Milos Forman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Milos or Melos (; , ; ) is a volcanic
was found in the ruins of the Pillar room and was executed with delicate colouring and graphic observation of nature in the graceful movement of a fish. Stylistic similarities to Minoan
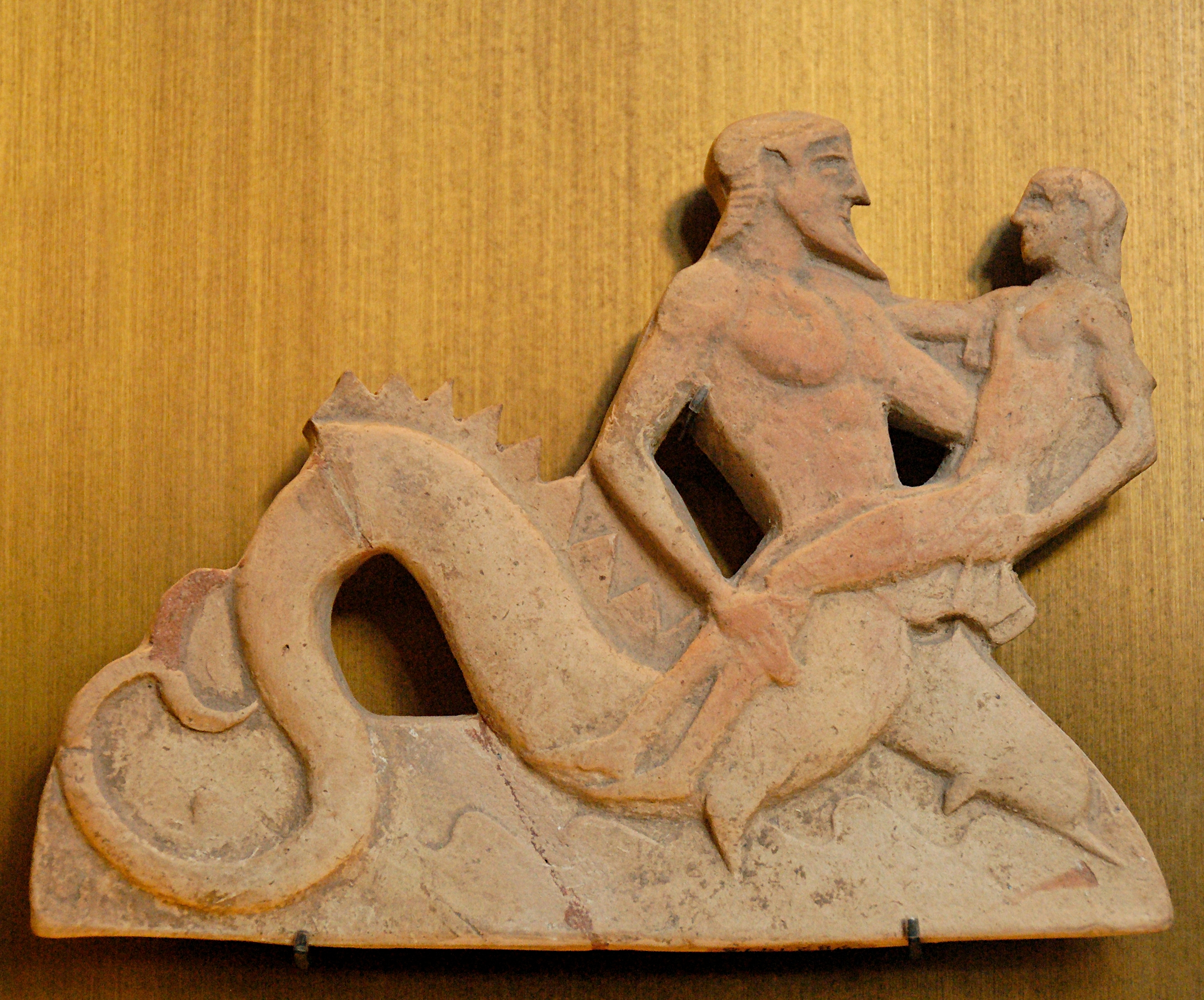
 From at least as early as 470 BC and ending with the siege of 416 BC, the Melians exported terracotta reliefs, which were typically use as door or chest ornaments and depicted scenes from mythology.
During the
From at least as early as 470 BC and ending with the siege of 416 BC, the Melians exported terracotta reliefs, which were typically use as door or chest ornaments and depicted scenes from mythology.
During the
''Hellenica'', 2.2.9
"Meantime Lysander, upon reaching Aegina, restored the state to the Aeginetans, gathering together as many of them as he could, and he did the same thing for the Melians also and for all the others who had been deprived of their native states."Plutarch
''Life of Lysander'', 14.3
"But there were other measures of Lysander upon which all the Greeks looked with pleasure, when, for instance, the Aeginetans, after a long time, received back their own city, and when the Melians and Scionaeans were restored to their homes by him, after the Athenians had been driven out and had delivered back the cities." Sparta annexed Melos, which would mean that like other liberated islands, it received a military governor (a '' harmost''). The cultural distinctiveness of Melos faded away as it was absorbed into mainstream Greek culture.Brian Sparkes, in Their coinage switched to the Rhodian standard (
 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the
 In the early 18th century, the population surpassed 6,000 and was almost entirely Greek and Christian. It was ruled by Turkish judge or '' kadi'', and a Turkish governor or ''
In the early 18th century, the population surpassed 6,000 and was almost entirely Greek and Christian. It was ruled by Turkish judge or '' kadi'', and a Turkish governor or ''
 Milos is the southwestern-most island in the Cyclades, due east from the
Milos is the southwestern-most island in the Cyclades, due east from the




"The Athenian Expedition to Melos in 416 B.C.," ''Historia'' 46 (1997) pp. 385–418.
* * * * * * * *Thucydides (c. 400 BC).
History of the Peloponnesian War
'. Translated by Richard Crawley (1914). * * * * * * *
Official website
{{Authority control Cyclades Islands of Greece Islands of the South Aegean Landforms of Milos (regional unit) Members of the Delian League Municipalities of the South Aegean Populated places in Milos (regional unit) Subduction volcanoes Submarine calderas Volcanoes of Greece Volcanoes of the Aegean Stratovolcanoes Pliocene volcanoes Pleistocene stratovolcanoes Dormant volcanoes Populated places in the ancient Aegean islands
Greek island
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227.
The largest Greek island by ...
in the Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some . In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn con ...
, just north of the Sea of Crete
300px, Map of the Sea of Crete
The Sea of Crete (, ''Kritiko Pelagos''), or Cretan Sea, is a sea, part of the Aegean Sea, located in its southern extremity, with a total surface area of . The sea stretches to the north of the island of Crete, eas ...
. It is the southwestern-most island of the Cyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
group.
The ''Venus de Milo
The ''Venus de Milo'' or ''Aphrodite of Melos'' is an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek marble sculpture that was created during the Hellenistic art, Hellenistic period. Its exact dating is uncertain, but the modern consensus places it in the 2nd ...
'' (now in the Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is a national art museum in Paris, France, and one of the most famous museums in the world. It is located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in the city's 1st arrondissement of Paris, 1st arron ...
), the ''Poseidon of Melos
The Poseidon of Melos () is a statue of Poseidon in the National Archaeological Museum, Athens (NAMA), with an inventory number 235, which is dated to the last quarter of the second century BC, thus to the Hellenistic Period.
The statue was foun ...
'' (now in the NAMA) and the ''Asclepius of Milos
The Asclepius of Milos or Asklepios of Melos is a marble head from what was once a colossal ancient Greek statue of Asclepius found on the island of Milos in Greece. It was acquired by the British Museum along with the rest of the Blacas collect ...
'' (now in the British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
) were all found on the island, as was an archaic Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
now in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
. Milos is a popular tourist destination during the summer. The municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality' ...
of Milos also includes the uninhabited offshore islands of Antimilos
Antimilos (; ) is a Greek island in the Cyclades group, northwest of Milos. Administratively, it is part of the municipality of Milos. Antimilos is an uninhabited mass of trachyte (671 m height), often called Erimomilos (Desert Milos). It is a v ...
and Akradies. The combined land area is and at the 2021 census the population was 5,193 inhabitants.
History
Obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
(a glass-like volcanic rock) from Milos was a commodity as early as 15,000 years ago. Natural glass from Milos was transported over long distances and used for razor-sharp "stone tools" well before farming began and later: "There is no early farming village in the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
that doesn't get obsidian". The mining of obsidian did not lead to the development of permanent habitation or manufacturing on the island. Instead, those in search of obsidian arrived by boat, beaching it in a suitable cove and cutting pieces of the volcanic glass from the quarries.
The position of Milos, between mainland Greece and Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, and its possession of obsidian, made it an important centre of early Aegean civilisation
Aegean civilization is a general term for the Bronze Age civilization
A civilization (also spelled civilisation in British English) is any complex society characterized by the development of state (polity), the state, social stratificat ...
. Milos lost its arms-making importance when bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
became the preferred material for the manufacture of weapons.Chalk and Jonassohn, 65
The Bronze Age
The first settlement atPhylakopi
Phylakopi (), located at the northern coast of the island of Milos, is one of the most important Bronze Age settlements in the Aegean and especially in the Cyclades. The importance of Phylakopi is in its continuity throughout the Bronze Age (i. ...
(Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
Φυλακωπή) arose in the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
, flourishing as the extraction of obsidian was in the decline. The first settlers were tuna
A tuna (: tunas or tuna) is a saltwater fish that belongs to the tribe Thunnini, a subgrouping of the Scombridae ( mackerel) family. The Thunnini comprise 15 species across five genera, the sizes of which vary greatly, ranging from the bul ...
fishermen. Lying on the north-east coast, 1896 excavations by the British School at Athens
The British School at Athens (BSA; ) is an institute for advanced research, one of the eight British International Research Institutes supported by the British Academy, that promotes the study of Greece in all its aspects. Under UK law it is a reg ...
and later in 1973 by the British archaeologist Colin Renfrew
Andrew Colin Renfrew, Baron Renfrew of Kaimsthorn, (25 July 1937 – 24 November 2024) was a British archaeologist, paleolinguist and Conservative peer noted for his work on radiocarbon dating, the prehistory of languages, archaeogenetics, ...
, revealed a town wall and a Minoan
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and Minoan art, energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe. The ruins of the Minoan pa ...
-inspired structure, dubbed the Pillar room, which contained fragments of vivid wall paintings. The famous fresco of the flying fishFlying fishwas found in the ruins of the Pillar room and was executed with delicate colouring and graphic observation of nature in the graceful movement of a fish. Stylistic similarities to Minoan
fresco
Fresco ( or frescoes) is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaster, the painting become ...
es are suggested, and it could perhaps have been the work of a Cretan artist. Part of the site has been washed away by the sea.
The antiquities found at the site covered three major periods, from the Early Cycladic period to the Mycenaean period
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
. At the site much pottery was excavated, with several changing styles and influences over the site's long occupation. In the early occupation of the site, there are many similarities and imports from other Cycladic islands and the settlement was very small. During the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
however, the site expanded significantly and the expansion of Minoan Crete saw an influx of Minoan pottery into the Cyclades, particularly at Akrotiri on Thera
Santorini (, ), officially Thira (, ) or Thera, is a Greek island in the southern Aegean Sea, about southeast from the mainland. It is the largest island of a small, circular archipelago formed by the Santorini caldera. It is the southernmos ...
, though much found its way to Phylakopi. The quantities found at the Cycladic sites have been taken to suggest a Minoan control over the region, though it could also be the consumptive nature of the islanders adopting Cretan fashions. There is more than just pottery at Phylakopi however, the eruption of the Thera volcano saw a reduction in Minoan presence in the Cyclades and it is at this time that Mycenaean involvement on the islands increases. At Phylakopi (and unknown in the rest of the Cyclades) a megaron
The ''megaron'' (; , , : ''megara'' ) was the great hall in very early Mycenae, Mycenean and Ancient Greece, ancient Greek palace complexes. Architecturally, it was a rectangular hall that was supported by four columns, fronted by an open, two- ...
structure, which is typically associated with the Mycenaean palaces, such as those at Tiryns
Tiryns ( or ; Ancient Greek: Τίρυνς; Modern Greek: Τίρυνθα) is a Mycenaean archaeological site in Argolis in the Peloponnese, and the location from which the mythical hero Heracles was said to have performed his Twelve Labours. It ...
, Pylos
Pylos (, ; ), historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of ...
and Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and sou ...
has been discovered. This has been taken to suggest that the Mycenaeans conquered the settlement and installed a seat of power for a governor. The evidence is not clear, though again it could be a legacy of the islanders adopting foreign elements into their culture. Particularly unexpected was the discovery in the 1970s of a shrine at the site, which contained many examples of Aegean figurines, including the famous "Lady of Phylakopi". The shrine is unprecedented in the Bronze Age Cyclades and has provided a valuable insight into the beliefs and rituals of the inhabitants of Phylakopi. The site was eventually abandoned and was never reoccupied.
Dorian settlement
The first Dorian settlement on Melos was established no earlier than the 1st millennium BC.Dorians
The Dorians (; , , singular , ) were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Greeks, Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans (tribe), Achaeans, and Ionians). They are almost alw ...
are the ethnic group to which the Spartans
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the valley of Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern P ...
belonged, but the Dorian settlers of Melos made themselves independent. They eventually established a city whose site lies on the eastern shore of the bay, just south-west of the present-day community of Trypiti.
From the 6th century BC up to the siege of 416 BC, Melos issued its own coinage, struck according to the Milesian weight standard: the base coin was the ''stater
The stater (; ) was an ancient coin used in various regions of Greece. The term is also used for similar coins, imitating Greek staters, minted elsewhere in ancient Europe.
History
The stater, as a Greek silver currency, first as ingots, and ...
'' which weighed just over 14 grams. Melos was the only island in the Aegean Sea to use this standard. Most coins bore the image of an apple, which is a pun because the ancient Greek word for "apple" (''mêlon'') sounded similar to the name of the island. The coins also often bore the name of its people: ΜΑΛΙΟΝ (''Malion'') or some abbreviation thereof.
By the 6th century BC, the Melians had also learned to write, and they used an archaic variant of the ancient Greek script that exhibited Cretan
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
and Thera
Santorini (, ), officially Thira (, ) or Thera, is a Greek island in the southern Aegean Sea, about southeast from the mainland. It is the largest island of a small, circular archipelago formed by the Santorini caldera. It is the southernmos ...
ic influences. It was discarded after the siege of 416 BC.

 From at least as early as 470 BC and ending with the siege of 416 BC, the Melians exported terracotta reliefs, which were typically use as door or chest ornaments and depicted scenes from mythology.
During the
From at least as early as 470 BC and ending with the siege of 416 BC, the Melians exported terracotta reliefs, which were typically use as door or chest ornaments and depicted scenes from mythology.
During the second Persian invasion of Greece
The second Persian invasion of Greece (480–479 BC) occurred during the Greco-Persian Wars, as King Xerxes I of Persia sought to conquer all of Greece. The invasion was a direct, if delayed, response to the defeat of the first Persian invasi ...
in 480 BC, the Melians refused to submit to Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
and contributed two warships to the Greek war effort, which were used at the Battle of Salamis
The Battle of Salamis ( ) was a naval battle fought in 480 BC, between an alliance of Greek city-states under Themistocles, and the Achaemenid Empire under King Xerxes. It resulted in a victory for the outnumbered Greeks.
The battle was fou ...
. After the battle, the Melians returned to their traditional isolationism.
Siege of 416 BC
During thePeloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
(431-404 BC) between Athens and Sparta, the Melians made some small donations to the Spartan war effort, but remained largely neutral despite sharing the Spartans' Dorian ethnicity. In 426 BC, the Athenians raided the Melian countryside, and the following year demanded tribute, but Melos refused. In the summer of 416 BC, Athens invaded again with 3,400 men, and demanded that Melos ally with them against Sparta, or be destroyed. The Melians rejected this, so the Athenian army laid siege to the city and eventually captured it in the winter. After the city's fall, the Athenians executed all the adult men, and sold the women and children into slavery. They then settled 500 of their own colonists on the island.
In 405 BC, with Athens losing the war, the Spartan general Lysander
Lysander (; ; 454 BC – 395 BC) was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played ...
expelled the Athenian settlers from Melos and repatriated the survivors of the siege.Xenophon''Hellenica'', 2.2.9
"Meantime Lysander, upon reaching Aegina, restored the state to the Aeginetans, gathering together as many of them as he could, and he did the same thing for the Melians also and for all the others who had been deprived of their native states."Plutarch
''Life of Lysander'', 14.3
"But there were other measures of Lysander upon which all the Greeks looked with pleasure, when, for instance, the Aeginetans, after a long time, received back their own city, and when the Melians and Scionaeans were restored to their homes by him, after the Athenians had been driven out and had delivered back the cities." Sparta annexed Melos, which would mean that like other liberated islands, it received a military governor (a '' harmost''). The cultural distinctiveness of Melos faded away as it was absorbed into mainstream Greek culture.Brian Sparkes, in Their coinage switched to the Rhodian standard (
tetradrachm
The tetradrachm () was a large silver coin that originated in Ancient Greece. It was nominally equivalent to four drachmae. Over time the tetradrachm effectively became the standard coin of the Antiquity, spreading well beyond the borders of the ...
s weighing 15.3 g) and ceased bearing the word ΜΑΛΙΟΝ. The production of its terracotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based non-vitreous ceramic OED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used for earthenware obj ...
reliefs also ceased.
The Hellenistic period
In 338 BC,Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon (; 382 BC – October 336 BC) was the king (''basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
defeated the Greeks at the Battle of Chaeroneia and became the overlord
An overlord in the English feudal system was a lord of a manor who had subinfeudated a particular manor, estate or fee, to a tenant. The tenant thenceforth owed to the overlord one of a variety of services, usually military service or ...
of Greece and the Cyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
. During this time, Melos and the nearby island Kimolos disputed each other over the ownership of the islands of Polyaigos, Heterea, and Libea (the last two are probably today's uninhabited islands of Agios Efstathios and Agios Georgios). In the past, this dispute would have been settled by war, but the two communities took their dispute to Argos on the Greek mainland. The Argives
Argos (; ; ) is a city and former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece and is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and the oldest in Europe. It is the largest city in Argolis and a major center in the same pr ...
decided the islands belonged to Kimolos.
The Roman and Byzantine period
In 197 BC, the Romans forced Philip V to withdraw from Greece, and Melos subsequently came under Roman influence. During the early 9th century CE theCyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
were harassed by Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
raiders, though how Milos fared at this time is unclear. Milos was mentioned in a Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
chrysobull
A golden bull or chrysobull was a decree issued by Byzantine emperors and monarchs in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance.
Description
A golden bull was a decree issued by Byzantine Emperors. It was later used by monarchs in Europe ...
of 1198, which shows it was still important to the Byzantines.
Medieval period
 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
(1204), the Venetian Marco Sanudo seized control of Milos and a number of other islands in the Cyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
. Sanudo declared himself the Duke of Naxos
The Duchy of the Archipelago (, , ), also known as Duchy of Naxos or Duchy of the Aegean, was a maritime state created by Venetian interests in the Cyclades archipelago in the Aegean Sea, in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade, centered on the i ...
, after the island where he established his capital. Sanudo did not make his duchy a vassal of Venice, but instead declared loyalty to the Latin Emperor
The Latin Emperor was the ruler of the Latin Empire, the historiographical convention for the Crusader realm, established in Constantinople after the Fourth Crusade (1204) and lasting until the city was reconquered by the Byzantine Greeks in 12 ...
. Sanudo's dynasty lasted nine generations, then was succeeded by the Crispos. Both families were Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
. The majority of the population was (and still is) Greek Orthodox
Greek Orthodox Church (, , ) is a term that can refer to any one of three classes of Christian Churches, each associated in some way with Greek Christianity, Levantine Arabic-speaking Christians or more broadly the rite used in the Eastern Rom ...
.
Up to this point, the population of Melos was overwhelmingly Greek Orthodox Christian, just like the rest of the archipelago. When the Venetians conquered the archipelago, they brought Catholicism with them. The first Catholic bishop of Milos was appointed in 1253.
Ottoman period
In 1566 the Venetians handed over the Duchy of Naxos to theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, and its last Catholic duke fled to Venice. The Ottoman sultan Selim II appointed a Portuguese Jew named Joseph Nasi as its duke. Upon Nasi's death in 1579, the Ottomans formally annexed the territory.
 In the early 18th century, the population surpassed 6,000 and was almost entirely Greek and Christian. It was ruled by Turkish judge or '' kadi'', and a Turkish governor or ''
In the early 18th century, the population surpassed 6,000 and was almost entirely Greek and Christian. It was ruled by Turkish judge or '' kadi'', and a Turkish governor or ''voivode
Voivode ( ), also spelled voivod, voievod or voevod and also known as vaivode ( ), voivoda, vojvoda, vaivada or wojewoda, is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe in use since the Early Mid ...
''. The ''voivode'' was responsible for collecting taxes and enforcing the decisions of the ''kadi''. The day-to-day affairs of the island were managed by three elected magistrates ('' epitropi''), although any of their decisions could be appealed to the ''kadi''. The island had two bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
s: one Greek Orthodox and one Latin Catholic. The Greek bishop was wealthier than his Latin counterpart, as he had a larger revenue base. Although the islanders enjoyed a great degree of autonomy, they chafed under the heavy taxation of their Ottoman overlords.
In 1771 the island was occupied by the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
for three years, then retaken by the Ottomans.
In the late 18th century, the population declined considerably for uncertain reasons. By 1798, it had fallen below 500 people. Visitors reported that up to two thirds of the buildings had fallen into ruin. It began growing again in the early 19th century, reaching 5,000 people by 1821. Reliable figures are hard to find as the Ottoman Empire never performed a census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ...
before 1881.
Modern period
Milos was one of the first islands to join theGreek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. In 1826, the Greeks were assisted ...
of 1821. The first naval battle of the war took place off the coast of Milos on 11 April 1821. Milos became a refuge for refugees from numerous islands, particularly Crete. The port town of Adamantas was founded by Cretan refugees from the Cretan Revolt in 1841.
When Theodore Bent toured the island in December 1883, note-taking for his guide to the Cyclades, he found that “There is a lack of energy nowadays in Melos, for Syra
Syros ( ), also known as Siros or Syra, is a Greece, Greek island in the Cyclades, in the Aegean Sea. It is south-east of Athens. The area of the island is and at the 2021 census it had 21,124 inhabitants.
The largest towns are Ermoupoli, Ano S ...
monopolises all the trade that once came here, and the Cretan exiles refuse to cultivate as they ought the fertile centre of the island, for they are only awaiting a favourable turn in events to return to their own island…”
During the 19th century, Milos was a major rendezvous point for American and British ships fighting Muslim pirates in the Mediterranean.
In February 1943, 14 male civilians were executed
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender b ...
for collecting material owned by the German occupation forces that was washed up after the sinking of a cargo ship by Allied aircraft.
The population peaked in 1928 at 6,562 people. In 2011 it was 4,977.
Geography
 Milos is the southwestern-most island in the Cyclades, due east from the
Milos is the southwestern-most island in the Cyclades, due east from the coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
of Laconia. From east to west it measures about , from north to south , and its area is estimated at . The greater portion is rugged and hilly, culminating in Mount Profitis Elias in the west. Like the rest of the cluster, the island is of volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
origin, with tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock co ...
, trachyte
Trachyte () is an extrusive igneous rock composed mostly of alkali feldspar. It is usually light-colored and aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained), with minor amounts of mafic minerals, and is formed by the rapid cooling of lava (or shallow intrus ...
and obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
among its ordinary rocks. Volcanic activity began 2 to 3 million years ago during the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
, and is considered to still be a dormant volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often ...
that could erupt again. The natural harbour
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be Mooring, moored. The t ...
is the hollow of the principal crater, which, with a depth diminishing from 70 to 30 fathom
A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to , used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an international standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally accepted non-SI unit. H ...
s (130–55 m), strikes in from the northwest so as to separate the island into two fairly equal portions (''see photo''), with an isthmus not more than broad. In one of the caves on the south coast, the heat from the volcano is still great, and on the eastern shore of the harbour, there are hot sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
ous springs.
Antimelos or Antimilos, north-west of Milos, is an uninhabited mass of trachyte, often called Erimomilos (Desert Milos). Kimolos, or Argentiera, to the north-east, was famous in antiquity for its figs and fuller's earth
Fuller's earth is a term for various clays used as an absorbent, filter, or bleaching agent. Products labeled fuller's earth typically consist of palygorskite (also known as attapulgite) or bentonite. Primary modern uses include as absorbents ...
, and contained a considerable city, the remains of which cover the cliff of St. Andrew's. Polyaigos (also called Polinos, Polybos or Polivo — alternative spelling Polyaegos) lies south-east of Kimolos. It was the subject of dispute between the Milians and Kimolians. It is now uninhabited.
The harbour town is Adamantas; from this there is an ascent to the plateau above the harbour, on which are situated Plaka
Pláka () is the old historical neighborhood of Athens, clustered around the northern and eastern slopes of the Acropolis, and incorporating labyrinthine streets and neoclassical architecture. Plaka is built on top of the residential areas of the ...
, the chief town, and Kastro, rising on a hill above it, and other villages. The ancient town of Milos was nearer to the entrance of the harbour than Adamas, and occupied the slope between the village of Trypiti and the landing-place at Klima. Here is a theatre of Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
date and some remains of town walls and other buildings, one with a fine mosaic
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
excavated by the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
school at Athens in 1896. Numerous fine works of art have been found on this site, notably the Aphrodite
Aphrodite (, ) is an Greek mythology, ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretism, syncretised Roman counterpart , desire, Sexual intercourse, sex, fertility, prosperity, and ...
in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, the Asclepius
Asclepius (; ''Asklēpiós'' ; ) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Religion in ancient Greece, Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis (lover of Apollo), Coronis, or Arsinoe (Greek myth), Ars ...
in London
London is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of both England and the United Kingdom, with a population of in . London metropolitan area, Its wider metropolitan area is the largest in Wester ...
, and the Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
and the archaic Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
in Athens. Other villages include Triovasalos, Peran Triovasalos, Pollonia and Zefyria (Kampos).
Climate
Milos has aMediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate ( ), also called a dry summer climate, described by Köppen and Trewartha as ''Cs'', is a temperate climate type that occurs in the lower mid-latitudes (normally 30 to 44 north and south latitude). Such climates typic ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: ''Csa'') with mild, rainy winters and warm to hot dry summers.
Natural resources
Volcanic minerals


Bentonite
Bentonite ( ) is an Absorption (chemistry), absorbent swelling clay consisting mostly of montmorillonite (a type of smectite) which can either be Na-montmorillonite or Ca-montmorillonite. Na-montmorillonite has a considerably greater swelli ...
, perlite
Perlite is an amorphous volcanic glass that has a relatively high water content, typically formed by the Hydrate, hydration of obsidian. It occurs naturally and has the unusual property of greatly expanding when heated sufficiently. It is an indu ...
, pozzolana
Pozzolana or pozzuolana ( , ), also known as pozzolanic ash (), is a natural siliceous or siliceous- aluminous material which reacts with calcium hydroxide in the presence of water at room temperature (cf. pozzolanic reaction). In this reaction ...
and small quantities of kaolin
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina (). ...
are actively collected via strip mine or open-pit mine
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or open-cut mining and in larger contexts mega-mining, is a surface mining technique that extracts rock or minerals from the earth.
Open-pit mines are used when deposits of commercially useful ore or ...
techniques in Milos and sold all over the world. In the past, baryte
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate (Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), ...
, sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
, millstones and gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
were also mined; Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
notes that Milos was the most abundant source of sulfur in the ancient world. In ancient times the alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium ...
of Milos was reckoned next to that of Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
(Pliny xxxv. 15 2. The Melian earth was employed as a pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
by ancient artists. Milos was a source of obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
during the Neolithic ages for the Aegean and Mediterranean.
Agricultural crops
Orange,olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
, cypress
Cypress is a common name for various coniferous trees or shrubs from the ''Cupressus'' genus of the '' Cupressaceae'' family, typically found in temperate climates and subtropical regions of Asia, Europe, and North America.
The word ''cypress'' ...
, tamarisk, juniper (''Juniperus oxycedrus
''Juniperus oxycedrus'', vernacularly called Cade, cade juniper, prickly juniper, prickly cedar, or sharp cedar, is a species of juniper, native across the Mediterranean region, growing on a variety of rocky sites from sea level. The specific ep ...
'') and arbutus
''Arbutus'' is a genus of 12 accepted speciesAct. Bot. Mex no.99 Pátzcuaro abr. 2012.''Arbutus bicolor''/ref> of flowering plants in the family Ericaceae, native to temperate regions of the Mediterranean, western Europe, the Canary Islands a ...
trees grow throughout the island, which, however, is too dry to have any profusion of vegetation. Vine
A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas, or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in wicker work.Jackson; Benjamin; Da ...
s, cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, and barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
are the main crops.
Medicinal plants
Almost all of the uninhabited western region of Milos is aNatura 2000
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectiv ...
site and is home to over 800 different taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
, including 35 which are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to Greece. In an ethnobotanical survey of Milos, numerous native and cultivated species were described as being used to treat a variety of conditions and for other purposes such as insect repellent
An insect repellent (also commonly called "bug spray" or "bug deterrent") is a substance applied to the skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects (and arthropods in general) from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellent ...
s, disinfectants, and to protect against the evil eye
The evil eye is a supernatural belief in a curse brought about by a malevolent glaring, glare, usually inspired by envy. Amulets to Apotropaic, protect against it have been found dating to around 5,000 years ago.
It is found in many cultures i ...
. The most frequently reported species was Greek sage. Local historical records of medicinal plant use date back to the 16th century.
Sister island
*Shōdoshima
Shōdoshima or is an island located in the Seto Inland Sea, Inland Sea of Japan. The name means "Island of Azuki bean, Small Beans". There are two towns on the island: Tonoshō, Kagawa, Tonoshō and Shodoshima, Kagawa, Shōdoshima, composing the ...
, Kagawa, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
(1989)

Demographics
Historical population
Modern popularity
While a lesser-known island within the extremely popularCyclades
The CYCLADES computer network () was a French research network created in the early 1970s. It was one of the pioneering networks experimenting with the concept of packet switching and, unlike the ARPANET, was explicitly designed to facilitate i ...
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
, Milos has grown in popularity as a vacation destination in the past several decades. With its traditional Greek architecture, slower pace compared to Santorini
Santorini (, ), officially Thira (, ) or Thera, is a Greek island in the southern Aegean Sea, about southeast from the mainland. It is the largest island of a small, circular archipelago formed by the Santorini caldera. It is the southern ...
and Mykonos
Mykonos (, ; ) is a Greek island, part of the Cyclades, lying between Tinos, Syros, Paros and Naxos. The island has an area of and rises to an elevation of at its highest point. At the 2021 census, there were 10,704 inhabitants, most of ...
, and varied beaches.
Popular culture
* The 2007 film '' To Fili Tis Zois'' was shot in Milos and specifically inPlaka
Pláka () is the old historical neighborhood of Athens, clustered around the northern and eastern slopes of the Acropolis, and incorporating labyrinthine streets and neoclassical architecture. Plaka is built on top of the residential areas of the ...
and the port of Adamas. The name of the island is also referred to during the movie.
* A Canadian Commercial ''Greek Oikos Yogurt Mermaid'' was shot at Fyriplaka Beach in Milos.
* The ending scenes of the 2025 science fiction comedy '' Bugonia'' were shot in Sarakiniko Beach in Milos.
People
* Antonio Millo (active 1557–1590), captain and cartographer *Antonio Vassilacchi
Antonio Vassilacchi (; ; 1556–1629), also called L'Aliense, was a Greek painter, who was active mostly in Venice and the Veneto.
Biography
Antonio Vassilacchi was born of Greeks, Greek descent, on the island of Milos, Greece in 1556. He left ve ...
(1556–1629), painter
* Diagoras (5th century BC), philosopher
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
* Melanippides (5th century BC), poet
See also
* Aegean Islands *Antimilos
Antimilos (; ) is a Greek island in the Cyclades group, northwest of Milos. Administratively, it is part of the municipality of Milos. Antimilos is an uninhabited mass of trachyte (671 m height), often called Erimomilos (Desert Milos). It is a v ...
* Arkoudes
* Catacombs of Milos
* Firiplaka
* Kimolos
* List of Aegean Islands
* Milos Island National Airport (MLO)
* Sarakiniko Beach
References
Sources
* * I.F. Stone, 1988, The trial of Socrates, Anthos. * Cambridge Ancient History, Vol.II, 1924, New York, MacMillan *Colin Renfrew
Andrew Colin Renfrew, Baron Renfrew of Kaimsthorn, (25 July 1937 – 24 November 2024) was a British archaeologist, paleolinguist and Conservative peer noted for his work on radiocarbon dating, the prehistory of languages, archaeogenetics, ...
and Malcolm Wagstaff (editors), 1982, An Island Polity, the Archaeology of Exploitation in Melos, Cambridge, Cambridge University Press.
* Colin Renfrew
Andrew Colin Renfrew, Baron Renfrew of Kaimsthorn, (25 July 1937 – 24 November 2024) was a British archaeologist, paleolinguist and Conservative peer noted for his work on radiocarbon dating, the prehistory of languages, archaeogenetics, ...
(editor), 1985, The Archaeology of Cult, the Sanctuary at Phylakopi
Phylakopi (), located at the northern coast of the island of Milos, is one of the most important Bronze Age settlements in the Aegean and especially in the Cyclades. The importance of Phylakopi is in its continuity throughout the Bronze Age (i. ...
, London, British School at Athens and Thames & Hudson.
* Leycester, "The Volcanic Group of Milo, Anti-Milo, &c.," in ''Jour. Roy. Geog. Soc.'' (1852).
* Tournefort, ''Voyage''.
* William Martin Leake
William Martin Leake FRS (14 January 17776 January 1860) was an English soldier, spy, topographer, diplomat, antiquarian, writer, and Fellow of the Royal Society. He served in the British Army, spending much of his career in the Mediterrane ...
, ''Northern Greece'', iii.
* Anton von Prokesch-Osten
Anton von Prokesch-Osten (; 10 December 1795, Graz – 26 October 1876, Vienna) was an Austrian diplomat, statesman and general.
Life
Anton von Prokesch was a man of great versatility, whose multi-faceted career as a soldier, then as a diploma ...
, ''Denkwürdigkeiten'', &c.
* Bursian, ''Geog. von Griechenland'', ii.; ''Journ. Hell. Stud'', xvi, xvii, xviii, ''Excavations at Phylakopi''; ''Inscr. grace'', xii. iii. 197 sqq.;
* on coins found in 1909, see Jameson in ''Rev. Num.'' 1909; 188 sqq.
*
* Seaman, Michael G."The Athenian Expedition to Melos in 416 B.C.," ''Historia'' 46 (1997) pp. 385–418.
* * * * * * * *Thucydides (c. 400 BC).
History of the Peloponnesian War
'. Translated by Richard Crawley (1914). * * * * * * *
External links
Official website
{{Authority control Cyclades Islands of Greece Islands of the South Aegean Landforms of Milos (regional unit) Members of the Delian League Municipalities of the South Aegean Populated places in Milos (regional unit) Subduction volcanoes Submarine calderas Volcanoes of Greece Volcanoes of the Aegean Stratovolcanoes Pliocene volcanoes Pleistocene stratovolcanoes Dormant volcanoes Populated places in the ancient Aegean islands