|
Three Bodies Doctrine
According to three bodies doctrine in Hinduism, the human being is composed of three ''shariras'' or "bodies" emanating from Brahman by avidya, "ignorance" or "nescience". They are often equated with the five koshas (sheaths), which cover the atman. This doctrine is an essential doctrine in Indian philosophy and religion, especially Yoga, Advaita Vedanta, Tantra and Shaivism. The three bodies Karana sarira – causal body ''Karana sarira'' or the causal body is merely the cause or seed of the subtle body and the gross body. It has no other function than being the seed of the subtle and the gross body. It is ''nirvikalpa rupam'', "undifferentiated form". It originates with ''avidya'', "ignorance" or "nescience" of the real identity of the atman, instead giving birth to the notion of ''jiva''. Swami Sivananda characterizes the causal body as "The beginningless ignorance that is indescribable". Siddharameshwar Maharaj, the guru of Nisargadatta Maharaj, also describes the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified by adherence to the concept of ''dharma'', a Ṛta, cosmic order maintained by its followers through rituals and righteous living, as expounded in the Vedas. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, it has also been described by the modern term ''Sanātana Dharma'' () emphasizing its eternal nature. ''Vaidika Dharma'' () and ''Arya dharma'' are historical endonyms for Hinduism. Hinduism entails diverse systems of thought, marked by a range of shared Glossary of Hinduism terms, concepts that discuss God in Hinduism, theology, Hindu mythology, mythology, among other topics in Hindu texts, textual sources. Hindu texts have been classified into Śruti () and Smṛti (). The major Hin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adi Shankara
Adi Shankara (8th c. CE), also called Adi Shankaracharya (, ), was an Indian Vedanga, Vedic scholar, Hindu philosophy, philosopher and teacher (''acharya'') of Advaita Vedanta. Reliable information on Shankara's actual life is scant, and his true impact lies in his "iconic representation of Hinduism, Hindu religion and Hindu culture, culture," despite the fact that most Hindus do not adhere to Advaita Vedanta. Tradition also portrays him as the one who reconciled the various Hindu denominations, sects (Vaishnavism, Shaivism, and Shaktism) with the introduction of the form of Puja (Hinduism), worship, the simultaneous worship of five deities – Ganesha, Surya, Vishnu, Shiva and Devi, arguing that all deities were but different forms of the one Brahman, the invisible Supreme Being.Klaus Klostermaier (2007), A Survey of Hinduism, Third Edition, State University of New York Press, , p. 40 While he is often revered as the most important Indian philosophy, Indian philosoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahamkara
Ahamkara (Sanskrit: अहंकार; Romanized: Ahaṁkāra), "I-making," is a Sanskrit term in Hindu philosophy referring to the construction of a Self-concept, or the false identification of the self ( Purusha, atman) with impermanent entities such as the body, mind, or material objects. It evolves from Mahat-tattva, and is one of the four '' Antaḥkaraṇa'' (functions of the mind). Ahamkara in the Bhagavad Gita In the Bhagavad Gita, ahamkara is presented as the ego, or the false identification of the self ( atman) with material nature, which obstructs spiritual liberation (moksha). In 3.27, Krishna warns that actions driven by ahamkara—believing “I am the doer”—bind the soul to karma: “All actions are performed by the gunas of nature, but one deluded by ahamkara thinks, ‘I am the doer.’" Easwaran notes that ahamkara fuels desires that obscure the true self, a theme evident in Krishna’s call for humility in 13.8–12, where virtues like “absence of pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citta
''Citta'' (Pali and Sanskrit: चित्त, or in Prakrit script 𑀘𑀺𑀢𑁆𑀢, pronounced ''chitta'' ͡ɕit̚.tɐ́sup>( key)) is one of three overlapping terms used in the Nikaya to refer to the mind, the others being '' manas'' and '' viññāṇa''. Each is sometimes used in the generic and non-technical sense of "mind" in general, and the three are sometimes used in sequence to refer to one's mental processes as a whole. However, their primary uses are distinct. Usage The Pali–English Dictionary translates ''citta'' as heart or heart-mind, emphasizing it as more the passionate side of the mind, as opposed to manas as the intellect that grasps mental objects (''dhamma''). ''Citta'' is the object of meditation in the third part of Satipatthana, also called Four Foundations of Mindfulness. ''Citta'' primarily represents one's mindset, or state of mind. It is the term used to refer to the quality of mental processes as a whole. ''Citta'' is classified as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mind
The mind is that which thinks, feels, perceives, imagines, remembers, and wills. It covers the totality of mental phenomena, including both conscious processes, through which an individual is aware of external and internal circumstances, and unconscious processes, which can influence an individual without intention or awareness. The mind plays a central role in most aspects of human life, but its exact nature is disputed. Some characterizations focus on internal aspects, saying that the mind transforms information and is not directly accessible to outside observers. Others stress its relation to outward conduct, understanding mental phenomena as dispositions to engage in observable behavior. The mind–body problem is the challenge of explaining the relation between matter and mind. Traditionally, mind and matter were often thought of as distinct substances that could exist independently from one another. The dominant philosophical position since the 20th century has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhi
''Buddhi'' (Sanskrit: बुद्धि) refers to the intellectual faculty and the power to "form and retain concepts, reason, discern, judge, comprehend, understand". Etymology ''Buddhi'' () is derived from the Vedic Sanskrit root ''Budh'' (बुध् ), which literally means "to wake, be awake, observe, heed, attend, learn, become aware of, to know, be conscious again". The term appears extensively in Rigveda and other Vedic literature. ''Buddhi'' means, states Monier Williams, the power to "form, retain concepts; intelligence, reason, intellect, mind", the intellectual faculty and the ability to "discern, judge, comprehend, understand" something. Buddhi is a feminine Sanskrit noun derived from ''*budh'', to be awake, to understand, to know. The same root is the basis for the more familiar masculine form ''Buddha'' and the abstract noun ''bodhi''. Buddhi contrasts from ''manas'' (मनस्) which means "mind", and '' ahamkara'' (अहंंकाऱ) which means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antahkarana
Antaḥkaraṇa (Sanskrit: अन्तःकरण) is a concept in Hindu philosophy, referring to the totality of the mind, including the thinking faculty, the sense of I-ness, and the discriminating faculty. Antaḥ means 'inner' and karaṇa means 'instrument', or, 'function'. Therefore, the word ''Antaḥkaraṇa'' can be understood as 'inner organ', 'inner functions', or, 'inner instrument'. Four Functions The antahkarana is composed of the four functions of the mind, namely the manas (the mind or lower mind), buddhi (the intellect or higher mind), chitta (memory, or, consciousness), and ahamkara (ego, or, I-maker). ''Antaḥkaraṇa'' has also been called the link between the middle and higher mind, the reincarnating part of the mind. In Vedāntic literature, this (''internal organ'') is organised into four parts: # ahaṃkāra (''ego'')—identifies the Atman (''self'') with the body as 'I'. The attachment or identification of the ego, also known as the 'I-maker'. # ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhi
''Buddhi'' (Sanskrit: बुद्धि) refers to the intellectual faculty and the power to "form and retain concepts, reason, discern, judge, comprehend, understand". Etymology ''Buddhi'' () is derived from the Vedic Sanskrit root ''Budh'' (बुध् ), which literally means "to wake, be awake, observe, heed, attend, learn, become aware of, to know, be conscious again". The term appears extensively in Rigveda and other Vedic literature. ''Buddhi'' means, states Monier Williams, the power to "form, retain concepts; intelligence, reason, intellect, mind", the intellectual faculty and the ability to "discern, judge, comprehend, understand" something. Buddhi is a feminine Sanskrit noun derived from ''*budh'', to be awake, to understand, to know. The same root is the basis for the more familiar masculine form ''Buddha'' and the abstract noun ''bodhi''. Buddhi contrasts from ''manas'' (मनस्) which means "mind", and '' ahamkara'' (अहंंकाऱ) which means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manas (early Buddhism)
''Manas'' (Pali Pāli (, IAST: pāl̤i) is a Classical languages of India, classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages, Middle Indo-Aryan language of the Indian subcontinent. It is widely studied because it is the language of the Buddhist ''Pali Canon, Pāli Can ...: मनस्) is one of three overlapping terms used in the nikayas to refer to the mind, the others being '' citta'' and '' viññāṇa''. Comparison with ''citta'' and ''viññāṇa'' ''Manas'', ''citta'', and ''viññāṇa'' are each sometimes used in the generic and non-technical sense of "mind" in general, and the three are sometimes used in sequence to refer to one's mental processes as a whole. Their primary uses are, however, distinct. In the distinction of Abhidhamma Pitaka of Theravada Buddhism, mana or mano is sort of the notion of mind as a whole, whereas a citta is each of instant steps or processes of mind, and viññāṇa is one of the several forms of citta, also being a step of a vithi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
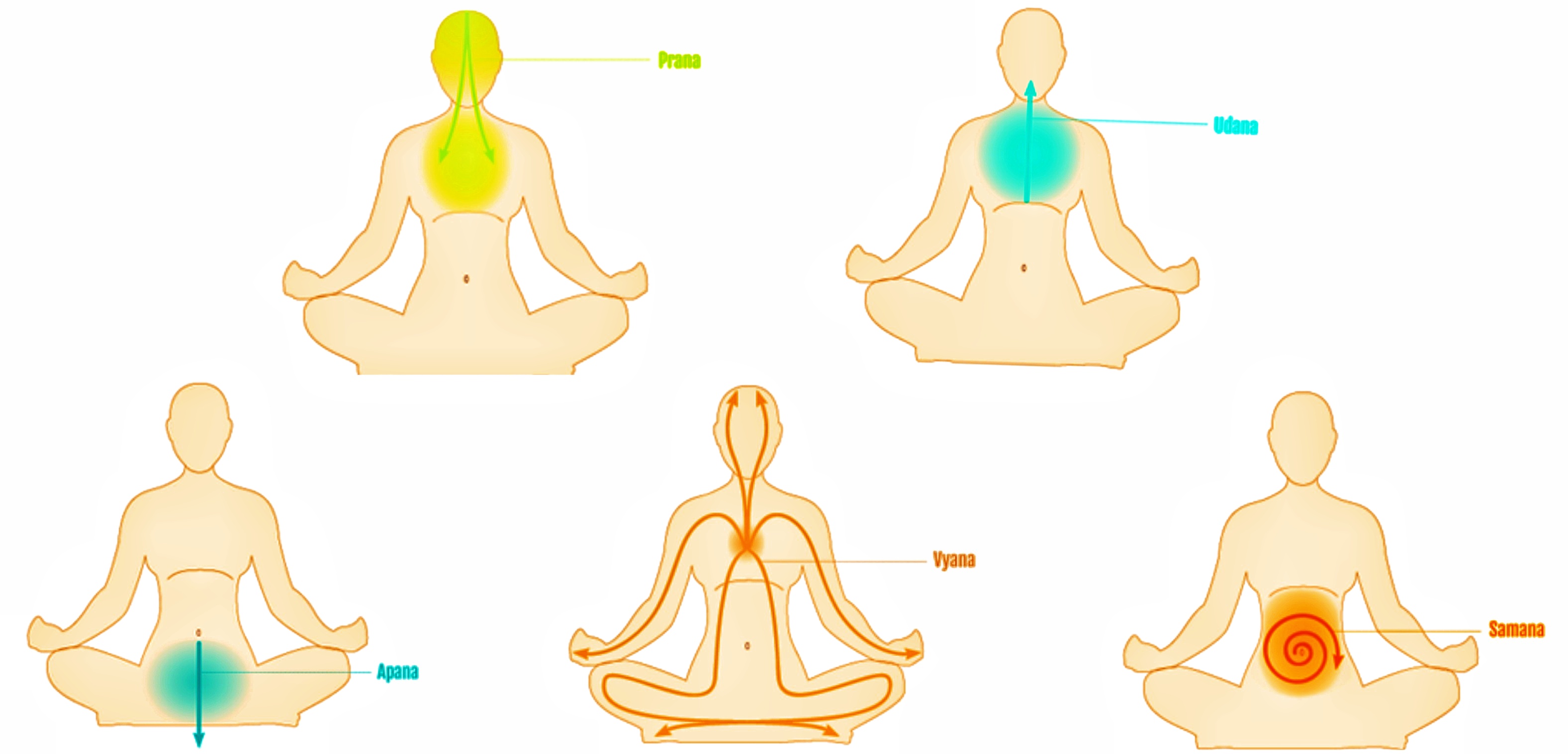
Prana
In yoga, Ayurveda, and Indian martial arts, prana (, ; the Sanskrit word for breath, " life force", or "vital principle") permeates reality on all levels including inanimate objects. In Hindu literature, prāṇa is sometimes described as originating from the Sun and connecting the elements. Five types of prāṇa, collectively known as the five '' vāyus'' ("winds"), are described in Hindu texts. Ayurveda, tantra and Tibetan medicine all describe ''prāṇa vāyu'' as the basic vāyu from which the other vāyus arise. Prana is divided into ten main functions: The five Pranas – Prana, Apana, Udana, Vyana and Samana – and the five Upa-Pranas – Naga, Kurma, Devadatta, Krikala and Dhananjaya. Pranayama, one of the eight limbs of yoga, is intended to expand conscious awareness of prana. Etymology V.S. Apte provides fourteen different meanings for the Sanskrit word ' () including breath or respiration; the breath of life, vital air, principle of life (usually plural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |