|
Coritani
The Corieltauvi (also the Coritani, and the Corieltavi) were a tribe of people living in Britain prior to the Roman conquest, and thereafter a ''civitas'' of Roman Britain. Their territory was in what is now the English East Midlands. They were bordered by the Brigantes to the north, the Cornovii to the west, the Dobunni and Catuvellauni to the south, and the Iceni to the east. Their capital was called '' Ratae Corieltauvorum'', known today as Leicester. Late Iron Age The Corieltauvi were a largely agricultural people who had few strongly defended sites or signs of centralised government. They appear to have been a federation of smaller, self-governing tribal groups. From the beginning of the 1st century, they began to produce inscribed coins: almost all featured two names, and one series had three, suggesting they had multiple rulers. The names on the earliest coins are so abbreviated as to be unidentifiable. Later coins feature the name of Volisios, apparently the paramou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
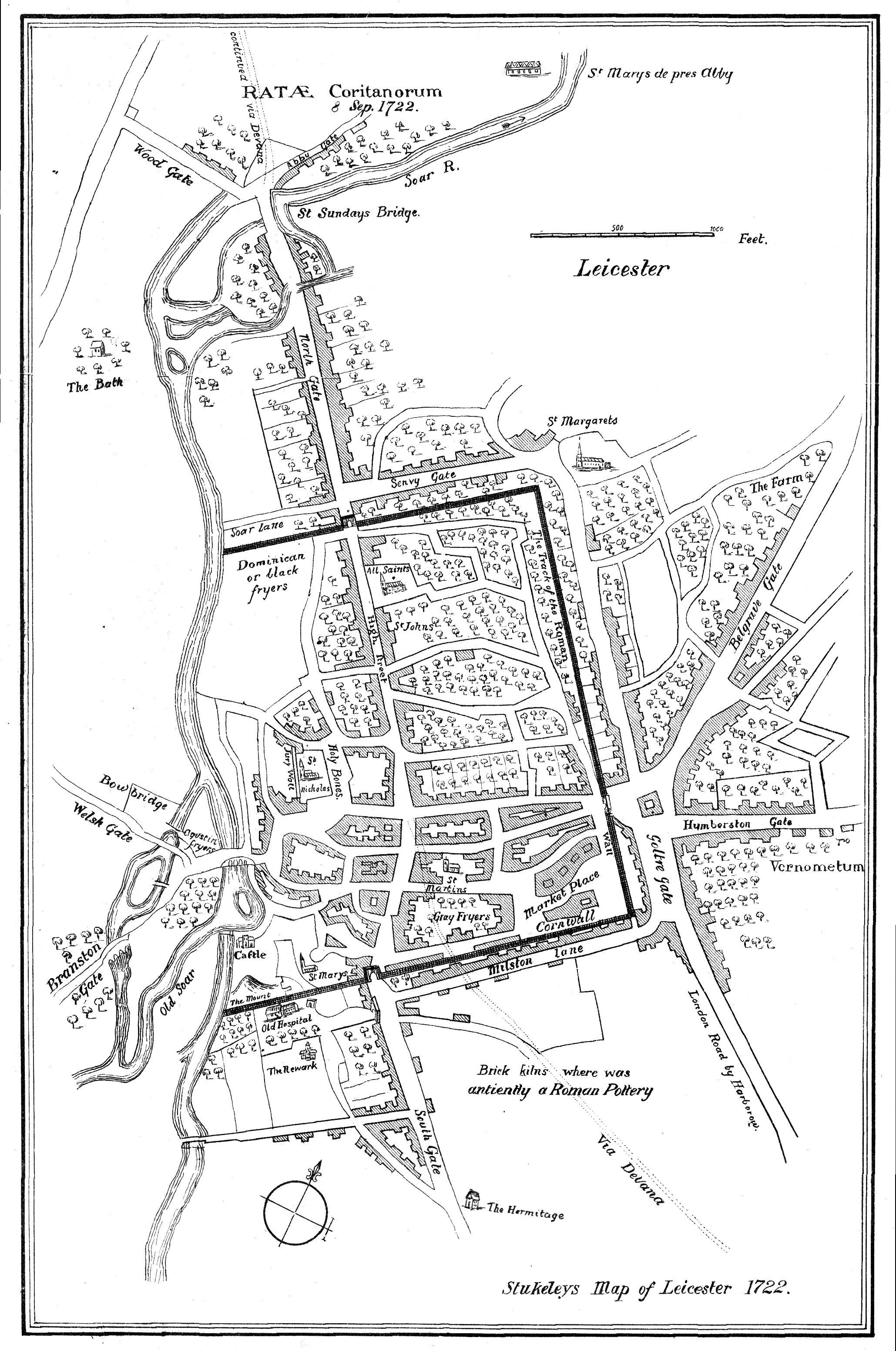
Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands. The city lies on the River Soar and close to the eastern end of the National Forest, England, National Forest. It is situated to the north-east of Birmingham and Coventry, south of Nottingham and west of Peterborough. The population size has increased by 38,800 ( 11.8%) from around 329,800 in 2011 to 368,600 in 2021 making it the most populous municipality in the East Midlands region. The associated Urban area#United Kingdom, urban area is also the 11th most populous in England and the List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, 13th most populous in the United Kingdom. Leicester is at the intersection of two railway lines: the Midland Main Line and the Birmingham to London Stansted Airport line. It is also at the confluence of the M1 motorway, M1/M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratae Corieltauvorum
Ratae Corieltauvorum or simply Ratae was a town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today it is known as Leicester, located in the English county of Leicestershire. Name ''Ratae'' is a latinate form of the Brittonic word for "ramparts" (cf. Gaelic '' rath''), suggesting the site was an Iron Age oppidum. This generic name was distinguished by "of the Corieltauvians", the name of the Celtic tribe whose capital it served as under the Romans. The town was mistakenly known as Ratae Coritanorum in later records. However, an inscription recovered in 1983 showed that it was corrupt and "Corieltauvorum" was the proper form of the name. History Prehistory The native settlement encountered by the Romans at the site seems to have developed in the 2nd or 1st centuries BC. This area of the Soar was split into two channels: a main stream to the east and a narrower channel on the west, with a presumably marshy island between. The settlement seems to have controlled a ford ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volisios
Volisios was a local ruler or king based in the English East Midlands, around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain. He is traditionally thought to have been a ruler of the Corieltavi, who inhabited this region in the Roman period and perhaps before. He is known only through inscriptions on coins. His name appears on three series of coins, minted c. AD 30-60, paired with three other names, which are thought to be allies or subordinate rulers, Dumnovellaunus, Dumnocoveros and Cartivellaunos. A large number of his coins were found in two hoards found at Lightcliffe and Honley in Yorkshire Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have .... External linksCoritaniaRoman-Britain.org {{authority control Briton rulers 1st-century monarchs in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumnocoveros
Dumnocoveros was a local ruler or king based in the English East Midlands, around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain. He is traditionally thought to have been a ruler of the Corieltavi, who inhabited this region in the Roman period and perhaps before. He is only known from coin inscriptions, which suggest that he was a co-ruler or subordinate of Volisios Volisios was a local ruler or king based in the English East Midlands, around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain. He is traditionally thought to have been a ruler of the Corieltavi, who inhabited this region in the Roman period and perhaps .... External linksCoritaniaRoman-Britain.co.uk {{authority control Briton rulers 1st-century monarchs in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumnovellaunus
Dubnovellaunus or Dumnovellaunus was the name of at least one, and possibly several kings of south-eastern Britain in the late 1st century BC/early 1st century AD, known from coin legends and from a mention in the ''Res Gestae Divi Augusti''. *Dubnovellaunus is the name of a king who, based on coin distribution, appears to have ruled over Kent east of the River Medway. He was the first king of the Cantiaci to issue inscribed coins: some of his coins appear to date from as early as 40-30 BC. Towards the end of the 1st century BC he seems to have been succeeded by a king called Vodenos or Vosenios, although it is possible the two kings' reigns were contemporary or overlapped. *A king called Dubnovellaunus succeeded his father Addedomarus as king of the Trinovantes ca. 10-5 BC and ruled for several years before being supplanted by Cunobelinus Cunobeline (or Cunobelin, from Latin , derived from Common Brittonic ''*Cunobelinos'' "Strong as a Dog", "Strong Dog") was a king in pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartivelios
Cartivellaunos was a local ruler or king based in the English East Midlands, around the time of the Roman conquest of Britain. He is traditionally thought to have been a ruler of the Corieltavi The Corieltauvi (also the Coritani, and the Corieltavi) were a tribe of people living in Britain prior to the Roman conquest, and thereafter a '' civitas'' of Roman Britain. Their territory was in what is now the English East Midlands. They were ..., who inhabited this region in the Roman period and perhaps before. He is known only through inscriptions on coins. His name appears on coins minted c. AD 30-60, paired with the name Volisios, who is thought to have been an ally or co-rulers. External linksCoritania Roman-Britain.co.uk {{authority control Briton rulers 1st-century monarchs in Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Roads In Britain
Roman roads in Britannia were initially designed for military use, created by the Roman Army during the nearly four centuries (AD 43–410) that Britannia was a province of the Roman Empire. It is estimated that about of paved trunk roads (surfaced roads running between two towns or cities) were constructed and maintained throughout the province. Most of the known network was complete by 180. The primary function of the network was to allow rapid movement of troops and military supplies, but it subsequently provided vital infrastructure for commerce, trade and the transportation of goods. A considerable number of Roman roads remained in daily use as core trunk roads for centuries after the end of Roman rule in Britain in 410. Some routes are now part of the UK's national road network. Others have been lost or are of archeological and historical interest only. After the Romans departed, systematic construction of paved highways in the United Kingdom did not resume unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derbyshire
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the East Midlands, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest. It borders Greater Manchester to the north-west, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the north-east, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire to the south-east, Staffordshire to the west and south-west and Cheshire to the west. Kinder Scout, at , is the highest point and Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, the lowest at . The north–south River Derwent is the longest river at . In 2003, the Ordnance Survey named Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms, near Swadlincote, as Britain's furthest point from the sea. Derby is a unitary authority area, but remains part of the ceremonial county. The county was a lot larger than its present coverage, it once extended to the boundaries of the City of Sheffield district in South Yorkshire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia ( Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis (Bath), Corinium (Cirencester), and Ratae Corieltauvorum ( Leicester). Roman route The word ''Fosse'' is derived from the Latin , meaning 'ditch'. For the first few decades after the Roman invasion of Britain in 43 CE, the Fosse Way marked the western frontier of Roman rule in Iron Age Britain. It is possible that the road began as a defensive ditch that was later filled in and converted into a road, or possibly a defensive ditch ran alongside the road for at least some of its length. The road joined Akeman Street and Ermin Way at Cirencester, crossed Watling Street at ''Venonis'' ( High Cross) south of Leicester, and joined Ermine Street at Lincoln. The Antonine Itinerary (a 2nd-century Roman register of roads) includes the section between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Churchover
Churchover is a small village and civil parish in Warwickshire, England. The population of the parish in the 2001 census was 230, increasing to 251 at the 2011 census. It is located around 4 miles (7 km) north of Rugby, and is administratively part of the borough of Rugby. The village lies just west of the A426 road, and just north of the M6 motorway on the border with Leicestershire. It was named in the Domesday Book as Church Wavre. Within the parish boundaries is Coton House, a mansion house dating from 1787. It was Grade II* listed in 1951. Royal Mail purchased the property in 1970 and used it as a training and conference centre. In 2010 the property was destroyed by fire, with the interiors becoming a blackened shell. Within five years however it has been restored to its former glory and sold to a private individual. The village contains the ''Holy Trinity Church'' which dates partly from the 15th century and is a Grade II* listed building. There was a village shop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |