A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of
chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
in the cells of a
species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes.
Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities.

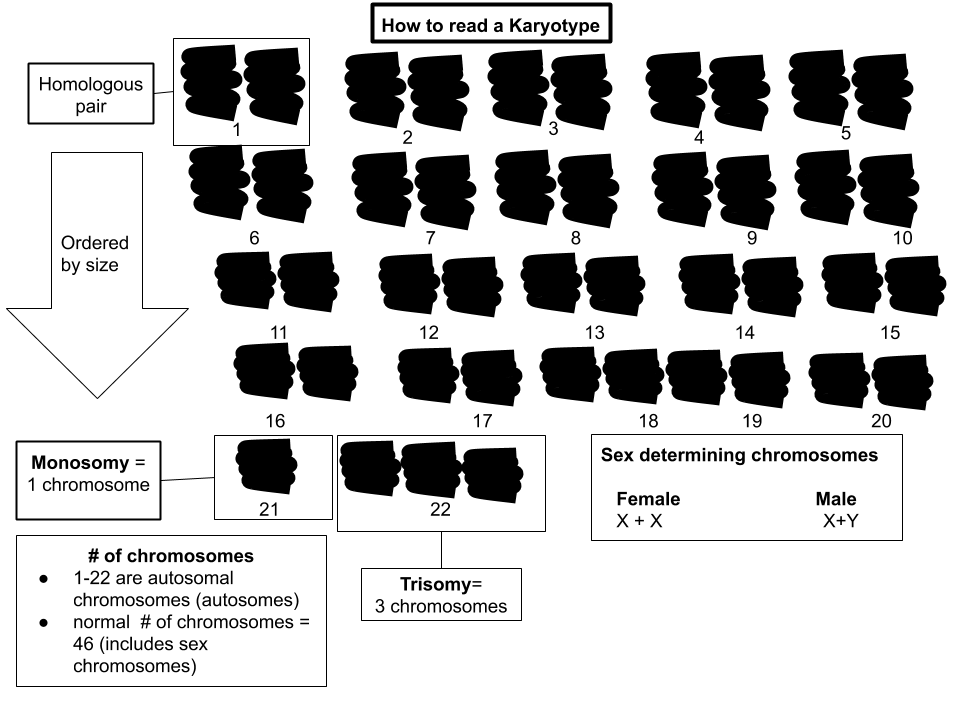
A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines
light microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view subjects too small to be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, el ...
and
photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
in the
metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, alig ...
of the
cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
, and results in a
photomicrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a mi ...
ic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a
schematic
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the sc ...
karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister
chromatid
A chromatid (Greek ''khrōmat-'' 'color' + ''-id'') is one half of a duplicated chromosome. Before replication, one chromosome is composed of one DNA molecule. In replication, the DNA molecule is copied, and the two molecules are known as chrom ...
s of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as one on photomicrographs as well unless the resolution is high enough to distinguish them. The study of whole sets of chromosomes is sometimes known as karyology.
Karyotypes describe the
chromosome count of an organism and what these chromosomes look like under a light
microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory equipment, laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic ...
. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the
centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
s, banding pattern, any differences between the
sex chromosome
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that
carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair ...
s, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of
cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
.
The basic number of chromosomes in the
somatic
Somatic may refer to:
* Somatic (biology), referring to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells
** Somatic cell, a non-gametic cell in a multicellular organism
* Somatic nervous system, the portion of the vertebrate nervous syst ...
cells of an individual or a species is called the ''somatic number'' and is designated ''2n''. In the
germ-line
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes ( eggs and sperm), which can come together to form a zygote. They dif ...
(the sex cells) the chromosome number is ''n'' (humans: n = 23).
Thus, in humans 2n = 46.
So, in normal
diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
organisms,
autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
chromosomes are present in two copies. There may, or may not, be
sex chromosomes
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that
carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair ...
.
Polyploid
Polyploidy is a condition in which the biological cell, cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of (Homologous chromosome, homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have Cell nucleus, nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning ...
cells have multiple copies of chromosomes and
haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
cells have single copies.
Karyotypes can be used for many purposes; such as to study
chromosomal aberration
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where ther ...
s,
cellular function,
taxonomic
280px, Generalized scheme of taxonomy
Taxonomy is a practice and science concerned with classification or categorization. Typically, there are two parts to it: the development of an underlying scheme of classes (a taxonomy) and the allocation ...
relationships,
medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
and to gather information about past
evolutionary
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certa ...
events (''
karyosystematics'').
Observations on karyotypes

Staining
The study of karyotypes is made possible by
staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic ...
. Usually, a suitable
dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
, such as
Giemsa
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups of ...
, is applied after
cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
* Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network
* Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization
* Electrochemical cell, a d ...
have been arrested during
cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell (biology), cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukar ...
by a solution of
colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to prevent and treat gout, to treat familial Mediterranean fever and Behçet's disease, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction. The American College of Rheumatology recommends colchicine, nonstero ...
usually in
metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, alig ...
or
prometaphase
Prometaphase is the phase of mitosis following prophase and preceding metaphase in eukaryotic somatic cells. In prometaphase, the nuclear membrane breaks apart into numerous "membrane vesicles," and the chromosomes inside form protein structure ...
when most condensed. In order for the
Giemsa
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups of ...
stain to adhere correctly, all chromosomal proteins must be digested and removed. For humans,
white blood cells
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are genera ...
are used most frequently because they are easily induced to divide and grow in
tissue culture
Tissue culture is the growth of tissue (biology), tissues or cell (biology), cells in an artificial medium separate from the parent organism. This technique is also called micropropagation. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-s ...
.
[Gustashaw K.M. 1991. Chromosome stains. In ''The ACT Cytogenetics Laboratory Manual'' 2nd ed, ed. M.J. Barch. The Association of Cytogenetic Technologists, Raven Press, New York.] Sometimes observations may be made on non-dividing (
interphase
Interphase is the active portion of the cell cycle that includes the G1, S, and G2 phases, where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for mitosis, respectively. Interphase was formerly called the "resting phase," but the cell i ...
) cells. The sex of an unborn
fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
can be predicted by observation of interphase cells (see
amniotic centesis and
Barr body
A Barr body (named after discoverer Murray Barr) or X-chromatin is an inactive X chromosome. In species with XY sex-determination (including humans), females typically have two X chromosomes, and one is rendered inactive in a process calle ...
).
Observations
Six different characteristics of karyotypes are usually observed and compared:
# Differences in absolute sizes of chromosomes. Chromosomes can vary in absolute size by as much as twenty-fold between genera of the same family. For example, the legumes ''
Lotus tenuis'' and ''
Vicia faba
''Vicia faba'', commonly known as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of vetch, a flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption, and also as a cover crop. Vari ...
'' each have six pairs of chromosomes, yet ''V. faba'' chromosomes are many times larger. These differences probably reflect different amounts of DNA duplication.
# Differences in the position of
centromeres
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
. These differences probably came about through
translocations
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" transloc ...
.
# Differences in relative size of chromosomes. These differences probably arose from segmental interchange of unequal lengths.
# Differences in basic number of chromosomes. These differences could have resulted from successive unequal translocations which removed all the essential genetic material from a chromosome, permitting its loss without penalty to the organism (the dislocation hypothesis) or through fusion. Humans have one pair fewer chromosomes than the great apes. Human chromosome 2 appears to have resulted from the fusion of two ancestral chromosomes, and many of the genes of those two original chromosomes have been translocated to other chromosomes.
# Differences in number and position of satellites.
Satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
are small bodies attached to a chromosome by a thin thread.
# Differences in degree and distribution of
GC content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of ...
(
Guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
-
Cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
pairs versus
Adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
-
Thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
). In metaphase where the karyotype is typically studied, all DNA is condensed, but most of the time, DNA with a high GC content is usually less condensed, that is, it tends to appear as
euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin (DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, which ...
rather than
heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a rol ...
. GC rich DNA tends to contain more
coding DNA
The coding region of a gene, also known as the coding DNA sequence (CDS), is the portion of a gene's DNA or RNA that codes for a protein. Studying the length, composition, regulation, splicing, structures, and functions of coding regions compared ...
and be more
transcriptionally active.
[ GC rich DNA is lighter on ]Giemsa staining
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups o ...
.[Thompson & Thompson Genetics in Medicine 7th Ed] Euchromatin regions contain larger amounts of Guanine
Guanine () (symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleotide bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside ...
-Cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleotide bases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attac ...
pairs (that is, it has a higher GC content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of ...
). The staining technique using Giemsa
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups of ...
staining is called G banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases (mainly chr ...
and therefore produces the typical "G-Bands".germ-line
In biology and genetics, the germline is the population of a multicellular organism's cells that develop into germ cells. In other words, they are the cells that form gametes ( eggs and sperm), which can come together to form a zygote. They dif ...
and soma
Soma may refer to:
Businesses and brands
* SOMA (architects), a New York–based firm of architects
* Soma (company), a company that designs eco-friendly water filtration systems
* SOMA Fabrications, a builder of bicycle frames and other bicycle ...
(between gametes
A gamete ( ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the Ge ...
and the rest of the body),
# between members of a population ( chromosome polymorphism),
# in geographic specialization, and
# in mosaics
A mosaic () is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/Mortar (masonry), mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and ...
or otherwise abnormal individuals.
Human karyogram

 Both the micrographic and schematic karyograms shown in this section have a standard chromosome layout, and display darker and lighter regions as seen on
Both the micrographic and schematic karyograms shown in this section have a standard chromosome layout, and display darker and lighter regions as seen on G banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases (mainly chr ...
, which is the appearance of the chromosomes after treatment with trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
(to partially digest the chromosomes) and staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic ...
with Giemsa stain
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups o ...
. Compared to darker regions, the lighter regions are generally more transcriptionally active, with a greater ratio of coding DNA
The coding region of a gene, also known as the coding DNA sequence (CDS), is the portion of a gene's DNA or RNA that codes for a protein. Studying the length, composition, regulation, splicing, structures, and functions of coding regions compared ...
versus non-coding DNA
Non-coding DNA (ncDNA) sequences are components of an organism's DNA that do not encode protein sequences. Some non-coding DNA is transcribed into functional non-coding RNA molecules (e.g. transfer RNA, microRNA, piRNA, ribosomal RNA, and reg ...
, and a higher GC content
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of ...
.[ ]
Both the micrographic and schematic karyograms show the normal human diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
karyotype, which is the typical composition of the genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
within a normal cell of the human body, and which contains 22 pairs of autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
chromosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that
carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair ...
(allosomes). A major exception to diploidy in humans is gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
s (sperm and egg cells) which are haploid with 23 unpaired chromosomes, and this ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
is not shown in these karyograms. The micrographic karyogram is converted into grayscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a greyscale (more common in Commonwealth English) or grayscale (more common in American English) image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample (signal), s ...
, whereas the schematic karyogram shows the purple hue as typically seen on Giemsa stain (and is a result of its azure B component, which stains DNA purple).
The schematic karyogram in this section is a graphical representation of the idealized karyotype. For each chromosome pair, the scale to the left shows the length in terms of million base pairs
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
, and the scale to the right shows the designations of the bands and sub-bands. Such bands and sub-bands are used by the International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature
The International System for Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature (ISCN; previously the International System for Human Cytogenetic Nomenclature) is an international standard for human chromosome nomenclature, which includes band names, symbols, and abbre ...
to describe locations of chromosome abnormalities
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where ther ...
. Each row of chromosomes is vertically aligned at centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
level.
Human chromosome groups
Based on the karyogram characteristics of size, position of the centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
and sometimes the presence of a chromosomal satellite (a segment distal to a secondary constriction), the human chromosomes are classified into the following groups:
Alternatively, the human genome can be classified as follows, based on pairing, sex differences, as well as location within the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
versus inside mitochondria
A mitochondrion () is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is us ...
:
* 22 homologous autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosome ...
chromosome pairs (chromosomes 1 to 22). Homologous means that they have the same genes in the same loci, and autosomal means that they are not sex chromomes.
* Two sex chromosome
Sex chromosomes (also referred to as allosomes, heterotypical chromosome, gonosomes, heterochromosomes, or idiochromosomes) are chromosomes that
carry the genes that determine the sex of an individual. The human sex chromosomes are a typical pair ...
(in green rectangle at bottom right in the schematic karyogram, with adjacent silhouettes of typical representative phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological propert ...
s): The most common karyotypes for females
An organism's sex is female (symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and male ...
contain two X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex chromosomes in many organisms, including mammals, and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-determination system. The X chromosome was named for its u ...
s and are denoted 46,XX; males
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to ...
usually have both an X and a Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the ...
denoted 46,XY. However, approximately 0.018% percent of humans are intersex
Intersex people are those born with any of several sex characteristics, including chromosome patterns, gonads, or genitals that, according to the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, "do not fit typical binar ...
, sometimes due to variations in sex chromosomes.
* The human mitochondrial genome (shown at bottom left in the schematic karyogram, to scale compared to the nuclear DNA in terms of base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s), although this is not included in micrographic karyograms in clinical practice. Its genome is relatively tiny compared to the rest.
Copy number
 Schematic karyograms generally display a DNA copy number corresponding to the G0 phase of the cellular state (outside of the replicative
Schematic karyograms generally display a DNA copy number corresponding to the G0 phase of the cellular state (outside of the replicative cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
) which is the most common state of cells. The schematic karyogram in this section also shows this state. In this state (as well as during the G1 phase of the cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA re ...
), each cell has two autosomal chromosomes of each kind (designated 2n), where each chromosome has one copy of each locus, making a total copy number of two for each locus (2c). At top center in the schematic karyogram, it also shows the chromosome 3 pair after having undergone DNA synthesis
DNA synthesis is the natural or artificial creation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecules. DNA is a macromolecule made up of nucleotide units, which are linked by covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds, in a repeating structure. DNA synthesis occu ...
, occurring in the S phase
S phase (Synthesis phase) is the phase of the cell cycle in which DNA is replicated, occurring between G1 phase and G2 phase. Since accurate duplication of the genome is critical to successful cell division, the processes that occur during S ...
(annotated as S) of the cell cycle. This interval includes the G2 phase and metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, alig ...
(annotated as "Meta."). During this interval, there is still 2n, but each chromosome will have two copies of each locus, wherein each sister chromatid
A sister chromatid refers to the identical copies ( chromatids) formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, with both copies joined together by a common centromere. In other words, a sister chromatid may also be said to be 'one-half' of the du ...
(chromosome arm) is connected at the centromere, for a total of 4c.[ ] The chromosomes on micrographic karyograms are in this state as well, because they are generally micrographed in metaphase, but during this phase the two copies of each chromosome are so close to each other that they appear as one unless the image resolution is high enough to distinguish them. In reality, during the G0 and G1 phases, nuclear DNA is dispersed as chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important r ...
and does not show visually distinguishable chromosomes even on micrography.
The copy number of the human mitochondrial genome per human cell varies from 0 (erythrocytes)[ ] up to 1,500,000 (oocytes
An oocyte (, oöcyte, or ovocyte) is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female ger ...
), mainly depending on the number of mitochondria per cell.[ ]
Diversity and evolution of karyotypes
Although the replication and transcription
Transcription refers to the process of converting sounds (voice, music etc.) into letters or musical notes, or producing a copy of something in another medium, including:
Genetics
* Transcription (biology), the copying of DNA into RNA, often th ...
of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
is highly standardized in eukaryotes
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms are eukaryotes. They constitute a major group of ...
, the same cannot be said for their karyotypes, which are highly variable. There is variation between species in chromosome number, and in detailed organization, despite their construction from the same macromolecules
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
. This variation provides the basis for a range of studies in evolutionary cytology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living an ...
.
In some cases there is even significant variation within species. In a review, Godfrey and Masters conclude:
Although much is known about karyotypes at the descriptive level, and it is clear that changes in karyotype organization has had effects on the evolutionary course of many species, it is quite unclear what the general significance might be.
Changes during development
Instead of the usual gene repression, some organisms go in for large-scale elimination of heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continuum between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a rol ...
, or other kinds of visible adjustment to the karyotype.
* Chromosome elimination. In some species, as in many sciarid flies, entire chromosomes are eliminated during development.
* Chromatin diminution (founding father: Theodor Boveri
Theodor Heinrich Boveri (12 October 1862 – 15 October 1915) was a German zoologist, comparative anatomist and co-founder of modern cytology. He was notable for the first hypothesis regarding cellular processes that cause cancer, and for descr ...
). In this process, found in some copepods
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthic (living on the sediments), several species have ...
and roundworms
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (hel ...
such as ''Ascaris suum
''Ascaris suum'', also known as the large roundworm of pig, is a parasitic nematode that causes ascariasis in pigs. While roundworms in pigs and humans are today considered as two species (''A. suum'' and '' A. lumbricoides'') with different ho ...
'', portions of the chromosomes are cast away in particular cells. This process is a carefully organised genome rearrangement where new telomeres are constructed and certain heterochromatin regions are lost. In ''A. suum'', all the somatic cell precursors undergo chromatin diminution.
* X-inactivation
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into ...
. The inactivation of one X chromosome takes place during the early development of mammals (see Barr body
A Barr body (named after discoverer Murray Barr) or X-chromatin is an inactive X chromosome. In species with XY sex-determination (including humans), females typically have two X chromosomes, and one is rendered inactive in a process calle ...
and dosage compensation
Dosage compensation is the process by which organisms equalize the expression of genes between members of different biological sexes. Across species, different sexes are often characterized by different types and numbers of sex chromosomes. In ord ...
). In placental mammals
Placental mammals ( infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguish ...
, the inactivation is random as between the two Xs; thus the mammalian female is a mosaic in respect of her X chromosomes. In marsupials
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a ...
it is always the paternal X which is inactivated. In human females some 15% of somatic cells escape inactivation, and the number of genes affected on the inactivated X chromosome varies between cells: in fibroblast
A fibroblast is a type of cell (biology), biological cell typically with a spindle shape that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework (Stroma (tissue), stroma) for animal Tissue (biology), tissues, and ...
cells up about 25% of genes on the Barr body escape inactivation.
Number of chromosomes in a set
A spectacular example of variability between closely related species is the muntjac
Muntjacs ( ), also known as the barking deer or rib-faced deer, (URL is Google Books) are small deer of the genus ''Muntiacus'' native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. Muntjacs are thought to have begun appearing 15–35 million years ago, ...
, which was investigated by Kurt Benirschke and Doris Wurster. The diploid number of the Chinese muntjac, '' Muntiacus reevesi'', was found to be 46, all telocentric
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
. When they looked at the karyotype of the closely related Indian muntjac, ''Muntiacus muntjak
The southern red muntjac (''Muntiacus muntjak'') is a deer species native to Southeast Asia. It was formerly known as the Indian muntjac or the common muntjac before the species was taxonomically revised to represent only populations of Thailan ...
'', they were astonished to find it had female = 6, male = 7 chromosomes.
The number of chromosomes in the karyotype between (relatively) unrelated species is hugely variable. The low record is held by the nematode
The nematodes ( or ; ; ), roundworms or eelworms constitute the phylum Nematoda. Species in the phylum inhabit a broad range of environments. Most species are free-living, feeding on microorganisms, but many are parasitic. Parasitic worms (h ...
'' Parascaris univalens'', where the haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
n = 1; and an ant: '' Myrmecia pilosula''. The high record would be somewhere amongst the fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s, with the adder's tongue fern ''Ophioglossum
''Ophioglossum'', the adder's-tongue ferns, is a genus of about 50 species of ferns in the family Ophioglossaceae. The genus name comes from Ancient Greek ὄφις (''óphis''), meaning "snake", and γλῶσσα (''glôssa''), meaning "tongue". ...
'' ahead with an average of 1262 chromosomes. Top score for animals might be the shortnose sturgeon
The shortnose sturgeon (''Huso brevirostrum'') is a small and endangered species of North American sturgeon. As with most sturgeons, it is an anadromous bottom-feeder, which migrates upstream to spawn but spends most of its life feeding in rive ...
'' Acipenser brevirostrum'' at 372 chromosomes.B chromosomes
In addition to the normal karyotype, wild populations of many animal, plant, and fungi species contain B chromosomes (also known as supernumerary, accessory, (conditionally-)dispensable, or lineage-specific chromosomes). By definition, these chr ...
means that chromosome number can vary even within one interbreeding population; and aneuploid
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cel ...
s are another example, though in this case they would not be regarded as normal members of the population.
Fundamental number
The fundamental number, ''FN'', of a karyotype is the number of visible major chromosomal arms per set of chromosomes.acrocentric
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
or telocentric
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers ...
) present. Humans have FN = 82,Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes in therian mammals and other organisms. Along with the X chromosome, it is part of the XY sex-determination system, in which the Y is the sex-determining chromosome because the presence of the ...
is also acrocentric). The fundamental autosomal number or autosomal fundamental number, ''FNa''autosome
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
s (non- sex-linked chromosomes).
Ploidy
Ploidy
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell.
* Polyploidy
Polyploidy is a condition in which the cells of an organism have more than two paired sets of ( homologous) chromosomes. Most species whose cells have nuclei (eukaryotes) are diploid, meaning they have two complete sets of chromosomes, one fro ...
, where there are more than two sets of homologous chromosomes in the cells, occurs mainly in plants. It has been of major significance in plant evolution according to Stebbins. The proportion of flowering plants which are polyploid was estimated by Stebbins to be 30–35%, but in grasses the average is much higher, about 70%. Polyploidy in lower plants (fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s, horsetails
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of vascular plants that reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a "living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass Equisetidae, which f ...
and psilotales
Psilotaceae is a family of ferns (class Polypodiopsida) consisting of two genera, ''Psilotum'' and ''Tmesipteris'' with about a dozen species. It is the only family in the order Psilotales.
Description
Once thought to be descendants of early vas ...
) is also common, and some species of ferns have reached levels of polyploidy far in excess of the highest levels known in flowering plants. Polyploidy in animals is much less common, but it has been significant in some groups.Polyploid series in related species which consist entirely of multiples of a single basic number are known as
euploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, re ...
.
* Haplo-diploidy, where one sex is diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
, and the other haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
. It is a common arrangement in the Hymenoptera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic.
Females typi ...
, and in some other groups.
* Endopolyploidy occurs when in adult differentiated tissues the cells have ceased to divide by mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
, but the nuclei contain more than the original somatic
Somatic may refer to:
* Somatic (biology), referring to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells
** Somatic cell, a non-gametic cell in a multicellular organism
* Somatic nervous system, the portion of the vertebrate nervous syst ...
number of chromosomes
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most importa ...
. In the ''endocycle'' ( endomitosis or endoreduplication
Endoreduplication (also referred to as endoreplication or endocycling) is replication of the nuclear genome in the absence of mitosis, which leads to elevated nuclear gene content and polyploidy. Endoreduplication can be understood simply as a vari ...
) chromosomes in a 'resting' nucleus undergo reduplication
In linguistics, reduplication is a Morphology (linguistics), morphological process in which the Root (linguistics), root or Stem (linguistics), stem of a word, part of that, or the whole word is repeated exactly or with a slight change.
The cla ...
, the daughter chromosomes separating from each other inside an ''intact'' nuclear membrane
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer polar membrane, membranes that in eukaryotic cells surround the Cell nucleus, nucleus, which encloses the genome, genetic material.
The nuclear envelope con ...
.In many instances, endopolyploid nuclei contain tens of thousands of chromosomes (which cannot be exactly counted). The cells do not always contain exact multiples (powers of two), which is why the simple definition 'an increase in the number of chromosome sets caused by replication without cell division' is not quite accurate.
This process (especially studied in insects and some higher plants such as maize) may be a developmental strategy for increasing the productivity of tissues which are highly active in biosynthesis.
The phenomenon occurs sporadically throughout the
eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
kingdom from protozoa
Protozoa (: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a polyphyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic debris. Historically ...
to humans; it is diverse and complex, and serves differentiation and morphogenesis
Morphogenesis (from the Greek ''morphê'' shape and ''genesis'' creation, literally "the generation of form") is the biological process that causes a cell, tissue or organism to develop its shape. It is one of three fundamental aspects of deve ...
in many ways.
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
is the condition in which the chromosome number in the cells is not the typical number for the species. This would give rise to a chromosome abnormality
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where the ...
such as an extra chromosome or one or more chromosomes lost. Abnormalities in chromosome number usually cause a defect in development. Down syndrome and Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) lea ...
are examples of this.
Aneuploidy may also occur within a group of closely related species. Classic examples in plants are the genus ''Crepis
''Crepis'', commonly known in some parts of the world as hawksbeard or hawk's-beard (but not to be confused with the related genus ''Hieracium'' with a similar common name), is a genus of annual and perennial flowering plants of the family Aster ...
'', where the gametic (= haploid) numbers form the series x = 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7; and ''Crocus
''Crocus'' (; plural: crocuses or croci) is a genus of seasonal flowering plants in the family Iridaceae (iris family) comprising about 100 species of perennial plant, perennials growing from corms. They are low growing plants, whose flower stem ...
'', where every number from x = 3 to x = 15 is represented by at least one species. Evidence of various kinds shows that trends of evolution have gone in different directions in different groups. In primates, the great apes
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); '' Gorilla'' (the ...
have 24x2 chromosomes whereas humans have 23x2. Human chromosome 2 was formed by a merger of ancestral chromosomes, reducing the number.
Chromosomal polymorphism
Some species are polymorphic for different chromosome structural forms. The structural variation may be associated with different numbers of chromosomes in different individuals, which occurs in the ladybird beetle ''Chilocorus stigma
''Chilocorus stigma'', commonly known as the twice-stabbed ladybug, is a native resident of the United States and Canada. It also has been introduced to Hawaii. It is shiny black, and there is one red spot on each elytron. The remainder of the bo ...
'', some mantids
Mantidae is one of the largest family (biology), families in the Order (biology), order of Mantodea, praying mantises, based on the type species ''Mantis religiosa''; most genera are tropical or subtropical. Historically, this was the only family ...
of the genus ''Ameles
''Ameles'' is a wide-ranging genus of praying mantises represented in Africa, Asia, and Europe.
Tree of Life Web Project. 2005
'', the European shrew ''Sorex araneus
The common shrew (''Sorex araneus''), also known as the Eurasian shrew, is the most common shrew, and one of the most common mammals, throughout Northern Europe, including Great Britain, but excluding Ireland. It is long and weighs , and has ve ...
''. There is some evidence from the case of the mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
'' Thais lapillus'' (the dog whelk
The dog whelk, dogwhelk, or Atlantic dogwinkle (''Nucella lapillus'') is a species of predatory sea snail, a carnivorous marine gastropod in the family Muricidae, the rock snails.
''Nucella lapillus'' was originally described by Carl Linnaeus i ...
) on the Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
coast, that the two chromosome morphs are adapted
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
to different habitats.
Species trees
The detailed study of chromosome banding in insects with polytene chromosomes can reveal relationships between closely related species: the classic example is the study of chromosome banding in Hawaiian drosophilids by Hampton L. Carson.
In about , the Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands () are an archipelago of eight major volcanic islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii in the south to nort ...
have the most diverse collection of drosophilid flies in the world, living from rainforests
Rainforests are forests characterized by a closed and continuous tree Canopy (biology), canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforests can be generally classified as tropi ...
to subalpine meadows. These roughly 800 Hawaiian drosophilid species are usually assigned to two genera, ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' (), from Ancient Greek δρόσος (''drósos''), meaning "dew", and φίλος (''phílos''), meaning "loving", is a genus of fly, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or p ...
'' and ''Scaptomyza
''Scaptomyza'' is a genus of vinegar flies, insects in the family Drosophilidae. , there are 273 described species of ''Scaptomyza''. Of those, 148 are endemic to the Hawaiian archipelago. This genus is part of the species-rich lineage of Hawaiia ...
'', in the family Drosophilidae
The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes species called fruit flies, although they are more accurately referred to as vinegar or pomace flies. Another distantly related family of flies, Tephritidae, are true f ...
.
The polytene banding of the 'picture wing' group, the best-studied group of Hawaiian drosophilids, enabled Carson to work out the evolutionary tree long before genome analysis was practicable. In a sense, gene arrangements are visible in the banding patterns of each chromosome. Chromosome rearrangements, especially inversions, make it possible to see which species are closely related.
The results are clear. The inversions, when plotted in tree form (and independent of all other information), show a clear "flow" of species from older to newer islands. There are also cases of colonization back to older islands, and skipping of islands, but these are much less frequent. Using K-Ar dating, the present islands date from 0.4 million years ago (mya) (Mauna Kea
Mauna Kea (, ; abbreviation for ''Mauna a Wākea''); is a dormant Shield volcano, shield volcano on the Hawaii (island), island of Hawaii. Its peak is above sea level, making it the List of U.S. states by elevation, highest point in Hawaii a ...
) to 10mya ( Necker). The oldest member of the Hawaiian archipelago still above the sea is Kure Atoll
Kure Atoll (; ; ) or Ocean Island is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean west-northwest of Midway Atoll in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands at . A coral ring across encloses a lagoon several meters deep. The atoll's largest island is called ''Gree ...
, which can be dated to 30 mya. The archipelago itself (produced by the Pacific Plate moving over a hot spot) has existed for far longer, at least into the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
. Previous islands now beneath the sea (guyot
In marine geology, a guyot (), also called a tablemount, is an isolated underwater volcanic mountain (seamount) with a flat top more than below the surface of the sea. The diameters of these flat summits can exceed . Guyots are most commonly fo ...
s) form the Emperor Seamount Chain.
All of the native ''Drosophila'' and ''Scaptomyza'' species in Hawaii have apparently descended from a single ancestral species that colonized the islands, probably 20 million years ago. The subsequent adaptive radiation
In evolutionary biology, adaptive radiation is a process in which organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available, alters biotic int ...
was spurred by a lack of competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
and a wide variety of niches. Although it would be possible for a single gravid
In biology and medicine, gravidity and parity are the number of times a female has been pregnant (gravidity) and carried the pregnancies to a viable gestational age (parity). These two terms are usually coupled, sometimes with additional terms, t ...
female to colonise an island, it is more likely to have been a group from the same species.
There are other animals and plants on the Hawaiian archipelago which have undergone similar, if less spectacular, adaptive radiations.
Chromosome banding
Chromosomes display a banded pattern when treated with some stains. Bands are alternating light and dark stripes that appear along the lengths of chromosomes. Unique banding patterns are used to identify chromosomes and to diagnose chromosomal aberrations, including chromosome breakage, loss, duplication, translocation or inverted segments. A range of different chromosome treatments produce a range of banding patterns: G-bands, R-bands, C-bands, Q-bands, T-bands and NOR-bands.
Depiction of karyotypes
Types of banding
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
employs several techniques to visualize different aspects of chromosomes:G-banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases (mainly ch ...
is obtained with Giemsa stain
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups o ...
following digestion of chromosomes with trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
. It yields a series of lightly and darkly stained bands — the dark regions tend to be heterochromatic, late-replicating and AT rich. The light regions tend to be euchromatic, early-replicating and GC rich. This method will normally produce 300–400 bands in a normal, human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as the DNA within each of the 23 distinct chromosomes in the cell nucleus. A small DNA molecule is found within individual Mitochondrial DNA, mitochondria. These ar ...
. It is the most common chromosome banding method.
* R-banding is the reverse of G-banding (the R stands for "reverse"). The dark regions are euchromatic (guanine-cytosine rich regions) and the bright regions are heterochromatic (thymine-adenine rich regions).
* C-banding: Giemsa binds to constitutive heterochromatin
Constitutive heterochromatin domains are regions of DNA found throughout the chromosomes of eukaryotes. The majority of constitutive heterochromatin is found at the pericentromeric regions of chromosomes, but is also found at the telomeres and thro ...
, so it stains centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fiber ...
s. The name is derived from centromeric or constitutive heterochromatin. The preparations undergo alkaline denaturation prior to staining leading to an almost complete depurination of the DNA. After washing the probe the remaining DNA is renatured again and stained with Giemsa solution consisting of methylene azure, methylene violet, methylene blue, and eosin. Heterochromatin binds a lot of the dye, while the rest of the chromosomes absorb only little of it. The C-bonding proved to be especially well-suited for the characterization of plant chromosomes.
* Q-banding is a fluorescent
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with color ...
pattern obtained using quinacrine
Mepacrine, also called quinacrine or by the trade names Atabrine or Atebrin, is a medication with several uses. It is related to chloroquine and mefloquine. Although available from compounding pharmacies, as of August 2020 approved formulation ...
for staining. The pattern of bands is very similar to that seen in G-banding. They can be recognized by a yellow fluorescence of differing intensity. Most part of the stained DNA is heterochromatin. Quinacrin (atebrin) binds both regions rich in AT and in GC, but only the AT-quinacrin-complex fluoresces. Since regions rich in AT are more common in heterochromatin than in euchromatin, these regions are labelled preferentially. The different intensities of the single bands mirror the different contents of AT. Other fluorochromes like DAPI or Hoechst 33258 lead also to characteristic, reproducible patterns. Each of them produces its specific pattern. In other words: the properties of the bonds and the specificity of the fluorochromes are not exclusively based on their affinity to regions rich in AT. Rather, the distribution of AT and the association of AT with other molecules like histones, for example, influences the binding properties of the fluorochromes.
* T-banding: visualize telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In ...
s.
* Silver staining: Silver nitrate
Silver nitrate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula . It is a versatile precursor to many other silver compounds, such as those used in photography. It is far less sensitive to light than the halides. It was once called ''lunar causti ...
stains the nucleolar organization region-associated protein. This yields a dark region where the silver is deposited, denoting the activity of rRNA genes within the NOR.
Classic karyotype cytogenetics
 In the "classic" (depicted) karyotype, a
In the "classic" (depicted) karyotype, a dye
Juan de Guillebon, better known by his stage name DyE, is a French musician. He is known for the music video of the single "Fantasy
Fantasy is a genre of speculative fiction that involves supernatural or Magic (supernatural), magical ele ...
, often Giemsa
Giemsa stain (), named after German chemist and bacteriologist Gustav Giemsa, is a nucleic acid stain used in cytogenetics and for the histopathological diagnosis of malaria and other parasites.
Uses
It is specific for the phosphate groups of ...
''(G-banding)'', less frequently mepacrine (quinacrine), is used to stain bands on the chromosomes. Giemsa is specific for the phosphate
Phosphates are the naturally occurring form of the element phosphorus.
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthop ...
groups of DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (; DNA) is a polymer composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other to form a double helix. The polymer carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth and reproduction of al ...
. Quinacrine binds to the adenine
Adenine (, ) (nucleoside#List of nucleosides and corresponding nucleobases, symbol A or Ade) is a purine nucleotide base that is found in DNA, RNA, and Adenosine triphosphate, ATP. Usually a white crystalline subtance. The shape of adenine is ...
-thymine
Thymine () (symbol T or Thy) is one of the four nucleotide bases in the nucleic acid of DNA that are represented by the letters G–C–A–T. The others are adenine, guanine, and cytosine. Thymine is also known as 5-methyluracil, a pyrimidine ...
-rich regions. Each chromosome has a characteristic banding pattern that helps to identify them; both chromosomes in a pair will have the same banding pattern.
Karyotypes are arranged with the short arm of the chromosome on top, and the long arm on the bottom. Some karyotypes call the short and long arms ''p'' and ''q'', respectively. In addition, the differently stained regions and sub-regions are given numerical designations from proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
to distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
on the chromosome arms. For example, Cri du chat
Cri du chat syndrome is a rare genetic disorder due to a partial chromosome deletion on chromosome 5. Its name is a French term ("cat-cry" or " call of the cat") referring to the characteristic cat-like cry of affected children. It was first ...
syndrome involves a deletion on the short arm of chromosome 5. It is written as 46,XX,5p-. The critical region for this syndrome is deletion of p15.2 (the locus on the chromosome), which is written as 46,XX,del(5)(p15.2).
Multicolor FISH (mFISH) and spectral karyotype (SKY technique)
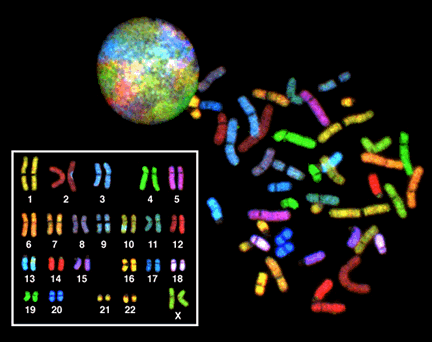 Multicolor
Multicolor FISH
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
and the older spectral karyotyping are molecular cytogenetic
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis an ...
techniques used to simultaneously visualize all the pairs of chromosome
A chromosome is a package of DNA containing part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes, the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with nucleosome-forming packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells, the most import ...
s in an organism in different colors. Fluorescent
Fluorescence is one of two kinds of photoluminescence, the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. When exposed to ultraviolet radiation, many substances will glow (fluoresce) with color ...
ly labeled probes for each chromosome are made by labeling chromosome-specific DNA with different fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with se ...
s. Because there are a limited number of spectrally distinct fluorophores, a combinatorial labeling method is used to generate many different colors. Fluorophore combinations are captured and analyzed by a fluorescence microscope using up to 7 narrow-banded fluorescence filters or, in the case of spectral karyotyping, by using an interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
attached to a fluorescence microscope. In the case of an mFISH image, every combination of fluorochromes from the resulting original images is replaced by a pseudo color in a dedicated image analysis software. Thus, chromosomes or chromosome sections can be visualized and identified, allowing for the analysis of chromosomal rearrangements.
In the case of spectral karyotyping, image processing software assigns a pseudo color to each spectrally different combination, allowing the visualization of the individually colored chromosomes.
Multicolor FISH is used to identify structural chromosome aberrations in cancer cells and other disease conditions when Giemsa banding or other techniques are not accurate enough.
Digital karyotyping
''Digital karyotyping'' is a technique used to quantify the DNA copy number on a genomic scale. Short sequences of DNA from specific loci all over the genome are isolated and enumerated. This method is also known as virtual karyotyping. Using this technique, it is possible to detect small alterations in the human genome, that cannot be detected through methods employing metaphase chromosomes. Some loci deletions are known to be related to the development of cancer. Such deletions are found through digital karyotyping using the loci associated with cancer development.
Chromosome abnormalities
Chromosome abnormalities can be numerical, as in the presence of extra or missing chromosomes, or structural, as in derivative chromosome
A derivative chromosome (der) is a structurally rearranged chromosome generated either by a chromosome rearrangement involving two or more chromosomes or by multiple chromosome aberrations within a single chromosome (e.g. an inversion and a deleti ...
, translocations
In genetics, chromosome translocation is a phenomenon that results in unusual rearrangement of chromosomes. This includes "balanced" and "unbalanced" translocation, with three main types: "reciprocal", "nonreciprocal" and "Robertsonian" transloc ...
, inversions, large-scale deletions or duplications. Numerical abnormalities, also known as aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, for example a human somatic (biology), somatic cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more plo ...
, often occur as a result of nondisjunction
Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division (mitosis/meiosis). There are three forms of nondisjunction: failure of a pair of homologous chromosomes to separate in meiosis I ...
during meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one c ...
in the formation of a gamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
; trisomy, trisomies, in which three copies of a chromosome are present instead of the usual two, are common numerical abnormalities. Structural abnormalities often arise from errors in homologous recombination. Both types of abnormalities can occur in gametes and therefore will be present in all cells of an affected person's body, or they can occur during mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
and give rise to a genetic mosaic individual who has some normal and some abnormal cells.
In humans
Chromosomal abnormalities that lead to disease in humans include
* Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) lea ...
results from a single X chromosome (45,X or 45,X0).
* Klinefelter syndrome, the most common male chromosomal disease, otherwise known as 47,XXY, is caused by an extra X chromosome.
* Edwards syndrome is caused by trisomy (three copies) of chromosome 18.
* Down syndrome, a common chromosomal disease, is caused by trisomy of chromosome 21.
* Patau syndrome is caused by trisomy of chromosome 13.
* Trisomy 9, believed to be the 4th most common trisomy, has many long lived affected individuals but only in a form other than a full trisomy, such as trisomy 9p syndrome or mosaic trisomy 9. They often function quite well, but tend to have trouble with speech.
* Also documented are trisomy 8 and trisomy 16, although they generally do not survive to birth.
Some disorders arise from loss of just a piece of one chromosome, including
* Cri du chat
Cri du chat syndrome is a rare genetic disorder due to a partial chromosome deletion on chromosome 5. Its name is a French term ("cat-cry" or " call of the cat") referring to the characteristic cat-like cry of affected children. It was first ...
(cry of the cat), from a truncated short arm on chromosome 5. The name comes from the babies' distinctive cry, caused by abnormal formation of the larynx.
* 1p36 deletion syndrome, 1p36 Deletion syndrome, from the loss of part of the short arm of chromosome 1.
* Angelman syndrome – 50% of cases have a segment of the long arm of chromosome 15 missing; a deletion of the maternal genes, example of genomic imprinting, imprinting disorder.
* Prader-Willi syndrome – 50% of cases have a segment of the long arm of chromosome 15 missing; a deletion of the paternal genes, example of imprinting disorder.
* Chromosomal abnormalities can also occur in cancerous cells of an otherwise genetically normal individual; one well-documented example is the Philadelphia chromosome, a translocation mutation commonly associated with chronic myelogenous leukemia and less often with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
History of karyotype studies
Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Wilhelm von Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, Heinrich Wilhelm Gottfried von Waldeyer-Hartz, Heinrich von Waldeyer in 1888. It is Neo-Latin from Ancient Greek κάρυον ''karyon'', "kernel", "seed", or "nucleus", and τύπος ''typos'', "general form")
The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated that chromosomes (that can be observed by karyotype) were the carrier of genes. The term karyotype as defined by the phenotypic appearance of the somatic
Somatic may refer to:
* Somatic (biology), referring to the cells of the body in contrast to the germ line cells
** Somatic cell, a non-gametic cell in a multicellular organism
* Somatic nervous system, the portion of the vertebrate nervous syst ...
chromosomes, in contrast to their gene, genic contents was introduced by Grigory Levitsky who worked with Lev Delaunay, Sergei Navashin, and Nikolai Vavilov. The subsequent history of the concept can be followed in the works of C. D. Darlington and Michael JD White.[White M.J.D. 1973. ''Animal cytology and evolution''. 3rd ed, Cambridge University Press.]
Investigation into the human karyotype took many years to settle the most basic question: how many chromosomes does a normal diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
human cell contain? In 1912, Hans von Winiwarter reported 47 chromosomes in spermatogonia and 48 in oogonia, concluding an XO sex-determination system, XX/XO sex determination mechanism. Theophilus Painter, Painter in 1922 was not certain whether the diploid of humans was 46 or 48, at first favoring 46, but revised his opinion from 46 to 48, and he correctly insisted on humans having an XY sex-determination system, XX/XY system. Considering the techniques of the time, these results were remarkable.
 Joe Hin Tjio working in Albert Levan's lab found the chromosome count to be 46 using new techniques available at the time:
# Using cells in
Joe Hin Tjio working in Albert Levan's lab found the chromosome count to be 46 using new techniques available at the time:
# Using cells in tissue culture
Tissue culture is the growth of tissue (biology), tissues or cell (biology), cells in an artificial medium separate from the parent organism. This technique is also called micropropagation. This is typically facilitated via use of a liquid, semi-s ...
# Pretreating cells in a Tonicity#Hypotonicity, hypotonic solution, which swells them and spreads the chromosomes
# Arresting mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identic ...
in metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, alig ...
by a solution of colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to prevent and treat gout, to treat familial Mediterranean fever and Behçet's disease, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction. The American College of Rheumatology recommends colchicine, nonstero ...
# Squashing the preparation on the slide forcing the chromosomes into a single plane
# Cutting up a photomicrograph and arranging the result into an indisputable karyogram.
The work took place in 1955, and was published in 1956. The karyotype of humans includes only 46 chromosomes.[Hsu T.C. 1979. ''Human and mammalian cytogenetics: a historical perspective''. Springer-Verlag, NY.] The other great apes
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); '' Gorilla'' (the ...
have 48 chromosomes. Human chromosome 2 is now known to be a result of an end-to-end fusion of two ancestral ape chromosomes.[Human chromosome 2 is a fusion of two ancestral. chromosomes](_blank)
Alec MacAndrew; accessed 18 May 2006.Evidence of common ancestry: human chromosome 2
(video) 2007
See also
*
*
References
External links
*
Making a karyotype an online activity from the University of Utah's Genetic Science Learning Center.
from the University of Arizona's Biology Project.
from Biology Corner, a resource site for biology and science teachers.
Bjorn Biosystems for Karyotyping and FISH
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017
Cell biology
Chromosomes
Cytogenetics
Evolutionary biology
Genetics techniques

 A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines
A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines 
 Both the micrographic and schematic karyograms shown in this section have a standard chromosome layout, and display darker and lighter regions as seen on
Both the micrographic and schematic karyograms shown in this section have a standard chromosome layout, and display darker and lighter regions as seen on  In the "classic" (depicted) karyotype, a
In the "classic" (depicted) karyotype, a 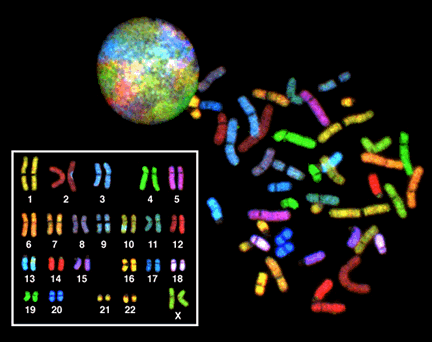 Multicolor
Multicolor  Joe Hin Tjio working in Albert Levan's lab found the chromosome count to be 46 using new techniques available at the time:
# Using cells in
Joe Hin Tjio working in Albert Levan's lab found the chromosome count to be 46 using new techniques available at the time:
# Using cells in