The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place between the 13th and the 18th centuries, establishing the
Indo-Muslim period
The Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent or Indo-Muslim period is conventionally said to have started in 712, after the conquest of Sindh and Multan by the Umayyad Caliphate under the military command of Muhammad ibn al-Qasim. It began in t ...
.
Earlier Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent include the invasions which started in the
northwestern Indian subcontinent
Northwest India is a loosely defined region of India. In modern-day, it consists of north-western states of the Republic of India. In historical contexts, it refers to the northwestern Indian subcontinent.
In contemporary definition, it gene ...
(modern-day
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
), especially the
Umayyad campaigns during the 8th century.
Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 ŌĆō 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
, sultan of the
Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''─Āaznaviy─ün'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus ...
, preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566ŌĆō653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
and invaded vast parts of
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panj─üb or Panj-─Ćb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
and
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
during the 11th century. After the capture of
Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the
Ghurid
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; ; self-designation: , ''┼Āansab─ün─½'') was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Tajik people, Tajik origin, which ruled from the 8th-century in the region of Ghor, and became an Emp ...
ruler
Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of
Muslim rule in India
The Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent or Indo-Muslim period is conventionally said to have started in 712, after the conquest of Sindh and Multan by the Umayyad Caliphate under the military command of Muhammad ibn al-Qasim. It began in ...
in 1192. In 1202,
Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiy─ür al-D─½n MußĖźammad Bin Bakhtiy─ür Khalj─½, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan Military General of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor, who led the Muslim conquests of the eastern Indian regions of Bengal and parts of Bi ...
led the Muslim conquest of
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
, marking the easternmost expansion of Islam at the time.
The Ghurid Empire soon evolved into the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. in 1206, ruled by
Qutb ud-Din Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak (; 1150 ŌĆō 4 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid emperor Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in 1206, he established his own ...
, the founder of the
Mamluk dynasty. With the Delhi Sultanate established,
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
was spread across most parts of the Indian subcontinent. In the 14th century, the
Khalji dynasty
The Khalji or Khilji dynasty was a Turco-Afghan dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate for three decades between 1290 and 1320. It was the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate which covered large swaths of the Indian subcontinent. under
Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
, extended Muslim rule southwards to
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
,
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
, and the
Deccan
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound by the mount ...
. The successor
Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
temporarily expanded its territorial reach to
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
. The disintegration of the Delhi Sultanate, capped by Timur's invasion in 1398, caused several Muslim sultanates and dynasties to emerge across the Indian subcontinent, such as the
Gujarat Sultanate
The Gujarat Sultanate or Sultanate of Gujarat was a late medieval Islamic Indian kingdom in Western India, primarily in the present-day state of Gujarat. The kingdom was established in 1394 when Muzaffar Shah I, the Governor of Gujarat, decla ...
,
Malwa Sultanate
The Malwa Sultanate was a late medieval kingdom in the Malwa, Malwa region, covering the present day Indian states of Madhya Pradesh and south-eastern Rajasthan from 1401 to 1562. It was founded by Dilawar Khan, who following Timur's invasion ...
,
Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellio ...
,
Jaunpur Sultanate
The Jaunpur Sultanate () was a late medieval Indian Muslim state which ruled over much of what is now the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh and Bihar and southern Nepal between 1394 and 1494. It was founded in 1394 by Khwajah-i-Jahan Malik Sarwar ...
,
Madurai Sultanate
Ma'bar Sultanate, also known as the Madurai Sultanate, was a short lived kingdom based in the city of Madurai in Tamil Nadu, India. It was dominated by Hindustani speaking Muslims. The sultanate was proclaimed in 1335 CE in Madurai led by Jala ...
, and the
Bengal Sultanate
The Bengal Sultanate (Middle Bengali: , Classical Persian: ) was a Post-classical history, late medieval sultanate based in the Bengal region in the eastern South Asia between the 14th and 16th century. It was the dominant power of the Ganges- ...
. Some of these, however, were followed by
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as San─ütan─½s) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym San─ütana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also be ...
reconquests and resistance from the native powers and states, such as the Telugu Nayakas,
Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara () is a city located in Vijayanagara district of Karnataka state in India.[Vijayanagara](_blank) , and
Rajput states
During the medieval and later feudal/ colonial periods, many parts of the Indian subcontinent were ruled as sovereign or princely states by various dynasties of Rajputs.
The Rajputs rose to political prominence after the large empires of anc ...
under the
Kingdom of Mewar
The Kingdom of Mewar was an independent Hindu kingdom that existed in the Rajputana region of the Indian subcontinent and later became a dominant state in medieval India. The kingdom was initially founded and ruled by the Guhila dynasty, foll ...
.
The Delhi Sultanate was replaced by the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
in 1526, which was one of the three
gunpowder empires
The gunpowder empires, or Islamic gunpowder empires, is a collective term coined by Marshall G. S. Hodgson and William H. McNeill at the University of Chicago, referring to three early modern Muslim empires: the Ottoman Empire, Safavid Empire a ...
. Emperor
Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, ŌĆō ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include a large portion of the subcontinent. Under Akbar, who stressed the importance of religious tolerance and winning over the goodwill of the subjects, a multicultural empire came into being with various non-Muslim subjects being actively integrated into the Mughal Empire's bureaucracy and military machinery. The economic and territorial zenith of the Mughals was reached at the end of the 17th century, when under the reign of emperor
Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 ŌĆō 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
the empire witnessed the full establishment of Islamic
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
through the
Fatawa al-Alamgir.
The Mughals went into a sudden decline immediately after achieving their peak following the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, due to a lack of competent and effective rulers among Aurangzeb's successors. Other factors included the expensive and bloody
Mughal-Rajput Wars and the
MughalŌĆōMaratha Wars
The Deccan wars were a series of military conflicts between the Mughal Empire and the descendants of the Maratha Empire, Maratha ruler Shivaji from the time of Shivaji's death in 1680 until the death of Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. Shivaji was ...
. The
Afsharid
The Guarded Domains of Iran, commonly referred to as Afsharid Iran or the Afsharid Empire, was an Iranian empire established by the Turkoman Afshar tribe in Iran's north-eastern province of Khorasan, establishing the Afsharid dynasty that wo ...
ruler
Nader Shah's invasion in 1739 was an unexpected attack which demonstrated the weakness of the Mughal Empire.
This provided opportunities for various regional states such as
Rajput states
During the medieval and later feudal/ colonial periods, many parts of the Indian subcontinent were ruled as sovereign or princely states by various dynasties of Rajputs.
The Rajputs rose to political prominence after the large empires of anc ...
,
Mysore Kingdom
The Kingdom of Mysore was a geopolitical realm in South India, southern India founded in around 1399 in the vicinity of the modern-day city of Mysore and prevailed until 1950. The territorial boundaries and the form of government transmuted su ...
,
Sind State
The Thatta Sarkar (1593ŌĆō1629), Thatta Subah (1629ŌĆō1737) or Sind State (1737ŌĆō1843), also referred to as Scinde or Sindh, was a Mughal Sarkar later a Subah, then a proto-state, and lastly a princely state in the Sindh region of the India ...
,
Nawabs of Bengal and Murshidabad
The Nawab of Bengal (, ) was the hereditary ruler of Bengal Subah in Mughal India. In the early 18th-century, the Nawab of Bengal was the ''de facto'' independent ruler of the three regions of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa which constitute the mod ...
,
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
,
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
, and
Nizams of Hyderabad
Nizam of Hyderabad was the title of the ruler of Hyderabad State ( part of the Indian state of Telangana, and the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka). ''Nizam'' is a shortened form of (; ), and was the title bestowed upon Asaf Jah I ...
to declare their independence and exercising control over large regions of the Indian subcontinent further accelerating the geopolitical disintegration of the Indian subcontinent.
The Maratha Empire replaced Mughals as the dominant power of the subcontinent from 1720 to 1818. The Muslim conquests in Indian subcontinent came to a halt after the
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey was a decisive victory of the British East India Company, under the leadership of Robert Clive, over the Nawab of Bengal and his French Indies Company, French allies on 23 June 1757. The victory was made possible by the de ...
(1757), the
Battle of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought between 22 and 23 October 1764, between the forces of the British East India Company, under the command of Major Hector Munro, against the combined armies of Balwant Singh, Maharaja of the Benaras State; Mir Qa ...
(1764),
Anglo-Mysore Wars (1767ŌĆō1799),
Anglo-Maratha Wars Anglo-Maratha Wars may refer to:
* First Anglo-Maratha War (1775ŌĆō1782)
* Second Anglo-Maratha War
Second Anglo-Maratha War (from 1803 ŌĆō1805) was a large conflict within the Maratha Confederacy, Maratha Empire involving the British East In ...
(1775ŌĆō1818),
Anglo-Sind War (1843) and
Anglo-Sikh Wars Anglo-Sikh War may refer to:
* First Anglo-Sikh war, 1845ŌĆō1846
* Second Anglo-Sikh war
The Second Anglo-Sikh War was a military conflict between the Sikh Empire and the East India Company which took place from 1848 to 1849. It resulted i ...
(1845ŌĆō1848) as the British
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
seized control of much of the Indian subcontinent up till 1857. Throughout the 18th century, European powers continued to exert a large amount of political influence over the Indian subcontinent, and by the end of the 19th century most of the Indian subcontinent came under
European colonial domination, most notably the
British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
until 1947.
First phase (8th to 10th centuries)
Early Muslim presence
The first ever recorded incursion by Arabs in India occurred around 636/7 AD, during the
Rashidun Caliphate
The Rashidun Caliphate () is a title given for the reigns of first caliphs (lit.ŌĆē"successors") ŌĆö Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali collectively ŌĆö believed to Political aspects of Islam, represent the perfect Islam and governance who led the ...
, long before any Arab army reached the frontier of India by land.
Uthman ibn Abi al-As al-Thaqafi
Uthman ibn Abi al-As al-Thaqafi (; died 671 or 675) was a companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad from the tribe of Banu Thaqif and the governor of Bahrayn (eastern Arabia) and Oman (southeastern Arabia) in 636ŌĆō650, during the reigns of calip ...
, the governor of Bahrain and Oman, had dispatched naval expeditions against the
Sasanian
The Sasanian Empire (), officially Eranshahr ( , "Empire of the Iranians"), was an Iranian empire that was founded and ruled by the House of Sasan from 224 to 651. Enduring for over four centuries, the length of the Sasanian dynasty's reign ...
coast, and further east to the borders of India, as confirmed by the contemporary Armenian historian,
Sebeos
Sebeos () was the reputed author of a 7th-century Armenian history. As this authorship attribution is widely accepted to be false (pseudepigraphical), the author is frequently referred to as Pseudo-Sebeos. Though his name is not known, he was likel ...
. Uthman, on his own initiative and without the sanction of Caliph
Umar
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Mu ...
, according to the history of
al-Baladhuri
╩ŠAßĖźmad ibn YaßĖźy─ü ibn J─übir al-Bal─üdhur─½ () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al ...
, had also launched two naval raids against ports of the Indian subcontinent, the first of these raids targeted
Thane
Thane (; previously known as Thana, List of renamed Indian cities and states#Maharashtra, the official name until 1996) is a metropolitan city located on the northwestern side of the list of Indian states, state of Maharashtra in India and on ...
(a small town near
Mumbai
Mumbai ( ; ), also known as Bombay ( ; its official name until 1995), is the capital city of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Mumbai is the financial capital and the most populous city proper of India with an estimated population of 12 ...
) and
Bharuch
Bharuch () is a city at the mouth of the river Narmada in Gujarat in western India. Bharuch is the administrative headquarters of Bharuch District.
The city of Bharuch and surroundings have been settled since times of antiquity. It was a shi ...
(a city in
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
). The second raid targeted
Debal
Debal (also called Daybul, Daibul or D─ōwal) was a commercial town and an ancient port in Sindh, now a province of Pakistan.
The exact location of the town has been difficult to determine. The proposed identifications with Karachi, Thatta, and ...
(a town near
Karachi
Karachi is the capital city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Sindh, Pakistan. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, largest city in Pakistan and 12th List of largest cities, largest in the world, with a popul ...
).
The assault on Thane, the first recorded Arab raid on India, was commanded by Uthman's brother al-Hakam, who also led the raid on Bharuch. The following raid on Debal was commanded by another brother, al-Mughira. The raids were probably launched in according to al-Baladhuri. These expeditions were not sanctioned by Caliph
Umar
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Mu ...
and Uthman escaped punishment only because there weren't any casualties.
[: "'Uthm├ón ibn-abu-l-'├é╚Öi ath-Tha─Ęafi ... sent his brother, al-Hakam, to al-Bahrain, and went himself to 'Um├ón, and sent an army across to T├ónah. When the army returned, he wrote to 'Umar, informing him of this expedition and its result. 'Umar wrote to him in reply, ' ... By Allah, I swear that if they had been smitten, I would exact from thy tribe the equivalent.' Al-Hakam sent an expedition against Barwa╚Ö ]roach
Roach or The Roach may refer to:
Animals
* Cockroach, various insect species of the order Blattodea
* Common roach (''Rutilus rutilus''), a fresh and brackish water fish of the family Cyprinidae
** ''Rutilus'' or roaches, a genus of fishes
* Cal ...
also, and sent his brother, al-Mughîrah ibn-abu-l-'Âsi, to the gulf of ad-Daibul, where he met the enemy in battle and won a victory."
The raids on Thane and Bharuch may have been successful as the Arabs had lost no men during these raids, but
al-Baladhuri
╩ŠAßĖźmad ibn YaßĖźy─ü ibn J─übir al-Bal─üdhur─½ () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al ...
does not specifically state these raids as successful,(), so some scholars are of the opinion that the Arabs raids may have been failures.
and forced the Arabs to retreat.
The raid on Debal may have occurred in 643 AD and faced success,
but it is unlikely as Umar was still the Caliph and Uthman was unlikely to disobey his directive on sea raids, and the source reporting this is deemed unreliable.
The motivation for these expeditions may have been to seek plunder or to attack pirates to safeguard Arabian trade in the
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
, not to start the conquest of India.
Shortly after the
Muslim conquest of Persia
As part of the early Muslim conquests, which were initiated by Muhammad in 622, the Rashidun Caliphate conquered the Sasanian Empire between 632 and 654. This event led to the decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been the official religion of ...
, the connection between the Sindh and
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
was established by the initial Muslim missions during the Rashidun Caliphate.
Rashidun Caliphate and the frontier kingdoms
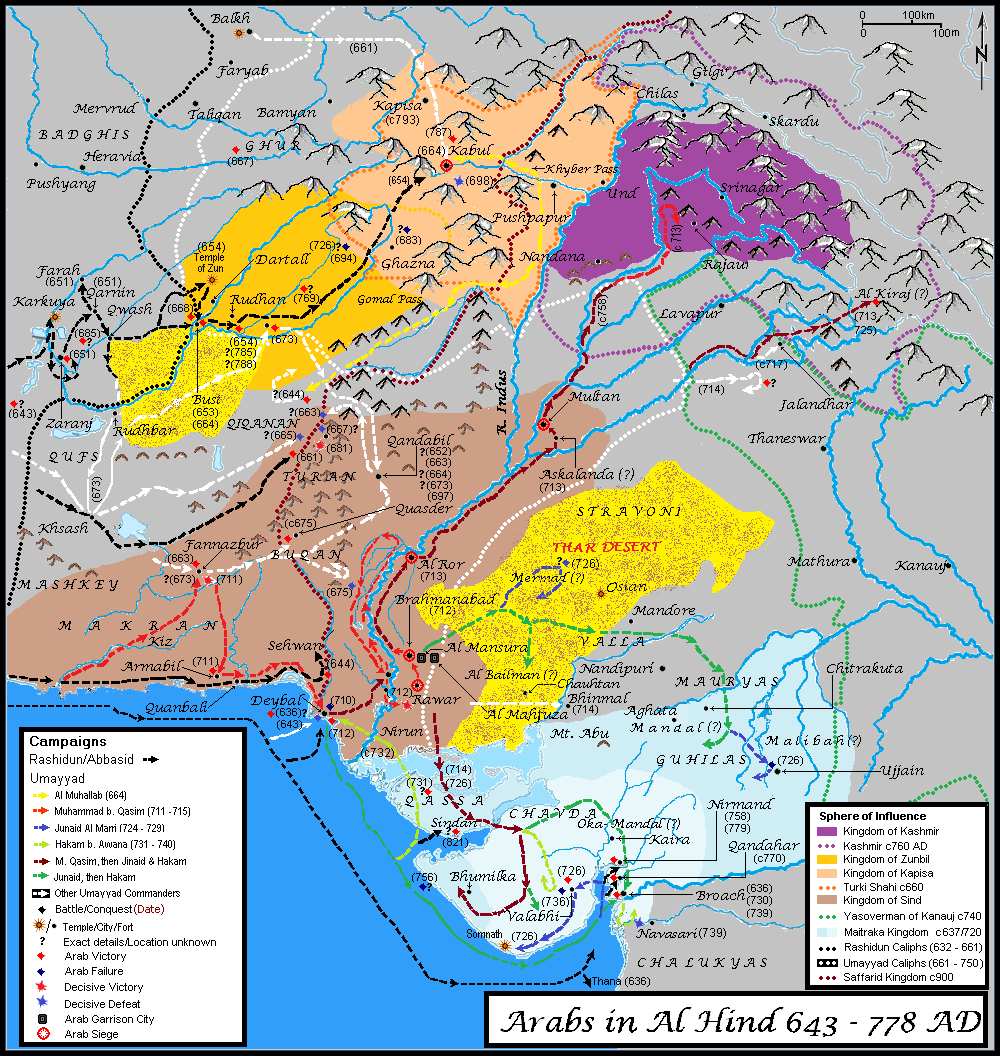
The kingdoms of
Kapisa-
Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
in modern-day Afghanistan,
Zabulistan
Zabulistan (, ''Z─übolist─ün'', ''Z─üwulist─ün'' or simply ), is an ancient and medieval name for a historical region that included mainly southeastern region ( Zabol) of Iran and some parts of what is now southern Afghanistan.
By the tenth ce ...
, and
Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
(which then held Makran) in modern-day Pakistan, all of which were culturally part of Indian subcontinent since ancient times, were known as "The Frontier of Al Hind" to the Arabs. Makran had been conquered by
Chach of Aror
Chach ( 631ŌĆō671 AD, ) was a Hindu Brahmin king of Sindh region of the Indian subcontinent in the mid-7th century AD. He was in service of the court of Rai Sahasi II and became a close confidate of the king and the queen. When Rai Sahasi died, ...
in 631 AD, but ten years later, it was described as "under the government of Persia" by
Xuanzang
Xuanzang (; ; 6 April 6025 February 664), born Chen Hui or Chen Yi (), also known by his Sanskrit Dharma name Mokß╣Żadeva, was a 7th-century Chinese Bhikkhu, Buddhist monk, scholar, traveller, and translator. He is known for the epoch-making ...
, who had visited the region in 641.
The first clash between a ruler of an Indian kingdom and the Arabs took place in 643, when Arab forces defeated Rutbil, the King of Zabulistan in
Sistan
Sist─ün (), also known as Sakast─ün (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspond ...
. Arabs led by Suhail b. Abdi later defeated a Sindhi army in the
Battle of Rasil
The Battle of Rasil () was fought between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Rai kingdom ruled by Raja Rasil in early 644. It was the first encounter of the Rashidun Caliphate in the Indian subcontinent. The exact location of the battle is not kn ...
in 644 on the Indian Ocean coast, then reached the
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
.
Caliph
Umar
Umar ibn al-Khattab (; ), also spelled Omar, was the second Rashidun caliph, ruling from August 634 until his assassination in 644. He succeeded Abu Bakr () and is regarded as a senior companion and father-in-law of the Islamic prophet Mu ...
ibn Al-Khattab denied Suhail permission to carry on across the river.
Al-Hakim ibn Jabalah al-Abdi, who attacked
Makran
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokr─ün'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. I ...
in the year 649 AD, was an early partisan of
Ali
Ali ibn Abi Talib (; ) was the fourth Rashidun caliph who ruled from until his assassination in 661, as well as the first Shia Imam. He was the cousin and son-in-law of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. Born to Abu Talib ibn Abd al-Muttalib an ...
ibn Abu Talib.
Abdullah ibn Aamir
Ab┼½ ╩┐Abd al-RaßĖźm─ün ╩┐Abd All─üh ibn ╩┐─Ćmir ibn Kurayz `Abd Allah ibn `Amir (; 626ŌĆō678) was a Rashidun Caliphate politician and general. He served as the Governor of Basra from 647 to 656 AD, during the reign of Rashidun Caliph Uthman ibn ...
led the invasion of Khurasan in 650 AD, and his general Rabi b. Ziyad Al Harithi attacked Sistan and took
Zaranj
Zaranj ( Persian/Pashto/) is a city in southwestern Afghanistan, which has a population of 160,902 people as of 2015. It is the capital of Nimruz Province and is linked by highways with Lashkargah and Kandahar to the east, Farah to the north an ...
and surrounding areas in 651 while
Ahnaf ibn Qais
Abu Bahr Al-Ahnaf ibn Qays () was a Muslim commander who lived during the time of Islamic prophet Muhammad. He hailed from the Arab tribe of Banu Tamim and was born of noble parents. Initially, his father named him ad-Dhahhak, but people called h ...
conquered the
Hepthalites
The Hephthalites (), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit and Prakrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during the 5th to 8th centuries CE, ...
of
Herat
Her─üt (; Dari/Pashto: ┘ćž▒ž¦ž¬) is an oasis city and the third-largest city in Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Se ...
and advanced up to
Balkh
Balkh is a town in the Balkh Province of Afghanistan. It is located approximately to the northwest of the provincial capital city Mazar-i-Sharif and approximately to the south of the Amu Darya and the AfghanistanŌĆōUzbekistan border. In 2021 ...
by 653. Arab conquests now bordered the Kingdoms of Kapisa, Zabul and Sindh in modern-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. The Arabs levied annual tributes on the newly captured areas, and after leaving 4,000 men garrisons at
Merv
Merv (, ', ; ), also known as the Merve Oasis, was a major Iranian peoples, Iranian city in Central Asia, on the historical Silk Road, near today's Mary, Turkmenistan. Human settlements on the site of Merv existed from the 3rd millennium& ...
and Zaranj, retired to
Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to IraqŌĆōSaudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to IraqŌĆōTurkey border, the north, Iran to IranŌĆōIraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
instead of pushing on against the frontier of India. Caliph Uthman b. Affan sanctioned an attack against Makran in 652, and sent a recon mission to Sindh in 653. The mission described Makran as inhospitable, and Caliph Uthman, probably assuming the country beyond the Indus was much worse, forbade any further incursions into Indian subcontinent. During the caliphate of Ali, many Hindus of Sindh had come under the influence of
Shi'ism
Shia Islam is the second-largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political Succession to Muhammad, successor (caliph) and as the spiritual le ...
and some even participated in the
Battle of Camel
The Battle of the Camel, also known as The Battle of Basra () took place outside of Basra, Iraq, in 36 AH (656 CE). The battle was fought between the army of the fourth caliph Ali (), on one side, and the rebel army led by Aisha, Talha and ...
and died fighting for Ali.
Under the Umayyads (661ŌĆō750 AD), many Shias sought
asylum
Asylum may refer to:
Types of asylum
* Asylum (antiquity), places of refuge in ancient Greece and Rome
* Benevolent asylum, a 19th-century Australian institution for housing the destitute
* Cities of Refuge, places of refuge in ancient Judea
* ...
in the region of Sindh, to live in relative peace in the remote area. Ziyad Hindi was one of those refugees.
Umayyad expansion in Al Hind
Mu'awiya I
Mu'awiya I (ŌĆōApril 680) was the founder and first caliph of the Umayyad Caliphate, ruling from 661 until his death. He became caliph less than thirty years after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and immediately after the four Rashid ...
established the
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate or Umayyad Empire (, ; ) was the second caliphate established after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty. Uthman ibn Affan, the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a membe ...
rule over the Arabs after the
First Fitna
The First Fitna () was the first civil war in the Islamic community. It led to the overthrow of the Rashidun and the establishment of the Umayyad Caliphate. The civil war involved three main battles between the fourth Rashidun caliph, Ali, an ...
in 661 AD, and resumed expansion of the Muslim empire.
Al-Baladuri
╩ŠAßĖźmad ibn YaßĖźy─ü ibn J─übir al-Bal─üdhur─½ () was a 9th-century West Asian historian. One of the eminent Middle Eastern historians of his age, he spent most of his life in Baghdad and enjoyed great influence at the court of the caliph al-M ...
wrote that, "In the year 44 H. (664 A.D.), and in the days of the Khalif Mu'awiya, Muhallib son of Abu Safra made war upon the same frontier, and advanced as far as Banna and Alahwar , which lie between
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
and
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
."
After 663-665 CE, the Arabs launched an invasion against Kapisa, Zabul and what is now Pakistani
Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; , ), also spelled as Baluchistan or Baluchestan, is a historical region in West and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. This arid region o ...
. Abdur Rahman b. Samurra besieged Kabul in 663 AD, while Haris b Marrah advanced against Kalat after marching through Fannazabur and Quandabil and moving through the
Bolan Pass
Bolan Pass () is a valley and a natural gateway through the Toba Kakar range in Balochistan province of Pakistan. It is situated south of Pakistan's border with Afghanistan. The pass is an stretch of the Bolan River valley from Rindli in the ...
King Chach of Sindh sent an army against the Arabs, the Arabs were trapped when the enemy blocked the mountain passes, Haris was killed and his army was annihilated.Al-Muhallab ibn Abi Sufra
Abū Saʿīd al-Muhallab ibn Abī Ṣufra al-Azdī (; 702) was an Arab general from the Azd tribe who fought in the service of the Rashidun, Umayyad and Zubayrid caliphs between the mid-640s and his death. He served successive terms as the go ...
took a detachment through the Khyber pass towards Multan in Southern
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panj─üb or Panj-─Ćb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
in modern-day Pakistan in 664 AD, then pushed south into Kikan, and may have also raided Quandabil. Turki Shah and Zunbil expelled Arabs from their respective kingdoms by 670, and Zunbil began assisting in organizing resistance against the Arabs in Makran.
This was the beginning of a prolonged struggle between the rulers of Kabul and Zabul in modern-day and Pakistan against successive Arab governors of Sistan, Khurasan and Makran. The
Kabul Shahi Kabul Shahi is a term used to denote two former non-Muslim dynasties based on Kabul:
* Turk Shahis (665ŌĆō850 CE)
* Hindu Shahi (850ŌĆō1026 CE)
{{disambig ...
kings and their
Zunbil
Zunbil, also written as Zhunbil, or Rutbils of Zabulistan, was a royal dynasty south of the Hindu Kush in present southern Afghanistan region. They were a dynasty of Hephthalite origin. They ruled from circa 680 AD until the Saffarid conquest in ...
kinsmen successfully blocked access to the
Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass (Urdu: ž»ž▒█é ž«█īž©ž▒; ) is a mountain pass in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, on the border with the Nangarhar Province of Afghanistan. It connects the town of Landi Kotal to the Valley of Peshawar at Jamrud by tr ...
and
Gomal Pass
Gomal Pass () is a mountain pass on the Durand Line border between Afghanistan and the southeastern portion of South Waziristan in Pakistan's Federally Administered Tribal Areas. It takes its name from the Gomal River and is midway between the ...
routes into India from 653 to 870 AD, while modern Balochistan, Pakistan, comprising the areas of Kikan or Qiqanan, Nukan, Turan, Buqan, Qufs, Mashkey and Makran, would face several Arab expeditions between 661 and 711 AD. The Arabs launched several raids against these frontier lands, but repeated rebellions in Sistan and Khurasan between 653 and 691 AD diverted much of their military resources in order to subdue these breakaway provinces and away from expansion into Al Hind. Muslim control of these areas ebbed and flowed repeatedly as a result until 870 AD. Arab troops disliked being stationed in Makran. Fierce resistance stalled Arab progress repeatedly in the "frontier zone".
and the Arabs had to focus on tribute extraction instead of systematic conquest as a result.
Battles in Makran and Zabulistan
Arabs launched several campaigns in eastern Balochistan between 661 and 681 AD. Four Arab commanders were killed during these campaigns, however, Sinan b. Salma managed to conquer parts of Makran including the Chagai area, and established a permanent base of operations by 673 AD.
Rashid b. Amr, the next governor of Makran, subdued Mashkey in 672 CE. Munzir b. Jarood Al Abadi managed to garrison Kikan and conquer Buqan by 681 CE, while Ibn Harri Al Bahili conducted several campaigns to secure the Arab hold on Kikan, Makran and Buqan by 683 AD. Zunbil saw off Arab campaigns in 668, 672 and 673 by paying tribute. Although Arabs occupied the areas south of Helmand in 673 permanently
Zunbil defeated Yazid b. Salm's army in 681 AD at Junzah, and Arabs had to pay 500,000 dirhams as ransom to get free their prisoners.
Al Hajjaj and the East
Al-Hajjaj ibn Yusuf Al Thaqifi, who had played a crucial role during the
Second Fitna
The Second Fitna was a period of general political and military disorder and civil war in the Islamic community during the early Umayyad Caliphate. It followed the death of the first Umayyad caliph Mu'awiya I in 680, and lasted for about twelve y ...
for the Umayyad cause, was appointed the governor of Iraq in 694 AD. Hajjaj received governorship of
Khurasan
KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarn├óma-e N├ósir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavv├ór: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235ŌĆō236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...
and
Sistan
Sist─ün (), also known as Sakast─ün (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspond ...
in 697 and he sponsored Muslim expansions in
Makran
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokr─ün'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. I ...
, Sistan,
Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (, now called the Amu Darya) is the Latin name for the region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
and Sindh.
Campaigns in Makran and Zabul
The Arab's hold on Makran weakened when Arab rebels seized the province, and Hajjaj had to send expeditions under three governors between 694 and 707 AD before Makran was partially recovered by 694 AD. Al Hajjaj also fought against Zunbil in 698 and 700 AD. The 20,000 strong army led by Ubaidullah ibn Abu Bakra was trapped by the armies of Zunbil and Turki Shah near Kabul in 698 AD, and lost 15,000 men to thirst and hunger, earning this force the title of the "Doomed Army".
Abd al-Rahman ibn Muhammad ibn al-Ash'ath next led 20,000 troops each from
Kufa
Kufa ( ), also spelled Kufah, is a city in Iraq, about south of Baghdad, and northeast of Najaf. It is located on the banks of the Euphrates, Euphrates River. The estimated population in 2003 was 110,000.
Along with Samarra, Karbala, Kadhimiya ...
and
Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the IranŌĆōIraq bor ...
(dubbed the "Peacock Army" due to the splendor of their equipment and the participation of numerous members of Arab nobility).
His methodical 699 AD campaign made gains, but he was contemptuously rebuked by Hajjaj at every step.
When Ibn al-Ash'ath paused his operation to consolidate, Hajjaj insulted him and ordered an immediate advance. This unreasonable demand led to mutiny.
The mutiny was put down by 704 AD, and Al-Hajjaj granted a 7-year truce to Zunbil.
Umayyad expansion in Sind and Multan

''
Meds'' pirates operated from their bases at
Kutch,
Debal
Debal (also called Daybul, Daibul or D─ōwal) was a commercial town and an ancient port in Sindh, now a province of Pakistan.
The exact location of the town has been difficult to determine. The proposed identifications with Karachi, Thatta, and ...
and
Kathiawar
Kathiawar (), also known as Saurashtra, is a peninsula in the south-western Gujarat state in India, bordering the Arabian Sea and covering about . It is bounded by the Kutch district in the north, the Gulf of Kutch in the northwest, and by the ...
and during one of their raids had kidnapped Muslim women travelling from
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
to
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, thus providing the ''
casus belli
A (; ) is an act or an event that either provokes or is used to justify a war. A ''casus belli'' involves direct offenses or threats against the nation declaring the war, whereas a ' involves offenses or threats against its allyŌĆöusually one bou ...
''
against Sindh
Raja Dahir
Raja Dahir (663 ŌĆō 712 CE) was the last Hindu ruler of Sindh (in present-day Pakistan). A Brahmin ruler, his kingdom was invaded in 711 CE by the Arab Umayyad Caliphate, led by Muhammad bin Qasim, where Dahir died. According to the Chach Nama, ...
.
Raja Dahir of Sindh had previously refused to return Arab rebels from Sindh and furthermore, he now expressed his inability to punish the pirates. Hajjaj sent two expeditions to Sindh, both of which were defeated. Al Hajjaj next equipped an army built around 6,000 Syrian
cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
and detachments of ''
mawali
''Mawl─ü'' (, plural ''maw─ül─½'' ), is a polysemous Arabic word, whose meaning varied in different periods and contexts.A.J. Wensinck, Encyclopedia of Islam 2nd ed, Brill. "Mawl─ü", vol. 6, p. 874.
Before the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the te ...
'' from Iraq, six thousand
camel riders, and a baggage train of 3,000 camels under his Nephew
Muhammad bin Qasim
MußĖźammad ibn al-Q─üsim al-Thaqaf─½ (; ŌĆō) was an Arabs, Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (and Punjab, part of ancient Sindh), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His m ...
to Sindh. His artillery of five
catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants ŌĆō particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
s were sent to Debal by sea
("manjaniks").
Conquest of Sindh
Muhammad bin Qasim departed from
Shiraz
Shiraz (; ) is the List of largest cities of Iran, fifth-most-populous city of Iran and the capital of Fars province, which has been historically known as Pars (Sasanian province), Pars () and Persis. As of the 2016 national census, the popu ...
in 710 AD, the army marched along the coast to Tiaz in Makran, where the army of Makran joined him, and the combined force moved to the Kech valley. Muhammad subdued the restive towns of Fannazbur and Armabil, finally completing the conquest of Makran. Then the army met up with the reinforcements and catapults sent by sea near Debal and took Debal through assault.
From Debal, the Arabs moved towards north along the Indus, clearing the region up to Budha. Some towns like Nerun and Sadusan (
Sehwan
Sehwan (; ; also commonly referred to as Sehwan Sharif or ''Noble Sehwan'') is a historic city located in Jamshoro District of Sindh province in Pakistan situated on the west bank of the Indus River north-west of Hyderabad. The city is renowned ...
) surrendered peacefully. Muhammad bin Qasim moved back to Nerun to resupply and receive reinforcements sent by Hajjaj. The Arabs crossed the Indus further South and defeated the army of Dahir, who was killed.
Brahmanabad
Mansura (; ), referred to as Brahmanabad or Bahmanabad (, ) in later centuries, was the historic capital of the caliphal province of Sindh, during the eighth century under the Umayyad Caliphate and then Abbasid Caliphate from the year 750 AD to ...
, then Alor (
Aror
Aror (or Alor or Arorkot) is the medieval name of the city of Rohri in Sindh, modern Pakistan. Aror once served as the capital of Sindh.
History
As Roruka, capital of the Sauvira Kingdom, it is mentioned as an important trading center in e ...
) and finally
Multan
Multan is the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, fifth-most populous city in the Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab province of Pakistan. Located along the eastern bank of the Chenab River, it is the List of cities in Pakistan by populatio ...
, were captured alongside other in-between towns with only light Muslim casualties. Arabs marched up to the foothills of Kashmir along the Jhelum in 713 AD, and stormed the Al-Kiraj (possibly the Kangra valley).
Muhammad was deposed after the death of Caliph Walid in 715 . Jai Singh, son of Dahir captured Brahmanabad and Arab rule was restricted to the Western shore of the Indus. Sindh was briefly lost to the caliph when the rebel Yazid b. Muhallab took over Sindh in 720.
Last Umayyad campaigns in Al Hind

Junaid b. Abd Al Rahman Al Marri became the governor of Sindh in 723 AD. He conquered Debal, defeated and killed Jai Singh, secured Sindh and Southern Punjab and then stormed Al Kiraj (Kangra valley) in 724 AD. Junaid next attacked a number of
Hindu king
In Hinduism, kingship was a monarchy institution guided by the religious laws of Hinduism, with corresponding complex and hierarchical structure. Hindu monarchies headed by Hindu kings were widespread in South Asia since about 1500 BC and later i ...
doms in what is now Rajasthan, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh aiming at permanent conquest,
but the chronology and area of operation of the campaigns during 725ŌĆō743 is difficult to follow because accurate, complete information is lacking. The Arabs moved east from Sindh in several detachments
and probably attacked from both the land and the sea, occupying ''Mirmad'' (Marumada, in
Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed ''The Golden city'', is a city in the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur, in the heart of the Thar Desert. It serves as the administrative headquarters of Jaisalmer district ...
), ''Al-Mandal'' (perhaps Okhamandal in Gujarat) or Marwar, and raiding ''Dahnaj'', not identified, ''al-Baylaman'' (
Bhilmal) and ''Jurz'' (Gurjara countryŌĆönorth Gujarat and southern Rajasthan), and attacking ''Barwas'' (
Broach
Broach may refer to:
* Broaching (metalworking), a machining operation that uses a metalworking tool with a series of chisel points mounted on one piece of steel
* Broach (nautical), a sudden loss of control of a vessel caused either by wind actio ...
).
Gurjara king Siluka repelled Arabs from "Stravani and Valla", probably the area North of Jaisalmer and
Jodhpur
Jodhpur () is the second-largest city of the north-western Indian state of Rajasthan, after its capital Jaipur. As of 2023, the city has a population of 1.83 million. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Jodhpur district and ...
, and the invasion of Malwa but were ultimately defeated by
Bappa Rawal
Bappa Rawal (c. 8th century) was a king of the Mewar kingdom in Rajasthan, India. The chronicles consider him to be the founder of the Guhila Rajput dynasty. He is credited with repelling the Arab invasion of India. He is identified as the r ...
and
Nagabhata I
Nagabhata I (r. c. 730 ŌĆō 760 CE) was the founder of the imperial Pratihara dynasty in northern India. He ruled the Avanti (or Malava) region in present-day Madhya Pradesh, from his capital at Ujjain. He may have extended his control over ...
in 725 AD near Ujjain. Arabs lost control over the newly conquered territories and part of Sindh due to Arab tribal infighting and Arab soldiers deserting the newly conquered territory in 731 AD.
Al Hakam b. Awana Al Kalbi founded the garrison city of Al Mahfuza on the eastern side of a lake near Brahmanabad.
Hakam next attempted to reclaim the conquests of Junaid in Al Hind. Arab records merely state that he was successful, Indian records at Navasari details that Arab forces defeated "Kacchella, Saindhava, Saurashtra, Cavotaka, Maurya and Gurjara" kings. The city of
Al Mansura was founded near Al Mahfuza by Amr b. Muhammad.
Al Hakam next invaded the Deccan in 739 with the intention of permanent conquest, but was decisively defeated at
Navsari
Navsari is the ninth biggest city in the state of Gujarat in India. It is the administrative headquarters of Navsari District. Navsari is between Surat and Mumbai. It is a twin city of Surat, 37 km to the north. At the 2011 Census of Ind ...
by the viceroy
Avanijanashraya Pulakeshin
The Chalukyas (IAST: C─ülukya) of Navasarika (modern Navsari) were an Indian dynasty that ruled parts of present-day Gujarat and Maharashtra during 7th and 8th centuries, as vassals of the Chalukyas of Vatapi. They are also known as the "Ear ...
of the
Chalukya Empire
The Chalukya dynasty () was a Classical Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynas ...
serving
Vikramaditya II
Vikramaditya II (reigned 733 ŌĆō 744 CE) was the son of King Vijayaditya and ascended the Badami Chalukya throne following the death of his father. This information comes from the Lakshmeshwar inscriptions in Kannada dated 13 January 735 A. ...
. Arab rule was restricted to the west of Thar desert.
Last days of Abbasid Caliphate control
When the
Abbasid Revolution overthrew the Umayyads in 750 AD after the
Third Fitna
The Third Fitna (), was a series of civil wars and uprisings against the Umayyad Caliphate. It began with a revolt against Caliph al-Walid II in 744, and lasted until 747, when Marwan II emerged as the victor. The war exacerbated internal tensi ...
, Sindh became independent and was captured by Musa b. K'ab al Tamimi in 752 AD. Zunbil had defeated the Arabs in 728 AD, and saw off two Abbasid invasions in 769 and 785.
Abbasids
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566ŌĆō653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes i ...
attacked Kabul several times and collected tribute between 787 and 815 AD and extracted tribute after each campaign. Abbasid's Governor of Sindh, Hisham (in office 768ŌĆō773) raided Kashmir, recaptured parts of Punjab from
Karkota
The Karkota dynasty (c. 625 ŌłÆ 855 CE) ruled over the Kashmir valley and some northern parts of the Indian subcontinent during 7th and 8th centuries. Their rule saw a period of political expansion, economic prosperity and emergence of Kashmir ...
control, and launched naval raids against ports of Gujarat. These raids like other Abbasid Naval raids launched in 776 and 779 AD, gained no territory. Arabs occupied Sindian (Southern Kutch) in 810, only to lose it in 841.
Civil war erupted in Sindh in 842 AD, and the Habbari dynasty occupied Mansurah, and by 871, five independent principalities had emerged, with the Banu Habbari clan controlling in Mansurah, Banu Munabbih occupying Multan, Banu Madan ruling in Makran, and Makshey and Turan falling to other rulers, all outside direct Caliphate control.
Ismaili
Ismailism () is a branch of Shia Islam. The Isma'ili () get their name from their acceptance of Imam Isma'il ibn Jafar as the appointed spiritual successor ( im─üm) to Ja'far al-Sadiq, wherein they differ from the Twelver Shia, who accept ...
missionaries found a receptive audience among both the
Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
and non-Muslim populations in Multan, which became a center of the Ismaili sect of Islam. The
Saffarid
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conque ...
Dynasty of Zaranj occupied Kabul and the kingdom of Zunbil permanently in 871 AD. A new chapter of Muslim conquests began when the
Samanid Dynasty
The Samanid Empire () was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, ruled by a dynasty of Iranian ''dehqan'' origin. The empire was centred in Khorasan and Transoxiana, at its greatest extent encompassing northeastern Iran and Central Asia, from 819 t ...
took over the Saffarid Kingdom and
Sabuktigin
Abu Mansur Nasir ad-Din wa'd-Dawla Sabuktigin (; 940s ŌĆō August-September 997) was the founder of the Ghaznavid dynasty, and amir of Ghazna from 977 to 997. Sabuktigin was a Turkic slave who was bought by Alp-Tegin, the commander of the r ...
seized
Ghazni
Ghazni (, ), historically known as Ghaznayn () or Ghazna (), also transliterated as Ghuznee, and anciently known as Alexandria in Opiana (), is a city in southeastern Afghanistan with a population of around 190,000 people. The city is strategica ...
.
Later Muslim invasions
After the
Decline of the Caliphate, Muslim incursions resumed under the later Turkic and Central Asian dynasties like the
Saffarid dynasty
The Saffarid dynasty () was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1002. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emerge after the Islamic conqu ...
and the
Samanid Dynasty
The Samanid Empire () was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, ruled by a dynasty of Iranian ''dehqan'' origin. The empire was centred in Khorasan and Transoxiana, at its greatest extent encompassing northeastern Iran and Central Asia, from 819 t ...
with more local capitals. They supplanted the
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate or Abbasid Empire (; ) was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566ŌĆō653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes ...
and expanded their domains both northwards and eastwards. Continuous raids from these empires in the north-west of India led to the loss of stability in the Indian kingdoms.
After three centuries of unremitting effort, Arab dominion in India was limited to two states of Multan and Mansurah
Second phase (11th to 12th centuries)
Ghaznavid Sultanate
Under
Sabuktigin
Abu Mansur Nasir ad-Din wa'd-Dawla Sabuktigin (; 940s ŌĆō August-September 997) was the founder of the Ghaznavid dynasty, and amir of Ghazna from 977 to 997. Sabuktigin was a Turkic slave who was bought by Alp-Tegin, the commander of the r ...
, the
Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''─Āaznaviy─ün'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus ...
found itself in conflict with the
Kabul Shahi Kabul Shahi is a term used to denote two former non-Muslim dynasties based on Kabul:
* Turk Shahis (665ŌĆō850 CE)
* Hindu Shahi (850ŌĆō1026 CE)
{{disambig ...
Raja
Jayapala
Jayapala was a ruler of the Hindu Shahi dynasty from 964 to 1001 CE. He ruled over the area which stretched from Laghman in the west, to Kashmir in the east and from Sirhind to Multan. He was the son of Hutpal and the father of Anandapala. ...
in the east. When Sabuktigin died and his son Mahmud ascended the throne in 998 AD, Ghazni was engaged in the North with the
Qarakhanids when the Shahi Raja renewed hostilities in east once again.
In the early 11th century,
Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 ŌĆō 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
launched seventeen expeditions into Indian subcontinent. In 1001, Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni defeated Raja Jayapala of the
Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis, also referred to as the Kabul Shahis and UßĖŹi ┼Ü─ühis, were a dynasty established between 843 CE and 1026 CE. They endured multiple waves of conquests for nearly two centuries and their core territory was described as having c ...
Dynasty of
Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
(in modern Afghanistan), in the
Battle of Peshawar and marched further towards the west of
Peshawar
Peshawar is the capital and List of cities in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa by population, largest city of the Administrative units of Pakistan, Pakistani province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. It is the sixth most populous city of Pakistan, with a district p ...
(in modern Pakistan) and, in 1005, made it the center for his forces.
In 1030,
Al Biruni reported on the devastation caused during the conquest of Gandhara and much of northwest India by Mahmud of Ghazni following his defeat of Jayapala in the Battle of Peshawar in 1001:
The Ghaznavid conquests were initially directed against the Ismaili
Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimid dynasty, Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa ...
s of Multan, who were engaged in an ongoing struggle with the provinces of the Abbasid Caliphate in conjunction with their compatriots of the
Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate (; ), also known as the Fatimid Empire, was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries CE under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, i ...
in North Africa and the Middle East; Mahmud apparently hoped to curry the favor of the Abbasids in this fashion. However, once this aim was accomplished, he moved onto the looting of Indian temples and monasteries. By 1027, Mahmud had captured parts of North India and obtained formal recognition of Ghazni's sovereignty from the Abbasid Caliph,
al-Qadir
Abu'l-Abbas Ahmad ibn Ishaq (; 28 September 947 ŌĆō 29 November 1031), better known by his regnal name al-Qadir (, , ), was the Abbasid caliph in Baghdad from 991 to 1031.
Born as an Abbasid prince outside the main line of succession, al-Qad ...
Billah.
Ghaznavid's rule in Northwestern India (modern Afghanistan and Pakistan) lasted over for 175 years, from 1010 to 1187. It was during this period that Lahore assumed considerable importance, apart from being the second capital, and later the only capital of the
Ghaznavid Empire
The Ghaznavid dynasty ( ''─Āaznaviy─ün'') was a Persianate Muslim dynasty of Turkic peoples, Turkic ''mamluk'' origin. It ruled the Ghaznavid Empire or the Empire of Ghazni from 977 to 1186, which at its greatest extent, extended from the Oxus ...
.
At the end of his reign, Mahmud's empire extended from
Kurdistan
Kurdistan (, ; ), or Greater Kurdistan, is a roughly defined geo- cultural region in West Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, and national identity have historically been based. G ...
in the west to
Samarkand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek language, Uzbek and Tajik language, Tajik: ąĪą░ą╝ą░čĆęøą░ąĮą┤ / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central As ...
in the Northeast, and from the
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
to the
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panj─üb or Panj-─Ćb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
in the west. Although his raids carried his forces across Northern and Western India, only Punjab came under his permanent rule while
Kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
, the
Doab
''Doab'' () is a term used in South Asia Quote: "Originally and chiefly in South Asia: (the name of) a strip or narrow tract of land between two rivers; spec. (with) the area between the rivers Ganges and Jumna in northern India." for the tract ...
, Rajasthan, and
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
remained nominal under the control of the local Indian dynasties. In 1030, Mahmud fell gravely ill and died at age 59. As with the invaders of three centuries ago, Mahmud's armies reached temples in
Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
,
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
,
Ujjain
Ujjain (, , old name Avantika, ) or Ujjayin─½ is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative as well as religious centre of Ujjain ...
,
Maheshwar
Maheshwar is a town, near Khargone city in Khargone district of Madhya Pradesh state, in central India. It is located on State Highway-38 ( Khargone city- Barwaha- Bandheri Highway),13.5 km east of National Highway 3 (Agra-Mumbai highway ...
, Jwalamukhi,
Somnath
Prabhas Patan, historically named Dev Patan, is a locality in Veraval, Gujarat. As the site of the Somnath temple and its associated Jyotirlinga (an aniconic representation of the god Shiva), it is an important place of Hindu pilgrimage.
Pl ...
and
Dwarka
Dwarka () is a town and municipality of Devbhumi Dwarka district in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Gujarat. It is located on the western shore of the Okhamandal Peninsula on the right bank of the Gomti river at ...
.
Ghurid Empire
Mu'izz al-Din, better known as Shah─üb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori was a conqueror from the region of
Ghor
Gh┼Źr, also spelled Ghowr or Ghur (), is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. It is located in the western Hindu Kush in central Afghanistan, towards the northwest. The province contains eleven districts, encompassing hundreds of vil ...
in modern
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the AfghanistanŌĆōIran borde ...
. Before 1160, the Ghaznavid Empire covered an area running from central Iran east to the Punjab, with capitals at Ghazni on the banks of Ghazni river in present-day Afghanistan, and at Lahore in present-day
Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
. In 1173, Muhammad of Ghor was crowned Ghazni. In 1186,
he conquered Lahore ending the Ghaznavid empire and bringing the last of Ghaznavid territory under his control. His early campaigns in the
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
were against the
Qarmatians
The Qarmatians (; ) were a militant Isma'ili Shia movement centred in Al-Ahsa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a religious state in 899 CE. Its members were part of a movement that adhered to a syncretic branch of Sevener Ismaili ...
of Multan.
In 1191, he invaded the territory of
Prithviraj III
Prithviraja III (IAST: Pß╣øthv─½-r─üja; 22 May 1166 ŌĆō February 1192), popularly known as Prithviraj Chauhan or Rai Pithora, was a king from the Chauhan (Chahamana) dynasty who ruled the territory of Sapadalaksha, with his capital at Ajmer ...
of
Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
, who ruled his territory from Delhi to
Ajmer
Ajmer () is a city in the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. It serves as the administrative headquarters of the Ajmer district and Ajmer division. It lies at the centre of Rajasthan, earning it the ...
in present-day
Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
, but was defeated at the
First Battle of Tarain
The First Battle of Tarain, also spelt as the First Battle of Taraori, was fought on 14 January 1191 between the invading Ghurid army led by Muhammad of Ghor and the Rajput Confederacy led by Prithviraj Chauhan, near Tarain (modern Taraori ...
. The following year, Mu'izz al-Din assembled 120,000 horsemen and once again invaded India. Mu'izz al-Din's army met Prithviraj's army again at Tarain, and this time Mu'izz al-Din won; Govindraj was slain, Prithviraj executed and Mu'izz al-Din advanced onto Delhi. Within a year, Mu'izz al-Din controlled North-Western Rajasthan and Northern Ganges-Yamuna Doab. After these victories in India, and Mu'izz al-Din's establishment Delhi as the capital of his Indian provinces, Multan was also incorporated as a major part of his empire.
Mu'izz al-Din then returned east to Ghazni to deal with the threat on his eastern frontiers from the Turks of the Khwarizmian Empire, whiles his armies continued to advance through Northern India, raiding as far as
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
.
Mu'izz al-Din returned to Lahore after 1200. In 1206, Mu'izz al-Din had to travel to Lahore to crush a revolt. On his way back to Ghazni his caravan rested at Damik near
Sohawa
Sohawa is a town in the Punjab province of Pakistan, and is the capital of the Sohawa Tehsil, which is an administrative subdivision of Jhelum District in Punjab. Sohawa has grown from a small village in 1947 to a large town in 2014, with major ...
(which is near the city of
Jhelum
Jhelum (; , ) is a city, located along the western bank of the Jhelum River, in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the 21st largest city in Punjab and 31st largest in Pakistan, by population. Located in northern Punjab, it serves as the capital of the ...
in the
Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panj─üb or Panj-─Ćb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
province of modern-day Pakistan). He was assassinated on 15 March 1206, while offering his evening prayers by the assassins from the Ismaili Muslim sect.
Third phase (13th to 16th centuries)
Delhi Sultanate
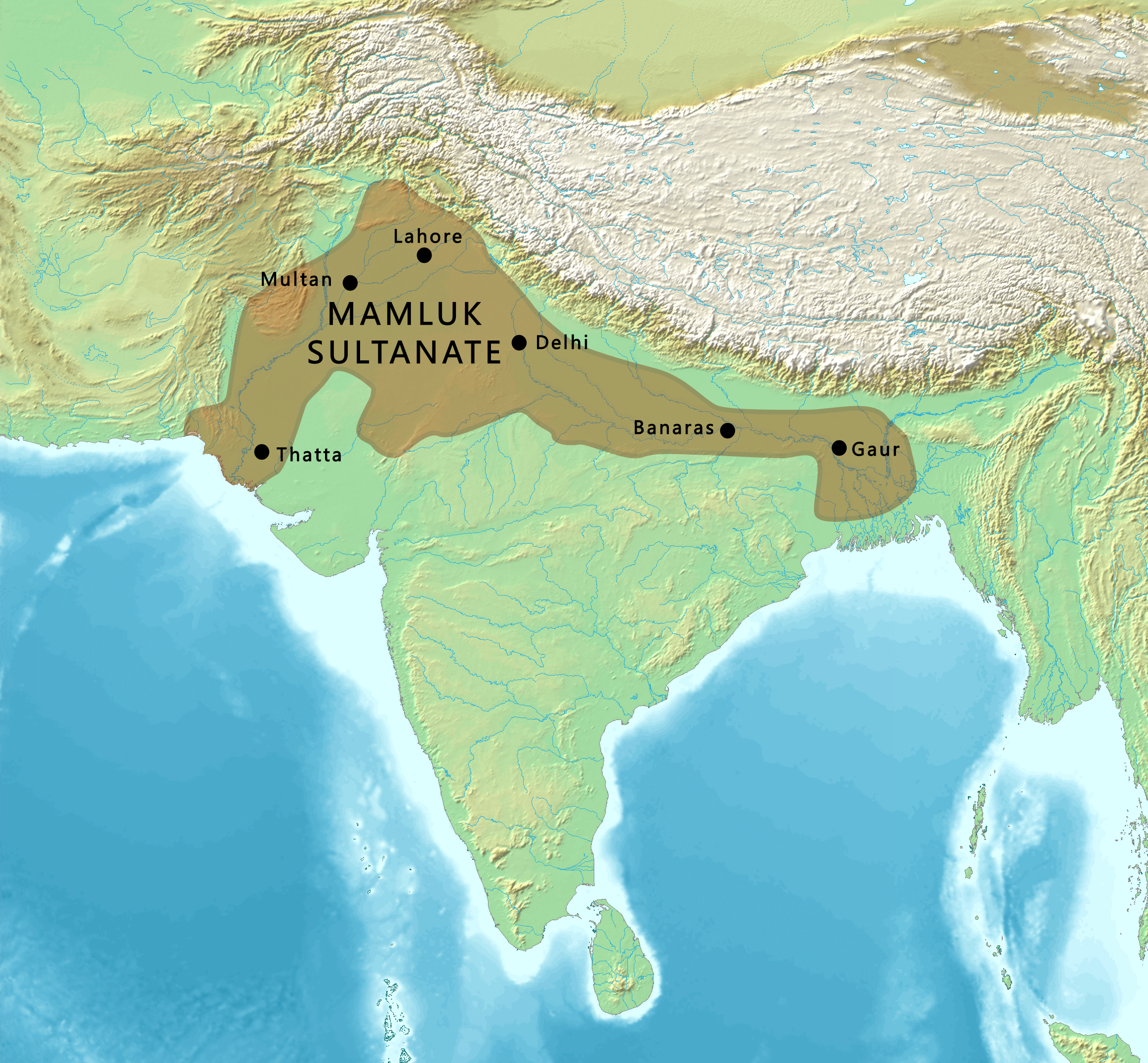
Muhammad Ghoris successors established the first dynasty of the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. , while the
Mamluk Dynasty in 1211 (however, the Delhi Sultanate is traditionally held to have been founded in 1206) seized the reins of the empire. ''
Mamluk
Mamluk or Mamaluk (; (singular), , ''mam─ül─½k'' (plural); translated as "one who is owned", meaning "slave") were non-Arab, ethnically diverse (mostly Turkic, Caucasian, Eastern and Southeastern European) enslaved mercenaries, slave-so ...
'' means "slave" and referred to the Turkic slave soldiers who became rulers. The territory under control of the Muslim rulers in Delhi expanded rapidly.
Several Turko-Afghan dynasties ruled from Delhi: the Mamluk (1206ŌĆō1290), the
Khalji (1290ŌĆō1320), the
Tughlaq
The Tughlaq dynasty (also known as the Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty; ) was the third dynasty to rule over the Delhi Sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath ...
(1320ŌĆō1414), the
Sayyid
''Sayyid'' is an honorific title of Hasanid and Husaynid lineage, recognized as descendants of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his daughter Fatima and Ali's sons Hasan ibn Ali, Hasan and Husayn ibn Ali, Husayn. The title may also refer ...
(1414ŌĆō51), and the
Lodhi (1451ŌĆō1526). By the mid-century, Bengal and much of central India was under the Delhi Sultanate.
Tughlaq invasions

The Tughlaqs conquered Delhi with the support of the
Khokhar tribes who formed the vanguard of the army. The Tughlaqs claimed to be "bound to all Indians by ties of blood and relation". Under the first ruler of the dynasty,
Ghiyath al-Din Tughlaq, the Tughlaq court wrote a war ballad known as the
Vaar
The V─ür or Vaar (, ), in Punjabi poetry, is a heroic ode or ballad which generally narrates legend such as stories of Punjabi folk heroes or a historical event.''The Encyclopaedia of Indian Literature (Volume One - A to Devo)''. Amaresh Datta, ...
in the
Punjabi language
Punjabi, sometimes spelled Panjabi, is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Punjab region of Pakistan and India. It is one of the most widely spoken native languages in the world, with approximately 150 million native sp ...
, describing the introduction of Ghazi Malik's rise to the throne. This was the earliest known Vaar in Punjabi poetry. The Tughalqs attacked and plundered Malwa, Gujarat, Mahratta, Tilang, Kampila, Dhur-samundar, Mabar, Lakhnauti, Chittagong, Sunarganw and Tirhut. The Tughlaqs chose
Daulatabad in southern India as the second administrative capital of the Delhi Sultanate. The Delhi Sultanate forced migration of the Muslim population of Delhi, including his royal family, the nobles, Syeds, Sheikhs and 'Ulema to settle in Daulatabad. The purpose of transferring the entire Muslim elite to Daulatabad was to act as propagandists who would adapt Islamic religious symbolism to the rhetoric of empire, and so the Sufis could by persuasion bring many of the inhabitants of the Deccan to become Muslim. These elite colonists from the capital of Delhi were
Urdu-speakers, who carried the
Urdu language
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
to the Deccan.
During the time of Delhi Sultanate, the
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
resisted attempts of Delhi Sultanate to establish dominion in the
Southern India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
, serving as a barrier against invasion by the Muslims.
The Sultans of Delhi enjoyed cordial, if superficial, relations with Muslim rulers in the Near East but owed them no allegiance. They based their laws on the ''
Quran
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a WaßĖźy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, All─üh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which ...
'' and the ''
sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
'' and permitted non-Muslim subjects to practice their own religions if they paid the ''
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
'' (poll tax). They ruled from urban centers, while military camps and trading posts provided the nuclei for towns that sprang up in the countryside.
Perhaps the most significant contribution of the Sultanate was its temporary success in insulating the subcontinent from the potential devastation of the Mongol invasion from Central Asia in the 13th century, which nonetheless led to the capture of Afghanistan and western Pakistan by the Mongols (see the
Ilkhanate
The Ilkhanate or Il-khanate was a Mongol khanate founded in the southwestern territories of the Mongol Empire. It was ruled by the Il-Khans or Ilkhanids (), and known to the Mongols as ''H├╝leg├╝ Ulus'' (). The Ilkhanid realm was officially known ...
Dynasty). Under the Sultanate, "Indo-Muslim" fusion left lasting monuments in architecture, music, literature, and religion. In addition it is surmised that the language of
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
(literally meaning "horde" or "camp" in various Turkic dialects) was born during the Delhi Sultanate period as a result of the mingling of Sanskritic Hindi and the Persian, Turkish, Arabic favoured by the Muslim invaders of India.
The Sultanate suffered significantly from the sacking of Delhi in 1398 by
Timur
Timur, also known as Tamerlane (1320s17/18 February 1405), was a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia, becoming the first ruler of the Timurid dynasty. An undefeat ...
, but revived briefly under the Lodi Dynasty. This was the final dynasty of the Sultanate before it was conquered by
Zahiruddin Babur in 1526, who subsequently founded the
Mughal dynasty
The Mughal dynasty () or the House of Babur (), was a Central Asian dynasty of Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol origin that ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from the early 16th to the 19th century. The dynasty was a cadet branch ...
that ruled from the 16th to the 18th centuries.
Timur
Tīmūr bin Taraghay Barlas, known in the West as Tamerlane or "Timur the lame", was a 14th-century
warlord
Warlords are individuals who exercise military, Economy, economic, and Politics, political control over a region, often one State collapse, without a strong central or national government, typically through informal control over Militia, local ...
of
Turco-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these khanates eventually ass ...
descent.
He had conquered much of western and central Asia, and founded the
Timurid Empire
The Timurid Empire was a late medieval, culturally Persianate, Turco-Mongol empire that dominated Greater Iran in the early 15th century, comprising modern-day Iran, Iraq, Afghanistan, much of Central Asia, the South Caucasus, and parts of co ...
(1370ŌĆō1507) in Central Asia which survived until 1857 as the
Mughal dynasty
The Mughal dynasty () or the House of Babur (), was a Central Asian dynasty of Turco-Mongol tradition, Turco-Mongol origin that ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent from the early 16th to the 19th century. The dynasty was a cadet branch ...
of India.

Informed about civil war in South Asia, Timur began a trek starting in 1398 to invade the reigning
Sultan
Sultan (; ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be use ...
Nasir-u Din Mehmud of the Tughlaq Dynasty in the north Indian city of Delhi. His campaign was politically pretexted that the Muslim Delhi Sultanate was too tolerant toward its "Hindu" subjects, but that could not mask the real reason being to amass the wealth of the Delhi Sultanate.
Timur's invasion did not go unopposed, however, and he did meet some resistance during his march to Delhi, most notably with the
Sarv Khap
A Khap is a community organisation representing a clan of different North Indian Castes, majorly found among Jat caste They are found mostly in northern India, particularly in the states of Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh Commonly among Jat ...
coalition in northern India, as well as the Governor of
Meerut
Meerut (, ISO 15919, ISO: ''M─ōraß╣Łh'') is a city in the western region of the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. Located in the Meerut district, it is northeast of the national capital, New Delhi, and is ...
. Although impressed and momentarily stalled by the valour of Ilyaas
Awan
Awan may refer to:
* Awan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Awana, also known as Awan is a clan of Gujjars in South Asia
* Awan (tribe), a social group of Pakistan
* Awan dynasty, an Elamite dynasty of Iran
* Awan languages, ...
, Timur was able to continue his relentless approach to Delhi, arriving in 1398 to combat the armies of Sultan Mehmud, already weakened by an internal battle for ascension within the royal family.
The Sultan's army was easily defeated on 17 December 1398. Timur entered Delhi and the city was sacked, destroyed, and left in ruins. Before the battle for Delhi, Timur executed more than 100,000 "Hindu" captives.
Timur's purported autobiography, the ''Tuzk-i-Timuri'' ("Memoirs of Temur") is a later fabrication.
Historian Irfan Habib wrote that in the 14th century, the word "Hindu" (people of "Al-Hind", "Hind" being "India") included "both Hindus and Muslims" in religious connotations.
Timur left Delhi in approximately January 1399. In April he had returned to his own capital beyond the
Oxus
The Amu Darya ( ),() also shortened to Amu and historically known as the Oxus ( ), is a major river in Central Asia, which flows through Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Ku ...
(Amu Darya). Immense quantities of spoils were taken from India. According to
Ruy Gonz├Īles de Clavijo Ruy or RUY may refer to:
Arts and Entertainment
*Ruy, the Little Cid, Spanish animated television series
*Ruy Blas, a character in the eponymous tragic drama by Victor Hugo
People
*another form of Rui, a Portuguese male given name
*another form o ...
, 90 captured elephants were employed merely to carry precious stones looted from his conquest, which was used to erect a mosque at Samarkand ŌĆō what historians today believe is the enormous
Bibi-Khanym Mosque
The Bibi-Khanym Mosque (; ; also variously spelled as Khanum, Khanom, Hanum, Hanim) is one of the most important monuments of Samarkand, Uzbekistan. In the 15th century, it was one of the largest and most magnificent mosques in the Islamic world. ...
. Ironically, the mosque was constructed too quickly and suffered from disrepair within a few decades of its construction.
Regional sultanates
The
Makran Sultanate
The Ma'danid dynasty was a medieval Islamic dynasty that ruled the Sultanate of Makran. It ruled Makran from the late 9th or early 10th centuryBosworth (1994), p. 256 until around the 11th century.
History
Makran had been one of the easternmost ...
was one of the first kingdom to transition from an emirate to a sultanate in the 13th century.
Kashmir Sultanate
The Kashmir Sultanate, historically Latinised as the Sultanate of Cashmere and officially known as the State of Kashmir, was a Medieval India, medieval kingdom established in the early 14th century, primarily in the Kashmir Valley, found in the ...
and
Sindh Sultanate were established by the
Shah Mir
Shamsu'd-Din Shah Mir (; – 6 July 1342) or simply as Shah Mir or Shah Mirza was the second Sultan of Kashmir and founder of the Shah Mir dynasty. Shah Mir is believed to have come to Kashmir during the rule of Suhadeva, where he rose to ...
and
Samma dynasties respectively in the 14th century while the
Multan Sultanate was established in the 15th century by the
Langah dynasty
The Langah Sultanate was a late medieval sultanate based in the Punjab region in the western Indian subcontinent between the 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the lower Doab tract with Multan at its centre. The Langah Sulta ...
. Regional kingdoms such as
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
,
Gujarat
Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ...
,
Malwa
Malwa () is a historical region, historical list of regions in India, region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic plateau, volcanic upland north of the ...
,
Khandesh
Khandesh is a geographic region in Maharashtra, India. It was made up of present Jalgaon, Dhule and Nandurbar districts. It also said that Burhanpur District of Madhya Pradesh was also its part.
The region have seen many geographical ch ...
,
Jaunpur,
Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is ...
and
Bahmani
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellion o ...
expanded at the expense of the Delhi Sultanate. Gaining conversions to Islam was easier under regional Sultanates.
Deccan sultanates

The term of Deccan Sultanates was used for five Muslim dynasties that ruled several
late medieval Indian kingdoms, namely
Bijapur Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a '' taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 14 ...
,
Golkonda Sultanate
The Sultanate of Golconda (; ) was an early modern kingdom in southern India, ruled by the Persianate, Shia Islamic Qutb Shahi dynasty of Turkoman origin. After the decline of the Bahmani Sultanate, the Sultanate of Golconda was established i ...
,
Ahmadnagar Sultanate
The Ahmadnagar Sultanate was a medieval Marathi Muslim kingdom located in the northwestern Deccan, between the sultanates of Gujarat and Bijapur, ruled by the Nizam Shahi dynasty. It was established when Malik Ahmed, the Bahmani governor o ...
,
Bidar Sultanate
The Sultanate of Bidar was an early modern Indian polity that ruled a territory in the central Deccan Plateau, Deccan centred at Bidar. As one of the five Deccan sultanates, the sultanate's initial territory corresponded to that of one of the ...
, and
Berar Sultanate in
South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
. The Deccan Sultanates ruled the
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound ...
between the
Krishna River
The Krishna River in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan plateau is the third-longest in India, after the Ganga, Ganga and Godavari. It is also the fourth-largest in terms of water inflows and river basin area in India, after the Ganga, Indus and Godav ...
and the
Vindhya Range
The Vindhya Range (also known as Vindhyachal) () is a complex, discontinuous chain of mountain ridges, hill ranges, highlands and plateau escarpments in west-central India.
Technically, the Vindhyas do not form a single mountain range in the ...
. These
sultanate
Sultan (; ', ) is a Royal and noble ranks, position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". La ...
s became independent during the separation of the
Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Kingdom or the Bahmani Sultanate was a late medieval Persianate kingdom that ruled the Deccan plateau in India. The first independent Muslim sultanate of the Deccan, the Bahmani Kingdom came to power in 1347 during the rebellio ...
, another Muslim empire.

The
ruling families
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.
Historians ...
of all these five sultanates were of diverse origin; the
Qutb Shahi dynasty
The Sultanate of Golconda (; ) was an early modern kingdom in southern India, ruled by the Persianate, Shia Islamic Qutb Shahi dynasty of Turkoman origin. After the decline of the Bahmani Sultanate, the Sultanate of Golconda was established ...
of Golconda Sultanate was of
Turkmen
Turkmen, T├╝rkmen, Turkoman, or Turkman may refer to:
Peoples Historical ethnonym
* Turkoman (ethnonym), ethnonym used for the Oghuz Turks during the Middle Ages
Ethnic groups
* Turkmen in Anatolia and the Levant (Seljuk and Ottoman-Turkish desc ...
origin, the
Barid Shahi dynasty
The Sultanate of Bidar was an early modern Indian polity that ruled a territory in the central Deccan centred at Bidar. As one of the five Deccan sultanates, the sultanate's initial territory corresponded to that of one of the five provinces o ...
of Bidar Sultanate being founded by a
Turkic slave, the
Adil Shahi dynasty
The Sultanate of Bijapur was an early modern kingdom in the western Deccan and South India, ruled by the Muslim Adil Shahi (or Adilshahi) dynasty. Bijapur had been a ''taraf'' (province) of the Bahmani Kingdom prior to its independence in 1490 ...
of Bijapur Sultanate was founded by a
Georgian slave while
Nizam Shahi dynasty
The Ahmadnagar Sultanate was a medieval Marathi Muslim kingdom located in the northwestern Deccan, between the sultanates of Gujarat and Bijapur, ruled by the Nizam Shahi dynasty. It was established when Malik Ahmed, the Bahmani governor o ...
of Ahmadnagar Sultanate and
Imad Shahi dynasty of Berar Sultanate were of
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as San─ütan─½s) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym San─ütana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also be ...
lineage (Ahmadnagar being
Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
and Berar being
Kanarese
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a s ...
).
Fourth phase (16th to 18th centuries)
Mughal Empire

India in the early 16th century presented a fragmented picture of rulers who lacked concern for their subjects and failed to create a common body of laws or institutions. Outside developments also played a role in shaping events. The circumnavigation of Africa by the Portuguese explorer
Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama ( , ; ŌĆō 24 December 1524), was a Portuguese explorer and nobleman who was the Portuguese discovery of the sea route to India, first European to reach India by sea.
Da Gama's first voyage (1497ŌĆō1499) was the first to link ...
in 1498 allowed Europeans to challenge Muslim control of the trading routes between Europe and Asia. In Central Asia and Afghanistan, shifts in power pushed
Babur
Babur (; 14 February 148326 December 1530; born Zah─½r ud-D─½n Muhammad) was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his father and mother respectively. He was also ...
of the
Timurid dynasty
The Timurid dynasty, self-designated as Gurkani (), was the ruling dynasty of the Timurid Empire (1370ŌĆō1507). It was a Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim dynasty or Barl─üs clan of Turco-Mongol originB.F. Manz, ''"T─½m┼½r Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of I ...
(in present-day
Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
) southward, first to Kabul and then to the heart of Indian subcontinent. The dynasty he founded endured for more than two centuries.
File:Akbar shoots Jaimal at the siege of Chitor.jpg, The Mughal Emperor
The emperors of the Mughal Empire, who were all members of the Timurid dynasty (House of Babur), ruled the empire from its inception on 21 April 1526 to its dissolution on 21 September 1857. They were supreme monarchs of the Mughal Empire in ...
Akbar shoots the Rajput warrior Jaimal during the Siege of Chittorgarh in 1567.
File:Bullocks dragging siege-guns up hill during the attack on Ranthambhor Fort.jpg, Bullocks dragging siege-guns up hill during Mughal Emperor Akbar's attack on Ranthambhor Fort in 1568.
File:Basawan. Battle of rival ascetics. Akbarnama, ca. 1590, V&A Museum.jpg, The Mughal Army
The army of the Mughal Empire was the force by which the Mughal emperors established their empire in the 16th century and expanded it to its greatest extent at the beginning of the 18th century. Although its origins, like the Mughals themselve ...
commanded by Akbar attack members of the Sannyasa
''Sannyasa'' (), sometimes spelled ''sanyasa'', is the fourth stage within the Hinduism, Hindu system of four life stages known as ''ashrama (stage), ashramas'', the first three being ''brahmacharya'' (celibate student), ''Gß╣øhastha, grihast ...
during the Battle of Thanesar.
File:Ibn Sayyid Murad al-Husayni - Young Hindu Girl Before the Mughal Emperor Akbar - Walters W64916A - Full Page.jpg, Mughal Emperor Akbar attempts to dissuade the young Hindu girl from committing sati
Sati or SATI may refer to:
Entertainment
* ''Sati'' (film), a 1989 Bengali film by Aparna Sen and starring Shabana Azmi
* ''Sati'' (novel), a 1990 novel by Christopher Pike
*Sati (singer) (born 1976), Lithuanian singer
*Sati, a character in ''Th ...
File:Akbar Fights with Raja Man Singh.jpg, The Mughal Emperor Akbar fights Pehlwani
Pehlwani, also known as Kushti, is a form of wrestling contested in the Indian subcontinent. It was developed in the Mughal Empire by combining Persian Pahlevani and zoorkhaneh rituals, Koshti pahlevani with influences from native Indian Malla- ...
with his Hindu general Raja Man Singh I
Mirza Raja Man Singh I (21 December 1550 – 6 July 1614) was the 24th Raja, Kachawaha Rajput ruler of the Kingdom of Amber from 1589 to 1614. He also served as the foremost imperial Subahdar of Bihar Subah from 1587 to 1594, then for Ben ...
of Jaipur
Jaipur (; , ) is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the List of cities and towns in Rajasthan, largest city of the north-western States and union territories of India, Indian state of Rajasthan. , the city had ...
.
File:The Burning of the Rajput women, during the siege of Chitor.jpg, Rajput women committing Jauhar
Jauhar, sometimes spelled Jowhar or Juhar, was a Hindu Rajput practice of mass self-immolation by women and girls in the Indian subcontinent to avoid capture, sex slavery, enslavement, and rape when facing certain defeat during a war. Some repo ...
during Akbar's invasion.
File:Jamal al-Din Husayn Inju Shirazi - Two Folios from the Akbarnama - Walters W684 - Detail A.jpg, A War elephant
A war elephant is an elephant that is Animal training, trained and guided by humans for combat purposes. Historically, the war elephant's main use was to charge (warfare), charge the enemy, break their ranks, and instill terror and fear. Elep ...
executing the opponents of the Emperor Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, ŌĆō ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
.
Babur
A descendant of both
Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Tem├╝jin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
and Timur, Babur combined strength and courage with a love of beauty, and military ability with cultivation. He concentrated on gaining control of Northwestern India, doing so in 1526 by defeating the last Lodhi Sultan in the
First battle of Panipat
The First Battle of Panipat, on 21 April 1526 was fought between the invading forces of Babur against Ibrahim Khan Lodi, the List of sultans of Delhi, Sultan of Delhi, in North India. Babur's forces, em ...
, a town north of Delhi. Babur then turned to the tasks of persuading his Central Asian followers to stay on in India and of overcoming other contenders for power, like the
Rajputs
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
and the
Afghans
Afghans (; ) are the citizens and nationals of Afghanistan, as well as their descendants in the Afghan diaspora. The country is made up of various ethnic groups, of which Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks are the largest. The three main lan ...
. He succeeded in both tasks but died shortly thereafter in 1530. The Mughal Empire was one of the largest centralized states in pre-modern history and was the precursor to the
British Indian Empire
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
.
Babur was followed by his great-grandson,
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 ŌĆō 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the ...
(1628ŌĆō1658), builder of the
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal ( ; ; ) is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was commissioned in 1631 by the fifth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his belo ...
and other magnificent buildings. Two other towering figures of the Mughal era were
Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, ŌĆō ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
(r. 1556ŌĆō1605) and
Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 ŌĆō 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
(r. 1658ŌĆō1707). Both rulers expanded the empire greatly and were able administrators. However, Akbar was known for his religious tolerance and administrative genius while Aurangzeb was a pious Muslim and fierce advocate of more orthodox Islam.
Aurangzeb
While some rulers were zealous in their spread of Islam, others were relatively liberal. The Mughal emperor Akbar, an example of the latter established a new religion,
Din E Elahi, which included beliefs from different faiths and even build many temples in his empire. He abolished the jizya twice. In contrast, his great-grandson
Aurangazeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 ŌĆō 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
was a more religious and orthodox ruler. Aurangzeb's Deccan campaign saw one of the largest death tolls in South Asian history, with an estimated 4.6 million people killed during his reign, Muslims and Hindus alike.
An estimated of 2.5 million of Aurangzeb's army were killed during the
MughalŌĆōMaratha Wars
The Deccan wars were a series of military conflicts between the Mughal Empire and the descendants of the Maratha Empire, Maratha ruler Shivaji from the time of Shivaji's death in 1680 until the death of Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. Shivaji was ...
(100,000 annually during a quarter-century), while 2 million civilians in war-torn lands died due to drought,
plague and
famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
.
In the century-and-a-half that followed the death of Aurangzeb, effective Muslim control started weakening. Succession to imperial and even provincial power, which had often become hereditary, was subject to intrigue and force. The
mansabdari
The Mansabdar was a military unit within the administrative system of the Mughal Empire introduced by Akbar later used in all over in early modern India. The word ''mansab'' is of Arabic origin meaning rank or position. The system determined th ...
system gave way to the zamindari system, in which high-ranking officials took on the appearance of hereditary landed aristocracy with powers of collecting rents. As Delhi's control waned, other contenders for power emerged and clashed, thus preparing the way for the eventual British takeover.
Durrani Empire

Ahmed Shah Abdali ŌĆō a
Pashtun
Pashtuns (, , ; ;), also known as Pakhtuns, or Pathans, are an Iranic ethnic group primarily residing in southern and eastern Afghanistan and northwestern Pakistan. They were historically also referred to as Afghans until 1964 after the ...
ŌĆō embarked on conquest in South Asia starting in 1747. In the short time of just over a quarter of a century, he forged one of the largest Muslim empires of the 18th century. The high point of his conquests was his victory over the powerful
Marathas
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
in the
Third Battle of Panipat
The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761 between the Maratha Empire and the invading army of the Durrani Empire. The battle took place in and around the city of Panipat, approximately north of Delhi. The Afghan (ethnonym), Af ...
, which occurred in 1761. In the Indian subcontinent, his empire stretched from the Indus at Attock all the way to the eastern Punjab. Uninterested in long-term of conquest or in replacing the Mughal Empire, he became increasingly pre occupied with revolts by the Sikhs.
Vadda Ghalughara took place under the Muslim provincial government based at Lahore to wipe out the Sikhs, with non-combatant women, children and old men being killed, an offensive that had begun with the Mughals, with the
Chhota Ghallughara
''Chhota Ghallughara'' ( , "Smaller Massacre") was a massacre of a significant proportion of the Sikh population by the Mughal Empire in 1746. The Mughal Army killed an estimated 7,000 Sikhs in these attacks while an additional 3,000 Sikhs w ...
. but after two months
Sikh Misls
The Sikh Confederacy was a confederation of twelve sovereign Sikh states (each known as a Misl, derived from the Arabic word ┘ģ┘Éž½┘Æ┘ä meaning 'equal'; sometimes spelt as Misal) which rose during the 18th century in the Punjab region in the n ...
again assembled and defeated Durranis in
Battle of Harnaulgarh
The Battle of Harnaulgarh was fought between the Durrani Empire and the Sikh Misls of Dal Khalsa in 1762.
Background
Battle
The Sikhs assembled in May 1762 and plundered the baggage of the Mughal governor of Sirhind, Zain Khan Sirhindi. The S ...
,
Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
Capture Sirhind Labore Multan His empire began to unravel decade before his death in 1772.
Decline of the Muslim rule
Maratha Empire

The single most important power to emerge in the Mughal dynasty was the Maratha Confederacy (1674ŌĆō1818). The Marathas are responsible, to a large extent for ending Mughal rule in India. The Maratha Empire ruled large parts of India following the decline of the Mughals. The long and futile war bankrupted one of the most powerful empires in the world. Mountstuart Elphinstone termed this a demoralizing period for the Muslims as many of them lost the will to fight against the Maratha Empire. The Maratha empire at its peak stretched from Trichinopoly (present day
Tiruchirappalli
Tiruchirappalli (), also known as Trichy, is a major tier II city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Tiruchirappalli district. The city is credited with being the best livable and the cleanest city of T ...
in Tamil Nadu) in the south to the Afghan border in the north. In early 1771, Mahadji, a notable Maratha general, recaptured Delhi and installed Shah Alam II as the puppet ruler on the Mughal throne. In north India, the Marathas thus regained the territory and the prestige lost as result of the defeat at Panipath in 1761.
Sikh Empire

In the Punjab, Mughal power waned in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Successive bands of Sikhs attacked Lahore, and by 1780 partitioned it among themselves.
Ranjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 ŌĆō 27 June 1839) was the founder and first maharaja of the Sikh Empire, in the northwest Indian subcontinent, ruling from 1801 until his death in 1839.
Born to Maha Singh, the leader of the Sukerchakia M ...
unified the Sikh ''
misl
Major Indoor Soccer League has been the name of three different American professional indoor soccer leagues:
*Major Indoor Soccer League (1978ŌĆō1992), known in its final two seasons as the Major Soccer League
*Major Indoor Soccer League (2001ŌĆō2 ...
dhars'' (commanders) and made Lahore the administrative capital of a new
Sikh Empire
The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab, Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the East India Company, Br ...
in 1799. In Afghanistan
Zaman Shah Durrani
Zaman Shah Durrani, or Zaman Shah Abdali ( Persian: ; 1767 ŌĆō 1844) was the third King of the Durrani Empire from 1793 until 1801. An ethnic Pashtun of the Sadozai clan, Zaman Shah was the grandson of Ahmad Shah Durrani and the fifth son of Timu ...
was defeated by powerful
Barakzai
B─ürakzai (, plur. , ) is the name of a Pashtun tribe from present-day Kandahar, Afghanistan. '"Barakzai" is a common name among the Pashtuns and it means "son of Barak" in Pashto. According to the Encyclop├”dia Iranica, "In the detailed Pash ...
chief
Fateh Khan
Fateh Khan or Dera Fateh Khan is a town and union council of Taunsa District in the Punjab province of Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependenc ...
who appointed
Mahmud Shah Durrani
Mahmud Shah Durrani (Pashto/ Persian: ); 1769 ŌĆō 18 April 1829) was born prince and later ruler of the Durrani Empire (Afghanistan) between 1801 and 1803, and again between 1809 and 1818. From 1818 to 1829 he was the ruler of Herat. From an eth ...
as the new ruler of Afghanistan and appointed himself as Wazir of Afghanistan. Sikhs however were now superior to the Afghans and started to annex Afghan provinces. The biggest victory of the Sikh Empire over the
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire, colloquially known as the Afghan Empire, or the Saddozai Kingdom, was an Afghanistan, Afghan empire founded by the Durrani tribe of Pashtuns under Ahmad Shah Durrani in 1747, which spanned parts of Central Asia, the Iranian ...
came in the
Battle of Attock
The Battle of Attock (also known as the Battle of Chuch or the Battle of Haidru) took place on 13 July 1813 between the Sikh Empire and the Durrani Empire. The battle was the first significant Sikh victory over the Durranis.
Background
In 181 ...
fought in 1813 between Sikh and Wazir of Afghanistan Fateh Khan and his younger brother
Dost Mohammad Khan
Dost Mohammad Khan Barakzai (Pashto/; 23 December 1792 ŌĆō 8 June 1863), nicknamed the Amir-i Kabir, was the founder of the Barakzai dynasty and one of the prominent rulers of Afghanistan during the First Anglo-Afghan War. With the decline of ...
. The Afghans were routed by the Sikh army and the Afghans lost over 9,000 soldiers in this battle. Dost Mohammad was seriously injured whereas his brother Wazir Fateh Khan fled back to Kabul fearing that his brother was dead. In 1819, the Sikhs defeated the Afghans at
Shopian
Shopian (), known as Shupyan () in Kashmiri, is an administrative division of the Shopian district. It is located in southern part of Kashmir Valley, of Jammu and Kashmir, India. Shopian is called the ''Apple town of Kashmir'' as majority o ...
and conquered Kashmir.
Impact on India, Islam and Muslims in India
The impact of the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent is a subject of considerable scholarly debate, reflecting a spectrum of interpretations regarding the socio-cultural, religious, and political transformations that ensued.
Divergent historical perspectives
Will Durant
William James Durant (; November 5, 1885 ŌĆō November 7, 1981) was an American historian and philosopher, best known for his eleven-volume work, '' The Story of Civilization'', which contains and details the history of Eastern and Western civil ...
, an American historian, characterized the Islamic conquest of India as "probably the bloodiest story in history," emphasizing the extensive violence and destruction associated with the invasions.
Conversely, historians like
Audrey Truschke
Audrey Truschke ( ) is a historian of South Asia and a professor at Rutgers University. Her work focuses on inter-community relations in medieval South Asia, especially during the Mughal Empire. In 2017, she was conferred with the John F. Richard ...
and
Romila Thapar
Romila Thapar (born 30 November 1931) is an Indian historian. Her principal area of study is ancient India, a field in which she is pre-eminent. Quotr: "The pre-eminent interpreter of ancient Indian history today. ... " Thapar is a Professor ...
argue that such portrayals are exaggerated and overlook the complexities of the period. Truschke highlights the
Mughal emperors
The emperors of the Mughal Empire, who were all members of the Timurid dynasty ( House of Babur), ruled the empire from its inception on 21 April 1526 to its dissolution on 21 September 1857. They were supreme monarchs of the Mughal Empire i ...
' engagement with
Sanskrit culture, suggesting a degree of cultural integration. Thapar contends that the narrative of continuous Hindu persecution under Muslim rule is historically untenable, noting instances of patronage and coexistence.
Religious dynamics and social structures
The Muslim conquests introduced new administrative and religious frameworks. While some rulers enforced policies like the
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
tax on non-Muslims, others, such as
Muhammad bin Qasim
MußĖźammad ibn al-Q─üsim al-Thaqaf─½ (; ŌĆō) was an Arabs, Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (and Punjab, part of ancient Sindh), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His m ...
, reportedly reinstated local
Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
officials and protected temples, indicating a pragmatic approach to governance.
The period also saw the
stratification of Muslim society in India, with distinctions between "
Ashraf
Shar─½f or Sherif (, 'noble', 'highborn'), also spelled shareef, feminine shar─½fa (), plural ashr─üf (), shuraf─ü╩Š (), or (in the Maghreb) shurf─ü╩Š, is a title used to designate a person descended, or claiming to be descended, from the famil ...
" (noble) and "Ajlaf" (commoner) Muslims, often correlating with lineage and conversion history. This hierarchy sometimes mirrored pre-existing social divisions, affecting the integration of converts.
Despite these conflicts, the era witnessed significant cultural synthesis. Architectural styles blended
Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
and
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Associated with India
* of or related to India
** Indian people
** Indian diaspora
** Languages of India
** Indian English, a dialect of the English language
** Indian cuisine
Associated with indigenous peoples o ...
elements, and languages like
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
emerged from the confluence of Persian,
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
, and local dialects. Institutions such as the
Aligarh Movement in the 19th century also aimed to modernize Muslim education for the British Indian population.
Conversion of non-Muslims

Considerable controversy exists both in scholarly and public opinion about the conversions to Islam typically represented by the following schools of thought:
# The bulk of Muslims are descendants of migrants from the
Iranian Plateau
The Iranian plateau or Persian plateau is a geological feature spanning parts of the Caucasus, Central Asia, South Asia, and West Asia. It makes up part of the Eurasian plate, and is wedged between the Arabian plate and the Indian plate. ...
or Arabs.
# Conversion of slaves to Islam. Children fathered by Muslims by non-Muslim slaves would be raised Muslim. Non-Muslim women who birthed them would convert to Islam to avoid rejection by their own communities.
# Conversions occurred for non-religious reasons of pragmatism and patronage such as social mobility among the Muslim ruling elite or for relief from taxes.
# Conversion was a result of the actions of
Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism.
Practitioners of Sufism are r ...
saints and involved a genuine change of heart.
# Conversion came from
Buddhists
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century BCE. It is the world's fourth ...
and the en masse conversions of lower castes for social liberation and as a rejection of the oppressive
Hindu caste strictures.
# A combination, initially made under duress followed by a genuine change of heart.
# As a socio-cultural process of diffusion and integration over an extended period of time into the sphere of the dominant
Muslim civilisation and global polity at large.
Embedded within this lies the concept of Islam as a foreign imposition and Hinduism being a natural condition of the natives who resisted, resulting in the failure of the project to
Islamize
The spread of Islam spans almost 1,400 years. The early Muslim conquests that occurred following the death of Muhammad in 632 CE led to the creation of the caliphates, expanding over a vast geographical area; conversion to Islam was boosted b ...
the Indian subcontinent and is highly embroiled within the politics of the
partition and
communalism
Communalism may refer to:
* African communalism, a system of interdependence in rural Africa
* Christian communism, form of religious communism based on Christianity
* Communalism (Bookchin), a theory of government in which autonomous communities ...
in India.
Historians such as
Will Durant
William James Durant (; November 5, 1885 ŌĆō November 7, 1981) was an American historian and philosopher, best known for his eleven-volume work, '' The Story of Civilization'', which contains and details the history of Eastern and Western civil ...
described Islamic invasions of India as "The bloodiest story in history.
Jadunath Sarkar
Sir Jadunath Sarkar, (10 December 1870 ŌĆō 19 May 1958) was a prominent Indian historian and a specialist on the Mughal dynasty.
Sarkar was educated in English literature and worked as a teacher for some time but later shifted his focus to h ...
contends that several Muslim invaders were waging a systematic
jihad
''Jihad'' (; ) is an Arabic word that means "exerting", "striving", or "struggling", particularly with a praiseworthy aim. In an Islamic context, it encompasses almost any effort to make personal and social life conform with God in Islam, God ...
against Hindus in India to the effect that "Every device short of massacre in cold blood was resorted to in order to convert heathen subjects".
Hindus who converted to Islam however were not completely immune to persecution due to the
caste system among Muslims
Muslim communities in South Asia have a system of social stratification arising from concepts other than "pure" and "impure", which are integral to the caste system in India. It developed as a result of relations among foreign conquerors, local up ...
in India established by
Ziauddin al-Barani in the ''Fatawa-i Jahandari'', where they were regarded as an "Ajlaf" caste and subjected to discrimination by the "Ashraf" castes.
Others argue that, during the Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent, Indian-origin religions experienced persecution from various Muslim conquerors who massacred Hindus, Jains and Buddhists, attacked temples and monasteries, and forced conversions on the battlefield.
Disputers of the "conversion by the sword" point to the presence of the large Muslim communities found in Southern India, Sri Lanka, Western Burma,
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
,
Southern Thailand
Southern Thailand (formerly Southern Siam and Tambralinga) is the southernmost cultural region of Thailand, separated from Central Thailand by the Kra Isthmus.
Geography
Southern Thailand is on the Malay Peninsula, with an area of around , bo ...
,
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, Malaysia and the Philippines coupled with the distinctive lack of equivalent Muslim communities around the heartland of historical Muslim empires in the Indian subcontinent as a refutation to the "conversion by the sword theory". The legacy of the Muslim conquest of South Asia is a hotly debated issue and argued even today.
Muslim invaders were not all simply raiders. Later rulers fought on to win kingdoms and stayed to create new ruling dynasties. The practices of these new rulers and their subsequent heirs (some of whom were born to Hindu wives) varied considerably. While some were uniformly hated, others developed a popular following. According to the memoirs of
Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
who travelled through Delhi in the 14th century, one of the previous sultans had been especially brutal and was deeply hated by Delhi's population. Batuta's memoirs also indicate that Muslims from the Arab world,
Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and
Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
were often favoured with important posts at the royal courts, suggesting that locals may have played a somewhat subordinate role in the Delhi administration. The term "Turk" was commonly used to refer to their higher social status. S.A.A. Rizvi (''The Wonder That Was India ŌĆō II'') however points to
Muhammad ibn Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq (; ; 1290 ŌĆō 20 March 1351), or Muhammad II, also named Jauna Khan as Crown Prince, further known by his epithets, The Eccentric Prince, or The Mad Sultan, was the eighteenth Sultan of Delhi. He reigned from 4 February ...
as not only encouraging locals but promoting artisan groups such as cooks, barbers and gardeners to high administrative posts. In his reign, it is likely that conversions to Islam took place as a means of seeking greater social mobility and improved social standing.
Numerous temples were destroyed by Muslim conquerors.
Richard M. Eaton lists a total of 80 temples that were desecrated by Muslim conquerors,
but notes this was not unusual in
medieval India
Medieval India was a long period of post-classical history in the Indian subcontinent between the ancient and modern periods. It is usually regarded as running approximately from the break-up of the Gupta Empire in the 6th century to the star ...
where numerous temples were also desecrated by Hindu and Buddhist kings against rival Indian kingdoms during conflicts between devotees of different Hindu deities, and between Hindus, Buddhists and Jains.
He also notes there were many instances of the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries. , which often had Hindu ministers, ordering the protection, maintenance and repairing of temples.
K. S. Lal, in his book ''
Growth of Muslim Population in Medieval India'', claimed that between 1000 and 1500 the Indian population decreased by 30 million, but stated his estimates were tentative and did not claim any finality.
His work has come under
criticism
Criticism is the construction of a judgement about the negative or positive qualities of someone or something. Criticism can range from impromptu comments to a written detailed response. , ''the act of giving your opinion or judgment about the ...
by historians such as
Simon Digby (
SOAS, University of London
The School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS University of London; ) is a public university, public research university in London, England, and a constituent college, member institution of the federal University of London. Founded in 1916, ...
) and
Irfan Habib
Irfan Habib (born 10 August 1931) is an Indian historian of ancient and medieval India, following the methodology of Marxist historiography in his contributions to economic history. He is known for his strong stance against Hindutva. He has au ...
for its agenda and lack of accurate data in pre-census times.
Different population estimates by economics historians
Angus Maddison
Angus Maddison (6 December 1926 ŌĆō 24 April 2010) was a distinguished British economist specialising in quantitative macro economic history, including the measurement and analysis of economic growth and development.
Maddison lectured at sev ...
and Jean-Noël Biraben also indicate that India's population did not decrease between 1000 and 1500, but increased by tens of millions during that time. The
Indian population estimates from other economic historians including
Colin Clark, John D. Durand and
Colin McEvedy
Colin Peter McEvedy (6 June 1930 ŌĆō 1 August 2005) was a British polymath scholar, psychiatrist, historian, demographer and non-fiction author.
Early life
Colin Peter McEvedy was born in Salford, Lancashire on 6 June 1930. He was the third ...
also show there was a population increase in India between 1000 and 1500.
Expansion of trade

Expansion of trade brought India into contact with Islam. Arab traders settled in Indian ports. In the seventh century, they converted to Islam, giving rise to small Muslim communities. These communities grew due to Indian conversions and because Hindu kings of south India (such as the
Cholas
The Chola dynasty () was a Tamil dynasty originating from Southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd cen ...
) hired Muslim
mercenaries
A mercenary is a private individual who joins an War, armed conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rath ...
.
A significant aspect of the Muslim period in world history was the emergence of Islamic
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' ...
courts capable of imposing a common commercial and legal system that extended from
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to AlgeriaŌĆōMorocc ...
in the West to
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
in the North East and Indonesia in the South East. While southern India was already in trade with Arabs/Muslims, northern India found new opportunities. As the Hindu and Buddhist kingdoms of Asia were subjugated by Islam, and as Islam spread through Africa, it became a highly centralising force that facilitated in the creation of a common legal system that allowed letters of credit issued in say
Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
or
Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
to be honoured in India or Indonesia (sharia has laws on the transaction of business with both Muslims and non-Muslims). To cement their rules, Muslim rulers initially promoted a system in which there was a revolving door between the clergy, the administrative nobility and the mercantile classes. The travels of explorer Muhammad Ibn-Abdullah
Ibn-Batuta were eased because of this system. He served as an Imam in Delhi, as a judicial official in the Maldives, and as an envoy and trader in the Malabar. There was never a contradiction in any of his positions because each of these roles complemented the other. Islam created a compact under which political power, law and religion became fused in a manner so as to safeguard the interests of the mercantile class. This led world trade to expand to the maximum extent possible in the medieval world.
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri (born Farid al-Din Khan; 1472 or 1486 ŌĆō 22 May 1545), also known by his title Sultan Adil (), was the ruler of Bihar from 1530 to 1540, and Sultan of Hindustan from 1540 until his death in 1545. He defeated the Mughal Empire, ...
took initiatives in improvement of trade by abolishing all taxes which hindered progress of free trade. He built large networks of roads and constructed
Grand Trunk Road
Grand Trunk Road (formerly known as Uttarapath, Sadak-e-Azam, Shah Rah-e-Azam, Badshahi Sadak, and Long Walk) is one of Asia's oldest and longest major roads. For at least 2,500 years it has linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. It r ...
(1540ŌĆō1544), which connects
Chittagong
Chittagong ( ), officially Chattogram, (, ) (, or ) is the second-largest city in Bangladesh. Home to the Port of Chittagong, it is the busiest port in Bangladesh and the Bay of Bengal. The city is also the business capital of Bangladesh. It ...
to
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A ...
; parts of it are still in use today. The geographic regions add to the diversity of languages and politics.
Cultural influence
The divide and rule policies, two-nation theory, and subsequent partition of
British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
in the wake of Independence from the
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
has polarised the sub-continental psyche, making objective assessment hard in comparison to the other settled agricultural societies of India from the North West. Muslim rule differed from these others in the level of assimilation and syncretism that occurred. They retained their identity and introduced legal and administrative systems that superseded existing systems of social conduct and ethics. While this was a source of friction it resulted in a unique experience the legacy of which is a Muslim community strongly Islamic in character while at the same time distinctive and unique among its peers.
The impact of Islam on Indian culture has been inestimable. It permanently influenced the development of all areas of human endeavour ŌĆō language, dress, cuisine, all the art forms, architecture and urban design, and social customs and values. Conversely, the languages of the Muslim invaders were modified by contact with local languages, to Urdu, which uses the
Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widel ...
. This language was also known as
Hindustani
Hindustani may refer to:
* something of, from, or related to Hindustan (another name of India)
* Hindustani language, an Indo-Aryan language, with Hindi and Urdu being its two standard registers
* Hindustani Muslims are the Urdu-speaking, Hindust ...
, an umbrella term used for the vernacular terminology of
Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
as well as
Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
, both major languages in South Asia today derived primarily from
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
grammatical structures and vocabulary.
Muslim rule saw a greater urbanisation of India and the rise of many cities and their urban cultures. The biggest impact was upon trade resulting from a common commercial and legal system extending from Morocco to Indonesia. This change of emphasis on mercantilism and trade from the more strongly centralised governance systems further clashed with the agricultural based traditional economy and also provided fuel for social and political tensions.
A related development to the shifting economic conditions was the establishment of Karkhanas, or small factories and the import and dissemination of technology through India and the rest of the world. The use of ceramic tiles was adopted from architectural traditions of Iraq, Iran, and Central Asia. Rajasthan's blue pottery was a local variation of imported Chinese pottery. There is also the example of Sultan Abidin (1420ŌĆō1470) sending Kashmiri artisans to
Samarqand
Samarkand ( ; Uzbek and Tajik: ąĪą░ą╝ą░čĆęøą░ąĮą┤ / Samarqand, ) is a city in southeastern Uzbekistan and among the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Central Asia. Samarkand is the capital of the Samarkand Region and a district-level ...
to learn book-binding and paper making. Khurja and Siwan became renowned for pottery,
Moradabad
Moradabad () is an industrial city, commissionerate, and municipal corporation in Moradabad district of the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is situated on the banks of the Ramganga river, at a distance of from the national capital, New Del ...
for brass ware,
Mirzapur
Mirzapur () is a city in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is known for its carpets and brassware industries, and the tradition of kajari and birha music. Straddled by the Kaimur extension of Vindhya mountains, it served as the headquarters of t ...
for carpets,
Firozabad
Firozabad () is a city near Agra in Firozabad district in the state of Uttar Pradesh in India. It is the centre of India's glassmaking industry and is known for the quality of the bangles and glassware produced here.
During the reign of Akba ...
for glass wares,
Farrukhabad
Farrukhabad is a city in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Farrukhabad tehsil. This city is on the banks of river Ganges is from the national capital Delhi and from the state capital Lucknow.
His ...
for printing,
Sahranpur and
Nagina
Nagina is a town and a municipal board in Bijnor district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh.
Name
According to Paul Whalley, the name ''Nag─½n─ü'' may ultimately come from Sanskrit ''n─üga''-ina', meaning "snake lord", via a regularly-de ...
for wood-carving,
Bidar
Bidar ( ) is a city and headquarters of the Bidar district in Karnataka state of India. Bidar is a prominent place on the archaeological map of India, it is well known for architectural, historical religious and rich heritage sites. Pictures ...
and
Lucknow
Lucknow () is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and the largest city of the List of state and union territory capitals in India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh and it is the administrative headquarters of the epon ...
for bidriware, Srinagar for papier-mache,
Benaras
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of ...
for jewellery and textiles, and so on. On the flip-side encouraging such growth also resulted in higher taxes on the peasantry.
Numerous Indian scientific and mathematical advances and the
Hindu numerals
Hindus (; ; also known as San─ütan─½s) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym San─ütana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also bee ...
were spread to the rest of the world
and much of the scholarly work and advances in the sciences of the age under Muslim nations across the globe were imported by the liberal patronage of arts and sciences by the rulers. The languages brought by Islam were modified by contact with local languages leading to the creation of several new languages, such as Urdu, which uses the modified
Arabic script
The Arabic script is the writing system used for Arabic (Arabic alphabet) and several other languages of Asia and Africa. It is the second-most widely used alphabetic writing system in the world (after the Latin script), the second-most widel ...
, but with more Persian words. The influences of these languages exist in several dialects in India today.
Islamic and Mughal architecture and art is widely noticeable in India, examples being the
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal ( ; ; ) is an ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in Agra, Uttar Pradesh, India. It was commissioned in 1631 by the fifth Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor, Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his belo ...
and
Jama Masjid
A congregational mosque or Friday mosque (, ''masjid j─ümiŌĆś'', or simply: , ''j─ümiŌĆś''; ), or sometimes great mosque or grand mosque (, ''j─ümiŌĆś kabir''; ), is a mosque for hosting the Friday noon prayers known as ''jumu'ah''.See:
*
*
*
*
...
. At the same time, Muslim rulers destroyed many of the ancient Indian architectural marvels and converted them into Islamic structures, most notably at
Varanasi
Varanasi (, also Benares, Banaras ) or Kashi, is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world.*
*
*
* The city has a syncretic tradition of I ...
,
Mathura
Mathura () is a city and the administrative headquarters of Mathura district in the states and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located south-east of Delhi; and about from the town of Vrindavan. In ancient ti ...
,
Ayodhya
Ayodhya () is a city situated on the banks of the Sarayu river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ayodhya district as well as the Ayodhya division of Uttar Pradesh, India. Ayodhya became th ...
and the Kutub Complex in New Delhi.
Migration of Hindus

Few groups of
Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as San─ütan─½s) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym San─ütana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35ŌĆō37 Historically, the term has also be ...
s including
Rajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
s were entering what is today
Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
before the
fall of Chittor due to regular invasions of Muslims in India.
After the fall of Chittorgarh in 1303 by the
Alauddin Khilji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
of the
Khalji dynasty
The Khalji or Khilji dynasty was a Turco-Afghan dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate for three decades between 1290 and 1320. It was the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate which covered large swaths of the Indian subcontinent. , Rajputs from the region immigrated in large groups into what is today Nepal due to heavy religious persecution. The incident is supported by both the Rajput and Nepalese traditions.
Historian John T Hitchcock and
John Whelpton
John Francis Whelpton (born 24 March 1950) is a historian and linguist and a specialist in the history of Nepal about which he has written a number of books.Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
s from the 12th century.
Religious policies
General effect
Parts of India have been subject to Muslim rule from the period of
Muhammad ibn Qasim
MußĖźammad ibn al-Q─üsim al-Thaqaf─½ (; ŌĆō) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (and Punjab, part of ancient Sindh), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His militar ...
till the fall of the
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
. While there is a tendency to view the Muslim conquests and Muslim empires as a prolonged period of violence against Hindu culture, in between the periods of wars and conquests, there were harmonious Hindu-Muslim relations in most Indian communities,
and the Indian population grew during the medieval Muslim times. No populations were expelled based on their religion by either the Muslim or Hindu kings, nor were attempts made to annihilate a specific religion.
[: 'Quite apart from Akbar, most Indian medieval communities experienced harmonious relations, as Stuart Gordon explains: "No Muslim or Hindu enclaves were seized; populations were not expelled on the basis of religion. No prince publicly committed himself and all of his resources to the annihilation of the Other. Both Hindus and Muslims were routinely and without comment recruited into all the armies of the period."']
According to Romila Thapar, with the onset of Muslim rule all Indians, higher and lower caste were lumped together in the category of "Hindus". While higher-caste Indians regarded lower castes to be impure, they were now regarded as belonging to a similar category, which "in part accounts for the belief among many upper caste Hindus today that Hinduism in the last one thousand years has been through the most severe persecution that any religion in the world has ever undergone." Thapar further notes that "The need to exaggerate the persecution at the hands of the Muslim is required to justify the inculcation of anti-Muslim sentiments among the Hindus of today."
Hindutva-allies have even framed the Muslim violence against Hindu expressions of faith as a "Hindu Holocaust".
Romila Thapar
Romila Thapar (born 30 November 1931) is an Indian historian. Her principal area of study is ancient India, a field in which she is pre-eminent. Quotr: "The pre-eminent interpreter of ancient Indian history today. ... " Thapar is a Professor ...
states that the belief in a severe persecution in the last millennium brushes away the "various expressions of religious persecution in India prior to the coming of the Muslims and particularly between the Śaiva and the Buddhist and Jaina sects". She questions what persecution means, and if it means religious conversions, she doubts that conversions can be interpreted as forms of persecution. It is quite correct to mention that Muslim iconoclasts destroyed temples and the broke images of Hindus, states Thapar, it should also be mentioned that Muslim rulers made donations to Hindu sects during their rule.
During the Islamic rule period, states
David Lorenzen
David Neal Lorenzen is a British-American historian, scholar of Religious studies, essayist, and emeritus professor of South Asian history at the Centre for Asian and African studies, El Colegio de M├®xico in Mexico City.
He is chiefly notable fo ...
, there was state-sponsored persecution against Hindus, yet it was sporadic and directed mostly at Hindu religious monuments. According to Deepa Ollapally, the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb was clearly discriminatory towards Hindu and all other non-Muslims, displaying an "unprecedented level of religious bigotry", but perhaps this was a consequence of the opposition he faced from a number of his family members. During the medieval span, she states, "episodes of direct religious persecution of Hindus were rare", as were communal riots between Hindus and Muslims.
Destruction of religious architecture
According to Wink, the mutilation and destruction of Hindu religious idols and temples were an attack on Hindu religious practice, and the Muslim destruction of religious architecture was a means to eradicate the vestiges of Hindu religious symbols. Muslim texts of this period justify it based on their contempt and abhorence for idols and idolators in Islamic thought. Jackson notes that the Muslim historians of the medieval era viewed the creation and expansion of Islamic Sultanates in Hindustan as "holy war" and a religious conquest, characterizing Muslim forces as "the army of Islam" and the Hindus as infidels.
Yet, states Jackson, these records need to be interpreted and relied upon with care given their tendencies to exaggerate. This was not a period of "uncompromising iconoclasm", states Jackson. Cities that quickly surrendered to the Islamic army, says Jackson, "got a better deal" for their religious monuments.
According to Richard Davis, targeting sacred temples was not unique to Muslim rulers in India. Some Hindu kings too, prior to the formation of first Islamic sultanates in India, expropriated sacred idols from temples and took it back to their capitals as a political symbol of victory. However, the sacred temples, icons and the looted image carried away was still sacred and treated with respect by the victorious Hindu king and his forces, states Richard Davis. There is hardly any evidence of "mutilation of divine images and intentional defilement" of Hindu sacred icons or temples by armies in control of Hindu rulers. The evidence that is available suggests that the victorious Hindu kings undertook significant effort to house the expropriated images in new, grand temples within their kingdom. According to Wink, Hindu destruction of Buddhist and Jain places of worship took place before the 10th century, but the evidence for such 'Hindu iconoclasm' is incidental, too vague, and unconvincing. According to Wink, mutilation and defilement of sacred icons is rarely evidenced in Hindu texts, in contrast to Muslim texts on the Islamic iconoclasm in India.
Effect on Hindu learning
The destruction of temples and educational institutions, the killings of learned monks and the scattering of students, led to a widespread decline in Hindu education. With the fall of Hindu kings, science research and philosophy faced some setbacks due to a lack of funding, royal support, and an open environment. Despite unfavourable treatment under the Muslim rule, Brahmanical education continued and was also patronised by rulers like Akbar and others.
Bukka Raya I
Bukka Raya I (reigned 1356ŌĆō24 February 1377) was an emperor of the Vijayanagara Empire from the Sangama Dynasty.Phrof A V Narasimha MurthyRare Royal Brothers: Hakka and Bukka He was a son of Bhavana Sangama, claimed by Harihara II to be of ...
, one of the founders of Vijaynagar Empire, had taken steps to rehabilitate Hindu religious and cultural institutions which suffered a serious setback under Muslim rule. Buddhists centres of learning decayed, leading to the rise to prominence of Brahmanical institutions.
While
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
language and research on Vedanta, Vedantic philosophy faced a period of struggle, with Muslim rulers often targeting well-established and well-known educational institutions that were often suffering at the time, the traditional educational institutions in villages continued as before,
vernacular regional languages based on Sanskrit thrived. A lot of Vedantic literature got translated into these languages between 12th to 15th centuries.
Muhammad bin-Qasim and the ''Chach Nama''
Muslim conquest of the Indian subcontinent began in early 8th century CE with a
Muhammad ibn Qasim
MußĖźammad ibn al-Q─üsim al-Thaqaf─½ (; ŌĆō) was an Arab military commander in service of the Umayyad Caliphate who led the Muslim conquest of Sindh (and Punjab, part of ancient Sindh), inaugurating the Umayyad campaigns in India. His militar ...
-led army. This campaign is narrated in the ''Chach Nama'' by Bakr Kūfī, a 13th-century manuscript which claimed to be based on an earlier Arabic record.
Content
The ''Chach Nama'' mentions temple demolitions, mass executions of resisting Sindhi forces and the enslavement of their dependents; kingdoms ruled by Hindu and Buddhist kings were attacked, their wealth plundered, tribute (''kharaj'') settled and hostages taken, often as slaves to Iraq. According to Andr├® Wink, a historian specializing in Indo-Islamic period in South Asia, these Hindus were given the choice to either convert to Islam and join the Arab armies, or be sealed (tattooing the hands) and pay Jizya (a tax).
The ''Chach Nama'' and evidence in other pre-11th century Persian texts suggests that these Hindu Jats also suffered restrictions and discrimination as non-Muslims, as was then usual elsewhere for the non-Muslim subjects (''ahl adh-dhimma'') per the Islamic law (Sharia), states Wink.
Yohanan Friedmann however finds that the ''Chach Nama'' holds that most contemporary religious as well as political authorities collaborated with the invaders, and those who promptly surrendered were not only gifted with huge sums of money but also entrusted to rule conquered territories.
Friedmann also notes that bin-Qasim "gave his unqualified blessing to the characteristic features of the society"ŌĆöhe reappointed every deposed Brahmin (of Brahmanabad) to their jobs, exempted them from Jizya, allowed holding of traditional festivals, and granted protection to temples but enforced the caste-hierarchy with enhanced vigor, drawing from Sharia, as evident from his treatment of Jats. Overall, Friedmann concludes that the conquest, as described in the ''Chach Nama'', did "not result in any significant changes in the structure of Indian society".
According to Johnson and Koyama, quoting Bosworth, there were "certainly massacres in the towns" in the early stages of campaign against pagan Hindus in Sind, but eventually they were granted ''dhimmi'' status and peace treaties were made with them.
After the conquest of Sindh, Qasim chose the Hanafi school of Islamic law which stated that, when under Muslim rule, people of Indic religions such as Hindus, Buddhists, and Jains are to be regarded as ''dhimmis'' (from the Arab term) as well as "People of the Book" and are required to pay
jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
for religious freedom.
Doubtful source
The historicity of the ''Chach Nama'' has been questioned. Francesco Gabrieli considers the ''Chach Nama'' to be a "historical romance" which was "a late and doubtful source" for information about bin-Qasim and must be carefully sieved to locate the facts; on such a reading, he admired bin-Qasim's proclamations concerning "principle of tolerance and religious freedom".
Peter Hardy (historian), Peter Hardy takes a roughly similar stance and lenses the work as a work of "political theory".
Manan Ahmed Asif criticizes the very premises of recovering portions of the ''Chach Nama'' as a historical chronicle of Muslim conquest; he argues that the site and times of production dictated its entire content, and that it must be read in entirety, as an original work in the genre of "political theory" where history is creatively extrapolated with romantic fiction to gain favor in the court of Nasiruddin Qabacha.
Wink states that some scholars treat the ''Chach Nama'' and other Muslim texts of its era, as "largely pseudo-history". He concurs that the skepticism about each individual source is justified and the ''Chach Nama'' is part fiction. Yet, adds Wink, taken together the common elements in these diverse sources suggest that Hindus were treated as ''dhimmis'' and targeted for certain discriminatory measures prescribed in the Sharia, as well as entitled to protection and limited religious freedoms in a Muslim state.
Early sultanates (11thŌĆō12th century)
Muslim texts of that period are replete with iconoclast rhetoric, descriptions of mass-slaughter of Hindus, and repeat ad nauseam that "the army of Islam obtain[ed] abundant wealth and unlimited riches" from the conquered sites.
The Hindus are described in these Islamic texts as infidels, Hindustan as war zone ("Dar-al-Harb"), and attacks on pagan Hindus as a part of a holy war (''jihad''), states Peter Jackson (historian), Peter Jackson. However, states Wink, this killing was not systematic and "was normally confined to the 'fighting men'" though the wars and episodes of routine violence did precipitate a great famine with civilian casualties in tens of thousands. The pervasive and most striking feature of the Arabic literature on Sind and Hind of the 11th to 13th-century is its constant obsession with idol worship and polytheism in the Indian subcontinent. There is piecemeal evidence of iconoclasm that began in Sind region, but the wholesale and more systematic onslaught against major Hindu religious monuments is evidenced in North India.
Richard M. Eaton, Richard Eaton, Sunil Kumar,
Romila Thapar
Romila Thapar (born 30 November 1931) is an Indian historian. Her principal area of study is ancient India, a field in which she is pre-eminent. Quotr: "The pre-eminent interpreter of ancient Indian history today. ... " Thapar is a Professor ...
, Richard H. Davis and others argue that these iconoclastic actions were not primarily driven by religious zeal, but were politically strategic acts of destruction in that temples in medieval India were sites associated with sovereignty, royal power, money, and authority.
According to Wink, the iconoclasm was a product of "religious, economic and political" motives and the practice undoubtedly escalated due to the "vast amounts of immobilized treasure" in these temples. As the Indo-Islamic conquests of the 11th and 12th centuries moved beyond Panjab and the Himalayan foothills of the northwest into the Ganges-Yamuna Doab region, states Andre Wink, "some of the most important sacred sites of Indian culture were destroyed and desecrated,"
and their broken parts consistently reused to make Islamic monuments. Phyllis Granoff notes that "medieval Indian religious groups faced a serious crisis as invading Muslim armies sacked temples and defaced sacred image".
The 11th and 12th centuries additionally witnessed the rise of irregulars and then Banjara-like groups who adopted Islam. These were "marauding bands" who caused much suffering and destruction in the countryside as they searched for food and supplies during the violent campaign of Ghurids against Hindustan. The religious icons of Hindus were one of the targets of these Islamic campaigns.
The 11th to 13th-century period did not witness any systematic attempts at forced conversions of Hindus into Muslims, nor is there evidence of widespread Islamicization in ''al-Hind'' that emerged from the violent conquest. The political power shifted from Hindu kings to Muslim sultans in conquered areas. If some temples were not destroyed in these areas, it did result in a loss to Hindu temple building patronage and an uprooting of Hindu sacred geography.
The second half of the 13th-century witnessed raids on Hindu kingdoms by Muslim forces controlling the northwest and north India, states Peter Jackson.
[ These did not lead to sustained persecution of the Hindus in the targeted kingdoms, because the Muslim armies merely looted the Hindus, took cattle and slaves, then left. The raids caused suffering, yet also rallied the Islamic faithfuls and weakened the infidel prince by weakening his standing among his Hindu subjects.]
Delhi Sultanate (13thŌĆō16th century)
The Delhi Sultanate started in the 13th-century and continued through the early 16th century, when the Mughal conquest replaced it. The Delhi Sultans of this period saw themselves first and foremost as Islamic rulers, states Peter Jackson, for the "people of Islam".[ These medieval Muslim rulers were "protecting and advancing the Islamic faith", with two Muslim texts of this period remarking that the Sultan had a duty "eradicate infidelity and humiliate his Hindu subjects".][
Some of the conquered Hindu subjects of the Delhi Sultanate served these Sultans, who states Jackson, were "doubtless usually slaves". These Hindus built the mosques of this era as well as developed the Indo-Islamic architecture, some served the court in roles such as treasurers, clerks, minting of new coins, and others. These Hindus were not persecuted, instead some were rewarded with immunities and tax exemptions.][ Some Sultans adopted Indian customs such as ceremonial riding of elephants by kings, thus facilitating the public perception of the new monarch. This suggest that the Sultans cultivated some Hindus to serve their aims, rather than indiscriminately persecute every Hindu.][
In general, Hindu subjects of Delhi Sultanate were generally accepted as people with ''dhimmi'' status, not equal to Muslims, but "protected", subject to Jizya tax and with a list of restrictions. Early Sultans of the Delhi Sultanate exempted the Brahmins from having to pay Jizya, thus dividing the Hindus and placing the discriminatory tax burden entirely on the non-Brahmin strata of the Hindu society. Firuz Shah was the first to impose the Jizya on Brahmins, and wrote in his autobiography that countless Hindus converted to Islam when he issued the edict that conversion would release them of the requirement to pay Jizya.][
The Muslim commanders of Delhi Sultanate regularly raided Hindu kingdoms for plunder, mulct their treasuries and looted the Hindu temples therein, states Jackson. These conquests of Delhi Sultanate armies damaged or destroyed many Hindu temples. Yet, in a few instances, after the war, the Sultans let the Hindus repair and reconstruct their temples. Such instances, states Jackson, has been cited by the Indian scholar P.B. Desai as evidence of "striking degree of tolerance" by Muslim Sultans. But, this happened in frontier areas after they had recently been conquered and placed in direct Muslim rule, where the Sultan's authority was "highly precarious".][
Some modern era Indian texts mention that Hindu and Jain temples of Delhi Sultanate era received endowments from Muslim authorities, presenting these as evidence of lack of persecution during this period. It is "not beyond the bounds of possibility" that in some instances this happened.][ But generally, states Jackson, the texts and even the memoirs written by the some Sultans themselves describe how they "set about destroying new temples and replacing them with mosques", and in one case depopulated a town of Hindus and resettled Muslims there. Jackson clarifies that the evidence suggests that the destroyed temples were "new temples", and not the old one's near Delhi whose devotees were already paying regular Jizya to the Sultan's treasuries.][
The Muslim nobles and advisors of the Sultans championed persecution of Hindus. The Muslim texts of that era, states Jackson, frequently mention themes such as the Hindu "infidels must on no account be allowed to live in ease and affluence", they should not be treated as "Peoples of the Book" and the Sultan should "at least refrain from treating Hindus with honour or permitting idolatry in the capital".][ Failure to slaughter the Hindus has led to polytheism taking root. Another ''wazir'' while theoretically agreeing to these view, stated that this would not be practical given the small population of Muslims and such a policy should be deferred till Muslims were in a stronger position. If eradication of Hindus is not possible, suggested another Muslim official, then the Hindus should at least be insulted, disgraced and dishonored.][ These views were not exceptions, rather consistent with Islamic thinking of that era and are "commonly encountered in polemical writing against the infidel in different parts of the Islamic world at different times", states Jackson.][
]
Madurai Sultanate
First campaigns
The army of Ala al-Din Khalji from Delhi Sultanate began their first campaign in 1310 against the Hindu kingdom in Madurai region ŌĆō called Ma'bar by court historians, under the pretext of helping Sundar Pandya. According to Mehrdad Shokoohy ŌĆō a scholar of Islamic studies and architectural history in Central and South Asia ŌĆō this campaign lasted for a year during which Madurai and other Tamil region cities were overrun by the Muslims, the Hindu temples were demolished and the towns looted.[ A detailed record about the campaign by Amir Khusrau the destruction and plunder.][ The governor later rebelled, founded the short lived Madurai Sultanate and renamed himself as Sultan Ahsan Shah in 1334. The successive sultans of the new Sultanate did not have the support of the regional Hindu population. The Madurai Sultanate's army, states Shokoohy, "often exercised fierce and brutal repressive methods on the local people".][ The Sultanate faced constant battles with neighboring Hindu states and assassination by its own nobles. Sultan Sikandar Shah was the last sultan. He was killed by the invading forces of Vijayanagara Empire army in 1377.][ Another record states, "he engaged in a holy war (ghaza) and killed a great number of infidels".]
Mughal Empire
The Mughal emperor Akbar has been a celebrated unusual example of tolerance. Indologist Richard Eaton writes that from Akbar's time to today, he has attracted conflicting labels, "from a strict Muslim to an apostate, from a free-thinker to a Crypto-Hinduism, crypto-Hindu, from a Zoroastrian to a proto-Christian, from an Atheism, atheist to a radical innovator". As a youth, states Eaton, Akbar studied Islam under both Shia and Sunni tutors, but as an adult he looked back with regret on his early life, confessing that in those days he had "persecuted men into conformity with my faith and deemed it Islam". In his later years he felt "an internal bitterness, acknowledging that his soul had been 'seized with exceeding sorrow for what he had done before launching his campaign to "treat all Mughal subjects, regardless of religion, on a basis of legal equality before the state".
Aurangzeb
The reign of Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 ŌĆō 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becomi ...
(1658ŌĆō1707) witnessed one of the strongest campaigns of religious violence in the Mughal Empire's history. Aurangzeb is a controversial figure in modern India, often remembered as a "vile oppressor of Hindus". During his rule Aurangzeb expanded the Mughal Empire, conquering much of southern India through long bloody campaigns against non-Muslims. He forcibly converted Hindus to Islam and destroyed Hindu temples. He also re-introduced the ''jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
'', a tax on non-Muslims, which had been suspended for the previous 100 years by his great-grandfather Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, ŌĆō ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
.
Aurangzeb ordered the desecration and destruction of temples when conquering new lands and putting down rebellions, punishing political leaders by destroying the temples that symbolized their power.[
The persecution during the Islamic period targeted non-Hindus as well. In some cases, such as towards the end of Mughal era, the violence and persecution was mutual. Hindus too attacked and damaged Muslim tombs, even when the troops had orders not to harm religious refuges of Muslims. These "few examples of disrespect for Islamic sites", states Indologist Nicholas Gier, "pale in comparison to the great destruction of temples and general persecution of Hindus by Muslims for 500 years".]
Iconoclasm
During the Muslim conquest of Sindh (Sindh Region)
Historian Upendra Thakur records the persecution of Hindus and Buddhists:
Iconoclasm under the Delhi Sultanate
Historian Richard Eaton has tabulated a campaign of destruction of idols and temples by Delhi Sultans, intermixed with instances of years where the temples were protected from desecration.Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
inscription notes that Sultan Muhammad bin Tughluq repaired a Siva temple in Bidar
Bidar ( ) is a city and headquarters of the Bidar district in Karnataka state of India. Bidar is a prominent place on the archaeological map of India, it is well known for architectural, historical religious and rich heritage sites. Pictures ...
after his Deccan Plateau, Deccan conquest. There was often a pattern of Delhi sultans plundering or damaging temples during conquest, and then patronizing or repairing temples after conquest. This pattern came to an end with the Mughal Empire, where Akbar
Akbar (Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar, ŌĆō ), popularly known as Akbar the Great, was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expa ...
's chief minister Abu'l-Fazl ibn Mubarak, Abu'l-Fazl criticized the excesses of earlier sultans such as Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 ŌĆō 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
.jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Soc ...
(fee, tax). For example, according to Ibn Battuta's account, a proposal by the Yuan dynasty emperor of China to repair Himalayan Buddhist temples destroyed by the Sultanate army was refused, on the grounds that such temple repairs were only allowed if the Chinese agreed to pay jizya tax to the treasury of the Sultanate. According to Eva De Clercq, an expert in the study of Jainism, the Delhi Sultans did not strictly prohibit construction of new temples in the sultanate, Islamic law notwithstanding. In his memoirs, Firoz Shah Tughlaq describes how he destroyed temples and built mosques instead and killed those who dared build new temples. Other historical records from ''wazirs'', ''amirs'' and the court historians of various Sultans of the Delhi Sultanate describe the grandeur of idols and temples they witnessed in their campaigns and how these were destroyed and desecrated.
Nalanda
In 1193, the Nalanda University complex was destroyed by Afghan people, Afghan Khalji dynasty, KhaljiŌĆōGhilzai Muslims under Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiy─ür al-D─½n MußĖźammad Bin Bakhtiy─ür Khalj─½, also known as Bakhtiyar Khalji, was a Turko-Afghan Military General of the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor, who led the Muslim conquests of the eastern Indian regions of Bengal and parts of Bi ...
; this event is seen as the final milestone in the decline of Buddhism in India. He also burned Nalanda's major Buddhist library and Vikramshila University, as well as numerous Buddhist monasteries in India. When the Tibetan translator, Chag Lotsawa Dharmasvamin (Chag Lo-tsa-ba, 1197ŌĆō1264), visited northern India in 1235, Nalanda was damaged, looted, and largely deserted, but still standing and functioning with seventy students.
Mahabodhi, Sompura, Vajrasan and other important monasteries were found to be untouched. The Ghuri ravages only afflicted those monasteries that lay in the direct path of their advance and were fortified in the manner of defensive forts.
By the end of the 12th century, following the Muslim conquest of the Buddhist stronghold in Bihar, Buddhism, having already declined in the South, declined in the North as well because survivors retreated to Nepal, Sikkim and Tibet or escaped to the South of the Indian sub-continent.
Martand
 The Martand Sun Temple was built by the third ruler of the Karkota dynasty, Lalitaditya Muktapida, in the 8th century CE. The temple was completely destroyed on the orders of the Muslim ruler Sikandar Butshikan in the early 15th century, with demolition lasting a year. He is remembered for his strenuous efforts to convert the Hindus of Kashmir to Islam. These efforts included the destruction of numerous old temples, prohibition of Hindu rites and rituals, and even the wearing of clothes in the Hindu style.
The Martand Sun Temple was built by the third ruler of the Karkota dynasty, Lalitaditya Muktapida, in the 8th century CE. The temple was completely destroyed on the orders of the Muslim ruler Sikandar Butshikan in the early 15th century, with demolition lasting a year. He is remembered for his strenuous efforts to convert the Hindus of Kashmir to Islam. These efforts included the destruction of numerous old temples, prohibition of Hindu rites and rituals, and even the wearing of clothes in the Hindu style.
Vijayanagara
The city flourished between the 14th century and 16th century, during the height of the Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
. During this time, it was often in conflict with the kingdoms which rose in the Northern Deccan, and which are often collectively termed the Deccan Sultanates. The Vijaynagara Empire successfully resisted Muslim invasions for centuries. But in 1565, the empire's armies suffered a massive and catastrophic defeat at the hands of an alliance of the Sultanates, and the capital was taken. The victorious armies then razed, depopulated and destroyed the city over several months. The empire continued its slow decline, but the original capital was not reoccupied or rebuilt.
Somnath
Around 1024 CE, during the reign of Bhima I, Mahmud of Ghazni
Abu al-Qasim Mahmud ibn Sabuktigin (; 2 November 971 ŌĆō 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi (), was Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, ruling from 998 to 1030. During his reign and in medieval sources, he is usuall ...
raided Gujarat, and plundered the Somnath temple. According to an 1169 inscription, Bhima rebuilt the temple. This inscription does not mention any destruction caused by Mahmud, and states that the temple had "decayed due to time".Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
's army under the leadership of Ulugh Khan defeated Karandev II of the Vaghela dynasty, and sacked the Somnath temple.
 File:Somnath temple ruins (1869).jpg, alt=The Somnath temple in Gujarat was repeatedly destroyed by Islamic armies and rebuilt by Hindus. It was destroyed by Delhi Sultanate's army in 1299 CE. The present temple was reconstructed in Chaulukya style of Hindu temple architecture and completed in May 1951., The Somnath temple in Gujarat was repeatedly destroyed by Islamic armies and rebuilt by Hindus. It was destroyed by Delhi Sultanate's army in 1299 CE. The present temple was reconstructed in M─üru-Gurjara architecture, Chaulukya style of Hindu temple architecture and completed in May 1951.
File:Somnath temple ruins (1869).jpg, alt=The Somnath temple in Gujarat was repeatedly destroyed by Islamic armies and rebuilt by Hindus. It was destroyed by Delhi Sultanate's army in 1299 CE. The present temple was reconstructed in Chaulukya style of Hindu temple architecture and completed in May 1951., The Somnath temple in Gujarat was repeatedly destroyed by Islamic armies and rebuilt by Hindus. It was destroyed by Delhi Sultanate's army in 1299 CE. The present temple was reconstructed in M─üru-Gurjara architecture, Chaulukya style of Hindu temple architecture and completed in May 1951.Qutb ud-Din Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak (; 1150 ŌĆō 4 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid emperor Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in 1206, he established his own ...
.
File:Sun temple martand indogreek.jpg, Ruins of the Martand Sun Temple. The temple was destroyed on the orders of Muslim Sultan Sikandar Butshikan in the early 15th century, with demolition lasting a year.
File:Temple de Mînâkshî01.jpg, The armies of Delhi Sultanate led by Muslim Commander Malik Kafur plundered the Meenakshi Temple and looted it of its valuables.
File:Warangal fort.jpg, Kakatiya Kala Thoranam (Warangal Gate) built by the Kakatiya dynasty in ruins; one of the many temple complexes destroyed by the Delhi Sultanate.Qutb ud-Din Aibak
Qutb ud-Din Aibak (; 1150 ŌĆō 4 November 1210) was a Turkic general of the Ghurid emperor Muhammad Ghori. He was in charge of the Ghurid territories in northern India, and after Muhammad Ghori's assassination in 1206, he established his own ...
between 1200 and 1210, and it was destroyed by Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
in 1298.Alauddin Khalji
Alauddin Khalji (; ), born Ali Gurshasp, was a ruler from the Khalji dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the Indian subcontinent. Alauddin instituted a number of significant administrative changes in the Delhi Sultanate, related to revenue ...
.
File:Exteriors Carvings of Shantaleshwara Shrine 02.jpg, Exterior wall reliefs at Hoysaleswara Temple. The temple was twice sacked and plundered by the Delhi Sultanate.
See also
* Islam in South Asia
* Outline of South Asian history
* History of Afghanistan
* History of India
* History of Pakistan
* History of Bangladesh
* History of Islam
* Spread of Islam
* Islam and other religions
* Islam in Asia
* Muslim kingdoms in the Indian subcontinent
* Ghazwa-e-Hind
* List of early HinduŌĆōMuslim military conflicts in the Indian subcontinent
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan
* Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent
* MughalŌĆōMaratha Wars
The Deccan wars were a series of military conflicts between the Mughal Empire and the descendants of the Maratha Empire, Maratha ruler Shivaji from the time of Shivaji's death in 1680 until the death of Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. Shivaji was ...
(1680ŌĆō1707)
* AhomŌĆōMughal conflicts (1615ŌĆō1682)
* Aniconism
* Aniconism in Islam
* Iconoclasm
* Conversion of non-Islamic places of worship into mosques
Notes and references
Notes
Footnotes
Bibliography
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Alternative link
*
*
Alternative link
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* ŌĆ
India
Pakistan
External links
by Neria Harish Hebbar (article with several pages)
(Including an e-book on the various phases of Muslim Rulers conquering India)
Story of Pakistan
The Battle Between King Chach of Sindh and the Arabs
{{DEFAULTSORT:Muslim conquests on the Indian subcontinent
Spread of Islam
Muslim period in the Indian subcontinent
Medieval history of India
Medieval Hinduism
History of South Asia
Medieval Islamic world
Hinduism in South Asia
Islam in South Asia
Invasions of India
 The kingdoms of Kapisa-
The kingdoms of Kapisa- '' Meds'' pirates operated from their bases at Kutch,
'' Meds'' pirates operated from their bases at Kutch,  Muhammad Ghoris successors established the first dynasty of the
Muhammad Ghoris successors established the first dynasty of the  The Tughlaqs conquered Delhi with the support of the Khokhar tribes who formed the vanguard of the army. The Tughlaqs claimed to be "bound to all Indians by ties of blood and relation". Under the first ruler of the dynasty, Ghiyath al-Din Tughlaq, the Tughlaq court wrote a war ballad known as the
The Tughlaqs conquered Delhi with the support of the Khokhar tribes who formed the vanguard of the army. The Tughlaqs claimed to be "bound to all Indians by ties of blood and relation". Under the first ruler of the dynasty, Ghiyath al-Din Tughlaq, the Tughlaq court wrote a war ballad known as the  Informed about civil war in South Asia, Timur began a trek starting in 1398 to invade the reigning
Informed about civil war in South Asia, Timur began a trek starting in 1398 to invade the reigning  The term of Deccan Sultanates was used for five Muslim dynasties that ruled several late medieval Indian kingdoms, namely
The term of Deccan Sultanates was used for five Muslim dynasties that ruled several late medieval Indian kingdoms, namely  The
The  India in the early 16th century presented a fragmented picture of rulers who lacked concern for their subjects and failed to create a common body of laws or institutions. Outside developments also played a role in shaping events. The circumnavigation of Africa by the Portuguese explorer
India in the early 16th century presented a fragmented picture of rulers who lacked concern for their subjects and failed to create a common body of laws or institutions. Outside developments also played a role in shaping events. The circumnavigation of Africa by the Portuguese explorer  A descendant of both
A descendant of both  Ahmed Shah Abdali ŌĆō a
Ahmed Shah Abdali ŌĆō a  The single most important power to emerge in the Mughal dynasty was the Maratha Confederacy (1674ŌĆō1818). The Marathas are responsible, to a large extent for ending Mughal rule in India. The Maratha Empire ruled large parts of India following the decline of the Mughals. The long and futile war bankrupted one of the most powerful empires in the world. Mountstuart Elphinstone termed this a demoralizing period for the Muslims as many of them lost the will to fight against the Maratha Empire. The Maratha empire at its peak stretched from Trichinopoly (present day
The single most important power to emerge in the Mughal dynasty was the Maratha Confederacy (1674ŌĆō1818). The Marathas are responsible, to a large extent for ending Mughal rule in India. The Maratha Empire ruled large parts of India following the decline of the Mughals. The long and futile war bankrupted one of the most powerful empires in the world. Mountstuart Elphinstone termed this a demoralizing period for the Muslims as many of them lost the will to fight against the Maratha Empire. The Maratha empire at its peak stretched from Trichinopoly (present day  Considerable controversy exists both in scholarly and public opinion about the conversions to Islam typically represented by the following schools of thought:
# The bulk of Muslims are descendants of migrants from the
Considerable controversy exists both in scholarly and public opinion about the conversions to Islam typically represented by the following schools of thought:
# The bulk of Muslims are descendants of migrants from the  Few groups of
Few groups of  The Martand Sun Temple was built by the third ruler of the Karkota dynasty, Lalitaditya Muktapida, in the 8th century CE. The temple was completely destroyed on the orders of the Muslim ruler Sikandar Butshikan in the early 15th century, with demolition lasting a year. He is remembered for his strenuous efforts to convert the Hindus of Kashmir to Islam. These efforts included the destruction of numerous old temples, prohibition of Hindu rites and rituals, and even the wearing of clothes in the Hindu style.
The Martand Sun Temple was built by the third ruler of the Karkota dynasty, Lalitaditya Muktapida, in the 8th century CE. The temple was completely destroyed on the orders of the Muslim ruler Sikandar Butshikan in the early 15th century, with demolition lasting a year. He is remembered for his strenuous efforts to convert the Hindus of Kashmir to Islam. These efforts included the destruction of numerous old temples, prohibition of Hindu rites and rituals, and even the wearing of clothes in the Hindu style.
