Leicester ( ) is a
city
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
,
unitary authority
A unitary authority is a type of local government, local authority in New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Unitary authorities are responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are ...
area, and the
county town
In Great Britain and Ireland, a county town is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county, and the place where public representatives are elected to parliament. Following the establishment of county councils in ...
of
Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in the East Midlands of England. It is bordered by Derbyshire, Nottinghamshire and Lincolnshire to the north, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire to the south-east, Warw ...
in the
East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire (except for North Lincolnshire and North East ...
of England. It is the largest city in the East Midlands with a population of in .
The greater
Leicester urban area
The Leicester Built Up Area (BUA), Leicester Urban Area, or Greater Leicester is an urban agglomeration defined by the Office of National Statistics (ONS), centred on the City of Leicester in the East Midlands, England. With a population of 559 ...
had a population of 559,017 in 2021, making it the 11th most populous in England, and the
13th most populous in the United Kingdom. A 2023 report ranked Leicester 16th out of the 50 largest UK cities on a range of economic measures, and the first of seven East Midlands cities.
The city lies on the
River Soar
The River Soar () is a major tributary of the River Trent in the East Midlands as well as the principal river of Leicestershire, England. The source of the river is midway between Hinckley and Lutterworth. The river then flows north throug ...
and is approximately north-northwest of London, east-northeast of
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
and northeast of
Coventry
Coventry ( or rarely ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands (county), West Midlands county, in England, on the River Sherbourne. Coventry had been a large settlement for centurie ...
.
Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located south-east of Sheffield and nor ...
and
Derby
Derby ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area on the River Derwent, Derbyshire, River Derwent in Derbyshire, England. Derbyshire is named after Derby, which was its original co ...
lie around to the north and northwest respectively, whilst
Peterborough
Peterborough ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in the City of Peterborough district in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The city is north of London, on the River Nene. A ...
is located to the east. Leicester is close to the eastern end of the
National Forest National Forest may refer to:
* National forest or state forest, a forest administered or protected by a sovereign state
** National forest (Brazil)
** National forest (France)
** National forest (United States)
** State Forests (Poland)
** The N ...
.
Leicester has a long history extending into ancient times. The site of an Iron Age
oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread acros ...
, it developed into the
Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
town of
Ratae Corieltauvorum
Ratae Corieltauvorum or simply Ratae was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Leicester, located in the English county of Leicestershire.
Name
''Ratae'' is a latinate form of the Brittonic word for "ramparts" (cf ...
following the
conquest
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or Coercion (international relations), coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or ...
. The ruins of Ratae were later settled by the
Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
s, and then captured by the
Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
who made it one of the
Five Boroughs of the Danelaw
The Five Boroughs or The Five Boroughs of the Danelaw were the five main towns of Danish Mercia (what is now the East Midlands) under the Danelaw. These were Derby, Leicester, Lincoln, Nottingham and Stamford. The first four later became coun ...
.
After the
Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
the town came under the authority of the
Beaumont and
De Montfort Earls
Earl () is a rank of the nobility in the United Kingdom. In modern Britain, an earl is a member of the peerage, ranking below a marquess and above a viscount. A feminine form of ''earl'' never developed; instead, ''countess'' is used.
The titl ...
, most notably the famous rebel
Simon de Montfort
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, 1st Earl of Chester ( – 4 August 1265), also known as Simon V de Montfort, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the baronial opposition to the rule of ...
. After his death in 1265 the town passed to the
House of Lancaster
The House of Lancaster was a cadet branch of the royal House of Plantagenet. The first house was created when King Henry III of England created the Earldom of Lancasterfrom which the house was namedfor his second son Edmund Crouchback in 1267 ...
and
Leicester Castle
Leicester Castle is in the city of the same name in the English county of Leicestershire. The complex is situated in the west of Leicester City Centre, between Saint Nicholas Circle to the north and De Montfort University to the south. A lar ...
became one of their strongholds, a royal residence when the family came to the throne in 1399. Leicester therefore became an important town in the wider nation, the meeting place of the parliaments of 1318,
1414
Year 1414 ( MCDXIV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar.
Events
January–March
* January 7 – Michael Küchmeister von Sternberg becomes the 28th Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, succeeding Heinrich ...
, and
1450, and a place frequently visited by the King and his court. Most famously
King Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
spent his last days in the town before his death at the
Battle of Bosworth
The Battle of Bosworth or Bosworth Field ( ) was the last significant battle of the Wars of the Roses, the civil war between the houses of Lancaster and York that extended across England in the latter half of the 15th century. Fought on 22 ...
and was buried there in August 1485. In the
Early Modern era
The early modern period is a historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date ...
Puritanism
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should ...
flourished in Leicester and the town was a supporter of the
Parliamentarian cause in the
Civil War
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same Sovereign state, state (or country). The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies.J ...
. In the
Victorian age
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed th ...
the town became known for its
hosiery
Hosiery, (, ) also referred to as legwear, describes garments worn directly on the foot, feet and human leg, legs. The term originated as the collective term for products of which a maker or seller is termed a hosier; and those products are also ...
and shoe manufacturing industries. It also rapidly expanded in population and size eventually gaining
city status
City status is a symbolic and legal designation given by a monarch, national or subnational government. A municipality may receive city status because it already has the qualities of a city, or because it has some special purpose.
Historically, ci ...
in 1919. Since the mid-20th century, immigration from countries of the
British Commonwealth
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an international association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire
The B ...
has seen Leicester become an ethnically diverse city, and one of the largest urban centres of the
Midlands
The Midlands is the central region of England, to the south of Northern England, to the north of southern England, to the east of Wales, and to the west of the North Sea. The Midlands comprises the ceremonial counties of Derbyshire, Herefor ...
.
Leicester is at the intersection of two railway lines: the
Midland Main Line
The Midland Main Line (MML), sometimes also spelt Midland Mainline, is a major Rail transport in Great Britain, railway line from London to Sheffield in Yorkshire via the East Midlands. It comprises the lines from London's St Pancras railway ...
and the
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
to
London Stansted Airport
Stansted Airport is an international airport serving London, the capital of England and the United Kingdom. It is located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Uttlesford, Essex, northeast of Central London.
As London's Airports of London, third-bu ...
line. It is also at the confluence of the
M1/
M69 motorway
The M69 is a dual three-lane dual carriageway motorway in Leicestershire and Warwickshire, England. It runs between junction 21 of the M1 near Leicester and junction 2 of the M6 near Coventry. It opened in 1977.
History
The motorway, also k ...
s and the
A6/
A46 trunk routes.
Leicester Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Saint Martin, Leicester, commonly known as Leicester Cathedral, is a Church of England cathedral in Leicester, England, and the seat of the Bishop of Leicester. One of the city centre's five surviving medieval ch ...
is home to the new
tomb
A tomb ( ''tumbos'') or sepulchre () is a repository for the remains of the dead. It is generally any structurally enclosed interment space or burial chamber, of varying sizes. Placing a corpse into a tomb can be called '' immurement'', alth ...
of Richard III who was reburied in the cathedral in 2015 after
being discovered nearby in the foundations of the lost
Greyfriars chapel, more than 500 years after his death. In sporting terms, Leicester is the home to
football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
club
Leicester City
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest city in the East Midlands with a popula ...
and
rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby union: 15 players per side
*** American flag rugby
*** Beach rugby
*** Mini rugby
*** Rugby sevens, 7 players per side
*** Rugby tens, 10 players per side
*** Snow rugby
*** Tou ...
club
Leicester Tigers
Leicester Tigers (officially Leicester Football Club) are a professional rugby union club based in Leicester, England. They play in Premiership Rugby, England's top division of rugby.
The club was founded in 1880 and since 1892 plays its home ...
.
Name
The name of Leicester comes from
Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
. It is first recorded in Latinised form in the early ninth century as ''Legorensis civitatis'' and in Old English itself in an ''
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons.
The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the ninth century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of ...
'' entry for 924 as ' (and, in various spellings, frequently thereafter). In the ''
Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
'' of 1086, it is recorded as '.
[''The Cambridge Dictionary of English Place-Names Based on the Collections of the English Place-Name Society'', ed. by Victor Watts (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2004), s.v. ''LEICESTER'', ''LEIRE''.]
The first element of the name is the name of a people, the ''Ligore'' (whose name appears in ''Ligera ceastre'' in the
genitive
In grammar, the genitive case ( abbreviated ) is the grammatical case that marks a word, usually a noun, as modifying another word, also usually a noun—thus indicating an attributive relationship of one noun to the other noun. A genitive can ...
plural form); their name came in turn from the river Ligor (now the
River Soar
The River Soar () is a major tributary of the River Trent in the East Midlands as well as the principal river of Leicestershire, England. The source of the river is midway between Hinckley and Lutterworth. The river then flows north throug ...
), the origin of whose name is uncertain but thought to be from
Brittonic (possibly cognate with the name of the
Loire
The Loire ( , , ; ; ; ; ) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône.
It rises in the so ...
).
[ citing Wilford, ''Asiatick Researches'' vol. ii. No. 2 (1812)]
p. 45
"The learned Somner says that the river which runs by it eicesterwas formerly called Leir by the same contraction rom Legora
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* R ...
and it is probably the river Liar of the anonymous geographer. Mr. Somner, if I be not mistaken, places the original own of ''Ligora'' near the source of the Lear, now the Soar".[Thompson (1849)]
Appendix B: Leograceaster—The Saxon Name of Leicester, pp. 448 f.
; Thompson (1849)
pp. 7 f
.
The second element of the name is the Old English word ''ceaster'' ("(Roman) fort, fortification, town", itself borrowed from Latin ''
castrum
''Castra'' () is a Latin language, Latin term used during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire for a military 'camp', and ''castrum'' () for a 'Fortification, fort'. Either could refer to a building or plot of land, used as a fortified milita ...
'').
A list of British cities in the ninth-century ''
History of the Britons
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions have ...
'' includes one '; Leicester has been proposed as the place to which this refers (and the
Welsh name for Leicester is '). But this identification is not certain.
Based on the Welsh name (given as ''Kaerleir''),
Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth (; ; ) was a Catholic cleric from Monmouth, Wales, and one of the major figures in the development of British historiography and the popularity of tales of King Arthur. He is best known for his chronicle '' The History of ...
proposed a king
Leir of Britain
Leir was a legendary king of the Britons whose story was recounted by Geoffrey of Monmouth in his pseudohistorical 12th-century '' History of the Kings of Britain''. According to Geoffrey's genealogy of the British dynasty, Leir reigned arou ...
as an
eponymous founder
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovati ...
in his ''
Historia Regum Britanniae
(''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a fictitious account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. It chronicles the lives of the List of legendary kings o ...
'' (12th century).
[ Geoffrey, Vol. II, Ch. 11.]
History
Prehistory
Leicester is one of the oldest cities in England, with a history going back at least two millennia. The
native
Native may refer to:
People
* '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood
* '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth
* Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory
** Nat ...
Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
settlement encountered by the
Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
at the site seems to have developed in the 2nd or 1st centuries
BC, around a century or so before the arrival of the Romans. Little is known about this settlement or the condition of the
River Soar
The River Soar () is a major tributary of the River Trent in the East Midlands as well as the principal river of Leicestershire, England. The source of the river is midway between Hinckley and Lutterworth. The river then flows north throug ...
at this time, although
roundhouses from this era have been excavated and seem to have clustered along roughly of the east bank of the Soar. This area of the Soar was split into two channels: a main stream to the east and a narrower channel on the west, with a presumably marshy island between. The settlement seems to have controlled a ford across the larger channel. The
later Roman name was a
latinate
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion o ...
form of the
Brittonic word for "ramparts" (cf.
Gaelic
Gaelic (pronounced for Irish Gaelic and for Scots Gaelic) is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". It may refer to:
Languages
* Gaelic languages or Goidelic languages, a linguistic group that is one of the two branches of the Insul ...
''
rath'' and the nearby villages of
Ratby and
Ratcliffe[), suggesting the site was an ]oppidum
An ''oppidum'' (: ''oppida'') is a large fortified Iron Age Europe, Iron Age settlement or town. ''Oppida'' are primarily associated with the Celts, Celtic late La Tène culture, emerging during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, spread acros ...
. The plural form of the name suggests it was initially composed of several villages.[Thompson (1849)]
Appendix A: Ratæ—Roman Leicester, pp. 443 ff
. The Celtic tribe
This is a list of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes.
Continental Celts
Continental Celts were the Celtic peoples that inhabited mainland Europe and Anatolia (also known as Asia Minor). In the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, Celts inhabited a large ...
holding the area was later recorded as the "Coritani
The Corieltauvi (also the Coritani, and the Corieltavi) were a Celtic tribe living in Britain prior to the Roman conquest, and thereafter a ''civitas'' of Roman Britain. Their territory was in what is now the English East Midlands. They were bor ...
ans" but an inscription recovered in 1983 showed this to have been a corruption of the original "Corieltauvi
The Corieltauvi (also the Coritani, and the Corieltavi) were a Celtic tribe living in British Iron Age, Britain prior to the Roman conquest of Britain, Roman conquest, and thereafter a ''civitas'' of Roman Britain. Their territory was in what is ...
ans".East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Derbyshire, Leicestershire, Lincolnshire (except for North Lincolnshire and North East ...
.
Roman
 It is believed that the
It is believed that the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
arrived in the Leicester area around AD 47, during their conquest
Conquest involves the annexation or control of another entity's territory through war or Coercion (international relations), coercion. Historically, conquests occurred frequently in the international system, and there were limited normative or ...
of southern Britain
South Britain is a term which was occasionally used in the 17th and 18th centuries, for England and Wales in relation to their position in the southern half of the island of Great Britain. It was used mainly by Scottish writers, in apposition to ...
.Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia ( Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis ( Ilchester), Aquae Sulis ( Bat ...
, a Roman road
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Em ...
between the legionary camps at Isca (Exeter
Exeter ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and the county town of Devon in South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter w ...
) and Lindum
Lindum Colonia was the Roman settlement which is now the City of Lincoln in Lincolnshire. It was founded as a Roman Legionary Fortress during the reign of the Emperor Nero (58–68 AD) or possibly later. Evidence from Roman tombstones ...
(Lincoln
Lincoln most commonly refers to:
* Abraham Lincoln (1809–1865), the 16th president of the United States
* Lincoln, England, cathedral city and county town of Lincolnshire, England
* Lincoln, Nebraska, the capital of Nebraska, U.S.
* Lincoln (na ...
). It remains unclear whether the Romans fortified and garrisoned the location, but it slowly developed from around the year 50 onwards as the tribal capital of the Corieltauvians under the name Ratae Corieltauvorum
Ratae Corieltauvorum or simply Ratae was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Leicester, located in the English county of Leicestershire.
Name
''Ratae'' is a latinate form of the Brittonic word for "ramparts" (cf ...
. In the 2nd century, it received a forum
Forum or The Forum may refer to:
Common uses
*Forum (legal), designated space for public expression in the United States
*Forum (Roman), open public space within a Roman city
**Roman Forum, most famous example
* Internet forum, discussion board ...
and bathhouse
Bathhouse may refer to:
* Public baths, public facilities for bathing
* Gay bathhouse
A gay bathhouse, also known as a gay sauna or a gay steambath, is a public bath targeted towards Gay men, gay and Bisexuality, bisexual men. In gay slang, a ...
. In 2013, the discovery of a Roman cemetery found just outside the old city walls and dating back to AD 300 was announced.Jewry Wall
The Jewry Wall is a substantial ruined wall of 2nd-century Roman masonry, with two large archways, in Leicester, England. It stands alongside St Nicholas' Circle and St Nicholas' Church. It formed the west wall of a public building in (Ro ...
; recovered artifacts are displayed at the adjacent museum.
Medieval
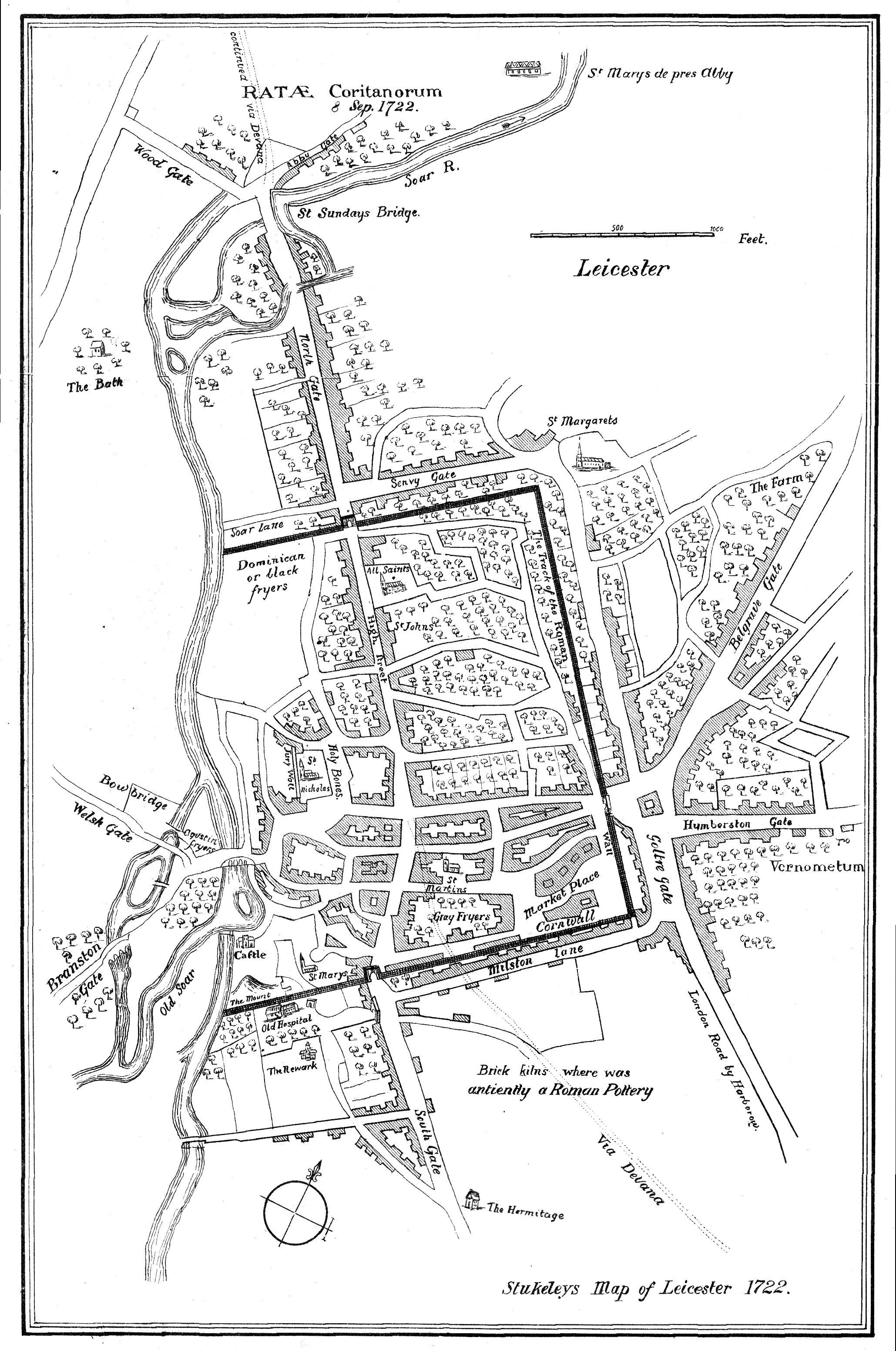 Knowledge of the town following the
Knowledge of the town following the Roman withdrawal from Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain occurred as the military forces of Roman Britain withdrew to defend or seize the Western Roman Empire's continental core, leaving behind an autonomous post-Roman Britain. In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus wit ...
is limited. It seems to have been continually occupied after Roman protection ceased through the 5th and 6th centuries, although with a significantly reduced population. Its memory was preserved as the 'Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
().
Theodor Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; ; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a German classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicists of the 19th ce ...
(). ''Historia Brittonum'', VI. Composed after AD 830. Hosted at Latin Wikisource.History of the Britons
''The History of the Britons'' () is a purported history of early Britain written around 828 that survives in numerous recensions from after the 11th century. The ''Historia Brittonum'' is commonly attributed to Nennius, as some recensions have ...
''.[Ford, David Nash.]
The 28 Cities of Britain
" at Britannia. 2000. Following the Saxon invasion of Britain
The settlement of Great Britain by Germanic peoples from continental Europe led to the development of an Anglo-Saxon cultural identity and a shared Germanic language—Old English—whose closest known relative is Old Frisian, spoken on the o ...
, Leicester was occupied by the Middle Angles
The Middle Angles were an important ethnic or cultural group within the larger kingdom of Mercia in England in the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon period.
Origins and territory
It is likely that Angles (tribe), Angles broke into the English Midlands ...
and subsequently administered by the kingdom of Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
. It was elevated to a bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
in either 679 or 680; this see survived until the 9th century, when Leicester was captured by Danish Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
. Their settlement became one of the Five Burghs
The Five Boroughs or The Five Boroughs of the Danelaw were the five main towns of Danish Mercia (what is now the East Midlands) under the Danelaw. These were Derby, Leicester, Lincoln, Nottingham and Stamford. The first four later became co ...
of the Danelaw
The Danelaw (, ; ; ) was the part of History of Anglo-Saxon England, England between the late ninth century and the Norman Conquest under Anglo-Saxon rule in which Danes (tribe), Danish laws applied. The Danelaw originated in the conquest and oc ...
, although this position was short-lived. The Saxon bishop, meanwhile, fled to Dorchester-on-Thames
Dorchester on Thames is a historic village and civil parish in South Oxfordshire, Oxfordshire, England, located about 9 miles (14 km) southeast of Oxford at the confluence of the River Thames and River Thame.
The village has evidence of prehi ...
and Leicester did not become a bishopric again until the Church of became Leicester Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Saint Martin, Leicester, commonly known as Leicester Cathedral, is a Church of England cathedral in Leicester, England, and the seat of the Bishop of Leicester. One of the city centre's five surviving medieval ch ...
in 1927. The settlement was recorded under the name ''Ligeraceaster'' in the early 10th century.
 Following the
Following the Norman conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
, Leicester was recorded by William
William is a masculine given name of Germanic languages, Germanic origin. It became popular in England after the Norman Conquest, Norman conquest in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle ...
's Domesday Book
Domesday Book ( ; the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book") is a manuscript record of the Great Survey of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 at the behest of William the Conqueror. The manuscript was originally known by ...
as ''Ledecestre''. It was noted as a city (''civitas'') but lost this status in the 11th century owing to power struggles between the Church
Church may refer to:
Religion
* Church (building), a place/building for Christian religious activities and praying
* Church (congregation), a local congregation of a Christian denomination
* Church service, a formalized period of Christian comm ...
and the aristocracy
Aristocracy (; ) is a form of government that places power in the hands of a small, privileged ruling class, the aristocracy (class), aristocrats.
Across Europe, the aristocracy exercised immense Economy, economic, Politics, political, and soc ...
and did not become a legal city again until 1919.
Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth (; ; ) was a Catholic cleric from Monmouth, Wales, and one of the major figures in the development of British historiography and the popularity of tales of King Arthur. He is best known for his chronicle '' The History of ...
composed his ''History of the Kings of Britain
(''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a fictitious account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. It chronicles the lives of the kings of the Britons ove ...
'' around the year 1136, naming a King Leir
''King Leir'' is an anonymous Elizabethan play about the life of the ancient Brythonic king Leir of Britain. It was published in 1605 but was entered into the Stationers' Register on 15 May 1594. The play has attracted critical attention prin ...
as an eponymous founder
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovati ...
figure.[Galfridus Monemutensis []Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth (; ; ) was a Catholic cleric from Monmouth, Wales, and one of the major figures in the development of British historiography and the popularity of tales of King Arthur. He is best known for his chronicle '' The History of ...
]. '':s:la:Historia Regum Britanniae, Historia Regum Britanniæ''. . J.A. Giles & al. (trans.) as :s:History of the Kings of Britain/Book 2#11, ''History of the Kings of Britain'', Vol. II, Ch. 11 in ''Six Old English Chronicles''. 1842. Hosted at :s:Main page, Wikisource. According to Geoffrey's narrative, Cordelia
Cordelia is a feminine given name. It was borne by the tragic heroine of Shakespeare's ''King Lear'' (1606), a character based on the legendary queen Cordelia. The name is of uncertain origin. It is popularly associated with Latin '' cor'' (gen ...
had buried her father beneath the river in a chamber dedicated to Janus
In ancient Roman religion and myth, Janus ( ; ) is the god of beginnings, gates, transitions, time, duality, doorways, passages, frames, and endings. He is usually depicted as having two faces. The month of January is named for Janus (''Ianu ...
and his feast day was an annual celebration.
When Simon de Montfort
Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, 1st Earl of Chester ( – 4 August 1265), also known as Simon V de Montfort, was an English nobleman of French origin and a member of the English peerage, who led the baronial opposition to the rule of ...
became Earl of Leicester
Earl of Leicester is a title that has been created seven times. The first title was granted during the 12th century in the Peerage of England. The current title is in the Peerage of the United Kingdom and was created in 1837.
History
Earl ...
in 1231, he gave the borough a grant to expel the Jewish population "in my time or in the time of any of my heirs to the end of the world". He justified his action as being "for the good of my soul, and for the souls of my ancestors and successors". Leicester's Jews were allowed to move to the eastern suburbs, which were controlled by de Montfort's great-aunt and rival, Margaret, Countess of Winchester, after she took advice from the scholar and cleric Robert Grosseteste
Robert Grosseteste ( ; ; 8 or 9 October 1253), also known as Robert Greathead or Robert of Lincoln, was an Kingdom of England, English statesman, scholasticism, scholastic philosopher, theologian, scientist and Bishop of Lincoln. He was born of ...
, at that time Archdeacon of Leicester
The Archdeacon of Leicester is a senior ecclesiastical officer in the Church of England Diocese of Leicester.
History
The first archdeacon of Leicester is recorded before 1092 – around the time when archdeacons were first appointed in England ...
. There is evidence that Jews remained there until 1253, and perhaps enforcement of the banishment within the city was not rigorously enforced. De Montfort however issued a second edict for the expulsion of Leicester's Jews in 1253, after Grosseteste's death. De Montfort's many acts of anti-Jewish persecution in Leicester and elsewhere were part of a wider pattern that led to the expulsion of the Jewish population from England in 1290.
 During the 14th century, the earls of Leicester and Lancaster enhanced the prestige of the town.
During the 14th century, the earls of Leicester and Lancaster enhanced the prestige of the town. Henry, 3rd Earl of Lancaster
Henry, 3rd Earl of Leicester and Lancaster ( – 22 September 1345) was a grandson of King Henry III of England (1216–1272) and was one of the principals behind the deposition of King Edward II (1307–1327), his first cousin.
Origins
He wa ...
and of Leicester founded a hospital for the poor and infirm in the area to the south of the castle now known as The Newarke (the "new work"). Henry's son, the great Henry of Grosmont
Henry of Grosmont, Duke of Lancaster (– 23 March 1361) was an English statesman, diplomat, soldier, and Christian writer. The owner of Bolingbroke Castle in Lincolnshire, Grosmont was a member of the House of Plantagenet, which was ruling ...
, 4th Earl of Lancaster and of Leicester, who was made first Duke of Lancaster, enlarged and enhanced his father's foundation, and built the collegiate Church of the Annunciation of Our Lady of The Newarke. This church (a little of which survives in the basement of the Hawthorn Building of De Montfort University) was destroyed during the reign of King Edward VI. It became an important pilgrimage site because it housed a thorn said to be from the Crown of Thorns, given to the Duke by the King of France. The church (described by Leland in the C16th as "not large but exceeding fair") also became, effectively, a Lancastrian mausoleum. Duke Henry's daughter Blanche of Lancaster
Blanche of Lancaster (25 March 1342 – 12 September 1368) was a member of the English-French royal House of Lancaster and the daughter of the kingdom's wealthiest and most powerful peer, Henry of Grosmont, 1st Duke of Lancaster. She was the f ...
married John of Gaunt
John of Gaunt, Duke of Lancaster (6 March 1340 – 3 February 1399), was an English royal prince, military leader and statesman. He was the fourth son (third surviving) of King Edward III of England, and the father of King Henry IV. Because ...
and their son Henry Bolingbroke became King Henry IV when he deposed King Richard II. The Church of the Annunciation was the burial place of Duke Henry, who had earlier had his father re-interred here. Later it became the burial place of Constance of Castile, Duchess of Lancaster
Constance of Castile (1354 – 24 March 1394) was a claimant to the Crown of Castile. She was the daughter of King Peter, who was deposed and killed by his half-brother, King Henry II. She married the English prince John of Gaunt, who fought ...
(second wife of John of Gaunt) and of Mary de Bohun
Mary de Bohun (c. 1369/70 – 4 June 1394) was the first wife of Henry Bolingbroke, Earl of Northampton, who after her death became King Henry IV. As she died before her husband came to the throne, Mary was never queen. She and Henry had six ch ...
, first wife of Henry Bolingbroke (Henry IV) and mother of King Henry V (she did not become queen because she died before Bolingbroke became king). John of Gaunt died at Leicester Castle in 1399. When his son became king, the Earldom of Leicester and the Duchy of Lancaster became royal titles (and the latter remains so).
At the end of the War of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses, known at the time and in following centuries as the Civil Wars, were a series of armed confrontations, machinations, battles and campaigns fought over control of the English throne from 1455 to 1487. The conflict was fo ...
, King
King is a royal title given to a male monarch. A king is an Absolute monarchy, absolute monarch if he holds unrestricted Government, governmental power or exercises full sovereignty over a nation. Conversely, he is a Constitutional monarchy, ...
Richard III
Richard III (2 October 1452 – 22 August 1485) was King of England from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the Plantagenet dynasty and its cadet branch the House of York. His defeat and death at the Battle of Boswor ...
was buried in Leicester's Greyfriars Church a Franciscan Friary and Church which was demolished after its dissolution in 1538. The site of that church is now covered by King Richard III Visitor Centre
King Richard III Visitor Centre is a museum in Leicester, England that showcases the life of King Richard III and the story of the discovery, exhumation, and reburial of his remains in 2012–2015.
For a long time, the burial place of Richa ...
(until 2012 by more modern buildings and a car park). There was a legend his corpse had been cast into the river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
, while some historians argued his tomb and remains were destroyed during the dissolution of the monasteries under Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
. However, in September 2012, an archaeological investigation of the car park revealed a skeleton which DNA testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
helped verify to be related to two descendants of Richard III's sister. It was concluded that the skeleton was that of Richard III because of the DNA evidence and the shape of the spine. In 2015 Richard III was reburied in pride of place near the high altar in Leicester Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Saint Martin, Leicester, commonly known as Leicester Cathedral, is a Church of England cathedral in Leicester, England, and the seat of the Bishop of Leicester. One of the city centre's five surviving medieval ch ...
.
Modern
Tudor
 On 4 November 1530,
On 4 November 1530, Cardinal Thomas Wolsey
Thomas Wolsey ( ; – 29 November 1530) was an English statesman and Catholic cardinal. When Henry VIII became King of England in 1509, Wolsey became the king's almoner. Wolsey's affairs prospered and by 1514 he had become the controlling fi ...
was arrested on charges of treason and taken from Yorkshire. On his way south to face dubious justice at the Tower of London
The Tower of London, officially His Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress of the Tower of London, is a historic citadel and castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamle ...
, he fell ill. The group escorting him was concerned enough to stop at Leicester to rest at Leicester Abbey. There, Wolsey's condition quickly worsened. He died on 29 November 1530 and was buried at Leicester Abbey
The Abbey of Saint Mary de Pratis, more commonly known as Leicester Abbey, was an Augustinian religious house in the city of Leicester, in the East Midlands of England. The abbey was founded in the 12th century by the Robert de Beaumont, 2nd E ...
, now Abbey Park.
Lady Jane Grey
Lady Jane Grey (1536/1537 – 12 February 1554), also known as Lady Jane Dudley after her marriage, and nicknamed as the "Nine Days Queen", was an English noblewoman who was proclaimed Queen of England and Ireland on 10 July 1553 and reigned ...
, who claimed the English throne for nine days in June 1553, was born at Bradgate Park
Bradgate Park () is a public park in Charnwood Forest, in Leicestershire, England, northwest of Leicester. It covers . The park lies between the villages of Newtown Linford, Anstey, Leicestershire, Anstey, Cropston, Woodhouse Eaves and Swithla ...
near Leicester around 1536.Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
's intimate and former suitor, Robert Dudley, was given the Earldom of Leicester
Earl of Leicester is a title that has been created seven times. The first title was granted during the 12th century in the Peerage of England. The current title is in the Peerage of the United Kingdom and was created in 1837.
History
Early ...
.
Stuart
After the Union of the Crowns
The Union of the Crowns (; ) was the accession of James VI of Scotland to the throne of the Kingdom of England as James I and the practical unification of some functions (such as overseas diplomacy) of the two separate realms under a single ...
, Anne of Denmark
Anne of Denmark (; 12 December 1574 – 2 March 1619) was the wife of King James VI and I. She was List of Scottish royal consorts, Queen of Scotland from their marriage on 20 August 1589 and List of English royal consorts, Queen of Engl ...
, Prince Henry, and Princess Elizabeth travelled to Leicester on 24 June 1603, after the courtier and usher Thomas Conway was assured that the town was free from infection or plague. Prince Charles, later King Charles I, travelled to London with his guardian Alexander Seton. The royal party stayed at Leicester for three days in August 1604 at the townhouse of William Skipwith.
The Corporation of Leicester opposed the efforts of Charles I to disafforest the nearby Leicester Forest, believing them to be likely to throw many of its residents into poverty and need of relief. Sir Miles Fleetwood was sent to commission the disafforestation and division of lands being used in common. Riots destroyed enclosures in spring 1627 and 1628, following a pattern of anti-enclosure disturbances found elsewhere including the Western Rising.
Petitions challenging the enclosures were presented by the Corporation of Leicester and borough residents to the King and Privy Council. They were unsuccessful so petitioned the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
in June 1628 who however supported Fleetwood but asked for proceedings made by the Crown against the rioters to be dropped. Compensation made to the legal residents of the forest was reasonably generous by comparison with other forests. The Corporation of Leicester received for relief of the poor.
Civil War
Leicester was a Parliamentarian (colloquially called Roundhead
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who ...
) stronghold during the English Civil War
The English Civil War or Great Rebellion was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Cavaliers, Royalists and Roundhead, Parliamentarians in the Kingdom of England from 1642 to 1651. Part of the wider 1639 to 1653 Wars of th ...
. In 1645, King Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of Kingdom of England, England, Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland, and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland from 27 March 1625 until Execution of Charles I, his execution in 1649.
Charles was born ...
and Prince Rupert
Prince Rupert of the Rhine, Duke of Cumberland, (17 December 1619 ( O.S.) 7 December 1619 (N.S.)– 29 November 1682 (O.S.) December 1682 (N.S) was an English-German army officer, admiral, scientist, and colonial governor. He first rose to ...
decided to attack the (then) town to draw the New Model Army
The New Model Army or New Modelled Army was a standing army formed in 1645 by the Parliamentarians during the First English Civil War, then disbanded after the Stuart Restoration in 1660. It differed from other armies employed in the 1639 t ...
away from the Royalist (colloquially called Cavaliers
The term ''Cavalier'' () was first used by Roundheads as a term of abuse for the wealthier royalist supporters of Charles I of England and his son Charles II of England, Charles II during the English Civil War, the Interregnum (England), Int ...
) headquarters of Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
. Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of gove ...
guns were set up on Raw Dykes
Raw Dykes () is a Roman earthwork and scheduled monument in Leicester. The monument consists of two parallel banks up to 20 metres apart, with an excavated channel running between them. A stretch 110 metres long survives, but originally the eart ...
and, after an unsatisfactory response to a demand for surrender, the assault began at 3pm on 30 May 1645 by a Royalist battery opposite the Newarke. The town – which only had approximately 2,000 defenders opposed to the Royalist Army of approximately 10,000 combatants – was sacked on 31 May 1645, and hundreds of people were killed by Rupert's cavalry. One witness said, "they fired upon our men out of their windows, from the tops of houses, and threw tiles upon their heads. Finding one house better manned than ordinary, and many shots fired at us out of the windows, I caused my men to attack it, and resolved to make them an example for the rest; which they did. Breaking open the doors, they killed all they found there without distinction". It was reported that 120 houses had been destroyed and that 140 wagons of plunder were sent to the Royalist stronghold of Newark.
Following the Parliamentarian victory over the Royalist Army at the Battle of Naseby
The Battle of Naseby took place on 14 June 1645 during the First English Civil War, near the village of Naseby in Northamptonshire. The Roundhead, Parliamentarian New Model Army, commanded by Thomas Fairfax, 3rd Lord Fairfax of Cameron, Sir Th ...
on 14 June 1645, Leicester was recovered by Parliament on 18 June 1645.
Industrial era
 The construction of the
The construction of the Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the Canals of the United Kingdom, British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another to Birmi ...
in the 1790s linked Leicester to London and Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the Lis ...
. The first railway station in Leicester opened in 1832, in the form of the Leicester and Swannington Railway
The Leicester and Swannington Railway (L&SR) was one of England's first railways, built to bring coal from West Leicestershire collieries to Leicester, where there was great industrial demand for coal. The line opened in 1832, and included a tun ...
which provided a supply of coal to the town from nearby collieries. The Midland Counties Railway
The Midland Counties' Railway (MCR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom which existed between 1839 and 1844, connecting Nottingham, Leicester and Derby with Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby and thence, via the London and Birmingham Railway, t ...
(running from Derby
Derby ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area on the River Derwent, Derbyshire, River Derwent in Derbyshire, England. Derbyshire is named after Derby, which was its original co ...
to Rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby union: 15 players per side
*** American flag rugby
*** Beach rugby
*** Mini rugby
*** Rugby sevens, 7 players per side
*** Rugby tens, 10 players per side
*** Snow rugby
*** Tou ...
) linked the town to the national network by 1840. A direct link to London St Pancras was established by the Midland Railway
The Midland Railway (MR) was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1844 in rail transport, 1844. The Midland was one of the largest railway companies in Britain in the early 20th century, and the largest employer in Derby, where it had ...
in the 1860s. These developments encouraged and accompanied a process of industrialisation which intensified throughout the reign of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
. Factories began to appear, particularly along the canal and river, and districts such as Frog Island and Woodgate were the locations of numerous large mills. Between 1861 and 1901, Leicester's population increased from to and the proportion employed in trade, commerce, building, and the city's new factories and workshops rose steadily. Hosiery
Hosiery, (, ) also referred to as legwear, describes garments worn directly on the foot, feet and human leg, legs. The term originated as the collective term for products of which a maker or seller is termed a hosier; and those products are also ...
, textiles, and footwear became the major industrial employers: manufacturers such as N. Corah & Sons and the Cooperative Boot and Shoe Company were opening some of the largest manufacturing premises in Europe. They were joined, in the latter part of the century, by engineering firms such as Kent Street's Taylor and Hubbard (crane makers and founders), Vulcan Road's William Gimson & Company (steam boilers and founders), Martin Street's Richards & Company (steel works and founders), and British United Shoe Machinery
British United Shoe Machinery Ltd. (BUSM) was formed in England around the turn of the 20th century, as a subsidiary of the American United Shoe Machinery Corporation, United Shoe Machinery Company. For most of the 20th century, USM was the worl ...
Co (manufacturer of footwear
Footwear refers to garments worn on the feet, which typically serve the purpose of protective clothing, protection against adversities of the environment such as wear from rough ground; stability on slippery ground; and temperature.
*Shoes and si ...
machinery and materials).
The politics of Victorian Leicester were lively and very often bitter. Years of consistent economic growth meant living standards generally increased, but Leicester was a stronghold of Radicalism. Thomas Cooper, the Chartist, kept a shop in Church Gate. There were serious Chartist riots in the town in 1842 and again six years later. The Leicester Secular Society Leicester Secular Society is the world's oldest Secularism, Secular Society. It meets at its headquarters, the Leicester Secular Hall in the centre of Leicester, England, at 75 Humberstone Gate.
Founding
Founded in 1851, the society is the oldest ...
was founded in 1851 but secularist
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on naturalistic considerations, uninvolved with religion. It is most commonly thought of as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state and may be broadened ...
speakers such as George Holyoake
George Jacob Holyoake (13 April 1817 – 22 January 1906) was an English secularist, British co-operative movement, co-operator and newspaper editor. He coined the terms secularism in 1851 and "jingoism" in 1878. He edited a secularist paper, '' ...
were often denied the use of speaking halls. It was not until 1881 that Leicester Secular Hall was opened. The second half of the 19th century also witnessed the creation of many other institutions, including the town council, the Royal Infirmary, and the Leicester Constabulary. It also benefited from general acceptance (and the Public Health Acts ) that municipal organisations had a responsibility to provide for the town's water supply, drainage, and sanitation. In 1853, backed with a guarantee of dividends by the Corporation of Leicester the Leicester Waterworks Company built a reservoir at Thornton for the supply of water to the town. This guarantee was made possible by the Public Health Act 1847 and an amending local Act of Parliament of 1851. In 1866 another amending Act enabled the Corporation of Leicester to take shares in the company to enable the construction of another reservoir at Cropston, completed in 1870. The Corporation of Leicester was later able to buy the waterworks and build another reservoir at Swithland, completed in the 1890s.
Leicester became a county borough in 1889, although it was abolished in 1974 as part of the Local Government Act
Local Government Act (with its variations) is a stock short title used for legislation in Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Ireland and the United Kingdom, relating to local government.
The Bill for an Act with this short title may have been know ...
, and was reformed as a non-metropolitan district and city. The city regained its unitary status, being administered separately from Leicestershire, in 1997. The borough had been expanding throughout the 19th century, but grew most notably when it annexed Belgrave, Aylestone, North Evington, Knighton, and Stoneygate
Stoneygate is part of the City of Leicester, England.
Situated on the south-east side of the city some two miles from the centre, Stoneygate is a mainly residential suburb characterised by its large Victorian houses. It straddles the London Roa ...
in 1892.
Early 20th century
 In 1900, the
In 1900, the Great Central Railway
The Great Central Railway in England was formed when the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway changed its name in 1897, anticipating the opening in 1899 of its Great Central Main Line, London Extension. On 1 January 1923, the company ...
provided another link to London, but the rapid population growth of the previous decades had already begun to slow by the time of Queen Victoria's death in 1901.
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and the subsequent epidemics had further impacts. Nonetheless, Leicester was finally recognised as a legal city once more in 1919 in recognition of its contribution to the British war effort. Recruitment to the armed forces was lower in Leicester than in other English cities, partly because of the low level of unemployment and the need for many of its industries, such as clothing and footwear manufacturing, to supply the army. As the war progressed, many of Leicester's factories were given over to arms production; Leicester produced the first batch of Howitzer shells by a British company which was not making ammunition before the war. After the war, the city received a royal visit; the king and queen received a march-past in Victoria Park of thousands of serving and demobilised soldiers. Following the end of the war, a memorial arch—the Arch of Remembrance—was built in Victoria Park and unveiled in 1925. The arch, one of the largest First World War memorials in the UK, was designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens
Sir Edwin Landseer Lutyens ( ; 29 March 1869 – 1 January 1944) was an English architect known for imaginatively adapting traditional architectural styles to the requirements of his era. He designed many English country houses, war memorials ...
, who also designed the Cenotaph
The Cenotaph is a war memorial on Whitehall in London, England. Designed by Sir Edwin Lutyens, it was unveiled in 1920 as the United Kingdom's national memorial to the dead of Britain and the British Empire of the First World War, was rededica ...
in London and is a grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
. A set of gates and lodges, again by Lutyens, were added in the 1930s, leading to the memorial from the University Road and London Road entrances to Victoria Park.
In 1927, Leicester again became a cathedral city on the consecration of Church as the cathedral. A second major extension to the boundaries following the changes in 1892 took place in 1935, with the annexation of the remainder of Evington
Evington is an area of Leicester, and electoral ward of the Leicester district, in the ceremonial county of Leicestershire, England. It used to be a small village centred on Main Street and the Anglican church of St Denys but was close enoug ...
, Humberstone, Beaumont Leys, and part of Braunstone. A third major revision of the boundaries took place in 1966, with the net addition to the city of just over . The boundary has remained unchanged since that time.
Leicester's diversified economic base and lack of dependence on primary industries meant it was much better placed than many other cities to weather the tariff wars of the 1920s and Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe global economic downturn from 1929 to 1939. The period was characterized by high rates of unemployment and poverty, drastic reductions in industrial production and international trade, and widespread bank and ...
of the 1930s. The Bureau of Statistics of the newly formed League of Nations
The League of Nations (LN or LoN; , SdN) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace ...
identified Leicester in 1936 as the second-richest city in Europe and it became an attractive destination for refugees fleeing persecution and political turmoil in continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous mainland of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by som ...
. Firms such as Corah and Liberty Shoes used their reputation for producing high-quality products to expand their businesses. These years witnessed the growth in the city of trade unionism
A trade union (British English) or labor union (American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers whose purpose is to maintain or improve the conditions of their employment, such as attaining better wages ...
and particularly the co-operative movement
The history of the cooperative movement concerns the origins and history of cooperatives across the world. Although cooperative arrangements, such as mutual insurance, and principles of cooperation existed long before, the cooperative movement bega ...
. The Co-op became an important employer and landowner; when Leicester played host to the Jarrow March
The Jarrow March of 5–31 October 1936, also known as the Jarrow Crusade, was an organised protest against the unemployment and poverty suffered in the English town of Jarrow during the 1930s. Around 200 men, or "Crusaders" as they preferred to ...
on its way to London in 1936, the Co-op provided the marchers with a change of boots. In 1938, Leicester was selected as the base for Squadron 1F, the first A.D.C.C (Air Defence Cadet Corp), the predecessor of the Air Training Corps
The Air Training Corps (ATC) is a British Youth organisations in the United Kingdom, volunteer youth organisation; aligned to, and fostering the knowledge and learning of military values, primarily focusing on military aviation. Part of the ...
.
World War II
Leicester was bombed on 19 November 1940. Although only three bombs hit the city, 108 people were killed in Highfields.
Contemporary
The years after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, particularly from the 1960s onwards, brought many social and economic challenges.
Urban expansion; central rapprochement
 Mass housebuilding continued across Leicester for some 30 years after 1945. Existing housing estates such as Braunstone were expanded, while several completely new estates – of both private and council tenure – were built. The last major development of this era was Beaumont Leys in the north of the city, which was developed in the 1970s as a mix of private and council housing.
There was a steady decline in Leicester's traditional manufacturing industries and, in the city centre, working factories and light industrial premises have now been almost entirely replaced. Many former factories, including some on Frog Island and at Donisthorpe Mill, have been badly damaged by fire. Rail and barge were finally eclipsed by automotive transport in the 1960s and 1970s: the Great Central and the Leicester and Swannington both closed and the northward extension of the
Mass housebuilding continued across Leicester for some 30 years after 1945. Existing housing estates such as Braunstone were expanded, while several completely new estates – of both private and council tenure – were built. The last major development of this era was Beaumont Leys in the north of the city, which was developed in the 1970s as a mix of private and council housing.
There was a steady decline in Leicester's traditional manufacturing industries and, in the city centre, working factories and light industrial premises have now been almost entirely replaced. Many former factories, including some on Frog Island and at Donisthorpe Mill, have been badly damaged by fire. Rail and barge were finally eclipsed by automotive transport in the 1960s and 1970s: the Great Central and the Leicester and Swannington both closed and the northward extension of the M1 motorway
The M1 motorway connects London to Leeds, where it joins the A1(M) motorway, A1(M) near Aberford, to connect to Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle. It was the first inter-urban motorway to be completed in the UK; the first motorway in the count ...
linked Leicester into England's growing motorway network. With the loss of much of the city's industry during the 1970s and 1980s, some of the old industrial jobs were replaced by new jobs in the service sector, particularly in retail. The opening of the Haymarket Shopping Centre in 1971 was followed by a number of new shopping centres in the city, including St Martin's Shopping Centre in 1984 and the Shire Shopping Centre in 1992. The Shires was subsequently expanded in September 2008 and rebranded as Highcross. By the 1990s, as well, Leicester's central position and good transport links had established it as a distribution centre; the southwestern area of the city has also attracted new service and manufacturing businesses.
Immigration
Since World War II Leicester has experienced large scale immigration from across the world. Many Polish servicemen were prevented from returning to their homeland after the war by the communist regime, and they established a small community in Leicester. Economic migrants from the Irish Republic
The Irish Republic ( or ) was a Revolutionary republic, revolutionary state that Irish Declaration of Independence, declared its independence from the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in January 1919. The Republic claimed jurisdict ...
continued to arrive throughout the post war period. Immigrants from the Indian sub-continent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakis ...
began to arrive in the 1960s, their numbers boosted by Asians
"Asian people" (sometimes "Asiatic people")United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purposes. is an umbrella term ...
arriving from Kenya and Uganda in the early 1970s.
In 1972, Idi Amin
Idi Amin Dada Oumee (, ; 30 May 192816 August 2003) was a Ugandan military officer and politician who served as the third president of Uganda from 1971 until Uganda–Tanzania War, his overthrow in 1979. He ruled as a Military dictatorship, ...
announced that the entire Asian community in Uganda had 90 days to leave the country.[ The initial advertisement was widely condemned, and taken as a marker of anti-Asian sentiment throughout Britain as a whole, although the attitudes that resulted in the initial advertisement were changed significantly in subsequent decades, not least because the immigrants included the owners of many of "Uganda's most successful businesses."
Forty years later, Leicester's mayor Sir ]Peter Soulsby
Sir Peter Alfred Soulsby (born 27 December 1948) is a British Labour Party politician serving as Mayor of Leicester since 2011. He was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Leicester South from 2005 until he resigned his seat in April 2011, in ...
expressed his regret for the behaviour of the council at the time.enlargement of the European Union
The European Union (EU) has expanded a number of times throughout its history by way of the accession of new member state of the European Union, member states to the Union. To join the EU, a state needs to fulfil economic and political condit ...
a significant number of East European
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountains, and i ...
migrants have settled in the city. While some wards in the northeast of the city are more than 70% South Asian, wards in the west and south are all over 70% white. The Commission for Racial Equality
In-Commission or commissioning may refer to:
Business and contracting
* Commission (remuneration), a form of payment to an agent for services rendered
** Commission (art), the purchase or the creation of a piece of art most often on behalf of anot ...
(CRE) had estimated that by 2011 Leicester would have approximately a 50% ethnic minority population, making it the first city in Britain not to have a white British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the White population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population was 49 ...
majority.University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public university, public research university in Manchester, England. The main campus is south of Manchester city centre, Manchester City Centre on Wilmslow Road, Oxford Road. The University of Manchester is c ...
School of Social Sciences said in September 2007 that the CRE had "made unsubstantiated claims and ignored government statistics" and that Leicester's immigrant and minority communities disperse to other places.Leicester Mercury
The ''Leicester Mercury'' is a British regional newspaper for the city of Leicester and the neighbouring counties of Leicestershire and Rutland. The paper began in the 19th century as the ''Leicester Daily Mercury'' and later changed to its pre ...
'', to co-ordinate community relations with members representing the council, police, schools, community and faith groups, and the media.
Coronavirus
The COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
has brought many social and economic challenges across the country and across the world. Leicester has been particularly badly affected in the United Kingdom; from July 2020 during the imposition of the first local lockdown which saw all non-essential retail closed again and businesses such as public houses, restaurants and hairdressers unable to reopen. Businesses such as these in areas such as Glenfield and that part of Braunstone Town which outside of the formal city council area, have since been allowed to reopen following a more tightly defined lockdown area from 18 July 2020.
Geography
The Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; ) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible fo ...
has defined a Leicester Urban Area
The Leicester Built Up Area (BUA), Leicester Urban Area, or Greater Leicester is an urban agglomeration defined by the Office of National Statistics (ONS), centred on the City of Leicester in the East Midlands, England. With a population of 559 ...
(LUA); broadly the immediate Leicester conurbation
A conurbation is a region consisting of a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which, through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ...
, although without administrative status. The LUA contains the unitary authority area and several towns, villages and suburbs outside the city's administrative boundaries.
Areas and suburbs
Suburbs and districts of Leicester (ancient villages now incorporated into the city are shown in bold)
Climate
Leicester experiences a maritime climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring ...
with mild to warm summers and cool winters, rain spread throughout the year, and low sunshine levels. The nearest official Weather Station was Newtown Linford, about northwest of Leicester city centre and just outside the edge of the urban area. However, observations stopped there in 2003. The current nearest weather station is Market Bosworth, about west of the city centre.
The highest temperature recorded at Newtown Linford was during August 1990, although a temperature of was achieved at Leicester University during August 2003. However, the highest temperature since records began in Leicester is on 15 July 1868. More typically the highest temperature would reach – the average annual maximum. 11.3 days of the year should attain a temperature of or above.
The lowest temperature recorded at Newtown Linford was during January 1963. Typically, 54.9 air frosts will be recorded during the course of the year.
Rainfall averages 684.4 mm per year, with 1 mm or more falling on 120.8 days. All averages refer to the period 1971–2000.
Governance
 On 5 May 2011, the directly elected
On 5 May 2011, the directly elected Mayor of Leicester
The Mayor of Leicester, styled ''City Mayor'' to distinguish from the Lord Mayor of Leicester, is the directly elected mayor responsible for the executive function of Leicester City Council in England. The incumbent is Peter Soulsby of the ...
role came into effect after the inaugural election. This post exists in addition to that of Lord Mayor
Lord mayor is a title of a mayor of what is usually a major city in a Commonwealth realm, with special recognition bestowed by the sovereign. However, the title or an equivalent is present in other countries, including forms such as "high mayor". A ...
which goes back to the Middle Ages and is these days a ceremonial role.
The first mayor of Leicester was a Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 9th and 10th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norma ...
knight, Peter fitz Roger ("Peter, son of Roger") in 1251. Following the restoration of city status in 1919 this title was elevated to "Lord Mayor." In 1987 the first Asian Mayor of Leicester was indirectly elected by the councillors, Councillor Gordhan Parmar. After institution of a directly elected mayor in 2011 the Lord Mayor of Leicester still exists as a ceremonial role under Leicester City Council
Leicester City Council is the local authority for the city of Leicester, in the ceremonial county of Leicestershire, England. Leicester has had a council from medieval times, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1997 the council ...
.
On 1 April 1997, Leicester City Council
Leicester City Council is the local authority for the city of Leicester, in the ceremonial county of Leicestershire, England. Leicester has had a council from medieval times, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1997 the council ...
became a unitary authority
A unitary authority is a type of local government, local authority in New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Unitary authorities are responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are ...
. Previously, local government had been a two-tier system: the city and county councils were responsible for different aspects of local-government services. That system is still in place in the rest of Leicestershire. Leicestershire County Council
Leicestershire County Council is the upper-tier local authority for the non-metropolitan county of Leicestershire, England. The non-metropolitan county is smaller than the ceremonial county, which additionally includes Leicester. The county coun ...
retained its headquarters at County Hall in Glenfield, just outside the city boundary but within the urban area. The administrative offices of Leicester City Council are in the centre of the city at City Hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or municipal hall (in the Philippines) is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses the city o ...
in Charles Street, having moved from Welford Place. The 1970s council offices at Welford Place were declared unsafe in 2010 and demolished on 22 February 2015. In 2018 a newly built New Walk Centre was completed as a privately funded mix of offices, shops and flats, alongside tree-lined open spaces. Some services (particularly the police and the ambulance service) still cover the whole of the city and county, but for the most part the councils are independent.
Leicester is divided into 21 electoral wards: Abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christians, Christian monks and nun ...
, Aylestone, Beaumont Leys, Belgrave, Braunstone Park
Braunstone Park is a large public park located in Braunstone, Leicester, England.
History
Braunstone Hall, which was built as a private house in 1775, became a school in 1932.
Facilities
The park covers an area of 168 acres, has two lakes, ...
& Rowley Fields, Castle, Evington
Evington is an area of Leicester, and electoral ward of the Leicester district, in the ceremonial county of Leicestershire, England. It used to be a small village centred on Main Street and the Anglican church of St Denys but was close enoug ...
, Eyres Monsell, Fosse, Humberstone & Hamilton, Knighton, North Evington, Rushey Mead
Rushey Mead is an area, suburb, Wards of the United Kingdom, electoral ward and administrative division of the city of Leicester, in the ceremonial county of Leicestershire, England. The population of the ward at the 2011 census was 15,962. It co ...
, Saffron, Spinney Hills, Stoneygate
Stoneygate is part of the City of Leicester, England.
Situated on the south-east side of the city some two miles from the centre, Stoneygate is a mainly residential suburb characterised by its large Victorian houses. It straddles the London Roa ...
, Thurncourt
Thurncourt is an electoral ward and administrative division of the city of Leicester, England. The population of the ward at the 2011 census was 10,596. It comprises the suburb and housing estate of Thurnby Lodge in eastern Leicester.
Geogra ...
, Troon, Westcotes, Western, and Wycliffe.
Political control
The current directly elected mayor is Sir Peter Soulsby of the Labour Party.
After a long period of Labour administration (since 1979), the city council from May 2003 was run by a Liberal Democrat
Several political parties from around the world have been called the Liberal Democratic Party, Democratic Liberal Party or Liberal Democrats. These parties have usually followed liberalism as ideology, although they can vary widely from very progr ...
/Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
coalition under Roger Blackmore, which collapsed in November 2004. The minority Labour group ran the city until May 2005, under Ross Willmott, when the Liberal Democrats and Conservatives formed a new coalition, again under the leadership of Roger Blackmore.
In the local government elections of 3 May 2007, Leicester's Labour Party once again took control of the council in what can be described as a landslide victory
A landslide victory is an election result in which the winning Candidate#Candidates in elections, candidate or political party, party achieves a decisive victory by an overwhelming margin, securing a very large majority of votes or seats far beyo ...
. Gaining 18 new councillors, Labour polled on the day 38 councillors, creating a governing majority of +20. Significantly however, the Green Party gained its first councillors in the Castle Ward, after losing on the drawing of lots in 2003, though one of these subsequently resigned and the seat was lost to Labour in a by-election on 10 September 2009. The Conservative Party saw a decrease in their representation. The Liberal Democrat Party was the major loser, dropping from 25 councillors in 2003 to only 6 in 2007. This was in part due to the local party splitting, with a number of councillors standing for the Liberal Party
The Liberal Party is any of many political parties around the world.
The meaning of ''liberal'' varies around the world, ranging from liberal conservatism on the right to social liberalism on the left. For example, while the political systems ...
.
In the local government elections of 5 May 2011 and those of May 2015, Labour won 52 of the city's 54 seats, with the Conservatives and Liberal Democrats winning one seat each. In the 2019 local elections, the Labour Party gained the sole Conservative held ward of Knighton leaving Nigel Porter of the Liberal Democrats as the only opposition member on the city council.
The current composition of Leicester City Council is as follows:
There have been four changes in party affiliation since the last full council election in May 2023. Councillor Diane Cank left the Labour group in August 2023. Councillor Sanjay Modhwadia, the Conservative Party candidate in the 2024 Leicester mayoral election, was suspended from the Conservative Party following an argument with group leader Deepak Bajaj in a public car park over who should be the next group leader. Conservative group leader Deepak Bajaj subsequently defected to the Labour Party on 8 April, lambasting a culture of violence, racism, religious divides, threats and bullying within the Conservative Party in Leicester. The conservative group was further reduced in June 2024 when councillor Nagarjun "Nags" Agath quit the party to stand as an independent candidate in Leicester East
Leicester East is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since July 2024 by Shivani Raja of the Conservative Party.
Constituency profile
This is an urban constituency, much of which is densely developed as hous ...
in the 2024 United Kingdom general election
The 2024 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday, 4 July 2024 to elect all 650 members of the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons. The opposition Labour Party (UK), Labour Party, led by Keir Starmer, won a lan ...
. Agath cited displeasure in the choice of the Conservative candidate, Shivani Raja, as his reason to stand, branding her as an "inexperienced candidate" that had been "dumped" on the city.
Representation at Westminster
In the 2024 general election
This is a list of elections that were held in 2024. The National Democratic Institute also maintains a calendar of elections around the world.
* 2024 United Nations Security Council election
* 2024 national electoral calendar
* 2024 local electo ...
, Leicester is divided into three Parliamentary constituencies: Leicester East
Leicester East is a constituency represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since July 2024 by Shivani Raja of the Conservative Party.
Constituency profile
This is an urban constituency, much of which is densely developed as hous ...
, represented by Conservative Party MP Shivani Raja
Shivani Rajnikant Raja (born 21 July 1994) is a British Conservative Party politician. She has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Leicester East since 2024. She gained the seat from Claudia Webbe.
Early life and career
Shivani was born i ...
, Leicester South, represented by independent MP Shockat Adam
Shockat Hussain Adam Patel (born November 1972) is a Malawi-born British businessman, optometrist, and independent politician who has served as the Member of Parliament for Leicester South since 2024.
In September 2024 he was a founder of the ...
, and Leicester West
Leicester West is a constituency in Leicestershire. The seat was created in 1974, and existed in a previous form from 1918 to 1950. The seat has been represented in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom by Liz Kendall of t ...
represented by Work and Pensions Secretary Liz Kendall
Elizabeth Louise Kendall (born 11 June 1971) is a British politician who has served as Secretary of State for Work and Pensions since July 2024. A member of the Labour Party, she has been the Member of Parliament (MP) for Leicester West sinc ...
of the Labour Party.
Coat of arms

 The Corporation of Leicester's
The Corporation of Leicester's coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon f ...
was first granted to the city at the Heraldic Visitation of 1619, and is based on the arms of the first Earl of Leicester
Earl of Leicester is a title that has been created seven times. The first title was granted during the 12th century in the Peerage of England. The current title is in the Peerage of the United Kingdom and was created in 1837.
History
Earl ...
, Robert Beaumont. The charge is a cinquefoil
''Potentilla'' is a genus containing over 500 species of annual, biennial and perennial herbaceous flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae.
Potentillas may also be called cinquefoils in English, but they have also been called five fin ...
ermine, on a red field, and this emblem is used by the city council.
After Leicester became a city again in 1919, the city council applied to add to the arms. Permission for this was granted in 1929, when the supporting lions, from the Lancastrian Earls of Leicester, were added.
The motto ''"Semper Eadem"'' was the motto of Queen Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was Queen of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudor. Her eventful reign, and its effect on history ...
, who granted a royal charter to the city. It means "always the same" but with positive overtones meaning unchanging, reliable or dependable, and united. The crest on top of the arms is a white or silver legless wyvern
The wyvern ( ), sometimes spelled wivern ( ), is a type of mythical dragon with bipedalism, two legs, two wings, and often a pointed tail.
The wyvern in its various forms is important in heraldry, frequently appearing as a mascot of schools an ...
with red and white wounds showing, on a wreath of red and white. The legless wyvern distinguishes it as a Leicester wyvern as opposed to other wyverns. The supporting lions are wearing coronets in the form of collars, with the white cinquefoil hanging from them.
Demography
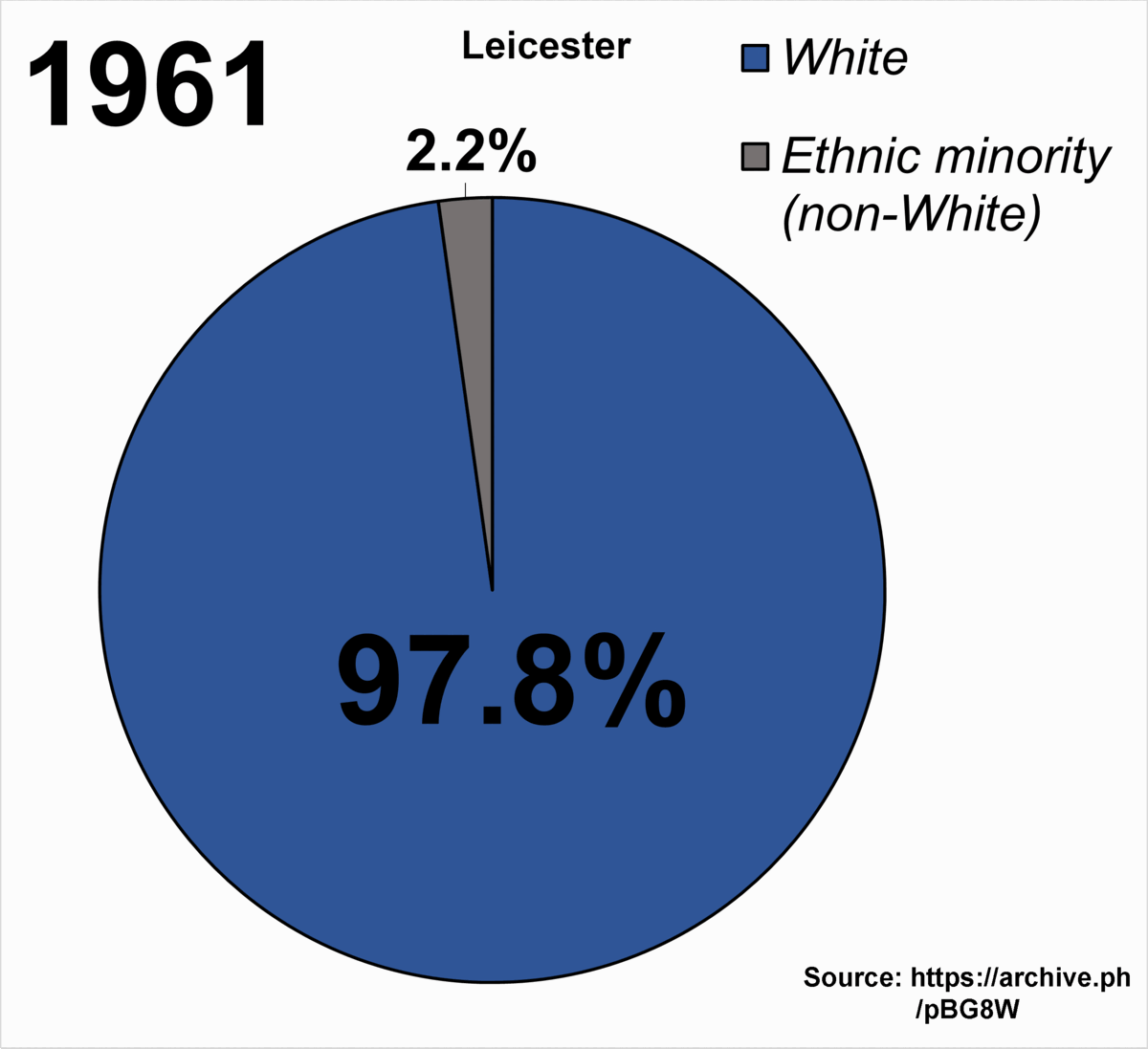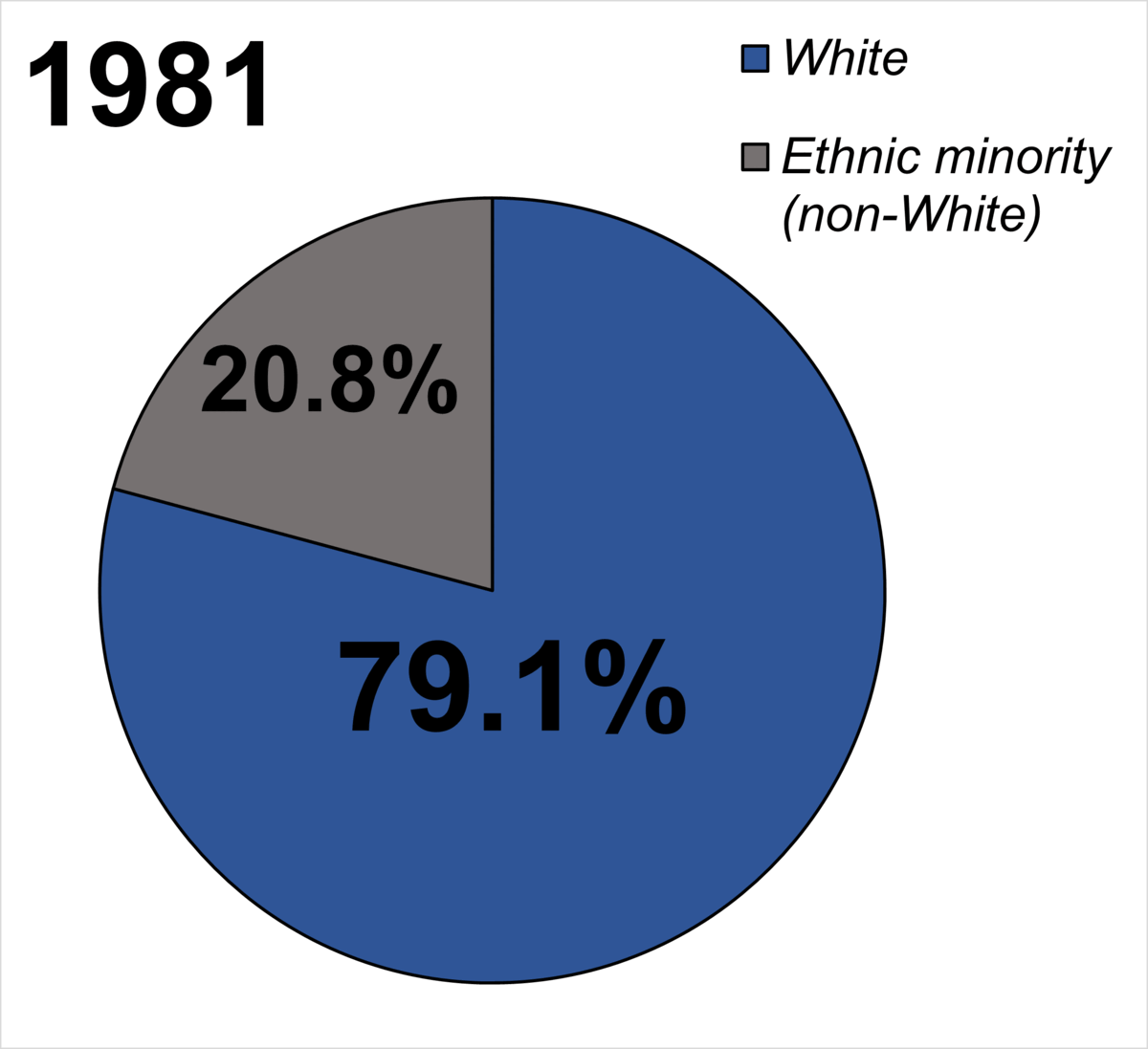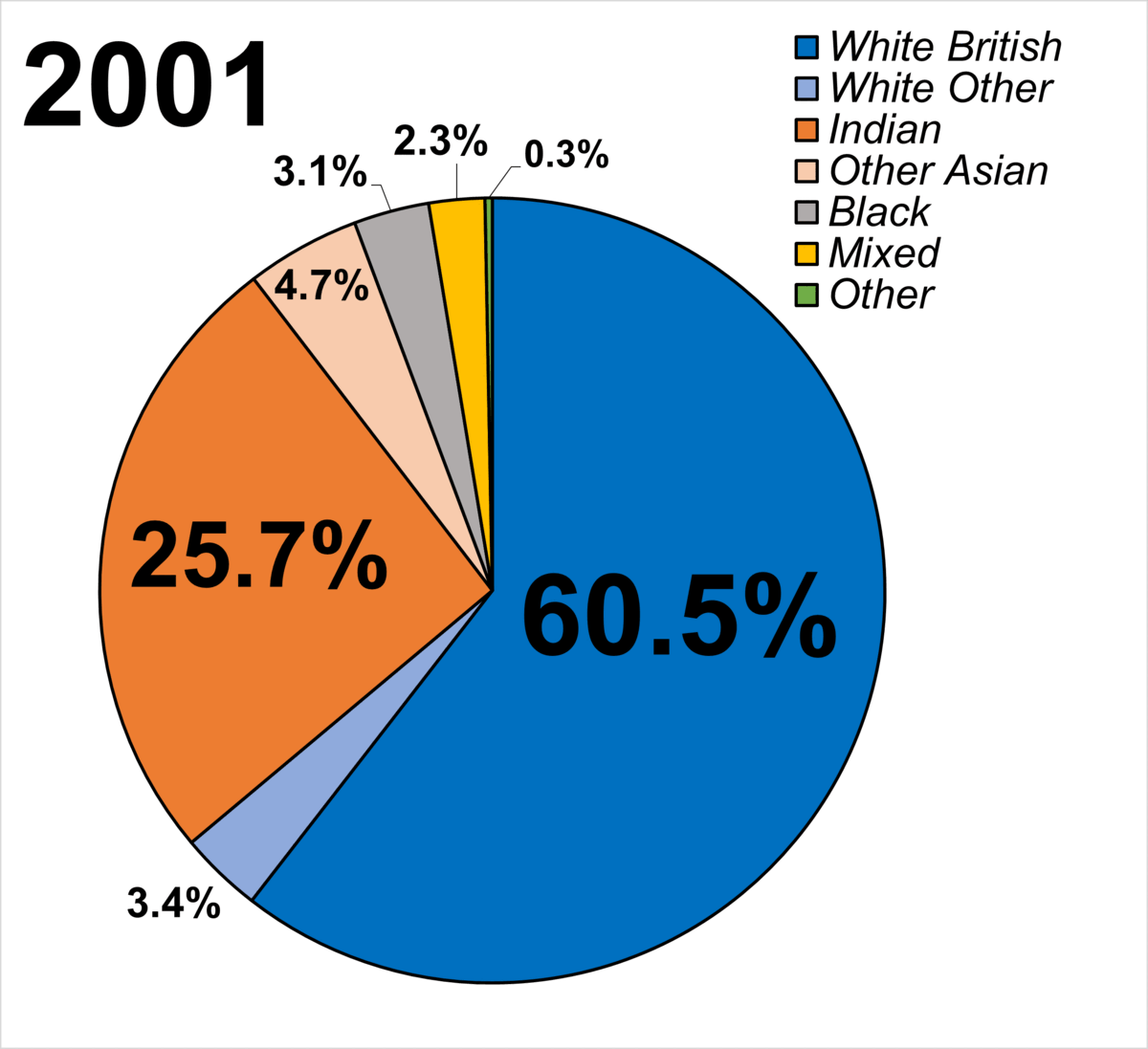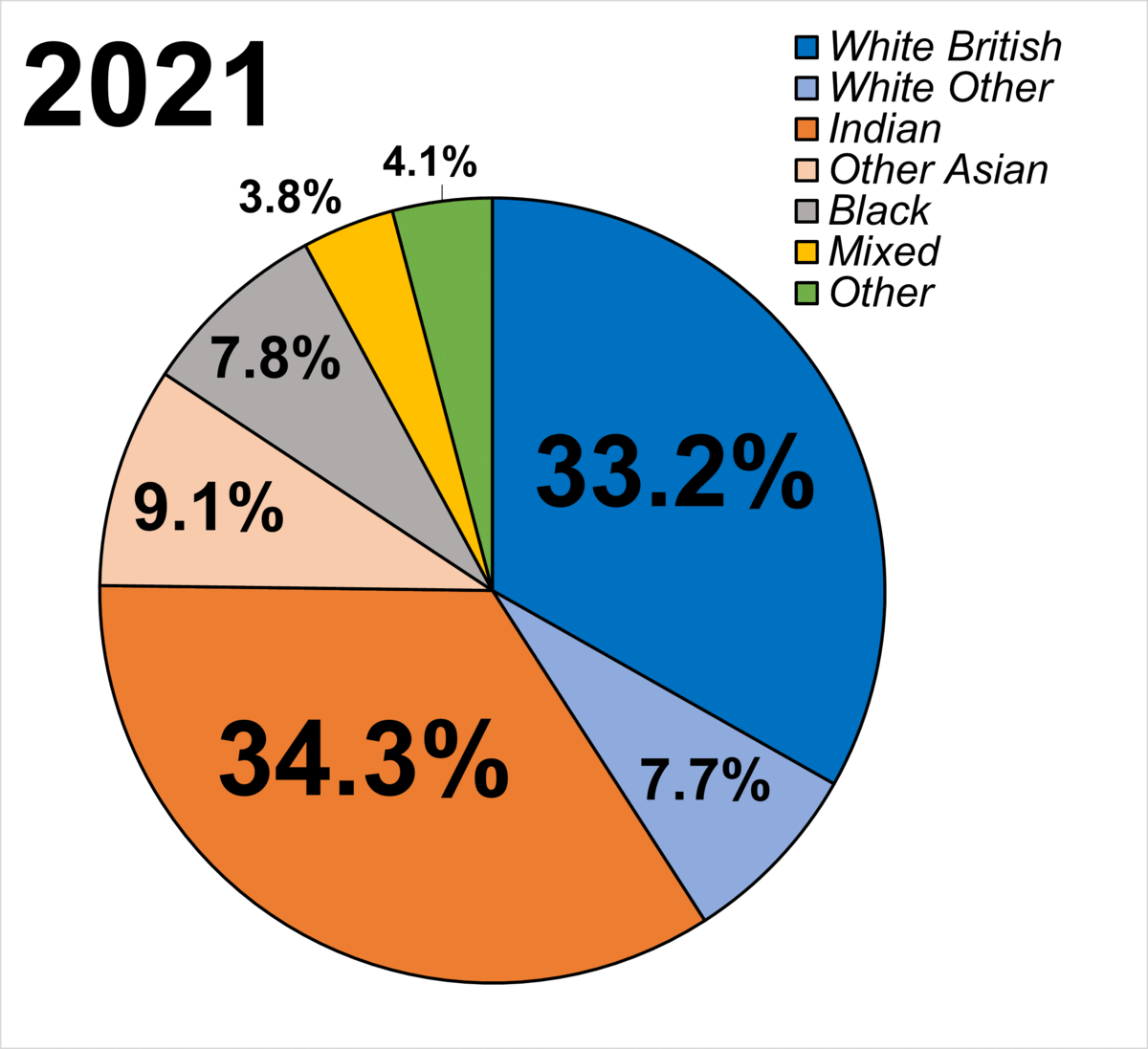
Comparing
In the 2021 census, the population of the Leicester unitary authority area was 368,581, an increase of 11.7% compared to the United Kingdom Census 2011
A Census in the United Kingdom, census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Inter ...
figure of 329,839. The wider Leicester Urban Area
The Leicester Built Up Area (BUA), Leicester Urban Area, or Greater Leicester is an urban agglomeration defined by the Office of National Statistics (ONS), centred on the City of Leicester in the East Midlands, England. With a population of 559 ...
,Eurostat
Eurostat ("European Statistical Office"; also DG ESTAT) is a department of the European Commission ( Directorate-General), located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statist ...
's Larger Urban Zone
The functional urban area (FUA), previously known as larger urban zone (LUZ), is a measure of the population and expanse of metropolitan and surrounding areas which may or may not be exclusively urban. It consists of a city and its commuting zo ...
lists the population of the Leicester LUZ at 886,673 (2017) below that of Nottingham; metropolitan and city region populations tend to be similar. According to the 2011 census Leicester had the largest proportion of people aged 19-and-under in the East Midlands at 27 per cent. Coventry, to the south west, has a population of 352,900 (2016 est.) compared to Leicester's 348,300 at the same date. Nonetheless, Coventry has an area one third greater than Leicester's, approximately equivalent to a combined 'Leicester + Oadby and Wigston
Oadby and Wigston is a local government district with borough status in Leicestershire, England. It covers the two towns of Oadby, where the council is based, and Wigston, which is the larger town. Both form part of the Leicester urban area, l ...
' with a respective population of 404,100 (2016 est.).
The Eurostat regional yearbook 2015 classifies Leicester as one of country's eleven 'Greater Cities', together with Birmingham and Nottingham in the Midlands. Leicester is second only to Bristol as the largest unitary authority
A unitary authority is a type of local government, local authority in New Zealand and the United Kingdom. Unitary authorities are responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are ...
city in England (List of English districts by population
This is a list of the districts of England ordered by population, according to estimated figures for from the Office for National Statistics.
The list consists of 164 non-metropolitan districts, 32 London boroughs, 36 metropolitan boroughs, 6 ...
2015 estimates), and ninth largest counting both unitary authority cities and cities within metropolitan counties.
In terms of ethnic composition, according to the 2021 census, 40.9% of the population was White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no chroma). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully (or almost fully) reflect and scatter all the visible wa ...
(33.2% White British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the White population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population was 49 ...
, 0.5% White Irish
White Irish is an ethnicity classification used in the census in the United Kingdom for England, Scotland and Wales. In the 2021 census, the White Irish population was 564,342 or 0.9% of Great Britain's total population. This was a slight fa ...
, 0.1% Gypsy
{{Infobox ethnic group
, group = Romani people
, image =
, image_caption =
, flag = Roma flag.svg
, flag_caption = Romani flag created in 1933 and accepted at the 1971 World Romani Congress
, po ...
or Irish Traveller
Irish Travellers (, meaning ''the walking people''), also known as Mincéirs (Shelta: ''Mincéirí'') or Pavees, are a traditionally List of nomadic peoples#Peripatetic, peripatetic Indigenous peoples, indigenous Ethnic group, ethno-cultural g ...
, 6.8% Other White
The term Other White, or White Other, is a classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom, used in documents such as the 2021 United Kingdom Census, to describe people who identify as white persons who are not of the English, Welsh, Scotti ...
), 43.4% Asian (34.3% Indian, 3.4% Pakistani
Pakistanis (, ) are the citizens and nationals of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Pakistan is the fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the second-largest Muslim population as of 2023. As much as ...
, 1.9% Bangladeshi
Bangladeshis ( ) are the citizens and nationals of Bangladesh, a South Asian country centred on the transnational historical region of Bengal along the Bay of Bengal, eponymous bay.
Bangladeshi nationality law, Bangladeshi citizenship was fo ...
, 0.7% Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
, 3.1% Other Asian), 3.8% of mixed race
The term multiracial people refers to people who are mixed with two or more
races and the term multi-ethnic people refers to people who are of more than one ethnicities. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mul ...
(1.4% White and Black Caribbean, 0.5% White and Black African, 1.0% White and Asian, 0.8% Other Mixed), 7.8% Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
(5.8% African, 1.4% Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, 0.8% Other Black
A number of different systems of classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom exist. These schemata have been the subject of debate, including about the nature of ethnicity, how or whether it can be categorised, and the relationship betwe ...
), 0.9% Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
and 3.2% of other ethnic heritage.
, Leicester is the second fastest growing city in the country.
Languages
A demographic profile of Leicester published by the city council in 2008 noted:
Certain European languages such as Polish will undoubtedly feature in current statistics, although their prevalence may reduce subsequently as future generations rapidly assimilate or return to places of origin, given cultural and geographic proximity and changes in the geo-political environment.
Population change
The ONS 2014 basis population projections indicate the city will be home to 400,000 inhabitants by around 2035.
Economy
 Leicester has the second largest economy in the East Midlands, after
Leicester has the second largest economy in the East Midlands, after Nottingham
Nottingham ( , East Midlands English, locally ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Nottinghamshire, East Midlands, England. It is located south-east of Sheffield and nor ...
.
Companies that have their principal offices or significant sites in Leicester and the surrounding area include; Brantano Footwear, Dunelm Mill
Dunelm Group plc, trading as Dunelm, is a British home furnishings retailer operating in the United Kingdom. One of the largest homeware retailers in the UK, the company headquarters are in Syston, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exch ...
, Next
NeXT, Inc. (later NeXT Computer, Inc. and NeXT Software, Inc.) was an American technology company headquartered in Redwood City, California that specialized in computer workstations for higher education and business markets, and later develope ...
, Shoe Zone
Shoe Zone (stylised as shoezone) is a budget footwear retailer in the United Kingdom. It has over 330 stores in different cities and towns throughout the UK and over 2,500 employees. The company has an annual turnover of £156 million. The compa ...
, Everards brewing and associated businesses, KPMG
KPMG is a multinational professional services network, based in London, United Kingdom. As one of the Big Four accounting firms, along with Ernst & Young (EY), Deloitte, and PwC. KPMG is a network of firms in 145 countries with 275,288 emplo ...
, Mazars
Forvis Mazars is an international audit, accounting and consulting business formed in June 2024 by an agreement between Mazars and Forvis. Combined, the firms operate in the US and over 100 other countries, being among the top 10 global audit f ...
, Cambridge & Counties Bank, HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc ( zh, t_hk=滙豐; initialism from its founding member The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation) is a British universal bank and financial services group headquartered in London, England, with historical and business li ...
and Santander banking, Hastings Insurance, British Gas
British Gas (trading as Scottish Gas in Scotland) is an energy and home services provider in the United Kingdom. It is the trading name of British Gas Services Limited and British Gas New Heating Limited, both subsidiaries of Centrica. Serving ...
, British Telecom
BT Group plc (formerly British Telecom) is a British Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered in London, England. It has operations in around 180 countries and is the largest provider of fixed-li ...
, Caterpillar
Caterpillars ( ) are the larval stage of members of the order Lepidoptera (the insect order comprising butterflies and moths).
As with most common names, the application of the word is arbitrary, since the larvae of sawflies (suborder ...
(Inc.), Topps Tiles and DHL
DHL (originally named after founders Dalsey, Hillblom and Lynn) is a multinational Import-Export Expert Company, founded in the United States and headquartered in Bonn, Germany. It provides courier, package delivery, and express mail service, ...
.
Textiles
The city has historically had a strong association with the production of textiles, clothing and shoes. While important companies such as Corah, Liberty Shoes and Equity Shoes have closed, companies such as Next and Boden are still active and ASOS
ASOS or Asos may refer to:
* Asos, a village in Greece
* ASOS (retailer), a UK online fashion store
* '' A Storm of Swords'', a book in the ''A Song of Ice and Fire'' saga by G. R. R. Martin
* Action short of strike, industrial action undertake ...
and New Look manufacture in the city. Moreover, in recent years the higher transport prices and longer lead-times associated with globalised
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
production in Asia mean some textile manufacturers are locating to the city.
There have long been concerns about the working conditions in this sector. Leicester's garment district is home to more than 1,000 factories employing as many as 10,000 workers. It has received fewer than 60 health and safety inspections and only 28 fire inspections since October 2017. HMRC
His Majesty's Revenue and Customs (commonly HM Revenue and Customs, or HMRC, and formerly Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs) is a Departments of the United Kingdom Government, department of the UK government responsible for the tax collectio ...
has made just 36 visits checking on compliance with minimum wage legislation; it has issued penalties to fewer than 10 textile firms and claimed just over £100,000 in arrears relating to 143 workers.Peter Soulsby
Sir Peter Alfred Soulsby (born 27 December 1948) is a British Labour Party politician serving as Mayor of Leicester since 2011. He was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Leicester South from 2005 until he resigned his seat in April 2011, in ...
, Mayor of Leicester called together 40 regulatory organisations to coordinate a response. He aimed to make sure that Leicester had the highest standards of employment; that workers are properly paid, well trained and work in safe environments,COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In January 2020, the disease spread worldwide, resulting in the COVID-19 pandemic.
The symptoms of COVID‑19 can vary but often include fever ...
non-compliance, made inspections and gave advice.
Engineering
Engineering companies include Jones & Shipman (machine tools and control systems), Richards Engineering (foundry equipment), Transmon Engineering (materials handling equipment) and Trelleborg
Trelleborg () is a town in Skåne County, Sweden, with 43,359 inhabitants as of 31 December 2015. It is the southernmost town in Sweden located some west from the Smygehuk, southernmost point of Sweden and the Scandinavian Peninsula. It is one ...
(suspension components for rail, marine, and industrial applications). Local commitment to nurturing British engineers includes apprenticeship schemes with local companies, and academic-industrial connections with the engineering departments at Leicester University
The University of Leicester ( ) is a public research university based in Leicester, England. The main campus is south of the city centre, adjacent to Victoria Park. The university's predecessor, University College, Leicester, gained university ...
, De Montfort University
De Montfort University Leicester (DMU) is a public university in the city of Leicester, England. It was established in accordance with the Further and Higher Education Act 1992, Further and Higher Education Act in 1992 as a degree awarding body ...
, and nearby Loughborough University
Loughborough University (abbreviated as ''Lough'' or ''Lboro'' for Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a public university, public research university in the market town of Loughborough, Leicestershire, England. It has been a university sinc ...
. Leicester was also home to the famous Gents' of Leicester clock manufacturers.
Shopping
 The city centre has two large shopping malls –
The city centre has two large shopping malls – Highcross Leicester
Highcross Leicester is a shopping centre in Leicester, England. It was opened as The Shires in 1991 to supplement the Haymarket Shopping Centre, also since re-developed. It was built on a central location within the city centre on Eastgates and ...
and the Haymarket Shopping Centre
The Haymarket Shopping Centre is a shopping centre in the Leicester City Centre, city centre of Leicester, England. It was opened on 4 June 1973 as part of the Haymarket Centre and was the country's second shopping centre after the Bull Ring, ...
. The Haymarket Shopping Centre opened in 1974 and has two levels of shopping, multi-storey parking for up to 500 cars, a bus station and is home to the Haymarket Theatre
The Theatre Royal Haymarket (also known as Haymarket Theatre or the Little Theatre) is a West End theatre in Haymarket, London, Haymarket in the City of Westminster which dates back to 1720, making it the third-oldest London playhouse still in ...
. Highcross Leicester opened in 2008 after work to redevelop "The Shires Centre" was completed at a cost of £350 million (creating 120 stores, 15 restaurants, a cinema, 110,000 m2 of shopping space).
St Martin's Square and the Leicester Lanes area has numerous designer and specialist shops; several of the city's Victorian arcades are located in the same neighbourhood. Leicester Market is the largest outdoor covered market in Europe. It central feature, the Leicester Corn Exchange, has been converted into a public house.
Central Leicester is the location for several department store
A department store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different areas of the store under one roof, each area ("department") specializing in a product category. In modern major cities, the department store mad ...
s including John Lewis
John Robert Lewis (February 21, 1940 – July 17, 2020) was an American civil rights activist and politician who served in the United States House of Representatives for from 1987 until his death in 2020. He participated in the 1960 Nashville ...
, Debenhams
Debenhams plc was a British department store chain that operated in the United Kingdom, Ireland and Denmark, as well as franchised locations across Europe and the Asia Pacific.
The company was founded in 1778 as a single store in London and gr ...
.
The Golden Mile is the name given to a stretch of Belgrave Road renowned for its authentic Indian restaurants, sari
A sari (also called sharee, saree or sadi)The name of the garment in various regional languages include:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a drape (cloth) and a women's garment in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-sti ...
shops, and jeweller
A bench jeweler is an artisan who uses a combination of skills to make and repair jewelry. Some of the more common skills that a bench jeweler might employ include antique restoration, silversmithing, goldsmithing, stone setting, engraving, ...
s; the Diwali
Diwali (), also called Deepavali (IAST: ''Dīpāvalī'') or Deepawali (IAST: ''Dīpāwalī''), is the Hindu festival of lights, with variations celebrated in other Indian religions such as Jainism and Sikhism. It symbolises the spiritual v ...
celebrations in Leicester are focused on this area and are the largest outside the sub-continent.
Food and drink
 Henry Walker was a successful pork butcher who moved from
Henry Walker was a successful pork butcher who moved from Mansfield
Mansfield is a market town and the administrative centre of the Mansfield District in Nottinghamshire, England. It is the largest town in the wider Mansfield Urban Area and the second largest settlement in Nottinghamshire (following the city ...
to Leicester in the 1880s to take over an established business in High Street. The first Walker's crisp production line was in the empty upper storey of Walker's Oxford Street factory in Leicester. In the early days the potatoes were sliced by hand and cooked in an ordinary deep fryer
A deep fryer (or deep fat fryer), sometimes referred to by the French name friteuse, is a kitchen appliance used to cook foods by full immersion in hot oil—deep frying. The cooking oil (or fats) are typically between temperatures of .
Long ...
. In 1971 the Walker's crisps business was sold to Standard Brands
Standard Brands was a packaged foods company, formed in 1929 by J. P. Morgan & Co. with the merger of:
* Fleischmann Company
*Royal Baking Powder Company
* E. W. Gillett Company of Canada (1929) - Toronto-based baking goods company (maker of Ma ...
, an American firm, who sold on the company to Frito-Lay
Frito-Lay, Inc. (; ) is an American food company that manufactures, markets, and sells snack foods. It began in the early 1930s as two companies, Fritos, the Frito Company and Lay's, H.W. Lay & Company, that merged in 1961. Frito-Lay itself merg ...
. Walker's crisps makes 10 million bags of crisps per day at two factories in Beaumont Leys, and is the UK's largest grocery brand. The Beaumont Leys manufacturing plant is world's largest crisp factory.
Meanwhile, the sausage and pie business was bought out by Samworth Brothers in 1986. Production outgrew the Cobden Street site and pork pies are now manufactured at a meat processing factory and bakery in Beaumont Leys, coincidentally near to the separately owned crisp factories. Sold under the Walker's name and under UK retailers own brands such as Tesco
Tesco plc () is a British multinational groceries and general merchandise retailer headquartered in the United Kingdom at its head offices in Welwyn Garden City, England. The company was founded by Jack Cohen (businessman), Sir Jack Cohen in ...
, over three million hot and cold pies are made each week. Henry Walker's butcher shop at 4–6 Cheapside sold Walker's sausages and pork pies until March 2012 when owner Scottish Fife Fine Foods ceased trading, although the shop was temporarily open and selling Walker's pies for the Christmas season of 2012.
Landmarks
 There are 10 scheduled monuments in Leicester, 13
There are 10 scheduled monuments in Leicester, 13 Grade I listed buildings
In the United Kingdom, a listed building is a structure of particular architectural or historic interest deserving of special protection. Such buildings are placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Hi ...
, and 35 Grade II* listed buildings. Some sites, such as Leicester Castle
Leicester Castle is in the city of the same name in the English county of Leicestershire. The complex is situated in the west of Leicester City Centre, between Saint Nicholas Circle to the north and De Montfort University to the south. A lar ...
and the Jewry Wall, are both scheduled monuments and listed buildings.
20th-century architecture: Leicester University Engineering Building (James Stirling & James Gowan : Grd II Listed), Kingstone Department Store, Belgrave Gate (Raymond McGrath : Grd II Listed), National Space Centre
The National Space Centre is a museum and educational resource covering the fields of space science and astronomy, along with a space research programme in partnership with the University of Leicester. It is located on the north side of the city ...
tower.
Older architecture:
Historic buildings: Jewry Wall
The Jewry Wall is a substantial ruined wall of 2nd-century Roman masonry, with two large archways, in Leicester, England. It stands alongside St Nicholas' Circle and St Nicholas' Church. It formed the west wall of a public building in (Ro ...
, the Castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
, Newarke Magazine Gateway, St Nicholas Church, St Margaret's Church, St Mary de Castro, All Saints, the Cathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
, the Abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christians, Christian monks and nun ...
, the Guildhall
A guildhall, also known as a guild hall or guild house, is a historical building originally used for tax collecting by municipalities or merchants in Europe, with many surviving today in Great Britain and the Low Countries. These buildings commo ...
, the Leicester Town Hall, Town Hall, Belgrave Hall, The City Rooms, Leicester, The City Rooms, the Haymarket Memorial Clock Tower, Clock Tower, the Leicester Secular Hall, Secular Hall.
Parks: Abbey Park, University of Leicester Botanic Garden, Botanic Gardens, Castle Gardens, Grand Union Canal (old), Grand Union Canal, Knighton Park, Nelson Mandela Park, River Soar
The River Soar () is a major tributary of the River Trent in the East Midlands as well as the principal river of Leicestershire, England. The source of the river is midway between Hinckley and Lutterworth. The river then flows north throug ...
, Victoria Park, Watermead Country Park.
Industry: Abbey Pumping Station, National Space Centre
The National Space Centre is a museum and educational resource covering the fields of space science and astronomy, along with a space research programme in partnership with the University of Leicester. It is located on the north side of the city ...
, Great Central Railway (preserved), Great Central Railway.
Shopping: Abbey Lane-''grandes surfaces'', Beaumont Shopping Centre, Belvoir Street/Market Street, Golden Mile, Haymarket Shopping Centre
The Haymarket Shopping Centre is a shopping centre in the Leicester City Centre, city centre of Leicester, England. It was opened on 4 June 1973 as part of the Haymarket Centre and was the country's second shopping centre after the Bull Ring, ...
, Highcross Leicester, Highcross, Leicester Lanes, Leicester Market, St Martin's Square, Silver Arcade area.
Sport: King Power Stadium – Leicester City FC, Welford Road Stadium, Welford Road – Leicester Tigers
Leicester Tigers (officially Leicester Football Club) are a professional rugby union club based in Leicester, England. They play in Premiership Rugby, England's top division of rugby.
The club was founded in 1880 and since 1892 plays its home ...
, Grace Road – Leicestershire County Cricket Club, Beaumont Park Stadium, Paul Chapman & Sons Arena, Leicester Lions, Leicester Lions Speedway, Leicester Sports Arena – Leicester Riders, Saffron Lane sports centre – Leicester Coritanian A.C., Leicester Coritanian Athletics Club.
Transport
Air
East Midlands Airport (EMA), at Castle Donington north-north-west of the city, is the closest international airport. The airport is a national hub for mail/freight networks.
Leicester Airport (LRC) is a small airport, some east of Leicester city centre; it does not operate scheduled services.
Road
Leicester is at the midpoint of the primary English north/south M1 motorway
The M1 motorway connects London to Leeds, where it joins the A1(M) motorway, A1(M) near Aberford, to connect to Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle. It was the first inter-urban motorway to be completed in the UK; the first motorway in the count ...
between London and Leeds, served by junctions 21, 21A and 22. This is where the M1 transects with one of the primary north-east to south-west routes, the M69 motorway
The M69 is a dual three-lane dual carriageway motorway in Leicestershire and Warwickshire, England. It runs between junction 21 of the M1 near Leicester and junction 2 of the M6 near Coventry. It opened in 1977.
History
The motorway, also k ...
/A46 road, A46 corridor linking to the A1 road (Great Britain), A1 and M6 motorway at Newark-on-Trent and Coventry respectively. The M42 motorway towards Birmingham Airport terminates in North West Leicestershire, north-west Leicestershire, some west-north-west of the Leicester urban area. Leicester is at the nexus of the A6/(A14), A50, A47 and A607 trunk roads and A426 and A5199 primary routes.
Buses
Leicester has two main bus stations: St Margaret's Bus Station, St. Margarets and Haymarket bus station, Leicester, Haymarket, which was recommissioned in May 2016. The main bus operators for Leicester and the surrounding area are Arriva Fox County, Centrebus, First Leicester, Arriva Midlands, Hinckley Bus (Part of Arriva Midlands), Kinchbus, Leicester Bus and Stagecoach in Northants, Stagecoach Midlands.
The Star trak real time system was introduced in 2000 by Leicester City Council; it allowed bus tracking and the retrieval of bus times by text message or online. The system was discontinued in 2011.
There are three permanent Park and Ride sites at Meynells Gorse (Leicester Forest East), Birstall and Enderby; buses operate every 15 mins from all sites. The park and ride services are branded as ''quicksilver shuttle'' and are contracted to Roberts' Coaches from the Leicester City Council, City Council and Leicestershire County Council, County Council; buses use a purpose-built terminal near St. Nicholas Circle.
Leicester has two circular bus services: Hop! which operates anticlockwise in the city centre via the railway station and Haymarket bus station, and the larger long Orbital (bus service), Orbital which operates in both directions.
Cycling
National Cycle Network National Cycle Route 6, Route 6 passes through Leicestershire along with other secondary routes. The Leicester Bike Park is in Town Hall Square. ''Cycle Works'' Bike Mechanic Training Centre is in Wellington Street Adult Education Centre and former Central Lending Library.
From 2021 to 2023, the city had an electric bicycle Bicycle-sharing system, sharing scheme, Santander Cycles Leicester. The scheme was a joint venture between Leicester City Council
Leicester City Council is the local authority for the city of Leicester, in the ceremonial county of Leicestershire, England. Leicester has had a council from medieval times, which has been reformed on numerous occasions. Since 1997 the council ...
, the operator Ride On, Enzen Global as delivery partner and additional funding provided through sponsorship with Santander.
Railway
Mainline rail
 The rail network is of growing importance in Leicester and, with the start of Eurostar international services from St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International in November 2007, Leicester railway station has gained connections at St. Pancras station to Lille, Brussels and Paris onwards.
Inter-city services are operated by East Midlands Railway providing connectivity on 'fast' and 'semi-fast' services to London, the south-east and to major locations in the East Midlands and Yorkshire; there are also local services operating within the East Midlands region. Trans-regional services to the West Midlands (region), West Midlands and East Anglia are provided by CrossCountry, enabling connections at nearby Nuneaton railway station, Nuneaton, onto the West Coast main line, and at Peterborough railway station, Peterborough to the East Coast Main Line.
The from Leicester Railway Station to St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International on the Midland Main Line are covered in an average of 1hour 25minutes during the morning peak, with journey times as low as 1hour 6minutes later in the day. Transfers onto London Underground or Thameslink (route), Thameslink train services to London City or West End add another 15 to 25minutes to the journey time; double that to Canary Wharf. The journey time to Sheffield is around one hour, with Leeds and York taking approximately two. Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham is 50minutes away and Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, via Peterborough, can be reached in around 1hour 55minutes with further direct services available onto Stansted Airport in north Essex.
The rail network is of growing importance in Leicester and, with the start of Eurostar international services from St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International in November 2007, Leicester railway station has gained connections at St. Pancras station to Lille, Brussels and Paris onwards.
Inter-city services are operated by East Midlands Railway providing connectivity on 'fast' and 'semi-fast' services to London, the south-east and to major locations in the East Midlands and Yorkshire; there are also local services operating within the East Midlands region. Trans-regional services to the West Midlands (region), West Midlands and East Anglia are provided by CrossCountry, enabling connections at nearby Nuneaton railway station, Nuneaton, onto the West Coast main line, and at Peterborough railway station, Peterborough to the East Coast Main Line.
The from Leicester Railway Station to St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International on the Midland Main Line are covered in an average of 1hour 25minutes during the morning peak, with journey times as low as 1hour 6minutes later in the day. Transfers onto London Underground or Thameslink (route), Thameslink train services to London City or West End add another 15 to 25minutes to the journey time; double that to Canary Wharf. The journey time to Sheffield is around one hour, with Leeds and York taking approximately two. Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham is 50minutes away and Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, via Peterborough, can be reached in around 1hour 55minutes with further direct services available onto Stansted Airport in north Essex.
Great Central Railway
The decommissioned Leicester Central railway station is on the late Victorian Great Central Railway line that ran from London Marylebone northwards. Beeching cuts closed the route in the late 1960s. A preserved section, however, remains operational in the East Midlands centred on Loughborough Central railway station providing tourist services through central Leicestershire'','' passing Swithland Reservoir on to the Leicester North railway station terminus.
Waterways
 Two navigable waterways join at Leicester: The Grand Union Canal#The Leicester Line, Leicester Line of the
Two navigable waterways join at Leicester: The Grand Union Canal#The Leicester Line, Leicester Line of the Grand Union Canal
The Grand Union Canal in England is part of the Canals of the United Kingdom, British canal system. It is the principal navigable waterway between London and the Midlands. Starting in London, one arm runs to Leicester and another to Birmi ...
, and the River Soar
The River Soar () is a major tributary of the River Trent in the East Midlands as well as the principal river of Leicestershire, England. The source of the river is midway between Hinckley and Lutterworth. The river then flows north throug ...
Navigation. The Grand Union Canal links Leicester with London and Birmingham to the south, and joins the Soar in Leicester, which links the city to the River Trent, and the Trent and Mersey Canal to the north.
Education
Schools
Leicester is home to a number of comprehensive schools and independent schools. There are three sixth form colleges, all of which were previously grammar schools.
The Leicester City Local Education Authority initially had a troubled history when formed in 1997 as part of the local government reorganisation – a 1999 Ofsted inspection found "few strengths and many weaknesses", although there has been considerable improvement since then.
Tudor Grange Samworth Academy an Academy (English school), academy whose catchment area includes the Saffron and Eyres Monsell estates, was co-sponsored by the Church of England and David Samworth, chairman of Samworth Brothers pasty makers.
Under the "Building Schools for the Future" project, Leicester City Council has contracted with developers Miller Consortium for £315 million to rebuild Beaumont Leys School, Judgemeadow Community College, the City of Leicester College in Evington, and Soar Valley College in Rushey Mead, and to refurbish Fullhurst Community College in Braunstone.
Leicester City Council underwent a major reorganisation of children's services in 2006, creating a new Children and Young People's Services department.
Tertiary
Leicester is home to two universities, the University of Leicester, which attained its Royal Charter in 1957 and was ranked 12th by the 2009 Complete University Guide, and De Montfort University
De Montfort University Leicester (DMU) is a public university in the city of Leicester, England. It was established in accordance with the Further and Higher Education Act 1992, Further and Higher Education Act in 1992 as a degree awarding body ...
, which opened in 1969 as Leicester Polytechnic and achieved university status in 1992.
It is also home to the National Space Centre
The National Space Centre is a museum and educational resource covering the fields of space science and astronomy, along with a space research programme in partnership with the University of Leicester. It is located on the north side of the city ...
off Abbey Lane, due in part to the University of Leicester being one of the few universities in the UK to specialise in space sciences.
Religion
The Cathedral Church of Saint Martin, Leicester, usually known as Leicester Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Saint Martin, Leicester, commonly known as Leicester Cathedral, is a Church of England cathedral in Leicester, England, and the seat of the Bishop of Leicester. One of the city centre's five surviving medieval ch ...
, is the Church of England cathedral and is the seat of the Bishop of Leicester. The church was elevated to a collegiate church in 1922 and made a cathedral in 1927 following the establishment of a new Diocese of Leicester in 1926.
Places of worship
Places of worship include: Holy Cross Priory, Leicester, Holy Cross Priory (Roman Catholic), Shree Jalaram Prarthana Mandal (Hindu temple), the Stake center, Stake Centre of the LDS Church's Stake (Latter Day Saints), Stake, four Christadelphian meeting halls, Jain, Jain Centre, Leicester Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Saint Martin, Leicester, commonly known as Leicester Cathedral, is a Church of England cathedral in Leicester, England, and the seat of the Bishop of Leicester. One of the city centre's five surviving medieval ch ...
, Leicester Central Mosque,
Masjid Umar (Mosque), Guru Nanak Gurdwara (Sikh), Neve Shalom Synagogue (Progressive Jewish).
Culture
 The city hosts annually a Leicester Caribbean Carnival, Caribbean Carnival and parade (the largest in the UK outside London),
The city hosts annually a Leicester Caribbean Carnival, Caribbean Carnival and parade (the largest in the UK outside London), Diwali
Diwali (), also called Deepavali (IAST: ''Dīpāvalī'') or Deepawali (IAST: ''Dīpāwalī''), is the Hindu festival of lights, with variations celebrated in other Indian religions such as Jainism and Sikhism. It symbolises the spiritual v ...
celebrations (the largest outside of India), the largest comedy festival in the UK Leicester Comedy Festival and a Pride Parade (Leicester Pride). Belgrave Road, not far from the city centre, is colloquially known as "The Golden Mile" because of the number of Jewellers.
The Leicester International Short Film Festival is an annual event; it commenced in 1996 under the banner title of "Seconds Out". It has become one of the most important short film festivals in the UK and usually runs in early November, with venues including the Phoenix Square, Phoenix Cinema and Arts Centre.
 Notable arts venues in the city include:
* Curve Theatre, Leicester, Curve: Purpose-designed performing arts centre, designed by Rafael Viñoly, opened in Autumn 2008,
* The De Montfort Hall
* The Leicester Haymarket Theatre, Haymarket Theatre
* The Little Theatre (Leicester), Little Theatre
* The Y Theatre at the YMCA
* The Peepul Centre, Designed by Andrzej Blonski Architects, the £15 million building was opened in 2005 and houses an auditorium, restaurant, cyber café, gym and dance studio for the local people, as well as being used for conferences and events. The centre has even been host to former Prime Minister Gordon Brown and other senior Labour Party figures for hustings during the deputy leadership contest.
* Phoenix Cinema and Arts Centre, in Midland street opened in 2009.
*The Sue Townsend Theatre in Upper Brown Street– which opened in the former Phoenix Arts Centre.
Notable arts venues in the city include:
* Curve Theatre, Leicester, Curve: Purpose-designed performing arts centre, designed by Rafael Viñoly, opened in Autumn 2008,
* The De Montfort Hall
* The Leicester Haymarket Theatre, Haymarket Theatre
* The Little Theatre (Leicester), Little Theatre
* The Y Theatre at the YMCA
* The Peepul Centre, Designed by Andrzej Blonski Architects, the £15 million building was opened in 2005 and houses an auditorium, restaurant, cyber café, gym and dance studio for the local people, as well as being used for conferences and events. The centre has even been host to former Prime Minister Gordon Brown and other senior Labour Party figures for hustings during the deputy leadership contest.
* Phoenix Cinema and Arts Centre, in Midland street opened in 2009.
*The Sue Townsend Theatre in Upper Brown Street– which opened in the former Phoenix Arts Centre.
Museums
File:Newarke Houses Museum Leicester.jpg, Newarke Houses Museum (Grade II*)
File:New Walk Museum Leicester 2.JPG, Leicester Museum & Art Gallery
File:Abbey Pumping station.JPG, Abbey Pumping Station
File:Jewry Wall and St Nicholas.jpg, Jewry Wall Museum
File:Belgrave Hall Museum - geograph.org.uk - 70266.jpg, Belgrave Hall
File:GasMuseumMay2010.JPG, Gas Museum (Leicester)
File:Leicester Guildhall.jpg, Leicester Guildhall, The Guildhall
File:Dynasty Death and Discovery, Richard III museum entrance.png, King Richard III Visitor Centre
King Richard III Visitor Centre is a museum in Leicester, England that showcases the life of King Richard III and the story of the discovery, exhumation, and reburial of his remains in 2012–2015.
For a long time, the burial place of Richa ...
Music
In popular culture
Leicester is the setting for the fictional diaries of Adrian Mole, created by Sue Townsend. In the early books he lives in a suburb of Leicester and attends a local school where he first meets "the love of his life", Pandora Braithwaite.
After a period of years spent working in Oxford and London, Mole returns to Leicester and gets a job in a second-hand bookshop and a flat in an "upmarket" development on a swan-infested waterfront, which is a barely disguised representation of the area near to St. Nicholas Circle. Vastly in debt he is forced to move to the fictional village of Mangold Parva. The local (fictional) Member of Parliament (United Kingdom), Member of Parliament (MP) for the town of Ashby de la Zouch is his old flame, Pandora Braithwaite.
Leicester is the setting for Rod Duncan's novels, the ''Fall of the Gas-Lit Empire'' series and the Riot trilogy.
Leicester and the surrounding county are settings for several Graham Joyce novels, including ''Dark Sister'', ''The Limits of Enchantment'' and ''Some Kind of Fairy Tale''.
The Clarendon Park and New Walk areas of the city, along with an unnamed Charnwood village ("vaguely based upon Cossington", according to the author) are some of the settings of the 2014 novel ''The Knot of Isis'' by Chrid McGordon.
Leicester is the setting for the British children book series, ''The Sleepover Club'', by authors Rose Impey, Narinder Dhami, Lorna Read, Fiona Cummings, Louis Catt, Sue Mongredien, Angie Bates, Ginny Deals, Harriet Castor and Jana Novotny Hunter.
Notable feature films made in the city are ''The Girl with Brains in Her Feet'' (1997), ''Jadoo (2013 film), Jadoo'' (2013) and ''Yamla Pagla Deewana 2'' (2013).
Sport
The city of Leicester has a successful record in sport, In 2016, it was named the UK's Greatest Sporting City, and in 2008, it was named as a European City of Sport.
Leicester City
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area, and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest city in the East Midlands with a popula ...
are a professional association football club who currently compete in the Premier League. The club attracted global attention after winning the Premier League title in 2016.Leicester Tigers
Leicester Tigers (officially Leicester Football Club) are a professional rugby union club based in Leicester, England. They play in Premiership Rugby, England's top division of rugby.
The club was founded in 1880 and since 1892 plays its home ...
have been the most successful English rugby union football club since the introduction of a league in 1987, winning it a record eleven times, five more than either Bath Rugby, Bath or Wasps RFC, Wasps. They won the Premiership title most recently in 2022.
 Leicester Riders are the oldest professional basketball team in the country. In 2016, they moved into the new Charter Street Leicester Community Sports Arena.
Leicestershire County Cricket Club who are a professional cricket club based at Grace Road, Leicester, currently play in the second tier of the county championship. They won the County Championship in 1975, 1996 and 1998.
Greyhound racing in the United Kingdom, Greyhound racing took place at two venues in the city; the main venue was the Leicester Stadium which hosted racing from 1928 to 1984, it also hosted motorcycle speedway, speedway. A smaller track existed at Leicester (Aylestone Road) Greyhound Track, Aylestone Road (1927–1929).
Leicester Riders are the oldest professional basketball team in the country. In 2016, they moved into the new Charter Street Leicester Community Sports Arena.
Leicestershire County Cricket Club who are a professional cricket club based at Grace Road, Leicester, currently play in the second tier of the county championship. They won the County Championship in 1975, 1996 and 1998.
Greyhound racing in the United Kingdom, Greyhound racing took place at two venues in the city; the main venue was the Leicester Stadium which hosted racing from 1928 to 1984, it also hosted motorcycle speedway, speedway. A smaller track existed at Leicester (Aylestone Road) Greyhound Track, Aylestone Road (1927–1929).
Public services
In the public sector, University Hospitals Leicester NHS Trust is one of the larger employers in the city, with over 12,000 employees working for the Trust. Leicester City Primary Care Trust employs over 1,000 full and part-time staff providing healthcare services in the city. Leicestershire Partnership NHS Trust employs 3,000 staff providing mental health and learning disability services in the city and county.
In the private sector are Nuffield Hospital Leicester and the Spire Hospital Leicester.
Notable people
Local media
Print and online
The ''Leicester Mercury
The ''Leicester Mercury'' is a British regional newspaper for the city of Leicester and the neighbouring counties of Leicestershire and Rutland. The paper began in the 19th century as the ''Leicester Daily Mercury'' and later changed to its pre ...
'' was founded by James Thompson (journalist), James Thompson in 1874. Until recently, it was based at 16–18 New Walk, but switched to an almost entirely remote operation after the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
.
Pukaar Group, a local media company, publishes the ''Leicester Times''.
A co-operative and independent newspaper, the ''Great Central Gazette'', was launched online in March 2023. It plans to launch a print edition in 2024.
National World has plans to launch online-only ''Leicester World''.
Television
The Midlands Asian Television channel known as MATV Channel 6 was broadcast in Leicester until late 2009.
Radio
BBC Radio Leicester was the first BBC Local Radio station in Britain, opening on 8 November 1967. Other analogue FM radio stations are Leicester Community Radio for English speaking over 35's (1449 AM/MW), Demon FM which is Leicester's community and student radio station broadcasting from De Montfort University, Takeover Radio is the first ever children's radio station in the UK to be produced and presented by children, Capital Midlands, Hits Radio East Midlands, Smooth East Midlands and Hindu Sanskar Radio, which only broadcasts during Hindu religious festivals. BBC Asian Network and Sabras Radio broadcast on AM.
The local Digital Audio Broadcasting, DAB multiplex includes Capital Midlands, BBC Radio Leicester, Hits Radio East Midlands and Smooth East Midlands.
Leicester's independent radio stations launched a new DAB multiplex in 2023.
There are two hospital radio stations in Leicester, Radio Fox and Radio Gwendolen. Leicester University has a radio station, University of Leicester#Galaxy Radio, Galaxy Radio.
Twin cities
Leicester is Twin towns and sister cities, twinned with six cities.
Freedom of the City
The following people and military units have received the Freedom of the City of Leicester.
Individuals
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Thomas Wright: 25 October 1892.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Edward Wood: 25 October 1892.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Thomas Windley: 31 March 1903.
* Colonel (United Kingdom), Colonel John Edward Sarson: 31 March 1903.
* Alexander Bains: 29 November 1904.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, William Wilkins Vincent: 28 November 1911.
* Thomas Smith (trade unionist), Thomas Smith: 3 July 1918.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Jonathan North: 28 January 1919.
* Admiral of the Fleet (Royal Navy), Admiral of the Fleet David Beatty, 1st Earl Beatty, Lord Beatty: 28 January 1919.
* Thomas Fielding Johnson: 8 July 1919.
* Field marshal (United Kingdom), Field Marshal Douglas Haig, 1st Earl Haig, Lord Haig: 28 February 1922.
* Charles John Bond: 28 April 1925.
* Captain (British Army and Royal Marines), Captain Robert Gee: 28 April 1925.
* Ramsay MacDonald, James Ramsay MacDonald: 29 October 1929.
* Cosmo Gordon Lang, Lord Laig of Lambeth: 28 May 1935.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Walter Ernest Wilford: 26 July 1949.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Thomas Rowland Hill: 3 January 1956.
* Lieutenant colonel (United Kingdom), Lieutenant Colonel Sir Robert Martin: 3 January 1961.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Sir Charles Robert Keene: 31 July 1962.
* Barnett Janner, Baron Janner, Lord Janner of the City of Leicester: 26 October 1971.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Sir Frederick Ernest Oliver: 26 October 1971.
* List of lord mayors of Leicester, Sidney William Bridges: 26 October 1971.
* Mac Goldsmith: 26 October 1971.
* David Attenborough, Sir David Attenborough: 30 November 1989.
* Richard Attenborough, Lord Attenborough of Kingston upon Thames: 30 November 1989.
* Professor Alec Jeffreys, Sir Alec Jeffreys: 26 November 1992.
* Gary Lineker: 26 November 1992.
* Frank Ephraim May: 12 July 2001.
* Rosemary Conley: 12 July 2001.
* Engelbert Humperdinck (singer), Engelbert Humperdinck: 25 February 2009.
* Sue Townsend, Susan Lillian Townsend: 25 February 2009.
* Alan Birchenall: 25 February 2009.
Military units
* The Royal Anglian Regiment: 25 January 1996.
Notes
References
Secondary sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Hoskins, W. G. "Leicester" ''History Today'' (Sep 1951) 1#9 pp 48–56.
*
*
* Levy, S. "Notes on Leicester Jewry." Transactions (Jewish Historical Society of England) 5 (1902): 34–42
NOTES ON LEICESTER JEWRY
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Newspapers
*
*
*
External links
Leicester City Council
{{Authority control
Leicester,
Local government in Leicestershire
Unitary authority districts of England
50 establishments
Cities in the East Midlands
County towns in England
Local government districts of the East Midlands
50s establishments in the Roman Empire
Populated places established in the 1st century
1st-century establishments in Roman Britain
Towns in Leicestershire
Unparished areas in Leicestershire
Boroughs in England
Former civil parishes in Leicestershire
 It is believed that the
It is believed that the  Knowledge of the town following the
Knowledge of the town following the  Following the
Following the  During the 14th century, the earls of Leicester and Lancaster enhanced the prestige of the town.
During the 14th century, the earls of Leicester and Lancaster enhanced the prestige of the town.  On 4 November 1530,
On 4 November 1530,  The construction of the
The construction of the  In 1900, the
In 1900, the  Mass housebuilding continued across Leicester for some 30 years after 1945. Existing housing estates such as Braunstone were expanded, while several completely new estates – of both private and council tenure – were built. The last major development of this era was Beaumont Leys in the north of the city, which was developed in the 1970s as a mix of private and council housing.
There was a steady decline in Leicester's traditional manufacturing industries and, in the city centre, working factories and light industrial premises have now been almost entirely replaced. Many former factories, including some on Frog Island and at Donisthorpe Mill, have been badly damaged by fire. Rail and barge were finally eclipsed by automotive transport in the 1960s and 1970s: the Great Central and the Leicester and Swannington both closed and the northward extension of the
Mass housebuilding continued across Leicester for some 30 years after 1945. Existing housing estates such as Braunstone were expanded, while several completely new estates – of both private and council tenure – were built. The last major development of this era was Beaumont Leys in the north of the city, which was developed in the 1970s as a mix of private and council housing.
There was a steady decline in Leicester's traditional manufacturing industries and, in the city centre, working factories and light industrial premises have now been almost entirely replaced. Many former factories, including some on Frog Island and at Donisthorpe Mill, have been badly damaged by fire. Rail and barge were finally eclipsed by automotive transport in the 1960s and 1970s: the Great Central and the Leicester and Swannington both closed and the northward extension of the  On 5 May 2011, the directly elected
On 5 May 2011, the directly elected 
 Leicester has the second largest economy in the East Midlands, after
Leicester has the second largest economy in the East Midlands, after  The city centre has two large shopping malls –
The city centre has two large shopping malls –  Henry Walker was a successful pork butcher who moved from
Henry Walker was a successful pork butcher who moved from  There are 10 scheduled monuments in Leicester, 13
There are 10 scheduled monuments in Leicester, 13  The rail network is of growing importance in Leicester and, with the start of Eurostar international services from St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International in November 2007, Leicester railway station has gained connections at St. Pancras station to Lille, Brussels and Paris onwards.
Inter-city services are operated by East Midlands Railway providing connectivity on 'fast' and 'semi-fast' services to London, the south-east and to major locations in the East Midlands and Yorkshire; there are also local services operating within the East Midlands region. Trans-regional services to the West Midlands (region), West Midlands and East Anglia are provided by CrossCountry, enabling connections at nearby Nuneaton railway station, Nuneaton, onto the West Coast main line, and at Peterborough railway station, Peterborough to the East Coast Main Line.
The from Leicester Railway Station to St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International on the Midland Main Line are covered in an average of 1hour 25minutes during the morning peak, with journey times as low as 1hour 6minutes later in the day. Transfers onto London Underground or Thameslink (route), Thameslink train services to London City or West End add another 15 to 25minutes to the journey time; double that to Canary Wharf. The journey time to Sheffield is around one hour, with Leeds and York taking approximately two. Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham is 50minutes away and Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, via Peterborough, can be reached in around 1hour 55minutes with further direct services available onto Stansted Airport in north Essex.
The rail network is of growing importance in Leicester and, with the start of Eurostar international services from St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International in November 2007, Leicester railway station has gained connections at St. Pancras station to Lille, Brussels and Paris onwards.
Inter-city services are operated by East Midlands Railway providing connectivity on 'fast' and 'semi-fast' services to London, the south-east and to major locations in the East Midlands and Yorkshire; there are also local services operating within the East Midlands region. Trans-regional services to the West Midlands (region), West Midlands and East Anglia are provided by CrossCountry, enabling connections at nearby Nuneaton railway station, Nuneaton, onto the West Coast main line, and at Peterborough railway station, Peterborough to the East Coast Main Line.
The from Leicester Railway Station to St Pancras railway station, London St Pancras International on the Midland Main Line are covered in an average of 1hour 25minutes during the morning peak, with journey times as low as 1hour 6minutes later in the day. Transfers onto London Underground or Thameslink (route), Thameslink train services to London City or West End add another 15 to 25minutes to the journey time; double that to Canary Wharf. The journey time to Sheffield is around one hour, with Leeds and York taking approximately two. Birmingham New Street railway station, Birmingham is 50minutes away and Cambridge railway station, Cambridge, via Peterborough, can be reached in around 1hour 55minutes with further direct services available onto Stansted Airport in north Essex.
 Two navigable waterways join at Leicester: The Grand Union Canal#The Leicester Line, Leicester Line of the
Two navigable waterways join at Leicester: The Grand Union Canal#The Leicester Line, Leicester Line of the  The city hosts annually a Leicester Caribbean Carnival, Caribbean Carnival and parade (the largest in the UK outside London),
The city hosts annually a Leicester Caribbean Carnival, Caribbean Carnival and parade (the largest in the UK outside London),  Notable arts venues in the city include:
* Curve Theatre, Leicester, Curve: Purpose-designed performing arts centre, designed by Rafael Viñoly, opened in Autumn 2008,
* The De Montfort Hall
* The Leicester Haymarket Theatre, Haymarket Theatre
* The Little Theatre (Leicester), Little Theatre
* The Y Theatre at the YMCA
* The Peepul Centre, Designed by Andrzej Blonski Architects, the £15 million building was opened in 2005 and houses an auditorium, restaurant, cyber café, gym and dance studio for the local people, as well as being used for conferences and events. The centre has even been host to former Prime Minister Gordon Brown and other senior Labour Party figures for hustings during the deputy leadership contest.
* Phoenix Cinema and Arts Centre, in Midland street opened in 2009.
*The Sue Townsend Theatre in Upper Brown Street– which opened in the former Phoenix Arts Centre.
Notable arts venues in the city include:
* Curve Theatre, Leicester, Curve: Purpose-designed performing arts centre, designed by Rafael Viñoly, opened in Autumn 2008,
* The De Montfort Hall
* The Leicester Haymarket Theatre, Haymarket Theatre
* The Little Theatre (Leicester), Little Theatre
* The Y Theatre at the YMCA
* The Peepul Centre, Designed by Andrzej Blonski Architects, the £15 million building was opened in 2005 and houses an auditorium, restaurant, cyber café, gym and dance studio for the local people, as well as being used for conferences and events. The centre has even been host to former Prime Minister Gordon Brown and other senior Labour Party figures for hustings during the deputy leadership contest.
* Phoenix Cinema and Arts Centre, in Midland street opened in 2009.
*The Sue Townsend Theatre in Upper Brown Street– which opened in the former Phoenix Arts Centre.
 Leicester Riders are the oldest professional basketball team in the country. In 2016, they moved into the new Charter Street Leicester Community Sports Arena.
Leicestershire County Cricket Club who are a professional cricket club based at Grace Road, Leicester, currently play in the second tier of the county championship. They won the County Championship in 1975, 1996 and 1998.
Greyhound racing in the United Kingdom, Greyhound racing took place at two venues in the city; the main venue was the Leicester Stadium which hosted racing from 1928 to 1984, it also hosted motorcycle speedway, speedway. A smaller track existed at Leicester (Aylestone Road) Greyhound Track, Aylestone Road (1927–1929).
Leicester Riders are the oldest professional basketball team in the country. In 2016, they moved into the new Charter Street Leicester Community Sports Arena.
Leicestershire County Cricket Club who are a professional cricket club based at Grace Road, Leicester, currently play in the second tier of the county championship. They won the County Championship in 1975, 1996 and 1998.
Greyhound racing in the United Kingdom, Greyhound racing took place at two venues in the city; the main venue was the Leicester Stadium which hosted racing from 1928 to 1984, it also hosted motorcycle speedway, speedway. A smaller track existed at Leicester (Aylestone Road) Greyhound Track, Aylestone Road (1927–1929).