
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of
Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the devel ...
's
processors from the pioneering
4-bit
In computer architecture, 4-bit integers, or other data units are those that are 4 bits wide. Also, 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, or data buses of t ...
4004 (1971) to the present high-end offerings. Concise technical data is given for each product.
Latest
13th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed "
Raptor Lake
Raptor Lake is Intel's codename for the 13th-generation of Intel Core processors based on a hybrid architecture, utilizing Raptor Cove performance cores and Gracemont efficient cores. Raptor Lake launched on October 20, 2022. Mobile versions a ...
")
12th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Alder Lake")
Mobile (codenamed " Alder Lake")
11th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Rocket Lake")
Mobile (codenamed " Tiger Lake")
10th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed " Comet Lake")
Mobile (codenamed " Comet Lake", " Ice Lake", and " Amber Lake")
9th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed "
Coffee Lake Refresh
Coffee Lake is Intel's codename for its eighth generation Core microprocessor family, announced on September 25, 2017. It is manufactured using Intel's second 14 nm process node refinement. Desktop Coffee Lake processors introduced i5 and ...
")
8th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed "
Coffee Lake
Coffee Lake is Intel's codename for its eighth generation Core microprocessor family, announced on September 25, 2017. It is manufactured using Intel's second 14 nm process node refinement. Desktop Coffee Lake processors introduced i5 and ...
")
Mobile (codenamed "
Coffee Lake
Coffee Lake is Intel's codename for its eighth generation Core microprocessor family, announced on September 25, 2017. It is manufactured using Intel's second 14 nm process node refinement. Desktop Coffee Lake processors introduced i5 and ...
", "
Amber Lake" and "
Whiskey Lake")
7th generation Core
Desktop (codenamed "
Kaby Lake
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's p ...
" and "
Skylake-X")
Mobile (codenamed "
Kaby Lake
Kaby Lake is Intel's codename for its seventh generation Core microprocessor family announced on August 30, 2016. Like the preceding Skylake, Kaby Lake is produced using a 14 nanometer manufacturing process technology. Breaking with Intel's p ...
" and "
Apollo Lake
Goldmont is a microarchitecture for low-power Atom, Celeron and Pentium branded processors used in systems on a chip (SoCs) made by Intel. They allow only one thread per core.
The ''Apollo Lake'' platform with 14 nm Goldmont core was unv ...
")
All processors
All processors are listed in chronological order.
The
4-bit
In computer architecture, 4-bit integers, or other data units are those that are 4 bits wide. Also, 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, or data buses of t ...
processors
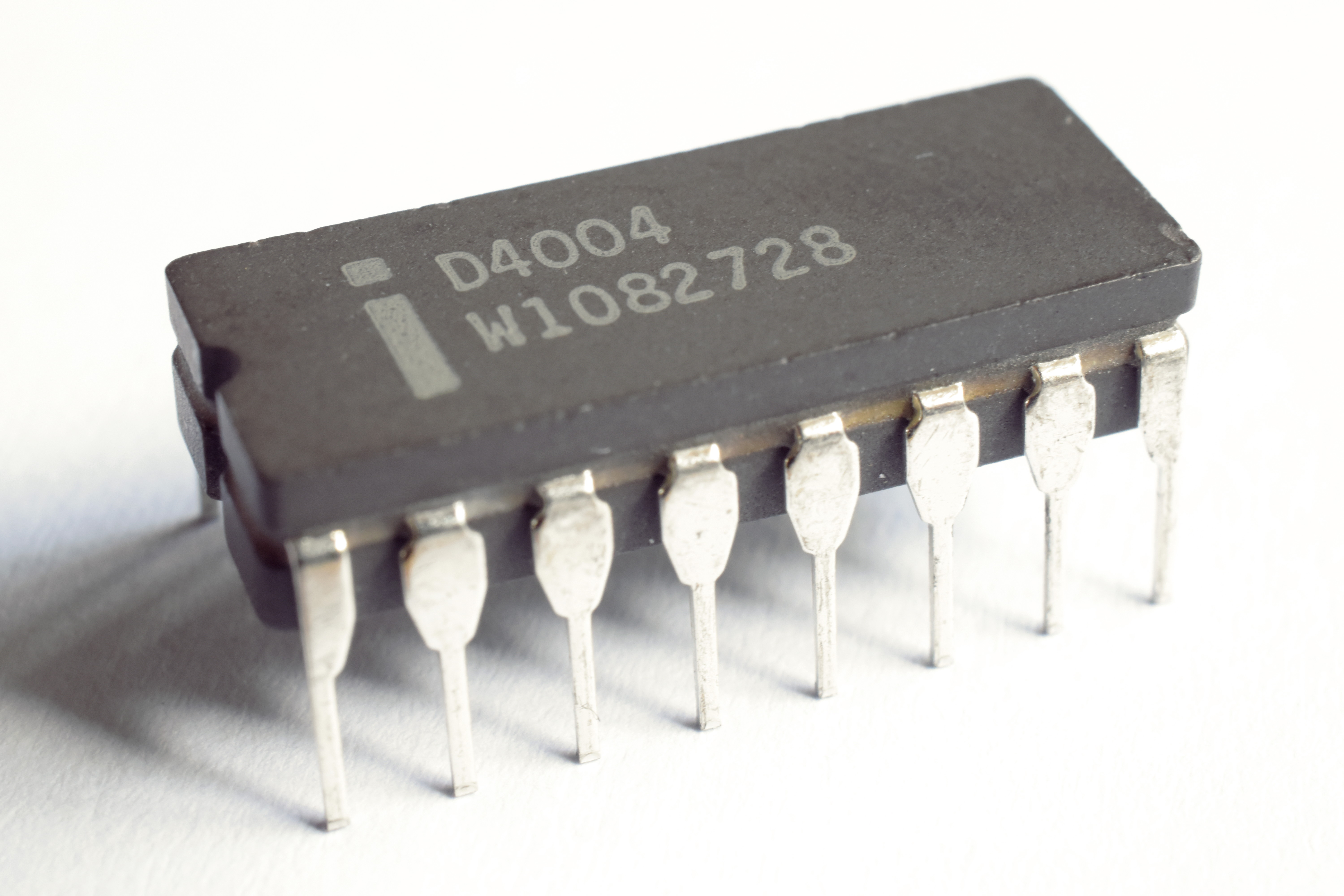

Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. Sold for US$60, it was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs.
The 4004 was the first signific ...
First
microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
(single-chip IC processor)
* Introduced November 15, 1971
* Clock rate 740
kHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one h ...
* 0.07
MIPS
* Bus width: 4 bits (multiplexed address/data due to limited pins)
*
PMOS
* 2,300 transistors at 10
μm
*
Addressable memory 640
byte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit ...
s
*
Program memory 4
KB (4096 B)
* Originally designed to be used in
Busicom
was a Japanese company that manufactured and sold computer-related products headquartered in Taito, Tokyo. It owned the rights to Intel's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, which they created in partnership with Intel in 1970.
Busicom as ...
calculator
MCS-4 family:
* 4004 –
CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, an ...
* 4001 –
ROM & 4-bit Port
* 4002 –
RAM & 4-bit Port
* 4003 – 10-bit Shift Register
* 4008 – Memory+I/O Interface
* 4009 – Memory+I/O Interface
* 4211 – General Purpose Byte I/O Port
* 4265 – Programmable General Purpose I/O Device
* 4269 – Programmable Keyboard Display Device
* 4289 – Standard Memory Interface for MCS-4/40
* 4308 – 8192-bit (1024 × 8) ROM w/ 4-bit I/O Ports
* 4316 – 16384-bit (2048 × 8) Static ROM
* 4702 – 2048-bit (256 × 8) EPROM
* 4801 – 5.185 MHz Clock Generator Crystal for 4004/4201A or 4040/4201A
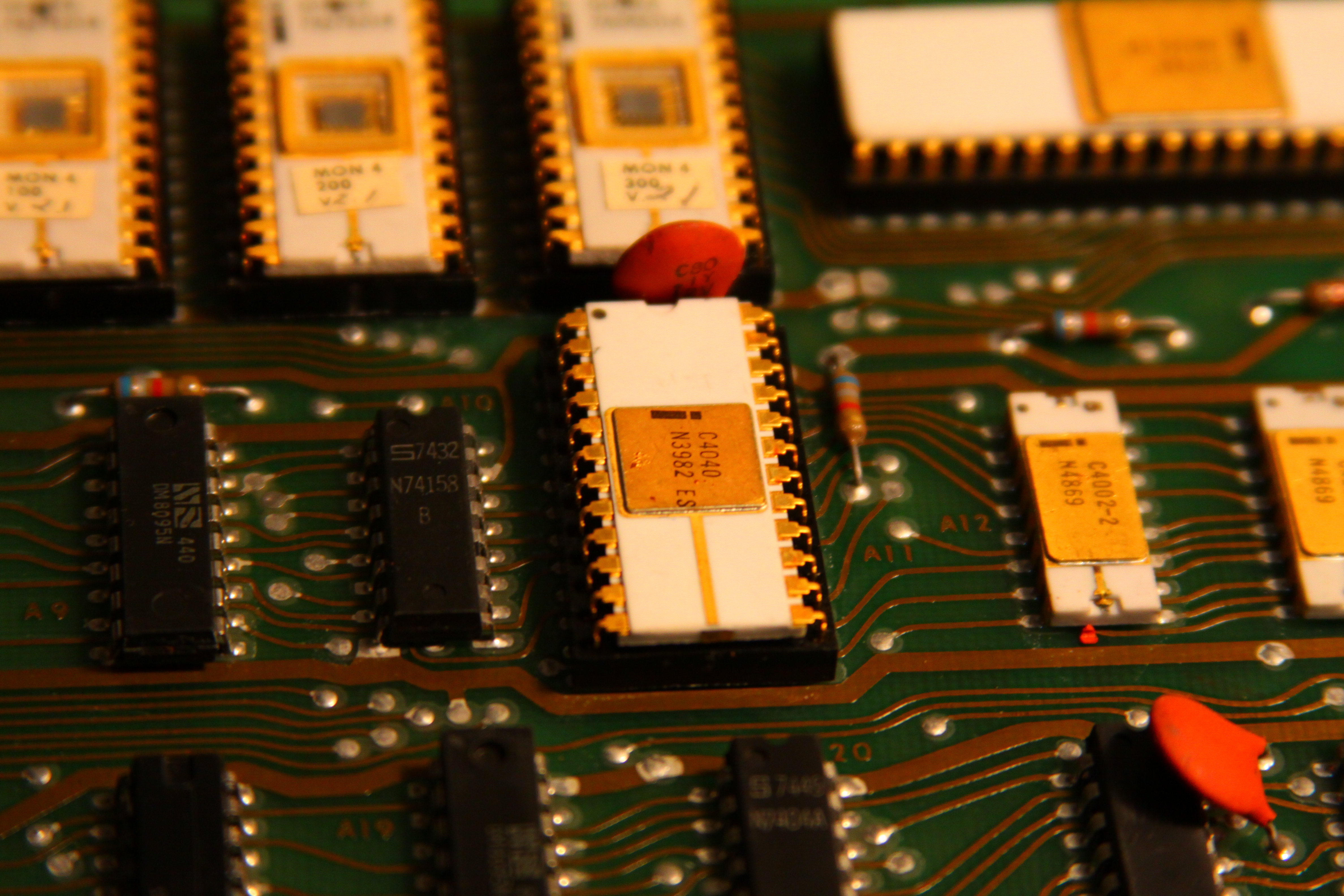
Intel 4040
The Intel 4040 microprocessor was the successor to the Intel 4004. It was introduced in 1974. The 4040 employed a 10 μm silicon gate enhancement load PMOS technology, was made up of 3,000 transistors and could execute approximately 62,000 in ...
* Introduced in 1974 by Intel
* Clock speed was 740 kHz (same as the 4004 microprocessor)
* 3,000 transistors
* Interrupt features were available
* Programmable memory size: 8 KB (8192 B)
* 640 bytes of data memory
* 24-pin DIP
The
8-bit
In computer architecture, 8-bit integers or other data units are those that are 8 bits wide (1 octet). Also, 8-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers or data buses of ...
processors

8008
* Introduced April 1, 1972
* Clock rate 500 kHz (8008-1: 800 kHz)
* 0.05 MIPS
* Bus width: 8 bits (multiplexed address/data due to limited pins)
* Enhancement load
PMOS logic
PMOS or pMOS logic (from p-channel metal–oxide–semiconductor) is a family of digital circuits based on p-channel, enhancement mode metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In the late 1960s and early 1970s, PMOS lo ...
* 3,500 transistors at 10 μm
* Addressable memory 16 KB
* Typical in early 8-bit microcomputers, dumb terminals, general calculators, bottling machines
* Developed in tandem with 4004
* Originally intended for use in the
Datapoint 2200 microcomputer
* Key volume deployment in Texas Instruments 742 microcomputer in >3,000 Ford dealerships

8080
The Intel 8080 (''"eighty-eighty"'') is the second 8-bit microprocessor designed and manufactured by Intel. It first appeared in April 1974 and is an extended and enhanced variant of the earlier 8008 design, although without binary compatibil ...
* Introduced April 1, 1974
* Clock rate 2 MHz (very rare 8080B: 3 MHz)
* 0.29 MIPS
* Data bus width: 8 bits, address bus: 16 bits
* Enhancement load
NMOS logic
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. These nMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type ...
* 4,500 transistors at 6 μm
*
Assembly language downward compatible with 8008
* Addressable memory 64 KB (64 × 1024 B)
* Up to 10× the performance of the 8008
* Used in e.g. the
Altair 8800
The Altair 8800 is a microcomputer designed in 1974 by MITS and based on the Intel 8080 CPU. Interest grew quickly after it was featured on the cover of the January 1975 issue of Popular Electronics and was sold by mail order through advertisemen ...
,
traffic light
Traffic lights, traffic signals, or stoplights – known also as robots in South Africa are signalling devices positioned at road intersections, pedestrian crossings, and other locations in order to control flows of traffic.
Traffic light ...
controller,
cruise missile
A cruise missile is a guided missile used against terrestrial or naval targets that remains in the atmosphere and flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhea ...
* Required six support chips versus 20 for the 8008


8085
* Introduced March 1976
* Clock rate 3 MHz
* 0.37
MIPS
* Data bus width: 8 bits, address bus: 16 bits
* Depletion load
NMOS logic
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type (-) MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors) to implement logic gates and other digital circuits. These nMOS transistors operate by creating an inversion layer in a p-type ...
* 6,500 transistors at
3 μm
*
Binary compatible
Binary-code compatibility (binary compatible or object-code-compatible) is a property of a computer system, meaning that it can run the same executable code, typically machine code for a general-purpose computer CPU, that another computer syste ...
downward with the 8080
* Used in
Toledo scales. Also used as a computer peripheral controller – modems, hard disks, printers, etc.
*
CMOS 80C85 in
Mars Sojourner
''Sojourner'' is a robotic Mars rover that landed in the Ares Vallis channel in the Chryse Planitia region of the Oxia Palus quadrangle on July 4, 1997. ''Sojourner'' was operational on Mars for 92 sols (95 Earth days). It was the first whee ...
,
Radio Shack Model 100 portable
Microcontrollers
They are ICs with CPU, RAM, ROM (or PROM or EPROM), I/O Ports, Timers & Interrupts

Intel 8048
The MCS-48 microcontroller series, Intel's first microcontroller, was originally released in 1976. Its first members were 8048, 8035 and 8748. The 8048 is probably the most prominent member of the family. Initially, this family was produced u ...
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. It contrasts with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and data share the same memory and pathways.
...
MCS-48 family:
* Intel 8020 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 Byte RAM, 13 I/O ports
* Intel 8021 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 Byte RAM, 21 I/O ports
* Intel 8022 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, With On-Chip A/D Converter
* Intel 8035 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 64 Byte RAM
* Intel 8039 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 128 Byte RAM
* Intel 8040 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 256 Byte RAM
* Intel 8048 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports, 0.73 MIPS @ 11 MHz
* Intel 8049 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 2 KB ROM, 128 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 8050 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 4 KB ROM, 256 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 8748 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB EPROM, 64 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 8749 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 2 KB EPROM, 128 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports,
* Intel 87P50 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, ext. ROM socket (2758/2716/2732), 256 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports
* Intel 8648 – Single-Component 8-bit Microcontroller, 1 KB OTP EPROM, 64 byte RAM, 27 I/O ports
* Intel 8041 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 64 byte RAM
* Intel 8041AH – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB ROM, 128 byte RAM
* Intel 8641 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller ?
* Intel 8741 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB EPROM, 64 byte RAM
* Intel 8741AH – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 1 KB EPROM, 128 byte RAM
* Intel 8042 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 2 KB ROM, 256 byte RAM
* Intel 8742 – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 2 KB EPROM, 128 byte RAM
* Intel 8742AH – Universal Peripheral Interface 8-bit Slave Microcontroller, 2 KB OTP EPROM, 256 byte RAM
* Intel 8243 – Input/Output Expander. The available 28-pin
PLCC version in sampling for first quarter of 1986.
* Intel 8244 – General Purpose Graphics Display Device (ASIC NTSC/SECAM)
* Intel 8245 – General Purpose Graphics Display Device (ASIC PAL)

Intel 8051
The Intel MCS-51 (commonly termed 8051) is a single chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton. Intel's original versions were pop ...
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. It contrasts with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and data share the same memory and pathways.
...
MCS-51
The Intel MCS-51 (commonly termed 8051) is a single chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton. Intel's original versions were ...
family:
* 8031 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8032 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8044 – High Performance 8-bit Microcontroller
* 8344 – High Performance 8-bit Microcontroller
* 8744 – High Performance 8-bit Microcontroller
* 8051 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8052 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8054 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8058 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8351 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8352 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8354 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8358 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8751 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8752 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8754 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 8758 – 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
Intel 80151
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. It contrasts with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and data share the same memory and pathways.
...
MCS-151
The Intel MCS-51 (commonly termed 8051) is a single chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton. Intel's original versions were po ...
family:
* 80151 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 83151 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 87151 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 80152 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
* 83152 – High Performance 8-bit Control-Oriented Microcontroller
Intel 80251
The Intel MCS-51 (commonly termed 8051) is a single chip microcontroller (MCU) series developed by Intel in 1980 for use in embedded systems. The architect of the Intel MCS-51 instruction set was John H. Wharton. Intel's original versions were po ...
* Single
accumulator Harvard architecture
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. It contrasts with the von Neumann architecture, where program instructions and data share the same memory and pathways.
...
MCS-251 family:
* 80251 – 8/16/
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
Microcontroller
* 80252 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 80452 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 83251 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 87251 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
* 87253 – 8/16/32-bit Microcontroller
MCS-96 family
* 8061 – 16-bit Microcontroller (parent of MCS-96 family ROMless With A/D, most sold to Ford)
* 8094 –
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
Microcontroller (48-Pin ROMLess Without A/D)
* 8095 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin ROMLess With A/D)
* 8096 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin ROMLess Without A/D)
* 8097 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin ROMLess With A/D)
* 8394 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With ROM Without A/D)
* 8395 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With ROM With A/D)
* 8396 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With ROM Without A/D)
* 8397 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With ROM With A/D)
* 8794 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With EROM Without A/D)
* 8795 – 16-bit Microcontroller (48-Pin With EROM With A/D)
* 8796 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With EROM Without A/D)
* 8797 – 16-bit Microcontroller (68-Pin With EROM With A/D)
* 8098 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 8398 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 8798 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 80196 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 83196 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 87196 – 16-bit Microcontroller
* 80296 – 16-bit Microcontroller
The bit-slice processor
3000 family

Introduced in the third quarter of 1974, these
bit-slicing components used
bipolar Schottky transistors. Each component implemented two bits of a processor function; packages could be interconnected to build a processor with any desired word length.
Members of the family:
* 3001 – Microcontrol Unit
* 3002 – 2-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit slice
* 3003 – Look-ahead Carry Generator
* 3205 – High-performance 1 of 8 Binary Decoder
* 3207 – Quad Bipolar-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver
* 3208 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3210 – TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3211 – ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3212 – Multimode Latch Buffer
* 3214 – Interrupt Control Unit
* 3216 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3222 – Refresh Controller for 4K (4096 B) NMOS DRAMs
* 3226 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3232 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 4K DRAMs
* 3242 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 16K (16 × 1024 B) DRAMs
* 3245 – Quad Bipolar TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3246 – Quad Bipolar ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3404 – High-performance 6-bit Latch
* 3408 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3505 – Next generation processor
Bus width 2''n'' bits data/address (depending on number ''n'' of slices used)
The
16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
processors: MCS-86 family
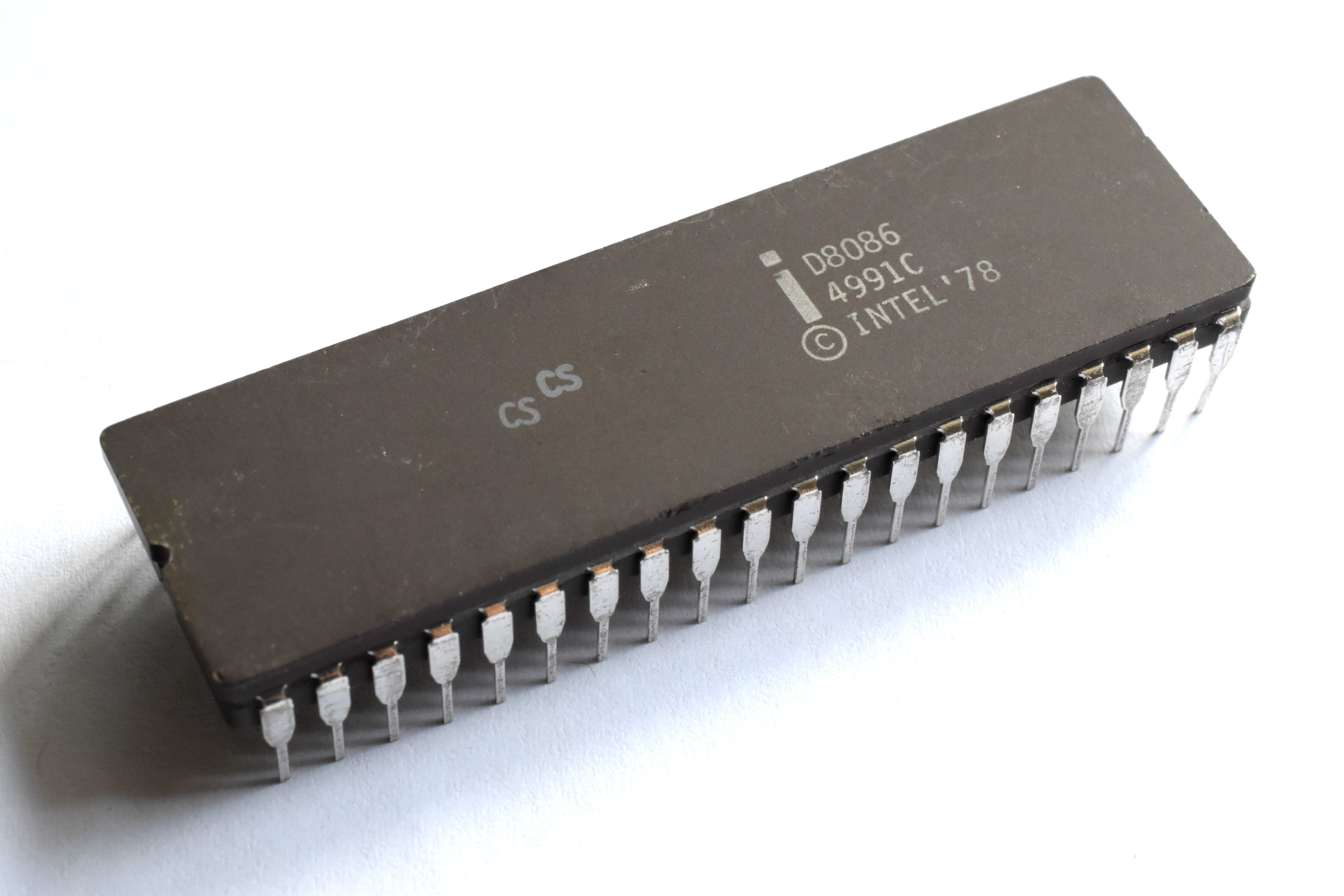
8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus (allo ...
* Introduced June 8, 1978
* Clock rates:
** 5 MHz, 0.33 MIPS
** 8 MHz, 0.66 MIPS
** 10 MHz, 0.75 MIPS
* The memory is divided into odd and even banks. It accesses both banks concurrently to read 16 bits of data in one clock cycle
* Data bus width: 16 bits, address bus: 20 bits
* 29,000 transistors at 3 μm
* Addressable memory 1 megabyte (1024B)
* Up to 10× the performance of 8080
* First used in the Compaq Deskpro IBM PC-compatible computers. Later used in portable computing, and in the
IBM PS/2 Model 25 and
Model 30. Also used in the
AT&T PC6300 / Olivetti M24, a popular IBM PC-compatible (predating the IBM PS/2 line)
* Used
segment registers to access more than 64 KB of data at once, which many programmers complained made their work excessively difficult.
* The first x86 CPU
* Later renamed the iAPX 86
[Intel IAPX 86,88 User's Manual, August 1981, Intel order number 210201-001]

8088
The Intel 8088 ("''eighty-eighty-eight''", also called iAPX 88) microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 has an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and ...
* Introduced June 1, 1979
* Clock rates:
** 4.77 MHz, 0.33 MIPS
** 8 MHz, 0.66 MIPS
* 16-bit internal architecture
* External data bus width: 8 bits, address bus: 20 bits
* 29,000 transistors at 3 μm
* Addressable memory 1 megabyte
* Identical to 8086 except for its 8-bit external bus (hence an ''8'' instead of a ''6'' at the end); identical Execution Unit (EU), different Bus Interface Unit (BIU)
* Used in
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a tea ...
and PC-XT and compatibles
* Later renamed the iAPX 88

80186
* Introduced 1982
* Clock rates
** 6 MHz, > 1 MIPS
* 55,000 transistors
* Included two timers, a
DMA controller, and an
interrupt controller on the chip in addition to the processor (these were at fixed addresses which differed from the IBM PC, although it was used by several PC compatible vendors such as Australian company Cleveland)
* Added a few opcodes and exceptions to the 8086 design, otherwise identical instruction set to 8086 and 8088
** BOUND, ENTER, LEAVE
** INS, OUTS
** IMUL imm, PUSH imm, PUSHA, POPA
** RCL/RCR/ROL/ROR/SHL/SHR/SAL/SAR reg, imm
* Address calculation and shift operations are faster than 8086
* Used mostly in embedded applications – controllers, point-of-sale systems, terminals, and the like
* Used in several non-PC compatible
DOS computers including
RM Nimbus,
Tandy 2000
The Tandy 2000 is a personal computer introduced by Radio Shack in September 1983 based on the 8 MHz Intel 80186 microprocessor running MS-DOS. By comparison, the IBM PC XT (introduced in March 1983) used the older 4.77 MHz Intel 80 ...
, and CP/M 86 Televideo PM16 server
* Later renamed to iAPX 186
80188
The Intel 80188 microprocessor was a variant of the Intel 80186. The 80188 had an 8-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 80186; this made it less expensive to connect to peripherals. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte add ...
* A version of the 80186 with an 8-bit external data bus
* Later renamed the iAPX 188

80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non- multiplexed address and data buses and also th ...
* Introduced February 2, 1982
* Clock rates:
** 6 MHz, 0.9 MIPS
** 8 MHz, 10 MHz, 1.5 MIPS
** 12.5 MHz, 2.66 MIPS
** 16 MHz, 20 MHz and 25 MHz available.
* Data bus width: 16 bits, address bus: 24 bits
* Included memory protection hardware to support multitasking operating systems with per-process address space.
* 134,000 transistors at
1.5 μm
* Addressable memory 16
MB
* Added protected-mode features to 8086 with essentially the same instruction set
* 3–6× the performance of the 8086
* Widely used in
IBM PC AT
The IBM Personal Computer/AT (model 5170, abbreviated as IBM AT or PC/AT) was released in 1984 as the fourth model in the IBM Personal Computer line, following the IBM PC/XT and its IBM Portable PC variant. It was designed around the Intel 80 ...
and AT clones contemporary to it
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
processors: the non-x86 microprocessors
iAPX 432
* Introduced January 1, 1981 as Intel's first
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
microprocessor
* Multi-chip CPU
* Object/capability architecture
* Microcoded operating system primitives
* One terabyte virtual address space
* Hardware support for fault tolerance
* Two-chip General Data Processor (GDP), consists of 43201 and 43202
* 43203 Interface Processor (IP) interfaces to I/O subsystem
* 43204 Bus Interface Unit (BIU) simplifies building multiprocessor systems
* 43205 Memory Control Unit (MCU)
* Architecture and execution unit internal data base paths: 32 bits
* Clock rates:
** 5 MHz
** 7 MHz
** 8 MHz
i960 a.k.a. 80960
* Introduced April 5, 1988
*
RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set compu ...
-like
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
architecture
* Predominantly used in embedded systems
* Evolved from the capability processor developed for the
BiiN joint venture with
Siemens
* Many variants identified by two-letter suffixes
i860 a.k.a. 80860
* Introduced February 26, 1989
*
RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set compu ...
32/
64-bit
In computer architecture, 64-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 64 bits wide. Also, 64-bit CPUs and ALUs are those that are based on processor registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. A comp ...
architecture, with floating point pipeline characteristics very visible to programmer
* Used in the
Intel iPSC/860 Hypercube
In geometry, a hypercube is an ''n''-dimensional analogue of a square () and a cube (). It is a closed, compact, convex figure whose 1-skeleton consists of groups of opposite parallel line segments aligned in each of the space's dimensions ...
parallel supercomputer
* Mid-life kicker in the i870 processor (primarily a speed bump, some refinement/extension of instruction set)
* Used in the
Intel Delta
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 series ...
massively parallel supercomputer prototype, emplaced at
California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
* Used in the
Intel Paragon
The Intel Paragon is a discontinued series of massively parallel supercomputers that was produced by Intel in the 1990s. The Paragon XP/S is a productized version of the experimental ''Touchstone Delta'' system that was built at Caltech, launc ...
massively parallel supercomputer, emplaced at
Sandia National Laboratory
Sandia National Laboratories (SNL), also known as Sandia, is one of three research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA). Headquartered in Kirtland Air Force Bas ...
XScale
* Introduced August 23, 2000
*
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
RISC
In computer engineering, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set compu ...
microprocessor based on the
ARM architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configure ...
* Many variants, such as the PXA2xx applications processors, IOP3xx I/O processors and IXP2xxx and IXP4xx network processors
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
processors: the 80386 range


80386DX
* Introduced October 17, 1985
* Clock rates:
** 16 MHz, 5 MIPS
** 20 MHz, 6 to 7 MIPS, introduced February 16, 1987
** 25 MHz, 7.5 MIPS, introduced April 4, 1988
** 33 MHz, 9.9 MIPS (9.4 SPECint92 on Compaq/i 16 KB L2), introduced April 10, 1989
* Data bus width: 32 bits, address bus: 32 bits
* 275,000 transistors at 1 μm
* Addressable memory 4
GB (4 × 1024 B)
*
Virtual memory
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that are actually available on a given machine" which "creates the illusion to users of a very ...
64
TB (64 × 1024 B)
* First x86 chip to handle
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
data sets
* Reworked and expanded memory protection support including
paged virtual memory and virtual-86 mode, features required at the time by
Xenix
Xenix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for various microcomputer platforms, licensed by Microsoft from AT&T Corporation in the late 1970s. The Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) later acquired exclusive rights to the software, and ...
and
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
. This memory capability spurred the development and availability of
OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 ...
and is a fundamental requirement for modern operating systems like
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which i ...
,
Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for ...
, and
macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
* First used by Compaq in the
Deskpro 386. Used in desktop computing
* Unlike the DX naming convention of the 486 chips, it had no math co-processor
* Later renamed Intel386 DX
80386SX
* Introduced June 16, 1988
* Clock rates:
** 16 MHz, 2.5 MIPS
** 20 MHz, 3.1 MIPS, introduced January 25, 1989
** 25 MHz, 3.9 MIPS, introduced January 25, 1989
** 33 MHz, 5.1 MIPS, introduced October 26, 1992
* 32-bit internal architecture
* External data bus width: 16 bits
* External address bus width: 24 bits
* 275,000 transistors at 1 μm
* Addressable memory 16 MB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Narrower buses enable low-cost 32-bit processing
* Used in entry-level desktop and portable computing
* No math co-processor
* No commercial software used protected mode or virtual storage for many years
* Later renamed Intel386 SX
80376

* Introduced January 16, 1989; discontinued June 15, 2001
* Variant of 386SX intended for embedded systems
* No "real mode", starts up directly in "protected mode"
* Replaced by much more successful
80386EX from 1994
80386SL
The Intel 386, originally released as 80386 and later renamed i386, is a 32-bit microprocessor introduced in 1985. The first versions had 275,000 transistors[
* First chip specifically made for portable computers because of low power consumption of chip
* Highly integrated, includes cache, bus, and memory controllers
]
80386EX
* Introduced August 1994
* Variant of 80386SX intended for embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' ...
s
* Static core (i.e. may run as slowly (and thus, power efficiently) as desired) down to full halt
* On-chip peripherals:
** Clock and power management
** Timers/counters
** Watchdog timer
A watchdog timer (sometimes called a ''computer operating properly'' or ''COP'' timer, or simply a ''watchdog'') is an electronic or software timer that is used to detect and recover from computer malfunctions. Watchdog timers are widely used in ...
** Serial I/O units (sync and async) and parallel I/O
** DMA
DMA may refer to:
Arts
* ''DMA'' (magazine), a defunct dance music magazine
* Dallas Museum of Art, an art museum in Texas, US
* Danish Music Awards, an award show held in Denmark
* BT Digital Music Awards, an annual event in the UK
* Doctor of M ...
** RAM refresh
** JTAG
JTAG (named after the Joint Test Action Group which codified it) is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.
JTAG implements standards for on-chip instrumentation in electronic design autom ...
test logic
* Significantly more successful than the 80376
* Used aboard several orbiting satellites and microsatellites
* Used in NASA's FlightLinux project
32-bit processors: the 80486 range

80486DX
* Introduced April 10, 1989
* Clock rates:
** 25 MHz, 20 MIPS (16.8 SPECint92, 7.40 SPECfp92)
** 33 MHz, 27 MIPS (22.4 SPECint92 on Micronics M4P 128 KB L2), introduced May 7, 1990
** 50 MHz, 41 MIPS (33.4 SPECint92, 14.5 SPECfp92 on Compaq/50L 256 KB L2), introduced June 24, 1991
* Bus width: 32 bits
* 1.2 million transistors at 1 μm; the 50 MHz was at 0.8 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
80486SX
* Introduced April 22, 1991
* Clock rates:
** 16 MHz, 13 MIPS
** 20 MHz, 16.5 MIPS, introduced September 16, 1991
** 25 MHz, 20 MIPS (12 SPECint92), introduced September 16, 1991
** 33 MHz, 27 MIPS (15.86 SPECint92), introduced September 21, 1992
* Bus width: 32 bits
* 1.185 million transistors at 1 μm and 900,000 at 0.8 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
80486DX2
The Intel i486DX2, rumored as 80486DX2 (later renamed IntelDX2) is a CPU produced by Intel that was first introduced in 1992. The i486DX2 was nearly identical to the i486DX, but it had additional clock multiplier circuitry. It was the first chi ...
* Introduced March 3, 1992
* Runs at twice the speed of the external bus (FSB)
* Fits in Socket 3
* Clock rates:
** 40 MHz
** 50 MHz, 41 MIPS
** 66 MHz, 54 MIPS
* Officially named Intel486 DX2
* Family 4 model 3

80486SL
* Introduced November 9, 1992
* Clock rates:
** 20 MHz, 15.4 MIPS
** 25 MHz, 19 MIPS
** 33 MHz, 25 MIPS
* Bus width: 32 bits
* 1.4 million transistors at 0.8 μm
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Officially named Intel486 SL
* Used in notebook computers
* Family 4 model 4

80486DX4
* Introduced March 7, 1994
* Clock rates:
** 75 MHz, 53 MIPS (41.3 SPECint92, 20.1 SPECfp92 on Micronics M4P 256 KB L2)
** 100 MHz, 70.7 MIPS (54.59 SPECint92, 26.91 SPECfp92 on Micronics M4P 256 KB L2)
* 1.6 million transistors at 0.6 μm
* Bus width: 32 bits
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Socket 3
Socket 3 was a series of CPU sockets for various x86 microprocessors. It was sometimes found alongside a secondary socket designed for a math coprocessor chip, such as the 487. Socket 3 resulted from Intel's creation of lower voltage microproce ...
168-pin PGA Package, or 208 sq. ftP package
* Officially named Intel486 DX4
* Used in high performance entry-level desktops and value notebooks
* Family 4 model 8
32-bit processors: P5 microarchitecture


Original
Pentium
Pentium is a brand used for a series of x86 architecture-compatible microprocessors produced by Intel. The original Pentium processor from which the brand took its name was first released on March 22, 1993. After that, the Pentium II and P ...
* Bus width: 64 bits
* System bus clock rate 60 or 66 MHz
* Address bus: 32 bits
* Addressable memory 4 GB
* Virtual memory 64 TB
* Superscalar
A superscalar processor is a CPU that implements a form of parallelism called instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. In contrast to a scalar processor, which can execute at most one single instruction per clock cycle, a sup ...
architecture
* Runs on 3.3 volts (except the very first generation "P5")
* Used in desktops
* 8 KB of instruction cache
* 8 KB of data cache
* P5 – 0.8 μm process technology
** Introduced March 22, 1993
** 3.1 million transistors
** The only Pentium to run on 5 Volts
** Socket 4
Socket 4, presented in 1993, was the first CPU socket designed for the early P5 Pentium microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or ...
273 pin PGA Package
** Package dimensions 2.16 in × 2.16 in
** Family 5 model 1
** Variants
*** 60 MHz, 100 MIPS (70.4 SPECint92, 55.1 SPECfp92 on Xpress 256 KB L2)
*** 66 MHz, 112 MIPS (77.9 SPECint92, 63.6 SPECfp92 on Xpress 256 KB L2)
* P54 – 0.6 μm process technology
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
** 3.2 million transistors
** Variants
*** 75 MHz, 126.5 MIPS (2.31 SPECint95, 2.02 SPECfp95 on Gateway P5 256K L2)
**** Introduced October 10, 1994
*** 90, 100 MHz, 149.8 and 166.3 MIPS respectively (2.74 SPECint95, 2.39 SPECfp95 on Gateway P5 256K L2 and 3.30 SPECint95, 2.59 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1ML2 respectively)
**** Introduced March 7, 1994
* P54CQS – 0.35 μm process technology
** Socket 5 296/320 pin PGA package
** 3.2 million transistors
** Variants
*** 120 MHz, 203 MIPS (3.72 SPECint95, 2.81 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced March 27, 1995
* P54CS – 0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
**
P54CS – 0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
** Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by ...
296/321-pin PGA package
*** 200 MHz, 270 MIPS (5.47 SPECint95, 3.68 SPECfp95)
**** Introduced June 10, 1996

Pentium with MMX Technology
* P55C – 0.35 μm process technology
** Introduced January 8, 1997
** Intel MMX (instruction set)
MMX is a ''single instruction, multiple data'' ( SIMD) instruction set architecture designed by Intel, introduced on January 8, 1997 with its Pentium P5 (microarchitecture) based line of microprocessors, named "Pentium with MMX Technology". It ...
support
** Socket 7
Socket 7 is a physical and electrical specification for an x86-style CPU socket on a personal computer motherboard. It was released in June 1995. The socket supersedes the earlier Socket 5, and accepts P5 Pentium microprocessors manufactured by ...
296/321 pin PGA (pin grid array) package
** 16 KB L1 instruction cache
** 16 KB data cache
** 4.5 million transistors
** System bus clock rate 66 MHz
** Basic P55C is family 5 model 4, mobile are family 5 model 7 and 8
** Variants
*** 166, 200 MHz introduced January 8, 1997
*** 233 MHz introduced June 2, 1997
*** 133 MHz (Mobile)
*** 166, 266 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 12, 1998
*** 200, 233 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 8, 1997
*** 300 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 7, 1999
32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform large calcula ...
processors: P6/Pentium M
The Pentium M is a family of mobile 32-bit single-core x86 microprocessors (with the modified Intel P6 (microarchitecture), P6 microarchitecture) introduced in March 2003 and forming a part of the Intel Centrino#Carmel platform (2003), Carmel no ...
microarchitecture

Pentium Pro
The Pentium Pro is a sixth-generation x86 microprocessor developed and manufactured by Intel and introduced on November 1, 1995. It introduced the P6 microarchitecture (sometimes termed i686) and was originally intended to replace the original ...
* Introduced November 1, 1995
* Multichip Module (2 die)
* Precursor to Pentium II and III
* Primarily used in server systems
* Socket 8 processor package (387 pins; Dual SPGA)
* 5.5 million transistors
* Family 6 model 1
* 0.6 μm process technology
** 16 KB L1 cache
** 256 KB integrated L2 cache
** 60 MHz system bus clock rate
** Variants
*** 150 MHz
* 0.35 μm process technology, (two die, a 0.35 μm CPU with 0.6 μm L2 cache)
** 5.5 million transistors
** 512 KB or 256 KB integrated L2 cache
** 60 or 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Variants
*** 150 MHz (60 MHz bus clock rate, 256 KB 0.5 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 166 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 512 KB 0.35 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 180 MHz (60 MHz bus clock rate, 256 KB 0.6 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 200 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 256 KB 0.6 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 200 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 512 KB 0.35 μm cache) introduced November 1, 1995
*** 200 MHz (66 MHz bus clock rate, 1 MB 0.35 μm cache) introduced August 18, 1997
Pentium II
The Pentium II brand refers to Intel's sixth-generation microarchitecture (" P6") and x86-compatible microprocessors introduced on May 7, 1997. Containing 7.5 million transistors (27.4 million in the case of the mobile Dixon with 256 KB ...
* Introduced May 7, 1997
* Pentium Pro with MMX and improved 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
performance
* 242-pin Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implem ...
(SEC) processor package
* Voltage identification pins
* 7.5 million transistors
* 32 KB L1 cache
* 512 KB frequency external L2 cache
* The ''Performance Enhanced'' mobile Pentium II (codenamed Dixon) had a full-speed 256 KB L2 cache
* Klamath – 0.35 μm process technology (233, 266, 300 MHz)
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Family 6 model 3
** Variants
*** 233, 266, 300 MHz introduced May 7, 1997
* Deschutes – 0.25 μm process technology (333, 350, 400, 450 MHz)
** Introduced January 26, 1998
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate (''333 MHz variant''), 100 MHz system bus clock rate for all subsequent models
** Family 6 model 5
** Variants
*** 333 MHz introduced January 26, 1998
*** 350, 400 MHz introduced April 15, 1998
*** 450 MHz introduced August 24, 1998
*** 233, 266 MHz (Mobile) introduced April 2, 1998
*** 333 MHz Pentium II Overdrive processor for Socket 8 Introduced August 10, 1998
*** 300 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 9, 1998
*** 333 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 25, 1999
Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed comp ...
(Pentium II-based)
* Covington – 0.25 μm process technology
** Introduced April 15, 1998
** 242-pin Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implem ...
SEPP (Single Edge Processor Package)
** 7.5 million transistors
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Slot 1
** 32 KB L1 cache
** No L2 cache
** Variants
*** 266 MHz introduced April 15, 1998
*** 300 MHz introduced June 9, 1998
* Mendocino – 0.25 μm process technology
** Introduced August 24, 1998
** 242-pin Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implem ...
SEPP (Single Edge Processor Package), Socket 370
Socket 370 (also known as the PGA370 socket) is a CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to first complement and later replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number ...
PPGA package
** 19 million transistors
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate
** Slot 1, Socket 370
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 128 KB integrated cache
** Family 6 model 6
** Variants
*** 300, 333 MHz introduced August 24, 1998
*** 366, 400 MHz introduced January 4, 1999
*** 433 MHz introduced March 22, 1999
*** 466 MHz
*** 500 MHz introduced August 2, 1999
*** 533 MHz introduced January 4, 2000
*** 266 MHz (Mobile)
*** 300 MHz (Mobile)
*** 333 MHz (Mobile) introduced April 5, 1999
*** 366 MHz (Mobile)
*** 400 MHz (Mobile)
*** 433 MHz (Mobile)
*** 450 MHz (Mobile) introduced February 14, 2000
*** 466 MHz (Mobile)
*** 500 MHz (Mobile) introduced February 14, 2000
Pentium II Xeon ''(chronological entry)''
* Introduced June 29, 1998
Pentium III
The Pentium III (marketed as Intel Pentium III Processor, informally PIII or P3) brand refers to Intel's 32-bit x86 desktop and mobile CPUs based on the sixth-generation P6 microarchitecture introduced on February 28, 1999. The brand's initial ...
* Katmai – 0.25 μm process technology
** Introduced February 26, 1999
** Improved PII (i.e. P6-based core) now including Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series of Central processing units (CPUs ...
(SSE)
** 9.5 million transistors
** 512 KB (512 × 1024 B) bandwidth L2 External cache
** 242-pin Slot 1
Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implem ...
SECC2 (Single Edge Contact cartridge 2) processor package
** System bus clock rate 100 MHz, 133 MHz (B-models)
** Slot 1
** Family 6 model 7
** Variants
*** 450, 500 MHz introduced February 26, 1999
*** 550 MHz introduced May 17, 1999
*** 600 MHz introduced August 2, 1999
*** 533, 600 MHz introduced (133 MHz bus clock rate) September 27, 1999
* Coppermine – 0.18 μm process technology
** Introduced October 25, 1999
** 28.1 million transistors
** 256 KB (512 × 1024 B) Advanced Transfer L2 cache (integrated)
** 242-pin Slot-1 SECC2 (Single Edge Contact cartridge 2) processor package, 370-pin FC-PGA (flip-chip pin grid array) package
** System Bus clock rate 100 MHz (E-models), 133 MHz (EB models)
** Slot 1, Socket 370
** Family 6 model 8
** Variants
*** 500 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate)
*** 533 MHz
*** 550 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate)
*** 600 MHz
*** 600 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate)
*** 650 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 667 MHz introduced October 25, 1999
*** 700 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 733 MHz introduced October 25, 1999
*** 750, 800 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced December 20, 1999
*** 850 MHz (100 MHz bus clock rate) introduced March 20, 2000
*** 866 MHz introduced March 20, 2000
*** 933 MHz introduced May 24, 2000
*** 1000 MHz introduced March 8, 2000 (not widely available at time of release)
*** 1100 MHz
*** 1133 MHz (first version recalled, later re-released)
*** 400, 450, 500 MHz (Mobile) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 600, 650 MHz (Mobile) introduced January 18, 2000
*** 700 MHz (Mobile) introduced April 24, 2000
*** 750 MHz (Mobile) introduced June 19, 2000
*** 800, 850 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 25, 2000
*** 900, 1000 MHz (Mobile) introduced March 19, 2001
* Tualatin – 0.13 μm process technology
** Introduced July 2001
** 28.1 million transistors
** 32 KB (32 × 1024 B) L1 cache
** 256 KB or 512 KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache (integrated)
** 370-pin FC-PGA2
A pin grid array (PGA) is a type of integrated circuit packaging. In a PGA, the package is square or rectangular, and the pins are arranged in a regular array on the underside of the package. The pins are commonly spaced 2.54 mm (0.1") a ...
(flip-chip pin grid array) package
** 133 MHz system bus clock rate
** Socket 370
** Family 6 model 11
** Variants
*** 1133 MHz (256 KB L2)
*** 1133 MHz (512 KB L2)
*** 1200 MHz
*** 1266 MHz (512 KB L2)
*** 1333 MHz
*** 1400 MHz (512 KB L2)
Pentium II
Xeon
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same a ...
and Pentium III Xeon
* PII Xeon
** Variants
*** 400 MHz introduced June 29, 1998
*** 450 MHz (512 KB L2 cache) introduced October 6, 1998
*** 450 MHz (1 MB and 2 MB L2 cache) introduced January 5, 1999
* PIII Xeon
** Introduced October 25, 1999
** 9.5 million transistors at 0.25 μm or 28 million at 0.18 μm
** L2 cache is 256 KB, 1 MB, or 2 MB Advanced Transfer Cache (Integrated)
** Processor Package Style is Single Edge Contact Cartridge (S.E.C.C.2) or SC330
** System Bus clock rate 133 MHz (256 KB L2 cache) or 100 MHz (1–2 MB L2 cache)
** System Bus width: 64 bits
** Addressable memory: 64 GB
** Used in two-way servers and workstations (256 KB L2) or 4- and 8-way servers (1–2 MB L2)
** Family 6 model 10
** Variants
*** 500 MHz ( 0.25 μm process) introduced March 17, 1999
*** 550 MHz (0.25 μm process) introduced August 23, 1999
*** 600 MHz ( 0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 667 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 733 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced October 25, 1999
*** 800 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced January 12, 2000
*** 866 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced April 10, 2000
*** 933 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache)
*** 1000 MHz (0.18 μm process, 256 KB L2 cache) introduced August 22, 2000
*** 700 MHz (0.18 μm process, 1–2 MB L2 cache) introduced May 22, 2000
Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed comp ...
(Pentium III Coppermine-based)
* Coppermine-128, 0.18 μm process technology
** Introduced March, 2000
** Streaming SIMD Extensions
In computing, Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE) is a single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) instruction set extension to the x86 architecture, designed by Intel and introduced in 1999 in their Pentium III series of Central processing units (CPUs ...
(SSE)
** Socket 370
Socket 370 (also known as the PGA370 socket) is a CPU socket first used by Intel for Pentium III and Celeron processors to first complement and later replace the older Slot 1 CPU interface on personal computers. The "370" refers to the number ...
, FC-PGA processor package
** 28.1 million transistors
** 66 MHz system bus clock rate, 100 MHz system bus clock rate from January 3, 2001
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 128 KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache
** Family 6 model 8
** Variants
*** 533 MHz
*** 566 MHz
*** 600 MHz
*** 633, 667, 700 MHz introduced June 26, 2000
*** 733, 766 MHz introduced November 13, 2000
*** 800 MHz introduced January 3, 2001
*** 850 MHz introduced April 9, 2001
*** 900 MHz introduced July 2, 2001
*** 950, 1000, 1100 MHz introduced August 31, 2001
*** 550 MHz (Mobile)
*** 600, 650 MHz (Mobile) introduced June 19, 2000
*** 700 MHz (Mobile) introduced September 25, 2000
*** 750 MHz (Mobile) introduced March 19, 2001
*** 800 MHz (Mobile)
*** 850 MHz (Mobile) introduced July 2, 2001
*** 600 MHz (LV Mobile)
*** 500 MHz (ULV Mobile) introduced January 30, 2001
*** 600 MHz (ULV Mobile)
XScale ''(chronological entry – non-x86 architecture)''
* Introduced August 23, 2000
Pentium 4 (not 4EE, 4E, 4F), Itanium, P4-based Xeon, Itanium 2 ''(chronological entries)''
* Introduced April 2000 – July 2002
Pentium III Tualatin-based
* Tualatin – 0.13 μm process technology
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 512KB Advanced Transfer L2 cache
** 133 MHz system bus clock rate
** Socket 370
** Variants
*** 1.0 GHz
*** 1.13 GHz
*** 1.26 GHz
*** 1.4 GHz
Celeron
Celeron is Intel's brand name for low-end IA-32 and x86-64 computer microprocessor models targeted at low-cost personal computers.
Celeron processors are compatible with IA-32 software. They typically offer less performance per clock speed comp ...
(Pentium III Tualatin-based)
* Tualatin Celeron – 0.13 μm process technology
** 32 KB L1 cache
** 256  This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of
This generational list of Intel processors attempts to present all of 







 Introduced in the third quarter of 1974, these bit-slicing components used bipolar Schottky transistors. Each component implemented two bits of a processor function; packages could be interconnected to build a processor with any desired word length.
Members of the family:
* 3001 – Microcontrol Unit
* 3002 – 2-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit slice
* 3003 – Look-ahead Carry Generator
* 3205 – High-performance 1 of 8 Binary Decoder
* 3207 – Quad Bipolar-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver
* 3208 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3210 – TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3211 – ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3212 – Multimode Latch Buffer
* 3214 – Interrupt Control Unit
* 3216 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3222 – Refresh Controller for 4K (4096 B) NMOS DRAMs
* 3226 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3232 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 4K DRAMs
* 3242 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 16K (16 × 1024 B) DRAMs
* 3245 – Quad Bipolar TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3246 – Quad Bipolar ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3404 – High-performance 6-bit Latch
* 3408 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3505 – Next generation processor
Bus width 2''n'' bits data/address (depending on number ''n'' of slices used)
Introduced in the third quarter of 1974, these bit-slicing components used bipolar Schottky transistors. Each component implemented two bits of a processor function; packages could be interconnected to build a processor with any desired word length.
Members of the family:
* 3001 – Microcontrol Unit
* 3002 – 2-bit Arithmetic Logic Unit slice
* 3003 – Look-ahead Carry Generator
* 3205 – High-performance 1 of 8 Binary Decoder
* 3207 – Quad Bipolar-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver
* 3208 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3210 – TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3211 – ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and High Voltage Clock Driver
* 3212 – Multimode Latch Buffer
* 3214 – Interrupt Control Unit
* 3216 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3222 – Refresh Controller for 4K (4096 B) NMOS DRAMs
* 3226 – Parallel, Inverting Bi-Directional Bus Driver
* 3232 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 4K DRAMs
* 3242 – Address Multiplexer and Refresh Counter for 16K (16 × 1024 B) DRAMs
* 3245 – Quad Bipolar TTL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3246 – Quad Bipolar ECL-to-MOS Level Shifter and Driver for 4K
* 3404 – High-performance 6-bit Latch
* 3408 – Hex Sense Amp and Latch for MOS Memories
* 3505 – Next generation processor
Bus width 2''n'' bits data/address (depending on number ''n'' of slices used)





 * Introduced January 16, 1989; discontinued June 15, 2001
* Variant of 386SX intended for embedded systems
* No "real mode", starts up directly in "protected mode"
* Replaced by much more successful 80386EX from 1994
* Introduced January 16, 1989; discontinued June 15, 2001
* Variant of 386SX intended for embedded systems
* No "real mode", starts up directly in "protected mode"
* Replaced by much more successful 80386EX from 1994








 P54CS – 0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
**
P54CS – 0.35 μm process technology
** 3.3 million transistors
** 90 mm2 die size
** Family 5 model 2
** Variants
** Socket 5 296/320-pin PGA package
*** 133 MHz, 218.9 MIPS (4.14 SPECint95, 3.12 SPECfp95 on Xpress 1 MB L2)
**** Introduced June 12, 1995
*** 150, 166 MHz, 230 and 247 MIPS respectively
**** Introduced January 4, 1996
** 
