medical textiles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Medical textiles are numerous fiber-based materials intended for
Medical textiles are numerous fiber-based materials intended for

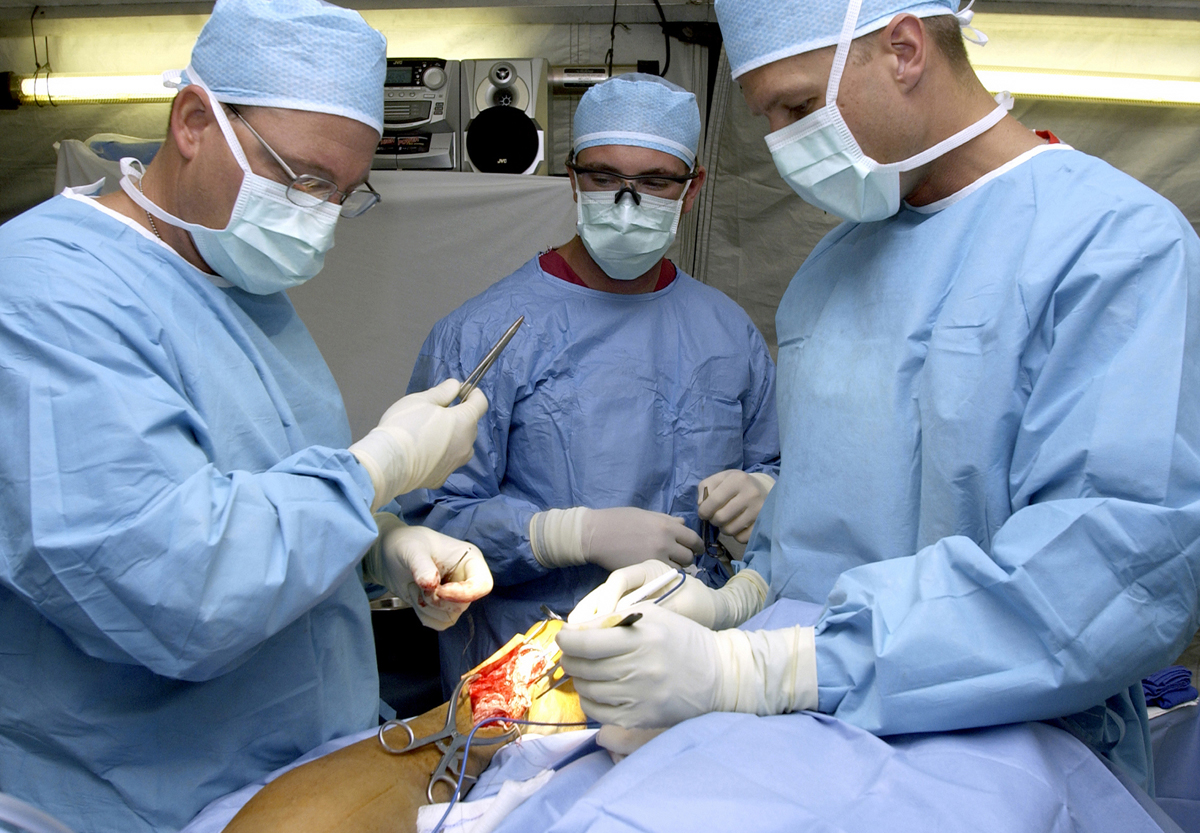 Medical gowns are a kind of PPE for medical professionals. Gowns are a component of a comprehensive infection-control approach. They protect the wearer from getting sick or getting infected if they come into contact with liquids or solids that could be contagious or harmful. Operating room gowns, surgical gowns, isolation gowns, nonsurgical gowns, and procedural gowns are all terms used to describe different gowns used in health care settings. The names of products are not standardized. The specifications of the products are important. ANSI/AAMI PB70 specifies a classification system for protective gear ncluding isolation gowns and surgical gownsused in healthcare facilities in the United States based on its liquid barrier performance. Quality requirements for various gowns include seam strength, lint generation, tear resistance, evaporative resistance, and breathability.
Medical gowns are a kind of PPE for medical professionals. Gowns are a component of a comprehensive infection-control approach. They protect the wearer from getting sick or getting infected if they come into contact with liquids or solids that could be contagious or harmful. Operating room gowns, surgical gowns, isolation gowns, nonsurgical gowns, and procedural gowns are all terms used to describe different gowns used in health care settings. The names of products are not standardized. The specifications of the products are important. ANSI/AAMI PB70 specifies a classification system for protective gear ncluding isolation gowns and surgical gownsused in healthcare facilities in the United States based on its liquid barrier performance. Quality requirements for various gowns include seam strength, lint generation, tear resistance, evaporative resistance, and breathability.
File:Surgical_face_mask.jpg, A surgical face mask, meant for single use. It is a type of the face masks often used to prevent the spread of
.
 Medical textiles are numerous fiber-based materials intended for
Medical textiles are numerous fiber-based materials intended for medical
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
purposes. Medical textile is a sector of technical textile
Technical textiles are a category of textiles specifically engineered and manufactured to serve functional purposes beyond traditional apparel and home furnishing applications. These textiles are designed with specific performance characteristic ...
s that emphasizes fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
-based products used in health care
Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement or maintenance of health via the preventive healthcare, prevention, diagnosis, therapy, treatment, wikt:amelioration, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other disability, physic ...
applications such as prevention, care, and hygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
.
The spectrum of applications of medical textiles ranges from simple cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
bandages to advanced tissue engineering. Common examples of products made from medical textiles include dressings, implants, surgical sutures, certain medical devices, healthcare textiles, diapers, menstrual pads, wipes, and barrier fabrics.
Medical textiles include many fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
types, yarn
Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. '' Thread'' is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern ...
s, fabrics, non-woven materials, woven, braided, as well as knitted fabric
Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can be more readily constructed into smaller ...
s. Physical and chemical alterations of fiber architectures, the use of functional finishes, and the production of stimuli-sensitive materials are major approaches for developing innovative medical textiles.
Advances in textile manufacturing and medical technologies have made medical healthcare an important industry in textiles. Textiles are used in the production of a variety of medical devices, including replacements for damaged, injured, or non-functioning organs. The manufacture of medical textiles is a growing sector. There are many reasons for its growth, such as new technology in both textiles and medicine; ageing populations; growing populations; changes in lifestyles; and longer life expectancies. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
generated higher demand for certain medical textile applications PPE, medical gown">Personal_protective_equipment.html" ;"title="uch as PPE, medical gowns and Face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic">face masks">Personal protective equipment">PPE, medical gowns and Face masks during the COVID-19 pandemic">face masks and there were shortages worldwide. Even China, the world's largest manufacturer of such applications, has struggled to keep up with demand.
History

Natural fiber
Natural fibers or natural fibres (see Spelling differences#-re, -er, spelling differences) are fibers that are produced by geology, geological processes, or from the bodies of plants or animals.
They can be used as a component of Composite mate ...
s have been used in medical applications since ancient times. The use of splints
Splints is an ailment of the horse or pony, characterized by a hard, bony swelling, usually on the inside of a front leg, lying between the splint and cannon bone or on the splint bone itself. It may be "hot," meaning that it occurred recently an ...
, bandages, and gauges is very old. An ancient Sanskrit text on medicine and surgery, the ''Sushruta Samhita'', categorises '' Kausheya'' under the "articles of bandaging." The concept of personal protective equipment (PPE) for medical practitioners dates all the way back to the 17th century. Plague doctor costumes were intended to protect plague doctors from the disease during outbreaks of the Bubonic Plague in Europe. According to descriptions, the costumes were typically composed of heavy fabric or leather and was waxed.
Significance
Medical textiles have a critical role in preserving human life. So, e.g., medical textile applications (PPE cover all, N95 masks), were in high demand and scarce supply during theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
, resulting in severe shortages. Considering the shortage, in February 2020, the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
restricted the use of medical essentials such as PPE and masks, etc. to front-line workers only (PPE includes gowns, aprons, masks, gloves, medical masks, goggles, face shields, and respirators, i.e., N95 or FFP2). PPE protects medical professionals from illness, infections rom virus or bacteria The PPE cloth acts as a barrier with the capacity to prevent contaminants from entering the body through respiratory secretions, blood, and bodily fluids.
Masks can protect healthy people from illness by limiting the spread of respiratory droplets and aerosols.
Types
Categories of fibers, fabrics and materials
There are four different groups of fibers, fabrics and materials used in medical textile products. Different types of fibers and manufacturing systems are utilized for the production of the various medical textile products.Extracorporeal devices category
Extracorporeal devices are the artificial organs that remain outside the body while treating a patient. Extracorporeal devices are useful in hemodialysis and cardiac surgery.Implantable materials category
Implants are medical devices used to replace a missing biological structure, to sustain a damaged biological structure, or to improve an existing biological structure. In contrast to a transplant, which is biomedical tissue that has been transplanted, medical implants are man-made devices such as artificial ligaments and vascular grafts, etc.Non-implantable materials category
Non-implantable materials are used externally and may or may not contact skin. For example, bandages, plaster, orthopedic belts, pressure garments, etc.Hygiene and healthcare products category
The term "hygiene and healthcare products" refers to a variety of materials used to maintain the hygiene, safety, and care of medical professionals and patients. Surgical drapes, gowns, uniforms, clothing, caps, wipes, masks, and hospital bed linens are all included in this categoryHuman textiles
Human textiles refer to textiles that utilize human materials, including bioengineered yarns made from human cells, for tissue regeneration. Textiles manufactured from human tissue-based 'yarn' can be intricately woven, knitted, or braided and have the potential to contribute to various applications, ranging from simple biocompatible sutures to complex woven tissues for surgical repairs, thereby aiding in the healing process of injuries. Human textiles offer a potential solution to mitigate the drawbacks associated with foreign agents that may induce adverse side effects.Cell-Assembled extracellular Matrix (CAM)
The Cell-Assembled Extracellular matrix (CAM) is both biologically sound and resilient, allowing for large-scale production suitable for clinical applications utilizing regular, adult human fibroblasts.Foreign body reaction
In the medical field, most permanent synthetic biomaterials are considered foreign by the innate immune system. This can lead to a foreign body reaction when implanted.Properties
Products made from medical textiles are specially engineered textile-based products used in medical applications. These products are used for prevention, care, and hygiene purposes. A combination of properties are considered while selecting the materials, which largely depends upon the particular use. The materials used in medical textile products must have the following properties: strength,softness
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by Pressing (metalworking), pressing or abrasion ...
, biocompatibility, elasticity, flexibility, nontoxicity, noncarcinogenic, non-allergenic, and air and water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
permeability.
Biotextiles are constructions made of textile fibers that are employed in both implantable and non-implant applications. Their performance is assessed according to their biofunctionality, biocompatibility, and biostability. For example, biostability in the presence of body fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the Body (biology), body of an organism. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total Human body weight, body weight; it ...
s and cells.
Material and technologies
Fibers
Overview
Medical devices are commonly made in whole or part from fibers. A medical device is defined as any device intended for medical purposes. It could be a machine, a reagent for use in the lab, software, an appliance, an instrument, or an implant. For medical use, fiber selection is based on certain criteria of intended use. Primarily, fibers are chosen on the basis of their biodegradability or non-biodegradability. Other than biodegradability, strength, elasticity, and absorbency are also considered.Natural fibers
Natural fibers such as cotton, silk, and viscose (a regenerated cellulosic fiber) are used in hygiene and healthcare products, as well as non-implantable materials. Polyester, nylon, polypropylene, glass, and carbon are all examples of synthetic fibers used in Medical textiles. Fibers absorbed within three months by ourbiological system
A biological system is a complex Biological network inference, network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is ...
are considered biodegradable, and fibers that require more than six months to absorb are called non-biodegradable. These fibers are categorized as below:
PLA and PGA fibers
Polylactic acid, also called PLA, is a biodegradable, biosorbable or bioabsorbablepolymer
A polymer () is a chemical substance, substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeat unit, repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their br ...
used in producing many type of implants such as naturally dissolving stents. Polyglycolide or polyglycolic acid, also called PGA, is a biodegradable and thermoplastic polymer. PGA suture is categorized as an absorbable synthetic braided multifilament.
Other polymers
Recent developments
The term "medical textile" refers to various products made of textile materials (fiber, yarn, or fabric) that are used in the medical environment. Although both natural andsynthetic fiber
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres (in British English; see spelling differences) are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants like cott ...
s are used in medical textiles, properties such as modulus of elasticity, tensile strength, and hardness are mostly fixed factors in natural fibers, and have proven to be more manageable in synthetic fibers. Recent fiber developments have a significant impact on four primary areas of medical textiles: hygiene products, implants, non-implantable medical textiles, and extracorporeal medical textiles.
Medical textiles serve as a bridge between biological sciences and engineering. The advancement of materials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries.
The intellectual origins of materials sci ...
and related research has resulted in the introduction of new fiber
Fiber (spelled fibre in British English; from ) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often inco ...
materials and manufacturing processes for the medical sector. As a result of new technologies such as 3D printing, electrospinning and melt blowing technology in textiles, medical professions now have access to a diverse choice of textile materials with varying designs and qualities.
Melt blowing is a well-established technology for fabricating micro- and nanofibers, in which a polymer melt is extruded via small nozzles surrounded by a high-speed blowing gas. Melt-blown microfibers typically have a fiber diameter of 2–4 μm, but can be as small as 0.3–0.6 μm or as large as 15–20 μm. Melt blowing technology helps in producing filtering products such as N95 masks, and female hygiene products.
Medical textiles use tubular fabrics with carefully chosen materials that are biocompatible, nonallergic, and nontoxic. For example, Dyneema, PTFE, Polyester, and Teflon are used for implants. The material type varies depending on the implant area; for example, Polytetrafluoroethylene
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene, and has numerous applications because it is chemically inert. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a corporate spin-of ...
is preferred for stent implants due to its non-stick
A non-stick surface is engineered to reduce the ability of other materials to stick to it. Non-sticking cookware is a common application, where the non-stick coating allows food to brown without sticking to the pan. Non-stick is often used to ref ...
properties, while polyolefin
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More speciali ...
is used for mesh implants.
Vectran, a manufactured fiber from liquid-crystal polymer, is used in producing medical devices, for example, implants and certain surgical devices.
Intelligent textiles can be used for disease management as well as remote monitoring. Intelligent textiles can monitor heart rate
Heart rate is the frequency of the cardiac cycle, heartbeat measured by the number of contractions of the heart per minute (''beats per minute'', or bpm). The heart rate varies according to the body's Human body, physical needs, including the nee ...
and blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
, which are critical components of medical diagnosis
Medical diagnosis (abbreviated Dx, Dx, or Ds) is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information ...
, and controlling them considerably reduces the incidence of serious health disorders. Movement patterns and electroencephalograms are used to diagnose neurological illnesses and to guide treatment decisions.
Phase-change materials are helpful in medical textiles because they can be utilized to reheat hypothermia patients softly and precisely. Additionally, the PCM can be incorporated therapeutically into elastic wraps or orthopedic joint supports. It makes it easy to provide heat or cold therapy to joints or muscles while wearing a bandage.
Materials with shape-memory polymers that have the capabilities of temperature adaptive moisture management can improve the thermo-physiological comfort of patients.
Nonwoven fabrics with two or more fibers layers are widely used in a variety of applications, including tissue engineering scaffolds, wipes, wound dressings, and barrier materials.
Microfluidic spinning technology is used for fabricating many type of fibers. Due to its ease of manipulation, high efficiency, controllability, and environmentally friendly chemical process, microfluidic systems have been identified as an appropriate microreactor platform for the production of anisotropic fibers.
Applications
Medical textiles cover a vast area of application that includes wound care, disease management, preventive clothing, bandages, hygiene ( hospital linen), etc. Medical textiles are useful in first aid, treating a wound or keeping a wound or illness in the right condition during medical treatment, they also helps in protecting the healthcare workers fromInfection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
and infectious diseases
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dise ...
.
Wound care
Knitting, weaving, braiding, crocheting, composite materials, and non-woven technologies are all different fabric manufacturing systems used in contemporary wound care. Research subjects in medical textiles include materials and products with significantly superior attributes produced using advanced technology and novel methodologies. New medical textiles are an emerging field with significant growth in wound treatment products. These are all important characteristics of wound care fibers and dressings. They are non-toxic, non-allergic, absorbent, hemostatic, biocompatible, breathable, and non-toxic. They also have good mechanical properties. Chitosan, Alginate, Collagen, branan ferulate, and carbon fiber-based goods offer numerous advantages over conventional materials. Materials used in wound care also include foams, hydrogels, films, hydrocolloids, and matrix (tissue engineering).Tissue engineering
Textile technologies are now being considered for biofabrication. The physical and chemical properties of fibers, the size of the pores, and the strength of the fabric all play a role in how textile technologies can be used in tissue engineering. Fibrous structures can be made and shaped with textile technology to meet the needs of a wide range of tissue engineering applications. Tissue engineering is the process of putting together scaffolds, cells, and biologically active molecules to make functional tissues. * It is possible to make meter-long core-shell hydrogel microfibers that contain ECM proteins and mature cells or somatic stem cells in a microfluidic device. and these microfibers have the morphologies and functions of live tissues. The fibers also have the potential to be reeled and spin or weave * Electrospinning can produce nanofibers with a range of desired fine microns that is usable to make nano- and submicron-sized fibrous scaffolds from polymer solutions that could be used as cell and tissue substrates.= Biomedical scaffolds
= Hydrogel fibers are used to construct scaffolds for the development of cells and the release of drugs.Antimicrobial dressing
Chitosan may function as an inhibitor of bacterial and fungal development. In 2003, the United StatesFood and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
approved chitosan-based wound dressings for medical use. Combat medics use Hemcon dressings, which is a dressing with Chitosan, to treat wounds because it stops the blood flow
Hemodynamics American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or haemodynamics are the Fluid dynamics, dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostasis, homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydrau ...
with its hemostasis
In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel (the opposite of hemostasis is hemorrhage). It is the first stage of wound healing. Hemostasis involves three ...
properties. Chitosan hemostatic agents are salts formed when chitosan is combined with an organic acid ( lactic acid, or Succinic acid). The hemostatic agent operates by interacting with the erythrocytes' (negatively charged) cell membrane and the protonated chitosan (positively charged), resulting in platelet involvement and fast thrombus formation. When the bandage comes into contact with blood, it becomes sticky, creating an adhesive-like effect that seals the cut.
Surgical suture thread
Materials in surgical sutures are textile based products. Suture material is frequently subdivided into absorbable thread and non-absorbable thread, and then into synthetic fibers and natural fibers. Whether a suture material is monofilament or polyfilament is an additional critical distinction.Bandages
A bandage is a piece of fabric used to cover, dress, and bind wounds. Bandages are typically manufactured from various textile materials. The dressing or splint is held in place using a bandage. Bandages are also used for medical purposes (strengthening and compressing) to support and restrict specific body parts.Compression bandages
Compression bandages are used to apply pressure while directed pressure is used to treat lymphatic disease or venous disease, such as in the treatment ofdeep vein thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enl ...
. The most common classifications for compression bandages are inelastic and elastic.
Antimicrobial textiles
Antimicrobial textiles are the textile materials (fibers, yarns and fabrics) treated with antimicrobial agents, they are used in hygiene care. Antimicrobial treated textiles either kill thebacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
or inhibit the growth of microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s. The exemplary products are wipes, gowns, Odor
An odor (American English) or odour ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive ...
less clothes, etc. Antimicrobial scrubs are hospital garments treated with anti bacterial chemicals. Their primary objective is to prevent the spread of hazardous microorganisms between healthcare staff and between patients. The applied chemicals work differently, for example, chemical binds to the microbe's DNA, effectively rendering reproduction impossible. Some antimicrobial chemicals dissolve the protein necessary for their growth, there are antimicrobials which attack specific bacteria such as Staphylococcus, Salmonella
''Salmonella'' is a genus of bacillus (shape), rod-shaped, (bacillus) Gram-negative bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. The two known species of ''Salmonella'' are ''Salmonella enterica'' and ''Salmonella bongori''. ''S. enterica'' ...
, and Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly fo ...
.
Antiviral textiles
Antiviral textiles are an extension of antimicrobial surfaces. These surfaces, which have antiviral capabilities, may be able to inactivate lipid-coated viruses. Polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) treated CVC fabric ( fabric with chief value cotton) kills 94% of thecoronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
in two hours. Henceforth, it is suitable for PPE for health workers. Chitosan, a natural polymer that is biocompatible, non-allergenic, biodegradable, and non-toxic, was also looked at for its antiviral properties. The chitosan-based compound also shows efficacy against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and cotton fabrics treated with copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
along with chitosan and citric acid. The treated material sustains the antiviral properties five to ten home laundry washes.
Medical gowns
 Medical gowns are a kind of PPE for medical professionals. Gowns are a component of a comprehensive infection-control approach. They protect the wearer from getting sick or getting infected if they come into contact with liquids or solids that could be contagious or harmful. Operating room gowns, surgical gowns, isolation gowns, nonsurgical gowns, and procedural gowns are all terms used to describe different gowns used in health care settings. The names of products are not standardized. The specifications of the products are important. ANSI/AAMI PB70 specifies a classification system for protective gear ncluding isolation gowns and surgical gownsused in healthcare facilities in the United States based on its liquid barrier performance. Quality requirements for various gowns include seam strength, lint generation, tear resistance, evaporative resistance, and breathability.
Medical gowns are a kind of PPE for medical professionals. Gowns are a component of a comprehensive infection-control approach. They protect the wearer from getting sick or getting infected if they come into contact with liquids or solids that could be contagious or harmful. Operating room gowns, surgical gowns, isolation gowns, nonsurgical gowns, and procedural gowns are all terms used to describe different gowns used in health care settings. The names of products are not standardized. The specifications of the products are important. ANSI/AAMI PB70 specifies a classification system for protective gear ncluding isolation gowns and surgical gownsused in healthcare facilities in the United States based on its liquid barrier performance. Quality requirements for various gowns include seam strength, lint generation, tear resistance, evaporative resistance, and breathability. ASTM International
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is a standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical international standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems and s ...
STM F2407guidelines include a list of them which are approved by FDA.
These gowns are either impermeable or made of a densely woven, water-resistant fabric. 510(K) is a premarket submission made to the Food and Drug Administration in order to demonstrate that the device to be sold is safe and effective. Surgical and surgical isolation gowns are regulated by the FDA as Class II medical devices that require a 510(k). Non-surgical gowns are class I medical devices that do not need a 510(k) clearance.
The different levels are categorized as follows:
Some more examples of medical textile applications in the medical environment include the following:
* Surgical mask is a mouth and nose cover against bacterial aerosols, these are often used for a particular purpose.
* N95 respirator
An N95 respirator is a disposable Respirator#Filtering facepiece, filtering facepiece respirator or reusable elastomeric respirator filter that meets the U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) N95 standard of air fi ...
s masks were one of the most effective means of protection against the coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
.
* Personal protective equipment or PPE protects the wearer from health hazards. For example, Viral barrier gowns can protect against virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es of nanometer size.
* Implants, textile based implants, surgical meshes, hernia repair, and regenerative medicines.
* Odor
An odor (American English) or odour ( Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a smell or a scent caused by one or more volatilized chemical compounds generally found in low concentrations that humans and many animals can perceive ...
control materials for medical purposes.
* Drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
loaded and drug releasing materials.
* Bandages
* Compression garments.
Gallery
Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
. They are used in countries with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreaks and are worn in hospitals as well as in public. They are not designed to protect the wearer from inhaling airborne bacteria or virus particles and are less effective than respirators, such as N95 or FFP masks.
File:广东再增本土无症状感染者_多地开展全员核酸检测.png, Health workers in PPE and people standing in row with surgical masks
.References
{{Reflist Textiles Medical terminology