North Island on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The North Island ( , 'the fish of Māui', historically New Ulster) is one of the two main
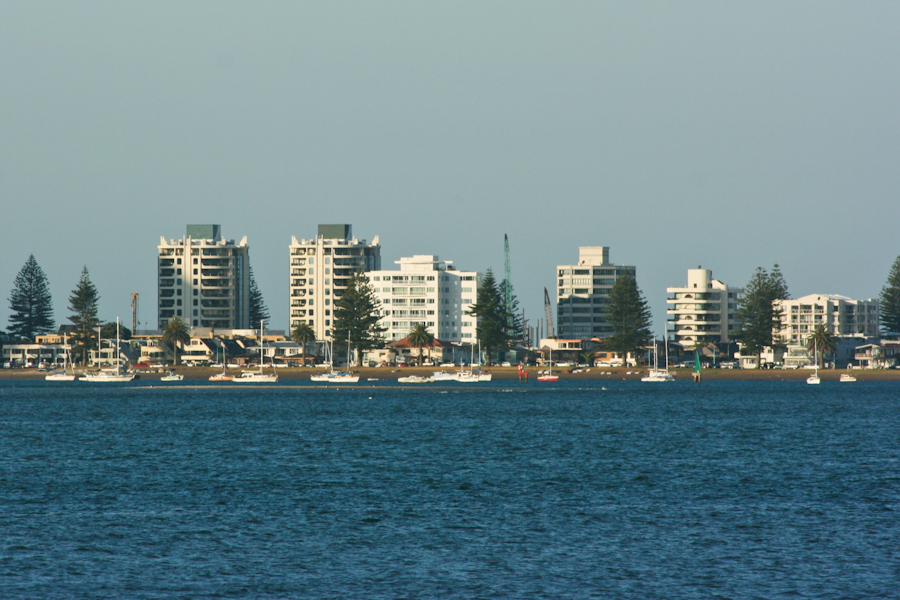

 The North Island has a larger population than the South Island, with the country's largest city, Auckland, and the capital, Wellington, accounting for nearly half of it.
There are 30 urban areas in the North Island with a population of 10,000 or more:
The North Island has a larger population than the South Island, with the country's largest city, Auckland, and the capital, Wellington, accounting for nearly half of it.
There are 30 urban areas in the North Island with a population of 10,000 or more:
islands
This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the #Other lists of islands, other lists of islands below.
Lists of islands by count ...
of New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
, separated from the larger but less populous South Island
The South Island ( , 'the waters of Pounamu, Greenstone') is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand by surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by ...
by Cook Strait. With an area of , it is the world's 14th-largest island, constituting 43% of New Zealand's land area. It has a population of which is % of New Zealand's residents, making it the most populous island in Polynesia
Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in ...
and the 28th-most-populous island in the world.
Twelve main urban areas (half of them officially cities) are in the North Island. From north to south, they are Whangārei
Whangārei () is the northernmost city in New Zealand and the largest settlement of the Northland Region. It is part of the Whangarei District, created in 1989 from the former Whangarei City, Whangarei County and Hikurangi Town councils to admi ...
, Auckland
Auckland ( ; ) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and ...
, Hamilton
Hamilton may refer to:
* Alexander Hamilton (1755/1757–1804), first U.S. Secretary of the Treasury and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States
* ''Hamilton'' (musical), a 2015 Broadway musical by Lin-Manuel Miranda
** ''Hamilton'' (al ...
, Tauranga, Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. It is sited on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authorities of New Zea ...
, Gisborne, New Plymouth
New Plymouth () is the major city of the Taranaki region on the west coast of the North Island of New Zealand. It is named after the English city of Plymouth, in Devon, from where the first English settlers to New Plymouth migrated. The New Pl ...
, Napier, Hastings
Hastings ( ) is a seaside town and Borough status in the United Kingdom, borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England,
east of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to th ...
, Whanganui, Palmerston North
Palmerston North (; , colloquially known as Palmerston or Palmy) is a city in the North Island of New Zealand and the seat of the Manawatū-Whanganui region. Located in the eastern Manawatū Plains, the city is near the north bank of the Manaw ...
, and New Zealand's capital city Wellington
Wellington is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the third-largest city in New Zealand (second largest in the North Island ...
, which is located at the south-west tip of the island.
Naming and usage
The island has been known in English as the North Island for many years. The official Māori name for it, ("the fish of Māui"), also has official recognition but it remains seldom used by most residents. Other Māori names include ''Te Ahi no Māui'' ("the fire of Māui", as first recorded by CaptainJames Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
in 1770) and '' Aotearoa'' ("land of the long white cloud"), which is more frequently applied to New Zealand as a whole. On some 19th-century maps, the North Island was named New Ulster (named after Ulster
Ulster (; or ; or ''Ulster'') is one of the four traditional or historic provinces of Ireland, Irish provinces. It is made up of nine Counties of Ireland, counties: six of these constitute Northern Ireland (a part of the United Kingdom); t ...
province in northern Ireland), which was also a province of New Zealand that included the North Island.
In 2009 the New Zealand Geographic Board found that, along with the South Island, the North Island had no official name. After a public consultation, the board officially named it ''North Island or Te Ika-a-Māui'' in October 2013. The official Māori name was chosen on the basis that it was "most common and consistent usage in oral tradition by Māori living on the island".
In prose, the two main islands of New Zealand are called ''the North Island'' and ''the South Island'', with the definite article. It is also normal to use the preposition
Adpositions are a part of speech, class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various thematic relations, semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositi ...
''in'' rather than ''on'', for example "Hamilton is in the North Island", "my mother lives in the North Island". Maps, headings, tables, and adjectival expressions use ''North Island'' without "the".
Māori mythology
According to Māori mythology, the North and South Islands of New Zealand arose through the actions of the demigod Māui. Māui and his brothers were fishing from their canoe (the South Island) when he caught a great fish and pulled it right up from the sea. While he was not looking, his brothers fought over the fish and chopped it up. This great fish became the North Island, and thus a Māori name for the North Island is Te Ika-a-Māui ("The Fish of Māui"). The mountains and valleys are believed to have been formed as a result of Māui's brothers' hacking at the fish. During Captain James Cook's voyage between 1769 and 1770, Tahitian navigator Tupaia accompanied the circumnavigation of New Zealand. The maps described the North Island as "Ea Heinom Auwe" and "Aeheinomowe", which recognises the "Fish of Māui" element. Names of certain tribes like Muaūpoko (''mua upoko'' "front of the head") and Muriwhenua (''muri whenua'', "backland") also reflect the locations of their settlement in this "fish" as well as levels of seniority between tribes. Another Māori name that was given to the North Island, but is now used less commonly, is Aotearoa. Use of Aotearoa to describe the North Island fell out of favour in the early 20th century, and it is now a collective Māori name for New Zealand as a whole.Geography
During the Last Glacial Period when sea levels were over 100 metres lower than present day levels, the North and South islands were connected by a vast coastal plain which formed at the South Taranaki Bight. During this period, most of the North Island was covered in thorn scrubland and forest, while the modern-dayNorthland Peninsula
The Northland Peninsula, called the North Auckland Peninsula in earlier times, is in the far north of the North Island of New Zealand. It is joined to the rest of the island by the Auckland isthmus, a narrow piece of land between the Waitemat� ...
was a subtropical rainforest. Sea levels began to rise 7,000 years ago, eventually separating the islands and linking the Cook Strait to the Tasman Sea
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about across and about from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 wa ...
.
Bays and coastal features
* Bay of Islands *Bay of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty () is a large bight (geography), bight along the northern coast of New Zealand's North Island. It stretches from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaway in the east. Called ''Te Moana-a-Toitehuatahi'' (the Ocean ...
* Hauraki Gulf
* Firth of Thames
* Hawke Bay
* Ninety Mile Beach
* North Taranaki Bight
* South Taranaki Bight
Lakes and rivers
* Lake Taupō * Waikato River *Whanganui River
The Whanganui River is a major river in the North Island of New Zealand. It is the country's third-longest river, and has special status owing to its importance to the region's Māori people. In March 2017 it became the world's second natur ...
Capes and peninsulas
* Coromandel Peninsula *Northland Peninsula
The Northland Peninsula, called the North Auckland Peninsula in earlier times, is in the far north of the North Island of New Zealand. It is joined to the rest of the island by the Auckland isthmus, a narrow piece of land between the Waitemat� ...
* Cape Palliser
* Cape Reinga
* East Cape
* North Cape
Forests and national parks
* Egmont National Park * Tongariro National Park * Waipoua Kauri Forest * Whanganui National Park *and many forest parks of New ZealandVolcanology
* Auckland Volcanic Field *Mount Ruapehu
Mount Ruapehu (; English ) is an active stratovolcano at the southern end of the Taupō Volcanic Zone and North Island North Island Volcanic Plateau, volcanic plateau in New Zealand. It is northeast of Ohakune and southwest of the southern s ...
* Mount Taranaki (''Taranaki Maunga'')
* Mount Tarawera
* Whakaari / White Island
* North Island Volcanic Plateau
Other
*Waitomo Caves
Waitomo is a rural community in the King Country region of New Zealand's North Island. There are several solutional cave systems in the area around the village, which are popular tourist attractions. Restaurants and accommodation are centred in ...
* Taumatawhakatangihangakoauauotamateaturipukakapikimaungahoronukupokaiwhenuakitanatahu
Demographics
The North Island has an estimated population of as of . The North Island had a population of 3,808,005 at the2023 New Zealand census
The 2023 New Zealand census, which took place on 7 March 2023, was the thirty-fifth national census in New Zealand. It implemented measures that aimed to increase the Census' effectiveness in response to the issues faced with the 2018 census, i ...
, an increase of 213,453 people (5.9%) since the 2018 census, and an increase of 570,957 people (17.6%) since the 2013 census. Of the total population, 733,893 people (19.3%) were aged under 15 years, 743,154 (19.5%) were 15 to 29, 1,721,427 (45.2%) were 30 to 64, and 609,534 (16.0%) were 65 or older.
Ever since the conclusion of the Otago gold rush in the 1860s, New Zealand's European population growth has experienced a steady 'Northern drift' as population centres in the North Island have grown faster than those of New Zealand's South Island. This population trend has continued into the twenty-first century, but at a much slower rate. While the North Island's population continues to grow faster than the South Island, this is solely due to the North Island having higher natural increase (i.e. births minus deaths) and international migration; since the late 1980s, the internal migration flow has been from the North Island to the South Island. In the year to June 2020, the North Island gained 21,950 people from natural increase and 62,710 people from international migration, while losing 3,570 people from internal migration.
Culture and identity
At the 2023 census, 63.1% of North Islanders identified as European (Pākehā
''Pākehā'' (or ''Pakeha''; ; ) is a Māori language, Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesians, Polynesian New Zealanders, New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zeala ...
), 19.8% as Māori, 10.6% as Pacific peoples, 19.3% as Asian, 1.9% as Middle Eastern/Latin American/African, and 1.1% as other ethnicities. Percentages add to more than 100% as people can identify with more than one ethnicity.
Māori form the majority in three districts of the North Island: Kawerau (63.2%), Ōpōtiki
Ōpōtiki (; from ''Ōpōtiki-Mai-Tawhiti'') is a town in the eastern Bay of Plenty in the North Island of New Zealand. It houses the headquarters of the Ōpōtiki District Council, the mayor of Ōpōtiki and comes under the Bay of Plenty Region ...
(66.2%) and Wairoa (68.5%). Europeans formed the plurality in the Auckland region (49.8%) and are the majority in the remaining 39 districts.
The proportion of North Islanders born overseas at the 2018 census were 29.3%. The most common foreign countries of birth were England (15.4% of overseas-born residents), Mainland China (11.3%), India (10.1%), South Africa (5.9%), Australia (5.5%) and Samoa (5.3%).
Cities and towns

 The North Island has a larger population than the South Island, with the country's largest city, Auckland, and the capital, Wellington, accounting for nearly half of it.
There are 30 urban areas in the North Island with a population of 10,000 or more:
The North Island has a larger population than the South Island, with the country's largest city, Auckland, and the capital, Wellington, accounting for nearly half of it.
There are 30 urban areas in the North Island with a population of 10,000 or more:
Economy
The sub-national GDP of the North Island was estimated at NZ$ 282.355 billion in 2021 (78% of New Zealand's national GDP).Governance

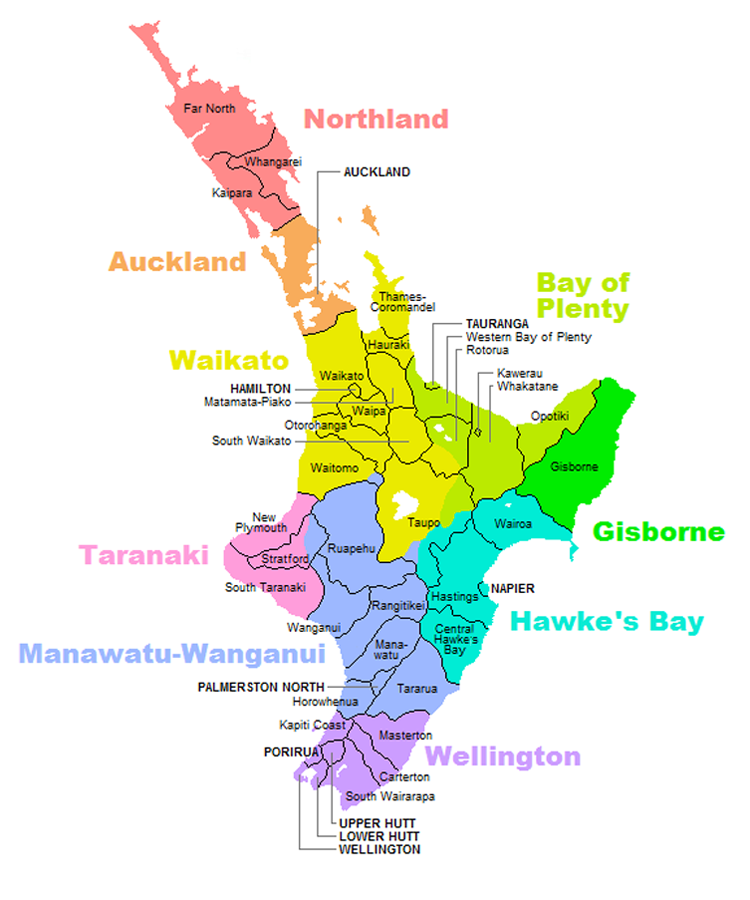
Regions
Nine local governmentregions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
cover the North Island and its adjacent islands and territorial waters.
* Northland
*Auckland
Auckland ( ; ) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. It has an urban population of about It is located in the greater Auckland Region, the area governed by Auckland Council, which includes outlying rural areas and ...
*Waikato
The Waikato () is a region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipā District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the nort ...
*Bay of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty () is a large bight (geography), bight along the northern coast of New Zealand's North Island. It stretches from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaway in the east. Called ''Te Moana-a-Toitehuatahi'' (the Ocean ...
* Gisborne
*Taranaki
Taranaki is a regions of New Zealand, region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano Mount Taranaki, Taranaki Maunga, formerly known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the ...
* Manawatū-Whanganui
* Hawke's Bay Region
* Wellington Region
Healthcare
Healthcare in the North Island is provided by fifteen District Health Boards (DHBs). Organised around geographical areas of varying population sizes, they are not coterminous with the Local Government Regions.See also
*List of islands of New Zealand
New Zealand consists of more than six hundred islands, mainly remnants of Zealandia, a larger land mass now beneath the sea. New Zealand is the List of island countries#UN member states and states with limited recognition, sixth-largest island ...
References
External links
* * {{Authority control Islands of New Zealand