|
Quinacrine
Mepacrine, also called quinacrine or by the trade names Atabrine or Atebrin, is a medication with several uses. It is related to chloroquine and mefloquine. Although available from compounding pharmacies, as of August 2020 approved formulations are not available in the United States. Medical uses The main uses of mepacrine are as an antiprotozoal, antirheumatic, and an intrapleural sclerosing agent. Possible reasons for the lack of an ''in vivo effect'' include inefficient penetration of the blood–brain barrier, as well as the existence of drug-resistant prion proteins that increase in number when selected for by treatment with mepacrine. Non-surgical sterilization for women The use of mepacrine for non-surgical sterilization for women has also been studied. The first report of this method claimed a first year failure rate of 3.1%. However, despite a multitude of clinical studies on the use of mepacrine and female sterilization, no randomized, controlled trials have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atabrine And Mosquito Poster - "Don't Be A Jerk" (MAMAS D44-170-1), National Museum Of Health And Medicine (302828613) (cropped)
Mepacrine, also called quinacrine or by the trade names Atabrine or Atebrin, is a medication with several uses. It is related to chloroquine and mefloquine. Although available from compounding pharmacies, as of August 2020 approved formulations are not available in the United States. Medical uses The main uses of mepacrine are as an antiprotozoal, antirheumatic, and an intrapleural sclerosing agent. Possible reasons for the lack of an ''in vivo effect'' include inefficient penetration of the blood–brain barrier, as well as the existence of drug-resistant prion proteins that increase in number when selected for by treatment with mepacrine. Non-surgical sterilization for women The use of mepacrine for non-surgical Sterilization (medicine), sterilization for women has also been studied. The first report of this method claimed a first year failure rate of 3.1%. However, despite a multitude of clinical studies on the use of mepacrine and female sterilization, no randomized, contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atabrine Advertisement In Guinea During WW2
Mepacrine, also called quinacrine or by the trade names Atabrine or Atebrin, is a medication with several uses. It is related to chloroquine and mefloquine. Although available from compounding pharmacies, as of August 2020 approved formulations are not available in the United States. Medical uses The main uses of mepacrine are as an antiprotozoal, antirheumatic, and an intrapleural sclerosing agent. Possible reasons for the lack of an ''in vivo effect'' include inefficient penetration of the blood–brain barrier, as well as the existence of drug-resistant prion proteins that increase in number when selected for by treatment with mepacrine. Non-surgical sterilization for women The use of mepacrine for non-surgical sterilization for women has also been studied. The first report of this method claimed a first year failure rate of 3.1%. However, despite a multitude of clinical studies on the use of mepacrine and female sterilization, no randomized, controlled trials have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
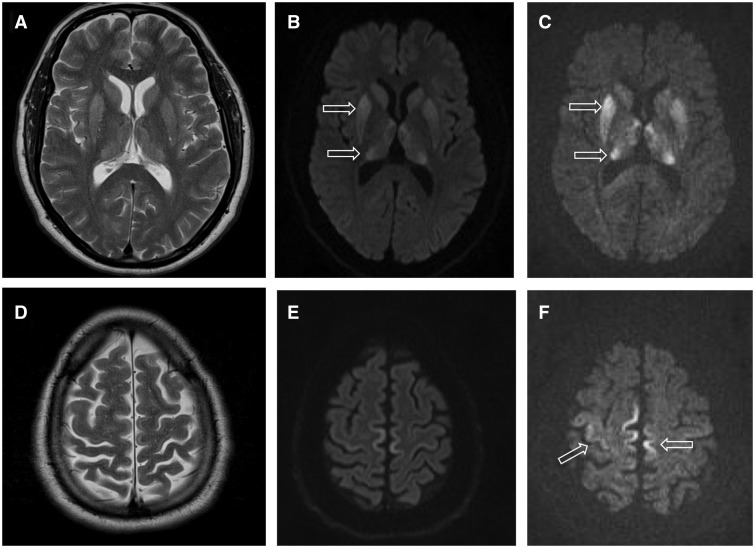
Creutzfeldt–Jakob Disease
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) is an incurable, always fatal neurodegenerative disease belonging to the transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSE) group. Early symptoms include memory problems, behavioral changes, poor coordination, visual disturbances and auditory disturbances. Later symptoms include dementia, involuntary movements, blindness, deafness, weakness, and coma. About 70% of sufferers die within a year of diagnosis. The name "Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease" was introduced by Walther Spielmeyer in 1922, after the German neurologists Hans Gerhard Creutzfeldt and Alfons Maria Jakob. CJD is caused by abnormal folding of a protein known as a prion. Infectious prions are misfolded proteins that can cause normally folded proteins to also become misfolded. About 85% of cases of CJD occur for unknown reasons, while about 7.5% of cases are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Exposure to brain or spinal tissue from an infected person may also result in spread. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
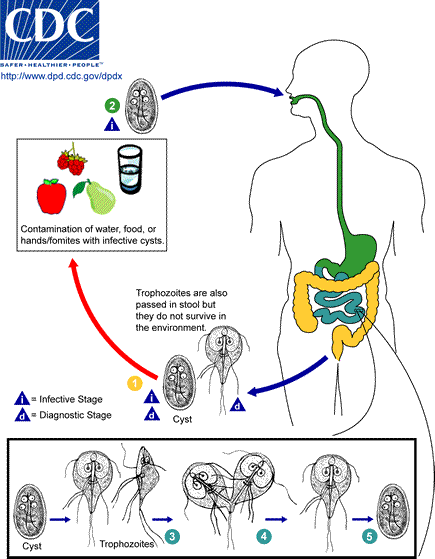
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by the protist enteropathogen ''Giardia duodenalis'' (also known as ''G. lamblia'' and ''G. intestinalis''), especially common in children and travellers. Infected individuals experience steatorrhea, a type diarrhea with fatty sticky stool; abdominal pain, weight loss, and weakness due to dehydration and malabsorption. Less common symptoms include skin rash, hives and joint swelling. Symptoms usually begin one to three weeks after exposure and, without treatment, may last two to six weeks or longer. Some infected individuals experience mild or no symptoms and remain infection carries for a long time. Giardiasis spreads via feca-oral route, when ''Giardia'' cysts excreted with faeces contaminate food or water that is later consumed orally. The disease can also spread between people and between people and animals, mainly via pets. Cysts may survive for nearly three months in cold water. The microscopic identification of ''Giardia'' an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine N-methyltransferase
Histamine ''N''-methyltransferase (HNMT) is a protein encoded by the ''HNMT'' gene in humans. It belongs to the methyltransferases Enzyme superfamily, superfamily of enzymes and plays a role in the inactivation of histamine, a biomolecule that is involved in various Physiological, physiological processes. Methyltransferases are present in every life form including archaeans, with 230 families of methyltransferases found across species. Specifically, HNMT transfers a methyl (-CH3) group from S-Adenosyl methionine, ''S''-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM-e) to histamine, forming an inactive metabolite called 1-Methylhistamine, ''Nτ''-methylhistamine, in a chemical reaction called Methylation, ''Nτ''-methylation. In mammals, HNMT operates alongside diamine oxidase (DAO) as the only two enzymes responsible for histamine metabolism; however, what sets HNMT apart is its unique presence within the central nervous system (CNS), where it governs histaminergic neurotransmission, that is a pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroquine
Chloroquine is an antiparasitic medication that treats malaria. It works by increasing the levels of heme in the blood, a substance toxic to the malarial parasite. This kills the parasite and stops the infection from spreading. Certain types of malaria, resistant strains, and complicated cases typically require different or additional medication. Chloroquine is also occasionally used for amebiasis that is occurring outside the intestines, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus erythematosus. While it has not been formally studied in pregnancy, it appears safe. It is taken by mouth. It was studied to treat COVID-19 early in the COVID-19 pandemic, pandemic, but these studies were largely halted in the northern summer of 2020, and the National Institutes of Health, NIH does not recommend its use for this purpose. Common side effects include muscle problems, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and skin rash. Serious side effects include problems with vision, muscle damage, seizures, and aplas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' (Latin language, Latin for "in glass"; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prion
A prion () is a Proteinopathy, misfolded protein that induces misfolding in normal variants of the same protein, leading to cellular death. Prions are responsible for prion diseases, known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathy (TSEs), which are fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases affecting both humans and animals. These proteins can misfold sporadically, due to genetic mutations, or by exposure to an already misfolded protein, leading to an abnormal Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure that can propagate misfolding in other proteins. The term ''prion'' comes from "proteinaceous infectious particle". Unlike other infectious agents such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi, prions do not contain nucleic acids (DNA or RNA). Prions are mainly twisted Protein isoform, isoforms of the major prion protein (PrP), a naturally occurring protein with an uncertain function. They are the hypothesized cause of various transmissible spongiform encephalopath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapeworm
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda (the other subclass being Cestodaria). Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodaria. All tapeworms are endoparasites of vertebrates, living in the digestive tract or related ducts. Examples are the pork tapeworm (''Taenia solium'') with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, and '' Moniezia expansa'', the definitive hosts of which are ruminants. Body structure Adult Eucestoda have a white-opaque dorso-ventrally flattened appearance, and are elongated, ranging in length from a few millimeters (about ¼") to 25 meters (80'). Almost all members, except members of the orders Caryophyllidea and Spathebothriidea, are polyzoic with repeated sets of reproductive organs down the body length, and almost all members, except members of the order Dioecocestidae, are protandral hermaphrodites. Most exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg cramps, quinine is not recommended for this purpose due to the risk of serious side effects. It can be taken by mouth or intravenously. Malaria resistance to quinine occurs in certain areas of the world. Quinine is also used as an ingredient in tonic water and other beverages to impart a bitter taste. Common side effects include headache, tinnitus, ringing in the ears, vision issues, and sweating. More severe side effects include deafness, thrombocytopenia, low blood platelets, and an irregular heartbeat. Use can make one more prone to sunburn. While it is unclear if use during pregnancy carries potential for fetal harm, treating malaria during pregnancy with quinine when appropriate is still recommended. Quinine is an alkaloid, a natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayer
Bayer AG (English: , commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies and biomedical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of business include: pharmaceuticals, consumer healthcare products, agricultural chemicals, seeds and biotechnology products. The company is a component of the EURO STOXX 50 stock market index. Bayer was founded in 1863 in Barmen as a partnership between dye salesman Friedrich Bayer (1825–1880) and dyer Friedrich Weskott (1821–1876). The company was established as a dyestuffs producer, but the versatility of aniline chemistry led Bayer to expand its business into other areas. In 1899, Bayer launched the compound acetylsalicylic acid under the trademarked name Aspirin. Aspirin is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2021, it was the 34th most commonly prescribed medication in the United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase A2
The enzyme phospholipase A2 (EC 3.1.1.4, PLA2, systematic name phosphatidylcholine 2-acylhydrolase) catalyses the cleavage of fatty acids in position 2 of phospholipids, hydrolyzing the bond between the second fatty acid "tail" and the glycerol molecule: :phosphatidylcholine + H2O = 1-acylglycerophosphocholine + a carboxylate This particular phospholipase specifically recognizes the ''sn''2 acyl bond of phospholipids and catalytically hydrolyzes the bond, releasing arachidonic acid and lysophosphatidyl choline, a precursor of lysophosphatidic acid. Upon downstream modification by cyclooxygenases or lipoxygenases, arachidonic acid is modified into active compounds called eicosanoids. Eicosanoids include prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which are categorized as anti-inflammatory and inflammatory mediators. PLA2 enzymes are commonly found in mammalian tissues as well as arachnid, insect, and snake venom. Venom from bees is largely composed of melittin, which is a stimulan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |