
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses)
is a hand-held
pointing device that detects
two-dimensional
A two-dimensional space is a mathematical space with two dimensions, meaning points have two degrees of freedom: their locations can be locally described with two coordinates or they can move in two independent directions. Common two-dimension ...
motion relative to a surface. This motion is typically translated into the motion of the
pointer (called a cursor) on a
display, which allows a smooth control of the
graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
of a
computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
.
The first public demonstration of a mouse controlling a computer system was done by
Doug Engelbart in 1968 as part of the
Mother of All Demos. Mice originally used two separate wheels to directly track movement across a surface: one in the x-dimension and one in the Y. Later, the standard design shifted to use a ball rolling on a surface to detect motion, in turn connected to internal rollers. Most modern mice use
optical movement detection with no moving parts. Though originally all mice were connected to a computer by a cable, many modern mice are cordless, relying on short-range radio communication with the connected system.
In addition to moving a
cursor, computer mice have one or more
buttons to allow operations such as the selection of a menu item on a display. Mice often also feature other elements, such as touch surfaces and
scroll wheels, which enable additional control and dimensional input.
Etymology
The earliest known written use of the term ''mouse'' in reference to a computer pointing device is in
Bill English's July 1965 publication, "Computer-Aided Display Control".
This likely originated from its resemblance to the shape and size of a
mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
, with the cord resembling its
tail
The tail is the elongated section at the rear end of a bilaterian animal's body; in general, the term refers to a distinct, flexible appendage extending backwards from the midline of the torso. In vertebrate animals that evolution, evolved to los ...
.
The popularity of wireless mice without cords makes the resemblance less obvious.
According to Roger Bates, a hardware designer under English, the term also came about because the
cursor on the screen was, for an unknown reason, referred to as "CAT" and was seen by the team as if it would be chasing the new desktop device.
The plural for the small rodent is always "mice" in modern usage. The plural for a computer mouse is either "mice" or "mouses" according to most dictionaries, with "mice" being more common.
The first recorded plural usage is "mice"; the online ''
Oxford Dictionaries'' cites a 1984 use, and earlier uses include
J. C. R. Licklider's "The Computer as a Communication Device" of 1968.
History
Stationary trackballs
The
trackball, a related pointing device, was invented in 1946 by
Ralph Benjamin as part of a post-
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
-era
fire-control
A fire-control system (FCS) is a number of components working together, usually a gun data computer, a Director (military), director and radar, which is designed to assist a ranged weapon system to target, track, and hit a target. It performs th ...
radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
plotting system called the
Comprehensive Display System (CDS). Benjamin was then working for the British
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
Scientific Service. Benjamin's project used
analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses physical phenomena such as Electrical network, electrical, Mechanics, mechanical, or Hydraulics, hydraulic quantities behaving according to the math ...
s to calculate the future position of target aircraft based on several initial input points provided by a user with a
joystick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Also known as the control column, it is the principal control devic ...
. Benjamin felt that a more elegant
input device was needed and invented what they called a "roller ball" for this purpose.
The device was patented in 1947,
but only a prototype using a metal ball rolling on two rubber-coated wheels was ever built, and the device was kept as a military secret.
Another early trackball was built by
Kenyon Taylor, a British
electrical engineer
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
working in collaboration with Tom Cranston and Fred Longstaff. Taylor was part of the original
Ferranti Canada, working on the
Royal Canadian Navy
The Royal Canadian Navy (RCN; , ''MRC'') is the Navy, naval force of Canada. The navy is one of three environmental commands within the Canadian Armed Forces. As of February 2024, the RCN operates 12 s, 12 s, 4 s, 4 s, 8 s, and several auxiliary ...
's
DATAR (Digital Automated Tracking and Resolving) system in 1952.
DATAR was similar in concept to Benjamin's display. The trackball used four disks to pick up motion, two each for the X and Y directions. Several rollers provided mechanical support. When the ball was rolled, the pickup discs spun and contacts on their outer rim made periodic contact with wires, producing pulses of output with each movement of the ball. By counting the pulses, the physical movement of the ball could be determined. A
digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', wh ...
calculated the tracks and sent the resulting data to other ships in a task force using
pulse-code modulation
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitud ...
radio signals. This trackball used a standard Canadian
five-pin bowling ball. It was not patented, since it was a secret military project.
Engelbart's first "mouse"
Douglas Engelbart of the Stanford Research Institute (now
SRI International
SRI International (SRI) is a nonprofit organization, nonprofit scientific research, scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California, United States. It was established in 1946 by trustees of Stanford Univer ...
) has been credited in published books by
Thierry Bardini,
,
Howard Rheingold
Howard Rheingold (born 1947) is an American critic, writer, and teacher, known for his specialties on the cultural, social and political implications of modern communication media such as the Internet, mobile telephony and virtual communities.
B ...
,
and several others
as the inventor of the computer mouse. Engelbart was also recognized as such in various obituary titles after his death in July 2013.
By 1963, Engelbart had already established a research lab at SRI, the
Augmentation Research Center
SRI International's Augmentation Research Center (ARC) was founded in the 1960s by electrical engineer Douglas Engelbart to develop and experiment with new tools and techniques for collaboration and information processing.
The main product to ...
(ARC), to pursue his objective of developing both hardware and software computer technology to "augment" human intelligence. That November, while attending a conference on computer graphics in
Reno, Nevada
Reno ( ) is a city in the northwest section of the U.S. state of Nevada, along the Nevada–California border. It is the county seat and most populous city of Washoe County, Nevada, Washoe County. Sitting in the High Eastern Sierra foothills, ...
, Engelbart began to ponder how to adapt the underlying principles of the
planimeter
A planimeter, also known as a platometer, is a measuring instrument used to determine the area of an arbitrary two-dimensional shape.
Construction
There are several kinds of planimeters, but all operate in a similar way. The precise way in whic ...
to inputting X- and Y-coordinate data.
On 14 November 1963, he first recorded his thoughts in his personal notebook about something he initially called a "
bug", which is a "3-point" form could have a "drop point and 2 orthogonal wheels".
He wrote that the "bug" would be "easier" and "more natural" to use, and unlike a stylus, it would stay still when let go, which meant it would be "much better for coordination with the keyboard".

In 1964,
Bill English joined ARC, where he helped Engelbart build the first mouse prototype.
They christened the device the ''mouse'' as early models had a cord attached to the rear part of the device which looked like a tail, and in turn, resembled the common
mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
. According to Roger Bates, a hardware designer under English, another reason for choosing this name was because the cursor on the screen was also referred to as "CAT" at this time.
As noted above, this "mouse" was first mentioned in print in a July 1965 report, on which English was the lead author.
On 9 December 1968, Engelbart publicly demonstrated the mouse at what would come to be known as
The Mother of All Demos. Engelbart never received any royalties for it, as his employer SRI held the patent, which expired before the mouse became widely used in personal computers. In any event, the invention of the mouse was just a small part of Engelbart's much larger project of augmenting human intellect.
Several other experimental pointing-devices developed for Engelbart's oN-Line System (
NLS) exploited different body movements – for example, head-mounted devices attached to the chin or nose – but ultimately the mouse won out because of its speed and convenience. The first mouse, a bulky device (pictured) used two
potentiometers perpendicular to each other and connected to wheels: the rotation of each wheel translated into motion along one
axis. At the time of the "Mother of All Demos", Engelbart's group had been using their second-generation, 3-button mouse for about a year.
First rolling-ball mouse

On 2 October 1968, three years after Engelbart's prototype but more than two months before his public
demo, a mouse device named ' (German for "Trackball control") was shown in a sales brochure by the German company
AEG The initials AEG are used for or may refer to:
Common meanings
* AEG (German company)
; AEG) was a German producer of electrical equipment. It was established in 1883 by Emil Rathenau as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte El ...
-
Telefunken as an optional input device for the SIG 100 vector graphics terminal, part of the system around their process computer
TR 86 and the main frame.
Based on an even earlier trackball device, the mouse device had been developed by the company in 1966 in what had been a parallel and
independent discovery.
As the name suggests and unlike Engelbart's mouse, the Telefunken model already had a ball (diameter 40 mm, weight 40 g
) and two mechanical 4-bit
rotational
position transducers
with
Gray code
The reflected binary code (RBC), also known as reflected binary (RB) or Gray code after Frank Gray (researcher), Frank Gray, is an ordering of the binary numeral system such that two successive values differ in only one bit (binary digit).
For ...
-like
states, allowing easy movement in any direction.
The bits remained stable for at least two successive states to relax
debouncing requirements.
This arrangement was chosen so that the data could also be transmitted to the TR 86 front-end process computer and over longer distance
telex lines with 50
baud.
Weighing , the device with a total height of about came in a diameter hemispherical injection-molded thermoplastic casing featuring one central push button.
As noted above, the device was based on an earlier trackball-like device (also named ') that was embedded into radar flight control desks.
This trackball had been originally developed by a team led by at Telefunken for the German ' (Federal Air Traffic Control). It was part of the corresponding workstation system SAP 300 and the terminal SIG 3001, which had been designed and developed since 1963.
Development for the TR 440 main frame began in 1965.
This led to the development of the TR 86 process computer system with its SIG 100-86
terminal. Inspired by a discussion with a university customer, Mallebrein came up with the idea of "reversing" the existing trackball into a moveable mouse-like device in 1966,
so that customers did not have to be bothered with mounting holes for the earlier trackball device. The device was finished in early 1968,
and together with
light pens and
trackballs, it was commercially offered as an optional input device for their system starting later that year.
Not all customers opted to buy the device, which added costs of per piece to the already up to 20-million DM deal for the main frame, of which only a total of 46 systems were sold or leased.
They were installed at more than 20 German universities including
RWTH Aachen
RWTH Aachen University (), in German ''Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen'', is a German public research university located in Aachen, North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With more than 47,000 students enrolled in 144 study prog ...
,
Technische Universität Berlin,
University of Stuttgart and
Konstanz.
Several mice installed at the
Leibniz Supercomputing Centre in Munich in 1972 are well preserved in a museum,
two others survived in a museum at Stuttgart University,
two in Hamburg, the one from Aachen at the
Computer History Museum in the US,
and yet another sample was recently donated to the
Heinz Nixdorf MuseumsForum (HNF) in Paderborn.
Anecdotal reports claim that Telefunken's attempt to patent the device was rejected by the German Patent Office due to lack of inventiveness.
For the air traffic control system, the Mallebrein team had already developed a precursor to
touch screen
A touchscreen (or touch screen) is a type of electronic visual display, display that can detect touch input from a user. It consists of both an input device (a touch panel) and an output device (a visual display). The touch panel is typically l ...
s in form of an ultrasonic-curtain-based pointing device in front of the display.
In 1970, they developed a device named "
Touchinput-" ("touch input device") based on a conductively coated glass screen.
First mice on personal computers and workstations

The
Xerox Alto was one of the first computers designed for individual use in 1973 and is regarded as the first modern computer to use a mouse.
Alan Kay
Alan Curtis Kay (born May 17, 1940) published by the Association for Computing Machinery 2012 is an American computer scientist who pioneered work on object-oriented programming and windowing graphical user interface (GUI) design. At Xerox ...
designed the 16-by-16 mouse cursor icon with its left edge vertical and right edge 45-degrees so it displays well on the bitmap.Inspired by
PARC's Alto, the
Lilith
Lilith (; ), also spelled Lilit, Lilitu, or Lilis, is a feminine figure in Mesopotamian and Jewish mythology, theorized to be the first wife of Adam and a primordial she-demon. Lilith is cited as having been "banished" from the Garden of Eden ...
, a computer which had been developed by a team around
Niklaus Wirth
Niklaus Emil Wirth ( IPA: ) (15 February 1934 – 1 January 2024) was a Swiss computer scientist. He designed several programming languages, including Pascal, and pioneered several classic topics in software engineering. In 1984, he won the Tu ...
at
ETH Zürich between 1978 and 1980, provided a mouse as well. The third marketed version of an integrated mouse shipped as a part of a computer and intended for personal computer navigation came with the
Xerox 8010 Star in 1981.
By 1982, the Xerox 8010 was probably the best-known computer with a mouse. The
Sun-1 also came with a mouse, and the forthcoming
Apple Lisa was rumored to use one, but the peripheral remained obscure; Jack Hawley of The Mouse House reported that one buyer for a large organization believed at first that his company sold
lab mice. Hawley, who manufactured mice for Xerox, stated that "Practically, I have the market all to myself right now"; a Hawley mouse cost $415.
In 1982,
Logitech introduced the P4 Mouse at the Comdex trade show in Las Vegas, its first hardware mouse. That same year
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
made the decision to make the
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
program
Microsoft Word
Microsoft Word is a word processor program, word processing program developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983, under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems. Subsequent versions were later written for several other platf ...
mouse-compatible, and developed the first PC-compatible mouse. The
Microsoft Mouse shipped in 1983, thus beginning the
Microsoft Hardware division of the company.
However, the mouse remained relatively obscure until the appearance of the
Macintosh 128K
The Macintosh, later rebranded as the Macintosh 128K, is the original Mac (computer), Macintosh personal computer from Apple Inc., Apple. It is the first successful mass-market All-in-one computer, all-in-one desktop personal computer with a gr ...
(which included an updated version of the single-button
Lisa Mouse) in 1984, and of the
Amiga 1000 and the
Atari ST
Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the company's Atari 8-bit computers, 8-bit computers. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985, and was widely available i ...
in 1985. Aftermarket mice were offered, from the mid 1980s, for many 8-bit home computers, the like of the
Commodore 1351 being offered for the Commodore 64 and 128, as was the NEOS Mouse that was also offered for the
MSX
MSX is a standardized home computer architecture, announced by ASCII Corporation on June 16, 1983. It was initially conceived by Microsoft as a product for the Eastern sector, and jointly marketed by Kazuhiko Nishi, the director at ASCII Corpo ...
range, while the
AMX Mouse was offered for the Acorn BBC Micro and Electron, Sinclair ZX Spectrum, and Amstrad CPC lines.
Operation
A mouse typically controls the motion of a
pointer in two dimensions in a graphical user interface (GUI). The mouse turns movements of the hand backward and forward, left and right into equivalent electronic signals that in turn are used to move the pointer.
The relative movements of the mouse on the surface are applied to the position of the pointer on the screen, which signals the point where actions of the user take place, so hand movements are replicated by the pointer.
Clicking or pointing (stopping movement while the cursor is within the bounds of an area) can select files, programs or actions from a list of names, or (in graphical interfaces) through small images called "icons" and other elements. For example, a text file might be represented by a picture of a paper notebook and clicking while the cursor points at this icon might cause a text editing program to open the file in a window.
Different ways of operating the mouse cause specific things to happen in the GUI:
* Point: stop the motion of the pointer while it is inside the boundaries of what the user wants to interact with. This act of pointing is what the "
pointer" and "pointing device" are named after. In web design lingo, pointing is referred to as "hovering". This usage spread to web programming and Android programming, and is now found in many contexts.
* Click: pressing and releasing a button.
** (left)
Single-click: clicking the main button.
** (left)
Double-click
A double-click is the act of pressing a computer mouse button twice quickly without moving the mouse. Double-clicking allows two different actions to be associated with the same mouse button. It was developed by Tim Mott of Xerox Palo Alto Resear ...
: clicking the button two times in quick succession counts as a different gesture than two separate single clicks.
** (left)
Triple-click
Triple-click is the action of clicking a computer mouse button three times quickly without moving the mouse. Along with clicking and double-clicking, triple-clicking allows three different actions to be associated with the same mouse button. Cr ...
: clicking the button three times in quick succession counts as a different gesture than three separate single clicks. Triple clicks are far less common in traditional navigation.
**
Right-click: clicking the secondary button. In modern applications, this frequently opens a
context menu.
** Middle-click: clicking the tertiary button. In most cases, this is also the scroll wheel.
** Clicking the fourth button.
** Clicking the fifth button.
** The USB standard defines up to 65535 distinct buttons for mice and other such devices, although in practice buttons above 3 are rarely implemented.
* Drag: pressing and holding a button, and moving the mouse before releasing the button. This is frequently used to move or copy files or other objects via
drag and drop
In computer graphical user interfaces, drag and drop is a pointing device gesture in which the user (computing), user selects a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object. In general, i ...
; other uses include selecting text and drawing in graphics applications.
*
Mouse button chording or chord clicking:
** Clicking with more than one button simultaneously.
** Clicking while simultaneously typing a letter on the keyboard.
** Clicking and rolling the mouse wheel simultaneously.
* Clicking while holding down a
modifier key.
* Moving the pointer a long distance: When a practical limit of mouse movement is reached, one lifts up the mouse, brings it to the opposite edge of the working area while it is held above the surface, and then lowers it back onto the working surface. This is often not necessary, because acceleration software detects fast movement, and moves the pointer significantly faster in proportion than for slow mouse motion.
* Multi-touch: this method is similar to a multi-touch touchpad on a laptop with support for tap input for multiple fingers, the most famous example being the Apple
Magic Mouse.
Gestures
Gestural interfaces have become an integral part of modern computing, allowing users to interact with their devices in a more intuitive and natural way. In addition to traditional pointing-and-clicking actions, users can now employ gestural inputs to issue commands or perform specific actions. These stylized motions of the mouse cursor, known as "gestures", have the potential to enhance user experience and streamline workflow.
To illustrate the concept of gestural interfaces, let's consider a drawing program as an example. In this scenario, a user can employ a gesture to delete a shape on the canvas. By rapidly moving the mouse cursor in an "x" motion over the shape, the user can trigger the command to delete the selected shape. This gesture-based interaction enables users to perform actions quickly and efficiently without relying solely on traditional input methods.
While gestural interfaces offer a more immersive and interactive user experience, they also present challenges. One of the primary difficulties lies in the requirement of finer motor control from users. Gestures demand precise movements, which can be more challenging for individuals with limited dexterity or those who are new to this mode of interaction.
However, despite these challenges, gestural interfaces have gained popularity due to their ability to simplify complex tasks and improve efficiency. Several gestural conventions have become widely adopted, making them more accessible to users. One such convention is the drag and drop gesture, which has become pervasive across various applications and platforms.
The drag and drop gesture is a fundamental gestural convention that enables users to manipulate objects on the screen seamlessly. It involves a series of actions performed by the user:
# Pressing the mouse button while the cursor hovers over an interface object.
# Moving the cursor to a different location while holding the button down.
# Releasing the mouse button to complete the action.
This gesture allows users to transfer or rearrange objects effortlessly. For instance, a user can drag and drop a picture representing a file onto an image of a trash can, indicating the intention to delete the file. This intuitive and visual approach to interaction has become synonymous with organizing digital content and simplifying file management tasks.
In addition to the drag and drop gesture, several other semantic gestures have emerged as standard conventions within the gestural interface paradigm. These gestures serve specific purposes and contribute to a more intuitive user experience. Some of the notable semantic gestures include:
* Crossing-based goal: This gesture involves crossing a specific boundary or threshold on the screen to trigger an action or complete a task. For example, swiping across the screen to unlock a device or confirm a selection.
* Menu traversal: Menu traversal gestures facilitate navigation through hierarchical menus or options. Users can perform gestures such as swiping or scrolling to explore different menu levels or activate specific commands.
* Pointing: Pointing gestures involve positioning the mouse cursor over an object or element to interact with it. This fundamental gesture enables users to select, click, or access contextual menus.
* Mouseover (pointing or hovering): Mouseover gestures occur when the cursor is positioned over an object without clicking. This action often triggers a visual change or displays additional information about the object, providing users with real-time feedback.
These standard semantic gestures, along with the drag and drop convention, form the building blocks of gestural interfaces, allowing users to interact with digital content using intuitive and natural movements.
Specific uses

At the end of 20th century,
digitizer mice (puck) with
magnifying glass was used with
AutoCAD for the
digitizations of
blueprint
A blueprint is a reproduction of a technical drawing or engineering drawing using a contact print process on light-sensitive sheets introduced by Sir John Herschel in 1842. The process allowed rapid and accurate production of an unlimited number ...
s.
Other uses of the mouse's input occur commonly in special application domains. In interactive
three-dimensional graphics, the mouse's motion often translates directly into changes in the virtual objects' or camera's orientation. For example, in the first-person shooter genre of games (see below), players usually employ the mouse to control the direction in which the virtual player's "head" faces: moving the mouse up will cause the player to look up, revealing the view above the player's head. A related function makes an image of an object rotate so that all sides can be examined. 3D design and animation software often modally chord many different combinations to allow objects and cameras to be rotated and moved through space with the few axes of movement mice can detect.
When mice have more than one button, the software may assign different functions to each button. Often, the primary (leftmost in a
right-handed
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to and causing it to be stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dext ...
configuration) button on the mouse will select items, and the secondary (rightmost in a right-handed) button will bring up a menu of alternative actions applicable to that item. For example, on platforms with more than one button, the
Mozilla web browser will follow a link in response to a primary button click, will bring up a contextual menu of alternative actions for that link in response to a secondary-button click, and will often open the link in a new
tab or
window
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent ma ...
in response to a click with the tertiary (middle) mouse button.
Types
Mechanical mice
The German company
Telefunken published on their early ball mouse on 2 October 1968.
Telefunken's mouse was sold as optional equipment for their computer systems.
Bill English, builder of Engelbart's original mouse, created a ball mouse in 1972 while working for
Xerox PARC.
The ball mouse replaced the external wheels with a single ball that could rotate in any direction. It came as part of the hardware package of the
Xerox Alto computer. Perpendicular
chopper wheels housed inside the mouse's body chopped beams of light on the way to light sensors, thus detecting in their turn the motion of the ball. This variant of the mouse resembled an inverted
trackball and became the predominant form used with
personal computer
A personal computer, commonly referred to as PC or computer, is a computer designed for individual use. It is typically used for tasks such as Word processor, word processing, web browser, internet browsing, email, multimedia playback, and PC ...
s throughout the 1980s and 1990s. The Xerox PARC group also settled on the modern technique of using both hands to type on a full-size keyboard and grabbing the mouse when required.

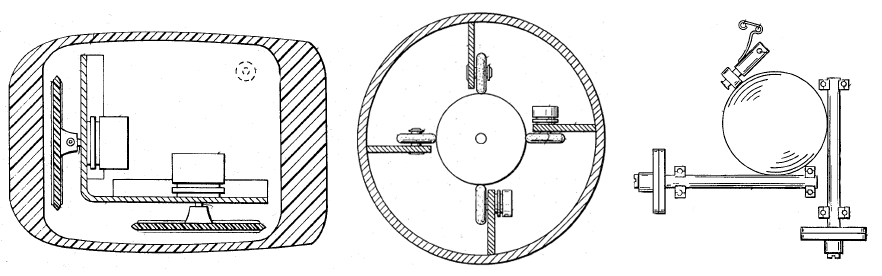
The ball mouse has two freely rotating rollers. These are located 90 degrees apart. One roller detects the forward-backward motion of the mouse and the other the left-right motion. Opposite the two rollers is a third one (white, in the photo, at 45 degrees) that is spring-loaded to push the ball against the other two rollers. Each roller is on the same shaft as an
encoder wheel that has slotted edges; the slots interrupt infrared light beams to generate electrical pulses that represent wheel movement. Each wheel's disc has a pair of light beams, located so that a given beam becomes interrupted or again starts to pass light freely when the other beam of the pair is about halfway between changes.
Simple logic circuits interpret the relative timing to indicate which direction the wheel is rotating. This
incremental rotary encoder scheme is sometimes called quadrature encoding of the wheel rotation, as the two optical sensors produce signals that are in approximately
quadrature phase. The mouse sends these signals to the computer system via the mouse cable, directly as logic signals in very old mice such as the Xerox mice, and via a data-formatting IC in modern mice. The driver software in the system converts the signals into motion of the mouse cursor along X and Y axes on the computer screen.

The ball is mostly steel, with a precision spherical rubber surface. The weight of the ball, given an appropriate working surface under the mouse, provides a reliable grip so the mouse's movement is transmitted accurately. Ball mice and wheel mice were manufactured for Xerox by Jack Hawley, doing business as The Mouse House in Berkeley, California, starting in 1975.
Based on another invention by Jack Hawley, proprietor of the Mouse House,
Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building automation, industrial automa ...
produced another type of mechanical mouse. Instead of a ball, it had two wheels rotating at off axes.
Key Tronic later produced a similar product.
Modern computer mice took form at the
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) under the inspiration of Professor
Jean-Daniel Nicoud and at the hands of
engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
and
watchmaker André Guignard. This new design incorporated a single hard rubber mouseball and three buttons, and remained a common design until the mainstream adoption of the scroll-wheel mouse during the 1990s. In 1985,
René Sommer added a
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor (computing), processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, a ...
to Nicoud's and Guignard's design.
Through this innovation, Sommer is credited with inventing a significant component of the mouse, which made it more "intelligent";
though optical mice from
Mouse Systems
Mouse Systems Corporation (MSC), formerly Rodent Associates, was founded in 1982 by Steve Kirsch. The company was responsible for bringing the mouse to the IBM PC for the first time.
History
Mouse Systems' optical mouse, wired to a Sun works ...
had incorporated microprocessors by 1984.
Another type of mechanical mouse, the "analog mouse" (now generally regarded as obsolete), uses
potentiometers rather than encoder wheels, and is typically designed to be
plug compatible with an analog joystick. The "Color Mouse", originally marketed by
RadioShack for their
Color Computer (but also usable on
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
machines equipped with analog joystick ports, provided the software accepted joystick input) was the best-known example.
Optical and laser mice
Early optical mice relied entirely on one or more
light-emitting diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corre ...
s (LEDs) and an imaging array of
photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and me ...
s to detect movement relative to the underlying surface, eschewing the internal moving parts a mechanical mouse uses in addition to its optics. A laser mouse is an optical mouse that uses coherent (laser) light.
The earliest optical mice detected movement on pre-printed mousepad surfaces, whereas the modern LED optical mouse works on most opaque diffuse surfaces; it is usually unable to detect movement on specular surfaces like polished stone. Laser diodes provide good resolution and precision, improving performance on opaque specular surfaces. Later, more surface-independent optical mice use an optoelectronic sensor (essentially, a tiny low-resolution video camera) to take successive images of the surface on which the mouse operates. Battery powered, wireless optical mice flash the LED intermittently to save power, and only glow steadily when movement is detected.
Inertial and gyroscopic mice
Often called "air mice" since they do not require a surface to operate, inertial mice use a tuning fork or other
accelerometer
An accelerometer is a device that measures the proper acceleration of an object. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change (mathematics), rate of change of velocity) of the object relative to an observer who is in free fall (tha ...
(US Patent 4787051) to detect rotary movement for every axis supported. The most common models (manufactured by Logitech and Gyration) work using 2 degrees of rotational freedom and are insensitive to spatial translation. The user requires only small wrist rotations to move the cursor, reducing user fatigue or "
gorilla arm".
Usually cordless, they often have a switch to deactivate the movement circuitry between use, allowing the user freedom of movement without affecting the cursor position. A patent for an inertial mouse claims that such mice consume less power than optically based mice, and offer increased sensitivity, reduced weight and increased
ease-of-use. In combination with a wireless keyboard an inertial mouse can offer alternative ergonomic arrangements which do not require a flat work surface, potentially alleviating some types of repetitive motion injuries related to workstation posture.
3D mice
A 3D mouse is a computer input device for
viewport
A viewport is a polygon viewing region in computer graphics.
In computer graphics theory, there are two region-like notions of relevance when rendering some objects to an image. In textbook terminology, the ''world coordinate window'' is the area ...
interaction with at least three degrees of freedom (
DoF), e.g. in
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
software for manipulating virtual objects, navigating in the viewport, defining camera paths, posing, and desktop
motion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mocap or mo-cap, for short) is the process of recording high-resolution motion (physics), movement of objects or people into a computer system. It is used in Military science, military, entertainment, sports ...
. 3D mice can also be used as
spatial controllers for
video game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
interaction, e.g.
SpaceOrb 360. To perform such different tasks the used
transfer function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a function (mathematics), mathematical function that mathematical model, models the system's output for each possible ...
and the device stiffness are essential for efficient interaction.
Transfer function
The virtual motion is connected to the 3D mouse control handle via a
transfer function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a function (mathematics), mathematical function that mathematical model, models the system's output for each possible ...
. Position control means that the virtual
position and
orientation is proportional to the mouse handle's deflection whereas velocity control means that
translation
Translation is the communication of the semantics, meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The English la ...
and
rotation
Rotation or rotational/rotary motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an ''axis of rotation''. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersect ...
velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
of the controlled object is proportional to the handle deflection. A further essential property of a transfer function is its interaction metaphor:
* Object-in-hand metaphor: An exterocentrical metaphor whereby the scene moves in correspondence with the input device. If the handle of the input device is twisted clockwise the scene rotates clockwise. If the handle is moved left the scene shifts left, and so on.
* Camera-in-hand metaphor: An egocentrical metaphor whereby the user's view is controlled by direct movement of a virtual camera. If the handle is twisted clockwise the scene rotates counter-clockwise. If the handle is moved left the scene shifts right, and so on.
Ware and Osborneperformed an experiment investigating these metaphors whereby it was shown that there is no single best metaphor. For manipulation tasks, the object-in-hand metaphor was superior, whereas for navigation tasks the camera-in-hand metaphor was superior.
Device stiffness Zhai
used and the following three categories for device stiffness:
* Isotonic Input: An input device with zero stiffness, that is, there is no self-centering effect.
*
Elastic
Elastic is a word often used to describe or identify certain types of elastomer, Elastic (notion), elastic used in garments or stretch fabric, stretchable fabrics.
Elastic may also refer to:
Alternative name
* Rubber band, ring-shaped band of rub ...
Input: A device with some stiffness, that is, the forces on the handle are proportional to the deflections.
*
Isometric Input: An elastic input device with infinite stiffness, that is, the device handle does not allow any deflection but records force and torque.
Isotonic 3D mice
Logitech 3D Mouse (1990) was the first ultrasonic mouse and is an example of an isotonic 3D mouse having six degrees of freedom (6DoF). Isotonic devices have also been developed with less than 6DoF, e.g. the Inspector at Technical University of Denmark (5DoF input).
Other examples of isotonic 3D mice are
motion controllers, i.e. is a type of
game controller
A game controller, gaming controller, or simply controller, is an input device or Input/Output Device, input/output device used with video games or entertainment systems to provide input to a video game. Input devices that have been classified as ...
that typically uses accelerometers to track motion. Motion tracking systems are also used for
motion capture
Motion capture (sometimes referred as mocap or mo-cap, for short) is the process of recording high-resolution motion (physics), movement of objects or people into a computer system. It is used in Military science, military, entertainment, sports ...
e.g. in the film industry, although that these tracking systems are not 3D mice in a strict sense, because motion capture only means recording 3D motion and not 3D interaction.
Isometric 3D mice
Early 3D mice for velocity control were almost ideally isometric, e.g.
SpaceBall 1003, 2003, 3003, and a device developed at
Deutsches Zentrum für Luft und Raumfahrt (DLR), cf. US patent US4589810A.
Elastic 3D mice
At DLR an elastic 6DoF sensor was developed that was used in Logitech's SpaceMouse and in the products of
3DConnexion. SpaceBall 4000 FLX has a maximum deflection of approximately at a maximum force of approximately 10N, that is, a stiffness of approximately . SpaceMouse has a maximum deflection of at a maximum force of , that is, a stiffness of approximately . Taking this development further, the softly elastic Sundinlabs SpaceCat was developed. SpaceCat has a maximum translational deflection of approximately and maximum rotational deflection of approximately 30° at a maximum force less than 2N, that is, a stiffness of approximately . With SpaceCa
Sundin and Fjeldreviewed five comparative experiments performed with different device stiffness and transfer functions and performed a further study comparing 6DoF softly elastic position control with 6DoF stiffly elastic velocity control in a positioning task. They concluded that for positioning tasks position control is to be preferred over velocity control. They could further conjecture the following two types of preferred 3D mouse usage:
* Positioning, manipulation, and docking using isotonic or softly elastic position control and an object-in-hand metaphor.
* Navigation using softly or stiffly elastic rate control and a camera-in-hand metaphor.
3DConnexion's 3D mice have been commercially successful over decades. They are used in combination with the conventional mouse for
CAD. The Space Mouse is used to orient the target object or change the viewpoint with the non-dominant hand, whereas the dominant hand operates the computer mouse for conventional CAD
GUI operation. This is a kind of space-multiplexed input where the 6 DoF input device acts as a graspable user interface that is always connected to the view port.
Force feedback
With
force feedback the device stiffness can dynamically be adapted to the task just performed by the user, e.g. performing positioning tasks with less stiffness than navigation tasks.
File:Logitech spacemouse 3D-IMG 8429-black.jpg, Logitech spacemouse 3D. On display at the Bolo Computer Museum, EPFL, Lausanne
File:Silicon Graphics Ball-IMG 4192.jpg, Silicon Graphics SpaceBall model 1003 (1988), allowing manipulation of objects with six degrees of freedom
File:Logitech 3D ultrasonice mouse 1990-IMG 7952-gradient.jpg, Logitech 3D Mouse (1990), the first ultrasonic mouse
File:Space-Navigator.jpg, A modern six-degrees-of-freedom (6 DOF) 3D mouse (2007)
File:Spaceball 4000 FLX - Optical Assembly.JPG, Mechanism of the modern 6 DOF mouse consisting of infrared LEDs and detectors with occluders that move with the ball
Tactile mice
In 2000,
Logitech introduced a "tactile mouse" known as the "iFeel Mouse" developed by
Immersion Corporation that contained a small
actuator
An actuator is a machine element, component of a machine that produces force, torque, or Displacement (geometry), displacement, when an electrical, Pneumatics, pneumatic or Hydraulic fluid, hydraulic input is supplied to it in a system (called an ...
to enable the mouse to generate simulated physical sensations. Such a mouse can augment user-interfaces with
haptic feedback, such as giving feedback when crossing a
window
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent ma ...
boundary. To surf the internet by touch-enabled mouse was first developed in 1996 and first implemented commercially by the Wingman Force Feedback Mouse. It requires the user to be able to feel depth or hardness; this ability was realized with the first electrorheological tactile mice but never marketed.
Pucks
Tablet digitizers are sometimes used with accessories called pucks, devices which rely on absolute positioning, but can be configured for sufficiently mouse-like relative tracking that they are sometimes marketed as mice.
Ergonomic mice
As the name suggests, this type of mouse is intended to provide optimum comfort and avoid injuries such as
carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a nerve compression syndrome associated with the collected signs and symptoms of Pathophysiology of nerve entrapment#Compression, compression of the median nerve at the carpal tunnel in the wrist. Carpal tunn ...
,
arthritis, and other
repetitive strain injuries. It is designed to fit natural hand position and movements, to reduce discomfort.
When holding a typical mouse, the
ulna and
radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
bones on the
arm are crossed. Some designs attempt to place the palm more vertically, so the bones take more natural parallel position.
Increasing mouse height and angling the mouse topcase can improve wrist posture without negatively affecting performance. Some limit wrist movement, encouraging arm movement instead, that may be less precise but more optimal from the health point of view. A mouse may be angled from the thumb downward to the opposite side – this is known to reduce wrist pronation. However such optimizations make the mouse right or left hand specific, making more problematic to change the tired hand. ''
Time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
'' has criticized manufacturers for offering few or no left-handed ergonomic mice: "Oftentimes I felt like I was dealing with someone who'd never actually met a left-handed person before."

Another solution is a pointing bar device. The so-called ''roller bar mouse'' is positioned snugly in front of the keyboard, thus allowing bi-manual accessibility.
Gaming mice
These mice are specifically designed for use in
computer games
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
. They typically employ a wider array of controls and buttons and have designs that differ radically from traditional mice. They may also have decorative monochrome or programmable RGB LED lighting. The additional buttons can often be used for changing the sensitivity of the mouse or they can be assigned (programmed) to
macros (i.e., for opening a program or for use instead of a key combination).
It is also common for game mice, especially those designed for use in
real-time strategy
Real-time strategy (RTS) is a Video game genre, subgenre of strategy video games that does not progress incrementally in turn-based game, turns, but allow all players to play simultaneously, in "real time." By contrast, in Turn-based strategy, tur ...
games such as ''
StarCraft'', or in
multiplayer online battle arena
Multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) is a Video game genre, subgenre of strategy video games in which two teams of Gamer, players compete on a structured battlefield, each controlling a single Player character, character with distinctive abilit ...
games such as
League of Legends
''League of Legends'' (''LoL'', commonly referred to as ''League'', is a multiplayer online battle arena video game developed and published by Riot Games. Inspired by ''Defense of the Ancients'', a Mod (video games), custom map for ''Warcraf ...
to have a relatively high sensitivity, measured in
dots per inch (DPI), which can be as high as 25,600. DPI and CPI are the same values that refer to the mouse's sensitivity. DPI is a misnomer used in the gaming world, and many manufacturers use it to refer to CPI, counts per inch.
Some advanced mice from gaming manufacturers also allow users to adjust the weight of the mouse by adding or subtracting weights to allow for easier control. Ergonomic quality is also an important factor in gaming mouse, as extended gameplay times may render further use of the mouse to be uncomfortable. Some mice have been designed to have adjustable features such as removable and/or elongated palm rests, horizontally adjustable thumb rests and pinky rests. Some mice may include several different rests with their products to ensure comfort for a wider range of target consumers.
Gaming mice are held by
gamers in three styles of
grip:
# Palm Grip: the hand rests on the mouse, with extended fingers.
# Claw Grip: palm rests on the mouse, bent fingers.
# Finger-Tip Grip: bent fingers, palm does not touch the mouse.
Connectivity and communication protocols

To transmit their input, typical cabled mice use a thin electrical cord terminating in a standard connector, such as
RS-232C,
PS/2,
ADB, or
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
. Cordless mice instead transmit data via
infrared
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those ...
radiation (see
IrDA) or
radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
(including
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is li ...
), although many such cordless interfaces are themselves connected through the aforementioned wired serial buses.
While the electrical interface and the format of the data transmitted by commonly available mice is currently standardized on USB, in the past it varied between different manufacturers. A
bus mouse used a dedicated interface card for connection to an
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the List of IBM Personal Computer models, IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible ''de facto'' standard. Released on ...
or compatible computer.
Mouse use in DOS applications became more common after the introduction of the
Microsoft Mouse, largely because Microsoft provided an open standard for communication between applications and mouse driver software. Thus, any application written to use the Microsoft standard could use a mouse with a driver that implements the same API, even if the mouse hardware itself was incompatible with Microsoft's. This driver provides the state of the buttons and the distance the mouse has moved in units that its documentation calls "
mickeys".
Early mice
In the 1970s, the
Xerox Alto mouse, and in the 1980s the Xerox
optical mouse, used a
quadrature-encoded X and Y interface. This two-bit encoding per dimension had the property that only one bit of the two would change at a time, like a
Gray code
The reflected binary code (RBC), also known as reflected binary (RB) or Gray code after Frank Gray (researcher), Frank Gray, is an ordering of the binary numeral system such that two successive values differ in only one bit (binary digit).
For ...
or
Johnson counter, so that the transitions would not be misinterpreted when asynchronously sampled.
The 1985
Sun-3 workstations would ship with a ball based, bus mouse, connected via an 3 pin mini din socket. Sun later replacing the ball for an optical mechanism dependent on a patterned, reflective, metallic mouse mat, with their type M4 mouse.
The earliest mass-market mice, such as the
original Macintosh,
Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
, and
Atari ST
Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the company's Atari 8-bit computers, 8-bit computers. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985, and was widely available i ...
mice used a
D-subminiature
The D-subminiature or D-sub is a common type of electrical connector. They are named for their characteristic D-shaped metal shield. When they were introduced, D-subs were among the smallest connectors used on computer systems.
Description ...
9-pin connector to send the quadrature-encoded X and Y axis signals directly, plus one pin per mouse button. The mouse was a simple optomechanical device, and the decoding circuitry was all in the main computer. The 1987
Acorn Archimedes line kept the quadrature-encoded mice of the 68000 computers, and the aftermarket mice sold for 8-bit home computers, like the
AMX Mouse, but opted for its own propriety 9 pin mini din connector.
Serial interface and protocol
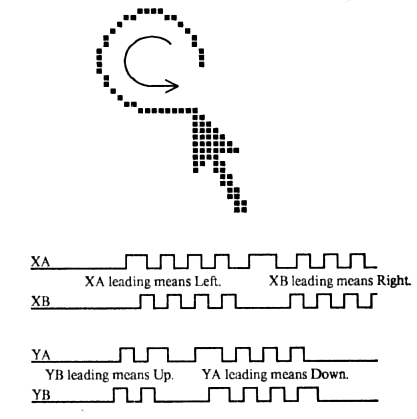
Because the IBM PC did not have a
quadrature decoder
Quadrature may refer to:
Mathematics
* Quadrature (geometry), drawing a square with the same area as a given plane figure (''squaring'') or computing that area
** Quadrature of the circle
** ''Quadrature of the Parabola''
** Quadrature of the h ...
built in, early PC mice used the
RS-232C serial port to communicate encoded mouse movements, as well as provide power to the mouse's circuits. The
Mouse Systems Corporation (MSC) version used a five-byte protocol and supported three buttons. The Microsoft version used a three-byte protocol and supported two buttons. Due to the incompatibility between the two protocols, some manufacturers sold serial mice with a mode switch: "PC" for MSC mode, "MS" for Microsoft mode.
Apple Desktop Bus

In 1986
Apple
An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus'' spp.). Fruit trees of the orchard or domestic apple (''Malus domestica''), the most widely grown in the genus, are agriculture, cultivated worldwide. The tree originated ...
first implemented the
Apple Desktop Bus allowing the
daisy chaining of up to 16 devices, including mice and other devices on the same bus with no configuration whatsoever. Featuring only a single data pin, the bus used a purely polled approach to device communications and survived as the standard on mainstream models (including a number of non-Apple workstations) until 1998 when Apple's
iMac line of computers joined the industry-wide switch to using
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
. Beginning with the Bronze Keyboard PowerBook G3 in May 1999, Apple dropped the external ADB port in favor of USB, but retained an internal ADB connection in the
PowerBook G4 for communication with its built-in keyboard and trackpad until early 2005.
PS/2 interface and protocol
With the arrival of the
IBM PS/2
The Personal System/2 or PS/2 is IBM's second generation of personal computers. Released in 1987, it officially replaced the IBM Personal Computer, IBM PC, IBM Personal Computer XT, XT, IBM Personal Computer/AT, AT, and IBM PC Convertible, PC Co ...
personal-computer series in 1987, IBM introduced the
eponym
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovati ...
ous
PS/2 port for mice and keyboards, which other manufacturers rapidly adopted. The most visible change was the use of a round 6-pin
mini-DIN, in lieu of the former 5-pin MIDI style full sized
DIN 41524 connector. In default mode (called ''stream mode'') a PS/2 mouse communicates motion, and the state of each button, by means of 3-byte packets. For any motion, button press or button release event, a PS/2 mouse sends, over a bi-directional serial port, a sequence of three bytes, with the following format:
Here, XS and YS represent the sign bits of the movement vectors, XV and YV indicate an overflow in the respective vector component, and LB, MB and RB indicate the status of the left, middle and right mouse buttons (1 = pressed). PS/2 mice also understand several commands for reset and self-test, switching between different operating modes, and changing the resolution of the reported motion vectors.
A IntelliMouse, Microsoft IntelliMouse relies on an extension of the PS/2 protocol: the ImPS/2 or IMPS/2 protocol (the abbreviation combines the concepts of "IntelliMouse" and "PS/2"). It initially operates in standard PS/2 format, for backward compatibility. After the host sends a special command sequence, it switches to an extended format in which a fourth byte carries information about wheel movements. The IntelliMouse Explorer works analogously, with the difference that its 4-byte packets also allow for two additional buttons (for a total of five).
Mouse vendors also use other extended formats, often without providing public documentation.
The Typhoon mouse uses 6-byte packets which can appear as a sequence of two standard 3-byte packets, such that an ordinary PS/2 device driver, driver can handle them. For 3D (or 6-degree-of-freedom) input, vendors have made many extensions both to the hardware and to software. In the late 1990s, Logitech created ultrasound based tracking which gave 3D input to a few millimeters accuracy, which worked well as an input device but failed as a profitable product. In 2008, Motion4U introduced its "OptiBurst" system using IR tracking for use as a Maya (graphics software) plugin.

USB
Almost all wired mice today use USB and the USB human interface device class for communication.
Cordless or wireless
Cordless or wireless mice transmit data via
radio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
. Some mice connect to the computer through
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is li ...
or Wi-Fi, while others use a receiver that plugs into the computer, for example through a USB port.
Many mice that use a USB receiver have a storage compartment for it inside the mouse. Some "nano receivers" are designed to be small enough to remain plugged into a laptop during transport, while still being large enough to easily remove.
File:Logitech metaphor-P4191183-black.jpg, The Logitech Metaphor, the first wireless mouse (1984). On display at the Musée Bolo, EPFL
File:Microsoft-wireless-mouse.jpg, An older Microsoft wireless mouse made for notebook computers
File:Microsoft Bluetooth Mobile Mouse 3600.jpg, Microsoft Bluetooth Mobile Mouse 3600
Operating system support
MS-DOS and Windows 1.0 support connecting a mouse such as a
Microsoft Mouse via multiple interfaces: BallPoint, Bus mouse, Bus (InPort), Serial port or PS/2.
Windows 98 added built-in support for USB Human Interface Device class (USB HID), with native vertical scrolling support.
Windows 2000 and Windows Me expanded this built-in support to 5-button mice.
Windows XP Service Pack 2 introduced a Bluetooth stack, allowing Bluetooth mice to be used without any USB receivers. Windows Vista added native support for horizontal scrolling and standardized wheel movement granularity for finer scrolling.
Windows 8 introduced BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) mouse/list of Bluetooth profiles#Human Interface Device Profile (HID), HID support.
Multiple-mouse systems
Some systems allow two or more mice to be used at once as input devices. Late-1980s era home computers such as the
Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
used this to allow computer games with two players interacting on the same computer (Lemmings (video game), Lemmings and The Settlers for example). The same idea is sometimes used in collaborative software, e.g. to simulate a whiteboard that multiple users can draw on without passing a single mouse around.
Microsoft Windows, since Windows 98, has supported multiple simultaneous pointing devices. Because Windows only provides a single screen cursor, using more than one device at the same time requires cooperation of users or applications designed for multiple input devices.
Multiple mice are often used in multi-user gaming in addition to specially designed devices that provide several input interfaces.
Windows also has full support for multiple input/mouse configurations for multi-user environments.
Starting with Windows XP, Microsoft introduced Windows Multipoint Mouse, an SDK for developing applications that allow multiple input devices to be used at the same time with independent cursors and independent input points. However, it no longer appears to be available.
The introduction of Windows Vista and Microsoft Surface (now known as Microsoft PixelSense) introduced a new set of input APIs that were adopted into Windows 7, allowing for 50 points/cursors, all controlled by independent users. The new input points provide traditional mouse input; however, they were designed with other input technologies like touch and image in mind. They inherently offer 3D coordinates along with pressure, size, tilt, angle, mask, and even an image bitmap to see and recognize the input point/object on the screen.
, Linux distributions and other operating systems that use X.Org Server, X.Org, such as OpenSolaris and FreeBSD, support 255 cursors/input points through Multi-Pointer X. However, currently no window managers support Multi-Pointer X leaving it relegated to custom software usage.
There have also been propositions of having a single operator use two mice simultaneously as a more sophisticated means of controlling various graphics and multimedia applications.
Buttons
Mouse buttons are miniature snap-action switch, microswitches which can be pressed to select or interact with an element of a
graphical user interface
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows user (computing), users to human–computer interaction, interact with electronic devices through Graphics, graphical icon (computing), icons and visual indicators such ...
, producing a distinctive clicking sound.
Since around the late 1990s, the three-button scrollmouse has become the de facto standard. Users most commonly employ the second button to invoke a context menu, contextual menu in the computer's software user interface, which contains options specifically tailored to the interface element over which the mouse cursor currently sits. By default, the primary mouse button sits located on the left-hand side of the mouse, for the benefit of right-handed users; left-handed users can usually reverse this configuration via software.
Scrolling
Nearly all mice now have an integrated input primarily intended for scrolling on top, usually a single-axis digital wheel or rocker switch which can also be depressed to act as a third button. Though less common, many mice instead have two-axis inputs such as a tiltable wheel,
trackball, or touchpad. Those with a trackball may be designed to stay stationary, using the trackball instead of moving the mouse.
Speed
Mickey (unit), Mickeys per second is a unit of measurement for the speed and movement direction of a computer mouse,
where direction is often expressed as "horizontal" versus "vertical" mickey count. However, speed can also refer to the ratio between how many pixels the cursor moves on the screen and how far the mouse moves on the mouse pad, which may be expressed as pixels per mickey, pixels per inch, or pixels per centimeter.
The computer industry often measures mouse sensitivity in terms of counts per inch (CPI), commonly expressed as dots per inch (DPI)the number of steps the mouse will report when it moves one inch. In early mice, this specification was called pulses per inch (ppi).
The mickey originally referred to one of these counts, or one resolvable step of motion. If the default mouse-tracking condition involves moving the cursor by one screen-pixel or dot on-screen per reported step, then the CPI does equate to DPI: dots of cursor motion per inch of mouse motion. The CPI or DPI as reported by manufacturers depends on how they make the mouse; the higher the CPI, the faster the cursor moves with mouse movement. However, operating system and application software can adjust the mouse sensitivity, making the cursor move faster or slower than its CPI. software can change the speed of the cursor dynamically, taking into account the mouse's absolute speed and the movement from the last stop-point.
For simple software, when the mouse starts to move, the software will count the number of "counts" or "mickeys" received from the mouse and will move the cursor across the screen by that number of pixels (or multiplied by a rate factor, typically less than 1). The cursor will move slowly on the screen, with good precision. When the movement of the mouse passes the value set for some threshold, the software will start to move the cursor faster, with a greater rate factor. Usually, the user can set the value of the second rate factor by changing the "acceleration" setting.
Operating systems sometimes apply acceleration, referred to as "ballistics", to the motion reported by the mouse. For example, versions of Microsoft Windows, Windows prior to Windows XP doubled reported values above a configurable threshold, and then optionally doubled them again above a second configurable threshold. These doublings applied separately in the X and Y directions, resulting in very nonlinear system, nonlinear response.
Mousepads
Engelbart's original mouse did not require a mousepad; the mouse had two large wheels which could roll on virtually any surface. However, most subsequent mechanical mice starting with the steel roller ball mouse have required a mousepad for optimal performance.
The mousepad, the most common mouse accessory, appears most commonly in conjunction with mechanical mice, because to roll smoothly the ball requires more friction than common desk surfaces usually provide. So-called "hard mousepads" for gamers or optical/laser mice also exist.
Most optical and laser mice do not require a pad, the notable exception being early optical mice which relied on a grid on the pad to detect movement (e.g.
Mouse Systems
Mouse Systems Corporation (MSC), formerly Rodent Associates, was founded in 1982 by Steve Kirsch. The company was responsible for bringing the mouse to the IBM PC for the first time.
History
Mouse Systems' optical mouse, wired to a Sun works ...
). Whether to use a hard or soft mousepad with an optical mouse is largely a matter of personal preference. One exception occurs when the desk surface creates problems for the optical or laser tracking, for example, a transparent or reflective surface, such as glass.
Some mice also come with small "pads" attached to the bottom surface, also called mouse feet or mouse skates, that help the user slide the mouse smoothly across surfaces.
In the marketplace

Around 1981, Xerox included mice with its Xerox Star, based on the mouse used in the 1970s on the Alto computer at
Xerox PARC. Sun Microsystems, Symbolics, Lisp Machines Inc., and Tektronix also shipped workstations with mice, starting in about 1981. Later, inspired by the Star, Apple Inc., Apple Computer released the
Apple Lisa, which also used a mouse. However, none of these products achieved large-scale success. Only with the release of the Macintosh 128K, Apple Macintosh in 1984 did the mouse see widespread use.
The Macintosh design, commercially successful and technically influential, led many other vendors to begin producing mice or including them with their other computer products (by 1986,
Atari ST
Atari ST is a line of personal computers from Atari Corporation and the successor to the company's Atari 8-bit computers, 8-bit computers. The initial model, the Atari 520ST, had limited release in April–June 1985, and was widely available i ...
,
Amiga
Amiga is a family of personal computers produced by Commodore International, Commodore from 1985 until the company's bankruptcy in 1994, with production by others afterward. The original model is one of a number of mid-1980s computers with 16-b ...
, Windows 1.0, GEOS (8-bit operating system), GEOS for the Commodore 64, and the Apple IIGS).
The widespread adoption of graphical user interfaces in the software of the 1980s and 1990s made mice all but indispensable for controlling computers. In November 2008,
Logitech built their billionth mouse.
Use in games

The device often functions as an interface for PC-based video game, computer games and sometimes for video game consoles. The Classic Mac OS Desk Accessory ''Puzzle'' in 1984 was the first game designed specifically for a mouse.
First-person shooters
First-person shooter, FPSs naturally lend themselves to separate and simultaneous control of the player's movement and aim, and on computers this has traditionally been achieved with a combination of keyboard and mouse. Players use the X-axis of the mouse for looking (or turning) left and right, and the Y-axis for looking up and down; the keyboard is used for movement and supplemental inputs.
Many shooting genre players prefer a mouse over a gamepad analog stick because the wide range of motion offered by a mouse allows for faster and more varied control. Although an analog stick allows the player more granular control, it is poor for certain movements, as the player's input is relayed based on a vector of both the stick's direction and magnitude. Thus, a small but fast movement (known as "flick-shotting") using a gamepad requires the player to quickly move the stick from its rest position to the edge and back again in quick succession, a difficult maneuver. In addition the stick also has a finite magnitude; if the player is currently using the stick to move at a non-zero velocity their ability to increase the rate of movement of the camera is further limited based on the position their displaced stick was already at before executing the maneuver. The effect of this is that a mouse is well suited not only to small, precise movements but also to large, quick movements and immediate, responsive movements; all of which are important in shooter gaming.
[Chris Klochek and I. Scott MacKenzie (2006). ]
Performance measures of game controllers in a three-dimensional environment
'. Proceedings of Graphics Interface 2006. pp. 73–79. Canadian Information Processing Society. This advantage also extends in varying degrees to similar game styles such as third-person shooters.
Some incorrectly porting, ported games or game engines have acceleration and interpolation curves which unintentionally produce excessive, irregular, or even negative acceleration when used with a mouse instead of their native platform's non-mouse default input device. Depending on how deeply hardcoded this misbehavior is, internal user patches or external 3rd-party software may be able to fix it. Individual game engines will also have their own sensitivities. This often restricts one from taking a game's existing sensitivity, transferring it to another, and acquiring the same 360 rotational measurements. A sensitivity converter is the preferred tool that FPS gamers use to translate correctly the rotational movements between different mice and between different games. Calculating the conversion values manually is also possible but it is more time-consuming and requires performing complex mathematical calculations, while using a sensitivity converter is a lot faster and easier for gamers.
Due to their similarity to the WIMP (computing), WIMP desktop metaphor interface for which mice were originally designed, and to their own tabletop game origins, computer strategy video game, strategy games are most commonly played with mice. In particular,
real-time strategy
Real-time strategy (RTS) is a Video game genre, subgenre of strategy video games that does not progress incrementally in turn-based game, turns, but allow all players to play simultaneously, in "real time." By contrast, in Turn-based strategy, tur ...
and multiplayer online battle arena, MOBA games usually require the use of a mouse.
The left button usually controls primary fire. If the game supports multiple fire modes, the right button often provides secondary fire from the selected weapon. Games with only a single fire mode will generally map secondary fire to ''ADS (video gaming), aim down the weapon sights''. In some games, the right button may also invoke accessories for a particular weapon, such as allowing access to the scope of a sniper rifle or allowing the mounting of a bayonet or silencer.
Players can use a scroll wheel for changing weapons (or for controlling scope-zoom magnification, in older games). On most first person shooter games, programming may also assign more functions to additional buttons on mice with more than three controls. A keyboard usually controls movement (for example, WASD keys, WASD for moving forward, left, backward, and right, respectively) and other functions such as changing posture. Since the mouse serves for aiming, a mouse that tracks movement accurately and with less lag (latency) will give a player an advantage over players with less accurate or slower mice. In some cases the right mouse button may be used to move the player forward, either in lieu of, or in conjunction with the typical WASD configuration.
Many games provide players with the option of mapping their own choice of a key or button to a certain control. An early technique of players, circle strafing, saw a player continuously strafing while aiming and shooting at an opponent by walking in circle around the opponent with the opponent at the center of the circle. Players could achieve this by holding down a key for strafing while continuously aiming the mouse toward the opponent.
Games using mice for input are so popular that many manufacturers make mice specifically for gaming. Such mice may feature adjustable weights, high-resolution optical or laser components, additional buttons, ergonomic shape, and other features such as adjustable #Mouse speed, CPI. Mouse Bungees are typically used with gaming mice because it eliminates the annoyance of the cable.
Many games, such as first- or third-person shooters, have a setting named "invert mouse" or similar (not to be confused with "button inversion", sometimes performed by handedness, left-handed users) which allows the user to look downward by moving the mouse forward and upward by moving the mouse backward (the opposite of non-inverted movement). This control system resembles that of aircraft control sticks, where pulling back causes pitch up and pushing forward causes pitch down; computer
joystick
A joystick, sometimes called a flight stick, is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Also known as the control column, it is the principal control devic ...
s also typically emulate this control-configuration.
After id Software's commercial hit of ''Doom (1993 video game), Doom'', which did not support vertical aiming, competitor Bungie's ''Marathon (video game), Marathon'' became the first first-person shooter to support using the mouse to aim up and down. Games using the Build engine had an option to invert the Y-axis. The "invert" feature actually made the mouse behave in a manner that users regard as non-inverted (by default, moving mouse forward resulted in looking down). Soon after, id Software released ''Quake (video game), Quake'', which introduced the invert feature as users know it.
Home consoles

In 1988, the VTech Socrates educational video game console featured a wireless mouse with an attached mouse pad as an optional controller used for some games. In the early 1990s, the Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game system featured a SNES Mouse, mouse in addition to its controllers. A mouse was also released for the Nintendo 64, although it was only released in Japan. The 1992 game ''Mario Paint'' in particular used the mouse's capabilities,
as did its Japanese-only successor ''Mario Artist'' on the N64 for its 64DD disk drive peripheral in 1999. Sega released official mice for their Sega Genesis, Genesis/Mega Drive, Sega Saturn, Saturn and Dreamcast consoles. NEC sold official mice for its TurboGrafx-16, PC Engine and PC-FX consoles. Sony Computer Entertainment, Sony released an official mouse product for the PlayStation (console), PlayStation console, included one along with the Linux for PlayStation 2 kit, as well as allowing owners to use virtually any
USB
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is an industry standard, developed by USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), for digital data transmission and power delivery between many types of electronics. It specifies the architecture, in particular the physical ...
mouse with the PlayStation 2, PS2, PlayStation 3, PS3, and PlayStation 4, PS4. Nintendo's Wii also had this feature implemented in a later software update, and this support was retained on its successor, the Wii U. Microsoft, Microsoft's Xbox line of game consoles (which used operaring systems based on modified versions of Windows NT) also had universal-wide mouse support using USB.
See also
* Computer accessibility
* Footmouse
* Graphics tablet
* Gesture recognition
* Human–computer interaction (HCI)
* Mouse keys
* Mouse tracking
* Optical trackpad
* Pointing stick
* Rotational mouse
* Trackball
Notes
References
Further reading
* (11 pages) (NB. This is based on an earlier German article published in 1996 in ''Lab. Jahrbuch 1995/1996 für Künste und Apparate'' (350 pages) by Kunsthochschule für Medien Köln mit dem Verein der Freunde der Kunsthochschule für Medien Köln; in Cologne, Germany. .)
*
External links
Doug Engelbart Institute mouse resources pageincludes stories and links
* The vide
segmentof
The Mother of All Demos with
Doug Engelbart showing the device from 1968
{{Authority control
American inventions
Computer mice,
Computing input devices
History of human–computer interaction
Pointing devices
Computer-related introductions in 1964
 A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects
A computer mouse (plural mice; also mouses) is a hand-held pointing device that detects  In 1964, Bill English joined ARC, where he helped Engelbart build the first mouse prototype. They christened the device the ''mouse'' as early models had a cord attached to the rear part of the device which looked like a tail, and in turn, resembled the common
In 1964, Bill English joined ARC, where he helped Engelbart build the first mouse prototype. They christened the device the ''mouse'' as early models had a cord attached to the rear part of the device which looked like a tail, and in turn, resembled the common  Several other experimental pointing-devices developed for Engelbart's oN-Line System ( NLS) exploited different body movements – for example, head-mounted devices attached to the chin or nose – but ultimately the mouse won out because of its speed and convenience. The first mouse, a bulky device (pictured) used two potentiometers perpendicular to each other and connected to wheels: the rotation of each wheel translated into motion along one axis. At the time of the "Mother of All Demos", Engelbart's group had been using their second-generation, 3-button mouse for about a year.
Several other experimental pointing-devices developed for Engelbart's oN-Line System ( NLS) exploited different body movements – for example, head-mounted devices attached to the chin or nose – but ultimately the mouse won out because of its speed and convenience. The first mouse, a bulky device (pictured) used two potentiometers perpendicular to each other and connected to wheels: the rotation of each wheel translated into motion along one axis. At the time of the "Mother of All Demos", Engelbart's group had been using their second-generation, 3-button mouse for about a year.
 On 2 October 1968, three years after Engelbart's prototype but more than two months before his public demo, a mouse device named ' (German for "Trackball control") was shown in a sales brochure by the German company
On 2 October 1968, three years after Engelbart's prototype but more than two months before his public demo, a mouse device named ' (German for "Trackball control") was shown in a sales brochure by the German company  The Xerox Alto was one of the first computers designed for individual use in 1973 and is regarded as the first modern computer to use a mouse.
The Xerox Alto was one of the first computers designed for individual use in 1973 and is regarded as the first modern computer to use a mouse.  At the end of 20th century, digitizer mice (puck) with magnifying glass was used with AutoCAD for the digitizations of
At the end of 20th century, digitizer mice (puck) with magnifying glass was used with AutoCAD for the digitizations of  The ball mouse has two freely rotating rollers. These are located 90 degrees apart. One roller detects the forward-backward motion of the mouse and the other the left-right motion. Opposite the two rollers is a third one (white, in the photo, at 45 degrees) that is spring-loaded to push the ball against the other two rollers. Each roller is on the same shaft as an encoder wheel that has slotted edges; the slots interrupt infrared light beams to generate electrical pulses that represent wheel movement. Each wheel's disc has a pair of light beams, located so that a given beam becomes interrupted or again starts to pass light freely when the other beam of the pair is about halfway between changes.
Simple logic circuits interpret the relative timing to indicate which direction the wheel is rotating. This incremental rotary encoder scheme is sometimes called quadrature encoding of the wheel rotation, as the two optical sensors produce signals that are in approximately quadrature phase. The mouse sends these signals to the computer system via the mouse cable, directly as logic signals in very old mice such as the Xerox mice, and via a data-formatting IC in modern mice. The driver software in the system converts the signals into motion of the mouse cursor along X and Y axes on the computer screen.
The ball mouse has two freely rotating rollers. These are located 90 degrees apart. One roller detects the forward-backward motion of the mouse and the other the left-right motion. Opposite the two rollers is a third one (white, in the photo, at 45 degrees) that is spring-loaded to push the ball against the other two rollers. Each roller is on the same shaft as an encoder wheel that has slotted edges; the slots interrupt infrared light beams to generate electrical pulses that represent wheel movement. Each wheel's disc has a pair of light beams, located so that a given beam becomes interrupted or again starts to pass light freely when the other beam of the pair is about halfway between changes.
Simple logic circuits interpret the relative timing to indicate which direction the wheel is rotating. This incremental rotary encoder scheme is sometimes called quadrature encoding of the wheel rotation, as the two optical sensors produce signals that are in approximately quadrature phase. The mouse sends these signals to the computer system via the mouse cable, directly as logic signals in very old mice such as the Xerox mice, and via a data-formatting IC in modern mice. The driver software in the system converts the signals into motion of the mouse cursor along X and Y axes on the computer screen.
 The ball is mostly steel, with a precision spherical rubber surface. The weight of the ball, given an appropriate working surface under the mouse, provides a reliable grip so the mouse's movement is transmitted accurately. Ball mice and wheel mice were manufactured for Xerox by Jack Hawley, doing business as The Mouse House in Berkeley, California, starting in 1975. Based on another invention by Jack Hawley, proprietor of the Mouse House,
The ball is mostly steel, with a precision spherical rubber surface. The weight of the ball, given an appropriate working surface under the mouse, provides a reliable grip so the mouse's movement is transmitted accurately. Ball mice and wheel mice were manufactured for Xerox by Jack Hawley, doing business as The Mouse House in Berkeley, California, starting in 1975. Based on another invention by Jack Hawley, proprietor of the Mouse House,  To transmit their input, typical cabled mice use a thin electrical cord terminating in a standard connector, such as RS-232C, PS/2, ADB, or
To transmit their input, typical cabled mice use a thin electrical cord terminating in a standard connector, such as RS-232C, PS/2, ADB, or  Because the IBM PC did not have a
Because the IBM PC did not have a  In 1986
In 1986 
 Around 1981, Xerox included mice with its Xerox Star, based on the mouse used in the 1970s on the Alto computer at Xerox PARC. Sun Microsystems, Symbolics, Lisp Machines Inc., and Tektronix also shipped workstations with mice, starting in about 1981. Later, inspired by the Star, Apple Inc., Apple Computer released the Apple Lisa, which also used a mouse. However, none of these products achieved large-scale success. Only with the release of the Macintosh 128K, Apple Macintosh in 1984 did the mouse see widespread use.
The Macintosh design, commercially successful and technically influential, led many other vendors to begin producing mice or including them with their other computer products (by 1986,
Around 1981, Xerox included mice with its Xerox Star, based on the mouse used in the 1970s on the Alto computer at Xerox PARC. Sun Microsystems, Symbolics, Lisp Machines Inc., and Tektronix also shipped workstations with mice, starting in about 1981. Later, inspired by the Star, Apple Inc., Apple Computer released the Apple Lisa, which also used a mouse. However, none of these products achieved large-scale success. Only with the release of the Macintosh 128K, Apple Macintosh in 1984 did the mouse see widespread use.
The Macintosh design, commercially successful and technically influential, led many other vendors to begin producing mice or including them with their other computer products (by 1986,  The device often functions as an interface for PC-based video game, computer games and sometimes for video game consoles. The Classic Mac OS Desk Accessory ''Puzzle'' in 1984 was the first game designed specifically for a mouse.
The device often functions as an interface for PC-based video game, computer games and sometimes for video game consoles. The Classic Mac OS Desk Accessory ''Puzzle'' in 1984 was the first game designed specifically for a mouse.
 In 1988, the VTech Socrates educational video game console featured a wireless mouse with an attached mouse pad as an optional controller used for some games. In the early 1990s, the Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game system featured a SNES Mouse, mouse in addition to its controllers. A mouse was also released for the Nintendo 64, although it was only released in Japan. The 1992 game ''Mario Paint'' in particular used the mouse's capabilities, as did its Japanese-only successor ''Mario Artist'' on the N64 for its 64DD disk drive peripheral in 1999. Sega released official mice for their Sega Genesis, Genesis/Mega Drive, Sega Saturn, Saturn and Dreamcast consoles. NEC sold official mice for its TurboGrafx-16, PC Engine and PC-FX consoles. Sony Computer Entertainment, Sony released an official mouse product for the PlayStation (console), PlayStation console, included one along with the Linux for PlayStation 2 kit, as well as allowing owners to use virtually any
In 1988, the VTech Socrates educational video game console featured a wireless mouse with an attached mouse pad as an optional controller used for some games. In the early 1990s, the Super Nintendo Entertainment System video game system featured a SNES Mouse, mouse in addition to its controllers. A mouse was also released for the Nintendo 64, although it was only released in Japan. The 1992 game ''Mario Paint'' in particular used the mouse's capabilities, as did its Japanese-only successor ''Mario Artist'' on the N64 for its 64DD disk drive peripheral in 1999. Sega released official mice for their Sega Genesis, Genesis/Mega Drive, Sega Saturn, Saturn and Dreamcast consoles. NEC sold official mice for its TurboGrafx-16, PC Engine and PC-FX consoles. Sony Computer Entertainment, Sony released an official mouse product for the PlayStation (console), PlayStation console, included one along with the Linux for PlayStation 2 kit, as well as allowing owners to use virtually any