Lake Constance (, ) refers to three
bodies of water
A body of water or waterbody is any significant accumulation of water on the surface of Earth or another planet. The term most often refers to oceans, seas, and lakes, but it includes smaller pools of water such as ponds, wetlands, or more ra ...
on the
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
at the northern foot of the
Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
:
Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''),
Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, called the
Seerhein (). These waterbodies lie within the Lake Constance Basin () in the
Alpine Foreland through which the
Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
flows.
[ The nearby '' Mindelsee'' is not considered part of Lake Constance.
The lake is situated where ]Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, and Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
meet. Its shorelines lie in the German states of Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
and Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
; the Swiss cantons of St. Gallen, Thurgau, and Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
; and the Austrian state of Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
. The actual locations of the country borders within the lake are disputed.
The Alpine Rhine forms, in its original course ( Alter Rhein), the Austro-Swiss border and flows into the lake from the south. The High Rhine flows westbound out of the lake and forms (with the exception of the Canton of Schaffhausen
The canton of Schaffhausen, also canton of Schaffhouse (; ; ; ), is the northernmost Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Switzerland. The principal city and capital of the canton is Schaffhausen. The canton's territory is divided into three non-co ...
, Rafzerfeld and Basel-Stadt) the German-Swiss border as far as to the city of Basel
Basel ( ; ), also known as Basle ( ), ; ; ; . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine (at the transition from the High Rhine, High to the Upper Rhine). Basel is Switzerland's List of cities in Switzerland, third-most-populo ...
.Überlingen
Überlingen (; ) is a German city on the northern shore of Lake Constance (Bodensee) in Baden-Württemberg near the German-Swiss border, border with Switzerland. After the city of Friedrichshafen, it is the second-largest city in the Bodenseek ...
and Kreuzlingen. The largest town on the Lower Lake is Radolfzell. The largest islands are Reichenau in the Lower Lake, and Lindau and Mainau in the Upper Lake. Bodanrück, a large peninsula, separates the Upper and Lower Lake.
While in English and in the Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, the lake is named after the city of Constance, the German name derives from the village of Bodman (municipality of Bodman-Ludwigshafen), in the northwesternmost corner of the lake.
Description
Lake Constance is located along the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
between the Alpine Rhine, its main tributary
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream (''main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which they ...
, and the High Rhine, its outflow. It is the third largest freshwater lake by surface area in Central and Western Europe (and the second largest in volume), after Lake Geneva and (in surface area) Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater rift lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the List of largest lakes of Europe, largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the larges ...
.
It is long, and, nearly at its widest point. It covers about , and is above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
. Its greatest depth is , exactly in the middle of the Upper Lake. Its volume is about .[
The connection between these two lakes is the Seerhein (lit.: "Rhine of the Lake(s)"). Geographically, usually it is not considered to be part of the lake, but a very short river.][
The Lower Lake Constance is loosely divided into three sections around the Island of Reichenau. The two German parts, the Gnadensee (lit.: "Lake Mercy") north of the island and north of the peninsula of Mettnau (the Markelfinger Winkel), and the Zeller See, south of Radolfzell and to the northwest of the Reichenau island, and the mainly Swiss Rheinsee (lit.: "Lake Rhine") – not to be mistaken for the ''Seerhein'' (lit.: "Rhine of the Lake(s)") at its start – to the south of the island and with its southwestern arm leading to its effluent in Stein am Rhein.][
The water of the regulated Alpine Rhine flows into the lake in the southeast near Bregenz, Austria, then through the Upper Lake Constance hardly targeting the ''Überlinger See'', into the ''Seerhein'' in the town of Konstanz, then through the ''Rheinsee'' virtually without feeding both German parts of the Lower Lake, and finally feeds the start of the High Rhine in Swiss town Stein am Rhein.][
The lake itself is an important source of drinking water for southwestern Germany.
The culminating point of the lake's drainage basin is the Swiss peak Piz Russein of the Tödi massif of the ]Glarus Alps
The Glarus Alps () are a mountain range in central Switzerland. They are bordered by the Uri Alps and the Schwyz Alps to the west, the Lepontine Alps to the south, the Appenzell Alps to the northeast. The eastern part of the Glarus Alps contains ...
at above sea level. It starts with the creek ''Aua da Russein'' (lit.: "Water of the Russein").
History
Lake Constance was formed by the Rhine Glacier during the Quaternary glaciation
The Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial period, glacial and interglacial, interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Year#SI prefix multipliers, Ma (million ...
ice age and is a '' Zungenbecken'' or Tongue lake. After the end of the last glacial period, about 10,000 years ago, the Obersee and Untersee still formed a single lake. The downward erosion of the High Rhine caused the lake level to gradually sink and a sill, the ''Konstanzer Schwelle'', to emerge.
The Rhine, the Bregenzer Ach, and the Dornbirner Ach carry sediments from the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
to the lake, thus gradually decreasing the depth and reducing the extension of the lake in the southeast.
In antiquity, the two lakes had different names; later, for reasons which are unknown, they came to have the same name.
In the 19th century, there were five different local time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
s around Lake Constance. Constance, belonging to the Grand Duchy of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden () was a German polity on the east bank of the Rhine. It originally existed as a sovereign state from 1806 to 1871 and later as part of the German Empire until 1918.
The duchy's 12th-century origins were as a Margravia ...
, adhered to Karlsruhe
Karlsruhe ( ; ; ; South Franconian German, South Franconian: ''Kallsruh'') is the List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, third-largest city of the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, after its capital Stuttgart a ...
time, Friedrichshafen used the time of the Duchy of Württemberg
The Duchy of Württemberg () was a duchy located in the south-western part of the Holy Roman Empire. It was a Imperial Estate, state of the Holy Roman Empire from 1495 to 1803. The dukedom's long survival for over three centuries was mainly du ...
, in Lindau, the Bavarian Munich time was observed, and Bregenz used Prague time, while the Swiss shore used Berne time. One would have needed to travel only to visit five time zones. Given the amount of trade and traffic over Lake Constance, this led to serious confusion. Public clocks in harbors used three different clock faces, depending on the destinations offered by the boat companies. In 1892, all German territories used CET, the Austrian railways had already introduced CET the previous year and Switzerland followed in 1894. Because traffic timetables had not been yet updated, CET became the sole valid time around and on Lake Constance in 1895.
Name
The earliest recorded reference to the lakes is by Roman geographer Pomponius Mela around AD 43, calling the upper lake ''Lacus Venetus'' and the lower lake ''Lacus Acronius'', the Rhine passing through both. Around AD 75, the naturalist Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
called them both ''Lacus Raetiae Brigantinus'' after the main Roman town on the lake, '' Brigantium'' (later Bregenz). This name is associated with the Celtic Brigantii who lived here, although it is not clear whether the place was named after the tribe or the inhabitants of the region were named after their main settlement. Ammianus Marcellinus later used the form ''Lacus Brigantiae''.Old High German
Old High German (OHG; ) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally identified as the period from around 500/750 to 1050. Rather than representing a single supra-regional form of German, Old High German encompasses the numerous ...
''bodamon'' which meant "on the soils", indicating a place on level terrain by the lake.early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
as a Frankish imperial palace (''Königspfalz''), Alamannian ducal seat and mint, which is why the name may have been transferred to the lake ("lake, by which Bodman is situated" = ''Bodmansee''). From 833 or 834, in Latin sources, the name appears in its Latinised form ''lacus potamicus''. Therefore, the name actually derived from the Bodman ''Pfalz'' (Latinized as ''Potamum'') was wrongly assumed by monastic scholars like Walahfrid Strabo to be derived from the Greek word ''potamos'' for "river" and meant "river lake". They may also have been influenced by the fact that the Rhine flowed through the lake.[
Wolfram von Eschenbach describes it in ]Middle High German
Middle High German (MHG; or ; , shortened as ''Mhdt.'' or ''Mhd.'') is the term for the form of High German, High German language, German spoken in the High Middle Ages. It is conventionally dated between 1050 and 1350, developing from Old High ...
as the ''Bodemensee'' or ''Bodemsee'' which has finally evolved into the present German name, ''Bodensee''. The name may be linked to that of the Bodanrück, the hill range between Lake Überlingen and the Lower Lake, and the history of the House of Bodman.
 The German name of the lake, ''Bodensee'', has been adopted by many other languages, for example: Dutch: ''Bodenmeer'', Danish: ''Bodensøen'', Norwegian: ''Bodensjøen'', Swedish: ''Bodensjön'', Finnish: ''Bodenjärvi'', Russian: ''Боденское озеро'', Polish: ''Jezioro Bodeńskie'', Czech: ''Bodamské jezero'', Slovak: ''Bodamské jazero'', Hungarian: ''Bodeni-tó'', Serbo-Croatian: ''Bodensko jezero'', Albanian: ''Liqeni i Bodenit''.
After the Council of Constance in the 15th century, the alternative name ''Lacus Constantinus'' was used in the (Roman Catholic) Romance language area. This name, which had been attested as early as 1187 in the form ''Lacus Constantiensis'',
The German name of the lake, ''Bodensee'', has been adopted by many other languages, for example: Dutch: ''Bodenmeer'', Danish: ''Bodensøen'', Norwegian: ''Bodensjøen'', Swedish: ''Bodensjön'', Finnish: ''Bodenjärvi'', Russian: ''Боденское озеро'', Polish: ''Jezioro Bodeńskie'', Czech: ''Bodamské jezero'', Slovak: ''Bodamské jazero'', Hungarian: ''Bodeni-tó'', Serbo-Croatian: ''Bodensko jezero'', Albanian: ''Liqeni i Bodenit''.
After the Council of Constance in the 15th century, the alternative name ''Lacus Constantinus'' was used in the (Roman Catholic) Romance language area. This name, which had been attested as early as 1187 in the form ''Lacus Constantiensis'',[ came from the town of Konstanz at the outflow of the Rhine from the Obersee, whose original name, Constantia, was in turn derived from the Roman emperor, Constantius Chlorus (around 300 AD). Hence the French: ''Lac de Constance'', Italian: ''Lago di Costanza'', Portuguese: ''Lago de Constança'', Spanish: ''Lago de Constanza'', Romanian: ''Lacul Constanța'', Greek: ''Λίμνη της Κωνσταντίας – Limni tis Konstantias''. The Arabic, بحيرة كونستانس ''buħaira Konstans'' and the Turkish, ''Konstanz gölü'', probably go back to the French form of the name. Even in Romance-influenced English the name "Lake Constance" gained a foothold and was then exported into other languages such as Hebrew: ימת קונסטנץ ''yamat Konstanz'' and Swahili: ''Ziwa la Konstanz''. In many languages both forms exist in parallel e.g. Romansh: ''Lai da Constanza'' and ''Lai Bodan'', Esperanto: ''Konstanca Lago'' and ''Bodenlago''.
The poetic name, " Swabian Sea", was adopted by authors of the early modern era and the Enlightenment from ancient authors, possibly ]Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
Tacitus’ two major historical works, ''Annals'' ( ...
. However, this assumption was based on an error (similar to that of the Teutoburg Forest and the Taunus): the Romans sometimes used the name ''Mare Suebicum'' for the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the ...
, not Lake Constance. In times when the Romans had located the so-called "Suebi
file:1st century Germani.png, 300px, The approximate positions of some Germanic peoples reported by Graeco-Roman authors in the 1st century. Suebian peoples in red, and other Irminones in purple.
The Suebi (also spelled Suavi, Suevi or Suebians ...
", then an Elbe Germanic tribe near a sea, this was understandable. The authors of the Early Modern Period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
overlooked this and adopted the name for the largest lake in the middle of the former Duchy of Swabia, which also included parts of today's Switzerland. Today the name Swabian Sea (''Schwäbisches Meer'') is only used jocularly as a hyperbolic term for Lake Constance.
Key facts
 No
No Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
finds have been made in the immediate vicinity of the lake, because the region of Lake Constance was long covered by the Rhine Glacier. The discovery of stone tools (microlith
A microlith is a small Rock (geology), stone tool usually made of flint or chert and typically a centimetre or so in length and half a centimetre wide. They were made by humans from around 60,000 years ago, across Europe, Africa, Asia and Austral ...
s) indicate that hunters and gatherers of the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
period (Middle Stone Age, 8,000–5,500 BC) frequented the area without settling, however. Only hunting camps have been confirmed. The earliest Neolithic farmers, who belonged to the Linear Pottery culture, also left no traces behind, because the Alpine foreland lay away from the routes along which they had spread during the 6th millennium BC. This changed only in the middle and late Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
when shore settlements were established, the so-called pile dwelling and wetland settlements, which have now been uncovered mainly on Lake Überlingen, the Constance Hopper and on the Obersee. At Unteruhldingen, a pile dwelling village has been reconstructed, and now forms an open air museum.
In 2015, a 20 km line of about 170 man-made dated in the Neolithic period or early Bronze Age was discovered on the south-west shore of the lake between Bottighofen and Romanshorn.[ (3 pages)][ :49/ref>
Grave finds from Singen am Hohentwiel date to the beginning of the Early ]Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
and shore settlements were repeatedly built during the Neolithic Period and the Bronze Age (up to 800 BC). During the following Iron Age
The Iron Age () is the final epoch of the three historical Metal Ages, after the Chalcolithic and Bronze Age. It has also been considered as the final age of the three-age division starting with prehistory (before recorded history) and progre ...
the settlement history is interrupted. The settlement of the shore of Lake Constance during the Hallstatt period is attested by grave mounds, which today are usually found in forests where they have been protected from the destruction by agriculture. Since the late Hallstatt period, the peoples living on Lake Constance are referred to as the Celts
The Celts ( , see Names of the Celts#Pronunciation, pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples ( ) were a collection of Indo-European languages, Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apoge ...
. During the La Tène period from 450 BC, the population density decreases, as can be deduced partly due from the fact that no more grave mounds were built. For the first time, written reports on Lake Constance have survived. Thus, we learn that the Helvetians settled by the lake in the south, the Rhaetians in the area of the Alpine Rhine Valley and the Vindelici in the north-east. The most important places on the lake were Bregenz (Celtic ''Brigantion'') and today's Constance.
In the course of the Roman Alpine campaign of 16/15 BC, the Lake Constance region was integrated into the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
. During the campaign, there was also supposed to have been a battle on Lake Constance. The geographer, Pomponius Mela, makes the first mention in 43 AD of Lake Constance as two lakes – the ''Lacus Venetus'' (Upper Lake) and the ''Lacus Acronius'' (Untersee) – with the Rhine flowing through both. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
referred to Lake Constance as ''Lacus Brigantinus'' for the first time. The most important Roman site was Bregenz, which soon became subject to Roman municipal law and later became the seat of the Prefect of the Lake Constance fleet. The Romans were also in Lindau, but settled only on the hills around Lindau as the lakeshore was swampy. Other Roman towns were ''Constantia'' (Constance) and ''Arbor Felix'' ( Arbon).
After the borders of the Roman Empire were drawn back to the Rhine boundary in the 3rd century BC, the Alemanni gradually settled on the north shore of Lake Constance and, later, on the south bank as well. After the introduction of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, the cultural significance of the region grew as a result of the founding of Reichenau Abbey and the Bishopric of Constance. Under the rule of the Hohenstaufen
The Hohenstaufen dynasty (, , ), also known as the Staufer, was a noble family of unclear origin that rose to rule the Duchy of Swabia from 1079, and to royal rule in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages from 1138 until 1254. The dynast ...
s, Imperial Diets (''Reichstage'') were held by Lake Constance. In Constance, too, a treaty was drawn up between the Hohenstaufen emperor and the Lombard League. Lake Constance also played an important role as a trading post for goods being traded between German and Italian states.
During the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, there were various conflicts over the control of the region during the Lake War (1632–1648).
After the War of the Second Coalition
The War of the Second Coalition () (1798/9 – 1801/2, depending on periodisation) was the second war targeting French Revolution, revolutionary French First Republic, France by many European monarchies, led by Kingdom of Great Britain, Britai ...
(1798–1802), which also affected the region and during which Austrian and French flotillas operated on Lake Constance, there was a reorganisation of state relationships.
Historical maps
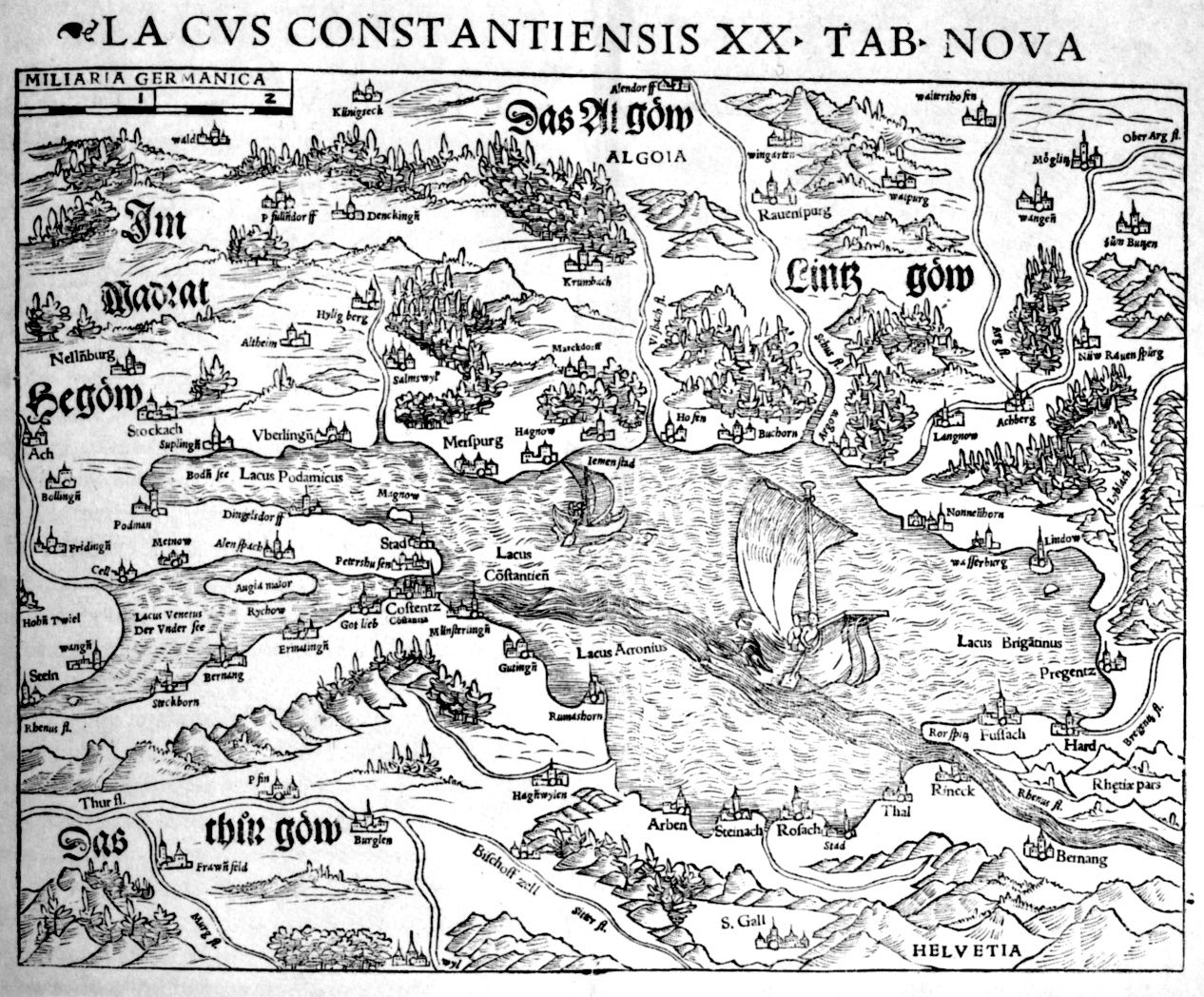 * 1540: the map ''Lacus Constantiensis'' by Johannes Zwick and Thomas Blarer shows topographic names, towns and the Rhine.
* 1555: the map of the route of the Rhine (''Rhinelaufkarte'') by Caspar Vopel includes a topographical map of Lake Constance with its larger towns, the tributaries and the course of the Rhine.
* 1633: the Swabian map by Johannes Janssonius, Amsterdam: ''Totius Sveviae novissima tabula'' shows Lake Constance with islands, tributaries, towns and villages.
* 1675: The Lake Constance map, ''Lacos Acronianus sive Bodamicus'', by Nikolaus David Hautt based on Andreas Arzet SJ shows Lake Constance with the adjacent lands.
* 1540: the map ''Lacus Constantiensis'' by Johannes Zwick and Thomas Blarer shows topographic names, towns and the Rhine.
* 1555: the map of the route of the Rhine (''Rhinelaufkarte'') by Caspar Vopel includes a topographical map of Lake Constance with its larger towns, the tributaries and the course of the Rhine.
* 1633: the Swabian map by Johannes Janssonius, Amsterdam: ''Totius Sveviae novissima tabula'' shows Lake Constance with islands, tributaries, towns and villages.
* 1675: The Lake Constance map, ''Lacos Acronianus sive Bodamicus'', by Nikolaus David Hautt based on Andreas Arzet SJ shows Lake Constance with the adjacent lands.
Geography
Divisions
Lake Constance is located in the foothills of the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
. The shore length of both main lakes is long. Of this, are located in Germany (Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
), run through Austria and through Switzerland. If the upper and lower lakes are combined, Lake Constance has a total area of , the third largest lake in Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
by area after Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater rift lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the List of largest lakes of Europe, largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the larges ...
() and Lake Geneva (). It is also the second largest by water volume ()[Uta Mürle, Johannes Ortlepp, Peter Rey, Internationale Gewässerschutzkommission für den Bodensee (publ.): ''Der Bodensee: Zustand – Fakten – Perspektiven.'' 2nd revised edition. Bregenz, 2004, , p. 10.] after Lake Geneva () and extends for over between Bregenz and Stein am Rhein. Its catchment area is around , and reaching as far south as Lago di Lei in Italy.
The area of the Obersee, or Upper Lake, is . It extends from Bregenz to Bodman-Ludwigshafen for over and is wide between Friedrichshafen and Romanshorn
Romanshorn is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Romanshorn was probably settled in the 7th century, and is first menti ...
. At its deepest point between Fischbach and Uttwil, it is deep.
The three small bays on the Vorarlberg
Vorarlberg ( ; ; , , or ) is the westernmost States of Austria, state () of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest popu ...
shore have their own names: the Bay of Bregenz, off Hard and Fußach is the Bay of Fussach and, west of that is the Wetterwinkel. Farther west, now in Switzerland, is the Bay of Rorschach. To the north, on the Bavarian side, is the Bay of Reutin. The railway embankment from the mainland to the island of Lindau and the motorway bridge over the lake border the so-called Little Lake (''Kleiner See''), which is located between the Lindau village of Aeschach and the island.
The northwestern, finger-shaped arm of the Obersee is called Überlinger See (or Überlingersee in Swiss Standard German), or Lake Überlingen. It is sometimes regarded as a separate lake, the boundary between Lake Überlingen and the rest of the Upper Lake runs approximately along the line between the southeast tip of Bodanrück (the ''Hörnle'', which belongs to the town of Konstanz) and Meersburg. The Constance Hopper lies between the German and Swiss shores east of Konstanz.
The Obersee and Untersee are connected by the Seerhein.
The Untersee, or Lower Lake, which is separated from the Obersee and from its north-west arm, the Überlinger See, by the large peninsula of Bodanrück, has an area of . It is strongly characterised and divided into different areas by end moraines, various glacial snouts and medial moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris ( regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice s ...
s. These various areas of the lake have their own names. North of Reichenau Island is the Gnadensee. West of the island of Reichenau, between the peninsula of Höri and the peninsula of Mettnau is the Zeller See (or Zellersee in Swiss Standard German), or Lake Zell. North of the peninsula and swamp land Mettnau lies the lake part Markelfinger Winkel. The drumlins of the southern Bodanrück continue along the bed of these northern parts of the lake. South of the Reichenau, from Gottlieben to Eschenz, stretches the ''Rheinsee'' (lit.: "Rhine Lake") with strong Rhine currents in places. Previously this lake part was named Lake Bernang after the village of Berlingen. On most of the maps the name of the ''Rheinsee'' is not shown, because this place is best suited for the name of the Untersee.[''Der Bodensee: drei Teile, ein See.''](_blank)
In: ''Seespiegel.'' Edition 20.
Emergence and future
The present-day shape of Lake Constance has resulted from the combination of several factors:
* The tectonic
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons.
These processes ...
Lake Constance Basin between the Alps and the Jura was created in the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
and Tertiary periods.
* The current Alpine Rhine was initially a tributary of the Danube.
* Over time, the basin was captured by the High Rhine as a result of headward erosion ( fluvial erosion).
** The capture was not always only along the present Rhine valley; Lake Überlingen marks part of an older valley course.
* The river valleys were deepened during several cold periods by the Rhine Glacier from the valley of the Alpine Rhine (glacial erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
).
* Behind the present impressive traces of the Würm Ice Age, the effects of older cold periods can no longer be explored in any detail. Lake Constance now represents, above all, a zungenbecken or glacial lake of the Würm Glaciation.
* During a later phase of the ice age, only the Obersee was glaciated. As the glacier retreated further, the glacial meltwaters flowed out of the emerging Überlingen See through the older more northerly valley into the present High Rhine valley.
* Due to the advancing headward erosion, the present course of the High Rhine was finally (again) reconnected to Lake Constance.
Like any glacial lake, Lake Constance will also silt up by sedimentation
Sedimentation is the deposition of sediments. It takes place when particles in suspension settle out of the fluid in which they are entrained and come to rest against a barrier. This is due to their motion through the fluid in response to th ...
. This process can best be observed at the mouths of the larger rivers, especially that of the Alpine Rhine. The silting up process is accelerated by ever-increasing erosion by the Rhine and the associated reduction in the level of the lake.
Tributaries
 The main tributary of Lake Constance is the Alpine Rhine. The Alpine Rhine and the Seerhein do not mix greatly with the waters of the lake and flow through the lakes along courses that change relatively little. There are also numerous smaller tributaries (236 in all). The most important tributaries of the Obersee are (counterclockwise) the Dornbirner Ach, Bregenzer Ach, Leiblach, Argen, Schussen, Rotach, Brunnisach, Seefelder Aach, Stockacher Aach, Salmsacher Aach, the Aach near Arbon, Steinach, Goldach and the Old Rhine. The outflow of the Obersee is the Seerhein, which in turn is the main tributary of the Untersee. The most important tributary of the Untersee is the Radolfzeller Aach. The source of the Radolfzeller Aach is the Aachtopf, a karst spring whose waters mostly derive from the Danube Sinkhole. Therefore, the
The main tributary of Lake Constance is the Alpine Rhine. The Alpine Rhine and the Seerhein do not mix greatly with the waters of the lake and flow through the lakes along courses that change relatively little. There are also numerous smaller tributaries (236 in all). The most important tributaries of the Obersee are (counterclockwise) the Dornbirner Ach, Bregenzer Ach, Leiblach, Argen, Schussen, Rotach, Brunnisach, Seefelder Aach, Stockacher Aach, Salmsacher Aach, the Aach near Arbon, Steinach, Goldach and the Old Rhine. The outflow of the Obersee is the Seerhein, which in turn is the main tributary of the Untersee. The most important tributary of the Untersee is the Radolfzeller Aach. The source of the Radolfzeller Aach is the Aachtopf, a karst spring whose waters mostly derive from the Danube Sinkhole. Therefore, the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
is indirectly also a tributary of the Rhine.
Because the Alpine Rhine brings with it drift from the mountains and deposits this material as sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
, the Bay of Bregenz will silt up in a few centuries time. The silting up of the entire Lake Constance is estimated to take another ten to twenty thousand years.
Outflows, evaporation, water extraction
The outflow of the Untersee is the High Rhine with the Rhine Falls at Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
. Both the average precipitation of 0.45 km3/a and evaporation which averages 0.29 km3/a cause a net change in the level of Lake Constance that is less when compared to the influence of the inflows and outflows.
Islands
 In Lake Constance there are ten
In Lake Constance there are ten island
An island or isle is a piece of land, distinct from a continent, completely surrounded by water. There are continental islands, which were formed by being split from a continent by plate tectonics, and oceanic islands, which have never been ...
s that are larger than .
By far the largest is the island of Reichenau in the Untersee, which belongs to the municipality of Reichenau. The former abbey of Reichenau is a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
due to its three early and highly medieval churches. The island is also known for its intensive cultivation of fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
and vegetables.
The island of Lindau is located in the east of the Obersee, and is the second largest island. On it is the old town and main railway station of Lindau.
The third largest island is Mainau in the southeast of Lake Überlingen. The owners, the family of Bernadotte, have set up the island as a tourist attraction and created botanical gardens and wildlife enclosures.
Relatively large, but uninhabited and inaccessible because of their status as nature reserves, are two islands off the Wollmatinger Ried: the Triboldingerbohl which has an area of and Mittler or Langbohl which is just in area.
Smaller islands in the Obersee are:
* Dominican Island (''Dominikanerinsel'') separated by a six-metre-wide ditch from the old town of Constance which is home to the Steigenberger Hotel ()
* The tiny island of Hoy near Lindau
* The ten artificial islands on the Rhine Causeway on the Fußach side
* The little island by the port of Romanshorn
Romanshorn is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Romanshorn was probably settled in the 7th century, and is first menti ...
* The Wollschweininsel (officially ''Wulesaueninsle'') by the Seepark in Kreuzlingen
In the Untersee are:
* the islands of Werd, Mittleres Werdli and Unteres Werdli which together form the Werd Islands group are located at the outflow of the Rhine from the Untersee at Stein am Rhein into the High Rhine.
* The so-called Liebesinsel ("Love Island", , southwest of the Mettnau peninsula.
Peninsulas
In Lake Constance there are several peninsulas which vary greatly in size:
* The Bodanrück, the largest peninsula, separates the Überlinger See (Obersee) from the Untersee. It covers an area of .
* The Mettnau in the Untersee, which extends towards the Island of Reichenau, separates Zeller See in the south from the Markelfinger Winkel in the north. It has a surface area of .
* The Höri, (about 45-square-kilometres) also extends towards the Island of Reichenau, and separates the Zeller See to the north from the Rheinsee to the south.
* In the southeast, near the mouth of the new Rhine Canal, the Rohrspitz juts out about into the lake and forms the western perimeter of the Bay of Fußach. It has an area of about 50 hectares.
* The Wasserburg peninsula has a castle, Schloss Wasserburg, and the parish church of St. George. The peninsula is on the northeastern shore of the Obersee between the Bay of Nonnenhorn in the west and Bay of Wasserburg in the east. It has an area of and was an island until 1720, when the Fuggers built a causeway. In March 2009, 27 people lived on the peninsula.
* The Galgeninsel ("Gallows Island") in the Bay of Reutin is also a peninsula that was formerly an island. It is only 0.16 hectares in area.
Shore
 The shores of Lake Constance consist mainly of gravel. In some places there are also sandy beaches, such as the Rohrspitz in the Austrian section of the lake, the Langenargen and Marienschlucht.
According to the data of the International Water Protection Commission for the Lake Constance, the approximate shore length is (see Coastline paradox). The inflow of water is constantly changing, mainly due to rain and the snow melt in the Alps. Its average surface area is about (in Switzerland the absolute value is slightly higher in m above sea level). The more or less regular seasonal fluctuations in the water level also lead to slight variations in shore length and differences in the shore zone habitats (depending on high and low water).
The shores of Lake Constance consist mainly of gravel. In some places there are also sandy beaches, such as the Rohrspitz in the Austrian section of the lake, the Langenargen and Marienschlucht.
According to the data of the International Water Protection Commission for the Lake Constance, the approximate shore length is (see Coastline paradox). The inflow of water is constantly changing, mainly due to rain and the snow melt in the Alps. Its average surface area is about (in Switzerland the absolute value is slightly higher in m above sea level). The more or less regular seasonal fluctuations in the water level also lead to slight variations in shore length and differences in the shore zone habitats (depending on high and low water).
Transportation
Road
Roads westbound Bundesstraße 33 (B 33, highway), Bundesautobahn 81 (A 81), at Stockach, Konstanz: Bundesautobahn 98 (A 98), Switzerland: Autobahn 7 (A7), Autobahn 1 (A 1), Autobahn 23 (A 23) and eastbound at Bregenz Rheintal/Walgau Autobahn (A 14), at Lindau Bundesautobahn 96 (A 96), Bundesstraße 31 (B 31)
Ship / Ferry

 There are eight main harbors offering boat services across the Upper Lake:
;Austria:
* Bregenz
;Switzerland:
* Rorschach
*
There are eight main harbors offering boat services across the Upper Lake:
;Austria:
* Bregenz
;Switzerland:
* Rorschach
* Romanshorn
Romanshorn is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Romanshorn was probably settled in the 7th century, and is first menti ...
;Germany:
* Lindau
* Friedrichshafen
* Meersburg
* Unteruhldingen (touristic harbor)
* Konstanz
Additionally, car ferries link Romanshorn to Friedrichshafen, and Konstanz to Meersburg.[ Between 1869 and 1976, there used to be train ferries across the lake.
Several smaller harbors on the Upper Lake offer boat trips along the German or Swiss coast (with one continuing over the Old Rhine to Rheineck).
The harbour in Konstanz is also served by the '' Schweizerische Schifffahrtsgesellschaft Untersee und Rhein'' (URh), which operates via the '' Seerhein'', Lower Lake and High Rhine to ]Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
. It docks at the harbours of Kreuzlingen, Konstanz, Gottlieben, Ermatingen
Ermatingen is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Kreuzlingen (district), Kreuzlingen in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
The Stone Age Westerfeld and Büge shoreline settlements w ...
, Reichenau, Mannenbach, Berlingen, Gaienhofen, Steckborn, Hemmenhofen, Wangen, Mammern, Öhningen, Stein am Rhein, Diessenhofen, Büsingen and Schaffhausen. Radolfzell and Iznang are also linked by a boat line over the Lower Lake (to Konstanz).
Rail
 A network of several railway lines surrounds the lake. The lines are operated by regional train services (
A network of several railway lines surrounds the lake. The lines are operated by regional train services (S-Bahn
The S-Bahn ( , ), , is a hybrid urban rail, urban–suburban rail system serving a metropolitan region predominantly in German language, German-speaking countries. Some of the larger S-Bahn systems provide service similar to rapid transit syst ...
, RegioExpress, Regional-Express) spreading over four countries (Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
). In Switzerland, they belong to S-Bahn St. Gallen and trains are operated by THURBO ( Swiss Federal Railways, SBB), Südostbahn (SOB) and Appenzell Railways (AB). The so-called belt railway () along the northern shore is operated by DB Regio and SBB GmbH. In Austria and Liechtenstein, train services are operated by Austrian Federal Railways (ÖBB) for the Vorarlberg S-Bahn. Regional train services around Lake Constance are marketed as Bodensee S-Bahn.
Railway station
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport using wheeled vehicles running in railway track, tracks, which usually consist of two parallel steel railway track, rails. Rail transport is one of the two primary means of ...
s close to harbours are, among others: , , , , , , and .
Long-distance trains ( RJ/RJX, EC/ECE, IC (DB)/ IC (SBB), IR, IRE) link larger lakeside railway stations (e.g., , , , , ) with major cities.
Air
Two airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial Aviation, air transport. They usually consist of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surf ...
s are located near the lake's shores: Friedrichshafen Airport (Germany) and St. Gallen–Altenrhein Airport (Switzerland). Zeppelin NT offers touristic zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155� ...
flights around Lake Constance departing from Friedrichshafen Airport.
Climate
 The climate of the Lake Constance area is characterised by mild temperatures with moderate gradients, thanks to the balancing and retarding effect of the large body of water.
It has a
The climate of the Lake Constance area is characterised by mild temperatures with moderate gradients, thanks to the balancing and retarding effect of the large body of water.
It has a subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
microclimate, which allows the cultivation of some exotic fruits and trees. Constance counts 2069 sunshine hours a year and is therefore considered one of the sunniest cities in Germany.
Winters are generally short and mild, although night temperatures can fall under 0°C, especially from December to February. Typically day temperatures range between +5 and +12°C, while nights with +1 to +8°C on average stay cold, though mostly without long and severe frosts.
The Föhn, a warm wind from the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, that regularly blows through the Alps, can cause temperatures between 15 and 20°C with sunshine for several days, while on the other hand fog creates a few cold days between 1 and 5°C each year. Generally, Lake Constance is affected more by fog than neighboring regions more inland.
Spring goes from March to May and is usually sunny, with day temperatures between 15 and 22°C but still relatively cold water. This is also resulting in still cold night temperatures that range between 4°C in March and 12°C in May only.
As the lake temperature heats up by the increasing warm days, the nights are also becoming milder, though moderated a little bit by the height and lake. This results in average morning lows of 16-18°C during the high summer months. Lake Constance counts one of the highest amount of tropical nights in Germany (lowest temperature at 20°C or more).
The days in Summers (June-September) are warm to hot with day temperatures of 26-33°C on average, decreasing to around 20°C until the end of September. Humidity levels raise noticeable and temperatures often move up to 35°C between June and August. This increases the heat index
The heat index (HI) is an index that combines air temperature and relative humidity, in shade (shadow), shaded areas, to posit a human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the Shade (s ...
, causing Lake Constance to have a stressful climate.
The region receives most of its sunny days during high summer. In the recent years, in 2018 and 2022, the water levels fall to new record lows due to weeks without significant rain. On the other hand, the closeness to the Alps can cause thunderstorms in the evenings that sometimes occur out of nowhere.
While the official bathing season ends in September, the average lake temperature stays around 20°C until October. Autumn is generally the time when Lake Constance starts to experience more foggy mornings again, but the day temperatures still range between 21 in the beginning and 10-12°C at the end of the season. Night temperatures fall from 13°C in September to an average of 5°C in November.
Lake Constance is one of the best known wine growing regions in Germany and experiences several outdoor events during harvest time in autumn.
 Lake Constance is also considered to be a risky and challenging lake for water sports because of the danger of gusty winds which can whip up waves as the weather changes suddenly. The most dangerous wind is the föhn, a warm down-slope wind from the Alps, which spreads out across the water, especially through the Alpine Rhine Valley and can generate waves several metres high.
Similarly dangerous for those unfamiliar with the area, are the sudden stormy gusts of wind during summer thunderstorms. They constantly claim victims from the water sports fraternity. During a thunderstorm in July 2006, waves reached heights of up to 3.50 metres.
For these reasons, there is a storm warning system in all three neighbouring countries. For storm warning purposes, Lake Constance is divided into three warning regions (west, centre and east). Warnings can be issued for each region independently. A "high winds" warning will be issued when squalls are expected of between 25 and 33 knots or registering
Lake Constance is also considered to be a risky and challenging lake for water sports because of the danger of gusty winds which can whip up waves as the weather changes suddenly. The most dangerous wind is the föhn, a warm down-slope wind from the Alps, which spreads out across the water, especially through the Alpine Rhine Valley and can generate waves several metres high.
Similarly dangerous for those unfamiliar with the area, are the sudden stormy gusts of wind during summer thunderstorms. They constantly claim victims from the water sports fraternity. During a thunderstorm in July 2006, waves reached heights of up to 3.50 metres.
For these reasons, there is a storm warning system in all three neighbouring countries. For storm warning purposes, Lake Constance is divided into three warning regions (west, centre and east). Warnings can be issued for each region independently. A "high winds" warning will be issued when squalls are expected of between 25 and 33 knots or registering force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
6 to 8 on the Beaufort scale. A gale warning announces the likelihood of gale-force winds, i.e. those at speeds as of 34 knots or more or force 8 on the Beaufort scale. In order to issue these warnings, orange-coloured flashing lights are installed around the lake, which flash at a frequency of 40 times per minute for high winds or 90 times per minute for gales. It can happen that, due to the differently regulated responsibilities and assessments, a gale warning is issued on the Swiss side of the Obersee, but not on the German or Austrian shores, and vice versa. Ships and ferries on Lake Constance indicate a gale warning by hoisting a ''Sturmballon'' ("storm ball") up the mast.
Freeze over
 A one-hundred year event is the freezing over of Lake Constance, when the Lower Lake and the Upper Lake are completely frozen over so that people can safely cross the lake on foot. The last so-called ''Seegfrörne'' ( Alemannic) event was in 1963. The following is a list of years in which Lake Constance froze over partially or completely:
*875, 895
*1074, 1076
*1108
*1217, 1227, 1277
*1323, 1325, 1378, 1379, 1383
*1409, 1431, 1435 (complete), 1460, 1465, 1470, 1479
*1512, 1517, 1553, 1560 (complete), 1564, 1565, 1571, 1573 (complete)
*1684, 1695 (complete)
*1788, 1796 (complete)
*1830 (complete), 1880 (complete)
*1929, 1963 (complete)
Certain parts of the lake freeze over more frequently, mainly due to their shallow depth of water and shelter, as is the case, for example, of the so-called Markelfinger Winkel between the municipality of Markelfingen and the Mettnau peninsula.
A one-hundred year event is the freezing over of Lake Constance, when the Lower Lake and the Upper Lake are completely frozen over so that people can safely cross the lake on foot. The last so-called ''Seegfrörne'' ( Alemannic) event was in 1963. The following is a list of years in which Lake Constance froze over partially or completely:
*875, 895
*1074, 1076
*1108
*1217, 1227, 1277
*1323, 1325, 1378, 1379, 1383
*1409, 1431, 1435 (complete), 1460, 1465, 1470, 1479
*1512, 1517, 1553, 1560 (complete), 1564, 1565, 1571, 1573 (complete)
*1684, 1695 (complete)
*1788, 1796 (complete)
*1830 (complete), 1880 (complete)
*1929, 1963 (complete)
Certain parts of the lake freeze over more frequently, mainly due to their shallow depth of water and shelter, as is the case, for example, of the so-called Markelfinger Winkel between the municipality of Markelfingen and the Mettnau peninsula.
Floods
* A 100-year flood around June 1999 ( Pfingsthochwasser 1999) raised the level about 2 metres above normal, flooding harbors and many shoreline buildings and hotels.
* In late August 2005, heavy rain raised the level by more than in a few days. The rains caused widespread flooding and washed out highways and railroads.
* Frequent rainfall and snowmelt in the summer of 2024 raised water levels to above normal level.

International borders
 The lake lies where the countries of Austria, Germany, and Switzerland meet.
The lake lies where the countries of Austria, Germany, and Switzerland meet.condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership regime in which a building (or group of buildings) is divided into multiple units that are either each separately owned, or owned in common with exclusive rights of occupation by individual own ...
", and Germany holds an ambiguous opinion. Legal questions pertaining to ship transport and fishing are regulated in separate treaties.
Disputes occasionally arise. One concerns a houseboat which was moored in two states ( ECJ c. 224/97 Erich Ciola); another concerns the rights to fish in the Bay of Bregenz. In relation to the latter, an Austrian family was of the opinion that it alone had the right to fish in broad portions of the bay. However, this was accepted neither by the Austrian courts nor by the organs and courts of the other states.
Ecology
Flora
Until the 19th century, Lake Constance was a natural lake. Since then, nature has been heavily influenced by clearing and the cultivation of much of the land around its shores. However, some near-natural areas have been largely conserved, especially in the nature reserves, or were re-naturalised. As a result, the Lake Constance region has some unusual ecological features. These include the large forested area on the Bodanrück, the occurrence of marsh gentian and orchid
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Eart ...
s of the genera '' Dactylorhiza'' and '' Orchis'' in the Wollmatinger Ried, and the Siberian iris (''Iris sibirica'') in the Eriskircher Ried, which was therefore given its own name.[Planet Wissen – Bodensee](_blank)
/ref> One unique species among the local flora is the Lake Constance forget-me-not (''Myosotis rehsteineri''), whose habitat is restricted to undisturbed limestone gravel beaches.
Fauna
Birds
 Lake Constance is also the home of numerous bird species, many of which nest in its nature reserves, such as the Wollmatinger Ried or the Mettnau peninsula. 412 species have so far been recorded.
Lake Constance is also the home of numerous bird species, many of which nest in its nature reserves, such as the Wollmatinger Ried or the Mettnau peninsula. 412 species have so far been recorded.
= Songbirds
=
The ten most common breeding bird species at Lake Constance according to a 2000–2003 survey in descending order are the: blackbird, chaffinch, house sparrow
The house sparrow (''Passer domesticus'') is a bird of the Old World sparrow, sparrow family Passeridae, found in most parts of the world. It is a small bird that has a typical length of and a mass of . Females and young birds are coloured pa ...
, great tit, blackcap, starling, robin, chiffchaff, greenfinch, and blue tit.
= Waterfowl
=
In spring, the Lake Constance is an important breeding ground, especially for the coot and great crested grebe. Typical waterfowl include the: shoveler, goldeneye, goosander, pochard, grey heron, pintail, tufted duck and mallard.
In December 2014, 1,389 cormorant were counted. The International Lake Constance Fishery Association (IBF) estimates the food requirements of the cormorants on Lake Constance at 150 tonnes of fish annually.[Franz Domgörgen: ''Stabile Verhältnisse im Vogelparadies.'' ''Stabile Verhältnisse im Vogelparadies.'' In: ''Südkurier.'' 3 January 2015.]
= Overwintering
=
Lake Constance is an important overwintering area for around 250,000 birds.[Bundesamt für Veterinärwesen: Forschungsprojekt "Constanze" am Bodensee gestartet](_blank)
annually. Bird species such as the dunlin, the curlew and the lapwing overwinter at Lake Constance. In the middle of December 2014 there were 56,798 heron, 51,713 coot and 43,938 pochard.
= Migration
=
During migration in late autumn there are also numerous loons on the lake ( black-throated and red-throated loon, as well as a few great northern loons). Lake Constance is also very important as a staging post during the bird migration
Bird migration is a seasonal movement of birds between breeding and wintering grounds that occurs twice a year. It is typically from north to south or from south to north. Animal migration, Migration is inherently risky, due to predation and ...
. Bird migration is often inconspicuous and most noticeable when there are special weather conditions that make day migration obvious. Only where there is a prolonged spell of widespread low-pressure is it common to observe the congestion of large groups of migratory birds. This can often be observed in autumn on the Eriskircher Ried on the northern shore of Lake Constance. This is where broad front migration converges on the lake and birds then try to move along the shore towards the northwest. The importance of Lake Constance as an important area for resting and overwintering is underlined by the Max Planck Institute for Ornithology's Radolfzell Bird Observatory (''Vogelwarte Radolfzell''), which is the bird ringing
Bird ringing (UK) or bird banding (US) is the attachment of a small, individually numbered metal or plastic tag to the leg or wing of a wild bird to enable individual identification. This helps in keeping track of the movements of the bird an ...
centre for the German states of Bavaria, Baden-Württemberg, Berlin, Rhineland-Palatinate and the Saarland as well as for Austria, and which researches bird migration.
Fish
Around 45 species of fish live in Lake Constance. The annual haul from fishing is 1.5 million kg. Unusual species occurring here considering the location of the lake are the whitefish (''Coregonus'' spec.) and the Arctic char (''Salvelinus alpinus''). Fish that are important for the fishing industry are:
* Bodenseefelchen (German: also ''Blaufelchen'', Lat.: ''Coregonus wartmanni'')
* Sandfelchen (German: also ''Weißfelchen'', Lat.: ''Coregonus arenicolus'')
* Gangfisch (Lat.: ''Coregonus macrophthalmus'')
* Lake Constance whitefish (German: ''Kilch'', Lat.: ''Coregonus gutturosus'')
* Grayling (German: ''Äsche'', Lat.: ''Thymallus thymallus'')
* Perch (German: ''Flussbarsch, Kretzer, Barschling,'' Swiss German: ''Egli'', Lat.: ''Perca fluviatilis'')
* Bream (German: ''Brachse'', ''Brasse'', Lat.: ''Abramis brama'')
* Northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (pikes). They are commonly found in brackish water, moderately salty and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). T ...
(German: ''Hecht'' (Lat.: ''Esox lucius'')
* Zander (Lat.: ''Sander lucioperca'')
* Burbot (German: ''Quappe'', ''Trüsche'', Lat.: ''Lota lota'')
* Eel (German: ''Aal'', Lat.: ''Anguilla anguilla'')
* Bullhead (German: ''Groppe'', Lat.: ''Cottus gobio'')
* Tench (German: ''Schleie'', Lat.: ''Tinca tinca'')
* Wels catfish (German: ''Wels'', Lat.: ''Silurus glanis'')
* Lake trout (German: ''Seeforelle'', Lat.: ''Salmo trutta lacustris'')
The Bodenseefelchen (''Coregonus wartmanni''), which was named after Lake Constance due to the great numbers found there, is often prepared whole or as a fillet, in the style of the miller's wife (''nach Müllerin Art''), in local fish restaurants in a similar way to other trout[Themenpark Umwelt des Umweltministeriums Baden-Württemberg – BodenseeWeb]
Fische
/ref> It is also often served smoked.
Two endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
species are known to have existed only in Lake Constance, the Bodensee-Kilch (''Coregonus gutturosus'') and deepwater char (''Salvelinus profundus''). The former is now assumed to be extinct, while the latter was feared extinct for decades until its rediscovery in the 2010s.
Introduced species
For many years non-native species have settled in the Lake Constance ecosystem and, in some cases, endangered or threatened native flora and fauna. At Lake Constance, non-native species have been increasing annually. Several have been transported from other waterbodies as 'stowaways' on the outside of boats, life jackets, anchor chains or ropes or diving gear.[Friedrich W. Strub: ''Tierische Neuankömmlinge im Bodensee.'' In: Südkurier dated 20 April 2016.] Others have immigrated from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
or the Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest sou ...
since the opening of the Main-Danube Canal. Others have been deliberately introduced.[Anna-Maria Schneider: ''Die heimliche Invasion unter Wasser.'' In: Südkurier date 8 September 2015.]
= Well-known non-native species
=
Even the rainbow trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributary, tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in North America and Asia. The steelhead (sometimes called steelhead trout) is an Fish migration#Classification, ...
(''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is not a native fish. It was introduced into Lake Constance around 1880 for economic reasons to enhance the local fauna.[Angela Schneider: ''Gepanzerte Truppe erobert den Bodensee.'' In: ''Südkurier.'' dated 9 October 2010.]
Among the foreign species of animal in Lake Constance are the zebra mussel (''Dreissena polymorpha'') which, since the 18th century, has spread from the Black Sea region across most of Europe and was carried into Lake Constance between 1960 and 1965. After a huge increase in numbers during the 1980s in the Rhine and large lakes, this species is now in retreat today. The zebra mussel causes problems because, among other things, it blocks water extraction pipes. In addition, the species can be a disaster for domestic shellfish, because it competes for their food.[Angela Schneider: ''Drei von vielen, die sich bereits im Bodensee etabliert haben.'' In: ''Südkurier.'' dated 9 October 2010.] Today, according to the Institute for Lake Research (''Institut für Seenforschung'', ISF), the zebra mussel is also an important food for overwintering waterfowl. In fact, the number of overwinterers has more than doubled in around 30 years.spinycheek crayfish
''Faxonius limosus'', Synonym (taxonomy), synonym ''Orconectes limosus'', is a species of crayfish in the family Cambaridae. It is native to the east coast of North America, from Quebec to the lower James River (Virginia), James River, Virginia, ...
(''Orconectes limosus''), which was introduced into European waters in the mid-19th century to increase the yield,signal crayfish
The signal crayfish (''Pacifastacus leniusculus'') is a species of crayfish indigenous to North America. Introduced to Europe in the 1960s to supplement the North European ''Astacus astacus'' fisheries, which were being damaged by crayfish plague ...
(''Pacifastacus leniusulus''). As these species of large crayfish are immune to crayfish plague, but spread the pathogen, they are a great danger to native species such as noble crayfish, white-clawed crayfish or stone crayfish. The animals are often undemanding, multiply rapidly and lead predatory lives, thus also posing a threat to various small species of fish.
Wrecks on the lake bed
After a collision with the '' Stadt Zürich'' in 1864 the wreck of the '' Jura'' has lain on the lake bed at a depth of 45 metres off the Swiss shore. In the early 20th century four ships were sunk in the Obersee after being taken out of service: in 1931 the '' Baden'', formerly the ''Kaiser Wilhelm'', in 1932 the ''Helvetia'', in 1933 the ''Säntis'' and in 1934 the ''Stadt Radolfzell''. The hull of the burnt-out '' Friedrichshafen'' was scuttled in 1944 off the mouth of the Argen in 100 to 150 metres of water.
Tourism, leisure and sports
The tourism and leisure industry is important for this region. Overnight stays reached 17,56m visitors in 2012 with a turnover of about 1.9bn Euros. The same amount comes from the 70 million visitors that visit Lake Constance each year.
 This region is known for sightseeing, water-sports, winter-sports like
This region is known for sightseeing, water-sports, winter-sports like Skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow for basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IOC), and the International S ...
, summer-sports like Swimming (sport)
Swimming is an individual or team Racing, racing sport that requires the use of one's entire body to move through water. The sport takes place in Swimming pool, pools or open water (e.g., in a sea or lake). Competitive swimming is one of the ...
, Sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, Windsurfing, windsurfer, or Kitesurfing, kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (Land sa ...
and recreation. It is also one of the few places where modern Zeppelin
A Zeppelin is a type of rigid airship named after the German inventor Ferdinand von Zeppelin () who pioneered rigid airship development at the beginning of the 20th century. Zeppelin's notions were first formulated in 1874Eckener 1938, pp. 155� ...
airships operate and 12–14 people can take a trip above the lake around various points of interest.
In cooperation with tourism service providers, tourism organizations and public institutions in Germany, Austria, Switzerland and Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
, the International Bodensee Tourismus GmbH (IBT GmbH) is responsible for the tourism marketing of the Lake Constance region.
Sights and cultural heritage
The lake and the region around it have a substantial touristic infrastructure as well as many attractions and points of interests. Important are especially towns like Konstanz, Überlingen
Überlingen (; ) is a German city on the northern shore of Lake Constance (Bodensee) in Baden-Württemberg near the German-Swiss border, border with Switzerland. After the city of Friedrichshafen, it is the second-largest city in the Bodenseek ...
, Meersburg, Friedrichshafen, Lindau, Romanshorn
Romanshorn is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Romanshorn was probably settled in the 7th century, and is first menti ...
, Rorschach and Bregenz as they are the big hubs for boating tourism and lake crossing ferries. The main tourism attractions are places like Rhine Falls, one of the three biggest waterfalls in Europe (located near Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
), the islands of Mainau, Lindau and Reichenau (UNESCO world heritage), the pilgrimage church Birnau, castles and palaces like Salem Abbey, Meersburg Castle as well as another UNESCO world heritage site, the Pfahlbaumuseum Unteruhldingen (German for Stilt house
Stilt houses (also called pile dwellings or lake dwellings) are houses raised on Stilts (architecture), stilts (or piles) over the surface of the soil or a body of water. Stilt houses are built primarily as a protection against flooding; they als ...
museum), Zeppelin Museum Friedrichshafen as well as the Church of St. George, Oberzell, Reichenau or the '' Rheinschauen'' heritage railway.
Overlooks
High mountain ranges are mainly located near the southeastern shore of the Upper Lake (''Obersee''). The lower foothills
Foothills or piedmont are geography, geographically defined as gradual increases in elevation at the base of a mountain range, higher hill range or an highland, upland area. They are a transition zone between plains and low terrain, relief hill ...
of the Appenzell Alps in Switzerland are accessible by bus routes and two railway lines: the Rorschach–Heiden railway between / near the lake shore and , and the Rheineck–Walzenhausen mountain railway between and . Both lines are operated by Appenzell Railways and part of St. Gallen S-Bahn and Bodensee S-Bahn, respectively. A popular overlook near Heiden is ''Fünfländerblick'' (). In Austria, the Pfänderbahn, an aerial tram, takes passengers from the valley station near to the top station on Pfänder mountain ( Allgäu Alps).
The Hegau region adjacent to Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee'') contains several higher mountains of volcanic origin, many with ruins of fortresses on their tops (e.g. Hohenkrähen, Mägdeberg). The southernly located of these Hegau volcanoes (e.g. Hohentwiel) also offer a view over the lakes.
Cultural events
Lake Constance is the location for the annual Bregenzer Festspiele, a well-known arts festival that, among other venues, takes place on a floating stage in Bregenz. The operas, plays and concerts performed are usually popular works, e.g. '' The Magic Flute'' by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
or '' Rigoletto'' by Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi ( ; ; 9 or 10 October 1813 – 27 January 1901) was an Italian composer best known for List of compositions by Giuseppe Verdi, his operas. He was born near Busseto, a small town in the province of Parma ...
.
Since 2001, the ART BODENSEE takes place in Dornbirn. It is an annual meeting point for the exchange between collectors, artists and art appreciators.
Biking
Biking around the lake is also possible on the long trail called "Bodensee-Radweg". It brings its visitors to the most interesting sites and goes around the whole lake. Nevertheless, various shortcuts via ferries allow shorter routes and the trail is suitable for all levels. Note: There is also a trail that goes by the name "Bodensee-Rundweg". This road was intended for pedestrians so biking is sometimes not suitable or allowed.
Hiking and pilgrim trails
 The 260 kilometers long Lake Constance circular route, signposted as "Bodensee Rundwanderweg", leads around Lake Constance through the territories of Germany, Austria and Switzerland. It is mainly intended for hiking; cyclists follow the sometimes slightly different managed Lake Constance cycle path. The trail can be walked in smaller stages of various lengths and offers nice views of the lake, landscape and wildlife. However, due to industrial settlements, buildings and nature reserves, not all the coastal zones are readily accessible. Furthermore, in the estuary of the rivers, such the Leiblach, Bregenzer Ach, canalized Rhine and Old Rhine ( Fußacher breakthrough), considerable distances have to be covered inland to the next bridge or river crossing point. Due to busy riverside roads, the Bodensee-Rundweg sometimes runs as a trail above the lake with some lookout possibilities.
Lake Constance is also a hub for long-distance hikers and pilgrims. It has been a crucial reference point of important pilgrimage routes since ancient times:
* Via Beuronensis, a Way of St. James from the Neckar region over the Swabian Alb
* the Upper Swabian pilgrimage-route of St. James, which leads from Upper Swabia to the lake and branches north of the lake both in the direction of Nonnenhorn and in the direction of Meersburg
* the Bavarian-Swabian route of St. James, which leads down from the West Allgäu to the lake
* the Schwabenweg, which ensures the connection to Switzerland to the lake near Konstanz
The 260 kilometers long Lake Constance circular route, signposted as "Bodensee Rundwanderweg", leads around Lake Constance through the territories of Germany, Austria and Switzerland. It is mainly intended for hiking; cyclists follow the sometimes slightly different managed Lake Constance cycle path. The trail can be walked in smaller stages of various lengths and offers nice views of the lake, landscape and wildlife. However, due to industrial settlements, buildings and nature reserves, not all the coastal zones are readily accessible. Furthermore, in the estuary of the rivers, such the Leiblach, Bregenzer Ach, canalized Rhine and Old Rhine ( Fußacher breakthrough), considerable distances have to be covered inland to the next bridge or river crossing point. Due to busy riverside roads, the Bodensee-Rundweg sometimes runs as a trail above the lake with some lookout possibilities.
Lake Constance is also a hub for long-distance hikers and pilgrims. It has been a crucial reference point of important pilgrimage routes since ancient times:
* Via Beuronensis, a Way of St. James from the Neckar region over the Swabian Alb
* the Upper Swabian pilgrimage-route of St. James, which leads from Upper Swabia to the lake and branches north of the lake both in the direction of Nonnenhorn and in the direction of Meersburg
* the Bavarian-Swabian route of St. James, which leads down from the West Allgäu to the lake
* the Schwabenweg, which ensures the connection to Switzerland to the lake near Konstanz
Swimming
Swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, such as saltwater or freshwater environments, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Swimmers achieve locomotion by coordinating limb and body movements to achieve hydrody ...
in the lake is usually best from mid-June to mid-September. Depending on the weather and exact location, the water temperatures reach . Within one day, differences of up to are possible with appropriate sunlight, so that the lake invites to swim, especially on warm summer evenings.
Diving
 Diving in Lake Constance is considered attractive and challenging. Most of the diving areas are located in the northern part of the lake (
Diving in Lake Constance is considered attractive and challenging. Most of the diving areas are located in the northern part of the lake (Überlingen
Überlingen (; ) is a German city on the northern shore of Lake Constance (Bodensee) in Baden-Württemberg near the German-Swiss border, border with Switzerland. After the city of Friedrichshafen, it is the second-largest city in the Bodenseek ...
, Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning "Ludwig I of Bavaria, Ludwig's Port upon the Rhine"; Palatine German dialects, Palatine German: ''Ludwichshafe''), is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in the German state of Rh ...
, Marienschlucht and others), a few also in the south. The areas should be dived exclusively by experienced divers under the guidance of one of the local diving schools or a seasoned diver. Diving at some spots like the devils table ("Teufelstisch") called rock needle in the lake in front of the Marienschlucht, is only allowed after approval by the district office Konstanz.
A famous freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
wreck in Europe is the paddle steamer
A paddle steamer is a steamship or steamboat powered by a steam engine driving paddle wheels to propel the craft through the water. In antiquity, paddle wheelers followed the development of poles, oars and sails, whereby the first uses were wh ...
Jura, which lies in front of Bottighofen at a depth of . The canton of Thurgau, the office for archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
in Frauenfeld, has placed the Jura under protection as an underwater industrial monument.
For all divers, the water in Lake Constance—even in summer—is already below from a depth of which requires suitable cold-water regulators that do not freeze at such temperatures.
Boating, recreational boating
 Pleasure boating is important. At the beginning of 2011, 57,875 amusement vehicles were registered for Lake Constance.
The legal basis for all shipping on the lake is the ordinance on shipping on Lake Constance, or "Bodensee-Schifffahrtsordnung". It is monitored on Lake Constance and on the Upper Rhine by the German, Swiss and Austrian Water Police, the "Seepolizei".
All boats must be registered, and boat drivers must hold a "Bodenseeschifferpatent" (authorization to drive a patented vehicle on Lake Constance). It is issued in Germany by the shipping offices of the district of Constance, the Lake Constance district, and the district of Lindau; in Switzerland by the cantonal authorities; and in Austria by the District Commission Bregenz. For pleasure boaters short-term guest licenses are possible (for the categories A for motorboats over 4.4 kW and D for
Pleasure boating is important. At the beginning of 2011, 57,875 amusement vehicles were registered for Lake Constance.
The legal basis for all shipping on the lake is the ordinance on shipping on Lake Constance, or "Bodensee-Schifffahrtsordnung". It is monitored on Lake Constance and on the Upper Rhine by the German, Swiss and Austrian Water Police, the "Seepolizei".
All boats must be registered, and boat drivers must hold a "Bodenseeschifferpatent" (authorization to drive a patented vehicle on Lake Constance). It is issued in Germany by the shipping offices of the district of Constance, the Lake Constance district, and the district of Lindau; in Switzerland by the cantonal authorities; and in Austria by the District Commission Bregenz. For pleasure boaters short-term guest licenses are possible (for the categories A for motorboats over 4.4 kW and D for sailboat
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture.
Types
Although sailboat terminology ...
s over 12 m2 sail area).
Boating events
* Since 1979, every year to the assumption of Mary
The Assumption of Mary is one of the four Catholic Mariology#Dogmatic teachings, Marian dogmas of the Catholic Church. Pope Pius XII defined it on 1 November 1950 in his apostolic constitution as follows:
It leaves open the question of w ...
, Europe's largest ship procession is held on Lake Constance.
* Every year (early summer) the spectacular all-around ("Rund-um") Regatta from Lindau to Lindau via Meersburg, Überlingen
Überlingen (; ) is a German city on the northern shore of Lake Constance (Bodensee) in Baden-Württemberg near the German-Swiss border, border with Switzerland. After the city of Friedrichshafen, it is the second-largest city in the Bodenseek ...
, Romanshorn
Romanshorn is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Romanshorn was probably settled in the 7th century, and is first menti ...
is organized.
* Since 2009, the annual water sports
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms ...
and sailing festival "International Lake Constanze week", a joint sports event takes place in Konstanz.
* In Friedrichshafen, one of the most important water sports fairs in Europe, the Interboot, takes place annually.
Settlements on the lake
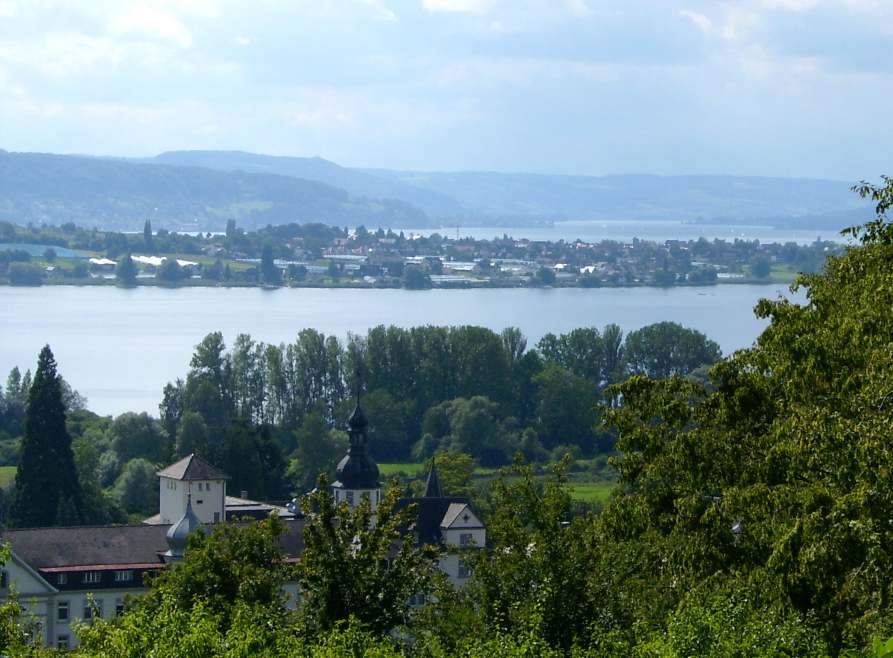







Austria
* Hard
* Hörbranz
* Bregenz
* Lochau
* Höchst
* Fussach
* Gaissau
Germany
From the entry of the Rhine, on the northern or right shore:
*On the Upper Lake (''Obersee'')
** Lindau (in Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
)
** Wasserburg
** Nonnenhorn
** Kressbronn (in Baden-Württemberg
Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i ...
)
** Langenargen
** Eriskirch
** Friedrichshafen
** Immenstaad
** Hagnau
** Stetten
** Meersburg
** Uhldingen-Mühlhofen (on the ''Überlinger See'')
**Überlingen
Überlingen (; ) is a German city on the northern shore of Lake Constance (Bodensee) in Baden-Württemberg near the German-Swiss border, border with Switzerland. After the city of Friedrichshafen, it is the second-largest city in the Bodenseek ...
** Sipplingen
**Ludwigshafen
Ludwigshafen, officially Ludwigshafen am Rhein (; meaning "Ludwig I of Bavaria, Ludwig's Port upon the Rhine"; Palatine German dialects, Palatine German: ''Ludwichshafe''), is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in the German state of Rh ...
** Bodman
* Konstanz with suburbs
** Wallhausen
** Dingelsdorf
** Litzelstetten
*On the Lower Lake (''Untersee'')
** Reichenau (including the island with same name)
** Allensbach (on the Gnadensee)
** Radolfzell am Bodensee (on the ''Zeller See'')
** Moos
** Gaienhofen
** Öhningen
Switzerland
From the entry of the Rhine, on the southern or left shore:
*On the Upper Lake (''Obersee'')
** Altenrhein, St. Gallen
** Staad, St. Gallen
** Rorschach, St. Gallen
** Goldach, St. Gallen
** Horn, Thurgau
** Steinach, St. Gallen
** Arbon, Thurgau (as all the following)
** Frasnacht
** Egnach
**Salmsach
Salmsach is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Salmsach is first mentioned in 1155 as ''Salmasa''. Salmsach was probab ...
**Romanshorn
Romanshorn is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Arbon (district), Arbon in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
Romanshorn was probably settled in the 7th century, and is first menti ...
** Uttwil
** Kesswil
** Güttingen
** Altnau
** Landschlacht
** Münsterlingen
** Scherzingen
** Bottighofen
** Kreuzlingen (and Konstanz, Germany)
*On the Seerhein
** Gottlieben
*On the Lower Lake (''Untersee'')
** Triboltingen
**Ermatingen
Ermatingen is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Kreuzlingen (district), Kreuzlingen in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
History
The Stone Age Westerfeld and Büge shoreline settlements w ...
** Mannenbach
** Eschlibach
** Berlingen
** Steckborn
** Mammern
** Eschenz
** Stein am Rhein, Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; ; ; ; ), historically known in English as Shaffhouse, is a list of towns in Switzerland, town with historic roots, a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of Schaffh ...
Fishing
The lake was frozen in the years 1077 (?), 1326 (partial), 1378 (partial), 1435, 1465 (partial), 1477 (partial), 1491 (partial?), 1517 (partial), 1571 (partial), 1573, 1600 (partial), 1684, 1695, 1709 (partial), 1795, 1830, 1880 (partial), and 1963.
About of fish were caught by 150 professional fishermen in 2001 which was below the previous ten-year average of per year. The Lake Constance trout (''Salmo trutta'') was almost extinct in the 1980s due to pollution, but thanks to protective measures they have made a significant return. Lake Constance is the home of the critically endangered species of trout '' Salvelinus profundus'', and formerly also the now extinct
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
Lake Constance whitefish ('' Coregonus gutturosus'').
See also
* Überlingen mid-air collision
* Württembergischer Yacht Club
*''Lake Constance'' is also the title of a track from Mike Oldfield
Michael Gordon Oldfield (born 15 May 1953) is an English retired musician, songwriter and producer best known for his debut studio album ''Tubular Bells'' (1973), which became an unexpected critical and commercial success. Though primarily a gu ...
's '' The Millennium Bell'' album
* Peter Handke's play, Ride Across lake Constance, was written in 1971.
Notes and references
Notes
References
Further reading
* (Pictures and texts of the cities around Lake Constance).
External links
*
*
*
Bodensee-Hochwasser
waterlevels
Internationale BodenseekonferenzLake Constance: pictures
Photos of Lake ConstanceBibliography on Water Resources and International Law
Peace Palace Library
GrenzRaumSee: A project from the ''Ludwig-Uhland-Institut für Empirische Kulturwissenschaft'' (Ludwig-Uhland-Department of European Ethnology / Empirical Cultural Science) of the University of Tübingen
*
Lake Constance AccommodationTourist Information Lake Constance
{{DEFAULTSORT:Constance
Lakes of Baden-Württemberg
Lakes of Bavaria
Lakes of Switzerland
Mountain lakes
Lakes of Thurgau
Lakes of the canton of St. Gallen
Lakes of Vorarlberg
Austria–Switzerland border
Austria–Germany border
International lakes of Europe
Germany–Switzerland border
Border tripoints
High Rhine basin
Lakes of the canton of Schaffhausen
Regions of Baden-Württemberg
 The German name of the lake, ''Bodensee'', has been adopted by many other languages, for example: Dutch: ''Bodenmeer'', Danish: ''Bodensøen'', Norwegian: ''Bodensjøen'', Swedish: ''Bodensjön'', Finnish: ''Bodenjärvi'', Russian: ''Боденское озеро'', Polish: ''Jezioro Bodeńskie'', Czech: ''Bodamské jezero'', Slovak: ''Bodamské jazero'', Hungarian: ''Bodeni-tó'', Serbo-Croatian: ''Bodensko jezero'', Albanian: ''Liqeni i Bodenit''.
After the Council of Constance in the 15th century, the alternative name ''Lacus Constantinus'' was used in the (Roman Catholic) Romance language area. This name, which had been attested as early as 1187 in the form ''Lacus Constantiensis'', came from the town of Konstanz at the outflow of the Rhine from the Obersee, whose original name, Constantia, was in turn derived from the Roman emperor, Constantius Chlorus (around 300 AD). Hence the French: ''Lac de Constance'', Italian: ''Lago di Costanza'', Portuguese: ''Lago de Constança'', Spanish: ''Lago de Constanza'', Romanian: ''Lacul Constanța'', Greek: ''Λίμνη της Κωνσταντίας – Limni tis Konstantias''. The Arabic, بحيرة كونستانس ''buħaira Konstans'' and the Turkish, ''Konstanz gölü'', probably go back to the French form of the name. Even in Romance-influenced English the name "Lake Constance" gained a foothold and was then exported into other languages such as Hebrew: ימת קונסטנץ ''yamat Konstanz'' and Swahili: ''Ziwa la Konstanz''. In many languages both forms exist in parallel e.g. Romansh: ''Lai da Constanza'' and ''Lai Bodan'', Esperanto: ''Konstanca Lago'' and ''Bodenlago''.
The poetic name, " Swabian Sea", was adopted by authors of the early modern era and the Enlightenment from ancient authors, possibly
The German name of the lake, ''Bodensee'', has been adopted by many other languages, for example: Dutch: ''Bodenmeer'', Danish: ''Bodensøen'', Norwegian: ''Bodensjøen'', Swedish: ''Bodensjön'', Finnish: ''Bodenjärvi'', Russian: ''Боденское озеро'', Polish: ''Jezioro Bodeńskie'', Czech: ''Bodamské jezero'', Slovak: ''Bodamské jazero'', Hungarian: ''Bodeni-tó'', Serbo-Croatian: ''Bodensko jezero'', Albanian: ''Liqeni i Bodenit''.
After the Council of Constance in the 15th century, the alternative name ''Lacus Constantinus'' was used in the (Roman Catholic) Romance language area. This name, which had been attested as early as 1187 in the form ''Lacus Constantiensis'', came from the town of Konstanz at the outflow of the Rhine from the Obersee, whose original name, Constantia, was in turn derived from the Roman emperor, Constantius Chlorus (around 300 AD). Hence the French: ''Lac de Constance'', Italian: ''Lago di Costanza'', Portuguese: ''Lago de Constança'', Spanish: ''Lago de Constanza'', Romanian: ''Lacul Constanța'', Greek: ''Λίμνη της Κωνσταντίας – Limni tis Konstantias''. The Arabic, بحيرة كونستانس ''buħaira Konstans'' and the Turkish, ''Konstanz gölü'', probably go back to the French form of the name. Even in Romance-influenced English the name "Lake Constance" gained a foothold and was then exported into other languages such as Hebrew: ימת קונסטנץ ''yamat Konstanz'' and Swahili: ''Ziwa la Konstanz''. In many languages both forms exist in parallel e.g. Romansh: ''Lai da Constanza'' and ''Lai Bodan'', Esperanto: ''Konstanca Lago'' and ''Bodenlago''.
The poetic name, " Swabian Sea", was adopted by authors of the early modern era and the Enlightenment from ancient authors, possibly  No
No  * 1540: the map ''Lacus Constantiensis'' by Johannes Zwick and Thomas Blarer shows topographic names, towns and the Rhine.
* 1555: the map of the route of the Rhine (''Rhinelaufkarte'') by Caspar Vopel includes a topographical map of Lake Constance with its larger towns, the tributaries and the course of the Rhine.
* 1633: the Swabian map by Johannes Janssonius, Amsterdam: ''Totius Sveviae novissima tabula'' shows Lake Constance with islands, tributaries, towns and villages.
* 1675: The Lake Constance map, ''Lacos Acronianus sive Bodamicus'', by Nikolaus David Hautt based on Andreas Arzet SJ shows Lake Constance with the adjacent lands.
* 1540: the map ''Lacus Constantiensis'' by Johannes Zwick and Thomas Blarer shows topographic names, towns and the Rhine.
* 1555: the map of the route of the Rhine (''Rhinelaufkarte'') by Caspar Vopel includes a topographical map of Lake Constance with its larger towns, the tributaries and the course of the Rhine.
* 1633: the Swabian map by Johannes Janssonius, Amsterdam: ''Totius Sveviae novissima tabula'' shows Lake Constance with islands, tributaries, towns and villages.
* 1675: The Lake Constance map, ''Lacos Acronianus sive Bodamicus'', by Nikolaus David Hautt based on Andreas Arzet SJ shows Lake Constance with the adjacent lands.
 The main tributary of Lake Constance is the Alpine Rhine. The Alpine Rhine and the Seerhein do not mix greatly with the waters of the lake and flow through the lakes along courses that change relatively little. There are also numerous smaller tributaries (236 in all). The most important tributaries of the Obersee are (counterclockwise) the Dornbirner Ach, Bregenzer Ach, Leiblach, Argen, Schussen, Rotach, Brunnisach, Seefelder Aach, Stockacher Aach, Salmsacher Aach, the Aach near Arbon, Steinach, Goldach and the Old Rhine. The outflow of the Obersee is the Seerhein, which in turn is the main tributary of the Untersee. The most important tributary of the Untersee is the Radolfzeller Aach. The source of the Radolfzeller Aach is the Aachtopf, a karst spring whose waters mostly derive from the Danube Sinkhole. Therefore, the
The main tributary of Lake Constance is the Alpine Rhine. The Alpine Rhine and the Seerhein do not mix greatly with the waters of the lake and flow through the lakes along courses that change relatively little. There are also numerous smaller tributaries (236 in all). The most important tributaries of the Obersee are (counterclockwise) the Dornbirner Ach, Bregenzer Ach, Leiblach, Argen, Schussen, Rotach, Brunnisach, Seefelder Aach, Stockacher Aach, Salmsacher Aach, the Aach near Arbon, Steinach, Goldach and the Old Rhine. The outflow of the Obersee is the Seerhein, which in turn is the main tributary of the Untersee. The most important tributary of the Untersee is the Radolfzeller Aach. The source of the Radolfzeller Aach is the Aachtopf, a karst spring whose waters mostly derive from the Danube Sinkhole. Therefore, the  In Lake Constance there are ten
In Lake Constance there are ten  The shores of Lake Constance consist mainly of gravel. In some places there are also sandy beaches, such as the Rohrspitz in the Austrian section of the lake, the Langenargen and Marienschlucht.
According to the data of the International Water Protection Commission for the Lake Constance, the approximate shore length is (see Coastline paradox). The inflow of water is constantly changing, mainly due to rain and the snow melt in the Alps. Its average surface area is about (in Switzerland the absolute value is slightly higher in m above sea level). The more or less regular seasonal fluctuations in the water level also lead to slight variations in shore length and differences in the shore zone habitats (depending on high and low water).
The shores of Lake Constance consist mainly of gravel. In some places there are also sandy beaches, such as the Rohrspitz in the Austrian section of the lake, the Langenargen and Marienschlucht.
According to the data of the International Water Protection Commission for the Lake Constance, the approximate shore length is (see Coastline paradox). The inflow of water is constantly changing, mainly due to rain and the snow melt in the Alps. Its average surface area is about (in Switzerland the absolute value is slightly higher in m above sea level). The more or less regular seasonal fluctuations in the water level also lead to slight variations in shore length and differences in the shore zone habitats (depending on high and low water).

 There are eight main harbors offering boat services across the Upper Lake:
;Austria:
* Bregenz
;Switzerland:
* Rorschach
*
There are eight main harbors offering boat services across the Upper Lake:
;Austria:
* Bregenz
;Switzerland:
* Rorschach
*  A network of several railway lines surrounds the lake. The lines are operated by regional train services (
A network of several railway lines surrounds the lake. The lines are operated by regional train services ( The climate of the Lake Constance area is characterised by mild temperatures with moderate gradients, thanks to the balancing and retarding effect of the large body of water.
It has a
The climate of the Lake Constance area is characterised by mild temperatures with moderate gradients, thanks to the balancing and retarding effect of the large body of water.
It has a  Lake Constance is also considered to be a risky and challenging lake for water sports because of the danger of gusty winds which can whip up waves as the weather changes suddenly. The most dangerous wind is the föhn, a warm down-slope wind from the Alps, which spreads out across the water, especially through the Alpine Rhine Valley and can generate waves several metres high.
Similarly dangerous for those unfamiliar with the area, are the sudden stormy gusts of wind during summer thunderstorms. They constantly claim victims from the water sports fraternity. During a thunderstorm in July 2006, waves reached heights of up to 3.50 metres.
For these reasons, there is a storm warning system in all three neighbouring countries. For storm warning purposes, Lake Constance is divided into three warning regions (west, centre and east). Warnings can be issued for each region independently. A "high winds" warning will be issued when squalls are expected of between 25 and 33 knots or registering
Lake Constance is also considered to be a risky and challenging lake for water sports because of the danger of gusty winds which can whip up waves as the weather changes suddenly. The most dangerous wind is the föhn, a warm down-slope wind from the Alps, which spreads out across the water, especially through the Alpine Rhine Valley and can generate waves several metres high.
Similarly dangerous for those unfamiliar with the area, are the sudden stormy gusts of wind during summer thunderstorms. They constantly claim victims from the water sports fraternity. During a thunderstorm in July 2006, waves reached heights of up to 3.50 metres.
For these reasons, there is a storm warning system in all three neighbouring countries. For storm warning purposes, Lake Constance is divided into three warning regions (west, centre and east). Warnings can be issued for each region independently. A "high winds" warning will be issued when squalls are expected of between 25 and 33 knots or registering  A one-hundred year event is the freezing over of Lake Constance, when the Lower Lake and the Upper Lake are completely frozen over so that people can safely cross the lake on foot. The last so-called ''Seegfrörne'' ( Alemannic) event was in 1963. The following is a list of years in which Lake Constance froze over partially or completely:
*875, 895
*1074, 1076
*1108
*1217, 1227, 1277
*1323, 1325, 1378, 1379, 1383
*1409, 1431, 1435 (complete), 1460, 1465, 1470, 1479
*1512, 1517, 1553, 1560 (complete), 1564, 1565, 1571, 1573 (complete)
*1684, 1695 (complete)
*1788, 1796 (complete)
*1830 (complete), 1880 (complete)
*1929, 1963 (complete)
Certain parts of the lake freeze over more frequently, mainly due to their shallow depth of water and shelter, as is the case, for example, of the so-called Markelfinger Winkel between the municipality of Markelfingen and the Mettnau peninsula.
A one-hundred year event is the freezing over of Lake Constance, when the Lower Lake and the Upper Lake are completely frozen over so that people can safely cross the lake on foot. The last so-called ''Seegfrörne'' ( Alemannic) event was in 1963. The following is a list of years in which Lake Constance froze over partially or completely:
*875, 895
*1074, 1076
*1108
*1217, 1227, 1277
*1323, 1325, 1378, 1379, 1383
*1409, 1431, 1435 (complete), 1460, 1465, 1470, 1479
*1512, 1517, 1553, 1560 (complete), 1564, 1565, 1571, 1573 (complete)
*1684, 1695 (complete)
*1788, 1796 (complete)
*1830 (complete), 1880 (complete)
*1929, 1963 (complete)
Certain parts of the lake freeze over more frequently, mainly due to their shallow depth of water and shelter, as is the case, for example, of the so-called Markelfinger Winkel between the municipality of Markelfingen and the Mettnau peninsula.

 The lake lies where the countries of Austria, Germany, and Switzerland meet. Beyond areas less than deep, considered to be under the jurisdiction of the nearest country, there is no legally binding agreement as to where the borders lie between the three countries. However, Switzerland holds the view that the border runs through the middle of the lake, Austria is of the opinion that the contentious area belongs to all the states on its banks, which is known as a "
The lake lies where the countries of Austria, Germany, and Switzerland meet. Beyond areas less than deep, considered to be under the jurisdiction of the nearest country, there is no legally binding agreement as to where the borders lie between the three countries. However, Switzerland holds the view that the border runs through the middle of the lake, Austria is of the opinion that the contentious area belongs to all the states on its banks, which is known as a " This region is known for sightseeing, water-sports, winter-sports like
This region is known for sightseeing, water-sports, winter-sports like  Diving in Lake Constance is considered attractive and challenging. Most of the diving areas are located in the northern part of the lake (
Diving in Lake Constance is considered attractive and challenging. Most of the diving areas are located in the northern part of the lake ( Pleasure boating is important. At the beginning of 2011, 57,875 amusement vehicles were registered for Lake Constance.
The legal basis for all shipping on the lake is the ordinance on shipping on Lake Constance, or "Bodensee-Schifffahrtsordnung". It is monitored on Lake Constance and on the Upper Rhine by the German, Swiss and Austrian Water Police, the "Seepolizei".
All boats must be registered, and boat drivers must hold a "Bodenseeschifferpatent" (authorization to drive a patented vehicle on Lake Constance). It is issued in Germany by the shipping offices of the district of Constance, the Lake Constance district, and the district of Lindau; in Switzerland by the cantonal authorities; and in Austria by the District Commission Bregenz. For pleasure boaters short-term guest licenses are possible (for the categories A for motorboats over 4.4 kW and D for
Pleasure boating is important. At the beginning of 2011, 57,875 amusement vehicles were registered for Lake Constance.
The legal basis for all shipping on the lake is the ordinance on shipping on Lake Constance, or "Bodensee-Schifffahrtsordnung". It is monitored on Lake Constance and on the Upper Rhine by the German, Swiss and Austrian Water Police, the "Seepolizei".
All boats must be registered, and boat drivers must hold a "Bodenseeschifferpatent" (authorization to drive a patented vehicle on Lake Constance). It is issued in Germany by the shipping offices of the district of Constance, the Lake Constance district, and the district of Lindau; in Switzerland by the cantonal authorities; and in Austria by the District Commission Bregenz. For pleasure boaters short-term guest licenses are possible (for the categories A for motorboats over 4.4 kW and D for 



