Nipmuc People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Nipmuc or Nipmuck people are an Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands, who historically spoke an Eastern Algonquian language, probably the Loup language. Their historic territory Nippenet, meaning 'the freshwater pond place', is in central

 On April 22, 1980, Zara Cisco Brough, landowner of Hassanamessit, submitted a letter of intention to petition for federal recognition as a Native American tribe.
On July 20, 1984, the BIA received the petition letter from the 'Nipmuc Tribal Council Federal Recognition Committee', co-signed by Zara Cisco Brough and her successor, Walter A. Vickers, of the Hassanamisco, and Edwin 'Wise Owl' W. Morse Sr. of the Chaubunagungamaug. In January 2001, a preliminary finding was made by the BIA in favor of the Nipmuc Nation of Sutton, Massachusetts, which had most of its membership in Massachusetts, while a negative preliminary finding was issued for the Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck Band of Dudley, Massachusetts, which had its membership about evenly split between Massachusetts and Connecticut. In 2004, the BIA notified the Nipmuc Nation that they had been rejected for federal recognition.
On April 22, 1980, Zara Cisco Brough, landowner of Hassanamessit, submitted a letter of intention to petition for federal recognition as a Native American tribe.
On July 20, 1984, the BIA received the petition letter from the 'Nipmuc Tribal Council Federal Recognition Committee', co-signed by Zara Cisco Brough and her successor, Walter A. Vickers, of the Hassanamisco, and Edwin 'Wise Owl' W. Morse Sr. of the Chaubunagungamaug. In January 2001, a preliminary finding was made by the BIA in favor of the Nipmuc Nation of Sutton, Massachusetts, which had most of its membership in Massachusetts, while a negative preliminary finding was issued for the Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck Band of Dudley, Massachusetts, which had its membership about evenly split between Massachusetts and Connecticut. In 2004, the BIA notified the Nipmuc Nation that they had been rejected for federal recognition.
 The
The
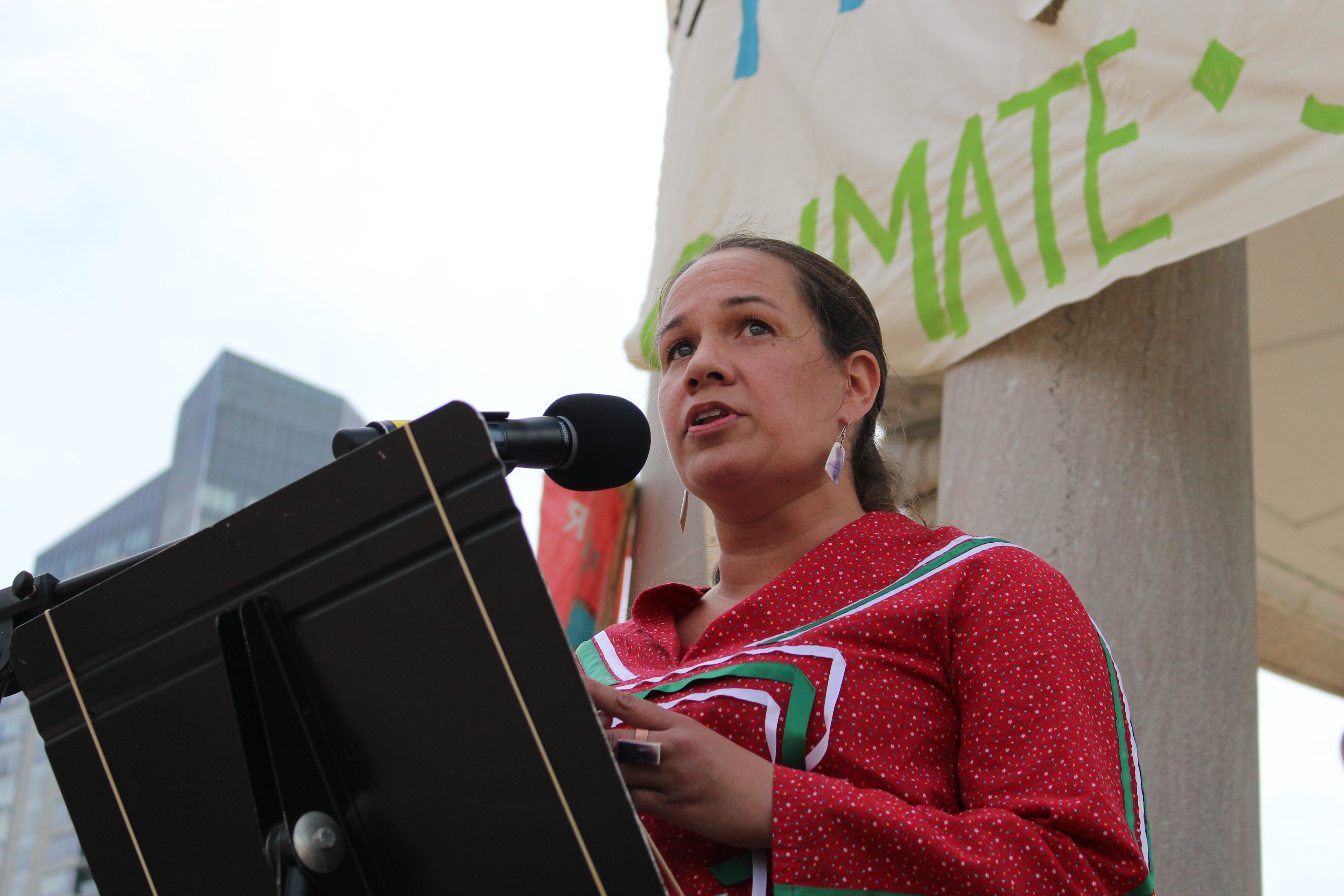 Local attitudes towards Native American culture and history changed as antiquarians,
Local attitudes towards Native American culture and history changed as antiquarians,
Commonwealth of Massachusetts Commission on Indian Affairs
Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck Indian Council
Hassanamisco Indian Museum
Nipmuc Indian Association of Connecticut
Project Mishoon
* {{authority control African–Native American relations Algonquian ethnonyms Eastern Algonquian peoples King Philip's War Native American tribes in Connecticut Native American tribes in Massachusetts Native American tribes in Rhode Island
Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
and nearby parts of Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
and Rhode Island
Rhode Island ( ) is a state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Connecticut to its west; Massachusetts to its north and east; and the Atlantic Ocean to its south via Rhode Island Sound and Block Is ...
.
The Nipmuc Tribe had contact with traders and fishermen from Europe prior to the colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization, colonization of the Americas, involving a number of European countries, took place primarily between the late 15th century and the early 19th century. Norse colonization of North ...
. The first recorded contact with Europeans was in 1630, when John Acquittamaug (Nipmuc) took maize to sell to the starving colonists of Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, Massachusetts. After the colonists encroached on their land, negotiated fraudulent land sales and introduced legislation designed to encourage further European settlement, many Nipmucs joined Metacomet
Metacomet (c. 1638 in Massachusetts – August 12, 1676), also known as Pometacom, Metacom, and by his adopted English name King Philip,King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1678 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodland ...
, in 1675, though they were unable to defeat the colonists. Many Nipmuc were held captive on Deer Island in Boston Harbor and died of disease and malnutrition, while others were executed or sold into slavery in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
.
Christian missionary John Eliot arrived in Boston in 1631. After learning the Massachusett language
The Massachusett language is an Algonquian languages, Algonquian language of the Algic languages, Algic language family that was formerly spoken by several peoples of eastern coastal and southeastern Massachusetts. In its revived form, it is s ...
, which was widely understood throughout New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, he converted numerous Native Americans to Christianity, and with the help of Wawaus, also known as James the Printer (Nipmuc), published a Bible translated in Massachusett and a Massachusett grammar. Backed by the colonial government, he established several "Indian plantations" or praying towns
Praying towns were settlements established by British colonization of the Americas, English colonial governments in New England from 1646 to 1675 in an effort to convert local Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianit ...
, where Native Americans were induced to settle and be instructed in European customs and converted to Christianity.
The state of Massachusetts has a government-to-government relationship with the Hassanamisco Nipmuc and the Chaubunagungamaug Band of Nipmuc Indians.
Name
The tribe is first mentioned in a 1631 letter by Deputy Governor Thomas Dudley as the ''Nipnet'', 'people of the freshwater pond', due to their inland location. This derives from ''Nippenet'' and includes variants such as ''Neipnett'', ''Neepnet'', ''Nepmet'', ''Nibenet'', ''Nopnat'' and ''Nipneet''. In 1637,Roger Williams
Roger Williams (March 1683) was an English-born New England minister, theologian, author, and founder of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Pl ...
recorded the tribe as the ''Neepmuck'', which derives from ''Nipamaug'', 'people of the freshwater fishing place,' and also appears spelled as ''Neetmock'', ''Notmook'', ''Nippimook'', ''Nipmaug'', ''Nipmoog,'' ''Neepemut'', ''Nepmet'', ''Nepmock,'' ''Neepmuk'', ''Nepmug'', as well as modern ''Nipmuc(k)''. Colonists and the Native Americans themselves used this term extensively after the growth of the praying towns
Praying towns were settlements established by British colonization of the Americas, English colonial governments in New England from 1646 to 1675 in an effort to convert local Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianit ...
. The French referred to most New England Native Americans as ''Loup'', meaning 'Wolf eople. But Nipmuc refugees who had fled to French Colonial Canada and settled among the Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
referred to themselves as ''ȣmiskanȣakȣiak'', meaning the 'beaver tail-hill people'.
Language
The Nipmuc most likely spoke Loup A, a Southern New England Algonquian language. The language is undergoing revival within the communities. There are several second-language speakers.Tribal divisions

Daniel Gookin
Danyell "Daniel" Gookin (1612 – 19 March 1687) was a Munster colonist, settler of Virginia and Massachusetts, and a writer on the subject of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indians.
Early life
He was born, perhaps in County Cork, ...
(1612–1687), Superintendent to the Native Americans and assistant of Eliot, was careful to distinguish the Nipmuc (proper), Wabquasset, Quaboag, and Nashaway tribes.Connole, D. A. (2007). ''Indians of the Nipmuck Country in Southern New England 1630–1750, An Historical Geography.'' Jefferson, NC: McFarland & Co. pp. 8–10. The situation was fluid since these Native groups were decentralized, and individuals unhappy with their chiefs freely joined other groups. In addition, shifting alliances were made based on kinship, military, and tributary relationships with other tribes.Hodge, F. W. (1910). "Nipmuc" in ''Handbook of American Indians North of Mexico.'' (Vol. III, p. 74). Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution.
The formation of the praying towns
Praying towns were settlements established by British colonization of the Americas, English colonial governments in New England from 1646 to 1675 in an effort to convert local Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianit ...
dissolved some tribal divisions, as members of different tribes settled together. Four groups that are associated with the Nipmuc peoples survive today.
* Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck, Dudley Indians
::Descendants of the Praying town of Chaunbunagungamaug, now part of Webster, on lands returned by the town of Dudley, Massachusetts. The tribe's reservation spans 2.5 acres in Thompson, CT, where its office is located, and across the border in Thompson, Connecticut
Thompson is a town in Windham County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Northeastern Connecticut Planning Region. The town was named after Sir Robert Thompson, an English landholder. The population was 9,189 at the 2020 census ...
.
* Hassanamisco Nipmuc Band, Grafton Indians
::Descendants of the Praying town of Hassanamessit, now part of Grafton, Massachusetts
Grafton is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 19,664 at the 2020 census. The town consists of the North Grafton, Grafton, and South Grafton geographic areas, each with a separate ZIP Code. Incorporated ...
. The tribe's reservation spans 3.2 acres and this parcel has never been out of the hands of the Nipmuc People.
* Natick Massachusett, Natick Nipmuc
::The descendants of the Praying town of Natick, Massachusetts
Natick ( ) is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is near the center of the MetroWest region of Massachusetts, with a population of 37,006 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. west of Boston, Natick is part o ...
do not retain any of their original lands. The Natick are primarily descended from the Massachusett
The Massachusett are a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
in addition to having Nipmuc ancestry. They qualify for state services as Nipmuc.Executive Office of Housing and Economic Development, Commission on Indian Affairs. (n.d.). Tuition waiver guidelines. Retrieved from Commonwealth of Massachusetts website: www.mass.gov/hed/docs/dhcd/ia/tuitionwaiver.doc.
* Connecticut Nipmuc
::Descendants of various Nipmuc who survived or relocated to Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
. The Nipmuc of Connecticut are not recognized by the state. The related Quinebaug band, believed to have Algonquian origins, lived in both Connecticut and Massachusetts at the time of European contact. As of 1774, the last remaining Quinebaugs, numbering about 25 members, were recorded living near present-day Plainfield, Connecticut. Descendants of the Quinebaug are thought to be living in Nipmuc communities near Gay Head, Mashpee and Worcester, Massachusetts
Worcester ( , ) is the List of municipalities in Massachusetts, second-most populous city in the U.S. state of Massachusetts and the list of United States cities by population, 113th most populous city in the United States. Named after Worcester ...
.
Legal status
State recognition
Massachusetts GovernorMichael Dukakis
Michael Stanley Dukakis ( ; born November 3, 1933) is an American politician and lawyer who served as governor of Massachusetts from 1975 to 1979 and from 1983 to 1991. He is the longest-serving governor in Massachusetts history and only the s ...
issued Executive Order #126 in 1976, which proclaimed that 'State agencies shall deal directly with ... he Hassanamisco Nipmuc ... on matters affecting the Nipmuc Tribe'(much progress has happened since and other Nipmuck bands have been acknowledged by the state), as well as calling for the creation of a state 'Commission on Indian Affairs.' The all-Indian Commission was established; it conferred state support for education, health care, cultural continuity, and protection of remaining lands for the descendants of the Wampanoag, Nipmuc and Massachusett tribes. The state also calls for the examination of all human remains discovered in the course of construction and other projects, requiring notification of the Commission, who after the investigation by the State Archaeologist (in part in an effort to determine age of remains, decide the appropriate course of action.
The Commonwealth of Massachusetts also cited the continuity of the Nipmuc(k) with the historic tribe and commended tribal efforts to preserve their culture and traditions. The state also symbolically repealed the General Court Act of 1675 that banned Native Americans from the City of Boston during King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1678 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodland ...
. The tribe also works closely with the state to undergo various archaeological excavations and preservation campaigns. The tribe, in conjunction with the National Congress of American Indians
The National Congress of American Indians (NCAI) is an Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indian and Alaska Natives, Alaska Native Indigenous rights, rights organization. It was founded in 1944 to represent the tribes and resist U.S. ...
were against the construction of the sewage treatment plant on Deer Island in Boston Harbor where many graves were desecrated by its construction, and annually hold a remembrance service for members of the tribe lost over the winter during their internment during King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1678 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodland ...
and protest against the destruction of Indian gravesites.
Federal recognition efforts
 On April 22, 1980, Zara Cisco Brough, landowner of Hassanamessit, submitted a letter of intention to petition for federal recognition as a Native American tribe.
On July 20, 1984, the BIA received the petition letter from the 'Nipmuc Tribal Council Federal Recognition Committee', co-signed by Zara Cisco Brough and her successor, Walter A. Vickers, of the Hassanamisco, and Edwin 'Wise Owl' W. Morse Sr. of the Chaubunagungamaug. In January 2001, a preliminary finding was made by the BIA in favor of the Nipmuc Nation of Sutton, Massachusetts, which had most of its membership in Massachusetts, while a negative preliminary finding was issued for the Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck Band of Dudley, Massachusetts, which had its membership about evenly split between Massachusetts and Connecticut. In 2004, the BIA notified the Nipmuc Nation that they had been rejected for federal recognition.
On April 22, 1980, Zara Cisco Brough, landowner of Hassanamessit, submitted a letter of intention to petition for federal recognition as a Native American tribe.
On July 20, 1984, the BIA received the petition letter from the 'Nipmuc Tribal Council Federal Recognition Committee', co-signed by Zara Cisco Brough and her successor, Walter A. Vickers, of the Hassanamisco, and Edwin 'Wise Owl' W. Morse Sr. of the Chaubunagungamaug. In January 2001, a preliminary finding was made by the BIA in favor of the Nipmuc Nation of Sutton, Massachusetts, which had most of its membership in Massachusetts, while a negative preliminary finding was issued for the Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck Band of Dudley, Massachusetts, which had its membership about evenly split between Massachusetts and Connecticut. In 2004, the BIA notified the Nipmuc Nation that they had been rejected for federal recognition.
Colonial-era history
17th century
European sailors, fishermen, and adventurers began visitingNew England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
during the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
. The first permanent settlements in the region did not begin until after the settling of Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
in 1620. These early seafarers introduced several infectious diseases to which the Native Americans had no prior exposure, resulting in epidemics
An epidemic (from Ancient Greek, Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of Host (biology), hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example ...
with mortality rates as high as 90 percent. Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
killed many of the Native Americans in 1617–1619, 1633, 1648–1649, and 1666. Similarly influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
, and measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
also afflicted the Native Americans throughout the period. In 2010 researchers developed a new hypothesis on epidemics between 1616 and 1619 as being from leptospirosis complicated by Weil syndrome.
As shown by the writings of Increase Mather
Increase Mather (; June 21, 1639 Old Style – August 23, 1723 Old Style) was a History of New England, New England Puritan clergyman in the Massachusetts Bay Colony and the sixth President of Harvard University, President of Harvard College (la ...
, the colonists attributed the decimation of the Native Americans to God's providence in clearing the new lands for settlement, but they were accustomed to interpreting their lives in such religious terms. At the time of contact, the Nipmuc were a fairly large grouping, subject to more powerful neighbors who provided protection, especially against the Pequot
The Pequot ( ) are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut includin ...
, Mohawk and Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
tribes that raided the area.Sultzman, L. (2008, October 29). Nipmuc history. Retrieved from http://www.dickshovel.com/nipmuc.html.
The colonists initially depended on the Native Americans for survival in the New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: ...
, and the Native Americans rapidly began to trade their foodstuffs, furs and wampum
Wampum is a traditional shell bead of the Eastern Woodlands tribes of Native Americans. It includes white shell beads hand-fashioned from the North Atlantic channeled whelk shell and white and purple beads made from the quahog or Western ...
for the copper kettles, arms and metal tools of the colonists. Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
settlers arrived in large numbers from 1620 to 1640, the ' Great Migration' that increased their need to acquire more land. Since the colonists had conflicting colonial and royal grants, the settlers depended on having Indian names on land deeds to mark legitimacy. This process had serious flaws, as John Wompas
John Wompas ( 1637-1642 – 1679) was a Nipmuc man born around 1637 in Nipmuc Country, in what would become the state of Massachusetts. He spent the first half of his childhood among his Native kin and the second half living with an English fa ...
deeded off many lands to the colonists to curry favor, many of which were not even his.
Indian plantations
The royal charter of the Massachusetts Bay Colony of 1629 called for the conversion of Native Americans to Christianity. The colonists did not begin this work in earnest until after thePequot War
The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place in 1636 and ended in 1638 in New England, between the Pequot nation and an alliance of the colonists from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Saybrook colonies and their allies from the Na ...
proved their military superiority, and they gained official backing in 1644.Shannon, T. J. (2005). Puritan conversion attempts. Retrieved from http://public.gettysburg.edu/~tshannon/hist106web/Indian Converts/the_puritans3.htm
Although many answered the call, the Rev. John Eliot, who had learned the Massachusett from tribe interpreters, compiled an Indian Bible and a grammar of the language. It was well understood from Cape Ann
Cape Ann is a rocky peninsula in northeastern Massachusetts on the Atlantic Ocean. It is about northeast of Boston and marks the northern limit of Massachusetts Bay. Cape Ann includes the city of Gloucester and the towns of Essex, Man ...
to Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
. In addition, colonial authorities supported settlement of the Native Americans on 'Indian plantations' or Praying towns
Praying towns were settlements established by British colonization of the Americas, English colonial governments in New England from 1646 to 1675 in an effort to convert local Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianit ...
. There they instructed the Native Americans in European farming methods, culture, and language, administered by Indian preachers and councilors who were often descended from the elite native families. The Native Americans melded indigenous and European culture, but were mistrusted by both the colonists and their non-converted brethren. The colonists and later state governments gradually sold off the plantations. By the end of the 19th century, only the Cisco homestead in Grafton was still owned by direct descendants of Nipmuc landholders.
Following is a list of Indian Plantations (Praying towns) associated with the Nipmuc:Nipmuc placenames of new england. (1995). istorical Series I ed. #III (Nipmuc Indian Association of Connecticut ), Retrieved from http://www.nativetech.org/Nipmuc/placenames/mainmass.html
Chaubunagungamaug, Chabanakongkomuk, Chaubunakongkomun, or Chaubunakongamaug
* 'The boundary fishing place,' 'fishing place at the boundary,' or 'at the boundary.'
* Webster, Massachusetts
Webster is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 17,776 at the 2020 census. Named after statesman Daniel Webster, the town was founded by industrialist Samuel Slater, and was home to several early Amer ...
(on lands ceded from Dudley
Dudley ( , ) is a market town in the West Midlands, England, southeast of Wolverhampton and northwest of Birmingham. Historically part of Worcestershire, the town is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Dudley. In the ...
).
Hassanamesit, Hassannamessit, Hassanameset, or Hassanemasset
* 'Place where there is uch
Uch (;
), frequently referred to as Uch Sharīf (;
; ''"Noble Uch"''), is a historic city in the Pakistan's Punjab province. Uch may have been founded as Alexandria on the Indus, a town founded by Alexander the Great during his invasion of t ...
gravel,' or 'at a place of small stones.'
* Grafton, Massachusetts
Grafton is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 19,664 at the 2020 census. The town consists of the North Grafton, Grafton, and South Grafton geographic areas, each with a separate ZIP Code. Incorporated ...
.
Magunkaquog, Makunkokoag, Magunkahquog, Magunkook, Maggukaquog or Mawonkkomuk
* 'Place of great trees,' 'granted place,' or 'place that is a gift.'
* Hopkinton, Massachusetts
Hopkinton is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, west of Boston. The town is best known as the starting point of the Boston Marathon, held annually on Patriots' Day each April, and as the he ...
.
Manchaug, Manchauge, Mauchage, Mauchaug, or Mônuhchogok
* 'Place of departure,' 'place of marvelling,' 'island of rushes,' or 'island where reeds grow.'(?)
* Sutton, Massachusetts
Sutton, officially the Town of Sutton, is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 9,357 in the 2020 United States census. Located in the Blackstone Valley, the town was design ...
.
Manexit, Maanexit, Mayanexit
* 'Where the road lies,' 'where we gather,' 'near the path,' or 'place of meekness.'
* Thompson, Connecticut
Thompson is a town in Windham County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Northeastern Connecticut Planning Region. The town was named after Sir Robert Thompson, an English landholder. The population was 9,189 at the 2020 census ...
.
Nashoba
* 'The place between' or 'between waters.'
* Littleton, Massachusetts
Littleton (historically ''Nashoba'') is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 10,141 at the 2020 census.
For geographic and demographic information on the neighborhood of Littleton Common, please see the a ...
.
* Also settled by the Pennacook
The Pennacook, also known by the names Penacook and Pennacock, were Algonquian Indigenous people who lived in what is now Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and southern Maine. They were not a united tribe but a network of politically and culturally ...
.
Natick
* 'Place of hills.'
* Natick, Massachusetts
Natick ( ) is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. It is near the center of the MetroWest region of Massachusetts, with a population of 37,006 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. west of Boston, Natick is part o ...
.
* Also settled by the Massachusett
The Massachusett are a Native American tribe from the region in and around present-day Greater Boston in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The name comes from the Massachusett language term for "At the Great Hill," referring to the Blue Hills ...
.
Okommakamesitt, Agoganquameset, Ockoocangansett, Ogkoonhquonkames, Ognonikongquamesit, or Okkomkonimset
* 'Plowed field place' or 'at the plantation.'
* Marlborough, Massachusetts
Marlborough is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 41,793 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Marlborough became a prosperous industrial town in the 19th century and made the transition to high ...
.
Packachoag, Packachoog, Packachaug, Pakachog, or Packachooge
* 'At the turning place,' 'bends,' 'bare mountain place, or 'treeless mountain.'
* Auburn, Massachusetts
Auburn is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 16,889 at the 2020 census.
History
The Auburn area was first settled in 1714. On April 10, 1778, parts of Worcester, Sutton, Leicester and Oxford, Massac ...
.
Quabaug, Quaboag, Squaboag
* 'Red pond,' 'bloody pond' or 'pond before.'
* Brookfield, Massachusetts
Brookfield is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. Brookfield was first settled by Europeans in 1660. The population was 3,439 at the 2020 census.
History
Brookfield was first settled by Europeans in 1660 and was offici ...
.
Quinnetusset, Quanatusset, Quantiske, Quantisset, or Quatiske, Quattissick
* 'Long brook' or 'little long river.'
* Thompson, Connecticut
Thompson is a town in Windham County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Northeastern Connecticut Planning Region. The town was named after Sir Robert Thompson, an English landholder. The population was 9,189 at the 2020 census ...
.
Wabaquasset, Wabaquassit, Wabaquassuck, Wabasquassuck, Wabquisset or Wahbuquoshish
* 'Mats for covering a lodge,' 'place of white stones,' or 'mats to cover the house.'
* Woodstock, Connecticut
Woodstock is a New England town, town in Windham County, Connecticut, Windham County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Northeastern Connecticut Planning Region, Connecticut, Northeastern Connecticut Planning Region. The populat ...
.
Wacuntuc, Wacantuck, Wacumtaug, Wacumtung, Waentg, or Wayunkeke
* 'A bend in the river.'
* Uxbridge, Massachusetts
Uxbridge is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States, first colonized in 1662 and incorporated in 1727. It was originally part of the town of Mendon, and named for the Earl of Uxbridge. The town is located southwest of Boston an ...
. originally Mendon, Massachusetts
Mendon is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 6,228 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Mendon is part of the Blackstone River Valley National Heritage Corridor, ...
sold by Nipmuck as "Squnshepauk" Plantation
Washacum or Washakim
* 'Surface of the sea.'
* Sterling, Massachusetts
Sterling is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 7,985 at the 2020 census.
History
Previous to its incorporation, it was "the Second Parish of Lancaster." It was commonly called by a portion of its In ...
.
* Also settled by the Pennacook
The Pennacook, also known by the names Penacook and Pennacock, were Algonquian Indigenous people who lived in what is now Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and southern Maine. They were not a united tribe but a network of politically and culturally ...
.
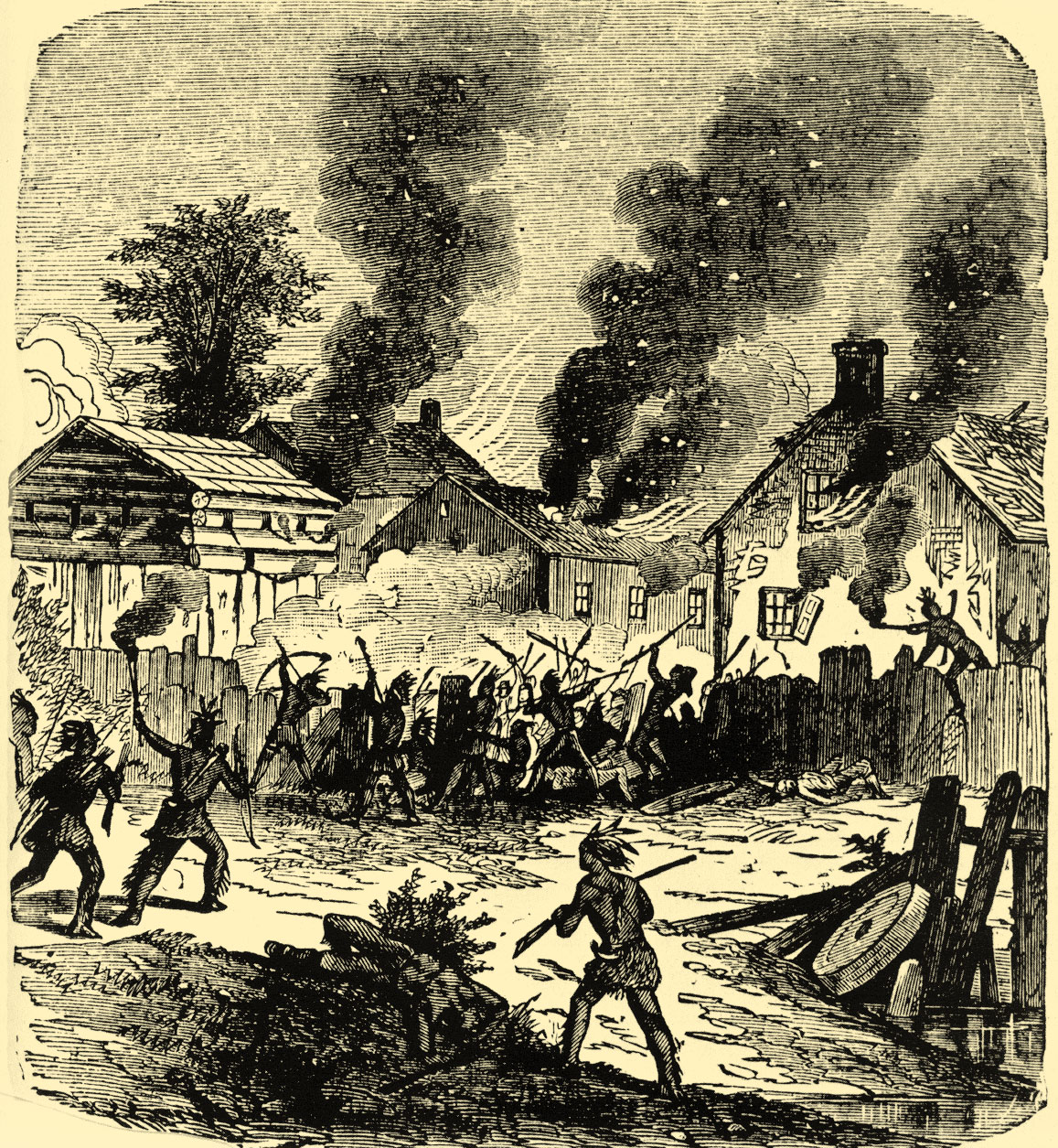
King Philip's War
 The
The Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1628–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around Massachusetts Bay, one of the several colonies later reorganized as the Province of M ...
passed numerous legislation against Indian culture and religion. New laws were passed to limit the influence of the powwows
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native American and First Nations communities. Inaugurated in 1923, powwows today are an opportunity for Indigenous people to socialize, dance, sing, and honor their ...
, or 'shamans', and restricted the ability of non-converted Native Americans to enter colonial towns on the Sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, Ten Commandments, commanded by God to be kept as a Holid ...
. The Nipmuc were also informed that any unimproved lands were fair game for incorporation into the growing colony. These draconian measures and the increasing amount of land lost to the settlers led many Nipmuc to join the Wampanoag
The Wampanoag, also rendered Wôpanâak, are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of the Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, Northeastern Woodlands currently based in southeastern Massachusetts and forme ...
chief Metacomet
Metacomet (c. 1638 in Massachusetts – August 12, 1676), also known as Pometacom, Metacom, and by his adopted English name King Philip,King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1678 between a group of indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodland ...
, which would ravage New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
from 1675 to 1676. The Native Americans that had already settled the Praying towns
Praying towns were settlements established by British colonization of the Americas, English colonial governments in New England from 1646 to 1675 in an effort to convert local Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianit ...
were interned on Deer Island in Boston Harbor over the winter where a great many perished from starvation and exposure to the elements. Although many of the Native Americans fled to join the uprising, other Native Americans joined the colonists. The Praying Indians were particularly at risk, as the war made all Native Americans suspect, but the Praying towns were also attacked by the 'wild' Native Americans that joined Metacomet's struggle. The Nipmuc were major participants in the siege of Lancaster
Lancaster may refer to:
Lands and titles
*The County Palatine of Lancaster, a synonym for Lancashire
*Duchy of Lancaster, one of only two British royal duchies
*Duke of Lancaster
*Earl of Lancaster
*House of Lancaster, a British royal dynasty
...
, Brookfield, Sudbury Sudbury may refer to:
Places Australia
* Sudbury Reef, Queensland
Canada
* Greater Sudbury, Ontario
** Sudbury (federal electoral district)
** Sudbury (provincial electoral district)
** Sudbury Airport
** Sudbury Basin, a meteorite impact cra ...
and Bloody Brook, all in Massachusetts, and the tribe prepared thoroughly for conflict by forming alliances, and the group even had "an experienced gunsmith, a lame man, who kept their weapons in good working order." The siege of Lancaster also lead to the capture of Mary Rowlandson
Mary Rowlandson, née White, later Mary Talcott (c. 1637January 5, 1711), was a colonial American woman who was captured by Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans in 1676 during King Philip's War and held for 11 weeks before being ...
, who was placed in captivity until ransomed for £20 and would later write a memoir of her captivity. The Native Americans lost the war, and survivors were hunted down, murdered, sold into slavery in the West Indies
The West Indies is an island subregion of the Americas, surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, which comprises 13 independent island country, island countries and 19 dependent territory, dependencies in thr ...
or forced to leave the area.
18th century
The Nipmuc regrouped around their formerPraying towns
Praying towns were settlements established by British colonization of the Americas, English colonial governments in New England from 1646 to 1675 in an effort to convert local Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans to Christianit ...
and were able to maintain a certain amount of autonomy using the remaining lands to farm or sell timber. The population of the tribe was reduced as several outbreaks of smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
returned in 1702, 1721, 1730, 1752, 1764, 1776, and 1792. Land sales continued unabated, much of it used to pay for legal fees, personal expenses, and improvements to the reserve lands. By 1727, Hassanamisset was reduced to 500 acres from the original 7,500 acres with that land incorporated into the town of Grafton, Massachusetts
Grafton is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 19,664 at the 2020 census. The town consists of the North Grafton, Grafton, and South Grafton geographic areas, each with a separate ZIP Code. Incorporated ...
, and in 1797, Chaubunagungamaug Reserve was reduced to 26 of their 200 acres. The switch to the cattle industry also disrupted the native economy, as the colonists' cattle ate the unfenced lands of the Nipmuc and the courts did not always side with the Native Americans, but the Native Americans rapidly adopted the husbandry of swine
Suina (also known as Suiformes) is a suborder of omnivorous, non-ruminant artiodactyl mammals that includes the domestic pig and peccaries. A member of this clade is known as a suine. Suina includes the family Suidae, termed suids, known in ...
since the changes in economy and loss of remaining pristine lands reduced ability to hunt and fish. Since the Native Americans had few assets besides land, much of the land was sold to pay for medical, legal and personal expenses, increasing the number of landless Native Americans. With smaller numbers and landholdings, Indian autonomy was worn away by the time of the Revolutionary War, the remaining reserve lands were overseen by colony- and later state-appointed guardians that were to act on the Native Americans' behalf. However, the Hassanamisco guardian Stephen Maynard, appointed in 1776, embezzled the funds and was never prosecuted.
Wars
New England rapidly became swept up in a series of wars between the French and British and their respective Indian allies. Many of the Native Americans of New England who had left the region joined theAbenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
, who were allied to the French; however, local Native Americans were often conscripted as guides or scouts for the colonists. Wars occupied much of the century, including King William's War
King William's War (also known as the Second Indian War, Father Baudoin's War, Castin's War, or the First Intercolonial War in French) was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War (1688–1697), also known as the War of the Grand Allian ...
, (1689–1699), Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War (1702–1713) or the Third Indian War was one in a series of French and Indian Wars fought in North America involving the colonial empires of Great Britain, France, and Spain; it took place during the reign of Anne, Queen of Gr ...
(1704–1713), Dummer's War
Dummer's War (1722–1725) (also known as Father Rale's War, Lovewell's War, Greylock's War, the Three Years War, the Wabanaki-New England War, or the Fourth Anglo-Abenaki War) was a series of battles between the New England Colonies and the Wab ...
(1722–1724), King George's War
King George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in ...
(1744–1748) and the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
(1754–1760). Many Native Americans also died in service of the Revolutionary War.
Emigration
The upheaval of the Indian Wars and growing mistrust of the Native Americans by the colonists lead to a steady trickle, and sometimes whole villages, that fled to increasingly mixed-tribe bands either northward to thePennacook
The Pennacook, also known by the names Penacook and Pennacock, were Algonquian Indigenous people who lived in what is now Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and southern Maine. They were not a united tribe but a network of politically and culturally ...
and Abenaki
The Abenaki ( Abenaki: ''Wαpánahki'') are Indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands of Canada and the United States. They are an Algonquian-speaking people and part of the Wabanaki Confederacy. The Eastern Abenaki language was pred ...
who were under the protection of the French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
or westward to join the Mahican
The Mohicans ( or ) are an Eastern Algonquian Native American tribe that historically spoke an Algonquian language. As part of the Eastern Algonquian family of tribes, they are related to the neighboring Lenape, whose indigenous territory was ...
at increasingly mixed settlements of Schagticoke or Stockbridge, the latter of which eventually migrated as far west as Wisconsin
Wisconsin ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest of the United States. It borders Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michig ...
.Calloway, C. G. C. (1997). ''After King Philip's war, presence and persistence in Indian New England''. (pp. 40-45). Dartmouth, NH: Dartmouth College. This further dwindled Indian presence in New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, although not all the Native Americans dispersed. Those Nipmuc that fled eventually assimilated into either the predominant host tribe or the conglomerate that developed.
Modern history
19th century
The Native Americans were reduced to wards of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and were represented by state-appointed non-Native guardians. Rapid acculturation and intermarriage led many to believe the Nipmuc had simply just vanished, due to a combination of romantic notions of who the Native Americans were and to justify the colonial expansion. Native Americans continued to exist but fewer and fewer were able to live on the dwindling reserve lands and most left to seek employment as domestics or servants in White households, out to sea as whalers or seafarers, or into the growing cities where they became labourers or barbers. Growing acculturation, intermarriage, and dwindling populations led to the extinction of the Natick Dialect of theMassachusett language
The Massachusett language is an Algonquian languages, Algonquian language of the Algic languages, Algic language family that was formerly spoken by several peoples of eastern coastal and southeastern Massachusetts. In its revived form, it is s ...
, and only one speaker could be found in 1798. A cultural practice that survived was peddling handcrafted, square-edged splint baskets and medicines. The Commonwealth of Massachusetts, after investigating the condition of the Native Americans, decided to grant citizenship to the Native Americans with the passage of the Massachusetts Enfranchisement Act of 1869, which ultimately led to the sale of any of the remaining lands. Hassanamessit was divided up among a few families. In 1897, the last of the Dudley lands were sold, and five of the families were placed in a tenement house on Lake Street in Webster, Massachusetts
Webster is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 17,776 at the 2020 census. Named after statesman Daniel Webster, the town was founded by industrialist Samuel Slater, and was home to several early Amer ...
. "The rest scattered, moving with other Nipmuc families living in Woodstock, Worcester, Providence, and Hassanamisco. Worcester developed strong Indian enclaves in mainly African-American neighborhoods. Nipmuc activities became centered on the Hassanamisco Reservation. Events such as the Annual Clambake and elections on the 4th of July were times for Nipmucs to gather and discuss tribal business."
Intermarriage
Intermarriage between Whites, Blacks (or ''Chikitis''), and Native Americans began in early colonial times. Africans and Native Americans shared a complementary gender imbalance as slave-traders imported few female enslaved Africans intoNew England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
and many of Indian men died in war or joined the whaling industry. Many Native American women married African men. Intermarriage with whites was uncommon, due to colonial anti-miscegenation
Anti-miscegenation laws are laws that enforce racial segregation at the level of marriage and intimate relationships by criminalizing interracial marriage sometimes, also criminalizing sex between members of different races.
In the United State ...
laws in place.Mandell, D. R. 'The Saga of Sarah Muckamugg: Indian and African Intermarriage in Colonial New England.' ''Sex, love, race: crossing boundaries in north american history''. ed. Martha Elizabeth Hodes. New York, NY: New York Univ Pr. pp. 72-83. The children of such unions were accepted into the tribe as Native Americans, due to the matrilineal focus of Nipmuc culture, but to the eyes of their sceptical White neighbours, the increasingly Black phenotypes
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properti ...
of some were seen to delegitimize their Indian identity. By the 19th century, only a handful of pure-blood Native Americans remained, and Native Americans vanish from state and federal census records but are listed as 'Black', 'mulatto
( , ) is a Race (human categorization), racial classification that refers to people of mixed Sub-Saharan African, African and Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the ...
', 'colored
''Colored'' (or ''coloured'') is a racial descriptor historically used in the United States during the Jim Crow era to refer to an African American. In many places, it may be considered a slur.
Dictionary definitions
The word ''colored'' wa ...
' or 'miscellaneous' depending on their appearance. In 1902 it was reported that the Last of John Eliot Praying Indians was living in Massachusetts a Mrs Patience Fidelia Clifton age70 of Brigham's Hill, Grafton, Massachusetts
Grafton is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 19,664 at the 2020 census. The town consists of the North Grafton, Grafton, and South Grafton geographic areas, each with a separate ZIP Code. Incorporated ...
formerly Indian community of Hassanamesitt
Censuses
In 1848, theMassachusetts Senate
The Massachusetts Senate is the upper house of the Massachusetts General Court, the bicameral state legislature of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. The Senate comprises 40 elected members from 40 single-member senatorial districts in the st ...
Joint Committee on Claims called for a report on the condition of several tribes that received aid from the Commonwealth. Three reports were listed: The 1848 'Denney Report' presented to the Senate the same year; the 1849 'Briggs Report', written by Commissioners F. W. Bird, Whiting Griswold and Cyrus Weekes and presented to Governor George N. Briggs; and the 1859 'Earle Report', written by Commissioner John Milton Earle that was submitted in 1861. Each report was more informative and thorough than the previous one. The Nipmuc require having an ancestor listed on these reports and the disbursement lists of funds from Nipmuc land sales. The lists did not count all Native Americans, as many Native Americans may have been well-integrated into other racial communities and due to the constant movement of Native Americans from place to place.
* Some of the tribes' ancestors were recorded as 'colored' including individuals of the Brown, Cisco, Freeman, Gigger, Hemenway, Hull, Humphrey, Walker and Willard families.
* Some individuals of the Gigger family are labelled as 'miscellaneous Indians.'
* Some individuals were recorded as 'mixed' including individuals in the Bakeman, Belden, Brown, Kyle and Hector families.
* Some individuals of the Hall, Hector and Hemenway families have no label.
20th and 21st centuries
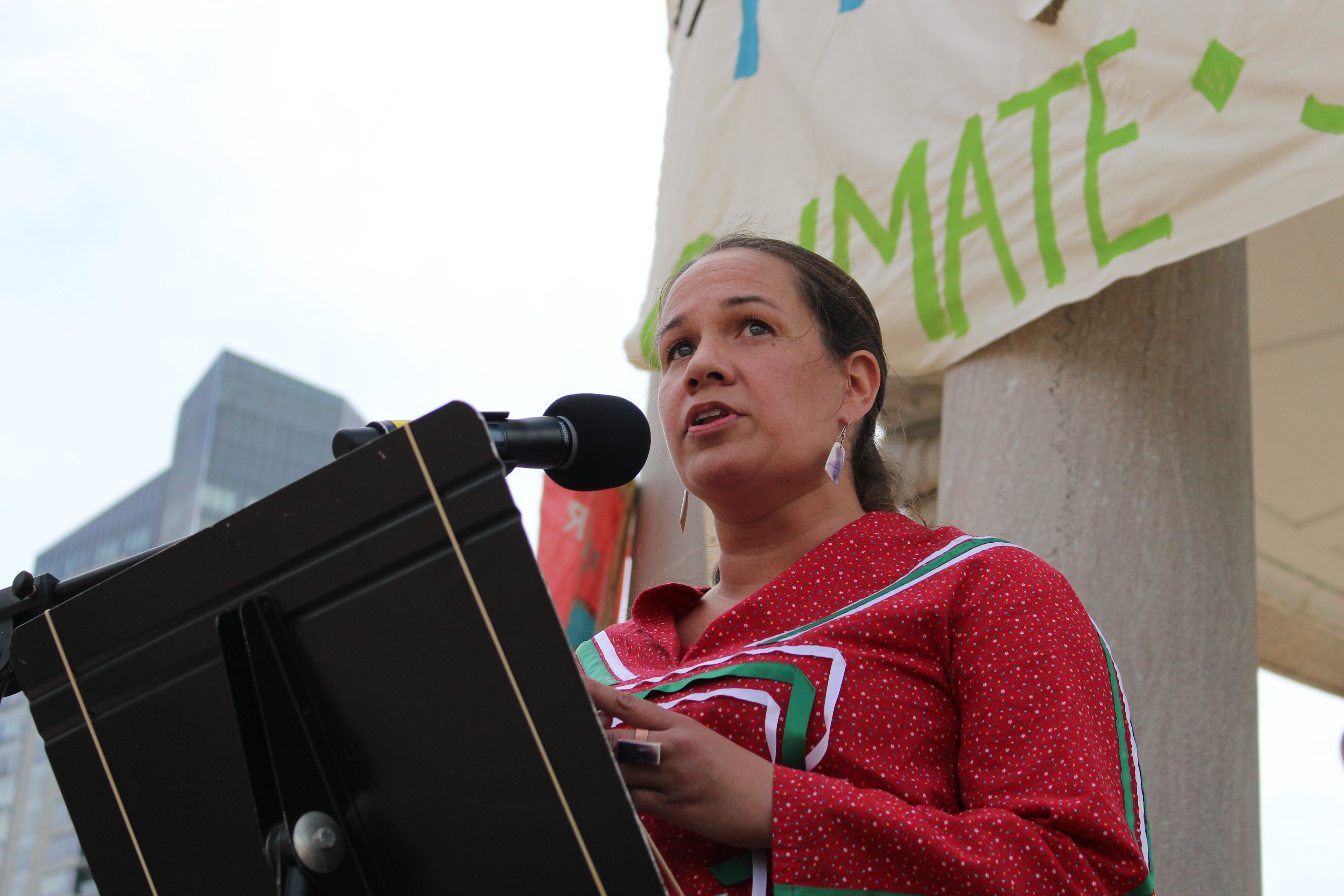 Local attitudes towards Native American culture and history changed as antiquarians,
Local attitudes towards Native American culture and history changed as antiquarians, anthropologists
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
, institutions like the Boy Scouts
Boy Scouts or Boy Scout may refer to:
* Members, sections or organisations in the Scouting Movement
** Scout (Scouting), a boy or a girl participating in the worldwide Scouting movement
** Scouting America, formerly known as Boy Scouts of America ...
as well as the 1907 appearance of Buffalo Bill Cody
William Frederick Cody (February 26, 1846January 10, 1917), better known as Buffalo Bill, was an American soldier, bison hunter, and showman. One of the most famous figures of the American Old West, Cody started his legend at the young age o ...
with many Native Americans in feathered headdresses paying respects to Uncas, Sachem of the Mohegan
The Mohegan are an Indigenous people originally based in what is now southeastern Connecticut in the United States. They are part of the Eastern Algonquian linguistic and cultural family and historically shared close ties with the neighboring ...
. Despite nearly four centuries of assimilation, acculturation, and the destruction of economic and community support from enfranchisement in the region, certain Indian families were able to maintain a distinct Indian identity and cultural identity. The turn of the century also saw active cultural and genealogical
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
research by James L. Cisco and his daughter Sara Cisco Sullivan from the Grafton homestead, and worked closely with the remnants of other closely related tribes, such as Gladys Tantaquidgeon
Gladys Iola Tantaquidgeon (June 15, 1899 – November 1, 2005) was a Mohegan medicine woman, anthropologist, author, tribal council member, and elder based in Connecticut.
and the Fielding families of the Mohegan Tribe
The Mohegan Tribe ( ) is a federally recognized Native American tribe and sovereign tribal nation based in Uncasville, Connecticut. Historically part of the Pequot people, the Mohegan emerged as a distinct group in the 17th century under the lead ...
, Atwood L. Williams of the Pequot
The Pequot ( ) are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of Connecticut. The modern Pequot are members of the federally recognized Mashantucket Pequot Tribe, four other state-recognized groups in Connecticut includin ...
, and William L. Wilcox of the Narragansett. Together, various tribal members began sharing cultural memory, with pan-Indianism
Pan-Indianism is a philosophical and political approach promoting unity and, to some extent, cultural homogenization, among different Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous groups in the Americas regardless of tribal distinctions and cultu ...
firmly taking root in the 1920s with Indian gatherings such as the Algonquin Indian Council of New England that met in Providence, Rhode Island
Providence () is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Rhode Island, most populous city of the U.S. state of Rhode Island. The county seat of Providence County, Rhode Island, Providence County, it is o ...
and dances or powwow
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native Americans in the United States, Native American and First Nations in Canada, First Nations communities. Inaugurated in 1923, powwows today are an opportunity fo ...
s such as those at Hassanamessit in 1924. Plains Indian
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nations peoples who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of North ...
clothing was often worn as potent statements of Indian identity and to prove their continued residence in the area and because much of the original culture had been lost. Other Nipmuc individuals appeared at town pageants and fairs, including the 1938 appearance at the Sturbridge, Massachusetts
Sturbridge is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. It is home to Old Sturbridge Village living museum, living history museum and other sites of historical interest such as Tantiusques.
The pop ...
bicentennial fair of many ancestors of today's Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck.
By the 1970s, the Nipmuc had made many strides. Many local members of the tribe were called upon to help with the development of the Native American exhibit at Old Sturbridge Village
Old Sturbridge Village is a living museum located in Sturbridge, Massachusetts, which recreates life in rural New England during the 1790s through 1830s. It is the largest living museum in New England, covering more than 200 acres (81 hectares ...
, a 19th-century living museum
A living museum, also known as a living history museum, is a type of museum which recreates historical settings to simulate a past time period, providing visitors with an experiential interpretation of history. It is a type of museum that recr ...
built in the heart of former Nipmuc territory. State recognition
Diplomatic recognition in international law is a unilateral declarative political act of a state that acknowledges an act or status of another state or government in control of a state (may be also a recognized state). Recognition can be accor ...
was also achieved by the end of the same decade, re-establishing the Nipmuc people's relationship with the state and providing limited social services. The Nipmuc sought federal recognition in the 1980s. Tension between the Nipmuc Nation, which included the Hassanamisco and many descendants of the Chaubunagungamaug, based in Webster, Massachusetts
Webster is a town in Worcester County, Massachusetts, United States. The population was 17,776 at the 2020 census. Named after statesman Daniel Webster, the town was founded by industrialist Samuel Slater, and was home to several early Amer ...
split the application (69A&69B) in the mid-1990s. Divisions were caused by the frustrations with the slow pace of recognition as well as disagreements about gambling.
Land, 190 acres, in the Hassanamessit Woods in Grafton, believed to contain the remains of the praying village were under agreement for development for more than 100 homes. This property has significant cultural importance to the Hassanamisco Nipmuc because it contains the meetinghouse and the center of the old praying village. However, The Trust for Public Land
The Trust for Public Land is a U.S. nonprofit organization with a mission to "create parks and protect land for people, ensuring healthy, livable communities for generations to come". Since its founding in 1972, the Trust for Public Land has compl ...
, the town of Grafton, the Grafton Land Trust, the Hassanamisco Nipmuc and the state of Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
intervened. The Trust for Public Land
The Trust for Public Land is a U.S. nonprofit organization with a mission to "create parks and protect land for people, ensuring healthy, livable communities for generations to come". Since its founding in 1972, the Trust for Public Land has compl ...
purchased the property and kept it off the market until 2004, after sufficient funding was procured to permanently protect the property. The property also has ecological significance as it is adjacent to 187 acres of Grafton owned land as well as 63 acres owned by the Grafton Land Trust. These properties will provide numerous recreational benefits to the public as well as play a role in protecting the water quality of local watersheds.
In July 2013, the Hassanamisco band selected a chief, Cheryll Toney Holley
Cheryll Toney Holley is a First Nations American historian, genealogist, and museum director. She serves as the Sonksq (female chief) of the Hassanamisco Nipmuc Band, a Massachusetts state-recognized tribe.
Career
She was selected to succee ...
to succeed Walter Vickers upon his resignation.
Notable Nipmuc people
*Cheryll Toney Holley
Cheryll Toney Holley is a First Nations American historian, genealogist, and museum director. She serves as the Sonksq (female chief) of the Hassanamisco Nipmuc Band, a Massachusetts state-recognized tribe.
Career
She was selected to succee ...
, historian, museum director, and Sonksq (female chief) of the Hassanamisco Nipmuc Band from 2013 to present.
* Wullumahchein, also known as Black James (before 1640 — ca. 1686), Nipmuc peace office and spiritual leader
See also
*Native American tribes in Massachusetts
Native may refer to:
People
* '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood
* '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Nat ...
* Hassanamisco Nipmuc
* Chaubunagungamaug Reservation
* Lake Chaubunagungamaug
Lake Chaubunagungamaug, also known as Webster Lake, is a lake in the town of Webster, Massachusetts. It is located near the Connecticut border and has a surface area of . Since 1921, the lake has also been known by a much longer name having 45 l ...
* Tantiusques
Tantiusques ("Tant-E-oos-kwiss") is a open space reservation and historic site registered with the National Register of Historic Places. The reservation is located in Sturbridge, Massachusetts, and is owned and managed by The Trustees of Rese ...
References
External links
Commonwealth of Massachusetts Commission on Indian Affairs
Chaubunagungamaug Nipmuck Indian Council
Hassanamisco Indian Museum
Nipmuc Indian Association of Connecticut
Project Mishoon
* {{authority control African–Native American relations Algonquian ethnonyms Eastern Algonquian peoples King Philip's War Native American tribes in Connecticut Native American tribes in Massachusetts Native American tribes in Rhode Island