|
Kimolos
Kimolos ( el, Κίμωλος; la, Cimolus) is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. It lies on the southwest of the island group of Cyclades, near the bigger island of Milos. Kimolos is the administrative center of the municipality of Kimolos, which also includes the uninhabited islands of Polyaigos, Agios Efstathios and Agios Georgios. The island has a land area of , while the municipality's land area is , and it reported a population of 910 inhabitants in the 2011 census. History Kimolos is an island with rich history records. According to tradition, it is named after Kimolos, the very first resident of the island. Echinousa is also a recorded name of the island during the ancient times, probably because of the snake Echidna (viper), being common even today on the island. Since the ancient era, it has been a battlefield between Ancient Athens, the ruler of the island, and Sparta, the ruler of Milos. In the Middle Ages it was known as Argentiera ( el, Αρτζεντιέρα), because ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimolos 1
Kimolos ( el, Κίμωλος; la, Cimolus) is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea The Aegean Sea ; tr, Ege Denizi (Greek: Αιγαίο Πέλαγος: "Egéo Pélagos", Turkish: "Ege Denizi" or "Adalar Denizi") is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans an .... It lies on the southwest of the island group of Cyclades, near the bigger island of Milos. Kimolos is the administrative center of the Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality of Kimolos, which also includes the uninhabited islands of Polyaigos, Agios Efstathios and Agios Georgios. The island has a land area of , while the municipality's land area is , and it reported a population of 910 inhabitants in the 2011 census. History Kimolos is an island with rich history records. According to tradition, it is named after Kimolos, the very first resident of the island. Echinousa is also a recorded name of the island during the ancient times, prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimolos (regional Unit)
Kimolos ( el, Κίμωλος; la, Cimolus) is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. It lies on the southwest of the island group of Cyclades, near the bigger island of Milos. Kimolos is the administrative center of the municipality of Kimolos, which also includes the uninhabited islands of Polyaigos, Agios Efstathios and Agios Georgios. The island has a land area of , while the municipality's land area is , and it reported a population of 910 inhabitants in the 2011 census. History Kimolos is an island with rich history records. According to tradition, it is named after Kimolos, the very first resident of the island. Echinousa is also a recorded name of the island during the ancient times, probably because of the snake Echidna (viper), being common even today on the island. Since the ancient era, it has been a battlefield between Ancient Athens, the ruler of the island, and Sparta, the ruler of Milos. In the Middle Ages it was known as Argentiera ( el, Αρτζεντιέρα), becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milos
Milos or Melos (; el, label= Modern Greek, Μήλος, Mílos, ; grc, Μῆλος, Mêlos) is a volcanic Greek island in the Aegean Sea, just north of the Sea of Crete. Milos is the southwesternmost island in the Cyclades group. The ''Venus de Milo'' (now in the Louvre) and the '' Asclepius of Milos'' (now in the British Museum) were both found on the island, as were a Poseidon and an archaic Apollo now in Athens. Milos is a popular tourist destination during the summer. The municipality of Milos also includes the uninhabited offshore islands of Antimilos and Akradies. The combined land area is and the 2021 census population was 5193 inhabitants. History Obsidian (a glass-like volcanic rock) from Milos was a commodity as early as 15,000 years ago. Natural glass from Milos was transported over long distances and used for razor-sharp "stone tools" well before farming began and later: "There is no early farming village in the Near East that doesn't get obsidian". The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyaigos
Polýaigos ( el, Πολύαιγος; la, Polyaegus) is an uninhabited Greek island in the Cyclades near Milos and Kimolos. It is part of the community of Kimolos (Κοινότητα Κιμώλου). Its name means "many goats", since it is inhabited only by goats. It was mentioned by several ancient geographers: Ptolemy, Pliny the Elder, and Pomponius Mela. Along its longest axis, it is and among its shortest wide. It has a surface area of approx. and a coastal length of . It is very close to the island of Kimolos ( north west from Polyaigos) and to the island of Milos ( west from Polyaigos). There are two mounts, Stroggylo which rises to and Psilo Vouno (). The island is to a great extent privately owned by the Greek Orthodox church, which sublets parts of it to local herdsmen from the nearby islands of Milos and Kimolos. Its goat population maintains Polyaigos as a barren island. It has, however, some magnificent beaches, mainly on the southern part of the island, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kimon Digenis
Kimon Digenis ( el, Κίμων Διγενής) (1871–1945) was a Hellenic Army officer who reached the rank of Major General. He was born in Kimolos, South Aegean in 1871. He enrolled in the Hellenic Military Academy, and graduated in 1891 as a Second Lieutenant of the Artillery. He fought in the Greco-Turkish War of 1897, the Balkan Wars, the Macedonian front of World War I and the Asia Minor Campaign. During World War I, after the electoral defeat of the Liberal Party in November 1920, he replaced the Venizelist Colonel Konstantinos Manetas as commander of the 13th Infantry Division and commanded it in the operations of the spring and summer of 1921. In 1922, as Major General, he was in command of the II Army Corps. Following the Battle of Dumlupınar, he became a prisoner of war A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
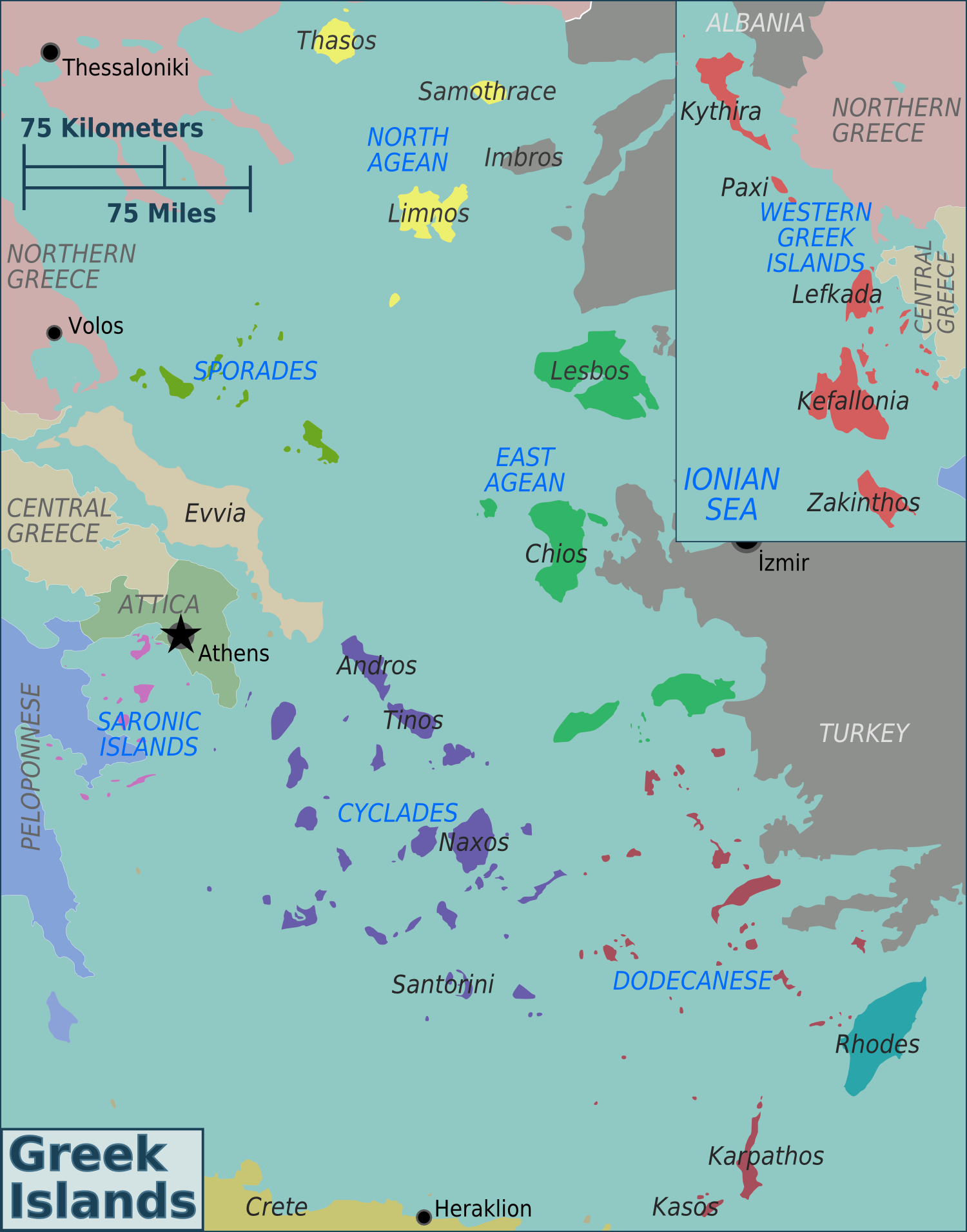
Greek Island
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by area is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection in the southeast between Crete and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclades
The Cyclades (; el, Κυκλάδες, ) are an island group in the Aegean Sea, southeast of mainland Greece and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands ''around'' ("cyclic", κυκλάς) the sacred island of Delos. The largest island of the Cyclades is Naxos, however the most populated is Syros. History The significant Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age Cycladic culture is best known for its schematic, flat sculptures carved out of the islands' pure white marble centuries before the great Middle Bronze Age Minoan civilization arose in Crete to the south. (These figures have been looted from burials to satisfy a thriving Cycladic antiquities market since the early 20th century.) A distinctive Neolithic culture amalgamating Anatolian and mainland Greek elements arose in the western Aegean before 4000 BCE, based on emmer and wild-type barley, sheep and goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milos (regional Unit)
Milos ( el, Περιφερειακή ενότητα Μήλου) is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of South Aegean. The regional unit covers the islands of Kimolos, Milos, Serifos, Sifnos and several smaller islands in the Aegean Sea. Administration As a part of the Kallikratis Programme, 2011 Kallikratis government reform, the Milos regional unit was created out of part of the former Cyclades Prefecture. It is subdivided into 4 municipalities. These are (number as in the map in the infobox): *Kimolos (9) *Milos (11) *Serifos (15) *Sifnos (17) Province The province of Milos ( el, Επαρχία Μήλου) was one of the provinces of Greece, provinces of the Cyclades Prefecture. It had the same territory as the present regional unit. It was abolished in 2006. References Milos (regional unit), Regional units of the South Aegean 2011 establishments in Greece Provinces of Greece {{SouthAegean-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Greece
Greece has many islands, with estimates ranging from somewhere around 1,200 to 6,000, depending on the minimum size to take into account. The number of inhabited islands is variously cited as between 166 and 227. The largest Greek island by area is Crete, located at the southern edge of the Aegean Sea. The second largest island is Euboea or Evvia, which is separated from the mainland by the 60m-wide Euripus Strait, and is administered as part of the Central Greece region. After the third and fourth largest Greek islands, Lesbos and Rhodes, the rest of the islands are two-thirds of the area of Rhodes, or smaller. The Greek islands are traditionally grouped into the following clusters: the Argo-Saronic Islands in the Saronic Gulf near Athens; the Cyclades, a large but dense collection occupying the central part of the Aegean Sea; the North Aegean islands, a loose grouping off the west coast of Turkey; the Dodecanese, another loose collection in the southeast between Crete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The Delian League
The members of the Delian League/Athenian Empire (c. 478-404 BC) can be categorized into two groups: the allied states (''symmachoi'') reported in the stone tablets of the Athenian tribute lists (454-409 BC), who contributed the ''symmachikos phoros'' ("allied tax") in money, and further allies, reported either in epigraphy or historiography, whose contribution consisted of ships, wood, grain, and military assistance; proper and occasional members, subject members and genuine allies. Analysis The study of the ''symmachikos phoros'' provides the following insights: The amount of tax paid by each state is written in Attic numerals. One-sixtieth is dedicated to Athena, the patron goddess of the city. The membership is not limited to Ionians or Greek city-states (see Ialysus, Mysians, Eteocarpathians and ''the Carians whom Tymnes rules''). Allied states of Western Greece are not categorized under a fiscal district the Thracian, Hellespontine, Insular, Carian and Ionian ''phoros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Aegean
The South Aegean ( el, Περιφέρεια Νοτίου Αιγαίου, translit=Periféria Notíou Eyéou, ) is one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It consists of the Cyclades and Dodecanese island groups in the central and southeastern Aegean Sea. Administration The South Aegean region was established in the 1987 administrative reform. With the 2010 Kallikratis plan, its powers and authority were redefined and extended. Along with the North Aegean region, it is supervised by the Decentralized Administration of the Aegean based at Piraeus. The capital of the region is situated in Ermoupoli on the island of Syros. The administrative region includes 50 inhabited islands, including the popular tourism destinations of Mykonos, Santorini and Rhodes. Until the Kallikratis reform, the region consisted of the two prefectures of the Cyclades (capital: Ermoupoli) and the Dodecanese (capital: Rhodes). Since 1 January 2011 it is divided into 13 regional units, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_SouthAegean_(relief-cropped).png)