mini-shinkansen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is the name given to the concept of converting
is the name given to the concept of converting
 The first mini-Shinkansen route to be built was the Yamagata Shinkansen, converted from the section of the
The first mini-Shinkansen route to be built was the Yamagata Shinkansen, converted from the section of the
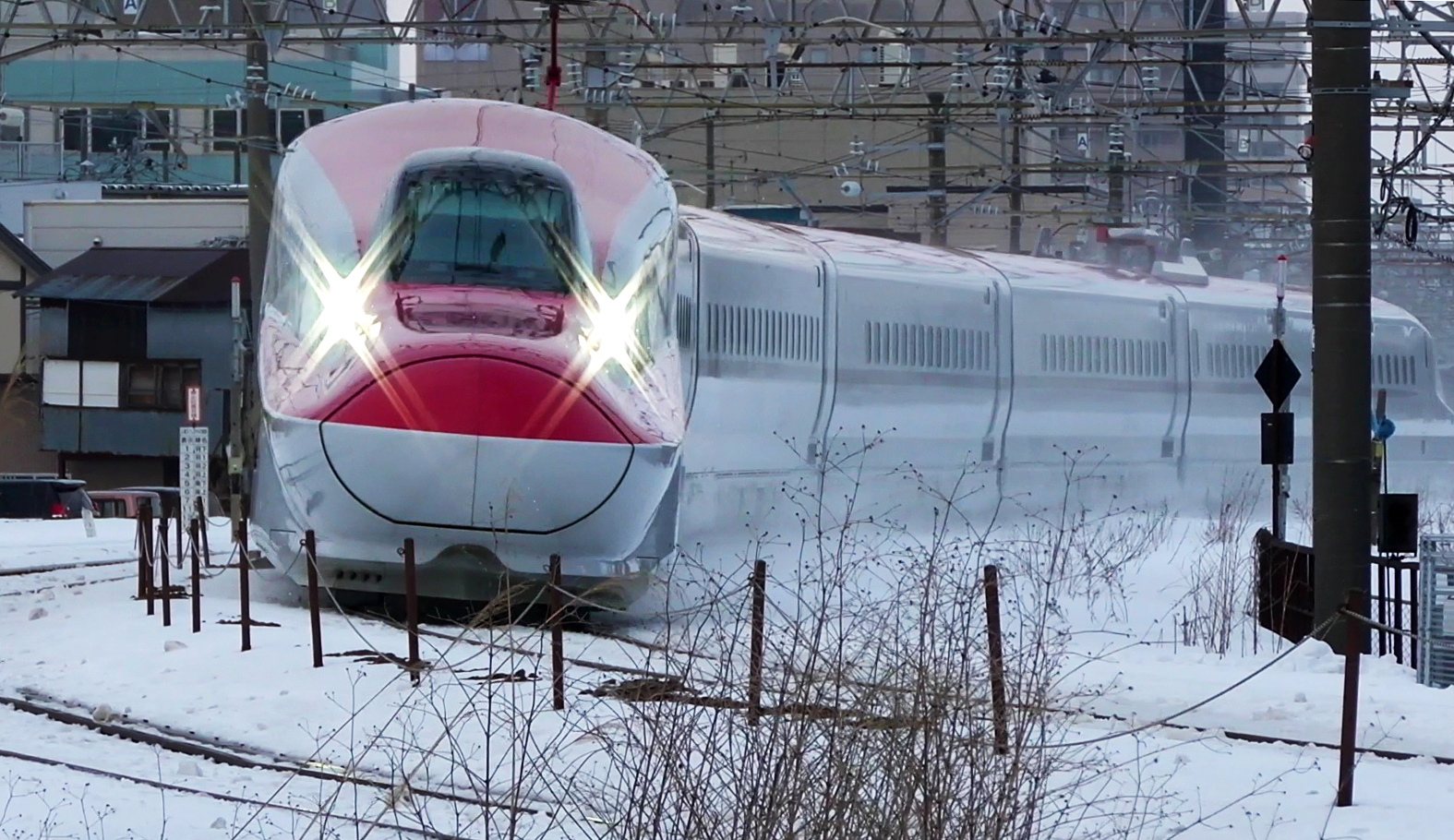 Following the success of the Yamagata Shinkansen conversion, a scheme was proposed to construct a second mini-Shinkansen route from Morioka in
Following the success of the Yamagata Shinkansen conversion, a scheme was proposed to construct a second mini-Shinkansen route from Morioka in
 The following rolling stock was built for use on mini-shinkansen lines.
* 400 Series Shinkansen, Yamagata Shinkansen (in service 1992â2010)
* E3 Series Shinkansen, Akita Shinkansen (in service 1997â2014) and Yamagata Shinkansen (from 1999)
* E926 ''East i'' track and overhead wire inspection train (from 2001)
* E955 ''Fastech 360Z'' experimental test train (2006-2008)
* E6 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Akita Shinkansen in March 2013
* E8 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Yamagata Shinkansen in March 2024
The following rolling stock was built for use on mini-shinkansen lines.
* 400 Series Shinkansen, Yamagata Shinkansen (in service 1992â2010)
* E3 Series Shinkansen, Akita Shinkansen (in service 1997â2014) and Yamagata Shinkansen (from 1999)
* E926 ''East i'' track and overhead wire inspection train (from 2001)
* E955 ''Fastech 360Z'' experimental test train (2006-2008)
* E6 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Akita Shinkansen in March 2013
* E8 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Yamagata Shinkansen in March 2024
 is the name given to the concept of converting
is the name given to the concept of converting narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with Minimum railw ...
railway lines to standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
for use by shinkansen
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. It was initially built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond lon ...
train services in Japan. Unlike the high-speed Shinkansen lines, the mini-Shinkansen lines have a maximum speed of only . Two mini-Shinkansen routes have been constructed: the Yamagata Shinkansen and Akita Shinkansen.
Concept
The Mini-Shinkansen concept was first developed in JNR days, but was not formally proposed until November 1987, following the formation of East Japan Railway Company (JR East). The concept involved regauging existing gauge lines to standard gauge and linking them to the Shinkansen network to allow through-running. While the track gauge was widened, theloading gauge
A loading gauge is a diagram or physical structure that defines the maximum height and width dimensions in railway vehicles and their loads. Their purpose is to ensure that rail vehicles can pass safely through tunnels and under bridges, and k ...
remained unchanged, requiring the construction of new Shinkansen trains with a narrower cross-section. These would be capable of running at high speed (the E6 series trains have a maximum speed capability of ) on Shinkansen tracks, either on their own or coupled to full-sized sets, and run at conventional narrow-gauge speeds (around ) on the mini-shinkansen tracks. Speeds on converted lines would also be raised where possible.
Yamagata Shinkansen
 The first mini-Shinkansen route to be built was the Yamagata Shinkansen, converted from the section of the
The first mini-Shinkansen route to be built was the Yamagata Shinkansen, converted from the section of the Åu Main Line
The is a railway line in Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Fukushima Station (Fukushima), Fukushima Station through Akita Station to Aomori Station. Since the opening of the Yamagata Shinkansen on July 1, 1 ...
between Fukushima on the Tohoku Shinkansen and Yamagata in Yamagata Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the TÅhoku region of Honshu. It has a population of 1,005,926 (1 February 2025) and an area of 9,325 Square kilometre, km2 (3,600 Square mile, sq mi). Its neighbours are Akita Prefectu ...
. Work started in 1988, with Yamagata Shinkansen services commencing on 1 July 1992. Services were operated by a new fleet of 400 Series Shinkansen trains, at up to on the TÅhoku Shinkansen and on the Yamagata Shinkansen section. The success of this initiative led to the conversion of a further of the line to , opening on 4 December 1999.
Akita Shinkansen
 Following the success of the Yamagata Shinkansen conversion, a scheme was proposed to construct a second mini-Shinkansen route from Morioka in
Following the success of the Yamagata Shinkansen conversion, a scheme was proposed to construct a second mini-Shinkansen route from Morioka in Iwate Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the TÅhoku region of Honshu. It is the second-largest Japanese prefecture (behind Hokkaido) at , with a population of 1,165,886 (as of July 1, 2023). Iwate Prefecture borders Aomori Pre ...
, then the northern terminus of the Tohoku Shinkansen, with Akita in Akita Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the TÅhoku region of Honshu.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "Provinces and prefectures" in ; "TÅhoku" in . Its population is estimated 915,691 as of 1 August 2023 and its geographi ...
. This involved regauging the Tazawako Line from Morioka to Åmagari and of the Åu Main Line
The is a railway line in Japan, operated by the East Japan Railway Company (JR East). It connects Fukushima Station (Fukushima), Fukushima Station through Akita Station to Aomori Station. Since the opening of the Yamagata Shinkansen on July 1, 1 ...
from Åmagari to Akita. This opened on 22 March 1997 with '' Komachi'' services using new E3 Series Shinkansen trains.
On 16 March 2013, E6 series trains entered service on this line, initially at a maximum speed of on the Tohoku Shinkansen section. In March 2014, the maximum speed on the Tohoku Shinkansen was increased to .
Rolling stock
 The following rolling stock was built for use on mini-shinkansen lines.
* 400 Series Shinkansen, Yamagata Shinkansen (in service 1992â2010)
* E3 Series Shinkansen, Akita Shinkansen (in service 1997â2014) and Yamagata Shinkansen (from 1999)
* E926 ''East i'' track and overhead wire inspection train (from 2001)
* E955 ''Fastech 360Z'' experimental test train (2006-2008)
* E6 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Akita Shinkansen in March 2013
* E8 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Yamagata Shinkansen in March 2024
The following rolling stock was built for use on mini-shinkansen lines.
* 400 Series Shinkansen, Yamagata Shinkansen (in service 1992â2010)
* E3 Series Shinkansen, Akita Shinkansen (in service 1997â2014) and Yamagata Shinkansen (from 1999)
* E926 ''East i'' track and overhead wire inspection train (from 2001)
* E955 ''Fastech 360Z'' experimental test train (2006-2008)
* E6 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Akita Shinkansen in March 2013
* E8 Series Shinkansen, introduced on the Yamagata Shinkansen in March 2024
See also
* Gauge Change Train, an experimental train designed to operate on both narrow-gauge and standard-gauge routes * Super Tokkyū, a concept of building narrow-gauge lines to Shinkansen standardsReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mini-Shinkansen Shinkansen Railway services introduced in 1992