mithuna on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Maithuna'' (
''Maithuna'' (

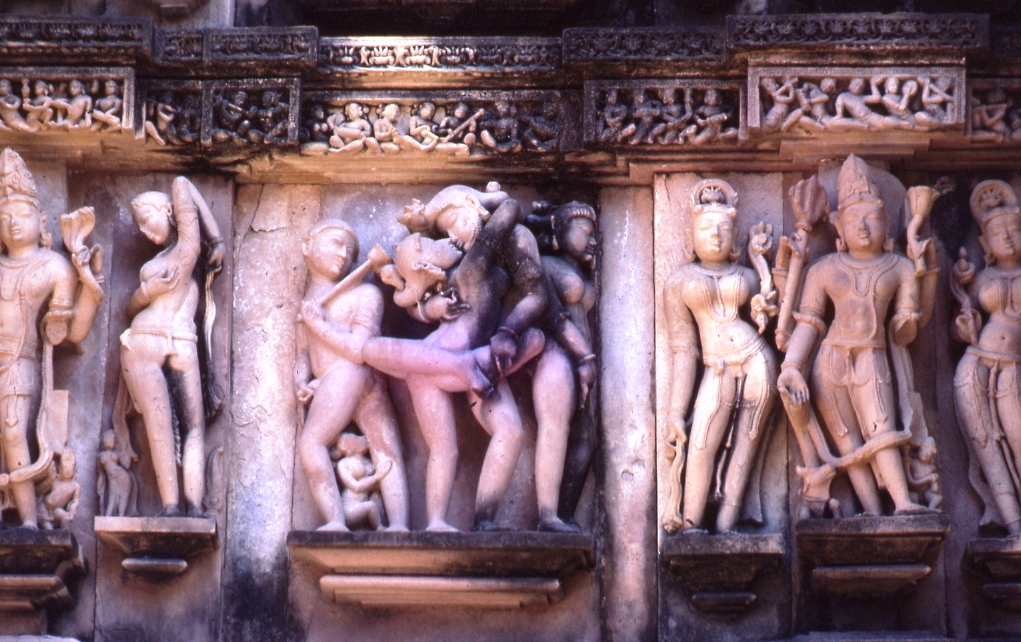 Maithuna intercourse has been traditionally interpreted to be performed with semen retention by the male practitioner, although other writers consider it optional, possibly relegated only to late Tantra. Early maithuna might have insisted on generating sexual fluids (''maithunam dravyam'', or solely ''maithuna'' by
Maithuna intercourse has been traditionally interpreted to be performed with semen retention by the male practitioner, although other writers consider it optional, possibly relegated only to late Tantra. Early maithuna might have insisted on generating sexual fluids (''maithunam dravyam'', or solely ''maithuna'' by
 ''Maithuna'' (
''Maithuna'' (Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; in script: , , ) is an Indic script used in the Indian subcontinent. It is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental Writing systems#Segmental systems: alphabets, writing system), based on the ancient ''Brāhmī script, Brā ...
: मैथुन) is a Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
term for sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
within Tantra
Tantra (; ) is an esoteric yogic tradition that developed on the India, Indian subcontinent beginning in the middle of the 1st millennium CE, first within Shaivism and later in Buddhism.
The term ''tantra'', in the Greater India, Indian tr ...
(Tantric sex
Tantric may refer to:
Religion Religious practices
* Tantra massage, a form of erotic massage
* Tantric sex, Hindu and Buddhist tantric practices that utilize sexual activity in a ritual or yogic context
* Tantric yoga, a form of yoga
* Tibetan ta ...
), or alternatively for the sexual fluids generated or the couple participating in the ritual. It is the most important of the Panchamakara
Panchamakara or Panchatattva, also known as the Five Ms, is the Tantric term for the five substances used in a Tantric practice. These are (alcohol), (meat), (fish), (grain), and '' '' (sexual intercourse). Taboo-breaking elements are only p ...
and constitutes the main part of the grand ritual of Tantra also known as Tattva Chakra. Maithuna means the union of opposing forces, underlining the nonduality
Nondualism includes a number of philosophical and spiritual traditions that emphasize the absence of fundamental duality or separation in existence. This viewpoint questions the boundaries conventionally imposed between self and other, min ...
between human and divine, as well as worldly enjoyment (''kama
''Kama'' (Sanskrit: काम, ) is the concept of pleasure, enjoyment and desire in Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. It can also refer to "desire, wish, longing" in Hindu, Buddhist, Jain, and Sikh literature.Monier Williamsका� ...
'') and spiritual liberation (''moksha
''Moksha'' (; , '), also called ''vimoksha'', ''vimukti'', and ''mukti'', is a term in Jainism, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism for various forms of emancipation, liberation, '' nirvana'', or release. In its soteriological and eschatologic ...
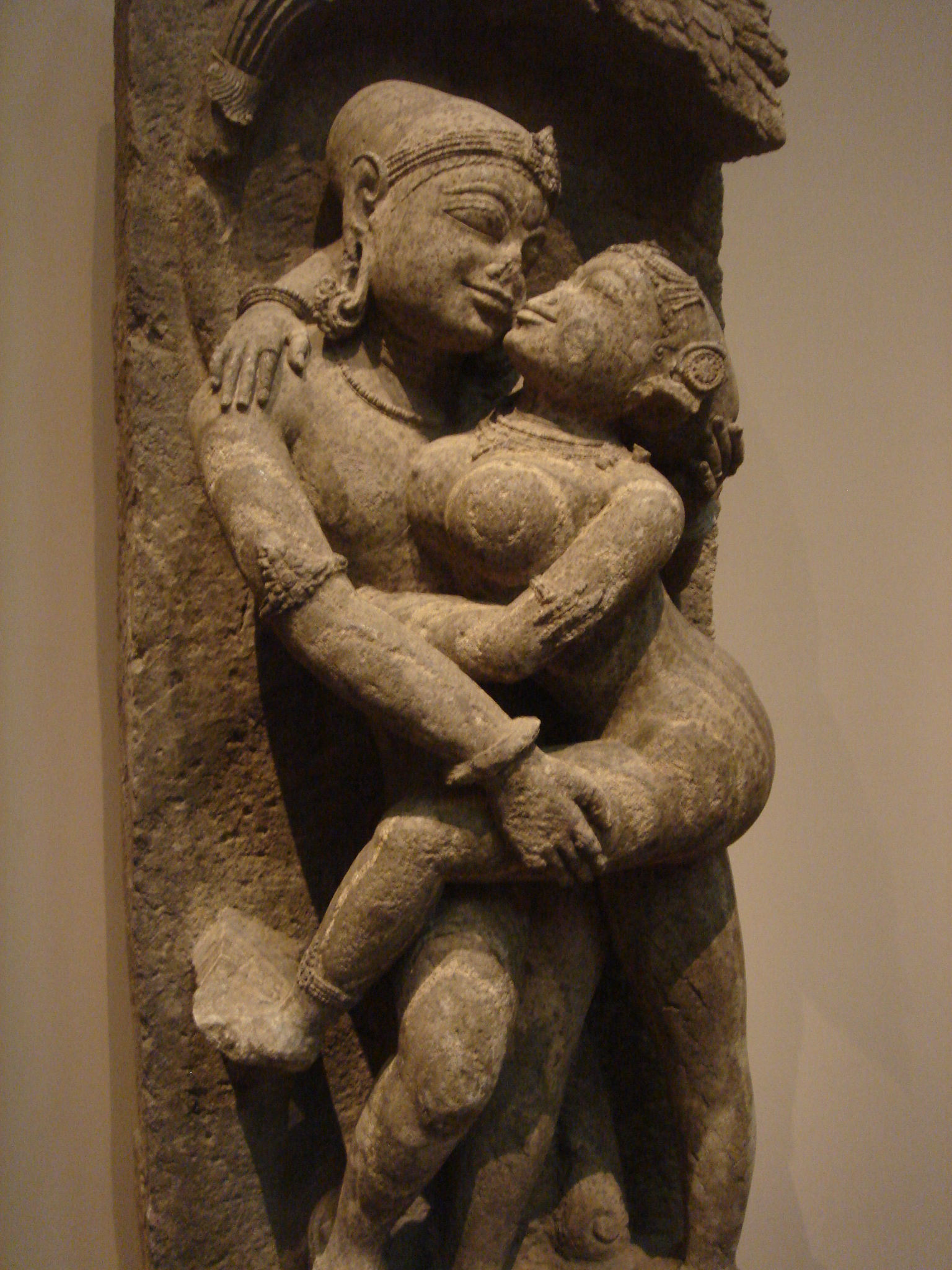
''). Maithuna is a popular icon in ancient Hindu art, portrayed as a couple engaged in physical loving.
Concept
Maithuna entails male-female couples and their union in the physical, sexual sense as synonymous with kriya nishpatti (mature cleansing). Just as neither spirit nor matter by itself is effective but both working together bring harmony so is maithuna effective only then when the union isconsecrated
Sacred describes something that is dedicated or set apart for the service or worship of a deity; is considered worthy of spiritual respect or devotion; or inspires awe or reverence among believers. The property is often ascribed to objects (a ...
. The couple become for the time being divine: she is Shakti
Shakti (Devanagari: शक्ति, IAST: Śakti; 'energy, ability, strength, effort, power, might, capability') in Hinduism, is the "Universal Power" that underlies and sustains all existence. Conceived as feminine in essence, Shakti refer ...
and he is Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
, and they confront ultimate reality and experiences bliss
BLISS is a system programming language developed at Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) by W. A. Wulf, D. B. Russell, and A. N. Habermann around 1970. It was perhaps the best known system language until C debuted a few years later. Since then, C ...
through union. The scriptures warn that unless this spiritual transformation occurs, the union is incomplete. However, some writers, sects and schools like Yogananda consider this to be a purely mental and symbolic act, without actual intercourse.
Yet it is possible to experience a form of maithuna not solely just through the physical union. The act can exist on a metaphysical plane with sexual energy penetration, in which the shakti and shakta transfer energy through their subtle bodies as well. It is when this transfer of energy occurs that the couple, incarnated as goddess and god via diminished egos, confronts ultimate reality and experiences bliss through sexual union of the subtle bodies.
History

 Maithuna intercourse has been traditionally interpreted to be performed with semen retention by the male practitioner, although other writers consider it optional, possibly relegated only to late Tantra. Early maithuna might have insisted on generating sexual fluids (''maithunam dravyam'', or solely ''maithuna'' by
Maithuna intercourse has been traditionally interpreted to be performed with semen retention by the male practitioner, although other writers consider it optional, possibly relegated only to late Tantra. Early maithuna might have insisted on generating sexual fluids (''maithunam dravyam'', or solely ''maithuna'' by metonymy
Metonymy () is a figure of speech in which a concept is referred to by the name of something associated with that thing or concept. For example, the word " suit" may refer to a person from groups commonly wearing business attire, such as sales ...
) in order to be ritually ingested, in a similar way to the other four edible Panchamakara. The shedding of semen is also compared to water-offering (''tarpana
''Tarpana'' or (, , , ) is a term in the Hinduism, Vedic practice that refers to an offering made to divine entities. It refers to the act of offering as well as the substance used in the offering. ''Tilatarpana'' (, , , ) is a specific form of ...
'').
Ascetics of the Shaivite
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the supreme being. It is the second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million Hindus, found widely across South Asia (predominantly in ...
school of Mantramarga, in order to gain supernatural power, reenacted the penance of Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
after cutting off one of Brahma
Brahma (, ) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the triple deity, trinity of Para Brahman, supreme divinity that includes Vishnu and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity, Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212– ...
's heads (Bhikshatana
Bhikshatana (; ; literally, "wandering about for alms, mendicancy") or Bhikshatana-murti () is an aspect of the Hinduism, Hindu god Shiva as the "Supreme mendicant" or the "Supreme Beggar". Bhikshtana is depicted as a nude four-armed man adorn ...
). They worshipped Shiva with impure substances like alcohol, blood and sexual fluids generated in orgiastic rites with their consorts. As part of tantric inversion of social regulations, sexual yoga often recommends the usage of consorts from the most taboo groups available, such as close relatives or people from the lowest sections of society. They must be young and beautiful, as well as initiates in tantra.
Jayanta Bhatta
Jayanta Bhatta ( CE – CE) was a poet, teacher, logician, and an advisor to King Sankaravarman of Kashmir. He was a philosopher of the Nyaya school of Hindu philosophy. He authored three works on Nyaya, Nyāya philosophy: one of which is not ...
, the 9th-century scholar of the Nyaya
Nyāya (Sanskrit: न्यायः, IAST: nyāyaḥ), literally meaning "justice", "rules", "method" or "judgment", is one of the six orthodox (Āstika) schools of Hindu philosophy. Nyāya's most significant contributions to Indian philosophy ...
school of Hindu philosophy
Hindu philosophy or Vedic philosophy is the set of philosophical systems that developed in tandem with the first Hinduism, Hindu religious traditions during the Iron Age in India, iron and Classical India, classical ages of India. In Indian ...
and who commented on Tantra literature, stated that the Tantric ideas and spiritual practices are mostly well placed, but it also has "immoral teachings" such as by the so-called "Nilambara" sect where its practitioners "wear simply one blue garment, and then as a group engage in unconstrained public sex" on festivals. He wrote that this practice is unnecessary and it threatens fundamental values of society.
Later sources like Abhinavagupta
Abhinavagupta (Devanāgarī अभिनवगुप्तः; c. 950 – 1016 CE) was a philosopher, mystic and aesthetician from Kashmir. He was also considered an influential musician, poet, dramatist, exegete, theologian, and logicianR ...
in the tenth century warn that results of maithuna are not meant to be consumed like the rest of Panchamakara, calling those who do so "brutes" (''pasus''). The 11th century '' Toḍala tantra'' places maithuna as the last of its ''pañcamakāra'' or "set of 5 M-words", namely ''madya'' (wine), ''māṃsa'' (meat), ''matsya'' (fish), ''mudrā'' (grain), and ''maithuna''.
Around the 12th century, practices seemed to turn towards the absorption of sexual fluids into the body of the practitioner, like that of ''vajroli mudra
''Vajroli mudra'' (Sanskrit: वज्रोली मुद्रा ''vajrolī mudrā''), the Vajroli Seal, is a practice in Hatha yoga which requires the yogi to preserve his semen, either by learning not to release it, or if released by draw ...
''. This is related to similar practices like ''rajapana'', the drinking of female discharge found in Kaula Tantra, and the mixing of all five ingredients into nectar (''amrita
''Amrita'' (, IAST: ''amṛta''), ''Amrit'' or ''Amata'' in Pali language, Pali, (also called ''Sudha'', ''Amiy'', ''Ami'') is a Sanskrit word that means "immortality". It is a central concept within Indian religions and is often referred to i ...
'') in the Jagannatha
Jagannath (; formerly ) is a Hindu deity worshipped in regional Hindu traditions in India as part of a triad along with (Krishna's) brother Balabhadra, and sister, Subhadra.
Jagannath, within Odia Hinduism, is the supreme god, '' Purushotta ...
temple of Puri
Puri, also known as Jagannath Puri, () is a coastal city and a Nagar Palika, municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India. It is the district headquarters of Puri district and is situated on the Bay of Bengal, south of the state ca ...
, as described by Frédérique Apffel-Marglin.
Douglas Renfrew Brooks states that the antinomian elements such as the use of intoxicating substances and sex were not animistic
Animism (from meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, rivers, Weather, ...
, but were adopted in some Kaula traditions to challenge the Tantric devotee to break down the "distinctions between the ultimate reality of Brahman and the mundane physical and mundane world". By combining erotic and ascetic techniques, states Brooks, the Tantric broke down all social and internal assumptions, became Shiva-like. In Kashmir Shaivism, states David Gray, the antinomian transgressive ideas were internalized, for meditation and reflection, and as a means to "realize a transcendent subjectivity".
References
Works cited
* * * *External links
{{Yoginis Tantric practices Hinduism and sexuality Religious sex rituals