K-class blimp on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The ''K''-class blimp was a class of
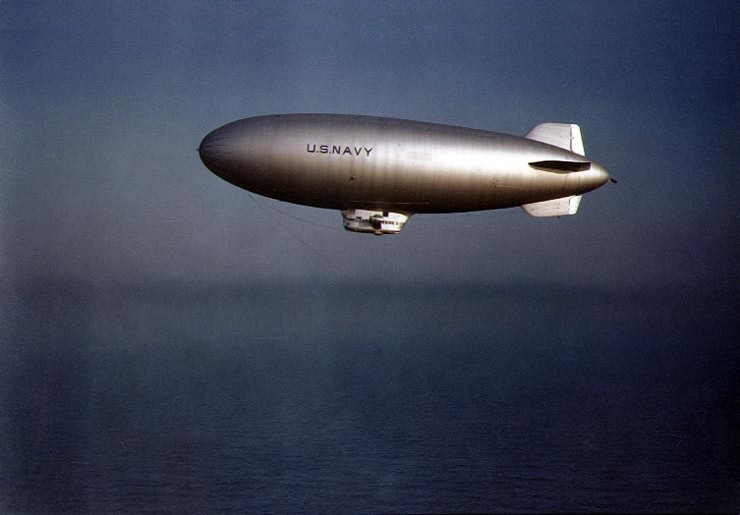 In 1937, ''K-2'' was ordered from Goodyear as part of a contract that also bought the ''L-1'', (Goodyear’s standard advertising and passenger blimp). ''K-2'' was the production
In 1937, ''K-2'' was ordered from Goodyear as part of a contract that also bought the ''L-1'', (Goodyear’s standard advertising and passenger blimp). ''K-2'' was the production
 The ''K''-ships were used for
The ''K''-ships were used for
 Several ''K''-class blimps were used for nuclear weapon effects tests at the
Several ''K''-class blimps were used for nuclear weapon effects tests at the
 * ''K-22'' Control car currently under restoration at the Moffett Field Museum on Moffett Federal Airfield in Santa Clara County, California.
* ''K-27'' and several other K class blimps were seen in the
* ''K-22'' Control car currently under restoration at the Moffett Field Museum on Moffett Federal Airfield in Santa Clara County, California.
* ''K-27'' and several other K class blimps were seen in the
United States Navy K-Type Airships Pilot’s Manual
{{DEFAULTSORT:K Class Blimp 1930s United States patrol aircraft 1940s United States patrol aircraft Airships of the United States Navy Goodyear aircraft
blimp
A non-rigid airship, commonly called a blimp (Help:IPA/English, /blɪmp/), is an airship (dirigible) without an internal structural framework or a keel. Unlike semi-rigid airship, semi-rigid and rigid airships (e.g. Zeppelins), blimps rely on th ...
s (non-rigid airship) built by the Goodyear Aircraft Company of Akron, Ohio
Akron () is a city in Summit County, Ohio, United States, and its county seat. It is the List of municipalities in Ohio, fifth-most populous city in Ohio, with a population of 190,469 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Akron metr ...
, for the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the naval warfare, maritime military branch, service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest Displacement (ship), displacement, at 4.5 millio ...
. These blimps were powered by two Pratt & Whitney ''Wasp'' nine-cylinder radial
Radial is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Mathematics and Direction
* Vector (geometric), a line
* Radius, adjective form of
* Radial distance (geometry), a directional coordinate in a polar coordinate system
* Radial set
* A ...
air-cooled engines, each mounted on twin-strut outriggers
An outrigger is a projecting structure on a boat, with specific meaning depending on types of vessel. Outriggers may also refer to legs on a wheeled vehicle that are folded out when it needs stabilization, for example on a crane that lifts he ...
, one per side of the control car that hung under the envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter (message), letter or Greeting card, card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one o ...
. Before and during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, 134 ''K''-class blimps were built and configured for patrol and anti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in the older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations ar ...
operations, and were extensively used in the Navy’s anti-submarine efforts in the Atlantic and Pacific Ocean areas.
Development
 In 1937, ''K-2'' was ordered from Goodyear as part of a contract that also bought the ''L-1'', (Goodyear’s standard advertising and passenger blimp). ''K-2'' was the production
In 1937, ''K-2'' was ordered from Goodyear as part of a contract that also bought the ''L-1'', (Goodyear’s standard advertising and passenger blimp). ''K-2'' was the production prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
for future ''K''-class airship purchases. ''K-2'' flew for the first time at Akron, Ohio on December 6, 1938 and was delivered to the Navy at NAS Lakehurst
Lakehurst Maxfield Field, formerly known as Naval Air Engineering Station Lakehurst (NAES Lakehurst), is the naval component of Joint Base McGuire–Dix–Lakehurst (JB MDL), a United States Air Force-managed joint base. The airfield is approximat ...
, New Jersey on December 16. The envelope capacity of the ''K-2''—404,000 ft³ (11,440 m³)—was the largest for any USN blimp up to that time. ''K-2'' was flown extensively as a prototype, and continued to operate testing new equipment, techniques, and performing whatever tasks were needed, including combat patrols in World War II.
On October 24, 1940, the Navy awarded a contract to Goodyear for six airships (''K-3'' through ''K-8'') that were assigned the designation Goodyear ZNP-K. These blimps were designed for patrol and escort duties and were delivered to the Navy in late 1941 and early 1942. ''K-3'' through ''K-8'' had only minor modifications to ''K-2''s design, the only major change was in engines from Pratt & Whitney R-1340-16s to Wright R-975-28s. The Wright engine/propeller combination proved excessively noisy and was replaced in later K-ships with slightly modified Pratt & Whitney engines. The K-3 cost $325,000. A series of orders for more K-class blimps followed. Twenty-one additional blimps (''K-9'' through ''K-30'') were ordered on 14 October 1942. On 9 January 1943, 21 more blimps (''K-31'' through ''K-50'') were ordered. The envelope size of ''K-9'' through ''K-13'' was increased to 416,000 ft³ (11,780 m³) and those delivered thereafter used an envelope of 425,000 ft³ (12,035 m³). The final contract for the ''K''-class blimp were awarded in mid-1943 for 89 airships. Four blimps from this order were later canceled. The remaining deliveries were assigned numbers ''K-51'' through ''K-136''. But, the number ''K-136'' was not assigned to a specific airship as the control car assigned for ''K-136'' was used to replace the car for ''K-113''. The original car for ''K-113'' was destroyed in a fire.
The US Navy's experiences with K-ships in tropical regions showed a need for a blimp with greater volume than the K-class to offset the loss of lift due to high ambient temperatures. Goodyear addressed these concerns with a follow-on design, the M-class blimp, which was 50% larger.
Variants
After World War II a number of ''K''-class blimps were modified with more advanced electronics, radar, sonar systems and larger envelopes. These modified blimps were designated: ;ZNP-K :The original designation of the ''K''-class blimps. Individual blimps were identified by a sequential suffix number, e.g. ZNP-K-2, ZNPK-8 etc. In everyday use only the K and numerical suffixes were used. Batches of blimps were built with sometimes major differences, but the designations remained in the ZNP-K range, until the later versions, listed below, emerged. ;ZPK :Revised designation of the ZNP-K series. ;ZP2K :A larger envelope with the volume increased to , sensors and other improvements re-designated ZSG-2. ;ZP3K :A larger envelope with the volume increased to , with systems and controls even more advanced than the ZP2Ks, re-designated ZSG-3. ;ZP4K :Delivered in 1953, retaining the envelope volume and length of , re-designated ZSG-4 in 1954.Operational history
 The ''K''-ships were used for
The ''K''-ships were used for anti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in the older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations ar ...
(ASW) duties in the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans as well as the Mediterranean Sea. All equipment was carried in a forty foot long control car. The installed communications and instrumentation equipment allowed night flying. The blimps were equipped with the ASG radar, that had a detection range of , sonobuoy
A sonobuoy (a portmanteau of sonar and buoy) is a small expendable sonar buoy dropped from aircraft or ships for anti-submarine warfare or underwater acoustic research. Sonobuoys are typically around in diameter and long. When floating on t ...
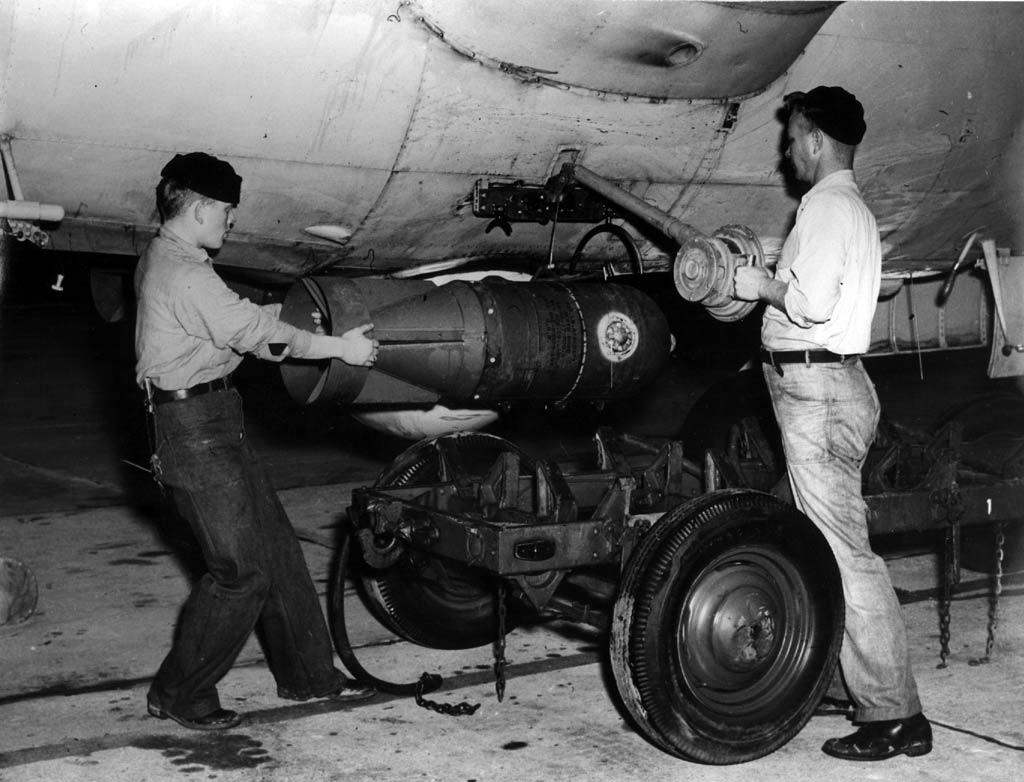
s, and magnetic anomaly detection (MAD) equipment. The ''K''-ships carried four depth bombs, two in a bomb bay and two externally, and were equipped with a machine gun in the forward part of the control car. An aircrew of 10 normally operated the ''K''-ships, consisting of a command pilot, two co-pilots, a navigator/pilot, airship rigger, an ordnanceman, two mechanics, and two radiomen.
On 1 June 1944, two K-class blimps of United States Navy (USN) Airship Patrol Squadron 14 (ZP-14) completed the first transatlantic crossing by non-rigid airships. ''K-123'' and ''K-130'' left South Weymouth, MA on 28 May 1944 and flew approximately 16 hours to Naval Station Argentia
Naval Station Argentia is a former base of the United States Navy that operated from 1941 to 1994. It was established in the community of Argentia in the Dominion of Newfoundland, which later became the tenth Canadian province, Newfoundland and ...
, Newfoundland. From Argentia, the blimps flew approximately 22 hours to Lajes Field
Lajes Field or Lajes Air Base (; ), officially designated Air Base No. 4 (''Base Aérea N.º 4'', BA4) , is a multi-use airfield near Lajes and northeast of Angra do Heroísmo on Terceira Island in the Azores, Portugal. It is home to the Port ...
on Terceira Island in the Azores. The final leg of the first transatlantic crossing was about a 20-hour flight from the Azores to Craw Field in Port Lyautey (Kenitra), French Morocco. The first pair of K-ships were followed by ''K-109'' & ''K-134'' and ''K-112'' & ''K-101'' which left South Weymouth on 11 and 27 June 1944, respectively. These six blimps initially conducted nighttime anti-submarine warfare operations to complement the daytime missions flown by FAW-15 aircraft ( PBYs and B-24
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models desi ...
s) using magnetic anomaly detection to locate U-boats in the relatively shallow waters around the Straits of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa.
The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles (14.2 kilometers, 8.9 miles) at its narrowest point. Fe ...
. Later, ZP-14 K-ships conducted minespotting and minesweeping
Minesweeping is the practice of removing explosive naval mines, usually by a specially designed ship called a minesweeper using various measures to either capture or detonate the mines, but sometimes also with an aircraft made for that purpos ...
operations in key Mediterranean ports and various escort missions including that of the convoy carrying Franklin Roosevelt and Winston Churchill to the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (), held 4–11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the postwar reorganization of Germany and Europe. The three sta ...
in early 1945. In late April 1945, ''K-89'' and ''K-114'' left Weeksville NAS in North Carolina and flew a southern transatlantic route to NAS Bermuda, the Azores, and Port Lyautey where they arrived on 1 May 1945 as replacements for Blimp Squadron ZP-14.
The ability of the ''K''-ships to hover and operate at low altitudes and slow speeds resulted in detection of numerous enemy submarines as well as assisting in search and rescue missions. The ''K''-ships had an endurance capability of over 24 hours which was an important factor in the employment of ASW tactics.
The mooring system for the ''K''-ship was a high triangular mooring mast
A mooring mast, or mooring tower, is a structure designed to allow for the docking of an airship outside of an airship hangar or similar structure. More specifically, a mooring mast is a mast or tower that contains a fitting on its top that allo ...
that was capable of being towed by a tractor. For advance bases where moving the mooring mast was not needed, a conventional stick mast was used. A large ground crew was needed to land the blimps and moor them to the mast.
During the war, only one ''K'' ship was lost to enemy action. On 18 July 1943, ''K-74'' was shot down by in the Straits of Florida
The Straits of Florida, Florida Straits, or Florida Strait () is a strait located south-southeast of the North American mainland, generally accepted to be between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, and between the Florida Keys (U.S.) an ...
. The crew was rescued eight hours later, except for one man who was attacked by a shark and drowned only minutes before the rescue. Five weeks later, ''U-134'' was sunk by a British frigate in the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay ( ) is a gulf of the northeast Atlantic Ocean located south of the Celtic Sea. It lies along the western coast of France from Point Penmarc'h to the Spanish border, and along the northern coast of Spain, extending westward ...
on its return voyage to Germany.
In 1947, Goodyear acquired the former Navy ''K-28'' and operated it as part of its commercial advertising blimp fleet. The ''K'' ship was named ''Puritan'' and was the largest ever Goodyear blimp. The airship was purchased from the Navy primarily to experiment with Trans-Lux illuminated running copy advertising signs attached to the envelope. Costly to operate and maintain, ''Puritan'' was retired from the Goodyear fleet in April, 1948 after only one year of operation. The blimp was deflated and placed in storage at Goodyear's base at Wingfoot Lake in Suffield, Ohio and was later sold back to the Navy.
''K-43'', the last operational Navy "''K'' Ship", was retired from service in March, 1959.
Nuclear weapon effects tests
 Several ''K''-class blimps were used for nuclear weapon effects tests at the
Several ''K''-class blimps were used for nuclear weapon effects tests at the Nevada Test Site
The Nevada National Security Sites (N2S2 or NNSS), popularized as the Nevada Test Site (NTS) until 2010, is a reservation of the United States Department of Energy located in the southeastern portion of Nye County, Nevada, about northwest of ...
(NTS) during the Operation Plumbbob
Operation Plumbbob was a series of nuclear tests that were conducted between May 28 and October 7, 1957, at the Nevada Test Site, following ''Project 57'', and preceding '' Project 58/58A''.
Background
The operation consisted of 29 explosions ...
series of tests in 1957. K-40, K-46, K-77 and K-92 were destroyed in Project 5.2, events Franklin (Fissile) and Stokes (19 kt, XW-30 device). The tests were to "determine the response characteristics of the model ZSG-3 airship when subject to a nuclear detonation in order to establish criteria for safe escape distances after airship delivery of antisubmarine warfare special weapons." According to the Navy, the "airship operations were conducted with extreme difficulty." The Navy was trying to determine whether the airship could be among the aircraft to deliver its planned Lulu (W-34) nuclear depth charge.
Airship designations
During the life of the ''K''-class airship, the U.S. Navy used three different designation systems. From 1922 through World War II, the Navy used a four character designator. The ''K''-class blimps were designated ZNP-K where the "Z" signified lighter-than-air; "N" denoted non-rigid; "P" denoted a patrol mission; and "K" denoted the type or class of airship. In April 1947, the General Board of the U.S. Navy modified the designation system for airships. The second character of the designator was dropped as the Board dropped the code for rigid airships so that the "N" for non-rigid was no longer needed. The designation for the ''K''-class blimps then became ZPK. In April 1954, the designation system for lighter-than-air airships was further modified so that it conformed to the designation system forheavier-than-air
The history of aviation spans over two millennia, from the earliest innovations like kites and attempts at tower jumping to supersonic and hypersonic flight in powered, heavier-than-air jet aircraft. Kite flying in China, dating back several ...
aircraft. By this time the ZPK blimps had been retired from service and only the later version K-Class blimps were in service. Under the 1954 system the ZP2K blimp became the ZSG-2, the ZP3K became the ZSG-3, the ZP4K became the ZSG-4, and the ZP5K became the ZS2G-1. In new designation system, the "Z" signified lighter-than-air; the "S" was the type denoting an anti-submarine warfare mission; the numeral (i.e., "2") was the model; and the "G" was for Goodyear, the manufacturer's letter in the Navy's designation system. The final numeral denoted the series of the vehicle within the type/model. The US Navy ordered a new type of airship in 1951 for the Korean War
The Korean War (25 June 1950 – 27 July 1953) was an armed conflict on the Korean Peninsula fought between North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea; DPRK) and South Korea (Republic of Korea; ROK) and their allies. North Korea was s ...
. The new air ship was designated ZP4K (later called ZSG-4), which had a different design than WW2 K-type. The first ZP4K was delivered in June 1954. A total of 15 were built. In 1955 an update version a called the ZP5K (later called ZS2G-1) was delivered, a total of 15 were built. The ZP5K has an inverted “Y” tail.
Surviving aircraft
 * ''K-22'' Control car currently under restoration at the Moffett Field Museum on Moffett Federal Airfield in Santa Clara County, California.
* ''K-27'' and several other K class blimps were seen in the
* ''K-22'' Control car currently under restoration at the Moffett Field Museum on Moffett Federal Airfield in Santa Clara County, California.
* ''K-27'' and several other K class blimps were seen in the Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc. (also known as Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Pictures, commonly shortened to MGM or MGM Studios) is an American Film production, film and television production and film distribution, distribution company headquartered ...
film ''This Man's Navy
''This Man's Navy'' (aka ''Airship Squadron No. 4.'' and ''Lighter Than Air'') is a 1945 World War II film about U.S. Navy blimps directed by William A. Wellman and starring Wallace Beery, Tom Drake, Jan Clayton and James Gleason. The support ...
'' (1945), one of the few motion pictures to depict U.S. Navy blimp operations. The film starred Wallace Beery
Wallace Fitzgerald Beery (April 1, 1885 – April 15, 1949) was an American film and stage actor. He is best known for his portrayal of Bill in '' Min and Bill'' (1930) opposite Marie Dressler, as General Director Preysing in '' Grand Hotel'' (1 ...
who actually served as a Navy blimp commander during World War II.
* ''K-28'' - Goodyear ''Puritan'' – Control car on static display at the New England Air Museum
The New England Air Museum (NEAM) is an American aerospace museum located adjacent to Bradley International Airport in Windsor Locks, Connecticut. The museum consists of three display hangars with additional storage and restoration hangars. Its ...
in Windsor Locks, Connecticut
Windsor Locks is a New England town, town in Hartford County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Capitol Planning Region, Connecticut, Capitol Planning Region. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, its population was ...
.
* ''K-47'' - Control car on static display at the National Naval Aviation Museum
The National Naval Aviation Museum, formerly known as the National Museum of Naval Aviation and the Naval Aviation Museum, is a military and aerospace museum located at Naval Air Station Pensacola, Florida.
Founded in 1962 and moved to its cur ...
in Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only incorporated city, city in Escambia County, Florida, Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. ...
. The K-47 was upgraded to the ZP3K configuration before it was retired in 1956.Shock, James R., U.S. Navy Airships 1915–1962, 2001, Atlantis Productions, Edgewater Florida, , page 113
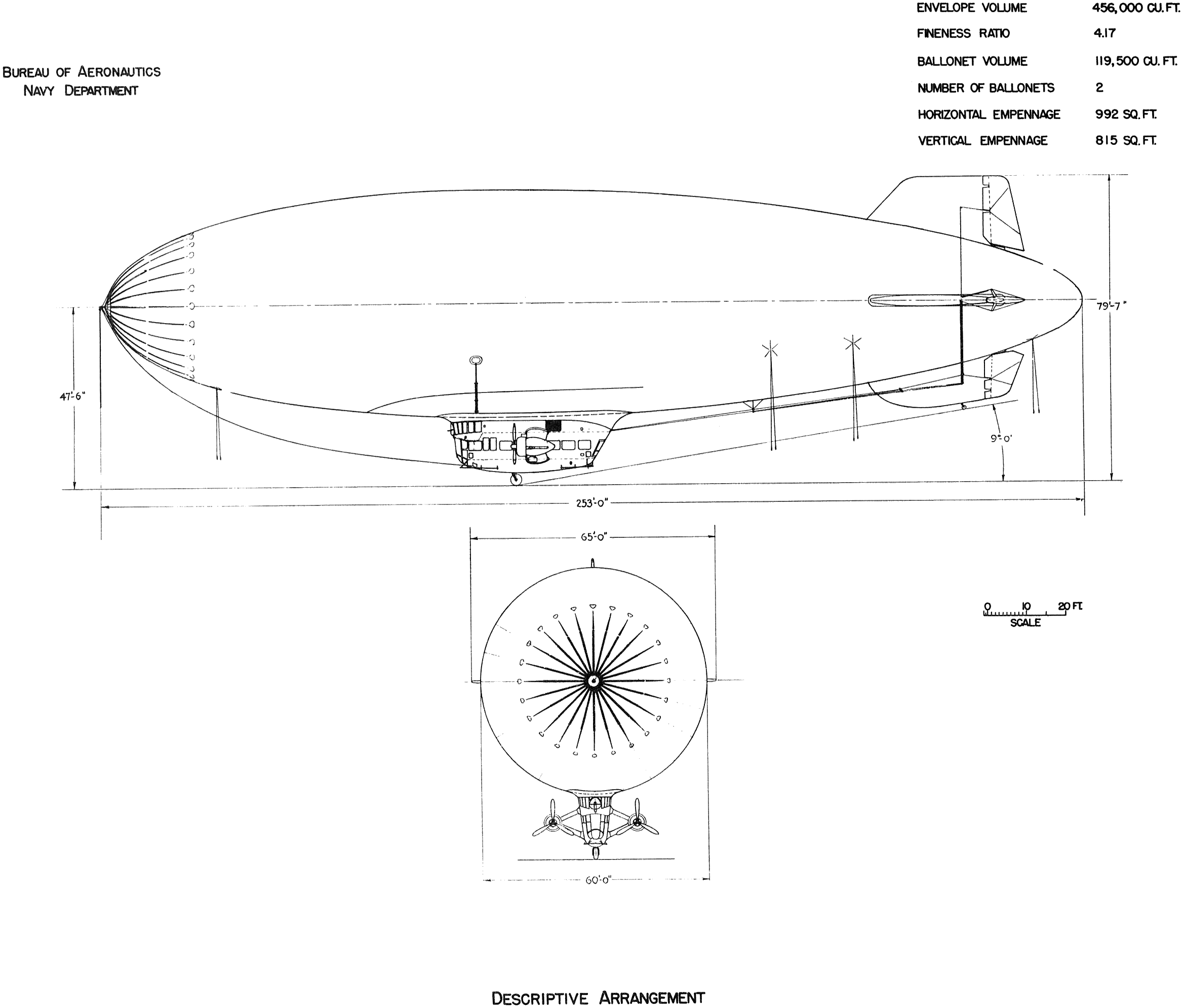
Specifications (''K-14'')

See also
*Aircraft Warning Service The Aircraft Warning Service (AWS) was a civilian service of the United States Army Ground Observer Corps instated during World War II to keep watch for enemy planes entering American airspace. It became inactive on May 29, 1944.
Purpose
During W ...
* Naval Air Station Hitchcock, Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
*US Navy airships during World War II
The United States Navy proposed to the U.S. Congress the development of a lighter-than-air station program for anti-submarine patrolling of the coast and harbors. This program proposed, in addition to the expansion at Naval Air Station and Lakehur ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * *External links
United States Navy K-Type Airships Pilot’s Manual
{{DEFAULTSORT:K Class Blimp 1930s United States patrol aircraft 1940s United States patrol aircraft Airships of the United States Navy Goodyear aircraft