|
G Banding
G-banding, G banding or Giemsa banding is a technique used in cytogenetics to produce a visible karyotype by staining condensed chromosomes. It is the most common chromosome banding method. It is useful for identifying genetic diseases (mainly chromosomal abnormalities) through the photographic representation of the entire chromosome complement.Speicher, Michael R. and Nigel P. Carter. "The New Cytogenetics: Blurring the Boundaries with Molecular Biology." ''Nature'' Reviews Genetics, Vol 6. Oct 2005. Method The metaphase chromosomes are treated with trypsin (to partially digest the chromosome) and Staining (biology), stained with Giemsa stain. Heterochromatin, Heterochromatic regions, which tend to be rich with adenine and thymine (AT-rich) DNA and relatively gene-poor, stain more darkly in G-banding. In contrast, less condensed chromatin (Euchromatin)—which tends to be rich with guanine and cytosine (GC-content, GC-rich) and more Transcription (genetics), transcriptionally acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Karyotype With Bands And Sub-bands
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA for the purpose of gene expression. Some segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins, called messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. In virology, the term transcription is used when referring to mRNA synthesis from a viral RNA molecule. The genome of many RNA viruses is composed of negative-sense RNA which acts as a template for positive sense viral messenger RNA - a necessary step in the synthesis of viral proteins needed for viral replication. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Background A DNA transcription unit encoding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
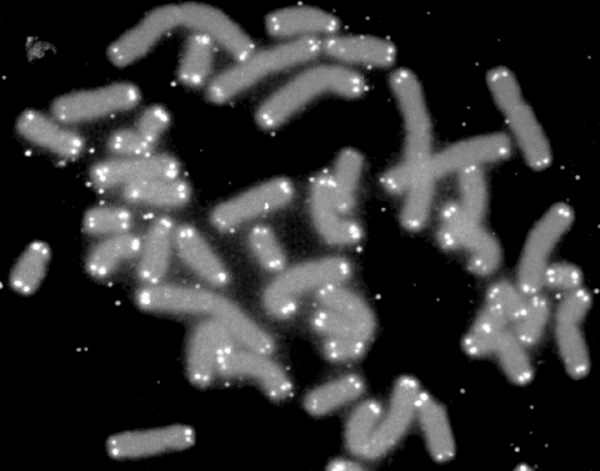
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
Fluorescence ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) is a molecular cytogenetic technique that uses fluorescent probes that bind to only particular parts of a nucleic acid sequence with a high degree of sequence complementarity. It was developed by biomedical researchers in the early 1980s to detect and localize the presence or absence of specific DNA sequences on chromosomes. Fluorescence microscopy can be used to find out where the fluorescent probe is bound to the chromosomes. FISH is often used for finding specific features in DNA for use in genetic counseling, medicine, and species identification. FISH can also be used to detect and localize specific RNA targets (mRNA, lncRNA and miRNA) in cells, circulating tumor cells, and tissue samples. In this context, it can help define the spatial-temporal patterns of gene expression within cells and tissues. Probes – RNA and DNA In biology, a probe is a single strand of DNA or RNA that is complementary to a nucleotide sequence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Mapping
Gene mapping or genome mapping describes the methods used to identify the location of a gene on a chromosome and the distances between genes. Gene mapping can also describe the distances between different sites within a gene. The essence of all genome mapping is to place a collection of molecular markers onto their respective positions on the genome. Molecular markers come in all forms. Genes can be viewed as one special type of genetic markers in the construction of genome maps, and mapped the same way as any other markers. In some areas of study, gene mapping contributes to the creation of new recombinants within an organism. Gene maps help describe the spatial arrangement of genes on a chromosome. Genes are designated to a specific location on a chromosome known as the locus and can be used as molecular markers to find the distance between other genes on a chromosome. Maps provide researchers with the opportunity to predict the inheritance patterns of specific traits, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic Chromosome Fine Structure
In genetics, eukaryotic chromosome fine structure refers to the structure of sequences for the chromosomes of eukaryotic organisms. Some fine sequences are included in more than one class, so the classification listed is not intended to be completely separate. Chromosomal characteristics Some sequences are required for a properly functioning chromosome: * Centromere: Used during cell division as the attachment point for the spindle fibers. * Telomere: Used to maintain chromosomal integrity by capping off the ends of the linear chromosomes. This region is a microsatellite, but its function is more specific than a simple tandem repeat. Throughout the eukaryotic kingdom, the overall structure of chromosome ends is conserved and is characterized by the telomeric tract - a series of short G-rich repeats. This is succeeded by an extensive subtelomeric region consisting of various types and lengths of repeats - the telomere associated sequences (TAS).Pryde FE, Gorham HC, Louis EJ (199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomeric
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ''telos'' (end) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinacrine
Mepacrine, also called quinacrine or by the trade names Atabrine or Atebrin, is a medication with several uses. It is related to chloroquine and mefloquine. Although available from compounding pharmacies, as of August 2020 approved formulations are not available in the United States. Medical uses The main uses of mepacrine are as an antiprotozoal, antirheumatic, and an intrapleural sclerosing agent. Possible reasons for the lack of an ''in vivo effect'' include inefficient penetration of the blood–brain barrier, as well as the existence of drug-resistant prion proteins that increase in number when selected for by treatment with mepacrine. Non-surgical sterilization for women The use of mepacrine for non-surgical sterilization for women has also been studied. The first report of this method claimed a first year failure rate of 3.1%. However, despite a multitude of clinical studies on the use of mepacrine and female sterilization, no randomized, controlled trials have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutive Heterochromatin
Constitutive heterochromatin domains are regions of DNA found throughout the chromosomes of eukaryotes. The majority of constitutive heterochromatin is found at the pericentromeric regions of chromosomes, but is also found at the telomeres and throughout the chromosomes. In humans there is significantly more constitutive heterochromatin found on chromosomes 1, 9, 16, 19 and Y. Constitutive heterochromatin is composed mainly of high copy number tandem repeats known as satellite repeats, minisatellite and microsatellite repeats, and Transposable element, transposon repeats. In humans these regions account for about 200Mb or 6.5% of the total human genome, but their repeat composition makes them difficult to sequence, so only small regions have been sequenced. Visualization of constitutive heterochromatin is possible by using the Cytogenetics, C-banding technique. The regions that stain darker are regions of constitutive heterochromatin. The constitutive heterochromatin stains darker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homologous Chromosomes
Homologous chromosomes or homologs are a set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell during meiosis. Homologs have the same genes in the same locus (genetics), loci, where they provide points along each chromosome that enable a pair of chromosomes to align correctly with each other before separating during meiosis. This is the basis for Mendelian inheritance, which characterizes inheritance patterns of genetic material from an organism to its offspring parent developmental cell at the given time and area. Overview Chromosomes are linear arrangements of condensed DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and histone proteins, which form a complex called chromatin. Homologous chromosomes are made up of chromosome pairs of approximately the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern, for genes with the same corresponding Locus (genetics), loci. One homologous chromosome is inherited from the organism's mother; the other is inherited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the Microscope, microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissue (biology), tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cell (biology), cells), and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses of diseases at the microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues (highlighting, for example, muscle fibers or connective tissue), cell (biology), cell populations (classifying different blood cells), or organelles within individual cells. In biochemistry, it involves adding a class-specific (DNA, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates) dye to a substrate to qualify or quantify the presence of a specific compound. Staining and fluorescent tagging can serve similar purposes. Biological staining is also used to mark cells in flow cytometry, and to flag proteins or nucleic acids in gel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophase
Prophase () is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin reticulum and the disappearance of the nucleolus. Staining and microscopy Microscopy can be used to visualize condensed chromosomes as they move through meiosis and mitosis. Various DNA stains are used to treat cells such that condensing chromosomes can be visualized as the move through prophase. The giemsa G-banding technique is commonly used to identify mammalian chromosomes, but utilizing the technology on plant cells was originally difficult due to the high degree of chromosome compaction in plant cells. G-banding was fully realized for plant chromosomes in 1990. During both meiotic and mitotic prophase, giemsa staining can be applied to cells to elicit G-banding in chromosomes. Silver staining, a more modern technology, in conj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grayscale
In digital photography, computer-generated imagery, and colorimetry, a greyscale (more common in Commonwealth English) or grayscale (more common in American English) image is one in which the value of each pixel is a single sample (signal), sample representing only an ''amount'' of light; that is, it carries only luminous intensity, intensity information. Grayscale images, are black-and-white or gray monochrome, and composed exclusively of shades of gray. The contrast (vision), contrast ranges from black at the weakest intensity to white at the strongest. Grayscale images are distinct from one-bit bi-tonal black-and-white images, which, in the context of computer imaging, are images with only two colors: black and white (also called ''bilevel'' or ''binary images''). Grayscale images have many shades of gray in between. Grayscale images can be the result of measuring the intensity of light at each pixel according to a particular weighted combination of frequencies (or wavelen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |