NBC Red Network on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The
 In early 1922, AT&T announced the establishment of a "toll" station in
In early 1922, AT&T announced the establishment of a "toll" station in  AT&T's radio network, commonly called the "WEAF chain", was first developed in the
AT&T's radio network, commonly called the "WEAF chain", was first developed in the
 A few weeks after AT&T consolidated its radio operations into the Broadcasting Company of America subsidiary, it agreed to sell BCA's assets to RCA for approximately $1 million (equivalent to $ in ), a deal made public on July 22, 1926. This sale transferred ownership of WEAF to RCA; included was WEAF's network of 15 stations, plus an agreement by AT&T to make its telephone lines readily available for networking. In a separate deal, WCAP was sold to RCA on July 28, 1926, its broadcast hours ceded to time-share partner WRC three days later. '' Variety'' regarded the sale as an economical one for AT&T, as the WEAF chain generated an annual income of $500,000, with little hope of turning a profit, "which even an affluent corporation like (AT&T) takes into consideration". While the deal was criticized for granting RCA a
A few weeks after AT&T consolidated its radio operations into the Broadcasting Company of America subsidiary, it agreed to sell BCA's assets to RCA for approximately $1 million (equivalent to $ in ), a deal made public on July 22, 1926. This sale transferred ownership of WEAF to RCA; included was WEAF's network of 15 stations, plus an agreement by AT&T to make its telephone lines readily available for networking. In a separate deal, WCAP was sold to RCA on July 28, 1926, its broadcast hours ceded to time-share partner WRC three days later. '' Variety'' regarded the sale as an economical one for AT&T, as the WEAF chain generated an annual income of $500,000, with little hope of turning a profit, "which even an affluent corporation like (AT&T) takes into consideration". While the deal was criticized for granting RCA a  On September 13, 1926, RCA chairman of the board Owen D. Young and president James G. Harbord announced the formation of the National Broadcasting Company, Inc., to begin operations upon RCA's acquisition of WEAF on November 15. A widely placed full-page company advertisement stated that: "The purpose of the National Broadcasting Company will be to provide the best program available for broadcasting in the United States. ... It is hoped that arrangements may be made so that every event of national importance may be broadcast widely throughout the United States." As part of a renegotiation of the cross-licensing agreements, NBC was also permitted to accept advertising. The purchase of WEAF and NBC's formation was seen as an achievement for RCA's general manager
On September 13, 1926, RCA chairman of the board Owen D. Young and president James G. Harbord announced the formation of the National Broadcasting Company, Inc., to begin operations upon RCA's acquisition of WEAF on November 15. A widely placed full-page company advertisement stated that: "The purpose of the National Broadcasting Company will be to provide the best program available for broadcasting in the United States. ... It is hoped that arrangements may be made so that every event of national importance may be broadcast widely throughout the United States." As part of a renegotiation of the cross-licensing agreements, NBC was also permitted to accept advertising. The purchase of WEAF and NBC's formation was seen as an achievement for RCA's general manager
 Following NBC's formation, RCA inaugurated a second network on January 1, 1927; called " the 'blue' network", it was led by WJZ along with Westinghouse's WBZ, KDKA and KYW; with the WEAF-led chain concurrently named "the 'red' network". The debut program, sponsored by the
Following NBC's formation, RCA inaugurated a second network on January 1, 1927; called " the 'blue' network", it was led by WJZ along with Westinghouse's WBZ, KDKA and KYW; with the WEAF-led chain concurrently named "the 'red' network". The debut program, sponsored by the
 During much of radio's "
During much of radio's " This practice of moving popular shows over to NBC Red, coupled with NBC Blue's reputation as a weaker network, likely originated the misperception that NBC Blue ''solely'' featured sustaining programs (e.g., news, cultural and educational programs which had no sponsor) and NBC Red ''solely'' featured commercial fare. As it was, networks had limited control over their schedules as advertisers bought available time periods for programs, regardless of what other sponsors broadcast in other time slots. Networks rented out studio facilities used to produce shows and sold air-time to sponsors. Sustaining programs were the only programs produced by the networks and were used to fill unsold time periods (affiliated stations had the option to "break away" from the network to air a local program during these periods) but the network had the "option" to take back the time period if a network sponsor wanted the time period. Dramatic programs, which comprised only 2 percent of program time on NBC Red in 1926, accounted for 25 percent of the network's airtime by 1942.
The network provided a rich variety of classical concert broadcasts, including performances by the
This practice of moving popular shows over to NBC Red, coupled with NBC Blue's reputation as a weaker network, likely originated the misperception that NBC Blue ''solely'' featured sustaining programs (e.g., news, cultural and educational programs which had no sponsor) and NBC Red ''solely'' featured commercial fare. As it was, networks had limited control over their schedules as advertisers bought available time periods for programs, regardless of what other sponsors broadcast in other time slots. Networks rented out studio facilities used to produce shows and sold air-time to sponsors. Sustaining programs were the only programs produced by the networks and were used to fill unsold time periods (affiliated stations had the option to "break away" from the network to air a local program during these periods) but the network had the "option" to take back the time period if a network sponsor wanted the time period. Dramatic programs, which comprised only 2 percent of program time on NBC Red in 1926, accounted for 25 percent of the network's airtime by 1942.
The network provided a rich variety of classical concert broadcasts, including performances by the
 As a result of the defections, CBS boasted in 1949 of having sixteen of the twenty top rated programs. The consequences carried over to television, where CBS maintained its newfound dominance for decades. Paley personally worked to woo the performers, while Sarnoff professed his indifference to the defections, stating at an annual meeting that "Leadership built over the years on a foundation of solid service cannot be snatched overnight by buying a few high-priced comedians. Leadership is not a laughing matter." In part due to the talent raids,. NBC president Niles Trammell—who had been with NBC since 1929 and RCA since 1933—resigned to help establish WCKT in
As a result of the defections, CBS boasted in 1949 of having sixteen of the twenty top rated programs. The consequences carried over to television, where CBS maintained its newfound dominance for decades. Paley personally worked to woo the performers, while Sarnoff professed his indifference to the defections, stating at an annual meeting that "Leadership built over the years on a foundation of solid service cannot be snatched overnight by buying a few high-priced comedians. Leadership is not a laughing matter." In part due to the talent raids,. NBC president Niles Trammell—who had been with NBC since 1929 and RCA since 1933—resigned to help establish WCKT in
 NBC Radio drastically revamped its programming lineup with ''
NBC Radio drastically revamped its programming lineup with ''
''Broadcasting'', April 21, 1975, pp. 46–47. Other major affiliates included WBAL-FM in In 1979, NBC launched The Source, a secondary network that targeted younger listeners, providing news, short features and music specials to FM rock stations. The Source also featured a talk show hosted by sex columnist
In 1979, NBC launched The Source, a secondary network that targeted younger listeners, providing news, short features and music specials to FM rock stations. The Source also featured a talk show hosted by sex columnist
 NBC made its final radio station acquisition in 1983 when it bought Boston station WJIB from GE, which was divesting its radio properties. In February 1984, the network sold WRC in Washington to
NBC made its final radio station acquisition in 1983 when it bought Boston station WJIB from GE, which was divesting its radio properties. In February 1984, the network sold WRC in Washington to
 Following the sale, NBC Radio added one long-form program to their lineup—a daily talk/variety show hosted by
Following the sale, NBC Radio added one long-form program to their lineup—a daily talk/variety show hosted by
"iHeartMedia's 24/7 News Network Joins Forces With NBC News To Launch 'NBC News Radio'"
, July 11, 2016 (allaccess.com)
at the Digital Deli {{American broadcast radio Westwood One Defunct radio networks in the United States Radio stations established in 1926 Radio stations disestablished in 1999 1926 establishments in New York (state) 1999 disestablishments in New York (state)
National Broadcasting Company
The National Broadcasting Company (NBC) is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the NBC Entertainment division of NBCUniversal, a subsidiary of Comcast. It is one of NBCUniversal's ...
's NBC Radio Network (also known as the NBC Red Network from 1927 to 1942) was an American commercial radio network which was in continuous operation from 1926 through 1999. Along with the NBC Blue Network
The Blue Network (previously known as the NBC Blue Network) was the on-air name of a now defunct American radio network, which broadcast from 1927 through 1945.
Beginning as one of the two radio networks owned by the National Broadcasting Co ...
, it was one of the first two nationwide networks established in the United States. Its major competitors were the Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS), founded in 1927, and the Mutual Broadcasting System
The Mutual Broadcasting System (commonly referred to simply as Mutual; sometimes referred to as MBS, Mutual Radio or the Mutual Radio Network) was an American commercial radio network in operation from 1934 to 1999. In the Golden Age of Radio, ...
, founded in 1934. In 1942, NBC was required to divest one of its national networks. As such, it sold NBC Blue, which was soon renamed the American Broadcasting Company
The American Broadcasting Company (ABC) is an American Commercial broadcasting, commercial broadcast Television broadcaster, television and radio Radio network, network that serves as the flagship property of the Disney Entertainment division ...
(ABC). After this separation, the Red Network continued as the NBC Radio Network.
For the first 61 years of its existence, this network was owned by the Radio Corporation of America
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghou ...
(RCA) with New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
radio station WEAF (renamed WNBC in 1946, WRCA in 1954 and again as WNBC in 1960) as its flagship station
In broadcasting, a flagship (also known as a flagship station or key station) is the broadcast station which originates a television network, or a particular radio or television program that plays a key role in the branding of and consumer loyal ...
. Following the emergence of television as the dominant entertainment medium and much of NBC Radio's talent migrating both to CBS and NBC television, the network made multiple investments in programming in hopes of retaining relevance. These included the weekend program umbrella ''Monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, Wes ...
'' (1955–1975), the all-news
All-news radio is a radio format devoted entirely to the discussion and broadcast of news.
All-news radio is available in both local and radio syndication, syndicated forms, and is carried on both major US satellite radio networks. All-news sta ...
focused NBC News and Information Service (1975–1977) and the talk radio
Talk radio is a radio format containing discussion about topical issues and consisting entirely or almost entirely of original spoken word content rather than outside music. They may feature monologues, dialogues between the hosts, Interview (jo ...
service NBC Talknet, all of which encountered varying degrees of success and failure.
Following General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston.
Over the year ...
's purchase of RCA in late 1986, GE sold the NBC Radio Network to Westwood One in 1987. Westwood One previously acquired Mutual in 1985 and gradually merged the two together. NBC Radio News, which was also folded into Mutual's news operations, saw most of its functions cease on April 17, 1999, after further consolidation merged both NBC and Mutual directly into CBS's radio news operations. Westwood One and its successor network continued to use "NBC" branding for some of its programming until 2020, partnering with NBC News
NBC News is the news division of the American broadcast television network NBC. The division operates under NBCUniversal Media Group, a division of NBCUniversal, which is itself a subsidiary of Comcast. The news division's various operations r ...
to operate NBC News Radio from 2003 until 2014, and with NBC Sports
NBC Sports is an American programming division for NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, that is responsible for sports broadcasts on their broadcast network NBC, the Cable television, cable channels NBC owns, and on Peacock (streaming service) ...
for NBC Sports Radio. From 2016 onward, iHeartMedia
iHeartMedia, Inc., or CC Media Holdings, Inc., is an American mass media corporation headquartered in San Antonio, Texas. It is the holding company of iHeartCommunications, Inc., formerly Clear Channel Communications, Inc., a company founded by ...
has handled production and distribution of NBC News Radio.
Early history
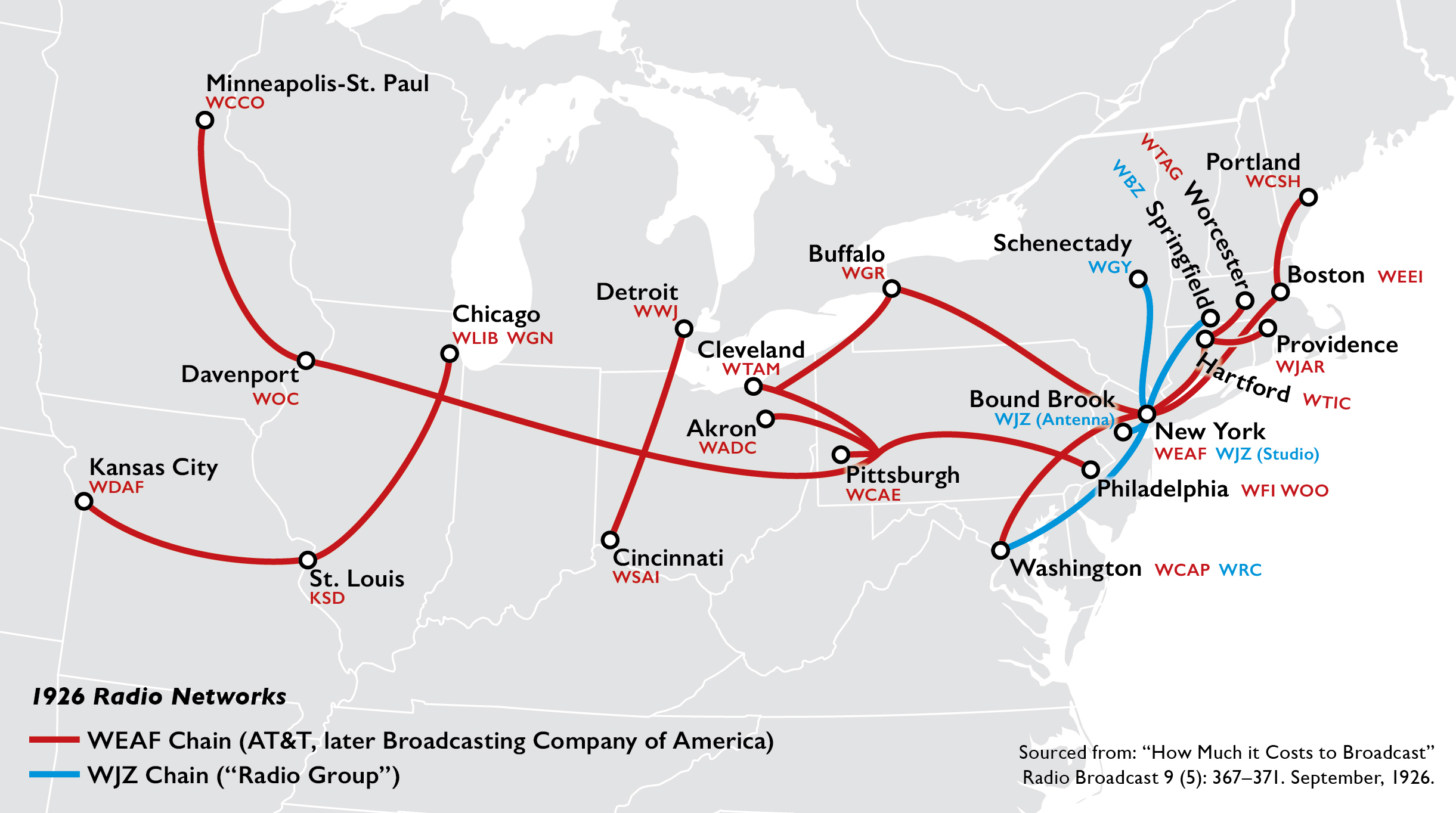
WEAF chain
The 1926 formation of the National Broadcasting Company was a consolidation and reorganization of earlier network radio operations developed by theAmerican Telephone & Telegraph
AT&T Corporation, an abbreviation for its former name, the American Telephone and Telegraph Company, was an American telecommunications company that provided voice, video, data, and Internet telecommunications and professional services to busi ...
Company (AT&T) beginning in 1922, in addition to more limited efforts conducted by the "radio group" companies, which consisted of the Radio Corporation of America
RCA Corporation was a major American electronics company, which was founded in 1919 as the Radio Corporation of America. It was initially a patent pool, patent trust owned by General Electric (GE), Westinghouse Electric Corporation, Westinghou ...
(RCA) and its corporate owners, General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) was an American Multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate founded in 1892, incorporated in the New York (state), state of New York and headquartered in Boston.
Over the year ...
(GE) and the Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company
The Westinghouse Electric Corporation was an American manufacturing company founded in 1886 by George Westinghouse and headquartered in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was originally named "Westinghouse Electric & Manufacturing Company" and was ...
(and, for a period of time, the United Fruit Company
The United Fruit Company (later the United Brands Company) was an American multinational corporation that traded in tropical fruit (primarily bananas) grown on Latin American plantations and sold in the United States and Europe. The company was ...
).
Organized radio broadcasting started in the early 1920s, with AT&T soon becoming an industry leader. In 1920 and 1921, AT&T concluded a series of patent cross-licensing agreements with the "radio group" companies. The "radio group" began negotiating under that name through a cross-licensing agreement between GE and Westinghouse, agreed to on July 1, 1921. Under these agreements, AT&T asserted that it held the sole right to sell commercial time on radio stations, which it called "toll broadcasting", although for the next few years the idea of radio advertising remained controversial. AT&T also recognized that its longline telephone network could be used to connect radio stations together to form networks to share programming and costs.
 In early 1922, AT&T announced the establishment of a "toll" station in
In early 1922, AT&T announced the establishment of a "toll" station in New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
and its intention to develop a nationwide commercial radio network using their Bell System
The Bell System was a system of telecommunication companies, led by the Bell Telephone Company and later by the AT&T Corporation, American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T), that dominated the telephone services industry in North America fo ...
infrastructure. The original plan for the "toll" station was to offer the station for leasing to different operators for fees based on the length of airtime and the specific daypart. Out of the two New York City stations AT&T set up, WEAF emerged as the more successful and served as the key station for AT&T's network development. Although the original plan was to build additional stations throughout the United States, the "broadcasting boom" of 1922 resulted in a total of over 500 assorted broadcasting stations by the end of the year, so AT&T only found it necessary to build one additional outlet, WCAP in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
, owned by its Chesapeake & Potomac subsidiary.
 AT&T's radio network, commonly called the "WEAF chain", was first developed in the
AT&T's radio network, commonly called the "WEAF chain", was first developed in the northeastern United States
The Northeastern United States (also referred to as the Northeast, the East Coast, or the American Northeast) is List of regions of the United States, census regions United States Census Bureau. Located on the East Coast of the United States, ...
. The first joint broadcast was a one-time effort made on January 4, 1923, when a program WEAF originated was relayed by WNAC in Boston, Massachusetts
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
. The first continuous link was established on July 1, 1923, when Colonel Edward H. R. Green arranged for AT&T to provide WEAF programming for rebroadcast by his station, WMAF at South Dartmouth, Massachusetts
Dartmouth ( Massachusett: ) is a coastal town in Bristol County, Massachusetts, United States. Old Dartmouth was the first area of Southeastern Massachusetts to be settled by Europeans in 1652, primarily English. Dartmouth is part of New Engl ...
. The first transcontinental link was made in early 1924, and that fall a coast-to-coast network of 23 stations broadcast a speech by President Calvin Coolidge
Calvin Coolidge (born John Calvin Coolidge Jr.; ; July 4, 1872January 5, 1933) was the 30th president of the United States, serving from 1923 to 1929. A Republican Party (United States), Republican lawyer from Massachusetts, he previously ...
. By the end of 1925, there were 26 affiliates
In the broadcasting industry (particularly in North America, and even more in the United States), a network affiliate or affiliated station is a local broadcaster, owned by a company other than the owner of the network, which carries some or al ...
in the standard "WEAF chain", extending west to St. Louis and Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City, Missouri, abbreviated KC or KCMO, is the largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri by List of cities in Missouri, population and area. The city lies within Jackson County, Missouri, Jackson, Clay County, Missouri, Clay, and Pl ...
.
One early success for the "WEAF chain" was '' The Eveready Hour'', the first sponsored program to be broadcast over a radio network, paid for by the National Carbon Company. Debuting over WEAF in December 1923, the program quickly grew in popularity; unlike most sponsored programs which typically featured music from a dance orchestra, it is credited as the first variety program and the first to utilize scripts and dress rehearsals prior to broadcast. ''The Eveready Hour''s installment on November 4, 1924, was notably interspersed with election returns read by WEAF's Graham McNamee and aired over the WEAF chain until "long after midnight". McNamee already had made another first for the "WEAF chain" one month earlier, calling play-by-play of the 1924 World Series
The 1924 World Series was the World Series, championship series of the 1924 Major League Baseball season. A best-of-seven playoff, the series was played between the American League (AL) pennant winner 1924 Washington Senators season, Washington ...
over an eight-station hookup.
On May 11, 1926, AT&T centralized its radio operations into a new subsidiary known as the Broadcasting Company of America. Although not widely known at the time, this was done in anticipation of selling the radio network, the result of a management decision that the radio operations were incompatible with the company's primary role as the leading U.S. supplier of telephone services.
WJZ chain
The "radio group" quickly recognized the value of network programming, but was badly handicapped in its attempts to effectively compete. AT&T's assertion that only it could sell radio advertising meant that the radio group stations had to be commercial-free, and thus were financed by their owners, which soon became a major drain on company profits. The radio group efforts centered on WJZ, aNewark, New Jersey
Newark ( , ) is the List of municipalities in New Jersey, most populous City (New Jersey), city in the U.S. state of New Jersey, the county seat of Essex County, New Jersey, Essex County, and a principal city of the New York metropolitan area. ...
, station RCA acquired from Westinghouse and moved to New York City on May 14, 1923, the same day WJY launched as a time-share, also owned by RCA and broadcasting from WJZ's Aeolian Hall facilities. RCA then inaugurated WRC in Washington, D.C., as a time-share with WCAP on August 1, 1923; much of RCA's early efforts involved linking WRC and WJZ just as WCAP was already doing for WEAF. However, AT&T generally refused access to its high-quality telephone lines to competitors, so these efforts generally tried to use telegraph lines, which were found to be incapable of good quality audio transmissions. Use of high-powered stations and shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (app ...
connections were also investigated, but none of these approaches matched the reliability and quality of AT&T's telephone links.
The first RCA network broadcast occurred on November 17, 1923, when WJZ rebroadcast play-by-play of a Princeton Tigers–Harvard Crimson
The Harvard Crimson is the nickname of the college sports teams of Harvard College. The school's teams compete in NCAA Division I. As of 2013, there were 42 Division I intercollegiate Varsity team, varsity sports teams for women and men at Harva ...
college football game over GE's WGY in Schenectady, New York
Schenectady ( ) is a City (New York), city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the United States Census 2020, 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-most populo ...
, linked together via the Western Union
The Western Union Company is an American multinational financial services corporation headquartered in Denver, Denver, Colorado.
Founded in 1851 as the New York and Mississippi Valley Printing Telegraph Company in Rochester, New York, the co ...
system. The first attempt at using shortwave for chain broadcasting took place on March 7, 1924, when Westinghouse's KFKX in Hastings, Nebraska
Hastings is a List of cities in Nebraska, city in and the county seat of Adams County, Nebraska, Adams County, Nebraska, United States. The population was 25,152 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List of cities in Neb ...
—constructed as an experimental repeater for KDKA and supplanting KDPM in Cleveland, Ohio
Cleveland is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County, Ohio, Cuyahoga County. Located along the southern shore of Lake Erie, it is situated across the Canada–United States border, Canada–U.S. maritime border ...
—was part of a four-station network involving WJZ, WGY and KDKA, with KGO in San Francisco
San Francisco, officially the City and County of San Francisco, is a commercial, Financial District, San Francisco, financial, and Culture of San Francisco, cultural center of Northern California. With a population of 827,526 residents as of ...
receiving KFKX's signal. While that experimental relay suffered from "barely distinguishable" audio on KGO's end, a second attempt (also including WRC) on November 15, 1924, was judged a transcontinental success as KGO was better able to pick up KFKX. The "WJZ chain" saw little growth compared to AT&T's efforts. President Coolidge's March 1925 inaugural speech was sent over an AT&T transcontinental network of 23 stations, but the WJZ chain's broadcast of the speech was carried by only four stations, all located in the East.
Formation of the National Broadcasting Company
 A few weeks after AT&T consolidated its radio operations into the Broadcasting Company of America subsidiary, it agreed to sell BCA's assets to RCA for approximately $1 million (equivalent to $ in ), a deal made public on July 22, 1926. This sale transferred ownership of WEAF to RCA; included was WEAF's network of 15 stations, plus an agreement by AT&T to make its telephone lines readily available for networking. In a separate deal, WCAP was sold to RCA on July 28, 1926, its broadcast hours ceded to time-share partner WRC three days later. '' Variety'' regarded the sale as an economical one for AT&T, as the WEAF chain generated an annual income of $500,000, with little hope of turning a profit, "which even an affluent corporation like (AT&T) takes into consideration". While the deal was criticized for granting RCA a
A few weeks after AT&T consolidated its radio operations into the Broadcasting Company of America subsidiary, it agreed to sell BCA's assets to RCA for approximately $1 million (equivalent to $ in ), a deal made public on July 22, 1926. This sale transferred ownership of WEAF to RCA; included was WEAF's network of 15 stations, plus an agreement by AT&T to make its telephone lines readily available for networking. In a separate deal, WCAP was sold to RCA on July 28, 1926, its broadcast hours ceded to time-share partner WRC three days later. '' Variety'' regarded the sale as an economical one for AT&T, as the WEAF chain generated an annual income of $500,000, with little hope of turning a profit, "which even an affluent corporation like (AT&T) takes into consideration". While the deal was criticized for granting RCA a monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce ...
on broadcasting, a charge RCA denied, then-Secretary of Commerce
The United States secretary of commerce (SecCom) is the head of the United States Department of Commerce. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to commerce. The secretary rep ...
Herbert Hoover
Herbert Clark Hoover (August 10, 1874 – October 20, 1964) was the 31st president of the United States, serving from 1929 to 1933. A wealthy mining engineer before his presidency, Hoover led the wartime Commission for Relief in Belgium and ...
declined to publicly comment; Chief Radio Supervisor W. D. Terrell stated that neither he or anyone else in the Commerce Department had legal jurisdiction to reject the deal inasmuch as they could not prevent a store from selling bread or meat.
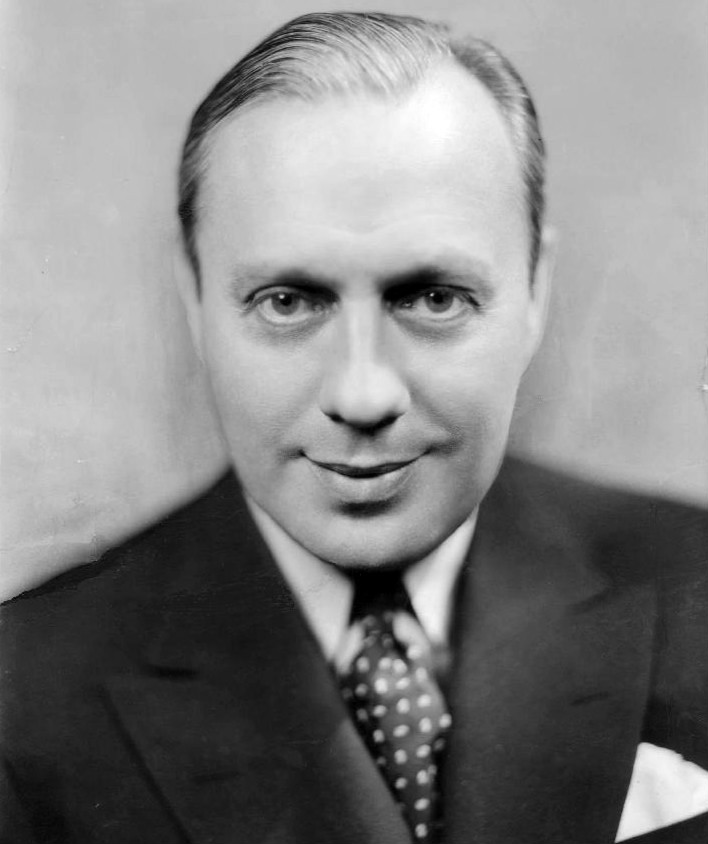
 On September 13, 1926, RCA chairman of the board Owen D. Young and president James G. Harbord announced the formation of the National Broadcasting Company, Inc., to begin operations upon RCA's acquisition of WEAF on November 15. A widely placed full-page company advertisement stated that: "The purpose of the National Broadcasting Company will be to provide the best program available for broadcasting in the United States. ... It is hoped that arrangements may be made so that every event of national importance may be broadcast widely throughout the United States." As part of a renegotiation of the cross-licensing agreements, NBC was also permitted to accept advertising. The purchase of WEAF and NBC's formation was seen as an achievement for RCA's general manager
On September 13, 1926, RCA chairman of the board Owen D. Young and president James G. Harbord announced the formation of the National Broadcasting Company, Inc., to begin operations upon RCA's acquisition of WEAF on November 15. A widely placed full-page company advertisement stated that: "The purpose of the National Broadcasting Company will be to provide the best program available for broadcasting in the United States. ... It is hoped that arrangements may be made so that every event of national importance may be broadcast widely throughout the United States." As part of a renegotiation of the cross-licensing agreements, NBC was also permitted to accept advertising. The purchase of WEAF and NBC's formation was seen as an achievement for RCA's general manager David Sarnoff
David Sarnoff (February 27, 1891 – December 12, 1971) was a Russian and American businessman who played an important role in the American history of radio and television. He led the Radio Corporation of America (RCA) for most of his career in ...
, who was later regarded as the founder of NBC.
NBC's network operations were officially launched with a gala broadcast beginning at 8 p.m. Eastern Time
The Eastern Time Zone (ET) is a time zone encompassing part or all of 23 states in the eastern part of the United States, parts of eastern Canada, and the state of Quintana Roo in Mexico.
* Eastern Standard Time (EST) is five hours behi ...
on November 15, 1926. In anticipation, one newspaper reported: "The most pretentious broadcasting program ever presented, featuring among other stars of the theatrical, concert and radio field, some of whom have never been heard on the air, will mark the introduction of the National Broadcasting company to the radio public Monday evening", with NBC president Merlin H. Aylesworth characterizing the event as "a four-hour program beginning at 8 p.m., which will live long in their memories as an occasion marking another milestone in the history of radio broadcasting". Carl Schlegel of the Metropolitan Opera opened the inaugural broadcast, which also featured Will Rogers
William Penn Adair Rogers (November 4, 1879 – August 15, 1935) was an American vaudeville performer, actor, and humorous social commentator. He was born as a citizen of the Cherokee Nation, in the Indian Territory (now part of Oklahoma ...
and Mary Garden
Mary Garden (20 February 1874 – 3 January 1967) was a Scottish-American operatic lyric soprano, then mezzo-soprano, with a substantial career in France and America in the first third of the 20th century. She spent the latter part of her chil ...
. This broadcast, which included a remote link from KYW in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, was coordinated through WEAF, and carried by twenty-two eastern and Midwestern stations, located as far west as WDAF in Kansas City, Missouri
Kansas City, Missouri, abbreviated KC or KCMO, is the largest city in the U.S. state of Missouri by List of cities in Missouri, population and area. The city lies within Jackson County, Missouri, Jackson, Clay County, Missouri, Clay, and Pl ...
.
Networks
Red and Blue networks
 Following NBC's formation, RCA inaugurated a second network on January 1, 1927; called " the 'blue' network", it was led by WJZ along with Westinghouse's WBZ, KDKA and KYW; with the WEAF-led chain concurrently named "the 'red' network". The debut program, sponsored by the
Following NBC's formation, RCA inaugurated a second network on January 1, 1927; called " the 'blue' network", it was led by WJZ along with Westinghouse's WBZ, KDKA and KYW; with the WEAF-led chain concurrently named "the 'red' network". The debut program, sponsored by the Victor Talking Machine Company
The Victor Talking Machine Company was an American recording company and phonograph manufacturer, incorporated in 1901. Victor was an independent enterprise until 1929 when it was purchased by the Radio Corporation of America (RCA) and became ...
, was carried on both chains and subsequently alternated between "red" and "blue" on a weekly basis.
WEAF historian William Peck Banning suggested the "red" and "blue" names originated from circuit maps drafted in colored pencil
A colored pencil (American English), coloured pencil (Commonwealth English), colour pencil (Indian English), map pencil, pencil crayon, or coloured/colouring lead (Canadian English, Newfoundland English) is a type of pencil constructed of a na ...
by Bell System engineers, which carried over as these circuits began to be used exclusively for radio, thus the former "WEAF chain"—mapped out in red—became "the 'red' network". RCA's ''Radio Age'' magazine outlined a similar reason in 1942, four years before Banning's book was published. Other possible explanations for the names included push-pins engineers used to mark affiliates of WEAF (red pins) and WJZ (blue pins), the colors of wires used for switchboards, or from jack panel connections. The names were not commonplace as newspapers also referred to "NBC-WEAF" or "NBC-WJZ"; NBC made "NBC Red" and "NBC Blue" official network designations by 1936.
Orange Network
As 1927 began, KFI inLos Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, ...
and KPO in San Francisco were successfully transmitting live programming to a regional network of their own, dubbed the " Orange Network", notably originating play-by-play of the 1927 Rose Bowl and a live performance of ''Carmen
''Carmen'' () is an opera in four acts by the French composer Georges Bizet. The libretto was written by Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy, based on the novella of the same title by Prosper Mérimée. The opera was first performed by the O ...
'' from the Philharmonic Auditorium on January 23, 1927; the latter broadcast was additionally relayed over CNVR in Vancouver
Vancouver is a major city in Western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the List of cities in British Columbia, most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the cit ...
, WAMD in Minneapolis
Minneapolis is a city in Hennepin County, Minnesota, United States, and its county seat. With a population of 429,954 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the state's List of cities in Minnesota, most populous city. Locat ...
, and WGY. Affiliating the chain with NBC, the Orange Network relayed an address by President Coolidge that jointly aired over the Red and Blue networks on February 22. The Orange Network formally relaunched as a part of NBC on April 5, 1927, adding KGO and three other stations. NBC eventually utilized the Orange Network to relay Red Network programming to the Pacific states, with the Red Network relaying Orange Network programming for the Eastern Seaboard.
Adding stations and "Radio City"
At the same time, NBC began acquiring radio stations to extend its reach, beginning with KGO and KOA inDenver, Colorado
Denver ( ) is a List of municipalities in Colorado#Consolidated city and county, consolidated city and county, the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of municipalities in Colorado, most populous city of the U.S. state of ...
, from GE in March 1930. Cleveland affiliate WTAM
WTAM (1100 AM broadcasting, AM) is a commercial radio station licensed to Cleveland, Ohio, that airs a news/talk and sports radio format, commonly known as "Newsradio WTAM 1100". Owned by iHeartMedia, WTAM serves Greater Cleveland and much of s ...
, a clear-channel station
A clear-channel station is a North American AM radio station that has the highest level of protection from interference from other stations, particularly from nighttime skywave signals. This classification exists to ensure the viability of cross ...
, was purchased from Cleveland Electric Illuminating and the Van Sweringen brothers on October 16, 1930. Chicago station WENR, time-sharing with WLS, was purchased in July 1931 from Samuel Insull for $1 million (equivalent to $ in ), a purchase price compared to the then-record set with WEAF in 1926. WENR was paired with Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS) affiliate WMAQ when NBC acquired it from the '' Chicago Daily News'' on November 1, 1931; like WTAM, WMAQ and WENR-WLS were also clear-channels. KPO was then purchased from Hale Bros. on June 10, 1932, officially pairing it with KGO. The previous October, KPO became one of the lead stations for the NBC Gold Network, a regional chain of stations that also relayed Blue Network programming. WRC was paired with WMAL in 1933 when NBC took over operations of that station from founding owner M. A. Leese via a lease agreement.
NBC's operations, including WEAF and WJZ, moved to 711 Fifth Avenue in 1927, designed by architect Lloyd Brown. The studios featured elements of Gothic architecture
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved f ...
, the Roman Forum
A forum (Latin: ''forum'', "public place outdoors", : ''fora''; English : either ''fora'' or ''forums'') was a public square in a municipium, or any civitas, of Ancient Rome reserved primarily for the vending of goods; i.e., a marketplace, alon ...
and Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
in stark contrast to radio studios of that era; Raymond Hood
Raymond Mathewson Hood (March 29, 1881 – August 14, 1934) was an American architect who worked in the Gothic Revival architecture, Neo-Gothic and Art Deco styles. He is best known for his designs of the Tribune Tower, American Radiator Building ...
designed the studios under the belief a well-designed studio could act as an audience for the performers. Due to NBC's rapid growth, the network outgrew these facilities. RCA agreed to a lease in May 1930 as the lead tenant for 30 Rockefeller Plaza
30 Rockefeller Plaza (officially the Comcast Building; formerly RCA Building and GE Building) is a skyscraper that forms the centerpiece of Rockefeller Center in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City, New York. Completed in 1933 ...
which was still under construction, including a studio complex for NBC and theaters for RCA-owned RKO Radio Pictures
RKO Radio Pictures Inc., commonly known as RKO Pictures or simply RKO, is an American film production and distribution company, historically one of the "Big Five" film studios of Hollywood's Golden Age. The business was formed after the Kei ...
. Named the RCA Building in May 1932, the deal was arranged through the Rockefeller Center
Rockefeller Center is a complex of 19 commerce, commercial buildings covering between 48th Street (Manhattan), 48th Street and 51st Street (Manhattan), 51st Street in the Midtown Manhattan neighborhood of New York City. The 14 original Art De ...
's founder and financier, John D. Rockefeller Jr., along with GE chairman Owen D. Young, David Sarnoff and Raymond Hood. RCA had been spun off as its own fully-independent company in 1932 through a consent decree
A consent decree is an agreement or settlement that resolves a dispute between two parties without admission of guilt (in a criminal case) or liability (in a civil case). Most often it is such a type of settlement in the United States. The ...
with the U.S. Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of federal laws and the administration of justice. It is equi ...
resolving antitrust
Competition law is the field of law that promotes or seeks to maintain market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies. Competition law is implemented through public and private enforcement. It is also known as antitrust l ...
charges; Westinghouse and GE gave up their ownership stakes in the company, while restrictions created through RCA's cross-licensing agreements for nearly 4,000 patents were also removed. A ceremonial broadcast over both NBC networks on November 11, 1933, formally opened the RCA Building's "Radio City" studios, with Sarnoff, Young, NBC president Merlin H. Aylesworth and BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
Director-General
A director general, general director or director-general (plural: ''directors general'', ''general directors'', ''directors-general'', ''director generals'' or ''director-generals'') is a senior executive officer, often the chief executive officer ...
John Reith participating in a live transatlantic conversation. "Radio City" occupied ten floors of the RCA Building with thirty-five studios supported by of wiring and of cables.
Notable programs
Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology, particularly the ''Works and Days'' of Hesiod, and is part of the description of temporal decline of the state of peoples through five Ages of Man, Ages, Gold being the first and the one during wh ...
", both NBC networks—in particular NBC Red—were home to multiple popular performers and programs. The two networks originally did not have distinct identities or "formats" and, beginning in 1929, shared use of the distinctive three-note " NBC chimes". The WEAF-led Red Network, with a robust affiliate lineup, was seen as carrying more popular, "big budget" sponsored programs in comparison to the WJZ-led Blue Network, which had a smaller lineup of often lower-powered stations. Both networks shared sales executives, off- and on-air staff, and production and studio facilities; it was not until that a concerted effort began to distinguish NBC Red and NBC Blue. One 1939 story in ''Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
'' magazine described NBC Blue as "... long considered a weak sister to NBC's Red Network".
Most network programs were owned by their sponsors and produced by advertising agencies
An advertising agency, often referred to as a creative agency or an ad agency, is a business dedicated to creating, planning, and handling advertising and sometimes other forms of promotion and marketing for its clients. An ad agency is generall ...
. For example, '' Lum and Abner'' was sponsored by Quaker Oats in 1931 when WMAQ originated the show regionally, became a sustaining program
A sustaining program is a radio or television program that, despite airing on a commercial broadcast station, does not have commercial sponsorship or advertising. This term, mostly used in the United States, was common in the early days of radio, b ...
when it debuted over NBC Red in 1932, then sponsored by Ford the following year (originating from WTAM). Moving to the Mutual Broadcasting System
The Mutual Broadcasting System (commonly referred to simply as Mutual; sometimes referred to as MBS, Mutual Radio or the Mutual Radio Network) was an American commercial radio network in operation from 1934 to 1999. In the Golden Age of Radio, ...
in 1934 and to NBC Blue in 1935, Horlicks became the sponsor. NBC Blue sometimes carried newer and untried programs that, if successful, moved "up" to the Red Network at the behest of the sponsor, these shows included ''Amos 'n' Andy
''Amos 'n' Andy'' was an American radio sitcom about black characters, initially set in Chicago then later in the Harlem section of New York City. While the show had a brief life on 1950s television with black actors, the 1928 to 1960 radio sho ...
'', '' Fibber McGee and Molly'',. '' Information, Please!'', ''The Bob Hope
Leslie Townes "Bob" Hope (May 29, 1903 – July 27, 2003) was an American comedian, actor, entertainer and producer with a career that spanned nearly 80 years and achievements in vaudeville, network radio, television, and USO Tours. He appeared ...
Show'' and ''The Jack Benny Program
''The Jack Benny Program'', starring Jack Benny, is a radio and television comedy series. The show ran for over three decades, from 1932 to 1955 on radio, and from 1950 to 1965 on television. It won numerous awards, including the 1959 and 19 ...
''.
 This practice of moving popular shows over to NBC Red, coupled with NBC Blue's reputation as a weaker network, likely originated the misperception that NBC Blue ''solely'' featured sustaining programs (e.g., news, cultural and educational programs which had no sponsor) and NBC Red ''solely'' featured commercial fare. As it was, networks had limited control over their schedules as advertisers bought available time periods for programs, regardless of what other sponsors broadcast in other time slots. Networks rented out studio facilities used to produce shows and sold air-time to sponsors. Sustaining programs were the only programs produced by the networks and were used to fill unsold time periods (affiliated stations had the option to "break away" from the network to air a local program during these periods) but the network had the "option" to take back the time period if a network sponsor wanted the time period. Dramatic programs, which comprised only 2 percent of program time on NBC Red in 1926, accounted for 25 percent of the network's airtime by 1942.
The network provided a rich variety of classical concert broadcasts, including performances by the
This practice of moving popular shows over to NBC Red, coupled with NBC Blue's reputation as a weaker network, likely originated the misperception that NBC Blue ''solely'' featured sustaining programs (e.g., news, cultural and educational programs which had no sponsor) and NBC Red ''solely'' featured commercial fare. As it was, networks had limited control over their schedules as advertisers bought available time periods for programs, regardless of what other sponsors broadcast in other time slots. Networks rented out studio facilities used to produce shows and sold air-time to sponsors. Sustaining programs were the only programs produced by the networks and were used to fill unsold time periods (affiliated stations had the option to "break away" from the network to air a local program during these periods) but the network had the "option" to take back the time period if a network sponsor wanted the time period. Dramatic programs, which comprised only 2 percent of program time on NBC Red in 1926, accounted for 25 percent of the network's airtime by 1942.
The network provided a rich variety of classical concert broadcasts, including performances by the Metropolitan Opera
The Metropolitan Opera is an American opera company based in New York City, currently resident at the Metropolitan Opera House (Lincoln Center), Metropolitan Opera House at Lincoln Center, situated on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. Referred ...
(1931–1940) and the NBC Symphony Orchestra (1937–1954) conducted by Arturo Toscanini
Arturo Toscanini (; ; March 25, 1867January 16, 1957) was an Italian conductor. He was one of the most acclaimed and influential musicians of the late 19th and early 20th century, renowned for his intensity, his perfectionism, his ear for orche ...
. Notable series include the '' General Motors Concerts'' (1929–1937) and ''The Eastman School of Music Symphony'' (1932–1942). From 1935 to 1950, it presented numerous live remote broadcasts of popular music from ballrooms, hotels, supper clubs and Army camps. Among the band leaders with regular time slots on NBC were Carmen Cavallaro
Carmen Cavallaro (May 6, 1913 – October 12, 1989) was an American pianist. He established himself as one of the most accomplished and admired light music pianists of his generation.
Music career
Carmen Cavallaro was born in New York City, Uni ...
, Nat King Cole
Nathaniel Adams Coles (March 17, 1919 – February 15, 1965), known professionally as Nat King Cole, alternatively billed as Nat "King" Cole, was an American singer, jazz pianist, and actor. Cole's career as a jazz and Traditional pop, pop ...
, Xavier Cugat, Tommy Dorsey
Thomas Francis Dorsey Jr. (November 19, 1905 – November 26, 1956) was an American jazz trombone, trombonist, composer, conductor and bandleader of the big band era. He was known as the "Sentimental Gentleman of Swing" because of his smooth-to ...
, Eddy Duchin
Edwin Frank Duchin (April 1, 1909 – February 9, 1951), commonly known as Eddy Duchin or alternatively Eddie Duchin, was an American popular music pianist and bandleader during the 1930s and 1940s.
Early career
Duchin was born on April 1, 1909, ...
, Benny Goodman
Benjamin David Goodman (May 30, 1909 – June 13, 1986) was an American clarinetist and bandleader, known as the "King of Swing". His orchestra did well commercially.
From 1936 until the mid-1940s, Goodman led one of the most popular swing bi ...
, Stan Kenton
Stanley Newcomb Kenton (December 15, 1911 – August 25, 1979) was an American popular music and jazz artist. As a pianist, composer, arranger and band leader, he led an innovative and influential jazz orchestra for almost four decades. Though ...
, Guy Lombardo
Gaetano Alberto "Guy" Lombardo (June 19, 1902 – November 5, 1977) was a Canadian and American bandleader, violinist, and hydroplane racing, hydroplane racer whose unique "sweet jazz" style remained popular with audiences for nearly five decade ...
, Glenn Miller
Alton Glen "Glenn" Miller (March 1, 1904 – December 15, 1944) was an American big band conductor, arranger, composer, trombonist, and recording artist before and during World War II, when he was an officer in the United States Army Air Forces ...
, Leo Reisman, and Paul Whiteman
Paul Samuel Whiteman (March 28, 1890 – December 29, 1967) was an American Jazz bandleader, composer, orchestral director, and violinist.
As the leader of one of the most popular dance bands in the United States during the 1920s and early 193 ...
. NBC's radio news service featured regular broadcasts by journalists and commentators, including Morgan Beatty, Alex Dreier, Pauline Frederick, Floyd Gibbons
Floyd Phillips Gibbons (July 16, 1887 – September 23, 1939) was the war correspondent for the ''Chicago Tribune'' during World War I. One of radio's first news reporters and commentators, he was famous for a fast-talking delivery style. Floyd ...
, John Gunther
John Gunther (August 30, 1901 – May 29, 1970) was an Americans, American journalist and writer.
His success came primarily by a series of popular sociopolitical works, known as the "Inside" books (1936–1972), including the best-sell ...
, Richard Harkness, George Hicks, H. V. Kaltenborn, John MacVane, Adela Rogers St. Johns, Dorothy Thompson
Dorothy Celene Thompson (July 9, 1893 – January 30, 1961) was an American journalist and radio broadcaster. She was the first American journalist to be expelled from Nazi Germany, in 1934, and was one of the few women news commentators broadc ...
, Edward Tomlinson, and Hendrik Willem van Loon.
Affiliates
From the network's formation, NBC was a dominant force on the radio landscape. In 1932, out of the 40 clear-channel stations licensed by theFederal Radio Commission
The Federal Radio Commission (FRC) was a government agency that regulated United States radio communication from its creation in 1927 until 1934, when it was succeeded by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC). The FRC was established by ...
(FRC), 28 were affiliated with either NBC network, 13 were affiliated with CBS, and two were independents. By 1939, the Red and Blue networks were competing with CBS and the Mutual Broadcasting System
The Mutual Broadcasting System (commonly referred to simply as Mutual; sometimes referred to as MBS, Mutual Radio or the Mutual Radio Network) was an American commercial radio network in operation from 1934 to 1999. In the Golden Age of Radio, ...
in providing nationwide coverage. NBC advertising rate cards of the period listed "basic" and "supplemental" affiliated stations. Advertisers were encouraged to buy time for their programs on the full "basic" line-up (plus any "supplemental" stations they wished) but this was open to negotiation. It was not unusual for Red Network advertisers to place shows on Blue Network stations in certain markets (and the other way around). Supplemental stations were generally located in smaller cities away from the network trunk lines. Such stations were usually offered to advertisers on both the Red and Blue Network line-ups.
As of early 1939, the Red Network was divided into five geographical regions. The East consisted of 16 basic and 16 supplemental stations; the Midwest had 8 basic and 15 supplemental stations; the South had 7 basic and 30 supplemental stations; Mountain had 2 basic and 9 supplemental stations, and Pacific had 5 basic and 7 supplemental stations. For example, in Louisville, Kentucky, a larger market, the basic station was WAVE
In physics, mathematics, engineering, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from List of types of equilibrium, equilibrium) of one or more quantities. ''Periodic waves'' oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium ...
, the supplemental was WGRC—also a primary Mutual affiliate.
Separation of NBC Red and NBC Blue
Concerned that NBC's control of two national radio networks gave it too much power over the industry, in May 1941 theFederal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, internet, wi-fi, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains j ...
(FCC) promulgated a rule, the Report on Chain Broadcasting, designed to force NBC to divest one of them. RCA fought the divestiture order, but divided NBC into two companies in case an appeal was lost. The Blue network became the "NBC Blue Network, Inc." and the NBC Red became "NBC Red Network, Inc." Effective January 10, 1942, the two networks had their operations formally divorced, and the Blue Network was referred to on the air as either "Blue" or "Blue Network," with its official corporate name being Blue Network Company, Inc. Consequently, the NBC Red Network became known on-air as simply "NBC" on September 1, 1942.
The FCC order was ultimately upheld by the U.S Supreme Court in '' National Broadcasting Co. v. United States'', asserting that the FCC had authority to regulate the networks and their associations with affiliates. Consequently, the Blue Network was sold on July 30, 1943, to candy magnate Edward J. Noble for $8 million (equivalent to $ in ). When the deal closed on October 12, the Blue Network came under ownership of "American Broadcasting System, Inc." The Blue Network was formally renamed as the American Broadcasting Company
The American Broadcasting Company (ABC) is an American Commercial broadcasting, commercial broadcast Television broadcaster, television and radio Radio network, network that serves as the flagship property of the Disney Entertainment division ...
on June 15, 1945.
After the "Golden Age of Radio"
Development of FM and television
NBC and RCA were one of the key forces in the development of television in the 1930s and 1940s, dating back to New York City experimental station W2XBS in 1928. Before the American entry intoWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
in 1941, W2XBS was officially licensed as WNBT (channel 1). NBC also launched W2XWG, an experimental Apex
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to:
Arts and media Fictional entities
* Apex (comics)
A-Bomb
Abomination
Absorbing Man
Abraxas
Abyss
Abyss is the name of two characters appearing in Ameri ...
station, in April 1939; after planned FM station W51NY failed due to World War II shortages preventing the station's transmitter from being built, NBC converted W2XWG to commercial operation in 1944 as WEAF-FM. In order to further align the network's radio flagship with the network, on November 1, 1946, WEAF and WEAF-FM changed call signs to WNBC and WNBC-FM, respectively. West Coast flagship KPO followed suit, becoming KNBC on November 23, 1947.
Following the lead of WNBT, NBC filed applications for multiple FM and television stations as adjuncts to their radio properties as early as 1943, including for TV outlets in Denver and San Francisco. The network ultimately built and signed on the following TV stations: WNBW in Washington, D.C. (June 27, 1947), WNBK in Cleveland (October 30, 1948), WNBQ in Chicago (January 9, 1949) and KNBH in Los Angeles (January 16, 1949); all five TV stations contained the letter combination "NB" within their call signs. FM stations built and signed on by NBC included: KOA-FM, WRC-FM (June 1947), WMAQ-FM (October 13, 1948), WTAM-FM (December 6, 1948) and KNBR-FM (October 12, 1949). In hopes of buying a Los Angeles radio outlet to complement KNBH, NBC sold KOA and KOA-FM in 1952 to a group that included Bob Hope. While initially only carrying NBC programming, WNBT started adding a slate of local shows and soon featured five hours of local programs during the daytime by May 1950.
The CBS "Paley raids" and television's emergence
For two decades the NBC radio network's roster of stars provided ratings consistently surpassing those of CBS, its main competitor. But in 1948, as the transition from radio to television was beginning, NBC's leadership came under attack due to what became known as the "Paley raids", named after the president of CBS,William S. Paley
William Samuel Paley (September 28, 1901 – October 26, 1990) was an American businessman, primarily involved in the media, and best known as the chief executive who built the Columbia Broadcasting System (CBS) from a small radio network into o ...
. After World War II the tax rate for annual incomes above $70,000 was 77 percent, while capital gains were taxed at 25 percent. Paley worked out an accounting technique whereby individual performers could set up corporations that allowed their earnings to be taxed at the significantly lower rate. Instead of NBC responding with a similar package, RCA's president, David Sarnoff, decided that this accounting method was legally and ethically wrong. NBC's performers did not agree, and most of the top stars, including ''Amos 'n' Andy'', Jack Benny
Jack Benny (born Benjamin Kubelsky; February 14, 1894 – December 26, 1974) was an American entertainer who evolved from a modest success as a violinist on the vaudeville circuit to one of the leading entertainers of the twentieth century with ...
, Red Skelton
Richard Bernard Skelton (July 18, 1913September 17, 1997) was an American entertainer best known for his national old-time radio, radio and television shows between 1937 and 1971, especially as host of the television program ''The Red Skelto ...
, Edgar Bergen
Edgar John Bergen (né Berggren; February 16, 1903 – September 30, 1978) was an American ventriloquist, comedian, actor, vaudevillian and radio performer. He was best known for his characters Charlie McCarthy and Mortimer Snerd. Bergen ...
, Burns and Allen
Burns and Allen were an American comedy duo consisting of George Burns and his wife, Gracie Allen. They worked together as a successful comedy team that entertained vaudeville, film, radio, and television audiences for over forty years.
The ...
, Ed Wynn
Isaiah Edwin Leopold (November 9, 1886 – June 19, 1966), better known as Ed Wynn, was an American actor and comedian. He began his career in vaudeville in 1903 and was known for his ''Perfect Fool'' comedy character, his pioneering radio show ...
, Fred Waring
Fredrick Malcolm Waring Sr. (June 9, 1900 – July 29, 1984) was an American musician, bandleader, choral director, and radio and television personality, sometimes referred to as "America's Singing Master" and "The Man Who Taught America How to ...
, Al Jolson
Al Jolson (born Asa Yoelson, ; May 26, 1886 – October 23, 1950) was a Lithuanian-born American singer, comedian, actor, and vaudevillian.
Self-billed as "The World's Greatest Entertainer," Jolson was one of the United States' most famous and ...
, Groucho Marx
Julius Henry "Groucho" Marx (; October 2, 1890 – August 19, 1977) was an American comedian, actor, writer, and singer who performed in films and vaudeville on television, radio, and the stage. He is considered one of America's greatest comed ...
and Frank Sinatra
Francis Albert Sinatra (; December 12, 1915 – May 14, 1998) was an American singer and actor. Honorific nicknames in popular music, Nicknamed the "Chairman of the Board" and "Ol' Blue Eyes", he is regarded as one of the Time 100: The Most I ...
moved from NBC to CBS. One notable exception was Bob Hope, who not only stayed, but moved to NBC television; by the time of his retirement in 1996, Hope's association with NBC spanned nearly 60 years.
Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
with the Cox and Knight
A knight is a person granted an honorary title of a knighthood by a head of state (including the pope) or representative for service to the monarch, the church, or the country, especially in a military capacity.
The concept of a knighthood ...
newspaper families. WCKT signed on with an NBC-TV affiliation, ostensibly as a reward for Trammell's loyalty. The "Paley raids" had other consequences for RCA itself: Sarnoff and Paley (who also headed up Columbia Records
Columbia Records is an American reco ...
) originally agreed to a new phonograph record
A phonograph record (also known as a gramophone record, especially in British English) or a vinyl record (for later varieties only) is an analog sound storage medium in the form of a flat disc with an inscribed, modulated spiral groove. The g ...
standard of 33 RPM
The LP (from long playing or long play) is an analog sound storage medium, specifically a phonograph record format characterized by: a speed of rpm; a 12- or 10-inch (30- or 25-cm) diameter; use of the "microgroove" groove specificati ...
to replace the long-standing 78 RPM standard. After Jack Benny defected to CBS, Sarnoff rescinded the agreement and began marketing the RCA-developed 45 RPM instead; pressured by record stores and other major labels, RCA eventually agreed to the 33 RPM standard, but the feud risked creating damage to the record industry as a whole.
Many NBC radio stars gravitated to television as it became more popular. Toscanini made ten appearances on NBC-TV simulcast on the radio network between 1948 and 1952. ''Texaco Star Theater
''Texaco Star Theater'' is an American comedy-variety show, broadcast on radio from 1938 to 1949 and telecast from 1948 to 1956. It was one of the first successful examples of American television broadcasting, remembered as the show that gave M ...
'', an umbrella title for various radio variety shows from 1938 to 1949, migrated to NBC-TV in 1948 with Milton Berle as host, becoming both a cultural landmark and the first successful hit program in the medium. In the first of what became several efforts to keep classic radio relevant, NBC sanctioned '' The Big Show'', a 90-minute Sunday night variety program which debuted on November 5, 1950. Hosted by stage actress Tallulah Bankhead
Tallulah Brockman Bankhead (January 31, 1902 – December 12, 1968) was an American actress. Primarily an actress of the stage, Bankhead also appeared in several films including an award-winning performance in Alfred Hitchcock's ''Lifeboat (194 ...
, it harked back to radio's earliest musical variety style along with sophisticated comedy and drama. ''The Big Show'' was also a challenge to CBS's Sunday night lineup, much of which had come from NBC, including—and especially—Jack Benny. Despite critical praise, ''The Big Show''s initial success failed to last as NBC cancelled it after only two years, purportedly losing a million dollars on the project.
To reflect RCA's ownership, some of NBC's radio and television stations adopted "RCA"-derived call signs in October 1954: WNBC/WNBT in New York became WRCA-AM-FM-TV, WNBW in Washington became WRC-TV, and KNBH in Los Angeles became KRCA. By 1960, the New York radio stations reverted to WNBC-AM-FM and WRCA-TV became WNBC-TV. In 1962, KRCA became KNBC, while KNBC-AM-FM in San Francisco became KNBR-AM-FM. WNBQ in Chicago became WMAQ-TV in 1964. NBC also purchased WKNB in New Britain, Connecticut
New Britain is a city in Hartford County, Connecticut, Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. It is located approximately southwest of Hartford, Connecticut, Hartford. The city is part of the Capitol Planning Region, Connecticut, Capitol ...
, in late 1956, and WJAS
WJAS (1320 AM broadcasting, AM) is a commercial radio station in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The station has a talk radio radio format, format. It is owned by St. Barnabas Broadcasting, a division of the Saint Barnabas Health System, with studios a ...
and WJAS-FM in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, second-most populous city in Pennsylvania (after Philadelphia) and the List of Un ...
, in 1957. The acquisition of WJAS was to offset KDKA's defection from the network several years earlier, while WKNB was included as part of the sale of its sister television station. NBC had no interest in owning a daytime-only station in the shadow of its powerful Hartford, Connecticut
Hartford is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. The city, located in Hartford County, Connecticut, Hartford County, had a population of 121,054 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 ce ...
, affiliate, WTIC, so the network sold WKNB in 1960. The Pittsburgh stations were sold in 1972.
1956 trade with Westinghouse
In 1956, NBC sought to get an owned-and-operated television station in the Philadelphia market, so it forced a station ownership/call sign
In broadcasting and radio communications, a call sign (also known as a call name or call letters—and historically as a call signal—or abbreviated as a call) is a unique identifier for a transmitter station. A call sign can be formally as ...
swap with Westinghouse Broadcasting
The Westinghouse Broadcasting Company, also known as Group W, was the broadcasting division of Westinghouse Electric Corporation. It owned several radio and television stations across the United States and distributed television shows for syndi ...
. NBC acquired Westinghouse's KYW radio and WPTZ television in Philadelphia (which became WRCV-AM-TV, for the "RCA Victor" record label) while Westinghouse received NBC's WTAM-AM-FM and WNBK television in Cleveland (all of which took the KYW call signs). Westinghouse also received $3 million in cash compensation.
After Westinghouse expressed its unhappiness with the arrangement, the United States Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a United States federal executive departments, federal executive department of the U.S. government that oversees the domestic enforcement of Law of the Unite ...
took NBC to court in late 1956. In a civil antitrust
Competition law is the field of law that promotes or seeks to maintain market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies. Competition law is implemented through public and private enforcement. It is also known as antitrust l ...
lawsuit filed against NBC and RCA, Westinghouse claimed the network threatened to pull their TV affiliation from Westinghouse's Philadelphia and Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
stations, and withhold an affiliation from their Pittsburgh TV property if Westinghouse did not agree to the trade. In August 1964 NBC's license for WRCV radio and television was renewed by the FCC—but only on the condition that the 1956 station swap be reversed. Following nearly a year of appeals by NBC, the Supreme Court
In most legal jurisdictions, a supreme court, also known as a court of last resort, apex court, high (or final) court of appeal, and court of final appeal, is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
declared the trade null and void in June 1965; the KYW call letters were moved back to Philadelphia with Westinghouse while NBC rechristened the Cleveland stations as WKYC-AM-FM-TV, a derivative of KYW. NBC kept ownership of the Cleveland radio stations until 1972, selling them off to Ohio Communications.
Major League Baseball (1957–1975)
In 1957, NBC Radio won the rights to broadcast theMajor League Baseball All-Star Game
The Major League Baseball All-Star Game, also known as the "Midsummer Classic", is an annual professional baseball game sanctioned by Major League Baseball (MLB) and contested between the all-stars from the American League (AL) and National ...
and World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB). It has been contested since between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winning team, determined through a best- ...
from Mutual, who had held exclusive rights since 1942 and 1939, respectively, for both events. It gave NBC sole control of the big events in baseball as they had been exclusively airing both the All Star Game and World Series on television since 1947. NBC ended its radio association with baseball after the 1975 season in order to clear space for its 24-hour "News And Information" service programming, though it continued broadcasting on its television network until 1989 (while splitting coverage with ABC in all but the first year of that period).
''Monitor''
Monitor
Monitor or monitor may refer to:
Places
* Monitor, Alberta
* Monitor, Indiana, town in the United States
* Monitor, Kentucky
* Monitor, Oregon, unincorporated community in the United States
* Monitor, Washington
* Monitor, Logan County, Wes ...
'', a continuous, all-weekend programming umbrella featuring a mix of music, news, interviews and features that debuted on June 12, 1955. ''Monitor'' boasted a variety of hosts including such well-known television personalities as Dave Garroway, Hugh Downs, Ed McMahon
Edward Leo Peter McMahon Jr. (March 6, 1923 – June 23, 2009) was an American announcer, game show host, comedian, actor, singer, and combat aviator. McMahon and Johnny Carson began their association in their first TV series, the American Bro ...
, Joe Garagiola
Joseph Henry Garagiola Sr. (February 12, 1926 – March 23, 2016) was an American professional baseball catcher, and later a radio and television personality with a varied career.
He played nine seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB) for the ...
and Gene Rayburn
Gene Rayburn (born Eugene Peter Jeljenic; December 22, 1917 – November 29, 1999) was an American radio and television personality. He is best known as the host of various editions of the American television game show ''Match Game'' for over tw ...
. The potpourri also tried to keep vintage radio alive in featuring segments from Jim and Marian Jordan (in character as Fibber McGee and Molly), '' Ethel and Albert'' and iconoclastic satirist Henry Morgan
Sir Henry Morgan (; – 25 August 1688) was a Welsh privateer, plantation owner, and, later, the lieutenant governor of Jamaica. From his base in Port Royal, Jamaica, he and those under his command raided settlements and shipping ports o ...
.
''Monitor'' is credited for succeeding in an era where television became the dominant entertainment medium, but after the mid-1960s, local stations with established music formats—especially in larger markets—became increasingly reluctant to run network fare, dropping the program block outright, including flagship WNBC. In turn, the number of sponsors for ''Monitor'' began to decline precipitously. ''Monitor''s final broadcast took place over the weekend of January 25–26, 1975. From that point onward, the NBC Radio Network's main lineup consisted of hourly newscasts and commentary segments, plus religious programs and ''Meet the Press
''Meet the Press'' is a weekly American television Sunday morning talk show broadcast on NBC. It is the List of longest-running television shows by category, longest-running program on American television, though its format has changed since th ...
'' on Sundays.
Other programming ventures
''Monitor'' was succeeded with another major programming investment: the NBC News and Information Service (NIS). Conceived by NBC Radio president Jack G. Thayer as a secondary network for local stations wishing to adopt anall-news radio
All-news radio is a radio format devoted entirely to the discussion and broadcast of news.
All-news radio is available in both local and radio syndication, syndicated forms, and is carried on both major US satellite radio networks. All-news sta ...
format, NIS supplied up to 55 minutes of news content per hour to stations. Thayer described NIS as "an over-all restyling" of NBC Radio providing "a more contemporary feel". While the main NBC Radio Network had been losing money in recent years, Thayer stressed NIS was not to replace it, nor was the main network threatened with closure. NBC assigned NIS to all but one of their FM stations—WNWS in New York (the former WNBC-FM), WNIS in Chicago (the former WJOI) and KNAI in San Francisco (the former KNBR-FM); WRC in Washington also became an affiliate, while WKYS (the former WRC-FM) assumed WRC's existing Top 40
In the music industry, the Top 40 is a list of the 40 currently most popular songs in a particular genre. It is the best-selling or most frequently broadcast popular music. Record charts have traditionally consisted of a total of 40 songs. "To ...
format."NBC news radio goes to O&Os in major cities"''Broadcasting'', April 21, 1975, pp. 46–47. Other major affiliates included WBAL-FM in
Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, KHVH in Honolulu
Honolulu ( ; ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, located in the Pacific Ocean. It is the county seat of the Consolidated city-county, consolidated City and County of Honol ...
, KQV in Pittsburgh and KRUX in Glendale–Phoenix.
At the end of 1975, NIS had 57 affiliates, significantly less than the 227 stations which carried either part or all of ''Monitor'' when it ceased; additionally, the NBC-owned NIS affiliates all failed to make a profit in 1975, but the network hoped for them to break even in the coming year. As 1976 progressed, however, only 62 affiliates remained with NIS after 18 months, some of which were competing against long-established news-focused stations. Assuming over $10 million (equivalent to $ in ) in losses, Thayer announced the closure of NIS in November 1976 in six months, allowing for affiliates to find alternate programming. While some former NIS affiliates—including WRC and KQV—remained with all-news formats, the NBC-owned FM stations all adopted music formats.
 In 1979, NBC launched The Source, a secondary network that targeted younger listeners, providing news, short features and music specials to FM rock stations. The Source also featured a talk show hosted by sex columnist
In 1979, NBC launched The Source, a secondary network that targeted younger listeners, providing news, short features and music specials to FM rock stations. The Source also featured a talk show hosted by sex columnist Ruth Westheimer
Karola Ruth Westheimer (née Siegel; June 4, 1928 – July 12, 2024), better known as Dr. Ruth, was a German and American sex therapist and talk show host.
Westheimer was born in Germany to a Jewish family. As the Nazis came to power, her paren ...
beginning in 1984, which originated at NBC's New York FM station WYNY. NBC Radio's last major programming venture occurred with the November 2, 1981, debut of NBC Talknet, a talk radio
Talk radio is a radio format containing discussion about topical issues and consisting entirely or almost entirely of original spoken word content rather than outside music. They may feature monologues, dialogues between the hosts, Interview (jo ...
program block for the late-evening hours. Headlined by advice host Sally Jessy Raphael
Sally Lowenthal (born February 25, 1935), better known as Sally Jessy Raphael, is an American retired talk show host, who is best known for her program '' Sally'' (originally called ''The Sally Jessy Raphael Show'').
Early life and education
Lo ...
and personal finance talker Bruce Williams, NBC Talknet was largely inspired by the success of the all-night ''Larry King Show
''The Larry King Show'' was an American overnight radio talk show hosted by Larry King. It was broadcast nationally over the Mutual Broadcasting System from January 1978 to May 1994. A typical program consisted of King interviewing a guest, the ...
'' on Mutual. When Williams was critically injured in a 1982 airplane crash, he resumed his NBC Talknet show four weeks later, conducting it from his hospital room. Williams' show proved to be very successful and ultimately outlived NBC Talknet itself.
NBC Radio Entertainment was established in December 1984 to handle the distribution of ''Jazz with David Sanborn
David William Sanborn (July 30, 1945 – May 12, 2024) was an American alto saxophonist. He worked in many musical genres; his solo recordings typically blended jazz with instrumental pop and R&B. He began playing the saxophone at the age o ...
'' and ''Live From the Hard Rock Cafe
Hard Rock Cafe, Inc. is a chain of theme restaurant, theme bar-restaurants, memorabilia shops, casinos, hotels and museums founded in 1971 by Isaac Tigrett and Peter Morton in London. In 1979, the cafe began covering its walls with rock and roll ...
'' with Paul Shaffer
Paul Allen Wood Shaffer (born November 28, 1949) is a Canadian musician, actor, and comedian who served as David Letterman's musical director, bandleader, and sidekick on ''Late Night with David Letterman'' (1982–1993) and ''Late Show with D ...
, along with an oldies
Oldies is a term for musical genres such as pop music, rock and roll, doo-wop, surf music from the second half of the 20th century, specifically from around the mid-1950s to the 1980s, as well as for a radio format playing this music.
Since 2 ...
show hosted by WNBC's Soupy Sales. NBC Radio also acquired the national play-by-play rights for NFL games for both the 1985
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a n ...
and 1986 seasons, outbidding long-standing rights holder CBS Radio.
Divestiture
 NBC made its final radio station acquisition in 1983 when it bought Boston station WJIB from GE, which was divesting its radio properties. In February 1984, the network sold WRC in Washington to
NBC made its final radio station acquisition in 1983 when it bought Boston station WJIB from GE, which was divesting its radio properties. In February 1984, the network sold WRC in Washington to Greater Media
Greater Media, Inc., known as Greater Media, was an American media company that specialized in radio stations. The markets where they owned radio stations included Boston, Detroit, Philadelphia, Charlotte, and the state of New Jersey. The comp ...
for $3.6 million (equivalent to $ in ).
On December 11, 1985, GE announced it was acquiring RCA in a $6.28 billion deal (equivalent to $ in ). Earlier in the year, RCA entertained merger talks with Universal Pictures
Universal City Studios LLC, doing business as Universal Pictures (also known as Universal Studios or simply Universal), is an American filmmaking, film production and film distribution, distribution company headquartered at the 10 Universal Ci ...
parent MCA Inc. while fending off hostile takeover
In business, a takeover is the purchase of one company (law), company (the ''target'') by another (the ''acquirer'' or ''bidder''). In the UK, the term refers to the acquisition of a public company whose shares are publicly listed, in contrast t ...
threats. GE requested in paperwork filed with the FCC that NBC's grandfathered status permitting radio-TV combinations in three markets be broken up within 18 months, retaining the five NBC-owned television stations and GE's KCNC-TV. A planned sale of the entire radio unit to Westinghouse Broadcasting at the end of 1986 collapsed, prompting Westwood One, a Culver City, California
Culver City is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 40,779. It is mostly surrounded by Los Angeles, but also shares a border with the unincorporated area of Ladera Heights, Californi ...
–based syndicator that acquired Mutual in 1985, to purchase the NBC Radio Network, The Source, NBC Talknet and NBC Radio Entertainment, along with leases to the radio network facilities at 1700 Broadway, for $50 million (equivalent to $ in ). As part of the deal, a long-term brand licensing
Brand licensing means renting or leasing of an intangible asset. It is a process of creating and managing contracts between the owner of a brand and a company or individual who wants to use the brand in association with a product, for an agreed ...
deal for the "NBC Radio" name was agreed to, while NBC Radio employees, including in the news division, were transferred to Westwood One. The remaining divisions and assets of RCA, including RCA Records
RCA Records is an American record label owned by Sony Music Entertainment, a subsidiary of Sony Group Corporation. It is one of Sony Music's four flagship labels, alongside Columbia Records (its former longtime rival), Arista Records and Epic R ...
were spun off to various companies, including Bertelsmann
The Bertelsmann SE & Co. KGaA, commonly known as Bertelsmann (), is a German privately held company, private multinational corporation, multinational conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation based in Gütersloh, North Rhine-Westphalia, ...
and Thomson SA
Vantiva SA (formerly Technicolor SA, Thomson SARL, Thomson SA, and Thomson Multimedia) is a French multinational corporation that provides technology products and services for the communication, media and entertainment industries. Headquarter ...
.
The seven NBC-owned radio stations, which initially agreed to remain with NBC Radio as affiliates, were all put up for sale and divested to various buyers between 1988 and 1989, including Emmis Communications
Emmis Corporation is an American media conglomerate based in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States. Emmis, based on the Hebrew word for "Truth" (''Emet'') was founded by Jeff Smulyan in 1980. Emmis has owned many radio stations, including KPWR ...
, Westinghouse and Susquehanna Radio Corporation. WNBC was included in Emmis's multi-station purchase; as Emmis already owned WFAN in New York City, it sold that station's license and transferred the intellectual property onto the WNBC license, supplanting it outright (WNBC was thus regarded in media coverage as "ceasing operation"). The last station to be sold, KNBR, was delayed due to a long-term play-by-play contract with the San Francisco Giants
The San Francisco Giants are an American professional baseball team based in San Francisco. The Giants compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (baseball), National League (NL) National League West, West Div ...
that ran through the 1989 season.
NBC Radio after 1987
Dissolution into Westwood One
 Following the sale, NBC Radio added one long-form program to their lineup—a daily talk/variety show hosted by
Following the sale, NBC Radio added one long-form program to their lineup—a daily talk/variety show hosted by Steve Allen
Stephen Valentine Patrick William Allen (December 26, 1921 – October 30, 2000) was an American television and radio personality, comedian, musician, composer, writer, and actor. In 1954, he achieved national fame as the co-creator and ...
based from WNEW that debuted in October 1987. Westwood One initially promoted the show as part of the new "Mutual P.M." program service, but it was moved to being under the NBC umbrella prior to launch. Failing to get enough affiliates for the program, Allen ended the show the following March. The Sunday morning religious program ''The Eternal Light
''The Eternal Light'' was an American radio and television program on the NBC Radio Network, produced in conjunction with the Jewish Theological Seminary of America, Jewish Theological Seminary, that was broadcast between 1944 and 1989. Featuring ...
'', for years the networks' only non-news program, ended its 45 year run on NBC Radio in 1989. Another NBC–branded program introduced following the Westwood One purchase was the morning newsmagazine '' First Light'', hosted by Dirk Van, which debuted in April 1990. ''First Light'' was complimentary to Mutual's existing morning newsmagazine, '' America in The Morning'' hosted by Jim Bohannon.
Within a year of Westwood One's takeover, several tenured NBC Radio News staffers resigned, including London bureau chief Fred Kennedy, who told ''Broadcasting'' magazine, "what was once a great network and broadcast news operation is becoming an audio wire service... and not even a good audio wire service." Some affiliates also expressed concern over a decline in technical and editorial quality, even as NBC Radio successfully added 90 affiliates since the sale. Norm Pattiz, Westwood One founder/CEO, defended the consolidation moves by noting the radio networks had been losing up to $10 million, but emphasized "we are not dismantling the NBC networks". By January 1989, Westwood One announced NBC Radio News would move to Mutual's Arlington, Virginia
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
, facility; engineering operations followed along with the affiliate relations department.
The Source, which had been reworked into both supplying short-form features and production elements for radio stations in 1988, moved their operations to Los Angeles by 1990. Mutual and NBC newscasts were further streamlined in 1992 with jointly-produced newscasts in overnights and weekends and both networks airing unbranded sportscasts through the weekend. NBC Talknet's operations also moved to the Arlington facilities in 1992 and largely continued until 1993, when it was limited solely to Bruce Williams' weeknight show—ceding the other three-hour slot to Jim Bohannon's Mutual talk show—and was eventually rebranded as a Westwood One program.
Infinity Broadcasting
Infinity Broadcasting Corporation was a radio company that existed from 1972 until 2005. It was founded by Michael A. Wiener and Gerald Carrus. It became associated with popular radio personalities like Howard Stern, Opie and Anthony, Don Im ...
took over operations of Westwood One in 1994 after it sold to them competing syndicator Unistar Radio Networks; as part of the deal, Infinity purchased 25 percent of Westwood One, becoming its largest shareholder. Westinghouse Broadcasting's parent Westinghouse Electric Corporation—which bought out CBS and renamed itself CBS Corporation
CBS Corporation was an American multinational media company with interests primarily in commercial broadcasting, publishing and television production. It was split from Viacom on December 31, 2005, alongside an entirely new Viacom; both ...
the following year—acquired Infinity for just shy of $5 billion in June 1996 (equivalent to $ in ). An agreement was then reached for Westwood One to manage the CBS Radio Network, merging the descendants of the three original U.S. radio networks: NBC, CBS and Mutual. Another realignment in the fall of 1997 had the "NBC Radio Network" name revived, but as an internal brand name for Westwood One affiliates that had adult contemporary and country formats; The Source was also reworked into a brand name for affiliates with formats that targeted 18–34 males.
On August 31, 1998, the combined Mutual/NBC newsroom in Arlington closed, with "Mutual" and "NBC" newscasts originating from CBS Radio News in New York. Westwood One then announced the full retirement of the Mutual name and ending of newscast production on April 17, 1999, with "NBC"–branded newscasts produced by CBS restricted to morning drive ( ET) on weekdays. This curtailing was made as affiliates largely aired "NBC" newscasts in the morning hours. Remaining NBC affiliates were offered CNN Radio
Cable News Network (CNN) is a multinational news organization operating, most notably, a website and a TV channel headquartered in Atlanta. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news ...
newscasts at all other times; CNN Radio was also offered as a replacement for former Mutual affiliates. The change notably forced WHIZ in Zanesville, Ohio
Zanesville is a city in Muskingum County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. Located at the confluence of the Licking River (Ohio), Licking and Muskingum River, Muskingum rivers, the city is approximately east of Columbus, Ohio, Columb ...
, an NBC affiliate since 1939, to switch to ABC News.
With only a very small number of affiliates that remained, an end date for production of "NBC"–branded newscasts cannot be determined, but Westwood One continued to promote the "NBC Radio Network" on their corporate website as late as 2004. While his show had been rebranded under his name, Bruce Williams left Westwood One in June 2001, effectively ending the NBC Talknet service. In 1999, the last remaining program from the original NBC Radio Network, ''First Light'', was changed to a Westwood One branded program and continued production until July 31, 2022.
NBC News Radio
The "NBC" name re-emerged on radio with NBC News Radio on March 31, 2003, featuring NBC andMSNBC
MSNBC is an American cable news channel owned by the NBCUniversal News Group division of NBCUniversal, a subsidiary of Comcast. Launched on July 15, 1996, and headquartered at 30 Rockefeller Plaza in Manhattan, the channel primarily broadcasts r ...
anchors and reporters, but limited to one-minute newscasts on weekdays; Westwood One made the new service available to all radio stations the syndicator was affiliated with. Westwood One also began distributing an audio simulcast of ''Meet the Press'' to radio stations in 2004, a practice which continues to this day.
Westwood One was spun off by majority owner CBS Corporation
CBS Corporation was an American multinational media company with interests primarily in commercial broadcasting, publishing and television production. It was split from Viacom on December 31, 2005, alongside an entirely new Viacom; both ...
(one of two successors to the first Viacom, which acquired the first CBS Corporation in 1999) to The Gores Group
The Gores Group, LLC is a private equity firm specializing in acquiring and partnering with mature and growing businesses. The company was founded in 1987 by its CEO and chairman, Alec Gores, Alec E. Gores.
Headquartered in Beverly Hills, Califor ...
in 2007. On October 21, 2011, Dial Global—a subsidiary of Oaktree Capital Management's Triton Media Group—acquired the majority of Westwood One's assets, including the distribution rights to NBC News Radio; this resulted in a wholesale re-branding of Westwood One programming. Dial Global announced on March 2, 2012, that it would end distribution of CNN Radio newscasts and make NBC News Radio a full-time operation, with a majority of CNN affiliates switching to NBC. The new format consisted of twice-hourly newscasts. By September 2012, NBC Sports Radio was launched as a joint venture between NBC Sports
NBC Sports is an American programming division for NBCUniversal, a division of Comcast, that is responsible for sports broadcasts on their broadcast network NBC, the Cable television, cable channels NBC owns, and on Peacock (streaming service) ...
and Dial Global.
With Cumulus Media acquiring Dial Global and amid plans to merge it into its own radio network, Dial Global reverted to using the Westwood One name in September 2013. On December 15, 2014, concurrent with the launch of Westwood One News, a white-label news service established with a content-sharing deal with CNN, Westwood One ended production of NBC News Radio newscasts. Failing to sign up enough major-market affiliates, Westwood One ended 24/7 programming on NBC Sports Radio at the end of 2018, and shut down operations outright in March 2020.
Beginning in July 2016, NBC Universal licensed the name "NBC News Radio" to iHeartMedia
iHeartMedia, Inc., or CC Media Holdings, Inc., is an American mass media corporation headquartered in San Antonio, Texas. It is the holding company of iHeartCommunications, Inc., formerly Clear Channel Communications, Inc., a company founded by ...
, utilizing talent and reporters from iHeartMedia's existing 24/7 News Network, made available to the group's approximately 850 radio stations. The reintroduced service included an hourly newscast along with ancillary specials and longform breaking news coverage., July 11, 2016 (allaccess.com)
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *External links
at the Digital Deli {{American broadcast radio Westwood One Defunct radio networks in the United States Radio stations established in 1926 Radio stations disestablished in 1999 1926 establishments in New York (state) 1999 disestablishments in New York (state)