Laminin-type EGF-like Domain on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Laminins are a
Laminins are a
The Laminin Protein
* * * * * (lecture by Professor Erhard Hoheneseter) {{InterPro content, IPR002049, IPR012679, IPR012680, IPR009254, IPR010307, IPR008211, IPR000034
 Laminins are a
Laminins are a family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
of glycoproteins
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glyco ...
of the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struc ...
of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The ba ...
(one of the layers of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellula ...
, migration, and adhesion.
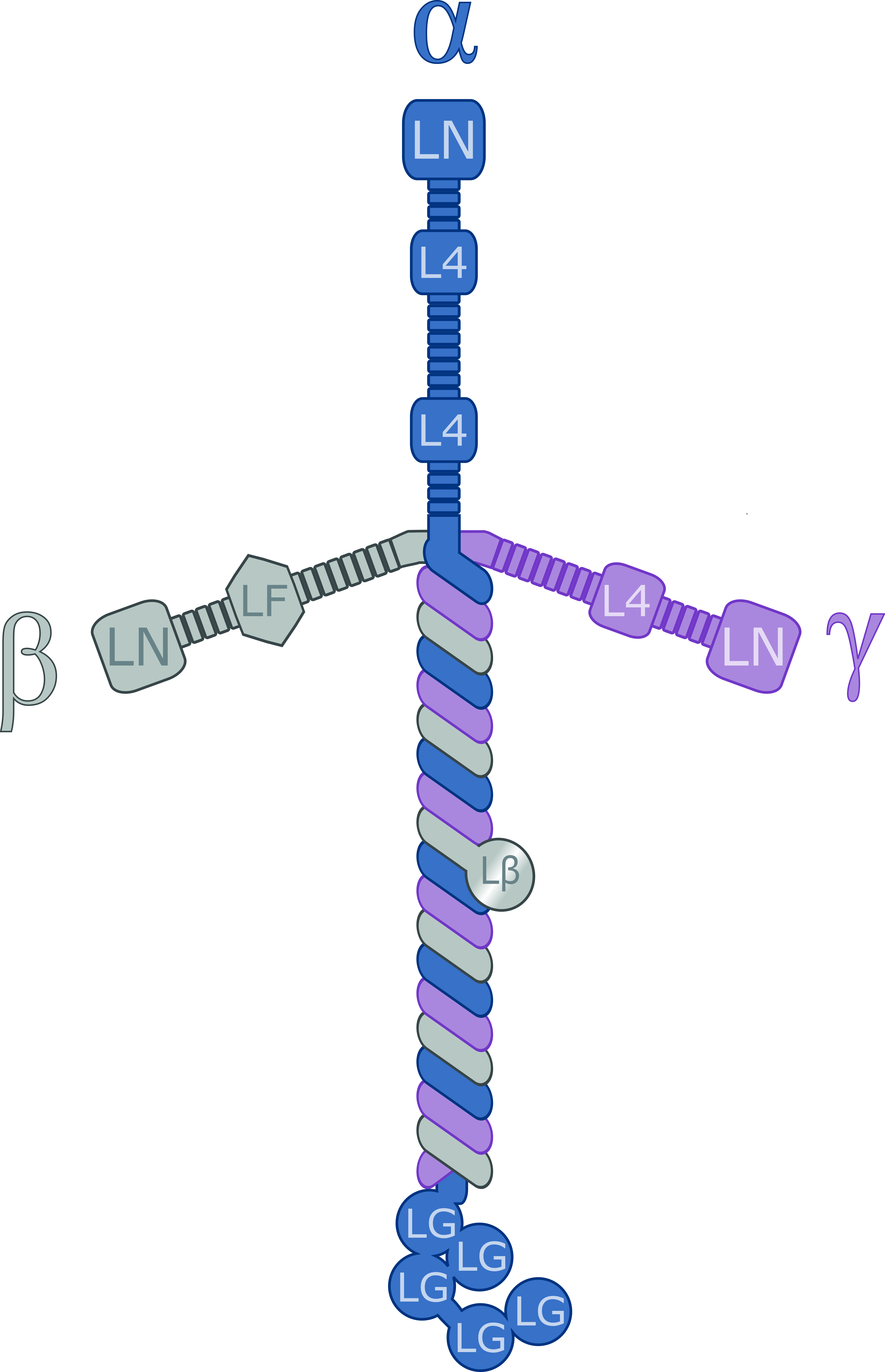
Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass
The molecular mass (''m'') is the mass of a given molecule: it is measured in daltons (Da or u). Different molecules of the same compound may have different molecular masses because they contain different isotopes of an element. The related quant ...
(~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a spe ...
genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the ...
and extracellular matrix molecules
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioc ...
. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, which allows them to form sheets. The long arm is capable of binding to cells, which helps anchor organized tissue cells to the basement membrane.
The laminin family of glycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as g ...
s is an integral part of the structural scaffolding in almost every tissue of an organism. They are secreted and incorporated into cell-associated extracellular matrices. Laminin is vital for the maintenance and survival of tissues. Defective laminins can cause muscles to form improperly, leading to a form of muscular dystrophy, lethal skin blistering disease ( junctional epidermolysis bullosa) and defects of the kidney filter (nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy ...
).
Types
In humans, fifteen laminin trimers have been identified. The laminins are combinations of different alpha-, beta-, and gamma-chains. *Five alpha-chain isoforms:LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
(which has three splice forms), LAMA4
Laminin subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA4'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major non collagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
*Four beta-chain isoforms: LAMB1
Laminin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMB2
Laminin subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB2'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated i ...
, LAMB3
Laminin subunit beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB3'' gene.
LAMB3 encodes the beta 3 subunit of laminin. Laminin is composed of three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma), and refers to a family of basement membrane proteins ...
, LAMB4
LAMB4 is a laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and ...
(note that no known laminin trimer incorporates LAMB4 and its function remains poorly understood)
*Three gamma-chain isoforms: LAMC1
Laminin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMC2
Laminin subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC2'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide v ...
, LAMC3
Laminin subunit gamma-3 also known as LAMC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC3'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They ...
Laminins were previously numbered as they were discovered, i.e. laminin-1, laminin-2, laminin-3, etc., but the nomenclature was changed to describe which chains are present in each isoform (laminin-111, laminin-211, etc.). In addition, many laminins had common names before either laminin nomenclature was in place.
Function
Laminins form independent networks and are associated withtype IV collagen
Collagen IV (ColIV or Col4) is a type of collagen found primarily in the basal lamina. The collagen IV C4 domain at the C-terminus is not removed in post-translational processing, and the fibers link head-to-head, rather than in parallel. Also ...
networks via entactin
Nidogen-1 (NID-1), formerly known as entactin, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NID1'' gene. Both nidogen-1 and nidogen-2 are essential components of the basement membrane alongside other components such as type IV collagen, proteog ...
, fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high-molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen ...
, and perlecan
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPG2'' gene. The HSPG2 gene codes for a 4,391 ami ...
. They also bind to cell membranes through integrin
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, ...
s and other plasma membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (t ...
molecules, such as the dystroglycan
Dystroglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DAG1'' gene.
Dystroglycan is one of the dystrophin-associated glycoproteins, which is encoded by a 5.5 kb transcript in ''Homo sapiens'' on chromosome 3. There are two exons that are s ...
glycoprotein complex and Lutheran blood group glycoprotein. Through these interactions, laminins critically contribute to cell attachment and differentiation, cell shape and movement, maintenance of tissue phenotype, and promotion of tissue survival. Some of these biological functions of laminin have been associated with specific amino-acid sequences or fragments of laminin. For example, the peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. ...
sequence TFALRGDNGDNGQ which is located on the alpha-chain of laminin, promotes the adhesion of endothelial cells.
Laminin alpha4 is distributed in a variety of tissues including peripheral nerves
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain an ...
, dorsal root ganglion
A dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion; also known as a posterior root ganglion) is a cluster of neurons (a ganglion) in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dor ...
, skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m ...
and capillaries; in the neuromuscular
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation to ...
junction, it is required for synaptic specialisation. The structure of the laminin-G domain has been predicted to resemble that of pentraxin
Pentraxins (PTX), also known as pentaxins, are an evolutionary conserved family of proteins characterised by containing a pentraxin protein domain. Proteins of the pentraxin family are involved in acute immunological responses. They are a cla ...
.
Role in neural development
Laminin-111 is a major substrate along which nerve axons will grow, both in vivo and in vitro. For example, it lays down a path that developing retinal ganglion cells follow on their way from the retina to the tectum. It is also often used as a substrate in cell culture experiments. The presence of laminin-1 can influence how the growth cone responds to other cues. For example, growth cones are repelled by netrin when grown on laminin-111 but are attracted to netrin when grown on fibronectin. This effect of laminin-111 probably occurs through a lowering of intracellular cyclic AMP.Role in peripheral nerve repair
Laminins are enriched at the lesion site after peripheral nerve injury and are secreted bySchwann cell
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial cells function to support neurons and in the PNS, also include satellite cells, olfactory ...
s. Neurons of the peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain a ...
express integrin receptors that attach to laminins and promote neuroregeneration
Neuroregeneration refers to the regrowth or repair of nervous tissues, cells or cell products. Such mechanisms may include generation of new neurons, glia, axons, myelin, or synapses. Neuroregeneration differs between the peripheral nervous syste ...
after injury.
Pathology
Dysfunctional structure of one particular laminin, laminin-211, is the cause of one form ofcongenital muscular dystrophy
Congenital muscular dystrophies are autosomal recessively-inherited muscle diseases. They are a group of heterogeneous disorders characterized by muscle weakness which is present at birth and the different changes on muscle biopsy that ranges fr ...
. Laminin-211 is composed of an α2, β1 and γ1 chains. This laminin's distribution includes the brain and muscle fibers. In muscle, it binds to alpha-dystroglycan and integrin alpha7— beta1 via the G domain, and via the other end, it binds to the extracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struc ...
.
Abnormal laminin-332, which is essential for epithelial cell adhesion to the basement membrane, leads to a condition called junctional epidermolysis bullosa, characterized by generalized blisters, exuberant granulation tissue of skin and mucosa, and pitted teeth.
Malfunctional laminin-521 in the kidney filter causes leakage of protein into the urine and nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes protein in the urine, low blood albumin levels, high blood lipids, and significant swelling. Other symptoms may include weight gain, feeling tired, and foamy ...
.
Role in cancer
Some of the laminin isoforms have been implicated in cancer pathophysiology. The majority of transcripts that harbor aninternal ribosome entry site An internal ribosome entry site, abbreviated IRES, is an RNA element that allows for translation initiation in a cap-independent manner, as part of the greater process of protein synthesis. In eukaryotic translation, initiation typically occurs at ...
(IRES) are involved in cancer development via corresponding proteins. A crucial event in tumor progression referred to as epithelial to mesenchymal transition
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
(EMT) allows carcinoma cells to acquire invasive properties. The translational activation of the extracellular matrix component laminin B1 (LAMB1) during EMT has been recently reported suggesting an IRES-mediated mechanism. In this study, the IRES activity of LamB1 was determined by independent bicistronic reporter assays. Strong evidences exclude an impact of cryptic promoter or splice sites on IRES-driven translation of LamB1. Furthermore, no other LamB1 mRNA species arising from alternative transcription start sites or polyadenylation signals were detected that account for its translational control. Mapping of the LamB1 5'-untranslated region (UTR) revealed the minimal LamB1 IRES motif between -293 and -1 upstream of the start codon. Notably, RNA affinity purification showed that the La protein interacts with the LamB1 IRES. This interaction and its regulation during EMT were confirmed by ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation. In addition, La was able to positively modulate LamB1 IRES translation. In summary, these data indicate that the LamB1 IRES is activated by binding to La which leads to translational upregulation during hepatocellular EMT.
Use in cell culture
Together with other major components of the ECM, such as collagens and fibronectin, laminins have been used to enhance mammalian cell culture, especially in the case of pluripotent stem cells, as well as some primary cell cultures, which can be difficult to propagate on other substrates. Two types of naturally-sourced laminins are commercially available. Laminin-111 extracted from mouse sarcomas is one popular laminin type, as well as laminin mixtures from human placenta, which may primarily correspond to laminin-211, 411 or 511, depending on the provider. The various laminin isoforms are practically impossible to isolate from tissues in pure form due to extensive cross-linking and the need for harsh extraction conditions, such as proteolytic enzymes or low pH, that cause degradation. Therefore, recombinant laminins have been produced since the year 2000. This made it possible to test if laminins could have a significant role ''in vitro'' as they have in the human body. In 2008, two groups independently showed that mouse embryonic stem cells can be grown for months on top of recombinant laminin-511. Later, Rodin ''et al.'' showed that recombinant laminin-511 can be used to create a totally xeno-free and defined cell culture environment to culture human pluripotent ES cells and human iPS cells.Laminin domains
Laminins contain several conservedprotein domains
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of se ...
.
Laminin I and Laminin II
Laminins are trimeric molecules; laminin-1 is an alpha1 beta1 gamma1 trimer. It has been suggested that the domains I and II from laminin A, B1 and B2 may come together to form a triple helical coiled-coil structure.Laminin B
The laminin B domain (also known as domain IV) is anextracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
module of unknown function. It is found in a number of different protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s that include, heparan sulphate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs as a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular m ...
proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to w ...
from basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
, a laminin-like protein from ''Caenorhabditis elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (r ...
'' and laminin. Laminin IV domain is not found in short laminin chains (alpha4 or beta3).
Laminin EGF-like
Beside different types of globular domains each laminin subunit contains, in its first half, consecutiverepeat
Repeat may refer to:
* Rerun, a rebroadcast of an episode of a radio or television program
* Repeated sequence (DNA), a pattern of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) that occurs in multiple copies throughout the genome
** CRISPR
* The smallest rectangle ...
s of about 60 amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ...
s in length that include eight conserved cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, s ...
s. The tertiary structure of this domain is remotely similar in its N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
to that of the EGF-like module. It is also known as a 'LE' or 'laminin-type EGF-like' domain. The number of copies of the laminin EGF-like domain in the different forms of laminins is highly variable; from 3 up to 22 copies have been found. In mouse
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
laminin gamma-1 chain, the seventh LE domain has been shown to be the only one that bind
BIND () is a suite of software for interacting with the Domain Name System (DNS). Its most prominent component, named (pronounced ''name-dee'': , short for ''name daemon''), performs both of the main DNS server roles, acting as an authoritative ...
s with a high affinity to nidogen Nidogens, formerly known as entactins, are a family of sulfated monomeric glycoproteins located in the basal lamina of parahoxozoans. Two nidogens have been identified in humans: nidogen-1 (NID1) and nidogen-2 (NID2). Remarkably, vertebrates are st ...
. The binding-sites are located on the surface within the loops C1-C3 and C5-C6. Long consecutive arrays of laminin EGF-like domains in laminins form rod-like elements of limited flexibility, which determine the spacing in the formation of laminin networks of basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
s.
Laminin G
The laminin globular (G) domain, also known as the LNS (Laminin-alpha, Neurexin and Sex hormone-binding globulin) domain, is on average 177 amino acids in length and can be found in one to six copies in various laminin family members as well as in a large number of otherextracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s. For example, all laminin alpha-chains have five laminin G domains, all collagen family proteins have one laminin G domain, the CNTNAP proteins have four laminin G domains, while neurexin 1 and 2 each hold six laminin G domains. On average, approximately one quarter of the proteins that hold laminin G domains is taken up by these laminin G domains themselves. The smallest laminin G domain can be found in one of the collagen proteins (COL24A1; 77 AA) and the largest domain in TSPEAR (219 AA).
The exact function of the Laminin G domains has remained elusive, and a variety of binding functions has been ascribed to different Laminin G modules. For example, the laminin alpha1 and alpha2 chains each have five C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
laminin G domains, where only domains LG4 and LG5 contain binding site
In biochemistry and molecular biology, a binding site is a region on a macromolecule such as a protein that binds to another molecule with specificity. The binding partner of the macromolecule is often referred to as a ligand. Ligands may inclu ...
s for heparin, sulphatide
Sulfatide, also known as 3-O-sulfogalactosylceramide, SM4, or sulfated galactocerebroside, is a class of sulfolipids, specifically a class of sulfoglycolipids, which are glycolipids that contain a sulfate group. Sulfatide is synthesized primarily ...
s and the cell surface receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integr ...
dystroglycan
Dystroglycan is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DAG1'' gene.
Dystroglycan is one of the dystrophin-associated glycoproteins, which is encoded by a 5.5 kb transcript in ''Homo sapiens'' on chromosome 3. There are two exons that are s ...
. Laminin G-containing protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s appear to have a wide variety of roles in cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indir ...
, signalling
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The ''IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing'' ...
, migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum l ...
, assembly and differentiation
Differentiation may refer to:
Business
* Differentiation (economics), the process of making a product different from other similar products
* Product differentiation, in marketing
* Differentiated service, a service that varies with the identity ...
.
Laminin N-terminal
Basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
assembly is a cooperative process in which laminins polymerise
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer, monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are ...
through their N-terminal domain (LN or domain VI) and anchor to the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
surface through their G domains. Netrins may also associate with this network through heterotypic LN domain interactions. This leads to cell signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellula ...
through integrins
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that facilitate cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, ...
and dystroglycan (and possibly other receptors) recruited to the adherent laminin. This LN domain-dependent self-assembly is considered to be crucial for the integrity of basement membranes, as highlighted by genetic forms of muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily af ...
containing the deletion of the LN module from the alpha 2 laminin chain. The laminin N-terminal domain is found in all laminin and netrin subunits except laminin alpha 3A, alpha 4 and gamma 2.
Human proteins containing laminin domains
*Laminin domain I: all laminin alpha chains (LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA4
Laminin subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA4'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major non collagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
)
*Laminin domain II: all laminin alpha chains (LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA4
Laminin subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA4'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major non collagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
)
*Laminin B (domain IV): all laminin alpha chains (LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA4
Laminin subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA4'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major non collagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
), gamma chains (LAMC1
Laminin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMC2
Laminin subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC2'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide v ...
, LAMC3
Laminin subunit gamma-3 also known as LAMC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC3'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They ...
), and perlecan (HSPG2
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPG2'' gene. The HSPG2 gene codes for a 4,391 amin ...
)
*Laminin EGF-like (domains III and V): all laminin chains (LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA4
Laminin subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA4'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major non collagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
, LAMB1
Laminin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMB2
Laminin subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB2'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated i ...
, LAMB3
Laminin subunit beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB3'' gene.
LAMB3 encodes the beta 3 subunit of laminin. Laminin is composed of three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma), and refers to a family of basement membrane proteins ...
, LAMB4
LAMB4 is a laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and ...
, LAMC1
Laminin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMC2
Laminin subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC2'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide v ...
, LAMC3
Laminin subunit gamma-3 also known as LAMC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC3'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They ...
), attractins (ATRN
Attractin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ATRN'' gene.
Attractin is a Group XI C-type lectin
A C-type lectin (CLEC) is a type of carbohydrate-binding protein known as a lectin. The C-type designation is from their requirement ...
, ATRNL1), cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptors (CELSR1
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 also known as flamingo homolog 2 or cadherin family member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELSR1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo su ...
, CELSR2
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELSR2'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. The flamingo subfamily consists ...
, CELSR3
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELSR3'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. The flamingo subfamily consist ...
), cysteine-rich with EGF-like domain proteins (CRELD1
Cysteine-rich with EGF-like domain protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRELD1'' gene.
Function
Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like repeats are a class of cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential protei ...
, CRELD2
Cysteine-rich with EGF-like domain protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRELD2'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." mean ...
), multiple EGF-like domain proteins ( MEGF6, MEGF8, MEGF9, MEGF10
Multiple EGF-like-domains 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MEGF10'' gene.
MEGF10 is a regulator of satellite cell myogenesis and interacts with Notch1 in myoblasts. It has been shown to be the cause of early-onset myopathy, ar ...
, PEAR1), most netrins ( NTN1, NTN3, NTN4, NTNG1, NTNG2), mucins 3A and 3B (MUC3A
Mucin 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUC3A'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or '' ...
, MUC3B), class F scavenger receptors ( SCARF1, SCARF2
A scarf, plural ''scarves'', is a piece of fabric worn around the neck or head for warmth, sun protection, cleanliness, fashion, religious reasons, or used to show the support for a sports club or team. They can be made in a variety of differ ...
), stabilins (STAB1
Stabilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STAB1'' gene.
This gene encodes a large, transmembrane receptor protein which may function in angiogenesis, lymphocyte homing, cell adhesion, or receptor scavenging. The protein contains ...
, STAB2
Stabilin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''STAB2'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a large, transmembrane receptor protein which may function in angiogenesis, lymphocyte homing, cell adhesion, or receptor scavenging. The protei ...
), agrin (AGRIN
Agrin is a large proteoglycan whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis. Agrin is named based on its involvement in the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis. I ...
), angiopoietin-1 receptor ( TEK), perlecan (HSPG2
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPG2'' gene. The HSPG2 gene codes for a 4,391 amin ...
), tenascin N ( TNN), and usherin (USH2A
Usherin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USH2A'' gene.
This gene encodes the protein Usherin that contains laminin EGF motifs, a pentraxin domain, and many fibronectin type III motifs. The encoded basement membrane-associated pr ...
).
*Laminin G domain: all laminin alpha chains (LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA4
Laminin subunit alpha-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA4'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major non collagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
), cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptors (CELSR1
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 also known as flamingo homolog 2 or cadherin family member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELSR1'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo su ...
, CELSR2
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELSR2'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. The flamingo subfamily consists ...
, CELSR3
Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELSR3'' gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the flamingo subfamily, part of the cadherin superfamily. The flamingo subfamily consist ...
), contactin-associated proteins (CNTNAP1
CASPR also known as Contactin associated protein 1, Paranodin and CASPR1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNTNAP1 gene.
CASPR is a part of the neurexin family of proteins, hence its another name "Neurexin IV". CASPR is a membrane ...
, CNTNAP2
Contactin-associated protein-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNTNAP2'' gene. Since the most recent reference human genome GRCh38, CNTNAP2 is the longest gene in the human genome
This gene encodes a member of the neurexin ...
, CNTNAP3, CNTNAP3B, CNTNAP4
Contactin-associated protein-like 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CNTNAP4'' gene.
This gene product belongs to the neurexin family, members of which function in the vertebrate nervous system as cell adhesion molecules and recept ...
, CNTNAP5), some collagens (COL5A1
Collagen alpha-1(V) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL5A1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' ...
, COL5A3
Collagen alpha-3(V) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL5A3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' ...
, COL9A1, COL11A1, COL11A2
Collagen alpha-2(XI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL11A2'' gene.
The COL11A2 gene produces one component of this type of collagen, called the pro-alpha2(XI) chain. Type XI collagen adds structure and strength to the tissu ...
, COL12A1
Collagen alpha-1(XII) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL12A1'' gene.
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XII collagen, a member of the FACIT (fibril-associated collagens with interrupted triple helices) collagen famil ...
, COL14A1
Collagen alpha-1(XIV) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL14A1'' gene.
It likely plays a role in collagen binding and cell-cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cel ...
, COL15A1
Collagen alpha-1(XV) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL15A1'' gene.
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XV collagen, a member of the FACIT collagen family (fibril-associated collagens with interrupted helices). Type X ...
, COL16A1
Collagen alpha-1(XVI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL16A1'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XVI collagen, a member of the FACIT collagen family (fibril-associated collagens with interrupted he ...
, COL18A1
Collagen alpha-1(XVIII) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL18A1'' gene.
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XVIII collagen. This collagen is one of the multiplexins, extracellular matrix proteins that contain multipl ...
, COL19A1
Collagen alpha-1(XIX) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL19A1'' gene.
This gene encodes the alpha chain of type XIX collagen, a member of the FACIT collagen family (fibril-associated collagens with interrupted helices). Al ...
, COL20A1, COL21A1
Collagen alpha-1(XXI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL21A1'' gene. The protein is an extracellular matrix component of blood vessel walls, secreted by smooth-muscle
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non- striated muscle, ...
, COL22A1
COL22A1 is a human gene encoding for collagen. The associated protein is thought to contribute to the stabilization of myotendinous junctions and strengthen skeletal muscle attachments during muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the ac ...
, COL24A1, COL27A1
Collagen alpha-1 (XXVII) chain (COL27A1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''COL27A1'' gene.
COL27A1 is a type XXVII collagen. It was discovered by James Pace. This gene appears to be turned on in cartilage, the eye, and in the ear ...
), crumbs homologs 1 and 2 (CRB1
Crumbs homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CRB1'' gene.
This gene encodes a protein which is similar to the Drosophila ''crumbs'' protein and localizes to the inner segment of mammalian photoreceptors. In Drosophila, crumbs ...
, CRB2), fat homologs (FAT1
Protocadherin FAT1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FAT1'' gene.
Function
This gene is an ortholog of the ''Drosophila'' fat gene, which encodes a tumor suppressor essential for controlling cell proliferation during Drosophila ...
, FAT2, FAT3, FAT4
Protocadherin Fat 4, also known as cadherin family member 14 (CDHF14) or FAT tumor suppressor homolog 4 (FAT4), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FAT4'' gene.
FAT4 is associated with the Hippo signaling pathway.
Clinical signif ...
), NEL-like proteins ( NELL1, NELL2), neurexins (NRXN1
Neurexin-1-alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRXN1'' gene.
Neurexins are a family of proteins that function in the vertebrate nervous system as cell adhesion molecules and receptors. They are encoded by several unlinked genes o ...
, NRXN2
Neurexin-2-alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRXN2'' gene.
Neurexins are a family of proteins that function in the vertebrate nervous system as cell adhesion molecules and receptors. They are encoded by several unlinked genes o ...
, NRXN3
Neurexin-3-alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NRXN3'' gene.
Neurexins are a family of proteins that function in the vertebrate nervous system as cell adhesion molecules and receptors. They are encoded by several unlinked genes o ...
), slit homologs (SLIT1
Slit homolog 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLIT1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, SLIT2
Slit homolog 2 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SLIT2'' gene.
Interactions
SLIT2 has been shown to interact
Advocates for Informed Choice, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofi ...
, SLIT3), thrombospondins ( THBS1, THBS2, THBS3, THBS4, TSPEAR), agrin (AGRIN
Agrin is a large proteoglycan whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis. Agrin is named based on its involvement in the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis. I ...
), chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 (CSPG4
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4, also known as melanoma-associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (MCSP) or neuron-glial antigen 2 (NG2), is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan that in humans is encoded by the ''CSPG4'' gene.
Function
CSPG4 ...
), eyes shut homolog (EYS
Eys (; li, Ees ) is a village in the municipality of Gulpen-Wittem, Limburg, the Netherlands. The town is located 3 km. from Gulpen and 17 km. from provincial capital Maastricht. Furthermore, it is characterised by its location in the h ...
), growth arrest-specific protein 6 (GAS6
Growth arrest – specific 6, also known as GAS6, is a human gene coding for the GAS6 protein. It is similar to the Protein S with the same domain organization and 43% amino acid identity. It was originally found as a gene upregulated by growth ...
), perlecan (HSPG2
Perlecan (PLC) also known as basement membrane-specific heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein (HSPG) or heparan sulfate proteoglycan 2 (HSPG2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPG2'' gene. The HSPG2 gene codes for a 4,391 amin ...
), pikachurin (EGFLAM
Pikachurin, also known as AGRINL (AGRINL) and EGF-like, fibronectin type-III and laminin G-like domain-containing protein (EGFLAM), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EGFLAM'' gene.
Pikachurin is a dystroglycan-interacting protein ...
), protein S ( PROS1), sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) or sex steroid-binding globulin (SSBG) is a glycoprotein that binds to androgens and estrogens. When produced by the Sertoli cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis, it has also been called androgen-bi ...
) and usherin (USH2A
Usherin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USH2A'' gene.
This gene encodes the protein Usherin that contains laminin EGF motifs, a pentraxin domain, and many fibronectin type III motifs. The encoded basement membrane-associated pr ...
)
*Laminin N-terminal (domain VI): most laminin chains (LAMA1
Laminin subunit alpha-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA2
Laminin subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA2'' gene.
Function
Laminin, an extracellular matrix protein, is a major component of the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of ...
, LAMA3
Laminin subunit alpha-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA3'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ' ...
, LAMA5
Laminin subunit alpha-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMA5'' gene.
Function
Components of the extracellular matrix exert myriad effects on tissues throughout the body. In particular, the laminins, a family of heterotrimeric ...
, LAMB1
Laminin subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMB2
Laminin subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB2'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated i ...
, LAMB3
Laminin subunit beta-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMB3'' gene.
LAMB3 encodes the beta 3 subunit of laminin. Laminin is composed of three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma), and refers to a family of basement membrane proteins ...
, LAMB4
LAMB4 is a laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and ...
, LAMC1
Laminin subunit gamma-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC1'' gene.
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They have been implicated in a wide var ...
, LAMC3
Laminin subunit gamma-3 also known as LAMC3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LAMC3'' gene.
Function
Laminins, a family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins, are the major noncollagenous constituent of basement membranes. They ...
), most netrins ( NTN1, NTN3, NTN4, NTNG1, NTNG2), and usherin (USH2A
Usherin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''USH2A'' gene.
This gene encodes the protein Usherin that contains laminin EGF motifs, a pentraxin domain, and many fibronectin type III motifs. The encoded basement membrane-associated pr ...
)
See also
* Substrate adhesion molecules *Laminin database
The Laminin database is a database of non-collagenous extracellular matrix proteins.
See also
* Laminin
References
External links
* http://www.lm.lncc.br
Biological databases
Laminins
{{Biodatabase-stub ...
* List of target antigens in pemphigoid
Circulating auto-antibodies in the human body can target normal parts of the skin leading to disease. This is a list of antigens in the skin that may become targets of circulating auto-antibodies leading to the various types of pemphigoid.
...
References
External links
The Laminin Protein
* * * * * (lecture by Professor Erhard Hoheneseter) {{InterPro content, IPR002049, IPR012679, IPR012680, IPR009254, IPR010307, IPR008211, IPR000034