Mimivirus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 ''Mimivirus'' is a genus of
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of
 The mimivirus is the fourth-largest virus, after the '' Megavirus chilensis'', ''
The mimivirus is the fourth-largest virus, after the '' Megavirus chilensis'', ''
 The stages of mimivirus replication are not well known, but as a minimum it is known that mimivirus attaches to a chemical receptor on the surface of an amoeba cell and is taken into the cell. Once inside, an ''eclipse phase'' begins, in which the virus disappears and all appears normal within the cell. After about 4 hours small accumulations can be seen in areas of the cell. 8 hours after infection many mimivirus virions are clearly visible within the cell. The cell
The stages of mimivirus replication are not well known, but as a minimum it is known that mimivirus attaches to a chemical receptor on the surface of an amoeba cell and is taken into the cell. Once inside, an ''eclipse phase'' begins, in which the virus disappears and all appears normal within the cell. After about 4 hours small accumulations can be seen in areas of the cell. 8 hours after infection many mimivirus virions are clearly visible within the cell. The cell
Viralzone: Mimiviridae
��images of mimivirus. *
The webpage for Mimivirus
Radiolab.org Shrink on the discovery of Mimivirus Thursday, July 30, 2015 - 08:54 PM
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1134104 Mimiviridae Virus genera
 ''Mimivirus'' is a genus of
''Mimivirus'' is a genus of giant virus
A giant virus, sometimes referred to as a girus, is a very large virus, some of which are larger than typical bacteria. All known giant viruses belong to the phylum ''Nucleocytoviricota''.
Description
While the exact criteria as defined in the sc ...
es, in the family ''Mimiviridae
''Mimiviridae'' is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family contains three subfamilies that contain nine genera., UCPMS ID: 1889607PDF/ref> Fig. 4 and §Discussion: "Considering that tupanviruses c ...
''. It is believed that Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ...
serve as their natural hosts. It also refers to a group of phylogenetically related large viruses.
In colloquial speech, APMV is more commonly referred to as just "mimivirus". Mimivirus, short for "mimicking microbe", is so called to reflect its large size and apparent Gram-staining properties.
Mimivirus has a large and complex genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
compared with most other viruses. Until 2013, when a larger virus ''Pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a proposed genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the third largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind Pithovirus and Megaklothovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with t ...
'' was described, it had the largest capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
diameter of all known viruses.
History
APMV was discovered accidentally in 1992 within theamoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; : amoebas (less commonly, amebas) or amoebae (amebae) ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of Cell (biology), cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by ...
'' Acanthamoeba polyphaga'', after which it is named, during research into legionellosis
Legionnaires' disease is a form of atypical pneumonia caused by any species of ''Legionella'' bacteria, quite often ''Legionella pneumophila''. Signs and symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, high fever, muscle pains, and headaches. Nau ...
by researchers from Marseille and Leeds. The virus was observed in a Gram stain
Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes ...
and mistakenly thought to be a Gram-positive
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain is ...
bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
. As a consequence it was named ''Bradfordcoccus'', after Bradford
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in West Yorkshire, England. It became a municipal borough in 1847, received a city charter in 1897 and, since the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 reform, the city status in the United Kingdo ...
, England, where the amoeba had originated. In 2003, researchers at the Université de la Méditerranée in Marseille
Marseille (; ; see #Name, below) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Bouches-du-Rhône and of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region. Situated in the ...
, France, published a paper in ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'' identifying the micro-organism as a virus. It was given the name "mimivirus" (for "mimicking microbe") as it resembles a bacterium on Gram staining
Gram stain (Gram staining or Gram's method), is a method of staining used to classify bacterial species into two large groups: gram-positive bacteria and gram-negative bacteria. It may also be used to diagnose a fungal infection. The name comes ...
.
The same team that discovered the mimivirus later discovered a slightly larger virus, dubbed the mamavirus, and the Sputnik virophage
Sputnik virophage (from Russian "satellite") is a subviral agent that reproduces in amoeba cells that are already infected by a certain helper virus; Sputnik uses the helper virus's machinery for reproduction and inhibits replication of the ...
that infects it.
Classification
''Mimivirus'' has been placed into a viral family by theInternational Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses
The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclature for viruses. The ICTV develops a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropri ...
as a member of the ''Mimiviridae
''Mimiviridae'' is a family of viruses. Amoeba and other protists serve as natural hosts. The family contains three subfamilies that contain nine genera., UCPMS ID: 1889607PDF/ref> Fig. 4 and §Discussion: "Considering that tupanviruses c ...
'', and has been placed into Group I of the Baltimore classification
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a disti ...
system.
Although not strictly a method of classification, mimivirus joins a group of large viruses known as nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses
''Nucleocytoviricota'' is a phylum of viruses. Members of the phylum are also known as the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV), which serves as the basis of the name of the phylum with the suffix - for virus phylum. These viruses are refe ...
(NCLDV). They are all large viruses which share both molecular characteristics and large genomes. The mimivirus genome also possesses 21 genes encoding homologs to proteins which are seen to be highly conserved in the majority of NCLDVs, and further work suggests that mimivirus is an early divergent of the general NCLDV group.
The genus ''Mimivirus'' contains the following species:
* ''Mimivirus bradfordmassiliense''
* ''Mimivirus lagoaense''
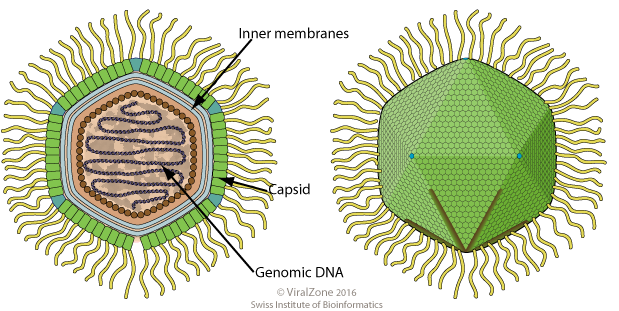
Structure
 The mimivirus is the fourth-largest virus, after the '' Megavirus chilensis'', ''
The mimivirus is the fourth-largest virus, after the '' Megavirus chilensis'', ''Pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a proposed genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the third largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind Pithovirus and Megaklothovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with t ...
'' and ''Pithovirus
''Alphapithovirus'', is a genus of giant virus known from two species, '' Alphapithovirus sibericum'', which infects amoebas, and '' Alphapithovirus massiliense''. It is DNA-based and is a member of the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses clade ...
''. Mimivirus has a capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or m ...
diameter of 400 nm. Protein filaments measuring 100 nm project from the surface of the capsid, bringing the total length of the virus up to 600 nm. Variation in scientific literature renders these figures as highly approximate, with the "size" of the virion
A virion (plural, ''viria'' or ''virions'') is an inert virus particle capable of invading a Cell (biology), cell. Upon entering the cell, the virion disassembles and the genetic material from the virus takes control of the cell infrastructure, t ...
being casually listed as anywhere between 400 nm and 800 nm, depending on whether total length or capsid diameter is actually quoted.
Its capsid appears hexagonal under an electron microscope
An electron microscope is a microscope that uses a beam of electrons as a source of illumination. It uses electron optics that are analogous to the glass lenses of an optical light microscope to control the electron beam, for instance focusing it ...
, therefore the capsid symmetry is icosahedral. It does not appear to possess an outer viral envelope, suggesting that the virus does not exit the host cell by exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis ...
.
Mimivirus shares several morphological characteristics with all members of the NCLDV group of viruses. The condensed central core of the virion appears as a dark region under the electron microscope. The large genome of the virus resides within this area. An internal lipid layer surrounding the central core is present in all other NCLDV viruses, so this features may also be present in mimivirus.
Several mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of Protein biosynthesis, synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is ...
transcripts can be recovered from purified virions. Like other NCLDVs, transcripts for DNA polymerase
A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates, the molecular precursors of DNA. These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create t ...
, a capsid protein and a TFII-like transcription factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ...
were found. However, three distinct aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its pre ...
enzyme transcripts and four unknown mRNA molecules specific to mimivirus were also found. These pre-packaged transcripts can be translated without viral gene expression and are likely to be necessary to Mimivirus for replication. Other DNA virus
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and t ...
es, such as the ''Human cytomegalovirus
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), also called human herpesvirus 5 (HHV-5), is a species of virus in the genus ''Cytomegalovirus'', which in turn is a member of the viral family known as ''Herpesviridae'' or herpesviruses. It is also commonly call ...
'' and '' Herpes simplex virus type-1'', also feature pre-packaged mRNA transcripts.
Genome
The mimivirus genome is a linear, double-stranded molecule ofDNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
with 1,181,404 base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s in length. This makes it one of the largest viral genomes known, outstripping the next-largest virus genome of the ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'' virus by about 450,000 base pairs. In addition, it is larger than at least 30 cellular clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach t ...
s.
In addition to the large size of the genome, mimivirus possesses an estimated 979 protein-coding gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s, far exceeding the minimum 4 genes required for viruses to exist (''cf.'' MS2 and Qβ viruses). Analysis of its genome revealed the presence of genes not seen in any other viruses, including aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (aaRS or ARS), also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its pre ...
s, and other genes previously thought only to be encoded by cellular organisms. Like other large DNA viruses, mimivirus contains several genes for sugar, lipid and amino acid metabolism, as well as some metabolic genes not found in any other virus. Roughly 90% of the genome was of coding capacity, with the other 10% being "junk DNA
Junk DNA (non-functional DNA) is a DNA sequence that has no known biological function. Most organisms have some junk DNA in their genomes—mostly pseudogenes and fragments of transposons and viruses—but it is possible that some organ ...
".
Replication
 The stages of mimivirus replication are not well known, but as a minimum it is known that mimivirus attaches to a chemical receptor on the surface of an amoeba cell and is taken into the cell. Once inside, an ''eclipse phase'' begins, in which the virus disappears and all appears normal within the cell. After about 4 hours small accumulations can be seen in areas of the cell. 8 hours after infection many mimivirus virions are clearly visible within the cell. The cell
The stages of mimivirus replication are not well known, but as a minimum it is known that mimivirus attaches to a chemical receptor on the surface of an amoeba cell and is taken into the cell. Once inside, an ''eclipse phase'' begins, in which the virus disappears and all appears normal within the cell. After about 4 hours small accumulations can be seen in areas of the cell. 8 hours after infection many mimivirus virions are clearly visible within the cell. The cell cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
continues to fill with newly synthesised virions, and about 24 hours after initial infection the cell likely bursts open to release the new mimivirus virions.
Little is known about the details of this replication cycle, most obviously attachment to the cell surface and entry, viral core
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or ma ...
release, DNA replication, transcription, translation, assembly and release of progeny virions. However, scientists have established the general overview given above using electron micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken ...
s of infected cells. These micrographs show mimivirus capsid assembly in the nucleus, acquisition of an inner lipid membrane via budding from the nucleus, and particles similar to those found in many other viruses, including all NCLDV members. These particles are known in other viruses as ''viral factories'' and allow efficient viral assembly by modifying large areas of the host cell.
Pathogenicity
Mimivirus may be a causative agent of some forms ofpneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
; this is based mainly on indirect evidence in the form of antibodies
An antibody (Ab) or immunoglobulin (Ig) is a large, Y-shaped protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily which is used by the immune system to identify and neutralize antigens such as bacteria and viruses, including those that caus ...
to the virus discovered in pneumonia patients. However, the classification of mimivirus as a pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
is tenuous at present as there have been only a couple of papers published potentially linking mimivirus to actual cases of pneumonia. A significant fraction of pneumonia cases are of unknown cause, though a mimivirus has been isolated from a Tunisian woman suffering from pneumonia.
There is evidence that mimivirus can infect macrophages
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
.
See also
* ''Cafeteria roenbergensis'' virus a giant marine virus * Mamavirus * Marseillevirus—another giant virus *Megavirus
''Megavirus'' is a viral genus, phylogenetically related to '' Acanthamoeba polyphaga mimivirus'' (APMV). In colloquial speech, ''Megavirus chilense'' is more commonly referred to as just "Megavirus". Until the discovery of pandoraviruses in 2 ...
—another giant virus
* ''Mycoplasma genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (also known as ''MG','' Mgen, or since 2018, ''Mycoplasmoides genitalium'') is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in ...
''—one of the smallest bacteria
* '' Nanoarchaeum equitans''—smallest known independent cell
* Nanobacterium
''Nanobacterium'' ( , pl. ''nanobacteria'' ) is the unit or member name of a former proposed class of living organisms, specifically cell-walled microorganisms, now discredited, with a size much smaller than the generally accepted lower limit ...
* Nanobe
* Non-cellular life
Non-cellular life, also known as acellular life, is life that exists without a cellular structure for at least part of its life cycle. Historically, most definitions of life postulated that an organism must be composed of one or more cells, ...
* Pandoravirus
''Pandoravirus'' is a proposed genus of giant virus, first discovered in 2013. It is the third largest in physical size of any known viral genus, behind Pithovirus and Megaklothovirus. Pandoraviruses have double stranded DNA genomes, with t ...
* Pithovirus
''Alphapithovirus'', is a genus of giant virus known from two species, '' Alphapithovirus sibericum'', which infects amoebas, and '' Alphapithovirus massiliense''. It is DNA-based and is a member of the nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses clade ...
—the largest known virus
* Parvovirus
Parvoviruses are a family of animal viruses that constitute the family ''Parvoviridae''. They have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes that typically contain two genes encoding for a replication initiator protein, called NS1, and the p ...
—smallest known virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es
* ''Pelagibacter ubique
"''Candidatus'' Pelagibacter", with the single species "''Ca.'' P. communis", was isolated in 2002 and given a specific name, although it has not yet been described as required by the bacteriological code. It is an abundant member of the SAR11 ...
''—possesses one of the smallest bacterial genomes
* Virophage
Virophages are small, double-stranded DNA viral phages that require the co-infection of another virus. The co-infecting viruses are typically giant viruses. Virophages rely on the viral replication factory of the co-infecting giant virus for t ...
—a virus that requires the host cell to be co-infected with a giant virus
* The Giant Virus Finder is a software tool that identifies giant viruses in environmental Metagenomes.
References
Further reading
* * * * *External links
Viralzone: Mimiviridae
��images of mimivirus. *
The webpage for Mimivirus
Radiolab.org Shrink on the discovery of Mimivirus Thursday, July 30, 2015 - 08:54 PM
{{Taxonbar, from=Q1134104 Mimiviridae Virus genera