|
Tupaia (navigator)
Tupaia (also spelled Tupaea or Tupia; 1725 – 20 December 1770) was a Tahitian Polynesian navigator and '' arioi'' (a kind of priest), originally from the island of Ra'iatea in the Pacific Islands group known to Europeans as the Society Islands. His remarkable navigational skills and Pacific geographical knowledge were used by Lt. James Cook, R.N. when he took him aboard HMS ''Endeavour'' as guide on its voyage of exploration to '' Terra Australis Incognita''. Tupaia travelled with Cook to New Zealand, acting as the expedition's navigator to the Polynesian Māori, and Australia. He died in December 1770 from a shipborne illness contracted when ''Endeavour'' was docked in Batavia for repairs ahead of its return journey to England. Early life Tupaia was born at Ha'amanino Harbour on Ra'iatea around 1725 and became a leading ''ariori'' priest for the Taputapuatea marae. Tupaia was trained in the ''fare-'ai-ra'a-'upu'', or schools of learning, about the origin of the cosmos, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bearing (navigation)
In navigation, bearing or azimuth is the horizontal angle between the direction of an object and north or another object. The angle value can be specified in various angular units, such as degrees, mils, or grad. More specifically: * Absolute bearing refers to the clockwise angle between the magnetic north (''magnetic bearing'') or true north (''true bearing'') and an object. For example, an object to due east would have an absolute bearing of 90 degrees. Thus, it is the same as azimuth.U.S. Army, ''Advanced Map and Aerial Photograph Reading'', Headquarters, War Department, Washington, D.C. (17 September 1941), pp. 24-2/ref> * #Relative, Relative bearing refers to the angle between the craft's forward direction ( heading) and the location of another object. For example, an object relative bearing of 0 degrees would be immediately in front; an object relative bearing 180 degrees would be behind. Bearings can be measured in mils, points, or degrees. Thus, it is the same as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anne Salmond (historian)
Dame Mary Anne Salmond (née Thorpe; born 16 November 1945) is a New Zealand anthropologist. She was New Zealander of the Year Awards, New Zealander of the Year in 2013. In 2020, she was appointed to the Order of New Zealand, the highest honour in New Zealand's royal honours system. Early life and family Born in Wellington in 1945, Mary Anne Thorpe was raised in Gisborne, New Zealand, Gisborne, before being sent to board at Solway College in Masterton, where she was Dux (education), dux in 1961. In 1962 and 1963, she attended Cleveland Heights High School in the US as an AFS Intercultural Programs, American Field Service scholar. At the University of Auckland, Salmond graduated with Bachelor of Arts in 1966 and Master of Arts in anthropology in 1968. In the same year at Auckland Secondary Teachers' College, she received a Teaching Diploma with Distinction. Salmond later attended the University of Pennsylvania, where she gained a PhD in 1972. Her thesis was titled ''Hui – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Wallis
Post-captain, Captain Samuel Wallis (23 April 1728 – 21 January 1795) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer who made the first recorded visit by a European navigator to Tahiti. Biography Wallis was born at Fenteroon Farm, near Camelford, Cornwall. He served under John Byron. In 1757, he was promoted to Royal Navy ranks, rates, and uniforms of the 18th and 19th centuries, captain and was given the command of HMS Dolphin (1751), HMS ''Dolphin'' as commander of an expedition accompanied by Philip Carteret on with an assignment to circumnavigate the globe.Quanchi, ''Historical Dictionary of the Discovery and Exploration of the Pacific Islands'', p. 248 As was reported in the press, he was also tasked with discovering the Southern Continent. The two ships were parted by a storm shortly after sailing through the Strait of Magellan. In June 1767, the expedition made the first European landfall on Tahiti, which he named "George III, King George the Third's Island" in honour of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purea
Purea, Tevahine-'ai-roro-atua-i-Ahurai, also called ''Oborea'' (floruit 1769), was a queen from the Landward Teva tribe and a self-proclaimed ruler of all Tahiti. Queen Purea is known from the first famous European expeditions to Tahiti. She ruled as chieftainess of her tribe area in 1767–1768, when she was encountered by the expedition of Samuel Wallis. Life Early life Purea's mother was the high chieftainess of the Ahurai marae in Faʻaʻā. Purea married Amo, a member of the Teva clan and high chief of Papara. Their marriage ended with the birth of their son Teri'irere, and Tupaia became her lover. Wallis expedition The first European to have visited Tahiti according to existing records was lieutenant Samuel Wallis, who was circumnavigating the globe in , and landed on 17 June 1767 in Matavai Bay, situated on the territory of the chiefdom of Pare (Arue/Mahina), governed by the female chieftain "Oberea" (Purea). Wallis named the island King George Island. The first conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
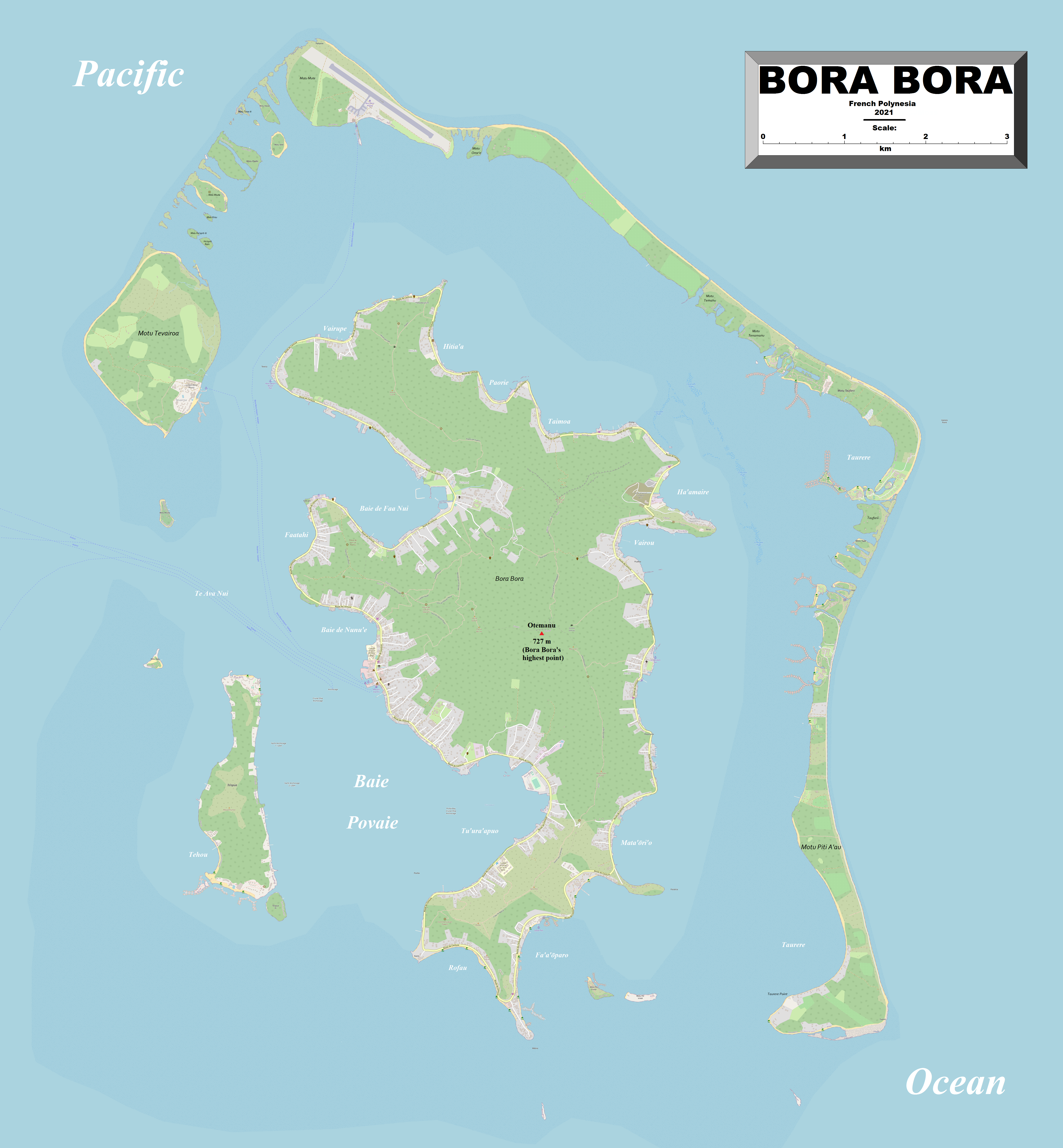
Bora Bora
Bora Bora (French language, French: ''Bora-Bora''; Tahitian language, Tahitian: ''Pora Pora'') is an island group in the Leeward Islands (Society Islands), Leeward Islands in the Pacific Ocean, South Pacific. The Leeward Islands comprise the western part of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, which is an Overseas France, overseas collectivity of the France, French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. Bora Bora has a total land area of . The Bora Bora Island, main island, located about northwest of Papeete, is surrounded by a lagoon and a coral reef, barrier reef. In the center of the island are the remnants of an extinct volcano, rising to two peaks, Mount Pahia and Mount Otemanu; the highest point is at . Bora Bora is part of the Communes of France, Commune of Bora-Bora (commune), Bora-Bora, which also includes the atoll of Tūpai. The main languages spoken in Bora Bora are Tahitian language, Tahitian and French language, French. However, due to the high tourist population, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotuma
Rotuma () is a self-governing heptarchy, generally designated a Local government in Fiji, dependency of Fiji. Rotuma commonly refers to the Rotuma Island, the only permanently inhabited and by far the largest of all the islands in the Rotuma Group. Officially, the Rotuma Act declares that Rotuma consists of Rotuma Island as well as its neighbouring islands, rocks, and reefs across the entire Rotuma Group. The dependency is situated around 500 km west of the French islands of Wallis and Futuna and a similar distance north of the Fijian mainland. Its capital is Ahau, a hamlet consisting of a number of Colony of Fiji, colonial-era buildings. Rotuma exists as a dependency of Fiji but itself contains its own socioreligious enclave, pene-enclave known traditionally as ''Faguta'' where the chiefs (of Juju (district), Juju and Pepjei) and their villages adhere to the practices of worship, Fara (Rotuman festivity), festival dates, and French language, French-based writing system of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokelau
Tokelau (; ; known previously as the Union Islands, and, until 1976, known officially as the Tokelau Islands) is a dependent territory of New Zealand in the southern Pacific Ocean. It consists of three tropical coral atolls: Atafu, Nukunonu, and Fakaofo. They have a combined land area of . In addition to these three, Swains Island (), which forms part of the same archipelago, is the subject of an ongoing territorial dispute; it is currently administered by the United States as part of American Samoa. Tokelau lies north of the Samoan Islands, east of Tuvalu, south of the Phoenix Islands, southwest of the more distant Line Islands, and northwest of the Cook Islands. Tokelau has a population of approximately 1,500 people; it has the List of countries and dependencies by population#Sovereign states and dependencies by population, fourth-smallest population of any sovereign state or dependency in the world. As of the 2016 census, around 45% of its residents List of sovereign states a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga, is an island country in Polynesia, part of Oceania. The country has 171 islands, of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. according to Johnson's Tribune, Tonga has a population of 104,494, 70% of whom reside on the main island, Tongatapu. The country stretches approximately north-south. It is surrounded by Fiji and Wallis and Futuna (France) to the northwest, Samoa to the northeast, New Caledonia (France) and Vanuatu to the west, Niue (the nearest foreign territory) to the east and Kermadec (New Zealand) to the southwest. Tonga is about from New Zealand's North Island. Tonga was first inhabited roughly 2,500 years ago by the Lapita civilization, Polynesian settlers who gradually evolved a distinct and strong ethnic identity, language, and culture as the Tongan people. They quickly established a powerful footing across the South Pacific, and this period of Tong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |