Lower Keys on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Florida Keys are a
The Florida Keys are a

 The climate and environment of the Florida Keys are closer to that of the
The climate and environment of the Florida Keys are closer to that of the
 The Florida Keys have distinctive plant and animals species, some found nowhere else in the United States, as the Keys define the northern extent of their ranges. The climate also allows many imported plants to thrive. Some exotic species which arrived as landscape plants now invade and threaten natural areas.
The native flora of the Keys is diverse, including members of both temperate families, such as red maple (''
The Florida Keys have distinctive plant and animals species, some found nowhere else in the United States, as the Keys define the northern extent of their ranges. The climate also allows many imported plants to thrive. Some exotic species which arrived as landscape plants now invade and threaten natural areas.
The native flora of the Keys is diverse, including members of both temperate families, such as red maple (''
 The Keys are occasionally threatened by
The Keys are occasionally threatened by
, accessed April 2014. *
 The Florida Keys has public bus transportation.
The Florida Keys has public bus transportation.
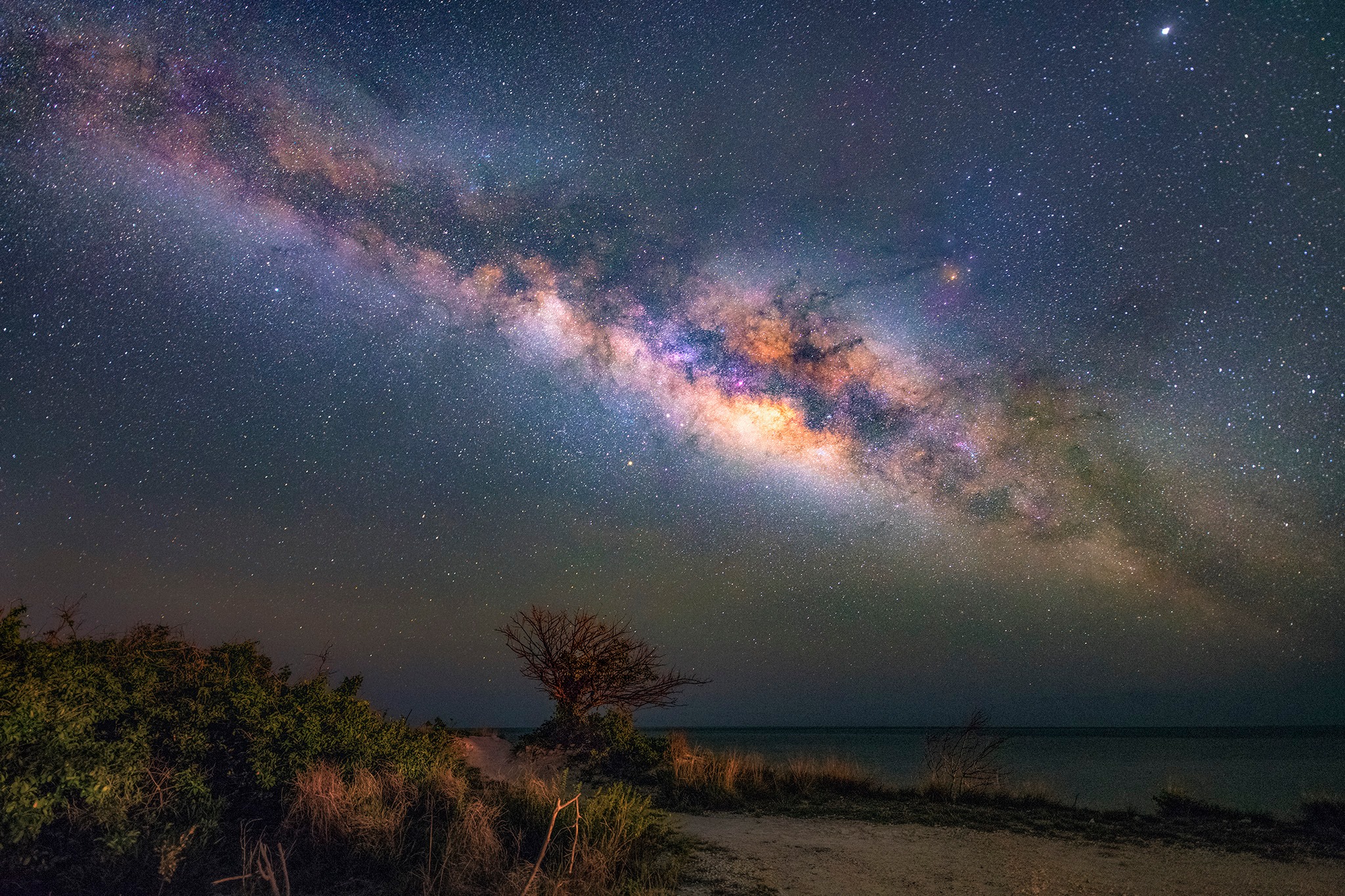
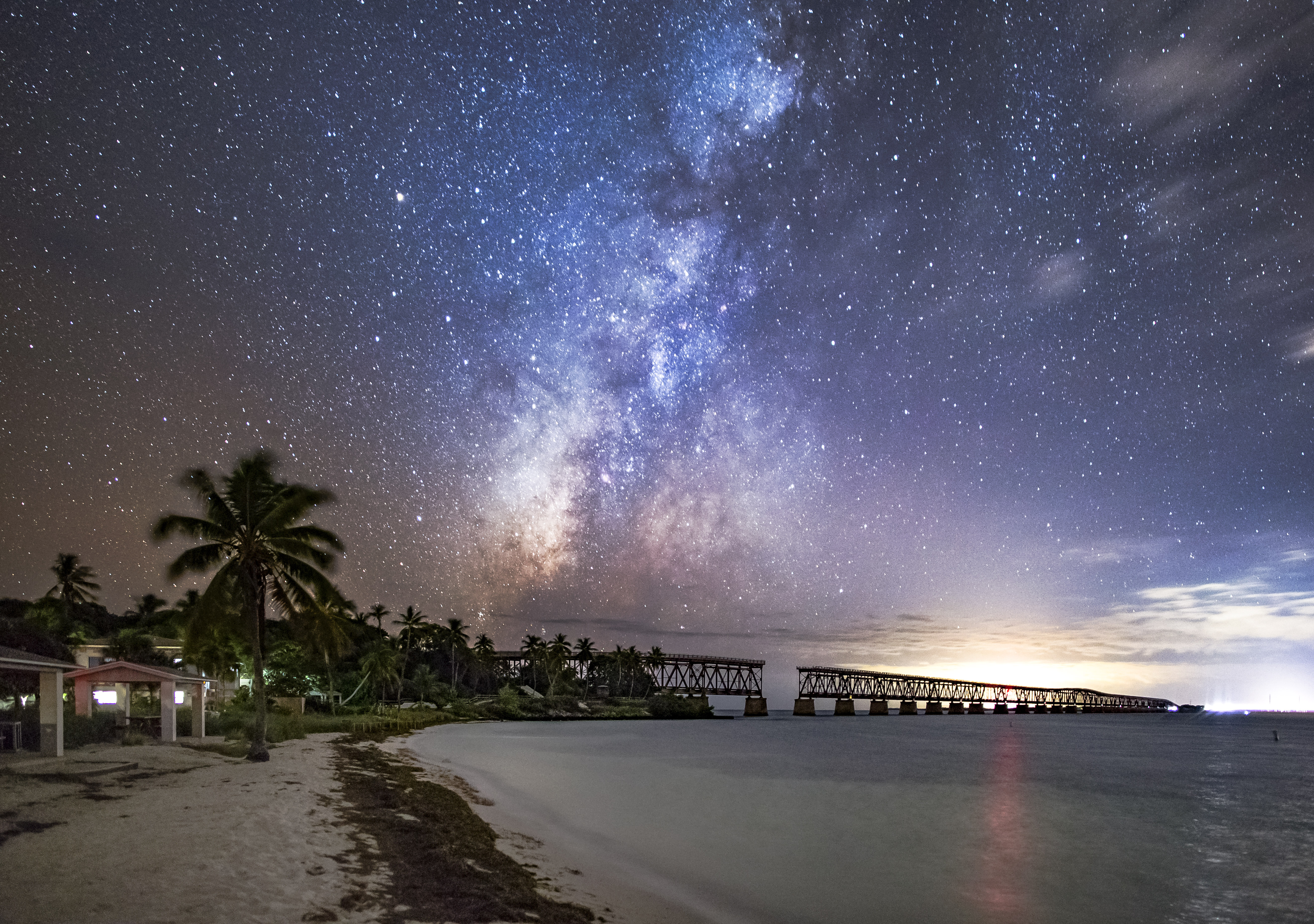
 Middle and Lower Florida Keys are among a few remaining South Florida dark skies locations accessible by car, thanks to their position along the Atlantic Ocean, and therefore with southern skies unobstructed by
Middle and Lower Florida Keys are among a few remaining South Florida dark skies locations accessible by car, thanks to their position along the Atlantic Ocean, and therefore with southern skies unobstructed by in Florida Keys Astronomy Club Events
/ref>
Jason Project The Story of Water Movement and Land Formation
– accessed January 28, 2006. *
Florida Keys Fish
A Gazetteer of the Florida Keys
*
City of Key West
City of Marathon
NOAA Marine Sanctuary
*
Key West Citizen
{{Authority control Outstanding Florida Waters Regions of Florida South Florida Archipelagoes of the United States
 The Florida Keys are a
The Florida Keys are a coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
cay
A cay ( ), also spelled caye or key, is a small, low-elevation, sandy island on the surface of a coral reef. Cays occur in tropical environments throughout the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, including in the Caribbean and on the Grea ...
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands. An archipelago may be in an ocean, a sea, or a smaller body of water. Example archipelagos include the Aegean Islands (the o ...
off the southern coast of Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
, about south of Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
and extend in an arc south-southwest and then westward to Key West
Key West is an island in the Straits of Florida, at the southern end of the U.S. state of Florida. Together with all or parts of the separate islands of Dredgers Key, Fleming Key, Sunset Key, and the northern part of Stock Island, it con ...
, the westernmost of the inhabited islands, and on to the uninhabited Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park of the United States located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico, in the United States. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the several Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most iso ...
. The islands lie along the Florida Straits
The Straits of Florida, Florida Straits, or Florida Strait () is a strait located south-southeast of the North American mainland, generally accepted to be between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, and between the Florida Keys (U.S.) ...
, dividing the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to the east from the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico () is an oceanic basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, mostly surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north, and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southw ...
to the northwest, and defining one edge of Florida Bay
Florida Bay is the bay located between the southern end of the Florida mainland (the Everglades, Florida Everglades) and the Florida Keys in the United States. It is a large, shallow estuary that while connected to the Gulf of Mexico, has limited ...
. The southern part of Key West is from Cuba
Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ...
. The Keys are located between about 24.3 and 25.5 degrees North latitude.
More than 95% of the land area lies in Monroe County, but a small portion extends northeast into Miami-Dade County
Miami-Dade County () is a county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Florida. The county had a population of 2,701,767 as of the 2020 census, making it the most populous county in Florida and the seventh-most-populous coun ...
, such as Totten Key
Totten Key is an island of the upper Florida Keys in Biscayne National Park. It is in Miami-Dade County, Florida.
It is located in southern Biscayne Bay, just west of Old Rhodes Key.
History
It was probably named for General Joseph Totten who ...
. The total land area is . At the 2010 census the population was 73,090, with an average density of , although much of the population is concentrated in a few areas of much higher density, such as the city of Key West, which has 32% of the Keys' total population. The 2014 Census population estimate was 77,136. The 2020 Census population estimate was 82,874.
The city of Key West is the county seat
A county seat is an administrative center, seat of government, or capital city of a county or parish (administrative division), civil parish. The term is in use in five countries: Canada, China, Hungary, Romania, and the United States. An equiva ...
of Monroe County. The county consists of a section on the mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or demogr ...
which is almost entirely in Everglades National Park
Everglades National Park is a List of national parks of the United States, national park of the United States that protects the southern twenty percent of the original Everglades in Florida. The park is the largest tropical wilderness in the Un ...
, and the Keys islands from Key Largo
Key Largo () is an island in the upper Florida Keys archipelago and is the largest section of the keys, at long. It is one of the northernmost of the Florida Keys in Monroe County, and the northernmost of the keys connected by U.S. Highway ...
to Dry Tortugas National Park
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park of the United States located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico, in the United States. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the several Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most iso ...
.
History
The Keys were originally inhabited by theCalusa
The Calusa ( , Calusa: *ka(ra)luś(i)) were a Native American people of Florida's southwest coast. Calusa society developed from that of archaic peoples of the Everglades region. Previous Indigenous cultures had lived in the area for thousands o ...
and Tequesta
The Tequesta, also Tekesta, Tegesta, Chequesta, Vizcaynos, were a Native American tribe on the Southeastern Atlantic coast of Florida. They had infrequent contact with Europeans and had largely migrated by the middle of the 18th century.
Loca ...
people and were later charted by Juan Ponce de León
Juan Ponce de León ( – July 1521) was a Spanish explorer and ''conquistador'' known for leading the first official European expedition to Puerto Rico in 1508 and Florida in 1513. He was born in Santervás de Campos, Valladolid, Spain, in ...
in 1513. De León named the islands ''Los Martires'' ("The Martyrs"), as they looked like suffering men from a distance. "Key" is derived from the Spanish word ''cayo'', meaning small island. For many years, Key West was the largest town in Florida, and it grew prosperous on wrecking revenues. The isolated outpost was well located for trade with Cuba and the Bahamas and was on the main trade route from New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
. Improved navigation led to fewer shipwrecks, and Key West went into a decline in the late nineteenth century.
Overseas Railway
The Keys were long accessible only by water. This changed with the completion ofHenry Flagler
Henry Morrison Flagler (January 2, 1830 – May 20, 1913) was an American industrialist and a founder of Standard Oil, which was first based in Ohio. He was also a key figure in the development of the Atlantic coast of Florida and founder ...
's Overseas Railway in the early 1910s. Flagler, a major developer of Florida's Atlantic coast, extended his Florida East Coast Railway
The Florida East Coast Railway is a Class II railroad operating in the U.S. state of Florida, currently owned by Grupo México.
Built primarily in the last quarter of the 19th century and the first decade of the 20th century, the FEC was a p ...
down to Key West with an ambitious series of oversea railroad trestles. Three hurricanes disrupted the project in 1906
Events
January–February
* January 12 – Persian Constitutional Revolution: A nationalistic coalition of merchants, religious leaders and intellectuals in Persia forces the shah Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar to grant a constitution, ...
, 1909
Events
January–February
* January 4 – Explorer Aeneas Mackintosh of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition escapes death by fleeing across ice floes.
* January 7 – Colombia recognizes the independence of Panama.
* Janu ...
, and 1910
Events
January
* January 6 – Abé people in the French West Africa colony of Côte d'Ivoire rise against the colonial administration; the rebellion is brutally suppressed by the military.
* January 8 – By the Treaty of Punakha, t ...
.
1935 Labor Day hurricane
The strongest hurricane to strike the U.S. made landfall near Islamorada in the Upper Keys on Labor Day, Monday, September 2, 1935. Winds were estimated to have gusted to , raising a storm surge more than above sea level that washed over the islands. More than 400 people were killed, though some estimates place the number of deaths at more than 600. The Labor Day hurricane was one of only four hurricanes to make landfall at Category 5 strength on the U.S. coast since reliable weather records began (about 1850). The other storms wereHurricane Camille
Hurricane Camille was a powerful, deadly and destructive tropical cyclone which became the second most intense on record to strike the United States (behind the 1935 Labor Day hurricane) and is one of the four Category 5 hurricanes to make ...
(1969), Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was a compact, but very powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It was the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures dama ...
(1992), and Hurricane Michael
Hurricane Michael was a powerful and destructive tropical cyclone that became the first Category 5 hurricane to make landfall in the contiguous United States since Andrew in 1992. It was the third-most intense Atlantic hurricane to make ...
(2018).
In 1935, new bridges were under construction to connect a highway through the entire Keys. Hundreds of World War I veterans working on the roadway as part of a government relief program were housed in non-reinforced buildings in three construction camps in the Upper Keys. When the evacuation train failed to reach the camps before the storm, more than 200 veterans perished. Their deaths caused anger and charges of mismanagement that led to a Congressional investigation.
The storm also ended the 23-year run of the Overseas Railway; the damaged tracks were never rebuilt, and the Overseas Highway
The Overseas Highway is a highway carrying U.S. Route 1 (US 1) through the Florida Keys to Key West. Large parts of it were built on the former right-of-way of the Overseas Railroad, the Key West Extension of the Florida East Coast Ra ...
( U.S. Highway 1) replaced the railroad as the main transportation route from Miami to Key West.
Seven Mile Bridge
One of the longest bridges when it was built, theSeven Mile Bridge
The Seven Mile Bridge is a bridge in the Florida Keys, in Monroe County, Florida, United States. It connects Knight's Key (part of the city of Marathon, Florida) in the Middle Keys to Little Duck Key in the Lower Keys. Among the longest br ...
connects Knight's Key (part of the city of Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of kilometres ( 26 mi 385 yd), usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There ...
in the Middle Keys) to Little Duck Key in the Lower Keys. The piling-supported concrete bridge is or 6.79 miles (10.93 km) long. The current bridge bypasses Pigeon Key
Pigeon Key is a small island containing the historic district of Pigeon Key, Florida. The island is home to 8 buildings on the National Register of Historic Places, some of which remain from its earliest incarnation as a work camp for the Fl ...
, a small island that housed workers building Henry Flagler
Henry Morrison Flagler (January 2, 1830 – May 20, 1913) was an American industrialist and a founder of Standard Oil, which was first based in Ohio. He was also a key figure in the development of the Atlantic coast of Florida and founder ...
's Florida East Coast Railway
The Florida East Coast Railway is a Class II railroad operating in the U.S. state of Florida, currently owned by Grupo México.
Built primarily in the last quarter of the 19th century and the first decade of the 20th century, the FEC was a p ...
in the 1900s, that the original Seven Mile Bridge crossed. A section of the old bridge remains for access to the island, although it was closed to vehicular traffic on March 4, 2008. The aging structure has been deemed unsafe by the Florida Department of Transportation
The Florida Department of Transportation (FDOT) is a decentralized agency charged with the establishment, maintenance, and regulation of public transportation in the U.S. state of Florida. The department was formed in 1969. It absorbed the power ...
. Costly repairs, estimated to be as much as $34 million, were expected to begin in July 2008. Monroe County was unable to secure a $17 million loan through the state infrastructure bank, delaying work for at least a year. On June 14, 2008, the old bridge section leading to Pigeon Key was closed to fishing as well. While still open to pedestrians—walking, biking and jogging—if the bridge were closed altogether, only a ferry subsidized by FDOT and managed by the county would transport visitors to the island.
Overseas Highway
After the destruction of the Keys railway by theLabor Day Hurricane of 1935
The 1935 Labor Day hurricane was an extremely powerful and devastating Atlantic hurricane that struck the southeastern United States in early September 1935. For several decades, it was the most intense Atlantic hurricane on record in terms of ...
, the railroad bridges, including the Seven Mile Bridge, were converted to automobile roadways. This roadway, U.S. Highway 1, became the Overseas Highway
The Overseas Highway is a highway carrying U.S. Route 1 (US 1) through the Florida Keys to Key West. Large parts of it were built on the former right-of-way of the Overseas Railroad, the Key West Extension of the Florida East Coast Ra ...
that runs from Key Largo south to Key West. Today this highway allows travel through the tropical islands of the Florida Keys and the viewing of exotic plants and animals found nowhere else on the US mainland and the largest coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
chain in the United States.
Cuban exiles
Following theCuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution () was the military and political movement that overthrew the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista, who had ruled Cuba from 1952 to 1959. The revolution began after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état, in which Batista overthrew ...
, many Cubans emigrated to South Florida. Key West traditionally had strong links with its neighbor ninety miles south by water, and large numbers of Cubans settled there. The Keys still attract Cubans leaving their home country, and stories of "rafters" coming ashore are not uncommon.
Conch Republic
In 1982, theUnited States Border Patrol
The United States Border Patrol (USBP) is a Federal law enforcement in the United States, federal law enforcement agency under the U.S. Customs and Border Protection, United States Customs and Border Protection (CBP) and is responsible for secu ...
established a roadblock and inspection points on US Highway 1
U.S. Route 1 or U.S. Highway 1 (US 1) is a major north–south United States Numbered Highway that serves the East Coast of the United States. It runs from Key West, Florida, north to Fort Kent, Maine, at the Canadian border, ma ...
, stopping all northbound traffic returning to the mainland at Florida City
Florida City is a city in Miami-Dade County, Florida, United States. It is the southernmost municipality in the South Florida metropolitan area. Florida City is primarily a Miami suburb and a major agricultural area. As of the 2020 census, it ...
, to search vehicles for illegal drugs and undocumented immigrants. The Key West City Council repeatedly complained about the roadblocks, which were a major inconvenience for travellers, and hurt the Keys' important tourism industry.
After various unsuccessful complaints and attempts to get a legal injunction against the blockade failed in federal court in Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
, on April 23, 1982, Key West mayor Dennis Wardlow
Dennis Wardlow (born c. 1944) is a former mayor of Key West, Florida, having served on three occasions.
He is known for being the prime minister of the Conch Republic, the micronation that seceded from the United States on April 23, 1982, in p ...
and the city council declared the independence of the city of Key West
Key West is an island in the Straits of Florida, at the southern end of the U.S. state of Florida. Together with all or parts of the separate islands of Dredgers Key, Fleming Key, Sunset Key, and the northern part of Stock Island, it con ...
, calling it the "Conch Republic
The Conch Republic () is a micronation declared as a secession of the city of Key West, Florida, from the United States on April 23, 1982. It has been maintained as a tourism booster for the city. Since then, the term "Conch Republic" has been e ...
", and declared war on the United States by striking an officer of the Key West Naval Air Station (NAS) on the head with a loaf of stale Cuban bread. After one minute of secession, he (as "Prime Minister") surrendered to the officer and requested US$1,000,000,000 in "foreign aid
In international relations, aid (also known as international aid, overseas aid, foreign aid, economic aid or foreign assistance) is – from the perspective of governments – a voluntary transfer of resources from one country to another. The ...
".
The stunt succeeded in generating great publicity for the Keys' plight, and the inspection station roadblock was removed. The idea of the Conch Republic has provided a new source of revenue for the Keys by way of tourist keepsake sales, and the Conch Republic has participated in later protests.
Geology
The northern and central sections of the Florida Keys are the exposed portions of an ancientcoral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
, the Key Largo Limestone
The Key Largo Limestone is a Formation (stratigraphy), geologic formation in Florida. It is a fossilized coral reef. The formation is exposed along the upper and middle Florida Keys from Soldier Key (at the north end of the Florida Keys) to the ...
. The northernmost island arising from the ancient reef formation is Elliott Key
Elliott Key is the northernmost of the true Florida Keys (those 'keys' which are ancient coral reefs lifted above the present sea level), and the largest key north of Key Largo. It is located entirely within Biscayne National Park, in Miami-Dade ...
, in Biscayne National Park
Biscayne National Park is a national park of the United States located south of Miami, Florida, in Miami-Dade County. The park preserves Biscayne Bay and its offshore barrier reefs. Ninety-five percent of the park is water, and the shore of th ...
. North of Elliott Key are several small transitional keys, composed of sand built up around small areas of exposed ancient reef. Further north, Key Biscayne
Key Biscayne () is an island located in Miami-Dade County, Florida, located between the Atlantic Ocean and Biscayne Bay. It is the southernmost of the barrier islands along the Atlantic coast of Florida, and lies south of Miami Beach and sout ...
and places north are barrier island
Barrier islands are a Coast#Landforms, coastal landform, a type of dune, dune system and sand island, where an area of sand has been formed by wave and tidal action parallel to the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of an ...
s, built up of sand. The islands in the southwestern part of the chain, from Big Pine Key
Big or BIG may refer to:
* Big, of great size or degree
Film and television
* ''Big'' (film), a 1988 fantasy-comedy film starring Tom Hanks
* ''Big'', a 2023 Taiwanese children's film starring Van Fan and Chie Tanaka
* ''Big!'', a Discovery ...
to the Marquesas Keys
The Marquesas Keys form an uninhabited island group about west of Key West, in diameter, and largely covered by mangrove forest. They are an unincorporated area of Monroe County, Florida and belong to the Lower Keys Census County Division. T ...
, are exposed areas of Miami Limestone
The Miami Limestone, originally called Miami Oolite, is a Formation (stratigraphy), geologic formation of limestone in southeastern Florida.
Miami Limestone forms the Atlantic Coastal Ridge in southeastern Florida, near the coast in Palm Beach ...
.
The Florida Keys have taken their present form as the result of the drastic changes in sea level associated with recent glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate be ...
s or ''ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
s''. Beginning some 130,000 years ago the Sangamonian Stage
The Sangamonian Stage (or Sangamon interglacial) is the term used in North America to designate the Last Interglacial (130,000-115,000 years ago) and depending on definition, part of the early Last Glacial Period, corresponding to Marine Isotope S ...
raised sea levels about above the current level. All of southern Florida was covered by a shallow sea. Several parallel lines of reef formed along the edge of the submerged Florida Platform
The Florida Platform is a flat geological feature with the emergent portion forming the Florida peninsula.
Structure
The platform forms an escarpment between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. The platform's western edge, or Florida Esca ...
, stretching south and then west from the present Miami area to what is now the Dry Tortugas. This reef formed the Key Largo Limestone that is exposed on the surface from Soldier Key
Soldier Key is an island in Biscayne National Park in Miami-Dade County, Florida. It is located between Biscayne Bay and the Atlantic Ocean, about three miles north of the Ragged Keys, five miles south of Cape Florida on Key Biscayne, seven-and ...
(midway between Key Biscayne and Elliott Key) to the southeast portion of Big Pine Key
Big or BIG may refer to:
* Big, of great size or degree
Film and television
* ''Big'' (film), a 1988 fantasy-comedy film starring Tom Hanks
* ''Big'', a 2023 Taiwanese children's film starring Van Fan and Chie Tanaka
* ''Big!'', a Discovery ...
and the Newfound Harbor Keys. The types of coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
that formed Key Largo Limestone can be identified on the exposed surface of these keys. Minor fluctuations in sea level exposed parts of the reef, subjecting it to erosion. Acidic water, which can result from decaying vegetation, dissolves limestone. Some of the dissolved limestone redeposited as a denser ''cap rock'', which can be seen as outcrops overlying the Key Largo and Miami limestones throughout the Keys. The limestone that eroded from the reef formed oolite
Oolite or oölite () is a sedimentary rock formed from ooids, spherical grains composed of concentric layers. Strictly, oolites consist of ooids of diameter 0.25–2 millimetres; rocks composed of ooids larger than 2 mm are called pis ...
s in the shallow sea behind the reef, and together with the skeletal remains of bryozoans, formed the Miami Limestone that is the current surface bedrock of the lower Florida peninsula and the lower keys from Big Pine Key to Key West. To the west of Key West the ancient reef is covered by recent calcareous
Calcareous () is an adjective meaning "mostly or partly composed of calcium carbonate", in other words, containing lime (mineral), lime or being chalky. The term is used in a wide variety of Science, scientific disciplines.
In zoology
''Calcare ...
sand. While the islands of the upper and middle keys, consisting of Key Largo Limestone, form a long narrow arc, the islands of the lower keys are perpendicular to the line of that arc. This configuration arose from an ancient tidal-bar system, in which tidal channel
A tidal creek or tidal channel is a narrow inlet or estuary that is affected by the ebb and flow of ocean tides. Thus, it has variable salinity and electrical conductivity over the tidal cycle, and flushes salts from inland soils. Tidal creeks a ...
s cut through a submerged oolitic deposit. The bars lithified
Lithification (from the Ancient Greek word ''lithos'' meaning 'rock' and the Latin-derived suffix ''-ific'') is the process in which sediments compact under pressure, expel connate fluids, and gradually become solid rock. Essentially, lithificati ...
into Miami Limestone, and with changes in sea level are presently exposed as the islands, while the channels between the bars now separate the islands.
Just offshore of the Florida Keys along the edge of the Florida Straits is the Florida Reef
The Florida Reef (also known as the Great Florida Reef, Florida reefs, Florida Reef Tract and Florida Keys Reef Tract) is the only living coral barrier reef in the continental United States. It lies a few miles seaward of the Florida Keys, is ...
(also known as the Florida Reef Tract), separated from the keys by the Hawk Channel
Hawk Channel is a shallow, elongated Oceanic basin, basin and Channel (geography), navigable passage along the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast of the Florida Keys. The channel makes up a smaller portion of the Florida Platform from Key West to the ...
. The Florida Reef extends from Fowey Rocks just east of Soldier Key to just south of the Marquesas Keys. It is the third-largest barrier reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
system in the world.
Environment

 The climate and environment of the Florida Keys are closer to that of the
The climate and environment of the Florida Keys are closer to that of the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
than the rest of Florida, though unlike the Caribbean's volcanic islands, the Keys were built by plants and animals. The Upper Keys islands are composed of sandy-type accumulations of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
grains produced by plants and marine organisms. The Lower Keys are the remnants of large coral reefs, which became fossilized and exposed when the sea level dropped.
The natural habitats of the Keys are upland forests, inland wetlands and shoreline zones. Soil ranges from sand to marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, Clay minerals, clays, and silt. When Lithification, hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
M ...
to rich, decomposed leaf litter
Plant litter (also leaf litter, tree litter, soil litter, litterfall, or duff) is dead plant material (such as leaves, bark, needles, twigs, and cladodes) that has fallen to the ground. This detritus or dead organic material and its constituen ...
. In some places, "caprock" (the eroded surface of coral formations) covers the ground. Rain falling through leaf debris becomes acidic and dissolves holes in the limestone, where soil accumulates and trees root.
Flora and fauna
 The Florida Keys have distinctive plant and animals species, some found nowhere else in the United States, as the Keys define the northern extent of their ranges. The climate also allows many imported plants to thrive. Some exotic species which arrived as landscape plants now invade and threaten natural areas.
The native flora of the Keys is diverse, including members of both temperate families, such as red maple (''
The Florida Keys have distinctive plant and animals species, some found nowhere else in the United States, as the Keys define the northern extent of their ranges. The climate also allows many imported plants to thrive. Some exotic species which arrived as landscape plants now invade and threaten natural areas.
The native flora of the Keys is diverse, including members of both temperate families, such as red maple (''Acer rubrum
''Acer rubrum'', the red maple, also known as swamp maple, water maple, or soft maple, is one of the most common and widespread deciduous trees of eastern and central North America. The U.S. Forest Service recognizes it as the most abundant nati ...
''), slash pine ( ''Pinus elliottii'' var. ''densa'') and oaks (''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
'' spp.), growing at the southern end of their ranges, and tropical families, including mahogany (''Swietenia mahagoni
''Swietenia mahagoni'', commonly known as American mahogany, Cuban mahogany, small-leaved mahogany, and West Indian mahogany, is a species of ''Swietenia'' native to the broader Caribbean bioregion. It is the species from which the original mahog ...
''), gumbo limbo (''Bursera simaruba
''Bursera simaruba'', commonly known as gumbo-limbo, the tourist tree, copperwood, almácigo, chaca, West Indian birch, naked Indian, and turpentine tree, is a tree species in the family Burseraceae, native to the Neotropics, from South Florid ...
''), stoppers (''Eugenia
''Eugenia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the myrtle family Myrtaceae. It has a worldwide, although highly uneven, distribution in tropical and subtropical regions. The bulk of the approximately 1,100 species occur in the New World tropics, ...
'' spp.), Jamaican dogwood (''Piscidia piscipula
''Piscidia piscipula'', commonly named Florida fishpoison tree, Jamaican dogwood, or fishfuddle, is a medium-sized, deciduous, tropical tree in the Fabaceae family. It is native to the Greater Antilles (except Puerto Rico), extreme southern Flori ...
''), and many others, which grow only in tropical climates. Several types of palms are native to the Florida Keys, including the Florida thatch palm (''Thrinax radiata
''Thrinax'' is a genus in the palm family, native to the Caribbean. It is closely related to the genera '' Coccothrinax'', '' Hemithrinax'' and '' Zombia''. Flowers are small, bisexual and are borne on small stalks.
Taxonomy
In the first edit ...
''), which grows to its greatest size in Florida on the islands of the Keys.
The Keys are also home to unique animal species, including the American crocodile
The American crocodile (''Crocodylus acutus'') is a species of crocodilian found in the Neotropics. It is the most widespread of the four Extant taxon, extant species of crocodiles from the Americas, with populations present from South Florida, ...
, Key deer
The Key deer (''Odocoileus virginianus clavium'') is an endangered subspecies of the white-tailed deer that lives only in the Florida Keys. It is the smallest extant North American deer species.
Description
This deer can be recognized by its ch ...
(protected by the National Key Deer Refuge), and the Key Largo woodrat. The Keys are part of the northernmost range of the American crocodile, which is found throughout the Neotropics
The Neotropical realm is one of the eight biogeographic realms constituting Earth's land surface. Physically, it includes the tropical terrestrial ecoregions of the Americas and the entire South American temperate zone.
Definition
In biogeog ...
. The Key Largo Woodrat is found only in the northern part of its namesake island and is a focus of management activities in Crocodile Lake National Wildlife Refuge. About 70 miles (110 km) west of Key West is Dry Tortugas National Park
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park of the United States located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico, in the United States. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the several Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most iso ...
.
The waters surrounding the Keys are part of a protected area known as the Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary
The Florida Keys National Marine Sanctuary is a U.S. National Marine Sanctuary in the Florida Keys. It includes the Florida Reef, the only barrier coral reef in North America and the third-largest coral barrier reef in the world. It also has e ...
.
Climate
The climate of the Florida Keys istropical savanna
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and t ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (te ...
: Aw). Other than some areas of coastal Miami (Miami Beach), the Florida Keys are the only areas in the continental United States to never report freezing temperatures since settlement. The record low in Key West is (in both 1886 and 1981), and low temperatures below are rare. Most of the Florida Keys fall into USDA zone 11a to 11b; Key West is zone 12a.
There are two main "seasons" in the Florida Keys, a hot and wet season from June through October, and a dry season from November through April, that features little rainfall, sunny skies, and warm breezy conditions. The warm and sunny winter climate, with average highs around and lows above , is the main tourist season in the Florida Keys. Key West is the driest city in Florida, and most of the Florida Keys can become quite dry at the height of the dry season. Some of the more exposed vegetation in the keys is scrub, stunted due to the intense sun, quick draining sandy soil, and arid winter climate.
Tropical cyclones
 The Keys are occasionally threatened by
The Keys are occasionally threatened by tropical storm
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its lo ...
s and hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...
s, leading to evacuations to the mainland. Hurricane Georges
Hurricane Georges () was a powerful and long-lived tropical cyclone which caused severe destruction as it traversed the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico in September 1998, making seven landfalls along its path. Georges was the seventh tropical storm ...
, after destroying much of the housing and infrastructure on many of the Caribbean islands
Most of the Caribbean countries are islands in the Caribbean Sea, with only a few in inland lakes. The largest islands include Cuba, Hispaniola, Jamaica and Puerto Rico. Some of the smaller islands are referred to as a ''rock'' or ''reef.''
''I ...
, caused damage and extensive flooding in the Lower Keys in 1998, before making landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
in Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
. In 2005, Hurricanes Katrina, Rita and Wilma affected the Keys (although none made a direct hit), causing widespread damage and flooding. The most severe hurricane to hit the area was the Labor Day Hurricane of 1935
The 1935 Labor Day hurricane was an extremely powerful and devastating Atlantic hurricane that struck the southeastern United States in early September 1935. For several decades, it was the most intense Atlantic hurricane on record in terms of ...
, a Category 5 hurricane.
Tropical cyclones present special dangers and challenges to the entire Keys. Because no area of the islands is more than above sea level (and many are only a few feet elevation), and water surrounds the islands, nearly every neighborhood is subject to flooding as well as hurricane winds. In response, many homes in the Keys are built on concrete stilts with the first floor being not legally habitable and enclosed by breakaway walls that are not strongly attached to the rest of the house. Nonetheless, Monroe County, as reported in the Federal Register, has estimated that there are between 8,000 and 12,000 illegal enclosures inhabited by people.
Because of the threat from storm surge, evacuations are routinely ordered when the National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weathe ...
issues a hurricane watch or warning, and are sometimes ordered for a tropical storm warning. Evacuation of the Keys depends on causeways and the two-lane highway to the mainland. Time estimates for evacuating the entire Keys range from 12 to 24 hours. Evacuation estimates are significant in emergency planning, of course, but also because they are a factor in local and state regulations for controlling development. The building permit allocation was increased in 2005 when local governments reduced estimates for evacuation.
On September 10, 2017, Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Hurricane Maria, Maria two weeks later. At the time, it was considered ...
made landfall in Cudjoe Key. The storm destroyed an estimated 25% of the houses on the Keys and another 65% suffered major damage. Most residents had evacuated before the storm hit the area. On September 12, parts of the Keys were still inaccessible by causeway and some areas were closed to the public. Governor Rick Scott
Richard Lynn Scott ( Myers; born December 1, 1952) is an American attorney, businessman, politician, and United States Navy, Navy veteran serving as the Seniority in the United States Senate, senior United States senator from the state of F ...
reported devastation; most areas were without power or water. The damage was the worst in the Lower Keys, though less severe in Key West; parts of the Lower Keys may be uninhabitable for months.
Major islands
U.S. Highway 1, the "Overseas Highway
The Overseas Highway is a highway carrying U.S. Route 1 (US 1) through the Florida Keys to Key West. Large parts of it were built on the former right-of-way of the Overseas Railroad, the Key West Extension of the Florida East Coast Ra ...
", runs over most of the inhabited islands of the Florida Keys. The islands are listed in order from southwest to north. Mile marker
A milestone is a numbered marker placed on a route such as a road, railway, railway line, canal or border, boundary. They can indicate the distance to towns, cities, and other places or landmarks like Mileage sign, mileage signs; or they c ...
s are listed for keys that the Overseas Highway runs across or near:FDOT straight line diagrams, accessed April 2014. *
Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park of the United States located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico, in the United States. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the several Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most iso ...
* Loggerhead Key
Loggerhead Key is an uninhabited tropical island within the Dry Tortugas National Park, Dry Tortugas group of islands in the Gulf of Mexico. At approximately 49 acres (19.8 hectares) in size, it is the largest island of the Dry Tortugas. Despi ...
* Marquesas Keys
The Marquesas Keys form an uninhabited island group about west of Key West, in diameter, and largely covered by mangrove forest. They are an unincorporated area of Monroe County, Florida and belong to the Lower Keys Census County Division. T ...
* Sunset Key
Sunset Key is a residential neighborhood and resort island in the city of Key West, Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico ...
* Wisteria Island
Wisteria Island is a federally owned, uninhabited island in the lower Florida Keys 645 yards (590 m) northwest of the northwestern corner of the main island and city of Key West, Florida, Monroe County, United States. It is located 280 yards ( ...
* Key West
Key West is an island in the Straits of Florida, at the southern end of the U.S. state of Florida. Together with all or parts of the separate islands of Dredgers Key, Fleming Key, Sunset Key, and the northern part of Stock Island, it con ...
(MM 0–4)
* Fleming Key
Fleming Key is an island off the northwest corner of the island of Key West, Florida in the lower Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral island, coral cay archipelago off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of th ...
* Sigsbee Park
Sigsbee Park, also known as ''Dredgers Key'', is an island about half a mile (800 m) north of Key West island in the lower Florida Keys; administratively it is within the City of Key West, Florida, United States.
It is connected to the isl ...
(off to the north at MM 2¾)
* Stock Island (MM 5)
* Raccoon Key (off to the north at MM 5¼)
* Boca Chica Key
Boca Chica Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys, about a mile () east of the island of Key West at its closest point. Its name is Spanish for "small mouth". It is mostly covered by salt marshes and mangrove trees, and is the home of the lar ...
(MM 7–8)
* Rockland Key (MM 9)
* East Rockland Key (MM 9½)
* Big Coppitt Key (MM 10)
* Geiger Key
Geiger Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys about east of Key West. It is located to the south of, and bridged to, Big Coppitt Key via Boca Chica Road ( County Road 941) at about mile marker 11 on U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway). It has ...
(off to the south at MM 10¾)
* Shark Key (off to the north at MM 11¼)
* Saddlebunch Keys
The Saddlebunch Keys are a series of mangrove islands about east of Key West, Florida.
The keys are scattered between Lower Sugarloaf Key and Shark Key.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway
The Overseas Highway is a highway carrying U.S. ...
(MM 12–16)
* Lower Sugarloaf Key
Lower Sugarloaf Key is the lower arm of an island known as Sugarloaf Key in the lower Florida Keys about east of Key West.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at about mile markers 16.5–17.5. Due to the routing of U.S. Route ...
(MM 17)
* Park Key (MM 18)
* Sugarloaf Key
Sugarloaf Key is a single island in the lower Florida Keys that forms a loop on the Atlantic Ocean side, giving the illusion of separate islands. Although frequently referred to simply and with technical accuracy as "Sugarloaf Key", this island ...
(MM 19–20)
* Cudjoe Key
Cudjoe, Codjoe or Captain Cudjoe (c. 1659 – 1744),Michael Sivapragasam''After the Treaties: A Social, Economic and Demographic History of Maroon Society in Jamaica, 1739–1842'' PhD Dissertation, African-Caribbean Institute of Jamaica libra ...
(MM 21–23)
* Knockemdown Key
* Summerland Key
Summerland Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys about east of Key West; it contains an unincorporated community of Monroe County of the same name.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway) crosses the island at approximately mile markers 24–2 ...
(MM 24–25)
* Ramrod Key
Ramrod Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys. Originally named Roberts Island, Ramrod Key was renamed for a ship named Ramrod, which was wrecked on a reef south of there in the early nineteenth century.
Description
Until the construction of ...
(MM 27)
* Middle Torch Key
Middle Torch Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys.
It is located between Ramrod Key
Ramrod Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys. Originally named Roberts Island, Ramrod Key was renamed for a ship named Ramrod, which was wrecked ...
, Big Torch Key (off to the north at MM 27¾)
* Little Torch Key
Little Torch Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys.
U.S. Route 1 (also known as the Overseas Highway), crosses the key at about mile markers 28–29. It is immediately preceded to the northeast by Big Pine Key, and is followed by Middle T ...
(MM 28½)
* Big Pine Key
Big or BIG may refer to:
* Big, of great size or degree
Film and television
* ''Big'' (film), a 1988 fantasy-comedy film starring Tom Hanks
* ''Big'', a 2023 Taiwanese children's film starring Van Fan and Chie Tanaka
* ''Big!'', a Discovery ...
(MM 30–32)
* No Name Key
No Name Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys in the United States. It is from US 1 and sparsely populated, with only 43 homes. It is only about in comparison to its larger neighbor, Big Pine Key, which lies about half a mile (800 m) ...
* Scout Key
Scout Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys. It was previously known as West Summerland Key until 2010. U.S. Route 1 in Florida, U.S. 1 (the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at approximately mile markers 34–35, between Spanish Harbor Key a ...
(MM 34–35), formerly known as West Summerland Key
* Bahia Honda Key
Bahia Honda ( , ; ) is an island in the lower Florida Keys.
U.S. 1 (the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at approximately mile markers 36-38.5, between Ohio Key and Spanish Harbor Key west of Marathon, close to the west end of the Seven ...
(MM 37–38)
* Ohio Key
U.S. Route 1 in Florida, US 1 (or the Overseas Highway) crosses the Ohio Key at approximately mile marker 39, between Missouri Key and Bahia Honda Key. Today it is also known as Sunshine Key, after a camping resort located there. The portion of t ...
(MM 38¾), also known as Sunshine Key
* Missouri Key (MM 39¼)
* Little Duck Key (MM 39¾)
The Seven Mile Bridge
The Seven Mile Bridge is a bridge in the Florida Keys, in Monroe County, Florida, United States. It connects Knight's Key (part of the city of Marathon, Florida) in the Middle Keys to Little Duck Key in the Lower Keys. Among the longest br ...
(MM 40–46¾) separates the Lower Keys from the Middle Keys:
* Pigeon Key
Pigeon Key is a small island containing the historic district of Pigeon Key, Florida. The island is home to 8 buildings on the National Register of Historic Places, some of which remain from its earliest incarnation as a work camp for the Fl ...
(off to the north near MM 45; access is at MM 46¾)
* Knights Key (MM 47)
* Vaca Key
Key Vaca is an island in the middle Florida Keys, located entirely within the borders of the city of Marathon, Florida.
Geography
Key Vaca is located in between Fat Deer Key and Knight's Key. Vaca Key was also connected via bridge to Boot Key ...
(MM 48–53)
* Boot Key
Boot Key is an island in the middle Florida Keys located adjacent to Key Vaca. Boot Key is within the city limits of Marathon, Florida, United States. The island is largely undeveloped. A draw bridge that once connected the island to Key Vaca w ...
(off to the south at MM 48; bridge closed)
* Fat Deer Key (MM 53¼-55)
* Shelter Key (off to the south at MM 53¾)
* Long Point Key (MM 56)
* Crawl Key
Crawl Key is an island in the middle Florida Keys.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway) traverses the key between Grassy Key and Long Point Key, which is part of a long stretch of road known as the Grassy Key Causeway.
It is entirely within the ci ...
(MM 56½)
* Grassy Key
Grassy Key, Florida, is an island in the middle Florida Keys. It is located on U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway), near mile markers 57—60, below the Conch Keys. It has an area of 3.65 km², with a population of 974 as of the census 2000.
I ...
(MM 58–60)
(Knights, Vaca, Boot, Long Point, Crawl, and Grassy Keys, as well as most of Fat Deer Key, are incorporated in the city of Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of kilometres ( 26 mi 385 yd), usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There ...
. The remaining portion of Fat Deer Key and most of Shelter Key are part of Key Colony Beach.):
* Duck Key
Duck Key is an island in Monroe County, Florida, United States, in the middle Florida Keys. It is part of the Duck Key, Florida census-designated place. The CDP also includes the neighboring island of Conch Key.
History
The key was the site ...
(MM 61)
* Conch Key
Conch ( , , ) is a common name of a number of different medium-to-large-sized sea snails. Conch shells typically have a high Spire (mollusc), spire and a noticeable siphonal canal (in other words, the shell comes to a noticeable point on both ...
(MM 62–63)
The Long Key Bridge (MM 63¼-65¼) separates the Middle Keys from the Upper Keys:
* Long Key
Long Key is an island in the middle Florida Keys. Long Key was called Cayo Víbora (Rattlesnake Key) by early Spanish explorers, a reference to the shape of the island, which resembles a snake with its jaws open, rather than to its denizens. The ...
(MM 66–70), formerly known as Rattlesnake Key
* Fiesta Key
Fiesta Key is the northeasternmost island in the middle Florida Keys, connected via causeway to U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway) at mile marker 70, between Long Key
Long Key is an island in the middle Florida Keys. Long Key was called Cayo V� ...
(off to the north at MM 70)
* Craig Key
Craig Key is an island city in the middle Florida Keys.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at approximately mile marker 72, between Lower Matecumbe Key and Fiesta Key.
History
Craig Key was originally named Camp Panama, and was no ...
(MM 72)
* Lower Matecumbe Key
Lower Matecumbe Key is an island in the upper Florida Keys, United States, located on U.S. 1 between mile markers 75–78.
All of the key is within the Village of Islamorada as of November 4, 1997, when it was incorporated.
It is home to the m ...
(MM 74–77)
* Lignumvitae Key
Lignumvitae Key is an island in the upper Florida Keys.
It is located due north of, and less than one mile from the easternmost tip of Lower Matecumbe Key. The island has been designated a National Natural Landmark, and an National Register of ...
* Indian Key
* Indian Key Fill (MM 79)
* Tea Table (MM 79½)
* Upper Matecumbe Key
Upper Matecumbe Key is an island in the upper Florida Keys.
U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway
The Overseas Highway is a highway carrying U.S. Route 1 (US 1) through the Florida Keys to Key West. Large parts of it were built on the for ...
(MM 80–83)
* Windley Key
Windley Key is an island in the upper Florida Keys in Monroe County, Florida, United States. U.S. 1 (the Overseas Highway) crosses it at approximately mile markers 84–85.5, between Plantation Key and Upper Matecumbe Key. All of the key is wit ...
(MM 85)
* Plantation Key
Plantation Key is an island in Monroe County, Florida, United States. It is located in the upper Florida Keys on U.S. 1 (or the Overseas Highway), between Key Largo and Windley Key.
All of the key is within the Village of Islamorada as of ...
(MM 86–90)
(Lower Matecumbe through Plantation Keys are incorporated as Islamorada
Islamorada (also sometimes Isla Morada) is an incorporated village in Monroe County, Florida, United States. It is located directly between Miami and Key West on five islands— Tea Table Key, Lower Matecumbe Key, Upper Matecumbe Key, Windl ...
, Village of Islands. The "towns" of Key Largo
Key Largo () is an island in the upper Florida Keys archipelago and is the largest section of the keys, at long. It is one of the northernmost of the Florida Keys in Monroe County, and the northernmost of the keys connected by U.S. Highway ...
, North Key Largo and Tavernier, all on the island of Key Largo, are not incorporated.):
* Key Largo
Key Largo () is an island in the upper Florida Keys archipelago and is the largest section of the keys, at long. It is one of the northernmost of the Florida Keys in Monroe County, and the northernmost of the keys connected by U.S. Highway ...
(MM 91–107)
* Tavernier Key
* Rodriguez Key
All keys north of Broad Creek are in Biscayne National Park
Biscayne National Park is a national park of the United States located south of Miami, Florida, in Miami-Dade County. The park preserves Biscayne Bay and its offshore barrier reefs. Ninety-five percent of the park is water, and the shore of th ...
and Miami-Dade County
Miami-Dade County () is a county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Florida. The county had a population of 2,701,767 as of the 2020 census, making it the most populous county in Florida and the seventh-most-populous coun ...
. The following are "true" Florida Keys (exposed ancient coral reefs):
* Old Rhodes Key
Old Rhodes Key is an island north of the upper Florida Keys in Biscayne National Park. It is in Miami-Dade County, Florida.
It is located just north of Broad Creek in the lower part of Biscayne Bay
Biscayne Bay is a lagoon with characteristi ...
* Totten Key
Totten Key is an island of the upper Florida Keys in Biscayne National Park. It is in Miami-Dade County, Florida.
It is located in southern Biscayne Bay, just west of Old Rhodes Key.
History
It was probably named for General Joseph Totten who ...
* Reid Key
* Rubicon Keys
* Adams Key
Adams Key is an island at the northern part of the upper Florida Keys in Biscayne National Park. It is in Miami-Dade County, Florida. It is located west of the southern tip of Elliott Key, on the north side of Caesar Creek in the lower part of Bi ...
* Elliott Key
Elliott Key is the northernmost of the true Florida Keys (those 'keys' which are ancient coral reefs lifted above the present sea level), and the largest key north of Key Largo. It is located entirely within Biscayne National Park, in Miami-Dade ...
The following are "transitional keys", made of exposed ancient reef surrounded by sand:
* Sands Key
* Boca Chita Key
* Ragged Keys
Ragged Keys are small islands north of the upper Florida Keys.
They are located in Biscayne Bay, just north of Sands Key, and are part of Biscayne National Park
Biscayne National Park is a national park of the United States located south ...
* Soldier Key
Soldier Key is an island in Biscayne National Park in Miami-Dade County, Florida. It is located between Biscayne Bay and the Atlantic Ocean, about three miles north of the Ragged Keys, five miles south of Cape Florida on Key Biscayne, seven-and ...
Key Biscayne
Key Biscayne () is an island located in Miami-Dade County, Florida, located between the Atlantic Ocean and Biscayne Bay. It is the southernmost of the barrier islands along the Atlantic coast of Florida, and lies south of Miami Beach and sout ...
is not one of the Florida Keys, but the southernmost of the barrier island
Barrier islands are a Coast#Landforms, coastal landform, a type of dune, dune system and sand island, where an area of sand has been formed by wave and tidal action parallel to the mainland coast. They usually occur in chains, consisting of an ...
s along the Atlantic coast of Florida.
Transportation
The main chain of Keys islands can be traveled by motor vehicles on theOverseas Highway
The Overseas Highway is a highway carrying U.S. Route 1 (US 1) through the Florida Keys to Key West. Large parts of it were built on the former right-of-way of the Overseas Railroad, the Key West Extension of the Florida East Coast Ra ...
, a section of U.S. 1, which runs from Key West to Fort Kent, Maine
Fort Kent ( French: ''Fort-Kent'') is a town in Aroostook County, Maine, United States, situated at the confluence of the Fish River and the Saint John River, on the border with New Brunswick, Canada. The population was 4,067 in the 2020 cens ...
in its entirety. The highway was built parallel to the original route of the Overseas Railway, which was not rebuilt following the Labor Day hurricane of 1935
The 1935 Labor Day hurricane was an extremely powerful and devastating Atlantic hurricane that struck the southeastern United States in early September 1935. For several decades, it was the most intense Atlantic hurricane on record in terms of ...
. Even before the hurricane, road sections and highway bridges allowed automobile traffic to travel from Miami to Lower Matecumbe Key, where a car ferry connected with another roadway section through the Lower Keys. Following the hurricane, some of the original railway bridges were converted to carry the highway roadbeds. These bridges were used until the 1980s, when new highway bridges were built alongside. Many of the original railroad and highway bridges remain today as pedestrian fishing piers.
Public transportation
Road hazards
Despite this reconstruction, U.S. 1 was not widened on a large scale, and today most of the route consists of just two lanes. Due to their tropical climate, the Florida Keys attract several hundred thousand tourists annually. While some visitors arrive viaKey West International Airport
Key West International Airport is an airport located in the City of Key West in Monroe County, Florida, United States, east of the main commercial center of Key West.
The relatively short runway limits the maximum size of aircraft that can ...
and Florida Keys Marathon Airport
The Florida Keys Marathon International Airport is a public airport located along the Overseas Highway (US1) in Marathon, in Monroe County, Florida, United States. The airport covers and has one runway.
History
The 8000-foot airstrip in Marat ...
in Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of kilometres ( 26 mi 385 yd), usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There ...
, cruise ship or ferry from Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
, Fort Myers
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lati ...
, or Marco Island, Florida, the vast majority of tourists drive down from the mainland on U.S. 1. This influx of traffic, coupled with the two-lane nature of U.S. 1 through most of its length in the Keys, and the fact that no alternative road routes are available mean that Monroe County has the highest per capita
''Per capita'' is a Latin phrase literally meaning "by heads" or "for each head", and idiomatically used to mean "per person".
Social statistics
The term is used in a wide variety of social science, social sciences and statistical research conte ...
rate of fatal automobile accidents
A traffic collision, also known as a motor vehicle collision, or car crash, occurs when a vehicle collides with another vehicle, pedestrian, animal, road debris, or other moving or stationary obstruction, such as a tree, pole or building. Tra ...
in the state of Florida.
Culture and recreation
The major industries are fishing and tourism, includingecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of nature-oriented tourism intended to contribute to the Ecological conservation, conservation of the natural environment, generally defined as being minimally impactful, and including providing both contributions to conserv ...
, with many visitors scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
in the area's protected waters. A ferry takes riders between Key West and Fort Myers
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Lati ...
, as well as Marco Island
Marco may refer to:
People Given name
* Marco (actor) (born 1977), South Korean model and actor
Surname
* Georg Marco (1863–1923), Romanian chess player of German origin
* Jindřich Marco (1921–2000), Czechoslovak photographer and numismat ...
due north on the mainland, along the western edge of Florida Bay.
Dark skies recreation

 Middle and Lower Florida Keys are among a few remaining South Florida dark skies locations accessible by car, thanks to their position along the Atlantic Ocean, and therefore with southern skies unobstructed by
Middle and Lower Florida Keys are among a few remaining South Florida dark skies locations accessible by car, thanks to their position along the Atlantic Ocean, and therefore with southern skies unobstructed by light pollution
Light pollution is the presence of any unwanted, inappropriate, or excessive artificial Visible spectrum, lighting. In a descriptive sense, the term ''light pollution'' refers to the effects of any poorly implemented lighting sources, during the ...
associated with urban development.
Scout Key
Scout Key is an island in the lower Florida Keys. It was previously known as West Summerland Key until 2010. U.S. Route 1 in Florida, U.S. 1 (the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at approximately mile markers 34–35, between Spanish Harbor Key a ...
is home to Winter Star Party
The Winter Star Party, aka WSP, is an annual convention of amateur astronomers where the primary activity is nighttime astronomical observation. This February event is run at Camp Wesumkee located on Scout Key in the Lower Florida Keys. It is host ...
, a prominent annual amateur astronomy event in the United States, and one of the Top 10 star parties in the world according to BBC Sky at Night
''BBC Sky at Night'' is a British monthly magazine about astronomy aimed at amateur astronomers and published by Immediate Media Company. Its title is taken from the television program produced by the BBC, ''The Sky at Night''. The magazine, i ...
. It is an international gathering that attracts 500+ people each year who enjoy stargazing, astrophotography and Milky Way photography.
Bahia Honda State Park
Bahia Honda ( , ; ) is an island in the lower Florida Keys.
U.S. Route 1 in Florida, U.S. 1 (the Overseas Highway) crosses the key at approximately mile markers 36-38.5, between Ohio Key and Spanish Harbor Key west of Marathon, Florida, Mara ...
is a well known dark skies location among locals offering unobstructed views of the southern night sky year-round. It also hosts amateur astronomy gatherings./ref>
See also
*Adam's Bridge
Adam's Bridge, also known as Rama's Bridge or ''Rama Setu'', is a chain of natural limestone shoals between Pamban Island, also known as Rameswaram Island, off the southeastern coast of Tamil Nadu, India, and Mannar Island, off the northwe ...
Notes
References
Other references
* Jeff, Ripple (1995). ''The Florida Keys: the Natural Wonders of an Island Paradise'', Photographs by Bill Keogh, Stillwater, Minnesota: Voyageur Press. .Jason Project The Story of Water Movement and Land Formation
– accessed January 28, 2006. *
Florida Keys Fish
External links
A Gazetteer of the Florida Keys
*
City of Key West
City of Marathon
NOAA Marine Sanctuary
*
Media
Key West Citizen
{{Authority control Outstanding Florida Waters Regions of Florida South Florida Archipelagoes of the United States