Kidney Cross Section on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering
 In humans, the kidneys are located high in the
In humans, the kidneys are located high in the
 The functional substance, or
The functional substance, or
File:Right kidney seen on abdominal ultrasound.jpg, Normal adult right kidney as seen on
 The kidneys excrete a variety of waste products produced by metabolism into the urine. The microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the
The kidneys excrete a variety of waste products produced by metabolism into the urine. The microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the

 Reabsorption is the transport of molecules from this ultrafiltrate and into the peritubular capillary network that surrounds the nephron tubules. It is accomplished via selective Cell surface receptor, receptors on the luminal cell membrane. Water is 55% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. Glucose at normal plasma levels is completely reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. The mechanism for this is the Na+/glucose cotransporter. A plasma level of 350 mg/dL will fully saturate the transporters and glucose will be lost in the urine. A plasma glucose level of approximately 160 is sufficient to allow glucosuria, which is an important clinical clue to diabetes mellitus.
Amino acids are reabsorbed by sodium dependent transporters in the proximal tubule. Hartnup disease is a deficiency of the tryptophan amino acid transporter, which results in pellagra.Le, Tao. ''First Aid for the USMLE Step 1'' 2013. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2013. Print.
Reabsorption is the transport of molecules from this ultrafiltrate and into the peritubular capillary network that surrounds the nephron tubules. It is accomplished via selective Cell surface receptor, receptors on the luminal cell membrane. Water is 55% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. Glucose at normal plasma levels is completely reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. The mechanism for this is the Na+/glucose cotransporter. A plasma level of 350 mg/dL will fully saturate the transporters and glucose will be lost in the urine. A plasma glucose level of approximately 160 is sufficient to allow glucosuria, which is an important clinical clue to diabetes mellitus.
Amino acids are reabsorbed by sodium dependent transporters in the proximal tubule. Hartnup disease is a deficiency of the tryptophan amino acid transporter, which results in pellagra.Le, Tao. ''First Aid for the USMLE Step 1'' 2013. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2013. Print.
 Dialysis is a treatment that substitutes for the function of normal kidneys. Dialysis may be instituted when approximately 85%–90% of kidney function is lost, as indicated by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 15. Dialysis removes metabolic waste products as well as excess water and sodium (thereby contributing to regulating blood pressure); and maintains many chemical levels within the body. Life expectancy is 5–10 years for those on dialysis; some live up to 30 years. Dialysis can occur via the blood (through a central venous catheter, catheter or arteriovenous fistula), or through the
Dialysis is a treatment that substitutes for the function of normal kidneys. Dialysis may be instituted when approximately 85%–90% of kidney function is lost, as indicated by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 15. Dialysis removes metabolic waste products as well as excess water and sodium (thereby contributing to regulating blood pressure); and maintains many chemical levels within the body. Life expectancy is 5–10 years for those on dialysis; some live up to 30 years. Dialysis can occur via the blood (through a central venous catheter, catheter or arteriovenous fistula), or through the
(CC-BY 4.0)
Other modalities, such as CT scan, CT and magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, should always be considered as supplementary imaging modalities in the assessment of renal disease.
File:Slide4nn.JPG, Right kidney
File:Slide5pp.JPG, Kidney
File:Slide3ppp.JPG, Right kidney
File:Right kidney.jpg, Right kidney
File:Left kidneys.jpg, Left kidney
File:Kidneys.jpg, Kidneys
File:Left kidney.jpg, Left kidney
Kidney at the Human Protein Atlas
{{Authority control Kidney, Endocrine system
organs
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to a ...
that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidney
The mammalian kidneys are a pair of excretory organs of the urinary system of mammals, being functioning Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys in postnatal-to-adult individuals (i. e. Kidney (vertebrates)#Metanephros, metanephric kidneys). The kidneys in ...
s, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the spatium, anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum ...
, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.
The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to a ...
; blood exits into the paired renal vein
The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar v ...
s. Each kidney is attached to a ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
, a tube that carries excreted urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
to the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
.
The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluid
Body fluids, bodily fluids, or biofluids, sometimes body liquids, are liquids within the Body (biology), body of an organism. In lean healthy adult men, the total body water is about 60% (60–67%) of the total Human body weight, body weight; it ...
s, fluid osmolality
In chemistry, molality is a measure of the amount of solute in a solution relative to a given mass of solvent. This contrasts with the definition of ''molarity'' which is based on a given volume of solution.
A commonly used unit for molality is ...
, acid-base balance, various electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
concentrations, and removal of toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. They occur especially as proteins, often conjugated. The term was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919), derived ...
. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus
''Glomerulus'' (; : glomeruli) is a common term used in anatomy to describe globular structures of entwined vessels, fibers, or neurons. ''Glomerulus'' is the diminutive of the Latin ''glomus'', meaning "ball of yarn".
''Glomerulus'' may refer to ...
: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
, sodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
, bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ...
, glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
, and amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
, ammonium
Ammonium is a modified form of ammonia that has an extra hydrogen atom. It is a positively charged (cationic) polyatomic ion, molecular ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation, addition of a proton (a hydrogen nucleu ...
, potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
and uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the meta ...
. The nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structu ...
is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains only about 12,500 nephrons. The kidneys also carry out functions independent of the nephrons. For example, they convert a precursor of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
to its active form, calcitriol
Calcitriol is a hormone and the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the exp ...
; and synthesize the hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s erythropoietin
Erythropoietin (; EPO), also known as erythropoetin, haematopoietin, or haemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted mainly by the kidneys in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production ( erythropoiesis) in th ...
and renin
Renin ( etymology and pronunciation), also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an aspartic protease protein and enzyme secreted by the kidneys that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—also known as the reni ...
.
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of long-term kidney disease, defined by the sustained presence of abnormal kidney function and/or abnormal kidney structure. To meet criteria for CKD, the abnormalities must be present for at least three mo ...
(CKD) has been recognized as a leading public health problem worldwide. The global estimated prevalence of CKD is 13.4%, and patients with kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney fa ...
needing renal replacement therapy
Renal replacement therapy (RRT) is therapy that replaces the normal blood-filtering function of the kidneys. It is used when the kidneys are not working well, which is called kidney failure and includes acute kidney injury and chronic kidney dis ...
are estimated between 5 and 7 million. Procedures used in the management of kidney disease include chemical and microscopic examination of the urine (urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, m ...
), measurement of kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and medical sign, signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Renal physiology, Functions of a healthy kidney include ...
by calculating the estimated glomerular filtration rate
Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance (medicine), clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; reg ...
(eGFR) using the serum creatinine
Creatinine (; ) is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body (depending on muscle mass).
Biological relevance
Serum creatinine (a blood measurement) is an impor ...
; and kidney biopsy
Renal biopsy (also kidney biopsy) is a medical procedure in which a small piece of kidney is removed from the body for examination, usually under a microscope. Microscopic examination of the tissue can provide information needed to diagnose, moni ...
and CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
to evaluate for abnormal anatomy. Dialysis
Dialysis may refer to:
* Dialysis (chemistry), a process of separating molecules in solution
**Electrodialysis, used to transport salt ions from one solution to another through an ion-exchange membrane under the influence of an applied electric po ...
and kidney transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantat ...
are used to treat kidney failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney fa ...
; one (or both sequentially) of these are almost always used when renal function drops below 15%. Nephrectomy
A nephrectomy is the surgical removal of a kidney, performed to treat a number of kidney diseases including kidney cancer. It is also done to remove a normal healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor, which is part of a kidney transplant pro ...
is frequently used to cure renal cell carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is a kidney cancer that originates in the lining of the Proximal tubule, proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the very small tubes in the kidney that transport primary urine. RCC is the most common type of kidney cance ...
.
Renal physiology
Renal physiology (Latin language, Latin ''renes'', "kidneys") is the study of the physiology of the kidney. This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodiu ...
is the study of kidney function
Assessment of kidney function occurs in different ways, using the presence of symptoms and medical sign, signs, as well as measurements using urine tests, blood tests, and medical imaging.
Renal physiology, Functions of a healthy kidney include ...
. Nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kid ...
is the medical specialty which addresses diseases of kidney ''function'': these include CKD, nephritic and nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes proteinuria, protein in the urine, hypoalbuminemia, low blood albumin levels, hyperlipidemia, high blood lipids, and significant edema, swelling. Other symptoms ...
s, acute kidney injury
Acute kidney injury (AKI), previously called acute renal failure (ARF), is a sudden decrease in renal function, kidney function that develops within seven days, as shown by an increase in serum creatinine or a decrease in urine output, or both.
...
, and pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications ...
. Urology
Urology (from Ancient Greek, Greek wikt:οὖρον, οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and ''wiktionary:-logia, -logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of t ...
addresses diseases of kidney (and urinary tract) ''anatomy'': these include cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Po ...
, renal cyst
A renal cyst is a fluid collection in or on the kidney. There are several types based on the Bosniak classification. The majority are benign, simple cysts that can be monitored and not intervened upon. However, some are cancerous or are suspicio ...
s, kidney stones
Kidney stone disease (known as nephrolithiasis, renal calculus disease, or urolithiasis) is a crystallopathy and occurs when there are too many minerals in the urine and not enough liquid or hydration. This imbalance causes tiny pieces of cr ...
and ureteral stones
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are line ...
, and urinary tract obstruction
Urinary tract obstruction is a urologic disease consisting of a decrease in the free passage of urine through one or both ureters and/or the urethra. It is a cause of urinary retention. Complete obstruction of the urinary tract requires prompt tre ...
.
The word "renal
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retrop ...
" is an adjective meaning "relating to the kidneys", and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney artery", other experts have advocated preserving the use of "renal" as appropriate including in "renal artery".
Structure
 In humans, the kidneys are located high in the
In humans, the kidneys are located high in the abdominal cavity
The abdominal cavity is a large body cavity in humans and many other animals that contain Organ (anatomy), organs. It is a part of the abdominopelvic cavity. It is located below the thoracic cavity, and above the pelvic cavity. Its dome-shaped roo ...
, one on each side of the spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Spinal column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoology), ...
, and lie in a retroperitoneal
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on thei ...
position at a slightly oblique angle. The asymmetry within the abdominal cavity, caused by the position of the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
, typically results in the right kidney being slightly lower and smaller than the left, and being placed slightly more to the middle than the left kidney. The left kidney is approximately at the vertebral level T12 to L3, and the right is slightly lower. The right kidney sits just below the diaphragm and posterior to the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
. The left kidney sits below the diaphragm and posterior to the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
. On top of each kidney is an adrenal gland
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer adrenal corte ...
. The upper parts of the kidneys are partially protected by the 11th and 12th rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s. Each kidney, with its adrenal gland is surrounded by two layers of fat: the perirenal fat
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their ...
present between renal fascia and renal capsule and pararenal fat
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their ...
superior to the renal fascia
The renal fascia is a dense, elastic connective tissue envelope enclosing the kidney and adrenal gland, together with the layer of perirenal fat surrounding these two.
The renal fascia separates the adipose capsule of kidney from the overlying ...
.
The human kidney is a bean-shaped structure with a convex
Convex or convexity may refer to:
Science and technology
* Convex lens, in optics
Mathematics
* Convex set, containing the whole line segment that joins points
** Convex polygon, a polygon which encloses a convex set of points
** Convex polytop ...
and a concave
Concave or concavity may refer to:
Science and technology
* Concave lens
* Concave mirror
Mathematics
* Concave function, the negative of a convex function
* Concave polygon
A simple polygon that is not convex is called concave, non-convex or ...
border. A recessed area on the concave border is the renal hilum
The renal hilum or renal pedicle is the recessed central fissure of the kidney where its vessels, nerves and ureter pass. The medial border of the kidney is concave in the center and convex toward either extremity; it is directed forward and a li ...
, where the renal artery
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.
The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to ...
enters the kidney and the renal vein
The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar v ...
and ureter
The ureters are tubes composed of smooth muscle that transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. In an adult human, the ureters typically measure 20 to 30 centimeters in length and about 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. They are lin ...
leave. The kidney is surrounded by tough fibrous tissue, the renal capsule
The renal capsule is a tough fibrous layer surrounding the kidney and covered in a layer of perirenal fat known as the adipose capsule of kidney. The adipose capsule is sometimes included in the structure of the renal capsule. It provides some ...
, which is itself surrounded by perirenal fat
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their ...
, renal fascia
The renal fascia is a dense, elastic connective tissue envelope enclosing the kidney and adrenal gland, together with the layer of perirenal fat surrounding these two.
The renal fascia separates the adipose capsule of kidney from the overlying ...
, and pararenal fat
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their ...
. The anterior (front) surface of these tissues is the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
, while the posterior (rear) surface is the transversalis fascia
The transversalis fascia (or transverse fascia) is the fascial lining of the anterolateral abdominal wall situated between the inner surface of the transverse abdominal muscle, and the preperitoneal fascia. It is directly continuous with the ilia ...
.
The superior pole of the right kidney is adjacent to the liver. For the left kidney, it is next to the spleen
The spleen (, from Ancient Greek '' σπλήν'', splḗn) is an organ (biology), organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter.
The spleen plays important roles in reg ...
. Both, therefore, move down upon inhalation.
A Danish study measured the median renal length to be on the left side and on the right side in adults. Median renal volumes were on the left and on the right.
Gross anatomy
parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
, of the human kidney is divided into two major structures: the outer renal cortex
The renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney between the renal capsule and the renal medulla. In the adult, it forms a continuous smooth outer zone with a number of projections ( cortical columns) that extend down between the pyramids. I ...
and the inner renal medulla
The renal medulla (Latin: ''medulla renis'' 'marrow of the kidney') is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which ...
. Grossly, these structures take the shape of eight to 18 cone-shaped renal lobe
The renal lobe is a portion of a kidney consisting of a renal pyramid and the renal cortex above it. In humans, on average there are 7 to 18 renal lobes.
It is visible without a microscope, though it is easier to see in humans than in other animal ...
s, each containing renal cortex surrounding a portion of medulla called a renal pyramid
The renal medulla (Latin: ''medulla renis'' 'marrow of the kidney') is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which ...
. Between the renal pyramids are projections of cortex called renal column
The renal columns, Bertin columns, or columns of Bertin, a.k.a. columns of Bertini are extensions of the renal cortex in between the renal pyramids. They allow the cortex to be better anchored. (Cortical extensions into the medullary space.)
Each ...
s.
The tip, or papilla
Papilla (Latin, 'nipple') or papillae may refer to:
In animals
* Papilla (fish anatomy), in the mouth of fish
* Papilla (worms), small bumps on the surface of certain worms
* Basilar papilla, a sensory organ of lizards, amphibians and fish
* ...
, of each pyramid empties urine into a minor calyx
The renal calyces ( calyx) are conduits in the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces form a cup-shaped drain around the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the m ...
; minor calyces empty into major calyces
The renal calyces ( calyx) are conduits in the kidney through which urine passes. The minor calyces form a cup-shaped drain around the apex of the renal pyramids. Urine formed in the kidney passes through a renal papilla at the apex into the ...
, and major calyces empty into the renal pelvis
The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the convergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous ...
. This becomes the ureter. At the hilum, the ureter and renal vein exit the kidney and the renal artery enters. Hilar fat and lymphatic tissue with lymph nodes surround these structures. The hilar fat is contiguous with a fat-filled cavity called the renal sinus
The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, ...
. The renal sinus collectively contains the renal pelvis and calyces and separates these structures from the renal medullary tissue.
The kidneys possess no overtly moving structures.
abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasonography (also called abdominal ultrasound imaging or abdominal sonography) is a form of medical ultrasonography (medicine, medical application of ultrasound technology) to visualise abdomen, abdominal anatomy, anatomical structu ...
with a pole to pole measurement of 9.34 cm
File:CTscankidney.jpg, A CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan), formerly called computed axial tomography scan (CAT scan), is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or ...
of the abdomen showing the position of the kidneys. The left cross-section in the upper abdomen shows the liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
on the left side of scan (right side of body). Center: cross-section showing the kidneys below the liver and spleen. Right: further cross-section through the left kidney.
File:Slide42222.JPG, Image showing the structures that the kidney lies near
File:Left kidney.jpg, Cross-section through a cadaver
A cadaver, often known as a corpse, is a Death, dead human body. Cadavers are used by medical students, physicians and other scientists to study anatomy, identify disease sites, determine causes of death, and provide tissue (biology), tissue to ...
ic specimen showing the position of the kidneys
Blood supply
The kidneys receive blood from therenal arteries
The renal arteries are paired arteries that supply the kidneys with blood. Each is directed across the crus of the diaphragm, so as to form nearly a right angle.
The renal arteries carry a large portion of total blood flow to the kidneys. Up to a ...
, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta
In human anatomy, the abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta (of the thorax).
Structure
The abdominal aorta begins at the level of the diaphragm ...
. The kidneys receive approximately 20–25% of cardiac output
In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols Q, \dot Q, or \dot Q_ , edited by Catherine E. Williamson, Phillip Bennett is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: tha ...
in adult human. Each renal artery branches into segmental arteries, dividing further into interlobar arteries
The interlobar arteries are vessels of the renal circulation
The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal artery, renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively sm ...
, which penetrate the renal capsule and extend through the renal columns between the renal pyramids. The interlobar arteries then supply blood to the arcuate arteries
The arcuate arteries of the kidney, also known as arciform arteries, are vessels of the renal circulation. They are located at the border of the renal cortex and renal medulla.
They are named after the fact that they are shaped in arcs due to the ...
that run through the boundary of the cortex and the medulla. Each arcuate artery supplies several interlobular
Cortical radial arteries, formerly known as interlobular arteries, are renal blood vessels given off at right angles from the side of the arcuate arteries looking toward the cortical substance. The interlobular arteries pass directly outward betw ...
arteries that feed into the afferent arteriole
The afferent arterioles are a group of blood vessels that supply the nephrons in many excretory systems. They play an important role in the regulation of blood pressure as a part of the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism.
The afferent arteriole ...
s that supply the glomeruli.
Blood drains from the kidneys, ultimately into the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of the ...
. After filtration occurs, the blood moves through a small network of small veins (venules
A venule is a very small vein in the microcirculation that allows blood to return from the capillary beds to drain into the venous system via increasingly larger veins. Post-capillary venules are the smallest of the veins with a diameter of bet ...
) that converge into interlobular veins
The stellate veins join to form the interlobular veins, which pass inward between the Medullary ray (anatomy), rays, receive branches from the plexuses around the convoluted tubules, and, having arrived at the bases of the renal pyramids, join with ...
. As with the arteriole distribution, the veins follow the same pattern: the interlobular provide blood to the arcuate veins
''Arcuate'' (Latin for "curved") can refer to:
Anatomy
* Arcuate fasciculus
* Arcuate line (disambiguation)
* Arcuate artery (disambiguation), several arteries
* Arcuate nucleus (hypothalamus)
* Arcuate nucleus (medulla)
* Arcuate ligaments ...
then back to the interlobar veins
The interlobar veins are veins of the renal circulation
The renal circulation supplies the blood to the kidneys via the renal artery, renal arteries, left and right, which branch directly from the abdominal aorta. Despite their relatively small si ...
, which come to form the renal vein
The renal veins in the renal circulation, are large-calibre veins that drain blood filtered by the kidneys into the inferior vena cava. There is one renal vein draining each kidney. Each renal vein is formed by the convergence of the interlobar v ...
s which exit the kidney.
Nerve supply
The kidney andnervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the complex system, highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its behavior, actions and sense, sensory information by transmitting action potential, signals to and from different parts of its body. Th ...
communicate via the renal plexus, whose fibers course along the renal arteries to reach each kidney. Input from the sympathetic nervous system triggers vasoconstriction in the kidney, thereby reducing renal blood flow. The kidney also receives input from the parasympathetic nervous system, by way of the renal branches of the vagus nerve; the function of this is yet unclear. Sensory input from the kidney travels to the T10–11 levels of the spinal cord and is sensed in the corresponding dermatome (anatomy), dermatome. Thus, pain in the flank region may be referred from corresponding kidney.
Microanatomy
Renal histology is the study of the microscopic structure of the kidney. The adult human kidney contains at least 26 distinct Cell type, cell types, including epithelial, endothelial, stromal and smooth muscle cells. Distinct cell types include: *Kidney glomerulus parietal cell *Kidney glomerulus podocyte *Intraglomerular mesangial cell *Extraglomerular mesangial cell *Juxtaglomerular cell *Kidney proximal tubule brush border cell *Loop of Henle thin segment cell *Thick ascending limb cell *Kidney distal tubule cell *Collecting duct system#Cells, Collecting duct principal cell *Collecting duct system#Cells, Collecting duct intercalated cell *Interstitial kidney cellsGene and protein expression
In humans, about 20,000 protein coding genes are expressed in human cells and almost 70% of these genes are expressed in normal, adult kidneys. Just over 300 genes are more specifically expressed in the kidney, with only some 50 genes being highly specific for the kidney. Many of the corresponding kidney specific proteins are expressed in the cell membrane and function as transporter proteins. The highest expressed kidney specific protein is Tamm–Horsfall protein, uromodulin, the most abundant protein in urine with functions that prevent calcification and growth of bacteria. Specific proteins are expressed in the different compartments of the kidney with podocin and nephrin expressed in glomeruli, Solute carrier family protein SLC22A8 expressed in proximal tubules, calbindin expressed in distal tubules and aquaporin 2 expressed in the collecting duct cells.Development
The mammalian kidney develops from intermediate mesoderm. Kidney development, also called ''nephrogenesis'', proceeds through a series of three successive developmental phases: the pronephros, mesonephros, and metanephros. The metanephros are primordia of the permanent kidney.Function
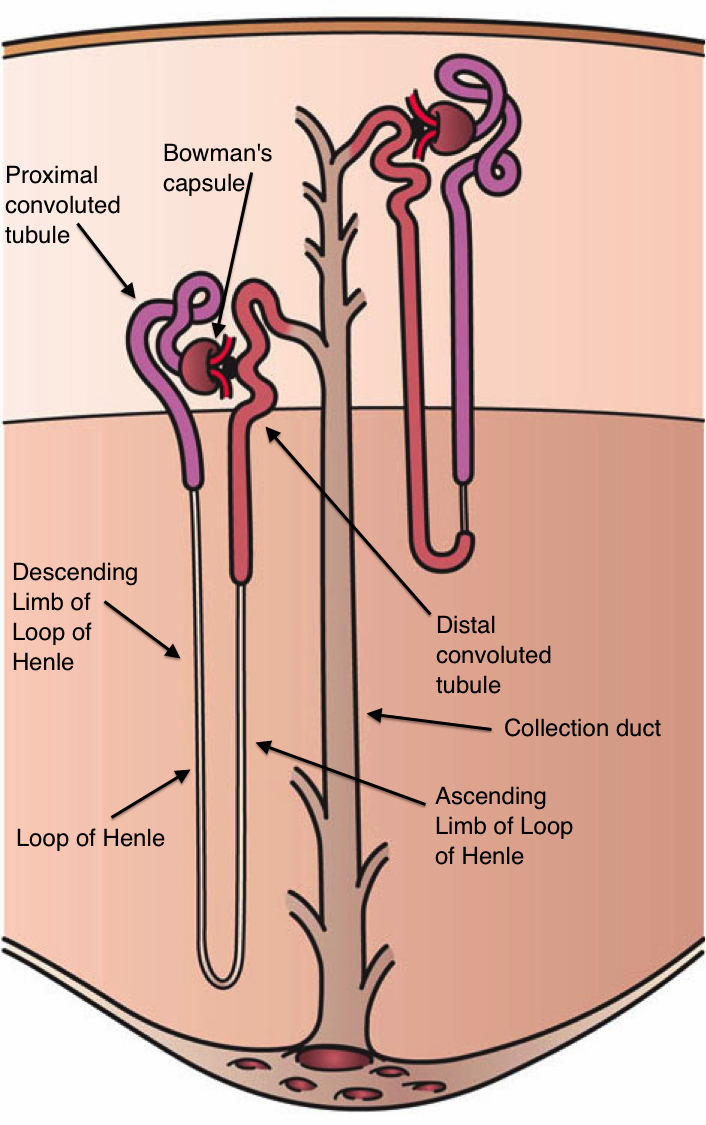
 The kidneys excrete a variety of waste products produced by metabolism into the urine. The microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the
The kidneys excrete a variety of waste products produced by metabolism into the urine. The microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney is the nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structu ...
. It processes the blood supplied to it via filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion; the consequence of those processes is the production of urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
. These include the nitrogenous wastes urea, from protein catabolism, and uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the Chemical formula, formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates, such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is a product of the meta ...
, from nucleic acid metabolism. The ability of mammals and some birds to concentrate wastes into a volume of urine much smaller than the volume of blood from which the wastes were extracted is dependent on an elaborate countercurrent multiplication mechanism. This requires several independent nephron characteristics to operate: a tight hairpin configuration of the tubules, water and ion permeability in the descending limb of the loop, water impermeability in the ascending loop, and active ion transport out of most of the ascending limb. In addition, passive countercurrent exchange by the vessels carrying the blood supply to the nephron is essential for enabling this function.
The kidney participates in whole-body homeostasis, regulating acid–base balance, electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
concentrations, extracellular fluid volume, and blood pressure. The kidney accomplishes these homeostatic functions both independently and in concert with other organs, particularly those of the endocrine system. Various endocrine hormones coordinate these endocrine functions; these include renin
Renin ( etymology and pronunciation), also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an aspartic protease protein and enzyme secreted by the kidneys that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—also known as the reni ...
, angiotensin II, aldosterone, antidiuretic hormone, and atrial natriuretic peptide, among others.
Formation of urine

Filtration
Filtration, which takes place at the renal corpuscle, is the process by which cells and large proteins are retained while materials of smaller molecular weights are filtered from the blood to make an Ultrafiltration (kidney), ultrafiltrate that eventually becomes urine. The adult human kidney generates approximately 180 liters of filtrate a day, most of which is reabsorbed. The normal range for a twenty four hour urine volume collection is 800 to 2,000 milliliters per day. The process is also known as hydrostatic filtration due to the hydrostatic pressure exerted on the capillary walls.Reabsorption
 Reabsorption is the transport of molecules from this ultrafiltrate and into the peritubular capillary network that surrounds the nephron tubules. It is accomplished via selective Cell surface receptor, receptors on the luminal cell membrane. Water is 55% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. Glucose at normal plasma levels is completely reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. The mechanism for this is the Na+/glucose cotransporter. A plasma level of 350 mg/dL will fully saturate the transporters and glucose will be lost in the urine. A plasma glucose level of approximately 160 is sufficient to allow glucosuria, which is an important clinical clue to diabetes mellitus.
Amino acids are reabsorbed by sodium dependent transporters in the proximal tubule. Hartnup disease is a deficiency of the tryptophan amino acid transporter, which results in pellagra.Le, Tao. ''First Aid for the USMLE Step 1'' 2013. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2013. Print.
Reabsorption is the transport of molecules from this ultrafiltrate and into the peritubular capillary network that surrounds the nephron tubules. It is accomplished via selective Cell surface receptor, receptors on the luminal cell membrane. Water is 55% reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. Glucose at normal plasma levels is completely reabsorbed in the proximal tubule. The mechanism for this is the Na+/glucose cotransporter. A plasma level of 350 mg/dL will fully saturate the transporters and glucose will be lost in the urine. A plasma glucose level of approximately 160 is sufficient to allow glucosuria, which is an important clinical clue to diabetes mellitus.
Amino acids are reabsorbed by sodium dependent transporters in the proximal tubule. Hartnup disease is a deficiency of the tryptophan amino acid transporter, which results in pellagra.Le, Tao. ''First Aid for the USMLE Step 1'' 2013. New York: McGraw-Hill Medical, 2013. Print.
Secretion
Secretion is the reverse of reabsorption: molecules are transported from the peritubular capillary through the interstitial fluid, then through the renal tubular cell and into the ultrafiltrate.Excretion
The last step in the processing of the ultrafiltrate is ''excretion'': the ultrafiltrate passes out of the nephron and travels through a tube called the ''collecting duct'', which is part of the collecting duct system, and then to the ureters where it is renamed ''urine''. In addition to transporting the ultrafiltrate, the collecting duct also takes part in reabsorption.Hormone secretion
The kidneys are essential for more than just filtration; they also secrete several important hormones that play pivotal roles in regulating various physiological processes.The kidneys secrete a variety of hormones, includingerythropoietin
Erythropoietin (; EPO), also known as erythropoetin, haematopoietin, or haemopoietin, is a glycoprotein cytokine secreted mainly by the kidneys in response to cellular hypoxia; it stimulates red blood cell production ( erythropoiesis) in th ...
, calcitriol
Calcitriol is a hormone and the active form of vitamin D, normally made in the kidney. It is also known as 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol. It binds to and activates the vitamin D receptor in the nucleus of the cell, which then increases the exp ...
, and renin
Renin ( etymology and pronunciation), also known as an angiotensinogenase, is an aspartic protease protein and enzyme secreted by the kidneys that participates in the body's renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)—also known as the reni ...
. Erythropoietin (EPO) is released in response to Hypoxia (medical), hypoxia (low levels of oxygen at tissue level) in the renal circulation. It stimulates erythropoiesis (production of red blood cells) in the bone marrow. Calcitriol, the activated form of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of structurally related, fat-soluble compounds responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, along with numerous other biological functions. In humans, the most important compo ...
, promotes intestinal absorption of calcium and the renal reabsorption of phosphate. Renin is an enzyme which regulates angiotensin and aldosterone levels.
* Erythropoietin (EPO): Produced in response to low oxygen levels, EPO stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow. Impaired EPO production, particularly in chronic kidney disease, can lead to anemia and cardiovascular complications.
* Renin: Secreted in response to low blood pressure or sodium levels, renin initiates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and fluid balance. Dysregulation of RAAS is linked to hypertension and cardiovascular diseases.
* Calcitriol: The active form of vitamin D, calcitriol helps regulate calcium and phosphate metabolism, supporting bone health and calcium absorption in the intestines. Impaired calcitriol synthesis can lead to bone mineralization issues in chronic kidney disease.
Hormonal interventions, including the introduction of therapies - such as gender-affirming treatments - may alter renal function, estrogen and testosterone and affect kidney function, electrolyte balance, and glomerular filtration rate. Monitoring kidney health is essential in adolescents undergoing such treatments to avoid potential long-term complications, especially in those with preexisting renal issues.
Blood pressure regulation
Although the kidney cannot directly sense blood, long-term regulation of blood pressure predominantly depends upon the kidney. This primarily occurs through maintenance of the extracellular fluid compartment, the size of which depends on the plasmasodium
Sodium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 element, group 1 of the peri ...
concentration. Renin is the first in a series of important chemical messengers that make up the renin–angiotensin system. Changes in renin ultimately alter the output of this system, principally the hormones angiotensin II and aldosterone. Each hormone acts via multiple mechanisms, but both increase the kidney's absorption of sodium chloride, thereby expanding the extracellular fluid compartment and raising blood pressure. When renin levels are elevated, the concentrations of angiotensin II and aldosterone increase, leading to increased sodium chloride reabsorption, expansion of the extracellular fluid compartment, and an increase in blood pressure. Conversely, when renin levels are low, angiotensin II and aldosterone levels decrease, contracting the extracellular fluid compartment, and decreasing blood pressure.
Acid–base balance
The two organ systems that help regulate the body's acid–base balance are the kidneys and lungs. Acid–base homeostasis is the maintenance of pH around a value of 7.4. The lungs are the part of respiratory system which helps to maintain acid–base homeostasis by regulating carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in the blood. The respiratory system is the first line of defense when the body experiences and acid–base problem. It attempts to return the body pH to a value of 7.4 by controlling the respiratory rate. When the body is experiencing acidic conditions, it will increase the respiratory rate which in turn drives off CO2 and decreases the H+ concentration, therefore increasing the pH. In basic conditions, the respiratory rate will slow down so that the body holds onto more CO2 and increases the H+ concentration and decreases the pH. The kidneys have two cells that help to maintain acid-base homeostasis: intercalated A and B cells. The intercalated A cells are stimulated when the body is experiencing acidic conditions. Under acidic conditions, the high concentration of CO2 in the blood creates a gradient for CO2 to move into the cell and push the reaction HCO3 + H ↔ H2CO3 ↔ CO2 + H2O to the left. On the luminal side of the cell there is a H+ pump and a H/K exchanger. These pumps move H+ against their gradient and therefore require ATP. These cells will remove H+ from the blood and move it to the filtrate which helps to increase the pH of the blood. On the basal side of the cell there is a HCO3/Cl exchanger and a Cl/K co-transporter (facilitated diffusion). When the reaction is pushed to the left it also increases the HCO3 concentration in the cell and HCO3 is then able to move out into the blood which additionally raises the pH. The intercalated B cell responds very similarly, however, the membrane proteins are flipped from the intercalated A cells: the proton pumps are on the basal side and the HCO3/Cl exchanger and K/Cl co-transporter are on the luminal side. They function the same, but now release protons into the blood to decrease the pH.Regulation of osmolality
The kidneys help maintain the water and salt level of the body. Any significant rise in plasma osmolality is detected by the hypothalamus, which communicates directly with the posterior pituitary gland. An increase in osmolality causes the gland to secrete antidiuretic hormone (ADH), resulting in water reabsorption by the kidney and an increase in urine concentration. The two factors work together to return the plasma osmolality to its normal levels.Measuring function
Various calculations and methods are used to try to measure kidney function. Renal clearance is the volume of plasma from which the substance is completely cleared from the blood per unit time. The filtration fraction is the amount of plasma that is actually filtered through the kidney. This can be defined using the equation. The kidney is a very complex organ and mathematical modelling has been used to better understand kidney function at several scales, including fluid uptake and secretion.Clinical significance
Nephrology
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function (renal physiology) and kidney disease (renal pathophysiology), the preservation of kid ...
is the subspeciality under Internal Medicine that deals with kidney function and disease states related to renal malfunction and their management including Kidney dialysis, dialysis and kidney Organ transplantation, transplantation. Urology
Urology (from Ancient Greek, Greek wikt:οὖρον, οὖρον ''ouron'' "urine" and ''wiktionary:-logia, -logia'' "study of"), also known as genitourinary surgery, is the branch of medicine that focuses on surgical and medical diseases of t ...
is the specialty under Surgery that deals with kidney structure abnormalities such as kidney cancer and cysts and problems with urinary tract. Nephrologists are internists, and urologists are surgeons, whereas both are often called "kidney doctors". There are overlapping areas that both nephrologists and urologists can provide care such as kidney stones
Kidney stone disease (known as nephrolithiasis, renal calculus disease, or urolithiasis) is a crystallopathy and occurs when there are too many minerals in the urine and not enough liquid or hydration. This imbalance causes tiny pieces of cr ...
and kidney related infections.
There are many causes of kidney disease. Some causes are acquired over the course of life, such as diabetic nephropathy whereas others are congenital, such as polycystic kidney disease.
Medical terms related to the kidneys commonly use terms such as ''renal'' and the prefix ''nephro-''. The adjective ''renal'', meaning related to the kidney, is from the Latin language, Latin ''rēnēs'', meaning kidneys; the prefix ''nephro-'' is from the Ancient Greek word for kidney, ''nephros (νεφρός)''. For example, surgical removal of the kidney is a ''nephrectomy'', while a reduction in kidney function is called ''renal dysfunction''.
Acquired Disease
*Diabetic nephropathy *Glomerulonephritis *Hydronephrosis is the enlargement of one or both of the kidneys caused by obstruction of the flow of urine. *Interstitial nephritis is inflammation of the area of the kidney known as the renal interstitium. *Kidney stones (nephrolithiasis) are a relatively common and particularly painful disorder. A chronic condition can result in scars to the kidneys. The removal of kidney stones involves ultrasound treatment to break up the stones into smaller pieces, which are then passed through the urinary tract. One common symptom of kidney stones is a sharp to disabling pain in the middle and sides of the lower back or groin. *Kidney tumour **Wilms tumor **Renal cell carcinoma *Lupus nephritis *Minimal change disease *Innephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a collection of symptoms due to kidney damage. This includes proteinuria, protein in the urine, hypoalbuminemia, low blood albumin levels, hyperlipidemia, high blood lipids, and significant edema, swelling. Other symptoms ...
, the glomerulus
''Glomerulus'' (; : glomeruli) is a common term used in anatomy to describe globular structures of entwined vessels, fibers, or neurons. ''Glomerulus'' is the diminutive of the Latin ''glomus'', meaning "ball of yarn".
''Glomerulus'' may refer to ...
has been damaged so that a large amount of protein in the blood enters the urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
. Other frequent features of the nephrotic syndrome include swelling, low serum albumin, and high cholesterol.
*Pyelonephritis is infection of the kidneys and is frequently caused by complication of a urinary tract infection.
*Kidney failure
** Acute kidney failure
** Chronic kidney disease, Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease
* Renal artery stenosis
* Renovascular hypertension
Kidney injury and failure
Generally, humans can live normally with just one kidney, as one has more functioning renal tissue than is needed to survive. Only when the amount of functioning kidney tissue is greatly diminished does one develop chronic kidney disease. Renal replacement therapy, in the form of Kidney dialysis, dialysis orkidney transplantation
Kidney transplant or renal transplant is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage kidney disease (ESRD). Kidney transplant is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantat ...
, is indicated when the glomerular filtration rate
Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance (medicine), clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; reg ...
has fallen very low or if the renal dysfunction leads to severe symptoms.
Dialysis
 Dialysis is a treatment that substitutes for the function of normal kidneys. Dialysis may be instituted when approximately 85%–90% of kidney function is lost, as indicated by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 15. Dialysis removes metabolic waste products as well as excess water and sodium (thereby contributing to regulating blood pressure); and maintains many chemical levels within the body. Life expectancy is 5–10 years for those on dialysis; some live up to 30 years. Dialysis can occur via the blood (through a central venous catheter, catheter or arteriovenous fistula), or through the
Dialysis is a treatment that substitutes for the function of normal kidneys. Dialysis may be instituted when approximately 85%–90% of kidney function is lost, as indicated by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 15. Dialysis removes metabolic waste products as well as excess water and sodium (thereby contributing to regulating blood pressure); and maintains many chemical levels within the body. Life expectancy is 5–10 years for those on dialysis; some live up to 30 years. Dialysis can occur via the blood (through a central venous catheter, catheter or arteriovenous fistula), or through the peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesotheli ...
(peritoneal dialysis) Dialysis is typically administered three times a week for several hours at free-standing dialysis centers, allowing recipients to lead an otherwise essentially normal life.
Congenital disease
*Congenital hydronephrosis *Congenital obstruction of urinary tract *Duplex kidneys, or double kidneys, occur in approximately 1% of the population. This occurrence normally causes no complications, but can occasionally cause urinary tract infections. *Duplicated ureter occurs in approximately one in 100 live births *Horseshoe kidney occurs in approximately one in 400 live births *Nephroblastoma (Syndromic Wilm's tumour) * Nutcracker syndrome *Polycystic kidney disease **Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease affects patients later in life. Approximately one in 1000 people will develop this condition **Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease is far less common, but more severe, than the dominant condition. It is apparent ''in utero'' or at birth. *Renal agenesis. Failure of one kidney to form occurs in approximately one in 750 live births. Failure of both kidneys to form used to be fatal; however, medical advances such as amnioinfusion therapy during pregnancy and peritoneal dialysis have made it possible to stay alive until a transplant can occur. *Renal dysplasia *Unilateral small kidney *Multicystic dysplastic kidney occurs in approximately one in every 2400 live births *Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction or UPJO; although most cases are congenital, some are acquired.Diagnosis
Many renal diseases are diagnosed on the basis of a detailed medical history, and physical examination. The medical history takes into account present and past symptoms, especially those of kidney disease; recent infections; exposure to substances toxic to the kidney; and family history of kidney disease. Renal function, Kidney function is tested by using blood tests and Clinical urine tests, urine tests. The most common blood tests are creatinine, urea andelectrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
s. Urine tests such as urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, m ...
can evaluate for pH, protein, glucose, and the presence of blood. Microscopic analysis can also identify the presence of urinary casts and crystals. The glomerular filtration rate
Renal functions include maintaining an acid–base balance; regulating fluid balance; regulating sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance (medicine), clearing toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; reg ...
(GFR) can be directly measured ("measured GFR", or mGFR) but this rarely done in everyday practice. Instead, special equations are used to calculate GFR ("estimated GFR", or eGFR).
Imaging
Renal ultrasonography is essential in the diagnosis and management of kidney-related diseases.Content initially copied from:(CC-BY 4.0)
Other modalities, such as CT scan, CT and magnetic resonance imaging, MRI, should always be considered as supplementary imaging modalities in the assessment of renal disease.
Biopsy
The role of the renal biopsy is to diagnose renal disease in which the etiology is not clear based upon noninvasive means (clinical history, past medical history, medication history, physical exam, laboratory studies, imaging studies). In general, a renal pathologist will perform a detailed morphological evaluation and integrate the morphologic findings with the clinical history and laboratory data, ultimately arriving at a pathological diagnosis. A renal pathologist is a physician who has undergone general training in anatomic pathology and additional specially training in the interpretation of renal biopsy specimens. Ideally, multiple core sections are obtained and evaluated for adequacy (presence of glomeruli) intraoperatively. A pathologist/pathology assistant divides the specimen(s) for submission for light microscopy, immunofluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy. The pathologist will examine the specimen using light microscopy with multiple staining techniques (hematoxylin and eosin/H&E, PAS, trichrome, silver stain) on multiple level sections. Multiple immunofluorescence stains are performed to evaluate for antibody, protein and complement deposition. Finally, ultra-structural examination is performed with electron microscopy and may reveal the presence of electron-dense deposits or other characteristic abnormalities that may suggest an etiology for the patient's renal disease.Other animals
In the majority of vertebrates, the mesonephros persists into the adult, albeit usually fused with the more advanced metanephros; only in amniotes is the mesonephros restricted to the embryo. The kidneys of fish and amphibians are typically narrow, elongated organs, occupying a significant portion of the trunk. The collecting ducts from each cluster of nephrons usually drain into an ''archinephric duct'', which is homology (biology), homologous with the vas deferens of amniotes. However, the situation is not always so simple; in cartilaginous fish and some amphibians, there is also a shorter duct, similar to the amniote ureter, which drains the posterior (metanephric) parts of the kidney, and joins with the archinephric duct at the bladder or cloaca. Indeed, in many cartilaginous fish, the anterior portion of the kidney may degenerate or cease to function altogether in the adult. In the most primitive vertebrates, the hagfish and lampreys, the kidney is unusually simple: it consists of a row of nephrons, each emptying directly into the archinephric duct. Invertebrates may possess excretory organs that are sometimes referred to as "kidneys", but, even in ''Amphioxus'', these are never homologous with the kidneys of vertebrates, and are more accurately referred to by other names, such as nephridia. In amphibians, kidneys and the urinary bladder harbour specialized parasites, monogeneans of the family Polystomatidae. The kidneys of reptiles consist of a number of lobules arranged in a broadly linear pattern. Each lobule contains a single branch of the ureter in its centre, into which the collecting ducts empty. Reptiles have relatively few nephrons compared with other amniotes of a similar size, possibly because of their lower metabolic rate. Birds have relatively large, elongated kidneys, each of which is divided into three or more distinct lobes. The lobes consists of several small, irregularly arranged, lobules, each centred on a branch of the ureter. Birds have small glomeruli, but about twice as many nephrons as similarly sized mammals. The human kidney is fairly typical of that of mammals. Distinctive features of the mammalian kidney, in comparison with that of other vertebrates, include the presence of the renal pelvis and renal pyramids and a clearly distinguishable cortex and medulla. The latter feature is due to the presence of elongated Loop of Henle, loops of Henle; these are much shorter in birds, and not truly present in other vertebrates (although the nephron often has a short ''intermediate segment'' between the convoluted tubules). It is only in mammals that the kidney takes on its classical "kidney" shape, although there are some exceptions, such as the multilobed reniculate kidneys of pinnipeds and cetaceans.Evolutionary adaptation
Kidneys of various animals show evidence of evolutionary adaptation and have long been studied in ecophysiology and comparative physiology. Kidney morphology, often indexed as the relative medullary thickness, is associated with habitat aridity among species of mammals and diet (e.g., carnivores have only long loops of Henle).Society and culture
Significance
Egyptian
In ancient Egypt, the kidneys, like the heart, were left inside the mummified bodies, unlike other organs which were removed. Comparing this to the biblical statements, and to drawings of human body with the heart and two kidneys portraying a set of scales for weighing justice, it seems that the Egyptian beliefs had also connected the kidneys with judgement and perhaps with moral decisions.Hebrew
According to studies in modern and ancient Hebrew, various body organs in humans and animals served also an emotional or logical role, today mostly attributed to the brain and the endocrine system. The kidney is mentioned in several biblical verses in conjunction with the heart, much as the bowels were understood to be the "seat" of emotion – grief, joy and pain. Similarly, the Talmud (''Berakhoth'' 61.a) states that one of the two kidneys counsels what is good, and the other evil. In the sacrifices offered at the biblical Tabernacle and later on at the temple in Jerusalem, the priests were instructed to remove the kidneys and the adrenal gland covering the kidneys of the sheep, goat and cattle offerings, and to burn them on the altar, as the holy part of the "offering for God" never to be eaten.India: Ayurvedic system
In ancient India, according to the Ayurveda, Ayurvedic medical systems, the kidneys were considered the beginning of the excursion channels system, the 'head' of the ''Mutra Srota''s, receiving from all other systems, and therefore important in determining a person's health balance and temperament by the balance and mixture of the three 'Dosha's – the three health elements: Vatha (or Vata) – air, Pitta – bile, and Kapha – mucus. The temperament and health of a person can then be seen in the resulting color of the urine. Modern Ayurveda practitioners, a practice which is characterized as pseudoscience, have attempted to revive these methods in medical procedures as part of Ayurveda Urine therapy. These procedures have been called "nonsensical" by skeptics.Medieval Christianity
The Latin term ''renes'' is related to the English word "reins", a synonym for the kidneys in Shakespearean English (e.g. ''Merry Wives of Windsor'' 3.5), which was also the time when the King James Version of the Bible was translated. Kidneys were once popularly regarded as the seat of the conscience and reflection, and a number of verses in the Bible (e.g. Ps. 7:9, Rev. 2:23) state that God searches out and inspects the kidneys, or "reins", of humans, together with the heart.History
Kidney stones have been identified and recorded about as long as written historical records exist. The urinary tract including the ureters, as well as their function to drain urine from the kidneys, has been described by Galen in the second century AD. The first to examine the ureter through an internal approach, called ureteroscopy, rather than surgery was Hampton Young in 1929. This was improved on by VF Marshall who is the first published use of a flexible endoscope based on fiber optics, which occurred in 1964. The insertion of a drainage tube into therenal pelvis
The renal pelvis or pelvis of the kidney is the funnel-like dilated part of the ureter in the kidney. It is formed by the convergence of the major calyces, acting as a funnel for urine flowing from the major calyces to the ureter. It has a mucous ...
, bypassing the uterers and urinary tract, called nephrostomy, was first described in 1941. Such an approach differed greatly from the open surgery, open surgical approaches within the urinary system employed during the preceding two millennia.
Additional images
See also
*Artificial kidney *Holonephros *Nephromegaly *Organ donation *Organ harvesting *Pelvic kidney *World Kidney Day *List of distinct cell types in the adult human body *List of human cell types derived from the germ layersReferences
Citations
General and cited references
*External links
Kidney at the Human Protein Atlas
{{Authority control Kidney, Endocrine system