Lynx X-ray Observatory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lynx X-ray Observatory (''Lynx'') is a
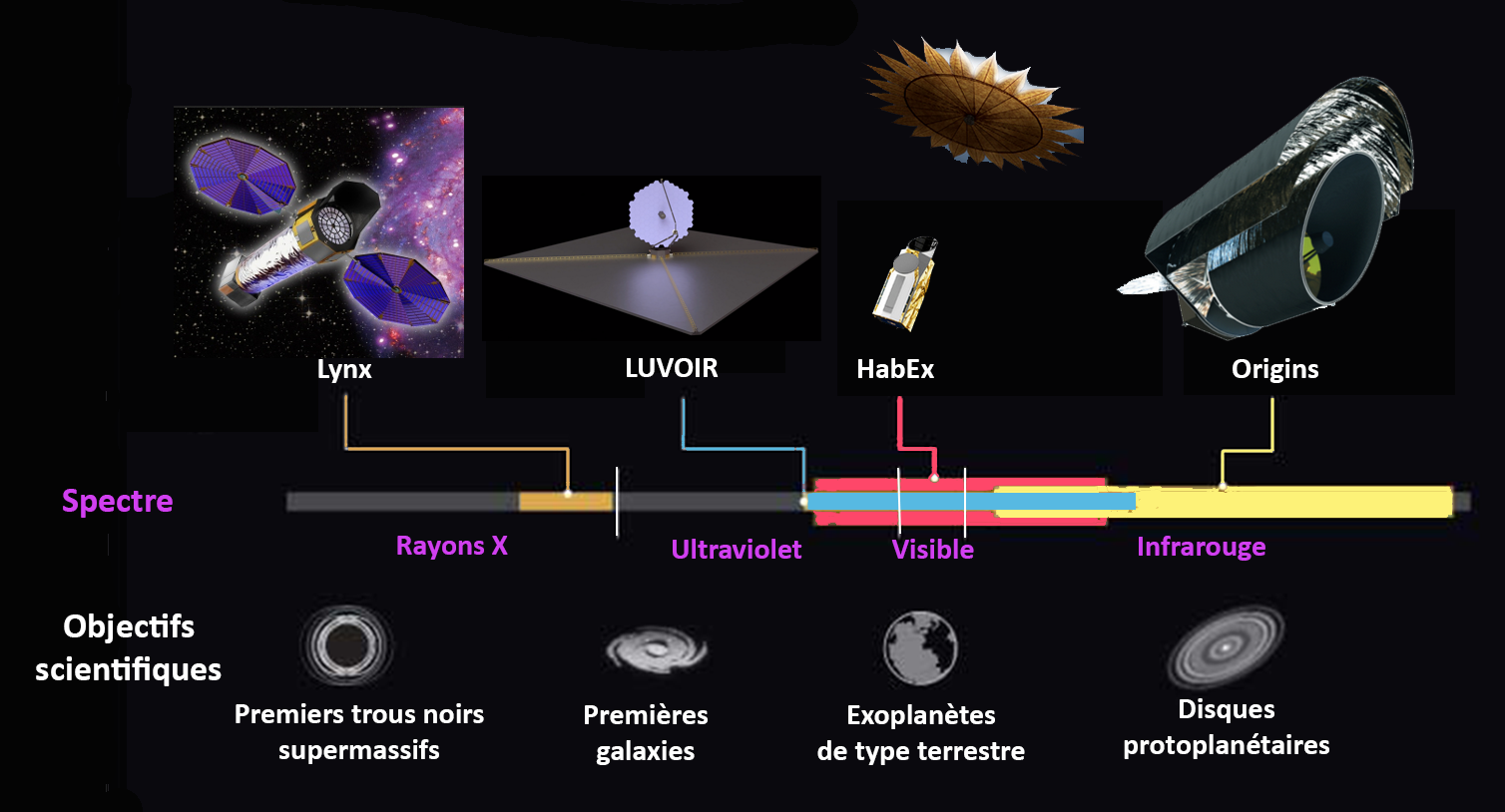 In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013,
In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013,
Roadmap document
'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
-funded Large Mission Concept Study commissioned as part of the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
2020 Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Decadal Survey is a review of astronomy and astrophysics literature produced approximately every ten years by the National Research Council of the National Academy of Sciences in the United States. The report survey ...
. The concept study phase is complete as of August 2019, and the ''Lynx'' final report has been submitted to the Decadal Survey for prioritization. If launched, ''Lynx'' would be the most powerful X-ray astronomy
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ...
observatory constructed to date, enabling order-of-magnitude advances in capability over the current Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources ...
and XMM-Newton
''XMM-Newton'', also known as the High Throughput X-ray Spectroscopy Mission and the X-ray Multi-Mirror Mission, is an X-ray space observatory launched by the European Space Agency in December 1999 on an Ariane 5 rocket. It is the second corners ...
space telescopes.
Background
 In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013,
In 2016, following recommendations laid out in the so-called Astrophysics Roadmap of 2013, NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
established four space telescope
A space telescope (also known as space observatory) is a telescope in outer space used to observe astronomical objects. Suggested by Lyman Spitzer in 1946, the first operational telescopes were the American Orbiting Astronomical Observatory, OAO ...
concept studies for future Large strategic science missions
NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions ...
. In addition to ''Lynx'' (originally called X-ray Surveyor in thRoadmap document
'','' they are the Habitable Exoplanet Imaging Mission (HabEx), the
Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor
The Large Ultraviolet Optical Infrared Surveyor, commonly known as LUVOIR (), is a multi-wavelength space telescope concept being developed by NASA under the leadership of a Science and Technology Definition Team. It is one of four large astro ...
(LUVOIR), and the Origins Space Telescope
Origins Space Telescope (''Origins'') is a concept study for a far-infrared survey space telescope mission.completed their final reports
in August 2019, and turned them over to both NASA and the
Final Report
the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission was intentionally optimized to enable major advances in the following three astrophysical discovery areas: * The dawn of
''Lynx'' Report
* The drivers of
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 2) * The energetic properties of stellar evolution and stellar ecosystems
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 3) Collectively, these serve as three "science pillars" that set the baseline requirements for the observatory. Those requirements include greatly enhanced sensitivity, a sub-arcsecond
''Lynx'' Report
, including

Final Report
''Lynx'' is designed as an
 The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features
The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features
Silicon Metashell Optics
(SMO), in which thousands of very thin, highly polished segments of nearly pure
 The Chandra X-ray Observatory experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate Lynx, leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single
The Chandra X-ray Observatory experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate Lynx, leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single
Final Report
the ''Lynx'' team commissioned five independent
Lynx home page
Lynx home page for scientists
at NASA {{Space observatories, show Space telescopes X-ray telescopes Proposed NASA space probes
in August 2019, and turned them over to both NASA and the
National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
, whose independent Decadal Survey
A decadal survey is a 10-year plan outlining scientific missions and goals created by the United States National Academies. It is a summary of input from scientists in the United States and beyond. Examples include:
* Astronomy and Astrophysics ...
committee advises NASA on which mission should take top priority. If it receives top prioritization and therefore funding, ''Lynx'' would launch in approximately 2036. It would be placed into a halo orbit around the second Sun–Earth Lagrange point (L2), and would carry enough propellant
A propellant (or propellent) is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicle ...
for more than twenty years of operation without servicing.
The ''Lynx'' concept study involved more than 200 scientists and engineers across multiple international academic institutions, aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
, and engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
companies. The ''Lynx'' Science and Technology Definition Team (STDT) was co-chaired by Alexey Vikhlinin and Feryal Özel
Feryal Özel (born May 27, 1975) is a Turkish American astrophysicist born in Istanbul, Turkey, specializing in the physics of compact objects and high energy astrophysical phenomena. As of 2022, Özel is the department chair and a professor at ...
. Jessica Gaskin was the NASA Study Scientist, and the Marshall Space Flight Center
Marshall Space Flight Center (officially the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center; MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville postal address), is the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government's ...
managed the ''Lynx'' Study Office jointly with the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory
The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory (SAO) is a research institute of the Smithsonian Institution, concentrating on Astrophysics, astrophysical studies including Galactic astronomy, galactic and extragalactic astronomy, cosmology, Sun, solar ...
, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian.
Scientific objectives
According to the concept study'Final Report
the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission was intentionally optimized to enable major advances in the following three astrophysical discovery areas: * The dawn of
black hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. Th ...
s (Chapter 1 of th''Lynx'' Report
* The drivers of
galaxy formation and evolution
In cosmology, the study of galaxy formation and evolution is concerned with the processes that formed a heterogeneous universe from a homogeneous beginning, the formation of the first galaxies, the way galaxies change over time, and the process ...
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 2) * The energetic properties of stellar evolution and stellar ecosystems
''Lynx'' Report
Chapter 3) Collectively, these serve as three "science pillars" that set the baseline requirements for the observatory. Those requirements include greatly enhanced sensitivity, a sub-arcsecond
point spread function
The point spread function (PSF) describes the response of a focused optical imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is the system's impulse response; the PSF is the impulse response or impulse response ...
stable across the telescope's field of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to elec ...
, and very high spectral resolution
The spectral resolution of a spectrograph, or, more generally, of a frequency spectrum, is a measure of its ability to resolve features in the electromagnetic spectrum. It is usually denoted by \Delta\lambda, and is closely related to the resolvi ...
for both imaging
Imaging is the representation or reproduction of an object's form; especially a visual representation (i.e., the formation of an image).
Imaging technology is the application of materials and methods to create, preserve, or duplicate images.
...
and gratings spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Spectro ...
. These requirements, in turn, enable a broad science case with major contributions across the astrophysical landscape (as summarized in Chapter 4 of th''Lynx'' Report
, including
multi-messenger astronomy
Multi-messenger astronomy is the coordinated observation and interpretation of multiple signals received from the same astronomical event. Many types of cosmological events involve complex interactions between a variety of astrophysical processes, ...
, black hole
A black hole is a massive, compact astronomical object so dense that its gravity prevents anything from escaping, even light. Albert Einstein's theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass will form a black hole. Th ...
accretion
Accretion may refer to:
Science
* Accretion (astrophysics), the formation of planets and other bodies by collection of material through gravity
* Accretion (meteorology), the process by which water vapor in clouds forms water droplets around nucl ...
physics, large-scale structure, Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
science, and even exoplanet
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet is a planet outside the Solar System. The first confirmed detection of an exoplanet was in 1992 around a pulsar, and the first detection around a main-sequence star was in 1995. A different planet, first det ...
s. The ''Lynx'' team markets the mission's science capabilities as "transformationally powerful, flexible, and long-lived", inspired by the spirit of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's Great Observatories program
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space telescope, space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy region ...
.
Mission design and payload

Spacecraft
As described in Chapters 6-10 of the concept study'Final Report
''Lynx'' is designed as an
X-ray observatory
X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to ...
with a grazing incidence X-ray telescope
An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets ...
and detectors that record the position, energy, and arrival time of individual X-ray photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can ...
s. Post-facto aspect reconstruction leads to modest requirements on pointing precision and stability, while enabling accurate sky locations for detected photons. The design of the ''Lynx'' spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
draws heavily on heritage from the ''Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources ...
'', with few moving parts and high technology readiness level
Technology readiness levels (TRLs) are a method for estimating the maturity of technologies during the acquisition phase of a program. TRLs enable consistent and uniform discussions of technical maturity across different types of technology. TR ...
elements. ''Lynx'' will operate in a halo orbit
A halo orbit is a periodic, non-planar orbit associated with one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics. Although a Lagrange point is just a point in empty space, its peculiar characteristic is th ...
around Sun-Earth L2
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium for small-mass objects under the gravitational influence of two massive orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the ...
, enabling high observing efficiency in a stable environment. Its maneuvers and operational procedures on-orbit are nearly identical to ''Chandras, and similar design approaches promote longevity. Without in-space servicing, ''Lynx'' will carry enough consumables
Consumables (also known as consumable goods, non-durable goods, or soft goods) are goods that are intended to be consumed. People have, for example, always consumed food and water. Consumables are in contrast to durable goods. Disposable product ...
to enable continuous operation for at least twenty years. The spacecraft and payload elements are, however, designed to be serviceable, potentially enabling an even longer lifetime.
Payload
 The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features
The major advances in sensitivity, spatial, and spectral resolution in the ''Lynx'' Design Reference Mission are enabled by the spacecraft's payload, namely the mirror assembly and suite of three science instruments. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that each of the payload elements features state-of-the-art
The state of the art (SOTA or SotA, sometimes cutting edge, leading edge, or bleeding edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contex ...
technologies while also representing a natural evolution of existing instrumentation technology development over the last two decades. The key technologies are currently at Technology Readiness Levels (TRL) 3 or 4. The ''Lynx'' Report notes that, with three years of targeted pre-phase A development in early 2020s, three of four key technologies will be matured to TRL 5 and one will reach TRL 4 by start of Phase A, achieving TRL 5 shortly thereafter. The ''Lynx'' payload consists of the following four major elements:
* The ''Lynx'' X-ray Mirror Assembly (LMA): The LMA is the central element of the observatory, enabling the major advances in sensitivity, spectroscopic throughput, survey speed, and greatly improved imaging relative to ''Chandra'' due to greatly improved off-axis performance. The ''Lynx'' design reference mission baselines a new technology calleSilicon Metashell Optics
(SMO), in which thousands of very thin, highly polished segments of nearly pure
silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
are stacked into tightly packed concentric shells. Of the three mirror technologies considered for ''Lynx'', the SMO design is currently the most advanced in terms of demonstrated performance (already approaching what is required for ''Lynx''). The SMO's highly modular design lends itself to parallelized manufacturing and assembly, while also providing high fault tolerance: if some individual mirror segments or even modules are damaged, the impact to schedule and cost is minimal.
* The High Definition X-ray Imager (HDXI): The HDXI is the main imager An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of curren ...
for ''Lynx'', providing high spatial resolution
In physics and geosciences, the term spatial resolution refers to distance between independent measurements, or the physical dimension that represents a pixel of the image. While in some instruments, like cameras and telescopes, spatial resoluti ...
over a wide field of view
The field of view (FOV) is the angle, angular extent of the observable world that is visual perception, seen at any given moment. In the case of optical instruments or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to elec ...
(FOV) and high sensitivity over the 0.2–10 keV
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV), also written electron-volt and electron volt, is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When us ...
bandpass
A band-pass filter or bandpass filter (BPF) is a device that passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects ( attenuates) frequencies outside that range.
It is the inverse of a '' band-stop filter''.
Description
In electronics and s ...
. Its 0.3 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
(0.3′′) pixels will adequately sample the ''Lynx'' mirror point spread function
The point spread function (PSF) describes the response of a focused optical imaging system to a point source or point object. A more general term for the PSF is the system's impulse response; the PSF is the impulse response or impulse response ...
over a 22′ × 22′ FOV. The 21 individual sensors of the HDXI are laid out along the optimal focal surface to improve the off-axis PSF. The ''Lynx'' DRM uses Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss
", , ) is a type of MOSFET, metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication, fabrication process that uses complementary an ...
(CMOS) Active Pixel Sensor (APS) technology, which is projected to have the required capabilities (i.e., high readout rates, high broad-band quantum efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction.
This article deals with the term as a measurement of ...
, sufficient energy resolution, minimal pixel crosstalk
In electronics, crosstalk (XT) is a phenomenon by which a signal transmitted on one circuit or channel of a transmission system creates an undesired effect in another circuit or channel. Crosstalk is usually caused by undesired capacitive, ...
, and radiation hardness). The ''Lynx'' team has identified three options with comparable TRL ratings (TRL 3) and sound TRL advancement roadmaps: the Monolithic CMOS, Hybrid CMOS, and Digital CCDs with CMOS readout. All are currently funded for technology development.
* The ''Lynx'' X-ray Microcalorimeter (LXM): The LXM is an imaging spectrometer
An imaging spectrometer is an instrument used in hyperspectral imaging and imaging spectroscopy to acquire a spectrally-resolved image of an object or scene, usually to support analysis of the composition the object being imaged. The spectral data ...
that provides high resolving power (''R'' ~ 2,000) in both the hard and soft X-ray bands, combined with high spatial resolution (down to 0.5′′ scales). To meet the diverse range of ''Lynx'' science requirements, the LXM focal plane includes three arrays that share the same readout technology. Each array is differentiated by its absorber pixel size and thickness, and by how the absorbers are connected to thermal readouts. The total number of pixels exceeds 100,000 — a major leap over past and currently planned X-ray microcalorimeters. This huge improvement does not entail a huge added cost: two of the LXM arrays feature a simple, already proven, “thermal” multiplexing approach where multiple absorbers are connected to a single temperature sensor. This design brings the number of sensors to read out (one of the main power and cost drivers for the X-ray microcalorimeters) to ~7,600. This is only a modest increase over what is planned for the X-IFU instrument on Athena. As of Spring 2019, prototypes of the focal plane have been made that include all three arrays at 2/3 full size. These prototypes demonstrate that arrays with the pixel form factor, size, and wiring density required by Lynx are readily achievable, with high yield. The energy resolution requirements of the different pixel types is also readily achievable. Although the LXM is technically still at TRL 3, there is a clear path for achieving TRL 4 by 2020 and TRL 5 by 2024.
* The X-ray Grating Spectrometer (XGS): The XGS will provide even higher spectral resolution ('' R'' = 5,000 with a goal of 7,500) in the soft X-ray band for point sources. Compared to the current state of the art (''Chandra
Chandra (), also known as Soma (), is the Hindu god of the Moon, and is associated with the night, plants and vegetation. He is one of the Navagraha (nine planets of Hinduism) and Dikpala (guardians of the directions).
Etymology and other ...
''), the XGS provides a factor of > 5 higher spectral resolution and a factor of several hundred higher throughput. These gains are enabled by recent advances in X-ray grating technologies. Two strong technology candidates are: critical angle transmission (used for the ''Lynx'' DRM) and off-plane reflection gratings. Both are fully feasible, currently at TRL 4, and have demonstrated high efficiencies and resolving powers of ~ 10,000 in recent X-ray tests.
Mission operations
 The Chandra X-ray Observatory experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate Lynx, leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single
The Chandra X-ray Observatory experience provides the blueprint for developing the systems required to operate Lynx, leading to a significant cost reduction relative to starting from scratch. This starts with a single prime contractor Prime contractor may refer to:
* Prime contractor (US Government), a specific term in the US law for contractors that work directly with the US government
* Prime contractor, a synonym of general contractor
A contractor (North American English) or ...
for the science and operations center, staffed by a seamless, integrated team of scientists, engineers, and programmers. Many of the system designs, procedures, processes, and algorithms developed for Chandra will be directly applicable for Lynx, although all will be recast in a software/hardware environment appropriate for the 2030s and beyond.
The science impact of Lynx will be maximized by subjecting all of its proposed observations to peer review, including those related to the three science pillars. Time pre-allocation can be considered only for a small number of multi-purpose key programs, such as surveys in pre-selected regions of the sky. Such an open General Observer (GO) program approach has been successfully employed by large missions such as Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
, Chandra X-ray Observatory
The Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), previously known as the Advanced X-ray Astrophysics Facility (AXAF), is a Flagship-class space telescope launched aboard the during STS-93 by NASA on July 23, 1999. Chandra is sensitive to X-ray sources ...
, and Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003, that was deactivated when operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicate ...
, and is planned for James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope designed to conduct infrared astronomy. As the largest telescope in space, it is equipped with high-resolution and high-sensitivity instruments, allowing it to view objects too old, Lis ...
and Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope
The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope (shortened as the Roman Space Telescope, Roman, or RST) is a NASA infrared space telescope in development and scheduled to launch to a Sun–Earth L2 orbit by May 2027. It is named after former NASA Chie ...
. The Lynx GO program will have ample exposure time to achieve the objectives of its science pillars, make impacts across the astrophysical landscape, open new directions of inquiry, and produce as yet unimagined discoveries.
Estimated cost
The cost of the ''Lynx X-ray Observatory'' is estimated to be between US$4.8 billion to US$6.2 billion (in FY20dollars
Dollar is the name of more than 25 currencies. The United States dollar, named after the international currency known as the Spanish dollar, was established in 1792 and is the first so named that still survives. Others include the Australian d ...
at 40% and 70% confidence levels, respectively). This estimated cost range includes the launch vehicle
A launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload (a crewed spacecraft or satellites) from Earth's surface or lower atmosphere to outer space. The most common form is the ballistic missile-shaped multistage ...
, cost reserves, and funding for five years of mission operations, while excluding potential foreign contributions (such as participation by the European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 ...
(ESA)). As described in Section 8.5 of the concept study'Final Report
the ''Lynx'' team commissioned five independent
cost estimates
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is ...
, all of which arrived at similar estimates for the total mission lifecycle cost.
See also
*Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics
Advanced Telescope for High-ENergy Astrophysics (''Athena'') is an X-ray observatory mission selected by European Space Agency (ESA) within its Cosmic Vision program to address the Hot and Energetic Universe scientific theme. ''Athena'' will o ...
* International X-ray Observatory
The International X-ray Observatory (IXO) is a cancelled X-ray telescope that was to be launched in 2021 as a joint effort by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). In May 2008, ESA and NASA e ...
* Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array
NuSTAR (Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, also named Explorer 93 and SMEX-11) is a NASA space-based X-ray telescope that uses a conical approximation to a Wolter telescope to focus high energy X-rays from astrophysical sources, especial ...
(NuSTAR)
* List of proposed space observatories
This list contains proposals for space telescopes, space-based (situated in space) astronomical observatories. It is a list of past and present space observatory plans, concepts, and proposals. For observatories in orbit, see list of space teles ...
References
External links
Lynx home page
Lynx home page for scientists
at NASA {{Space observatories, show Space telescopes X-ray telescopes Proposed NASA space probes