List Of Scotland-related Topics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Environment of Scotland
* Climate of Scotland
** Climate change in Scotland
* Ecology of Scotland
** Renewable energy in Scotland
*
Environment of Scotland
* Climate of Scotland
** Climate change in Scotland
* Ecology of Scotland
** Renewable energy in Scotland
*
 Municipalities of Scotland
*
Municipalities of Scotland
*




 *
*
Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
is a country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, ...
which is part of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, having previously been an independent, sovereign country prior to the 1707 union with England. Established in 843, this would make Scotland the second oldest country in Europe and the fifth oldest country in the world. It's monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for the rest of their life, or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic (constitutio ...
is amongst the oldest in the world, and is the oldest recorded monarchy in Europe.
Occupying the northern third of the largest island, it shares a border
Borders are generally defined as geography, geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by polity, political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other administrative divisio ...
with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Denmark, Norway, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France. A sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian Se ...
to the east, the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea
The Irish Sea is a body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the Celtic Sea in the south by St George's Channel and to the Inner Seas off the West Coast of Scotland in the north by the North Ch ...
to the southwest. In addition to the mainland, Scotland consists of over 790 islands including the Northern Isles
The Northern Isles (; ; ) are a chain (or archipelago) of Island, islands of Scotland, located off the north coast of the Scottish mainland. The climate is cool and temperate and highly influenced by the surrounding seas. There are two main is ...
and the Hebrides
The Hebrides ( ; , ; ) are the largest archipelago in the United Kingdom, off the west coast of the Scotland, Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Ou ...
.
The countries head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
is the First Minister
A first minister is any of a variety of leaders of government cabinets. The term literally has the same meaning as "prime minister" but is typically chosen to distinguish the office-holder from a superior prime minister. Currently the title of ' ...
who is the head of the Scottish Government
The Scottish Government (, ) is the executive arm of the devolved government of Scotland. It was formed in 1999 as the Scottish Executive following the 1997 referendum on Scottish devolution, and is headquartered at St Andrew's House in ...
and Keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland
The keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland (Scottish Gaelic: ''Neach-gleidhidh Seula Mòr na h-Alba'') is one of the great officers of state in Scotland held concurrently with the post of first minister of Scotland. The office holder is the keeper ...
. The First Minister chairs the Scottish cabinet and is accountable to the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
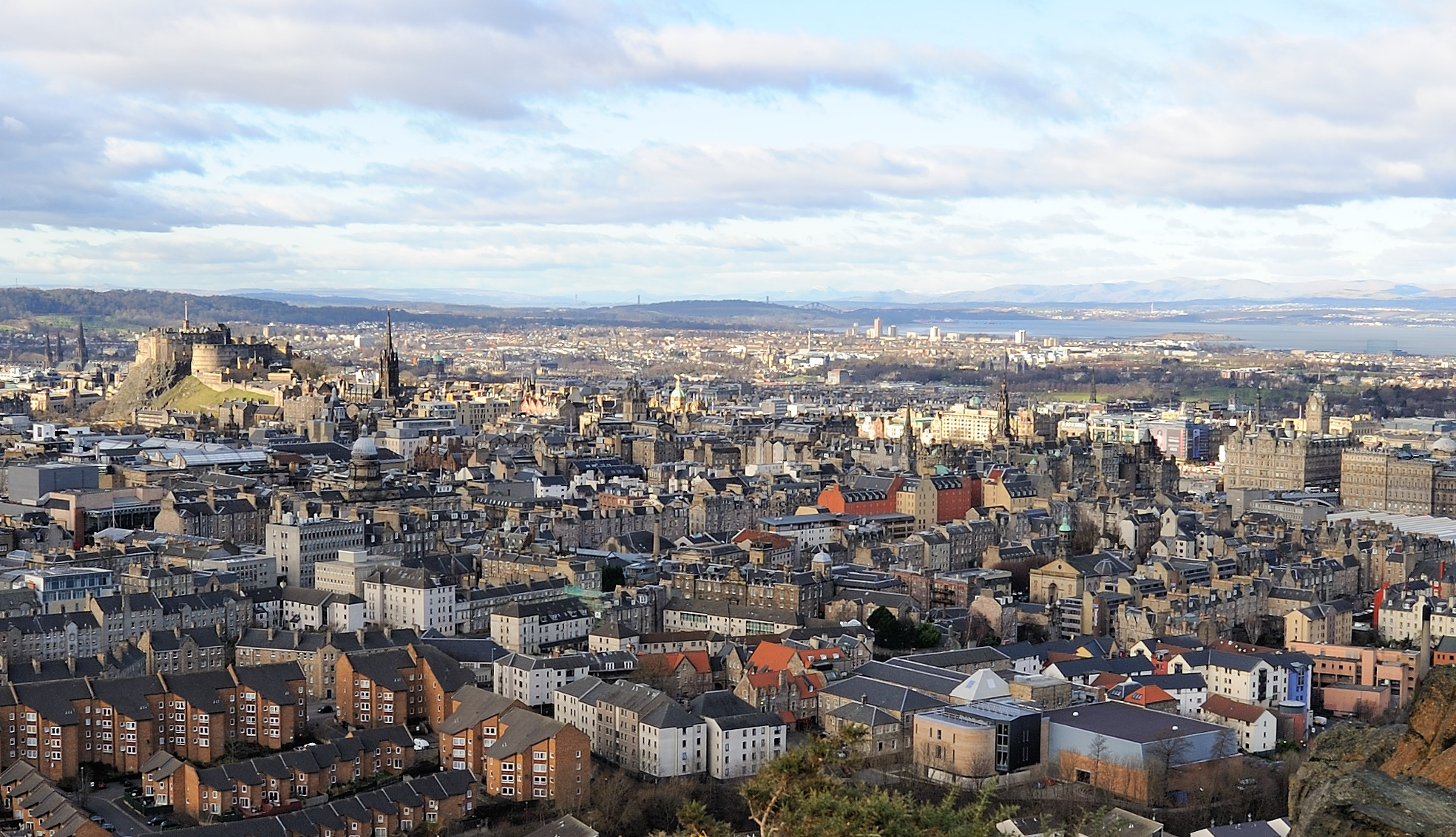
which is situated in the countries capital city, Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
.
General reference
* Pronunciation: * Etymology of "Scotland" * Common English country name(s):Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
* Official English country name(s): Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
* Common endonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
(s): Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English-language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingd ...
* Official endonym(s):
* Adjectival(s): Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
, Scots, Scotch
* Demonym
A demonym (; ) or 'gentilic' () is a word that identifies a group of people ( inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place ( hamlet, village, town, city, region, ...
(s): Scottish, Scots
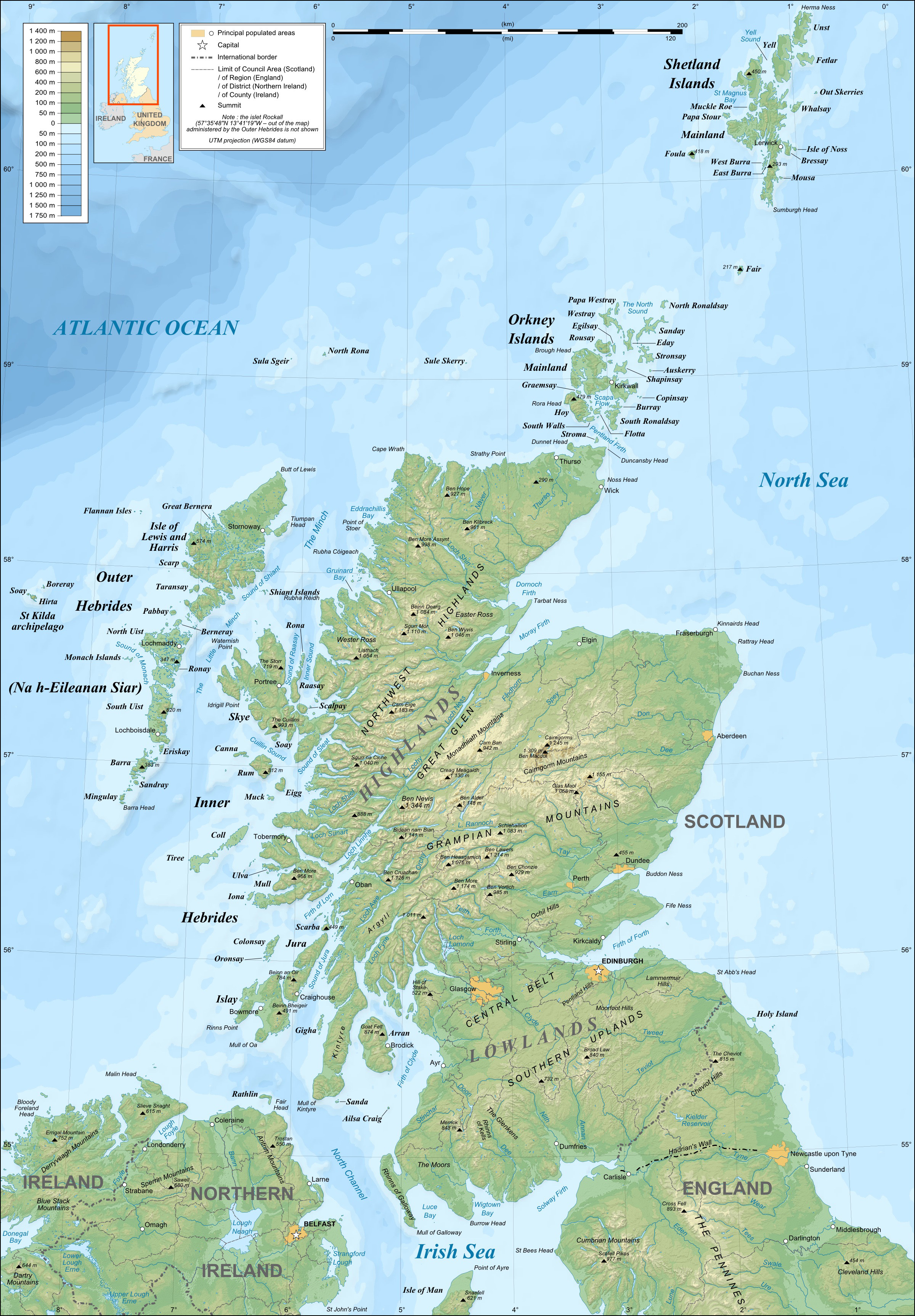
Geography of Scotland

Geography of Scotland
The geography of Scotland is varied from rural lowlands to unspoilt uplands, and from large cities to sparsely inhabited islands. Located in Northern Europe, Scotland comprises the northern part of the island of Great Britain as well as 790 su ...
* Scotland is: a country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, ...
of the United Kingdom.
* Scotland was: an independent, sovereign country until 1707 when it formed a union with England
* Population of Scotland: 5,436,600 (2022 census)
* Area of Scotland: 78 772 km2 (30,414 square miles), approximately 32% of the area of the United Kingdom (UK)
* Places in Scotland
* Atlas of Scotland
Location
* Scotland is situated within the following regions **Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
** Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined by humans as being in the same celestial sphere, celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the Solar ...
, on the Prime Meridian
A prime meridian is an arbitrarily chosen meridian (geography), meridian (a line of longitude) in a geographic coordinate system at which longitude is defined to be 0°. On a spheroid, a prime meridian and its anti-meridian (the 180th meridian ...
** Eurasia
Eurasia ( , ) is a continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. According to some geographers, Physical geography, physiographically, Eurasia is a single supercontinent. The concept of Europe and Asia as distinct continents d ...
(but not on the mainland
Mainland is defined as "relating to or forming the main part of a country or continent, not including the islands around it egardless of status under territorial jurisdiction by an entity" The term is often politically, economically and/or demogr ...
)
*** Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
( outline)
**** Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
***** British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
****** Great Britain (the northern third of the island)
****** Several hundred other Islands of Scotland
* Extreme points of Scotland
** Northerly point: Out Stack, Shetland
Shetland (until 1975 spelled Zetland), also called the Shetland Islands, is an archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands, and Norway, marking the northernmost region of the United Kingdom. The islands lie about to the ...
Islands
** Highest peak: Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis ( ; , ) is the highest mountain in Scotland, the United Kingdom, and the British Isles. Ben Nevis stands at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the Highland region of Lochaber, close to the town of Fort William.
The mount ...
, Lochaber
Lochaber ( ; ) is a name applied to a part of the Scottish Highlands. Historically, it was a provincial lordship consisting of the parishes of Kilmallie and Kilmonivaig. Lochaber once extended from the Northern shore of Loch Leven, a distric ...
at
* Land boundaries: 154 km
Environment of Scotland

 Environment of Scotland
* Climate of Scotland
** Climate change in Scotland
* Ecology of Scotland
** Renewable energy in Scotland
*
Environment of Scotland
* Climate of Scotland
** Climate change in Scotland
* Ecology of Scotland
** Renewable energy in Scotland
* Geology of Scotland
The geology of Scotland is unusually varied for a country of its size, with a large number of different geology, geological features.Keay & Keay (1994) page 415. There are three main geographical sub-divisions: the Highlands and Islands is a dive ...
* Protected areas of Scotland
Many parts of Scotland are protected in accordance with a number of national and international designations because of their environmental, historical or cultural value. Protected areas can be divided according to the type of resource which each ...
** Biosphere reserves in Scotland
** National parks of Scotland
The national parks of Scotland () are managed areas of outstanding landscape where some forms of development are restricted to preserve the landscape and natural environment. At present, Scotland has two national parks: Loch Lomond and The Tross ...
* Wildlife of Scotland
** Flora of Scotland
** Fauna of Scotland
The fauna of Scotland is generally typical of the northwest European part of the Palearctic realm, although several of the country's larger mammals were hunted to extinction in historic times and human activity has also led to various species o ...
*** Birds of Scotland
*** Mammals of Scotland
* Domesticated breeds
Natural geographic features of Scotland
* Firths * Demographic history of Scotland * Islands of Scotland **Hebrides
The Hebrides ( ; , ; ) are the largest archipelago in the United Kingdom, off the west coast of the Scotland, Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Ou ...
*** Inner Hebrides
The Inner Hebrides ( ; ) is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which experience a mild oceanic climate. The Inner Hebrides compri ...
*** Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides ( ) or Western Isles ( , or ), sometimes known as the Long Isle or Long Island (), is an Archipelago, island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland.
It is the longest archipelago in the British Isles. The islan ...
** Orkney Islands
Orkney (), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago off the north coast of mainland Scotland. The plural name the Orkneys is also sometimes used, but locals now consider it outdated. Part of the Northern Isles along with Shetland ...
** Shetland Islands
Shetland (until 1975 spelled Zetland), also called the Shetland Islands, is an archipelago in Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the Uni ...
** Islands of the Clyde
The Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the Firth of Clyde between Argyll and Bute in the west and Inverclyde, No ...
** Islands of the Forth
** List of freshwater islands in Scotland
* Lochs
''Loch'' ( ) is a word meaning "lake" or " sea inlet" in Scottish and Irish Gaelic, subsequently borrowed into English. In Irish contexts, it often appears in the anglicized form "lough". A small loch is sometimes called a lochan. Lochs which ...
** Lochs in Scotland
* Mountains and hills of Scotland
Scotland is the most mountainous country in the United Kingdom. Scotland's mountain ranges can be divided in a roughly north to south direction into: the Scottish Highlands, the Central Belt and the Southern Uplands, the latter two primarily belo ...
**List of Munros
This is a list of Munro mountains and Munro Tops in Scotland by height. Lists of mountains and hills in the British Isles#Munros, Munros are defined as Scottish mountains over in height, and which are on the Scottish Mountaineering Club ("SMC") ...
** Volcanoes in Scotland
* Rivers of Scotland
** Waterfalls of Scotland
* Valleys of Scotland
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a ve ...
* World Heritage Sites in Scotland
Regions of Scotland
*Central Belt
The Central Belt of Scotland is the Demographics of Scotland, area of highest population density within Scotland. Depending on the definition used, it has a population of between 2.4 and 4.2 million (the country's total was around 5.4 million in ...
* Scottish Midlands
* Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gae ...
* Scottish Lowlands
The Lowlands ( or , ; , ) is a cultural and historical region of Scotland.
The region is characterised by its relatively flat or gently rolling terrain as opposed to the mountainous landscapes of the Scottish Highlands. This area includes ci ...
* Scottish Borders
The Scottish Borders is one of 32 council areas of Scotland. It is bordered by West Lothian, Edinburgh, Midlothian, and East Lothian to the north, the North Sea to the east, Dumfries and Galloway to the south-west, South Lanarkshire to the we ...
* Galloway
Galloway ( ; ; ) is a region in southwestern Scotland comprising the counties of Scotland, historic counties of Wigtownshire and Kirkcudbrightshire. It is administered as part of the council areas of Scotland, council area of Dumfries and Gallow ...
* Northern Isles
The Northern Isles (; ; ) are a chain (or archipelago) of Island, islands of Scotland, located off the north coast of the Scottish mainland. The climate is cool and temperate and highly influenced by the surrounding seas. There are two main is ...
Ecoregions of Scotland
List of ecoregions in ScotlandAdministrative divisions of Scotland
Administrative divisions of Scotland *Council areas of Scotland
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" (), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Gaelic Names) (Sc ...
**Civil parishes in Scotland
Civil parishes are small divisions used for statistical purposes and formerly for local government in Scotland.
Civil parishes gained legal functions in 1845 when parochial boards were established to administer the poor law. Their local governmen ...
**List of burghs in Scotland
The following list includes all effective burghs in Scotland from the coming into force of the Burgh Police (Scotland) Act 1892 ( 55 & 56 Vict. c. 55), in 1893. "Ineffective" burghs, which had not used legislation to adopt a "police system", t ...
** Municipalities of Scotland
* Unitary authorities of Scotland
= Municipalities of Scotland
= Municipalities of Scotland
*
Municipalities of Scotland
* Capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
of Scotland: Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
( outline)
* Largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metrop ...
: Glasgow
Glasgow is the Cities of Scotland, most populous city in Scotland, located on the banks of the River Clyde in Strathclyde, west central Scotland. It is the List of cities in the United Kingdom, third-most-populous city in the United Kingdom ...
* Largest Metropolitan area: Greater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government ...
* Cities of Scotland
Scotland has eight cities. Edinburgh is the Cities of Scotland#Capital, capital city and Glasgow is the most populous. Scottish towns were granted Burgh, burghs or royal burgh status by Scottish kings, including by David I of Scotland and Will ...
* Towns in Scotland
This list of towns and cities in Scotland with a population of more than 15,000 is ordered by population, as defined and compiled by the National Records of Scotland organisation. Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland by population, whilst t ...
Demography of Scotland

Demographics of Scotland
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analy ...
* List of census localities in Scotland
*National Records of Scotland
National Records of Scotland () is a non-ministerial department of the Scottish Government. It is responsible for civil registration, the census in Scotland, demography and statistics, family history, as well as the national archives and hist ...
**General Register Office for Scotland
The General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) () was a non-ministerial directorate of the Scottish Government that administered the registration of births, deaths, marriages, divorces and adoptions in Scotland from 1854 to 2011. It was also re ...
**National Archives of Scotland
The National Archives of Scotland (NAS) is the previous name of the National Records of Scotland (NRS), and are the national archives of Scotland, based in Edinburgh. The NAS claims to have one of the most varied collection of archives in Europ ...
* Black Scottish people
* Census (Amendment) (Scotland) Act 2019
* New Scot
* Registration of Births, Deaths and Marriages (Scotland) Act 1965
* List of Scottish council areas by number of Scottish Gaelic speakers
*Statistical Accounts of Scotland
The ''Statistical Accounts of Scotland'' are a series of documentary publications, related in subject matter though published at different times, covering life in Scotland in the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries.
The ''Old (or First) Statistica ...
*By place
** Demographics of Edinburgh
** Demographics of Glasgow
Government and politics of Scotland

Politics of Scotland
The politics of Scotland () operate within the constitution of the United Kingdom, of which Scotland is a Constituent countries of the United Kingdom, country. Scotland is a democracy, being represented in both the Scottish Parliament and the ...
* Form of government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a m ...
: Devolved parliamentary legislature within a constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. ...
* Capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
of Scotland: Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. The city is located in southeast Scotland and is bounded to the north by the Firth of Forth and to the south by the Pentland Hills. Edinburgh ...
*Elections in Scotland
Scotland has elections to several bodies: the Scottish Parliament, the United Kingdom Parliament, local councils and community councils. Before the United Kingdom left the European Union, Scotland elected members to the European Parliament.
...
** Electoral systems in Scotland
* List of political parties in Scotland
* Pressure Groups in Scotland
*Scottish independence
Scottish independence (; ) is the idea of Scotland regaining its independence and once again becoming a sovereign state, independent from the United Kingdom. The term Scottish independence refers to the political movement that is campaignin ...
** Fiscal autonomy
**National Conversation
The National Conversation was the name given to the Scottish Government's public consultation exercise regarding possible future changes in the power of the devolved Scottish Parliament and the possibility of Scottish independence, a policy obje ...
*Scotland Office
The Scotland Office (Scottish Gaelic: ''An Oifis Albannach''), known as the Office of the Secretary of State for Scotland from 2018 to 2024, is a department of His Majesty's Government headed by the secretary of state for Scotland and respon ...
(Department of UK Government)
**Secretary of State for Scotland
The secretary of state for Scotland (; ), also referred to as the Scottish secretary, is a Secretary of State (United Kingdom), secretary of state in the Government of the United Kingdom, with responsibility for the Scotland Office. The incum ...
The Scottish government
Government of Scotland
The Scottish Government (, ) is the Executive (government), executive arm of the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved government of Scotland. It was formed in 1999 as the Scottish Executive following the 1997 Scottish devolution refere ...
* History of Scottish devolution
Government
*Head of government
In the Executive (government), executive branch, the head of government is the highest or the second-highest official of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presid ...
: First Minister of Scotland
The first minister of Scotland () is the head of government of Scotland. The first minister leads the Scottish Government, the Executive (government), executive branch of the devolved government and is th ...
(also the Keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland
The keeper of the Great Seal of Scotland (Scottish Gaelic: ''Neach-gleidhidh Seula Mòr na h-Alba'') is one of the great officers of state in Scotland held concurrently with the post of first minister of Scotland. The office holder is the keeper ...
)
** Deputy First Minister of Scotland
The deputy first minister of Scotland is the second highest minister in the executive branch of the Scottish Government, after the First Minister of Scotland, first minister of Scotland. The post-holder deputises for the first minister during ...
* Scottish Government
The Scottish Government (, ) is the executive arm of the devolved government of Scotland. It was formed in 1999 as the Scottish Executive following the 1997 referendum on Scottish devolution, and is headquartered at St Andrew's House in ...
** Scottish Cabinet
*** Dewar government (1999–2000)
*** McLeish government (2000–01)
*** First McConnell government (2001–03)
*** Second McConnell government
The second McConnell government (20 May 2003 – 16 May 2007) was formed following the 2003 general election to the 2nd Scottish Parliament. Jack McConnell was re-appointed as First Minister on 20 May 2003 and headed another Labour– Liber ...
(2003–07)
*** First Salmond government
The first Salmond government, which was sworn in on 17 May 2007 at the start of the 3rd Scottish Parliament, was an SNP minority government.
Having won the largest number of seats in the general election (47 of 129) the SNP sought to form a c ...
(2007–11)
*** Second Salmond government (2011–14)
*** First Sturgeon government (2014–16)
*** Second Sturgeon government (2016–21)
*** Third Sturgeon government
Nicola Sturgeon formed the third Sturgeon government following her Scottish National Party's victory in the 2021 Scottish Parliament election. Sturgeon was nominated by a vote of the 6th Scottish Parliament for appointment to the post of First ...
(2021–23)
*** First Yousaf government (2023–2024)
*** Second Yousaf government (2024)
*** Swinney government
John Swinney formed the Swinney government on 8 May 2024, following his appointment as First Minister of Scotland at the Court of Session. The government was approved by parliamentary vote thanks to the abstention of Green Party of Scotland, Scotti ...
(2024–)
** International relations of Scotland
The International relations of Scotland conducted by the Scottish Government seek to promote Scotland and Scottish interests overseas by promoting its Culture of Scotland, culture, Education in Scotland, education and research, Economy of Scotla ...
* St Andrew's House; main headquarters of the Scottish Government located in Edinburgh
* Bute House
Bute House () is the official residence and workplace of the first minister of Scotland. Located at 6 Charlotte Square in the New Town of Edinburgh, it is the central house on the north side of the square and was designed by Robert Adam. It ...
; the official residence and workplace of the First Minister
Legislative
*Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
** List of acts of the Scottish Parliament from 1999
Local government in Scotland

Local government in Scotland
Local government in Scotland comprises thirty-two local authorities, commonly referred to as ''councils''. Each council provides public services, including education, social care, waste management, libraries and planning. Councils receive th ...
*Local government areas of Scotland
Local government areas covering the whole of Scotland were first defined by the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889. As currently defined, they are a result, for the most part, of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994.
The 1889 act crea ...
**History of local government in Scotland
The history of local government in Scotland is a complex tale of largely ancient and long established Scottish political units being replaced after the mid 20th century by a frequently changing series of different local government arrangements. ...
* Local Government (Gaelic Names) (Scotland) Act 1997
*Local Governance (Scotland) Act 2004
The Local Governance (Scotland) Act 2004 (asp 9) is an Act of the Scottish Parliament which provided, amongst other things, for the election of councillors to the local government in Scotland, local authorities in Scotland by the single transfera ...
* Accounts Commission for Scotland
* Armorial of local councils in Scotland
* Provost
*Lord provost
A lord provost () is the convenor of the local authority, the civic head and the lord-lieutenant of one of the principal cities of Scotland. The office is similar to that of a lord mayor. Only the cities of Aberdeen, Dundee, Edinburgh, Stirlin ...
**Lieutenancy areas of Scotland
The lieutenancy areas of Scotland are the areas used for the ceremonial lord-lieutenants, the British monarch, monarch's representatives, in Scotland. The lord-lieutenants' titles chosen by the British monarch, monarch and his legal advisers are ...
Legal system
Scots law
Scots law () is the List of country legal systems, legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing Civil law (legal system), civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different histori ...
* Capital punishment in Scotland: There has been a history of capital punishment but it is not used now.
* Human rights in Scotland
** Freedom of religion in Scotland
** LGBT rights in Scotland
* Law enforcement in Scotland
Police Scotland (), officially the Police Service of Scotland (), is the national police force of Scotland. It was formed in 2013, through the merging of eight regional police forces in Scotland, as well as the specialist services of the Scottish ...
**Police Scotland
Police Scotland (), officially the Police Service of Scotland (), is the national police force of Scotland. It was formed in 2013, through the merging of eight regional police forces in Scotland, as well as the specialist services of the Scottis ...
**Scottish Prison Service
The Scottish Prison Service (SPS) () is an executive agency of the Scottish Government tasked with managing prisons and Young Offender Institutions.
The Chief Executive of the Scottish Prison Service, currently Teresa Medhurst, is responsible ...
*** Prison population of Scotland
*Manrent
Manrent refers to a Scottish contract of the mid-15th century to the early 17th century, usually military in nature and involving Scottish clans. The bond of manrent was commonly an instrument in which a weaker man or clan pledged to serve, in ...
*Marriage in Scotland
Marriage in Scotland is recognised in the form of both civil and religious unions between individuals. Due to Scotland's history as a previously independent country, the laws around marriage developed differently in Scotland compared to other jur ...
* Rights of way in Scotland
A right of way (also right-of-way) is a specific route that people, animals, vehicles, watercraft, or utility lines travel, or the legal status that gives them the right to do so. Rights-of-way in the physical sense include controlled-access h ...
* Udal law
Udal law is a Norsemen, Norse-derived legal system, found in Shetland and Orkney in Scotland, and in Manx law in the Isle of Man. It is closely related to Odelsrett; both terms are from Proto-Germanic Odal (rune), *''Ōþalan'', meaning "herita ...
* College of Justice
The College of Justice () includes the Supreme Courts of Scotland, and its associated bodies. The constituent bodies of the national supreme courts are the Court of Session, the High Court of Justiciary, the Office of the Accountant of Court, ...
; includes the Supreme Courts of Scotland
** High Court of Justiciary
The High Court of Justiciary () is the supreme criminal court in Scotland. The High Court is both a trial court and a court of appeal. As a trial court, the High Court sits on circuit at Parliament House or in the adjacent former Sheriff C ...
; Scotland's supreme criminal court
** Court of Session
The Court of Session is the highest national court of Scotland in relation to Civil law (common law), civil cases. The court was established in 1532 to take on the judicial functions of the royal council. Its jurisdiction overlapped with othe ...
; Scotland's supreme civil court
** Office of the Accountant of Court
The Office of the Accountant of Court () is a public body which is a constituent part of the Supreme Courts of Scotland. The Accountant of Court is administered by the Scottish Courts and Tribunals Service. The Accountant of Court's Office f ...
** Lord President of the Court of Session
The Lord President of the Court of Session and Lord Justice General () is the most senior judge in Scotland, the head of the judiciary, and the presiding judge of the College of Justice, the Court of Session, and the High Court of Justiciary. ...
** Senator of the College of Justice
The senators of the College of Justice in Scotland are judges of the College of Justice, a set of legal institutions involved in the administration of justice in Scotland. There are three types of senator: Lords of Session (judges of the Court ...
*** Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC) is the final court of appeal for all civil cases in the United Kingdom and all criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland, as well as some limited criminal cases ...
; Scotland's supreme courts can appeal to the Supreme Court of the UK
* Sheriff Appeal Court
The Sheriff Appeal Court () is a court in Scotland that hears appeals from summary criminal proceedings in the sheriff courts and justice of the peace courts, and hears appeals on bail decisions made in solemn proceedings in the sheriff co ...
* Sheriff court
A sheriff court () is the principal local civil and criminal court in Scotland, with exclusive jurisdiction over all civil cases with a monetary value up to , and with the jurisdiction to hear any criminal case except treason, murder, and ra ...
* Justice of the peace court
A justice of the peace court is the lowest authoritative type of criminal court in Scotland. The court operates under summary procedure and deals primarily with less serious criminal offences.
History
The commission of the peace was origina ...
* Court of the Lord Lyon
The Court of the Lord Lyon, or Lyon Court, is a standing court of law, based in New Register House in Edinburgh, which regulates heraldry in Scotland. The Lyon Court maintains the register of grants of arms, known as the Public Register of All ...
* Scottish Land Court
The Scottish Land Court () is a Courts of Scotland, Scottish court of law based in Edinburgh with subject-matter jurisdiction covering disputes between landlords and tenants relating to Tenant farmer, agricultural tenancies, and matters relat ...
* Lands Tribunal for Scotland
The Lands Tribunal for Scotland () is a tribunal with jurisdiction over land and property in Scotland, relating to title obligations, compulsory purchase and other private rights. The Tribunal was established under the Lands Tribunal Act 194 ...
* Children's hearing
* Courts of Scotland
The courts of Scotland () are responsible for administration of justice in Scotland, under Primary and secondary legislation, statutory, common law and Equity (law), equitable provisions within Scots law. The courts are presided over by the jud ...
** List of courts in Scotland
* Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service
The Crown Office and Procurator Fiscal Service () is the independent public prosecution service for Scotland, and is a Ministerial Department of the Scottish Government. The department is headed by His Majesty's Lord Advocate, who under t ...
* Faculty of Advocates
The Faculty of Advocates () is an independent body of lawyers who have been admitted to practise as advocates before the courts of Scotland, especially the Court of Session and the High Court of Justiciary. The Faculty of Advocates is a const ...
* Lord Advocate
His Majesty's Advocate, known as the Lord Advocate (), is the principal legal adviser of both the Scottish Government and the Crown in Scotland for civil and criminal matters that fall within the devolution, devolved powers of the Scottish P ...
* Lord President of the Court of Session
The Lord President of the Court of Session and Lord Justice General () is the most senior judge in Scotland, the head of the judiciary, and the presiding judge of the College of Justice, the Court of Session, and the High Court of Justiciary. ...
* Procurator Fiscal
A procurator fiscal (pl. ''procurators fiscal''), sometimes called PF or fiscal (), is a public prosecutor in Scotland, who has the power to impose fiscal fines. They investigate all sudden and suspicious deaths in Scotland (similar to a corone ...
*Solicitor General for Scotland
His Majesty's Solicitor General for Scotland () is one of the Law Officers of the Crown, and the deputy of the Lord Advocate, whose duty is to advise the Scottish Government on Scots Law. They are also responsible for the Crown Office and P ...
Military
*Armed forces in Scotland
Since the passing of the Treaty of Union in 1707 which unified the Kingdom of Scotland with the Kingdom of England to the create the Kingdom of Great Britain, Scottish armed forces were merged with the English armed forces and remain part of ...
** Scotland had its own military until 1707. Scotland's military merged with the British Armed Forces
The British Armed Forces are the unified military, military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its British Overseas Territories, Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests ...
, with the exception of the Atholl Highlanders.
** Scots Guards
The Scots Guards (SG) is one of the five Foot guards#United Kingdom, Foot Guards regiments of the British Army. Its origins are as the personal bodyguard of King Charles I of England and Scotland. Its lineage can be traced back to 1642 in the Ki ...
** Royal Scots
The Royal Scots (The Royal Regiment), once known as the Royal Regiment of Foot, was the oldest and most senior infantry regiment line infantry, of the line of the British Army, having been raised in 1633 during the reign of Charles I of England ...
** Royal Regiment of Scotland
The Royal Regiment of Scotland (SCOTS) is the British Army Order of Precedence, senior and only current Scottish regiment, Scottish line infantry Regiment#British Army, regiment of the British Army Infantry. It consists of three regular (form ...
** King's Own Scottish Borderers
The King's Own Scottish Borderers (KOSBs) was a line infantry regiment of the British Army, part of the Scottish Division. On 28 March 2006 the regiment was amalgamated with the Royal Scots, the Royal Highland Fusiliers, Royal Highland Fusiliers ...
** Royal Scots Borderers
The Royal Scots Borderers, 1st Battalion, the Royal Regiment of Scotland (1 SCOTS) was a battalion of the Royal Regiment of Scotland. The battalion formed on 1 August 2006 when its antecedent regiments - the Royal Scots and the King's Own Scottis ...
** Royal Highland Fusiliers
** Black Watch
The Black Watch, 3rd Battalion, Royal Regiment of Scotland (3 SCOTS) is an infantry battalion of the Royal Regiment of Scotland. The regiment was created as part of the Childers Reforms in 1881, when the 42nd (Royal Highland) Regiment ...
** Highlanders (Seaforth, Gordons and Camerons)
** Argyll and Sutherland Highlanders
The Argyll and Sutherland Highlanders (Princess Louise's) is a light infantry company (military unit), company (designated as Balaklava Company, 5th Battalion, Royal Regiment of Scotland) and was a line infantry regiment of the British Army tha ...
** 51st Highland Volunteers
The 51st Highland Volunteers (51 HIGHLAND) is a battalion in the British Army's Army Reserve or reserve force in the Scottish Highlands, forming the 7th Battalion of the Royal Regiment of Scotland, also known as 7 SCOTS. It is one of two R ...
** 52nd Lowland Volunteers
The 52nd Lowland Volunteers (52 LOWLAND) is a battalion in the British Army's Army Reserve or reserve force in the Scottish Lowlands, forming the 6th Battalion of the Royal Regiment of Scotland, also known as 6 SCOTS. Due to its erstwhile as ...
*** Band of the Royal Regiment of Scotland
*** Lowland Band of the Royal Regiment of Scotland
* Military history of Scotland
Historically, Scotland has a long British military history, military tradition that predates the Acts of Union 1707, Act of Union with England in 1707. Its soldiers today form part of the armed forces of the United Kingdom, more usually referre ...
Census of Scotland
1891 Census of ScotlandHistory of Scotland
* Battles between Scotland and England *Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
** Parliament of Scotland
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
** Peerage of Scotland
The Peerage of Scotland (; ) is one of the five divisions of peerages in the United Kingdom and for those peers created by the King of Scots before 1707. Following that year's Treaty of Union 1707, Treaty of Union, the Kingdom of Scots and the ...
By period
* Timeline of Scottish history *Prehistoric Scotland
Archaeology and geology continue to reveal the secrets of prehistoric Scotland, uncovering a complex past before the Romans brought Scotland into the scope of recorded history. Successive human cultures tended to be spread across Europe or fur ...
*Timeline of prehistoric Scotland
This timeline of prehistoric Scotland is a chronologically ordered list of important archaeological sites in Scotland and of major events affecting Scotland's human inhabitants and culture during the List of time periods#Prehistoric periods, pre ...
* Declaration of Arbroath
*List of monarchs of Scotland
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, Kenneth I MacAlpin () was the founder and first King of the Kingdom of Scotland (although he never held the title historically, being King of t ...
*Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
*Scotland in the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages of Scotland encompass Scotland in the era between the death of Donald II of Scotland, Domnall II in 900 AD and the death of King Alexander III of Scotland, Alexander III in 1286, which was an indirect cause of the Wars of S ...
*Wars of Scottish Independence
The Wars of Scottish Independence were a series of military campaigns fought between the Kingdom of Scotland and the Kingdom of England in the late 13th and 14th centuries.
The First War (1296–1328) began with the English invasion of Scotla ...
*Scotland in the Late Middle Ages
Scotland in the late Middle Ages, between the deaths of Alexander III of Scotland, Alexander III in 1286 and James IV of Scotland, James IV in 1513, established its independence from England under figures including William Wallace in the late ...
*Scottish Reformation
The Scottish Reformation was the process whereby Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland broke away from the Catholic Church, and established the Protestant Church of Scotland. It forms part of the wider European 16th-century Protestant Reformation.
Fr ...
*Scottish colonization of the Americas
The Scottish colonization of the Americas comprised a number of Scottish colonial settlements in the Americas during the early modern period. These included the colony of Nova Scotia in 1629, East Jersey in 1683, Stuarts Town, Carolina in 168 ...
*Parliament of Scotland
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
**List of acts of the Parliament of Scotland
This is a list of acts of the Parliament of Scotland, which was in existence until 1707.
* List of acts of the Parliament of Scotland from 1424
* List of acts of the Parliament of Scotland from 1425
* List of acts of the Parliament of Scotla ...
*Treaty of Union 1707
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new political state of Great Britain. The treaty, effective since 1707, brought the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Ki ...
*Jacobitism
Jacobitism was a political ideology advocating the restoration of the senior line of the House of Stuart to the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British throne. When James II of England chose exile after the November 1688 Glorious Revolution, ...
*Scottish Enlightenment
The Scottish Enlightenment (, ) was the period in 18th- and early-19th-century Scotland characterised by an outpouring of intellectual and scientific accomplishments. By the eighteenth century, Scotland had a network of parish schools in the Sco ...
*Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860.
The first phase resulted from Scottish Agricultural R ...
*Lowland Clearances
The Lowland Clearances were one of the results of the Scottish Agricultural Revolution, which changed the traditional system of agriculture which had existed in Lowland Scotland in the seventeenth century. Thousands of cottars and tenant far ...
By region
* History of Angus *History of Dundee
Dundee () is the fourth-largest City status in the United Kingdom, city in Scotland with a population of around 150,000 people. It is situated on the north bank of the Firth of Tay on the east coast of the Central Lowlands of Scotland. The Dunde ...
*History of Edinburgh
While the area around modern-day Edinburgh has been inhabited for thousands of years, the history of Edinburgh as a definite settlement can be traced to the Scotland in the Early Middle Ages, early Middle Ages when a hillfort was established in ...
*History of Fife
Fife ( , ; ; ) is a council area and lieutenancy area in Scotland. A peninsula, it is bordered by the Firth of Tay to the north, the North Sea to the east, the Firth of Forth to the south, Perth and Kinross to the west and Clackmannanshire t ...
* History of Glasgow
*History of Orkney
Humans have inhabited Orkney, an archipelago in the north of Scotland, for about 8,800 years: Archeological evidence dates from Mesolithic times. Scandinavian clans dominated the area from the 8th century CE, using the islands as a base for furt ...
* History of the Outer Hebrides
By subject
*History of education in Scotland
The history of education in Scotland in its modern sense of organised and institutional learning, began in the Middle Ages, when Church choir schools and grammar schools began educating boys. By the end of the 15th century schools were also being ...
* History of the Jews in Scotland
The history of the Jews in Scotland goes back to at least the 17th century. It is not known when Jews first arrived in Scotland, with the earliest concrete historical references to a Jewish presence in Scotland being from the late 17th cen ...
* History of local government in Scotland
The history of local government in Scotland is a complex tale of largely ancient and long established Scottish political units being replaced after the mid 20th century by a frequently changing series of different local government arrangements. ...
* History of the Scots language
* History of universities in Scotland
* Military history of Scotland
Historically, Scotland has a long British military history, military tradition that predates the Acts of Union 1707, Act of Union with England in 1707. Its soldiers today form part of the armed forces of the United Kingdom, more usually referre ...
Culture of Scotland

Culture of Scotland
The culture of Scotland includes its distinct legal system, financial institutions, sports, literature, art, music, media, cuisine, philosophy, folklore, languages, and religious traditions. Scots law is separate from English law and remai ...
* Architecture of Scotland
The architecture of Scotland includes all human building within the modern borders of Scotland, from the Neolithic era to the present day. The earliest surviving houses go back around 9500 years, and the first villages 6000 years: Skara Brae o ...
** Architecture of Scotland in the Prehistoric era
** Architecture of Scotland in the Roman era
** Architecture of Scotland in the Middle Ages
** Architecture in early modern Scotland
Architecture in early modern Scotland encompasses all building within the borders of the kingdom of Scotland, from the early sixteenth century to the mid-eighteenth century. The time period roughly corresponds to the Early modern Europe, early mo ...
** Architecture of Scotland in the Industrial Revolution
** Architecture in modern Scotland
** Baronial architecture in Scotland
** Church architecture in Scotland
*** Cathedrals in Scotland
** Castles in Scotland
*** Castles in Scotland
** Hill forts in Scotland
Hillforts in Scotland are earthworks, sometimes with wooden or stone enclosures, built on higher ground, which usually include a significant settlement, built within the modern boundaries of Scotland. They were first studied in the eighteenth ce ...
** Historic houses in Scotland
** Housing in Scotland
Housing in Scotland includes all forms of built habitation in what is now Scotland, from the earliest period of human occupation to the present day. The oldest house in Scotland dates from the Mesolithic era. In the Neolithic era settled far ...
* Cuisine of Scotland
** Harris Tweed
**Hogmanay
Hogmanay ( , ) is the Scots language, Scots word for the last day of the old year and is synonymous with the celebration of the New Year in the Scottish manner. It is normally followed by further celebration on the morning of New Year's Day (1 ...
**Scottish clan
A Scottish clan (from Scottish Gaelic , literally 'children', more broadly 'kindred') is a kinship group among the Scottish people. Clans give a sense of shared heritage and descent to members, and in modern times have an official structure r ...
** Scotch whisky
***Bean Nighe
The (Scottish Gaelic for 'washerwoman' or 'laundress'; ) is a female spirit in Scottish folklore, regarded as an omen of death and a messenger from the Otherworld. She is a type of (, anglicized as "banshee") that haunts desolate streams and ...
** Tartan
Tartan or plaid ( ) is a patterned cloth consisting of crossing horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours, forming repeating symmetrical patterns known as ''setts''. Originating in woven wool, tartan is most strongly associated wi ...
***Tartan Day
Tartan Day is a celebration of Scottish heritage and the cultural contributions of Scottish and Scottish-diaspora figures of history. The name refers to tartan, a patterned woollen cloth associated with Scotland. The event originated in Nova ...
( List of tartans)
* Ethnic minorities in Scotland
* Gardens in Scotland
* Festivals in Scotland
* Humour in Scotland
* Inventions and discoveries of Scottish origin
* Languages of Scotland
The languages of Scotland belong predominantly to the Germanic languages, Germanic and Celtic languages, Celtic language families. The main language now spoken in Scotland is English, while Scots language, Scots and Scottish Gaelic are mi ...
** Scottish Gaelic language
Scottish Gaelic (, ; Endonym and exonym, endonym: ), also known as Scots Gaelic or simply Gaelic, is a Celtic language native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a member of the Goidelic language, Goidelic branch of Celtic, Scottish Gaelic, alongs ...
** Lowland Scots
** Scottish English
Scottish English is the set of varieties of the English language spoken in Scotland. The transregional, standardised variety is called Scottish Standard English or Standard Scottish English (SSE). Scottish Standard English may be defined ...
** Highland English
* Marriage in Scotland
Marriage in Scotland is recognised in the form of both civil and religious unions between individuals. Due to Scotland's history as a previously independent country, the laws around marriage developed differently in Scotland compared to other jur ...
** Civil partnership in Scotland Civil partnerships have been recognised for same-sex couples in Scotland since 2005 following the enactment of the ''Civil Partnership Act 2004''. The Act gives same-sex couples most (but not all) of the Legal consequences of marriage and civil part ...
* Media in Scotland
** Television in Scotland
* Museums in Scotland
* Mythology of Scotland
* National symbols of Scotland
** Coat of arms of Scotland
The coat of arms of Scotland, colloquially called the Lion Rampant, is the coat of arms historically used as arms of dominion by the monarchs of the Kingdom of Scotland, and later used within the coat of arms of Great Britain and the present co ...
** Flag of Scotland
The flag of Scotland (; , also known as St Andrew's Cross or the Saltire) is the national flag of Scotland, which consists of a white saltire Defacement (flag), defacing a blue field. The Saltire, rather than the Royal Standard of Scotland, i ...
** National anthem of Scotland
* Prostitution in Scotland
* Public holidays in Scotland
** Christmas in Scotland
* Scottish national identity
Scottish national identity, including Scottish nationalism, are terms referring to the sense of national identity as embodied in the shared and characteristic culture of Scotland, culture, Languages of Scotland, languages, and :Scottish traditi ...
* World Heritage Sites in Scotland
Art in Scotland
 *
*Scottish art
Scottish art is the body of visual art made in what is now Scotland, or about Scottish subjects, since prehistoric times. It forms a distinctive tradition within European art, but the political union with England has led its partial subsumation ...
** Celtic art
**Migration Period art
Migration Period art denotes the artwork of the Germanic peoples during the Migration period (c. 300 – 800). It includes the Migration art of the Germanic tribes on the continent, as well the start of the Insular art or Hiberno-Saxon art of the ...
**National Gallery of Scotland
The National (formerly the Scottish National Gallery) is the national art gallery of Scotland. It is located on The Mound in central Edinburgh, close to Princes Street. The building was designed in a neoclassical style by William Henry Playfa ...
* Cinema of Scotland
The film and cinema industry in Scotland is largely supported by Creative Scotland, Screen Scotland, the Non-departmental public body, executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government which provides financial support, direction ...
* Comedy in Scotland
* Dance in Scotland
** Scottish country dance
Scottish country dance (SCD) is the distinctively Scottish form of country dance, itself a form of social dance involving groups of couples of dancers tracing progressive patterns. A dance consists of a sequence of figures. These dances are ...
** Scottish highland dance
** Ghillies
** Jig
** Scottish sword dances
*** Dirk dance
* Literature of Scotland
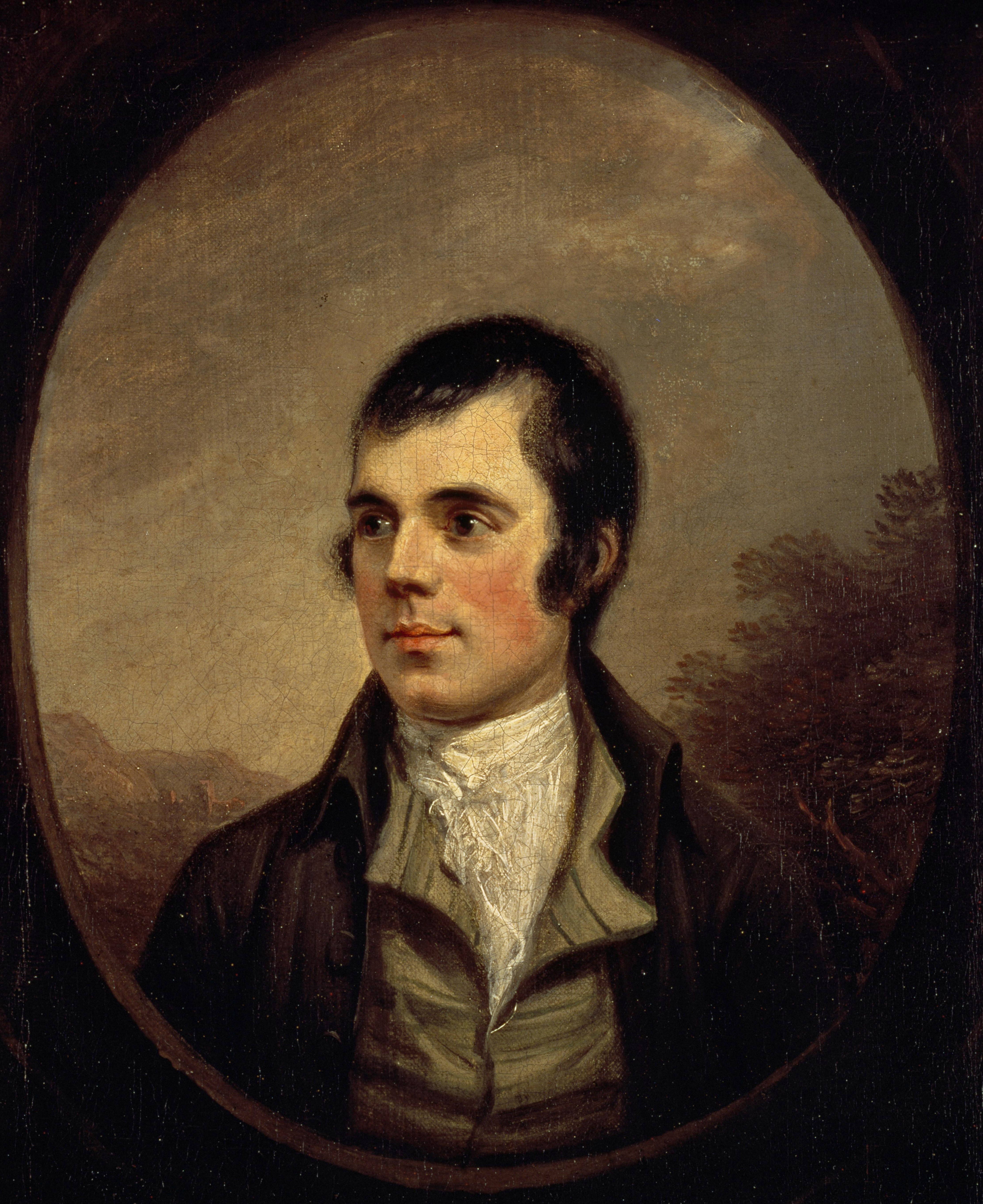
**Robert Burns
Robert Burns (25 January 1759 – 21 July 1796), also known familiarly as Rabbie Burns, was a Scottish poet and lyricist. He is widely regarded as the List of national poets, national poet of Scotland and is celebrated worldwide. He is the be ...
; Scotland's national poet, best known for "Auld Lang Syne
"Auld Lang Syne" () is a Scottish song. In the English-speaking world, it is traditionally sung to bid farewell to the old year at the stroke of midnight on Hogmanay/New Year's Eve. It is also often heard at funerals, graduations, and as a far ...
", written in the Scots language and commonly sung internationally at New Years
** Scottish writers
This list of Scottish writers is an incomplete alphabetical list of Scottish writers who have a Wikipedia page. Those on the list were born and/or brought up in Scotland. They include writers of all genres, writing in English, Scots language, Lowl ...
**Ossian
Ossian (; Irish Gaelic/Scottish Gaelic: ''Oisean'') is the narrator and purported author of a cycle of epic poems published by the Scottish poet James Macpherson, originally as ''Fingal'' (1761) and ''Temora (poem), Temora'' (1763), and later c ...
*Music of Scotland
Scotland is internationally known for its traditional music, often known as Scottish folk music, which remained vibrant throughout the 20th century and into the 21st when many traditional forms worldwide lost popularity to pop music. Traditiona ...
**Bagpipes
Bagpipes are a woodwind instrument using enclosed reeds fed from a constant reservoir of air in the form of a bag. The Great Highland bagpipes are well known, but people have played bagpipes for centuries throughout large parts of Europe, N ...
***Great Highland bagpipe
The great Highland bagpipe ( 'the great pipe') is a type of bagpipe native to Scotland, and the Scottish analogue to the great Irish warpipes. It has acquired widespread recognition through its usage in the British Armed Forces, British mili ...
***Pipe band
A pipe band is a musical ensemble consisting of pipers and drummers. The term pipes and drums, used by military pipe bands is also common.
The most common form of pipe band consists of a section of pipers playing the Great Highland bagpipe, ...
** Church music in Scotland
** Classical music in Scotland
** Court music in Scotland
** Folk music of Scotland
** Music of Scotland in the nineteenth century
** Opera in Scotland
** Scottish country dance music
* Scottish photography
* Theatre in Scotland
** Scottish Playwrights
People of Scotland
*Scottish people
Scottish people or Scots (; ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Scotland. Historically, they emerged in the Scotland in the Early Middle Ages, early Middle Ages from an amalgamation of two Celtic peoples, the Picts and Gaels, who f ...
**Celt
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
**Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ; ; ) are an Insular Celts, Insular Celtic ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland, and the Isle of Man. They are associated with the Goidelic languages, Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic languages comprising ...
** Modern Celts
* Lists of Scots
**List of monarchs of Scotland
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, Kenneth I MacAlpin () was the founder and first King of the Kingdom of Scotland (although he never held the title historically, being King of t ...
*** List of Queens of Scotland
*** Scottish monarchs family tree
**List of Scottish musicians
This list of notable Scottish musicians is part of the List of Scots series.
0–9
* 18 Wheeler, band
* 1990s, indie rock band
A
* John Abell, countertenor, composer and lutenist
* Aberfeldy, pop band
* AC Acoustics
* Maggie Adamson
* Stuar ...
** List of Scottish novelists
** List of Scottish scientists
** List of Scottish writers
* Scottish surnames
Religion in Scotland
*Religion in Scotland
As of the 2022 census, None was the largest category of belief in Scotland, chosen by 51.1% of the Scottish population identifying when asked: "What religion, religious denomination or body do you belong to?" This represented an increase from ...
** Buddhism in Scotland
Buddhism in Scotland is a relatively recent phenomenon. In Scotland, Buddhists represented about 0.3% of the population (15,501) in the 2022 census. 'All of Scotland' > 'Ethnic group, national identity, language and religion' > 'Religion'
Hi ...
** Christianity in Scotland
*** Baptist Union of Scotland
***Scottish Episcopal Church
The Scottish Episcopal Church (; ) is a Christian denomination in Scotland. Scotland's third largest church, the Scottish Episcopal Church has 303 local congregations. It is also an Ecclesiastical province#Anglican Communion, ecclesiastical provi ...
***Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland (CoS; ; ) is a Presbyterian denomination of Christianity that holds the status of the national church in Scotland. It is one of the country's largest, having 245,000 members in 2024 and 259,200 members in 2023. While mem ...
****General Assembly of the Church of Scotland
The General Assembly of the Church of Scotland is the sovereign and highest court of the Church of Scotland, and is thus the Church's governing body.''An Introduction to Practice and Procedure in the Church of Scotland'' by A. Gordon McGillivray, ...
***** List of moderators of the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland
*** Roman Catholicism in Scotland
The Catholic Church in Scotland, overseen by the Scottish Bishops' Conference, is part of the worldwide Catholic Church headed by the Pope. Christianity first arrived in Roman Britain and was strengthened by the conversion of the Picts th ...
** Hinduism in Scotland
** Judaism in Scotland
** Islam in Scotland
** History of the Jews in Scotland
The history of the Jews in Scotland goes back to at least the 17th century. It is not known when Jews first arrived in Scotland, with the earliest concrete historical references to a Jewish presence in Scotland being from the late 17th cen ...
*** List of Scottish Jews
** Sikhism in Scotland
Sikhism in Scotland includes all aspects of Sikh life and Sikhism in Scotland. Sikhs have been present in Scotland for over a century, with the first documented Sikh, Maharaja Daleep Singh, arriving in Perthshire in 1855. The next wave of mig ...
Sports in Scotland
Sports in Scotland * American football in Scotland ** Scottish Claymores * Australian rules football in Scotland * Basketball in Scotland ** Scotland national basketball team * Chess in Scotland ** Scottish Chess Federation * Commonwealth Games Council for Scotland * Cricket in Scotland ** Scottish national cricket team *Curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide #Curling stone, stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area that is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take t ...
* Field Hockey in Scotland
** Scotland women's national field hockey team
*Football in Scotland
Association football is one of the national sports of Scotland and the most popular sport in the country. There is a long tradition of "football" games in Orkney, Lewis and southern Scotland, especially the Scottish Borders, although many of ...
**Scotland national football team
The Scotland national football team represents Scotland in men's international Association football, football and is controlled by the Scottish Football Association. They compete in three major professional tournaments: the FIFA World Cup, UEFA ...
** Scotland women's national football team
**Scottish Football Association
The Scottish Football Association (; also known as the Scottish FA and the SFA) is the governing body of football in Scotland and has the ultimate responsibility for the control and development of football in Scotland. Members of the SFA incl ...
**Scottish Professional Football League
The Scottish Professional Football League (SPFL) is the national men's association football league in Scotland. The league was formed in June 2013 following a merger between the Scottish Premier League and the Scottish Football League. As well ...
**Scottish Cup
The Scottish Football Association Challenge Cup,Scotland GAA
*


 *
*
Scotland.org
– the official online gateway to Scotland, managed by the Scottish Government
Scottish Government
– official site of the
Scottish Parliament
– official site of the
National Archives of Scotland
– official site of the
Homecoming Scotland 2009
an
at the
Gazetteer for Scotland
– Extensive guide to the places and people of Scotland, by the
Scottish economic statistics 2005
(pdf) – from the Scottish Executive
Scottish Census Results On Line
– official government site for Scotland's census results
Scottish Neighbourhood Statistics
– Scottish Government's programme of small area statistics in Scotland
Visit Scotland
– official site of Scotland's national tourist board
ScotlandsPeople
– official government resource for Scottish genealogy
Scotlandpictures.net
Scotland in photos {{DEFAULTSORT:Scotland Outlines of countries 1 Outlines
Golf in Scotland
Golf in Scotland was first recorded in the Scotland in the late Middle Ages, Scottish late Middle Ages, and the modern game of golf was first developed and established in the country. The game plays a key role in the Sport in Scotland, national s ...
**The R&A
The R&A (or more formally, the R&A Trust Company (No. 1) Limited) is the collective name of a group of companies that together play a significant role within the game of golf. Historically, "the R&A" was a colloquial name for the Royal and A ...
** Moray Golf Club
**The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews
The Royal and Ancient Golf Club of St Andrews is one of the oldest golf clubs in the world. It is a private members-only club based in St Andrews in Scotland. It was previously known colloquially as "The R&A", but in 2004, a new organisation kn ...
* Highland Games
** Tossing the caber
* Lacrosse in Scotland
* National sports teams of Scotland
* Netball
** Scotland national netball team
* Campaign for a Scottish Olympic Team – Scotland does not compete at the Olympic Games, Scottish athletes compete as part of the Great Britain team instead. There is however a long running campaign to get a team.
* Rugby in Scotland
** Rugby league in Scotland
** Rugby union in Scotland
Rugby union in Scotland is a popular team sport. Scotland's national side today competes in the annual Six Nations Championship and the Rugby World Cup. The first ever international rugby match was played on 27 March 1871, at Raeburn Place in E ...
*** Scottish Rugby Union
The Scottish Rugby Union (SRU; ) is the Sport governing body, governing body of rugby union in Scotland. Now marketed as Scottish Rugby, it is the second-oldest Rugby Union, having been founded in 1873. The SRU oversees the national league sys ...
***Scotland national rugby union team
The Scotland national rugby union team represents the Scottish Rugby Union in men's international rugby union. The team takes part in the annual Six Nations Championship, where they are the current Doddie Weir Cup holders. They also participa ...
*** History of rugby union in Scotland
Rugby union in Scotland in its modern form has existed since the mid-19th century. Scotland has one of the oldest rugby union traditions and has introduced various innovations including rugby sevens.
As with the history of rugby union itself ho ...
*** Murrayfield Stadium
Murrayfield Stadium is a rugby union stadium located in the Murrayfield area of Edinburgh, Scotland. The stadium is owned by the Scottish Rugby Union (SRU) who has its headquarters based at the stadium, and is the national stadium of the Scotla ...
*** List of Scottish rugby union players
*** Rugby union in the Borders
** Rugby Sevens
Rugby sevens (commonly known simply as sevens, and originally seven-a-side rugby) is a variant of rugby union in which teams are made up of seven players playing seven-minute halves, instead of the usual 15 players playing 40-minute halves. R ...
(invented in Scotland)
*** Edinburgh Sevens
*** Melrose Sevens
Melrose Sevens is an annual rugby sevens event held by Melrose Rugby Club, at The Greenyards in Melrose, Scotland. It is the oldest rugby sevens competition in the world, dating back to 1883 when the tournament was suggested by former Melros ...
* Shinty
Shinty () is a team sport played with sticks and a ball. It is played mainly in the Scottish Highlands and among Highland migrants to the major cities of Scotland. The sport was formerly more widespread in Scotland and even played in Northern ...
** Camanachd Association
The Camanachd Association (in Scottish Gaelic, ''Comann na Camanachd'') is the world Sport governing body, governing body of the Scotland, Scottish sport of shinty. The body is based in Inverness, Highland (council area), Highland, and is in ...
** Composite rules shinty-hurling
** Women's shinty
Economy and infrastructure of Scotland


 *
* Economy of Scotland
The economy of Scotland is an Open economy, open mixed economy, mainly services based, which is the Economy of the United Kingdom#Economy by country, second largest economy amongst the countries of the United Kingdom. It had an estimated nominal ...
** Economic rank (by nominal GDP): (6th; 2023), as a country of the United Kingdom
** Agriculture in Scotland
Agriculture in Scotland includes all land use for arable, horticultural or pastoral activity in Scotland, or around its coasts. The first permanent settlements and farming date from the Neolithic period, from around 6,000 years ago. From the begi ...
** Banking in Scotland
*** Bank of Scotland
The Bank of Scotland plc (Scottish Gaelic: ''Banca na h-Alba'') is a commercial bank, commercial and clearing (finance), clearing bank based in Edinburgh, Scotland, and is part of the Lloyds Banking Group. The bank was established by the Par ...
***Royal Bank of Scotland
The Royal Bank of Scotland Public Limited Company () is a major retail banking, retail and commercial bank in Scotland. It is one of the retail banking subsidiaries of NatWest Group, together with NatWest and Ulster Bank. The Royal Bank of Sco ...
***Clydesdale Bank
Clydesdale Bank () is a trading name used by Clydesdale Bank plc for its retail banking operations in Scotland.
In June 2018, it was announced that Clydesdale Bank plc's holding company, CYBG, would acquire Virgin Money for £1.7 billi ...
* Communications in Scotland
**Scottish media
There are several types of mass media in Scotland: television, Cinema of Scotland, cinema, radio, newspapers, magazines, game design and websites. The majority of Scotland's media is located in Glasgow, the countries largest city, which serves ...
**List of newspapers in Scotland
This is a list of newspapers in Scotland.
Daily newspapers
:
Traditionally newspapers could be divided into 'quality', serious-minded newspapers (usually referred to as 'broadsheets' due to their large size) and 'tabloids', or less serious news ...
** Television in Scotland
***BBC Scotland
BBC Scotland is a division of the BBC and the main public broadcaster in Scotland. Its headquarters are in Glasgow, employing approximately 1,250 staff as of 2017, to produce 15,000 hours of television and radio programming per year. BBC Scotla ...
*** STV
** Internet in Scotland
***.scot
.scot is a GeoTLD for Scotland and Scottish culture, including the Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic and Scots language, Scots languages.
In 2008 dotCYMRU, dotEUS, dotSCOT and dotBZH formed ECLID. Later it was decided to allow newly proposed top-level d ...
* Companies of Scotland
* Currency
A currency is a standardization of money in any form, in use or circulation as a medium of exchange, for example banknotes and coins. A more general definition is that a currency is a ''system of money'' in common use within a specific envi ...
of the United Kingdom: Pound Sterling
Sterling (symbol: £; currency code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound is the main unit of sterling, and the word '' pound'' is also used to refer to the British currency general ...
* Economic history of Scotland
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with ...
* Energy in Scotland
** Energy policy of Scotland
** Oil industry in Scotland
***North Sea Oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.
In the petroleum industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian ...
** Power stations in Scotland
** Renewable energy in Scotland
**Nuclear power in Scotland
Scotland has a long history of nuclear research and electricity generation. Work started on the Dounreay reactor in 1955.
Four other sites provided electricity to the National Grid in Scotland, however generation ceased at Hunterson A in 1990 a ...
* Fire services in Scotland
* Health care in Scotland
** Hospitals in Scotland
**NHS Scotland
NHS Scotland, sometimes styled NHSScotland, is the publicly–funded healthcare system in Scotland and one of the four systems that make up the National Health Service in the United Kingdom. It operates 14 territorial NHS boards across Scotland ...
***Scottish Ambulance Service
The Scottish Ambulance Service () is part of NHS Scotland, which serves all of Scotland, Scotland's population. The Scottish Ambulance Service is governed by a NHS Scotland#Special health boards, special health board and is funded directly by t ...
* Mining in Scotland
** Gold mining in Scotland
** Lead mining in Scotland
Lead ore has been mined and refined in Scotland for centuries, primarily in the form of galena. It was a versatile material used for roofing material high-status buildings, fabricating the pipework of Linlithgow Palace fountain, glazing windows, a ...
** National Mining Museum Scotland
* Tourism in Scotland
* Transport in Scotland
** Airports in Scotland
** Ports and harbours in Scotland
** Rail transport in Scotland
** Roads in Scotland
* Water supply and sanitation in Scotland
* Wild Scotland
Education in Scotland
*Education in Scotland
Education in Scotland is provided in state schools, private school, private schools and by individuals through homeschooling. Mandatory education in Scotland begins for children in Primary 1 (P1) at primary school and ends in Fifth Year (S5) a ...
**''Curriculum for Excellence
''Curriculum for Excellence'' (Scottish Gaelic: ''Curraicealam airson Sàr-mhathais'') is the national curriculum in Scotland, used by Scottish schools for learners ages 3–18. The implementation of ''Curriculum for Excellence'' is overseen by ...
'', the national 3–18 school curriculum
**Education Scotland
Education Scotland () is an Executive agencies of the Scottish Government, executive agency of the Scottish Government, tasked with improving the quality of the country's Scottish education system, education system. Education Scotland is respon ...
** Care Inspectorate
**General Teaching Council for Scotland
The General Teaching Council for Scotland (GTC Scotland) () is a fee based registered charity and the world's first independent registration and regulation body for teaching. The current Chief Executive and Registrar is Pauline Stephen. The GTC Sc ...
** Cabinet Secretary for Education and Skills
*List of universities in Scotland
There are fifteen universities based in Scotland, the Open University, and three other institutions of higher education.
The first university in Scotland was St John's College, St Andrews, founded in 1418. St Salvator's College was added ...
* List of schools in Scotland
*Scottish Qualifications Authority
The Scottish Qualifications Authority (SQA; Scottish Gaelic, Gaelic: ''Ùghdarras Theisteanas na h-Alba'') is the Scottish public bodies, executive non-departmental public body of the Scottish Government responsible for accrediting educationa ...
(SQA)
Specific schools
* State schools in Scotland ** State schools in City Council Areas ** State schools in Council Areas A–D ** State schools in Council Areas E–H ** State schools in Council Areas I–R ** State schools in Council Areas S–W * Private schools in Scotland * Gaelic medium schools in Scotland * Catholic schools in Scotland *Universities
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
Notes
See also
* Outline of geography * Outline of the United Kingdom *List of international rankings
This is a list of international rankings by country.
By category
Agriculture
* Production
**Apple
** Apricot
** Artichoke
** Avocado
**Barley
**Cereal
** Cherry
**Coconut
** Coffee
** Corn
** Cucumber
**Eggplant
**Fruit
** Garlic
**Grape
** Papay ...
References
External links
Scotland.org
– the official online gateway to Scotland, managed by the Scottish Government
Scottish Government
– official site of the
Scottish Government
The Scottish Government (, ) is the executive arm of the devolved government of Scotland. It was formed in 1999 as the Scottish Executive following the 1997 referendum on Scottish devolution, and is headquartered at St Andrew's House in ...
Scottish Parliament
– official site of the
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
National Archives of Scotland
– official site of the
National Archives of Scotland
The National Archives of Scotland (NAS) is the previous name of the National Records of Scotland (NRS), and are the national archives of Scotland, based in Edinburgh. The NAS claims to have one of the most varied collection of archives in Europ ...
Homecoming Scotland 2009
an
at the
National Library of Scotland
The National Library of Scotland (NLS; ; ) is one of Scotland's National Collections. It is one of the largest libraries in the United Kingdom. As well as a public programme of exhibitions, events, workshops, and tours, the National Library of ...
Gazetteer for Scotland
– Extensive guide to the places and people of Scotland, by the
Royal Scottish Geographical Society
The Royal Scottish Geographical Society (RSGS) is an educational charity based in Perth, Scotland, founded in 1884. The purpose of the society is to advance the subject of geography worldwide, inspire people to learn more about the world around ...
and University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under th ...
Scottish economic statistics 2005
(pdf) – from the Scottish Executive
Scottish Census Results On Line
– official government site for Scotland's census results
Scottish Neighbourhood Statistics
– Scottish Government's programme of small area statistics in Scotland
Visit Scotland
– official site of Scotland's national tourist board
ScotlandsPeople
– official government resource for Scottish genealogy
Scotlandpictures.net
Scotland in photos {{DEFAULTSORT:Scotland Outlines of countries 1 Outlines