomyomas, and caseous nodules. This occurs as a reaction to tissue damage, including as a consequenc ...
* Mechanostat, a model describing ossification and bone loss
* Ossicone
Ossicones are columnar or conical skin-covered bone structures on the heads of giraffes, male okapi, and some of their extinct relatives. Ossicones are distinguished from the superficially similar structures of Horn (anatomy), horns and antlers ...
, the horn-like (or antler-like) protuberances on the heads of giraffes and related species
* Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
, a juvenile bone disease
* Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (; FOP), also called Münchmeyer disease or formerly myositis ossificans progressiva, is an extremely rare connective tissue disease in which fibrous connective tissue such as muscle, tendons, and ligamen ...
, an extremely rare genetic disease which causes fibrous tissue (muscle, tendon, ligament etc.) to ossify when damaged
* Primrose syndrome, a rare genetic disease in which cartilage becomes ossified.
References
{{Authority control Animal physiology Skeletal system *Ossification