Japanese architecture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors ('' fusuma'') and other traditional partitions were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to be customized for different occasions. People usually sat on cushions or otherwise on the floor, traditionally; chairs and high tables were not widely used until the 20th century. Since the 19th century, however, Japan has incorporated much of Western, modern, and post-modern architecture into construction and design, and is today a leader in cutting-edge architectural design and technology.
The earliest Japanese architecture was seen in prehistoric times in simple pit-houses and stores adapted to the needs of a hunter-gatherer population. Influence from
has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors ('' fusuma'') and other traditional partitions were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to be customized for different occasions. People usually sat on cushions or otherwise on the floor, traditionally; chairs and high tables were not widely used until the 20th century. Since the 19th century, however, Japan has incorporated much of Western, modern, and post-modern architecture into construction and design, and is today a leader in cutting-edge architectural design and technology.
The earliest Japanese architecture was seen in prehistoric times in simple pit-houses and stores adapted to the needs of a hunter-gatherer population. Influence from
Kotobank. During the Meiji Restoration of 1868 the history of Japanese architecture was radically changed by two important events. The first was the Kami and Buddhas Separation Act of 1868, which formally separated Buddhism from
File:Yoshinogari1.jpg, Reconstructed raised-floor building in
File:Horyu-ji11s3200.jpg, Kon-dō and pagoda at Hōryū-ji, Ikaruga, Nara
Built in 7th century File:Hokiji03ds1536.jpg, Pagoda at Hokki-ji, Ikaruga, Nara
Built in 706 File:Yakushiji Toto.jpg, Pagoda at Yakushi-ji, Nara, Nara
Originally built in 730 File:Todaiji10s3200.jpg, Hokkedō at Tōdai-ji, Nara, Nara
Founded in 743 File:Shoso-in.jpg, Shōsō-in at Tōdai-ji, Nara, Nara
Built in 8th century File:Toshodaiji Nara Nara pref01s5s4290.jpg, Golden Temple at Tōshōdai-ji, Nara, Nara
Built in 8th century
Kotobank.Shinden-zukuri.
Kotobank.Seiroku Ota (1987) ''Study of Shinden-zukuri'' p.22. Yoshikawa Kōbunkan. A Buddhist architectural style called '' Wayō'', which developed in accordance with the Japanese climate and aesthetic sense, was established. The priest Kūkai (best known by the posthumous title Kōbō Daishi, 774–835) journeyed to China to study Shingon, a form of
File:Byodo-in Uji01pbs2640.jpg, Phoenix Hall at Byōdō-in, Uji, Kyoto
Built in 1053 File:Ujigami jinja01 2816.jpg, Ujigami Shrine, Uji, Kyoto
Built in 1060 File:Itsukushima Honden Haiden.jpg, Itsukushima Shrine
Built in 1168 File:Ichijoji Kasai13bs4272.jpg, Pagoda of Ichijō-ji, Kasai, Hyōgo
Built in 1171 File:Japan Tottori MitokuSan Nageiredo DSC01248.jpg, Nageire-dō of Sanbutsu-ji, Misasa, Tottori File:Gassho-zukuri farmhouse-01.jpg, Typical minka-style ''
 During the Muromachi period, ''shinden-zukuri'' style, which was the mainstream of the residences of Japanese nobles, declined, and '' shoin-zukuri'', which developed from ''buke-zukuri'' of samurai class residences, became the mainstream. ''Shoin-zukuri'' had a lasting impact on later Japanese housing and is the basis of modern Japanese housing. In the old architectural style, '' tatami'' mats were laid only in a part of the room, but in the ''shoin-zukuri'' style, ''tatami'' mats were laid all over the room. In this style, sliding doors called '' fusuma'' were used to separate rooms, and an inner window called '' shoji'', which was made by pasting paper permeable to sunlight on a wooden frame, was installed inside the wooden shutters. In the room, '' tokonoma'' (alcove for the display of art objects) and ''
During the Muromachi period, ''shinden-zukuri'' style, which was the mainstream of the residences of Japanese nobles, declined, and '' shoin-zukuri'', which developed from ''buke-zukuri'' of samurai class residences, became the mainstream. ''Shoin-zukuri'' had a lasting impact on later Japanese housing and is the basis of modern Japanese housing. In the old architectural style, '' tatami'' mats were laid only in a part of the room, but in the ''shoin-zukuri'' style, ''tatami'' mats were laid all over the room. In this style, sliding doors called '' fusuma'' were used to separate rooms, and an inner window called '' shoji'', which was made by pasting paper permeable to sunlight on a wooden frame, was installed inside the wooden shutters. In the room, '' tokonoma'' (alcove for the display of art objects) and ''
Kotobank.tatami.
Kotobank. In an attempt to rein in the excess of the upper classes, the Zen masters introduced the tea ceremony. In architecture this promoted the design of '' chashitsu'' (tea houses) to a modest size with simple detailing and materials. A typically sized ''Chashitsu'' is 4 1/2 ''tatami'' mats in size. In the garden, Zen principles replaced water with sand or gravel to produce the dry garden ('' karesansui'') like the one at
File:Jyodoji-ono001.JPG, ''Jōdodō'' of Jōdo-ji,
Built in 1194 File:Koyasan Danjogaran Fudodo.JPG, Danjogaran Fudo-dō in Mt. Kōya, Wakayama
Built in 1197. File:Sanjusangendo temple02s2040.jpg, Sanjūsangen-dō, Kyoto
Built in 1266 File:Kozanji Temple (Shimonoseki).JPG, ''Butsuden'' of Kōzan-ji, Shimonoseki, Yamaguchi
Built in 1320 File:Shofukuji Jizo Hall Left Front.JPG, Shōfuku-ji, Tokyo, Completed in 1407 File:GinkakujiTemple.jpg, Ginkaku-ji, Kyoto
Built in the 15th century File:Negoroji03s3200.jpg, Pagoda of
Built in 1547. File:RyoanJi-Dry garden.jpg,
File:Himeji Castle 01s2048.jpg, Himeji Castle in Himeji, Hyōgo,
Completed in 1618 File:Matsumoto Castle05s5s4592.jpg, Matsumoto Castle in Matsumoto, Nagano,
Completed in 1600. File:Kumamoto Castle 02n3200.jpg, Dry stone walls of Kumamoto Castle,
Completed in 1600. File:Nijo Castle.jpg, Ninomaru Palace within Nijō Castle, Kyoto File:Byobu.jpg, A six-panel byōbu from the 17th century
 The
The
File:Matsue castle01bs4592.jpg, Tenshu of Matsue Castle in Matsue, Shimane Prefecture
Built in 1607 File:Hirosakijo.jpg, Tenshu of Hirosaki Castle in Hirosaki, Aomori
Completed in 1611 File:Genkyuen03s3000.jpg, Hikone Castle in Hikone, Shiga
Completed in 1622 File:Kiyomizu-dera in Kyoto-r.jpg, Hondo of Kiyomizu-dera,
Built in 1641 File:NikkoYomeimon5005.jpg, Yomeimon of Tōshō-gū, Nikkō, Tochigi File:Shokin-tei.jpg, Inside the Shokintei at Katsura Imperial Villa, Kyoto
Built in 17th century File:Kochi Castle04s3872.jpg, Tenshu of Kōchi Castle in
Built in 1748 File:Engyoji05s4592.jpg, Three halls of Engyō-ji in Himeji, Hyōgo, Completed in 18th century File:Edogura.jpg, Townhouse with black (edoguro) colouring to upper floor
 One of the prime examples of early western architecture was the '' Rokumeikan'', a large two-story building in Tokyo, completed in 1883, which was to become a controversial symbol of Westernisation in the
One of the prime examples of early western architecture was the '' Rokumeikan'', a large two-story building in Tokyo, completed in 1883, which was to become a controversial symbol of Westernisation in the  In contrast to Waters's neoclassical style building, Japanese carpenters developed a pseudo-Japanese style known as ''giyōfū'' chiefly using wood. A good example of which is Kaichi Primary School in Nagano Prefecture built in 1876. The master carpenter Tateishi Kiyoshige travelled to Tōkyō to see which Western building styles were popular and incorporated these in the school with traditional building methods. Constructed with a similar method to traditional () storehouses, the wooden building plastered inside and out incorporates an octagonal Chinese tower and has stone-like quoins to the corners. Traditional
In contrast to Waters's neoclassical style building, Japanese carpenters developed a pseudo-Japanese style known as ''giyōfū'' chiefly using wood. A good example of which is Kaichi Primary School in Nagano Prefecture built in 1876. The master carpenter Tateishi Kiyoshige travelled to Tōkyō to see which Western building styles were popular and incorporated these in the school with traditional building methods. Constructed with a similar method to traditional () storehouses, the wooden building plastered inside and out incorporates an octagonal Chinese tower and has stone-like quoins to the corners. Traditional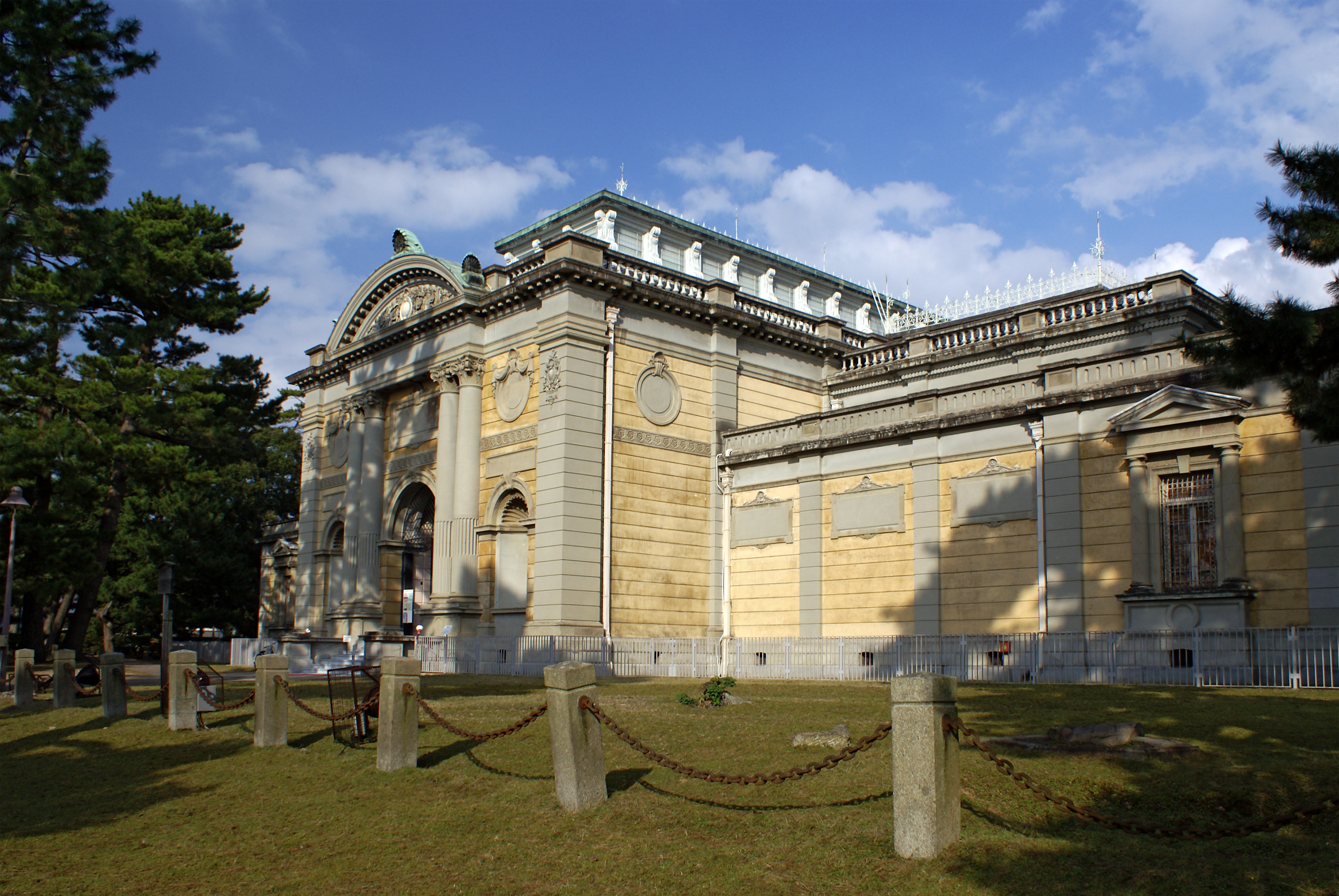  The Japanese government also invited foreign architects to both work in Japan and teach new Japanese architects. One of these, the British architect went on to train many of the most prominent of the Japanese Meiji era architects, including
The Japanese government also invited foreign architects to both work in Japan and teach new Japanese architects. One of these, the British architect went on to train many of the most prominent of the Japanese Meiji era architects, including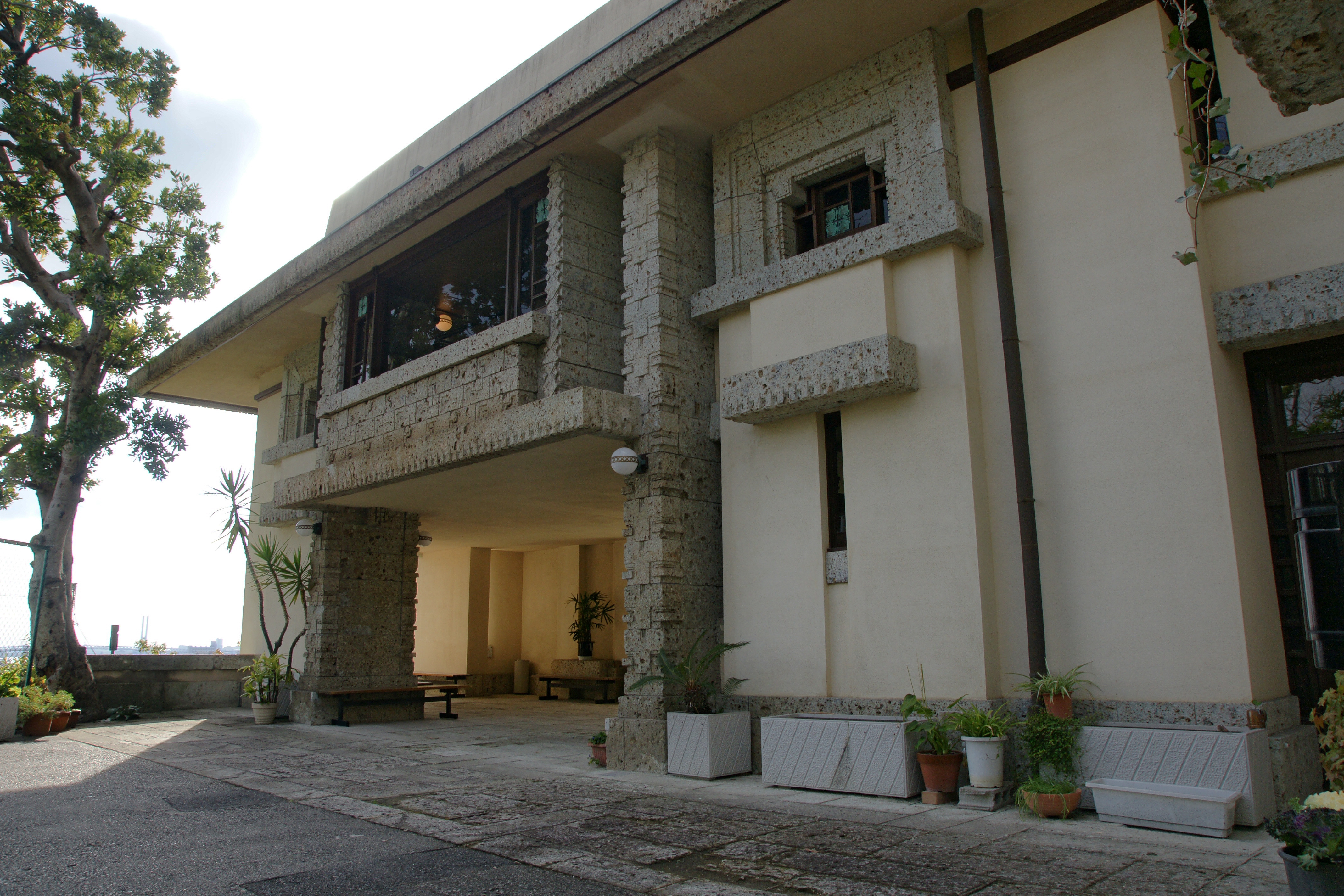  In the Taishō and early Shōwa periods two influential American architects worked in Japan. The first was
In the Taishō and early Shōwa periods two influential American architects worked in Japan. The first was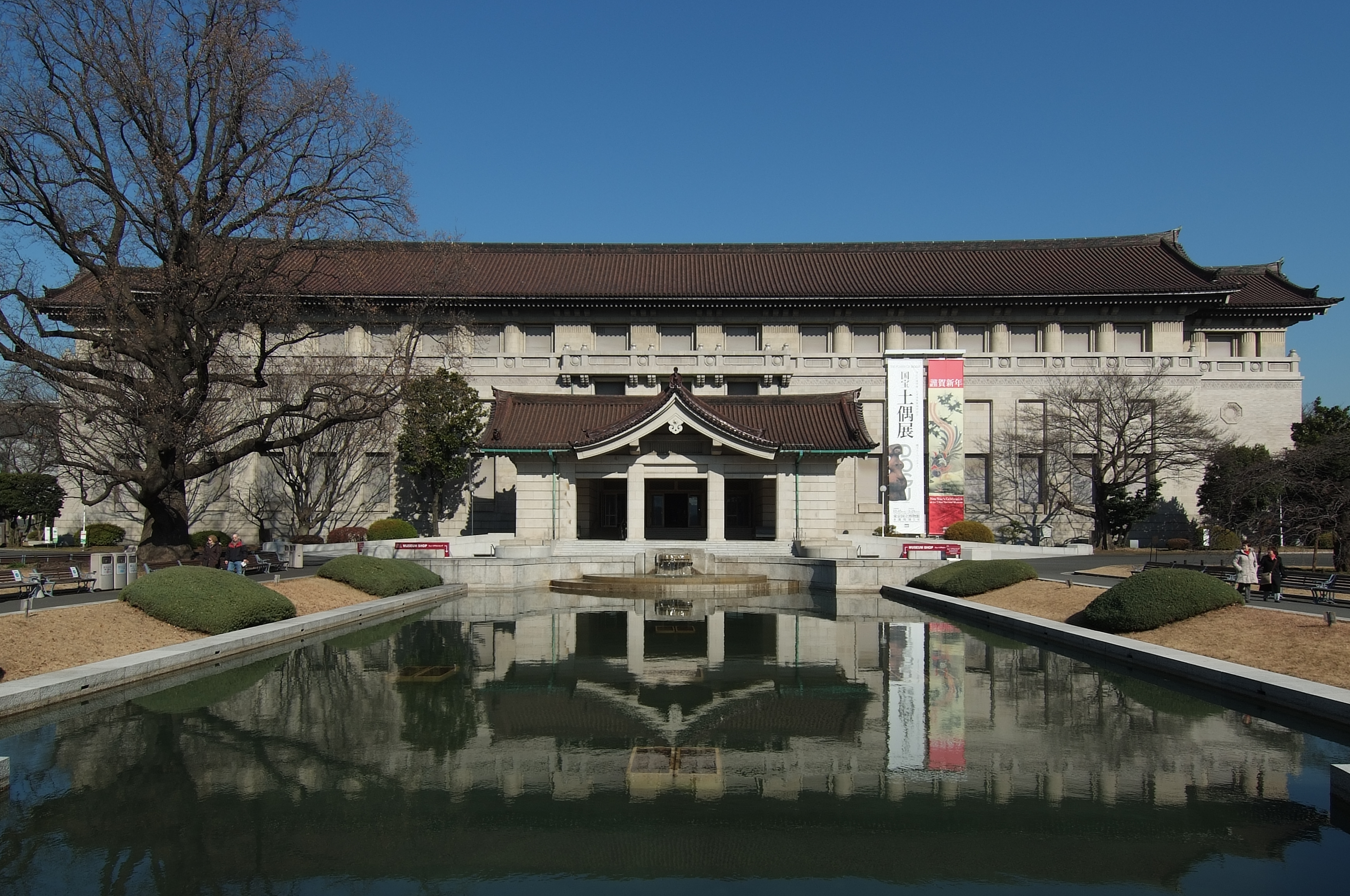  Running contrary to modernism in Japan was the so-called Imperial Crown style (''teikan yōshiki''). Buildings in this style were characterised by having a Japanese-style roof such as the Tōkyō Imperial Museum (1937) by Hitoshi Watanabe and Nagoya City Hall and the Aichi Prefectural Government Office. The increasingly militaristic government insisted that major buildings be designed in a "Japanese Style" limiting opportunities for modernist design to works of infrastructure such as Bunzō Yamaguchi's Number 2 Power Plant for the Kurobe Dam, (1938).
A large number of buildings from the Meiji, Taishō and Shōwa eras were lost during and after World War II, such as the Rokumeikan. Taniguchi Yoshirō (谷口 吉郎, 1904–79), an architect, and Moto Tsuchikawa established Meiji Mura in 1965, close to Nagoya, where a large number of rescued buildings are re-assembled. A similar museum is the Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum.
Running contrary to modernism in Japan was the so-called Imperial Crown style (''teikan yōshiki''). Buildings in this style were characterised by having a Japanese-style roof such as the Tōkyō Imperial Museum (1937) by Hitoshi Watanabe and Nagoya City Hall and the Aichi Prefectural Government Office. The increasingly militaristic government insisted that major buildings be designed in a "Japanese Style" limiting opportunities for modernist design to works of infrastructure such as Bunzō Yamaguchi's Number 2 Power Plant for the Kurobe Dam, (1938).
A large number of buildings from the Meiji, Taishō and Shōwa eras were lost during and after World War II, such as the Rokumeikan. Taniguchi Yoshirō (谷口 吉郎, 1904–79), an architect, and Moto Tsuchikawa established Meiji Mura in 1965, close to Nagoya, where a large number of rescued buildings are re-assembled. A similar museum is the Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum.
 The colonial authorities constructed a large number of public buildings, many of which have survived. Examples include the large-scale concept of what is today
The colonial authorities constructed a large number of public buildings, many of which have survived. Examples include the large-scale concept of what is today
File:臺灣總督府臺北醫院.jpg, National Taiwan University Hospital in Taipei, built in 1921
File:Taipei Taiwan Presidential-Office-Building-01.jpg, Presidential Office Building in Taipei, built in 1919
File:Seoul-City.Hall-02.jpg,
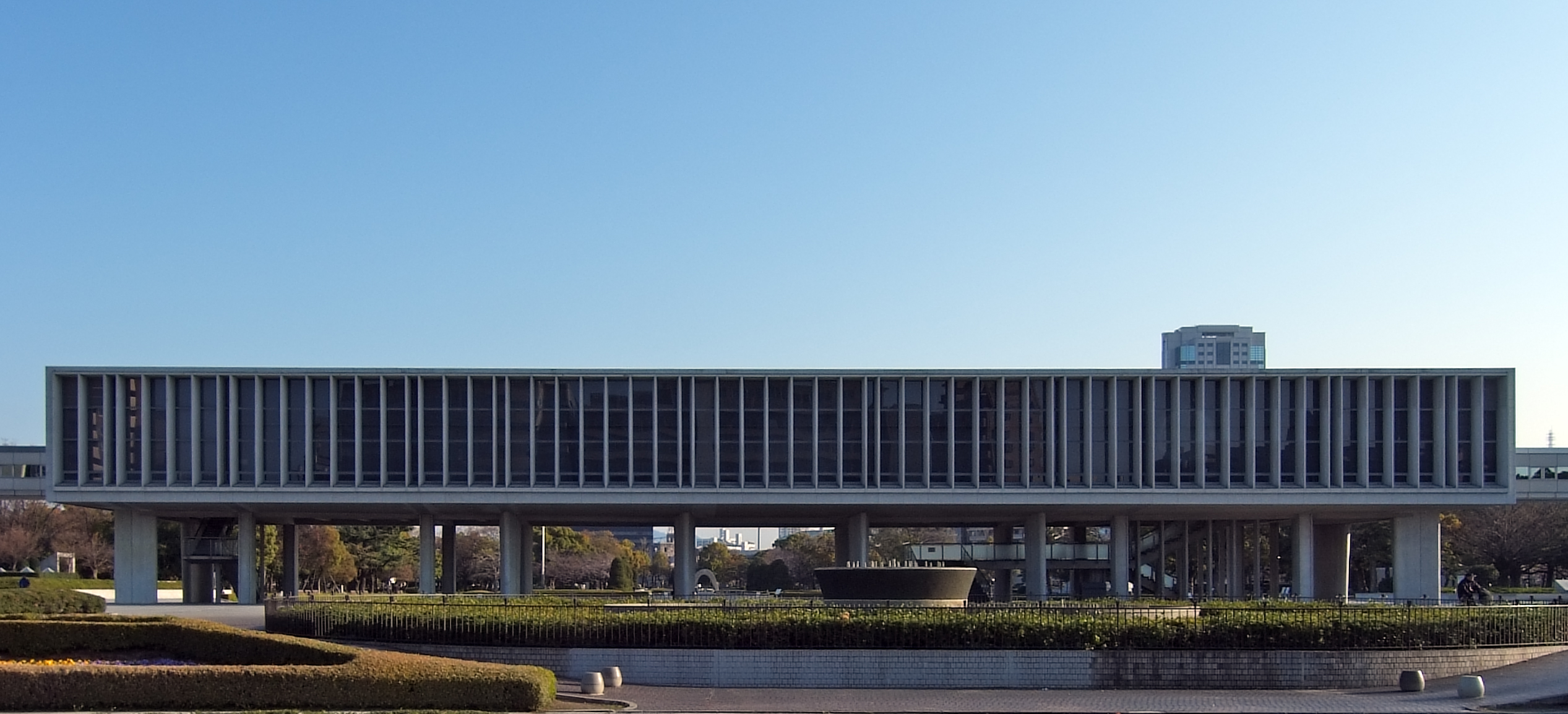 After the war and under the influence of the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers, General Douglas MacArthur, Japanese political and religious life was reformed to produce a demilitarised and democratic country. Although a new
After the war and under the influence of the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers, General Douglas MacArthur, Japanese political and religious life was reformed to produce a demilitarised and democratic country. Although a new  In 1955, Le Corbusier was asked by the Japanese government to design the National Museum of Western Art in Tōkyō. He was assisted by his three former students: Maekawa, Sakakura and
In 1955, Le Corbusier was asked by the Japanese government to design the National Museum of Western Art in Tōkyō. He was assisted by his three former students: Maekawa, Sakakura and  The 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo saw a large boost to new design. Venues were constructed and the Yoyogi National Gymnasium, built between 1961 and 1964 by Kenzo Tange, became a landmark structure famous for its suspension roof design, recalling traditional elements of Shinto shrines. Other structures include the Nippon Budokan, the
The 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo saw a large boost to new design. Venues were constructed and the Yoyogi National Gymnasium, built between 1961 and 1964 by Kenzo Tange, became a landmark structure famous for its suspension roof design, recalling traditional elements of Shinto shrines. Other structures include the Nippon Budokan, the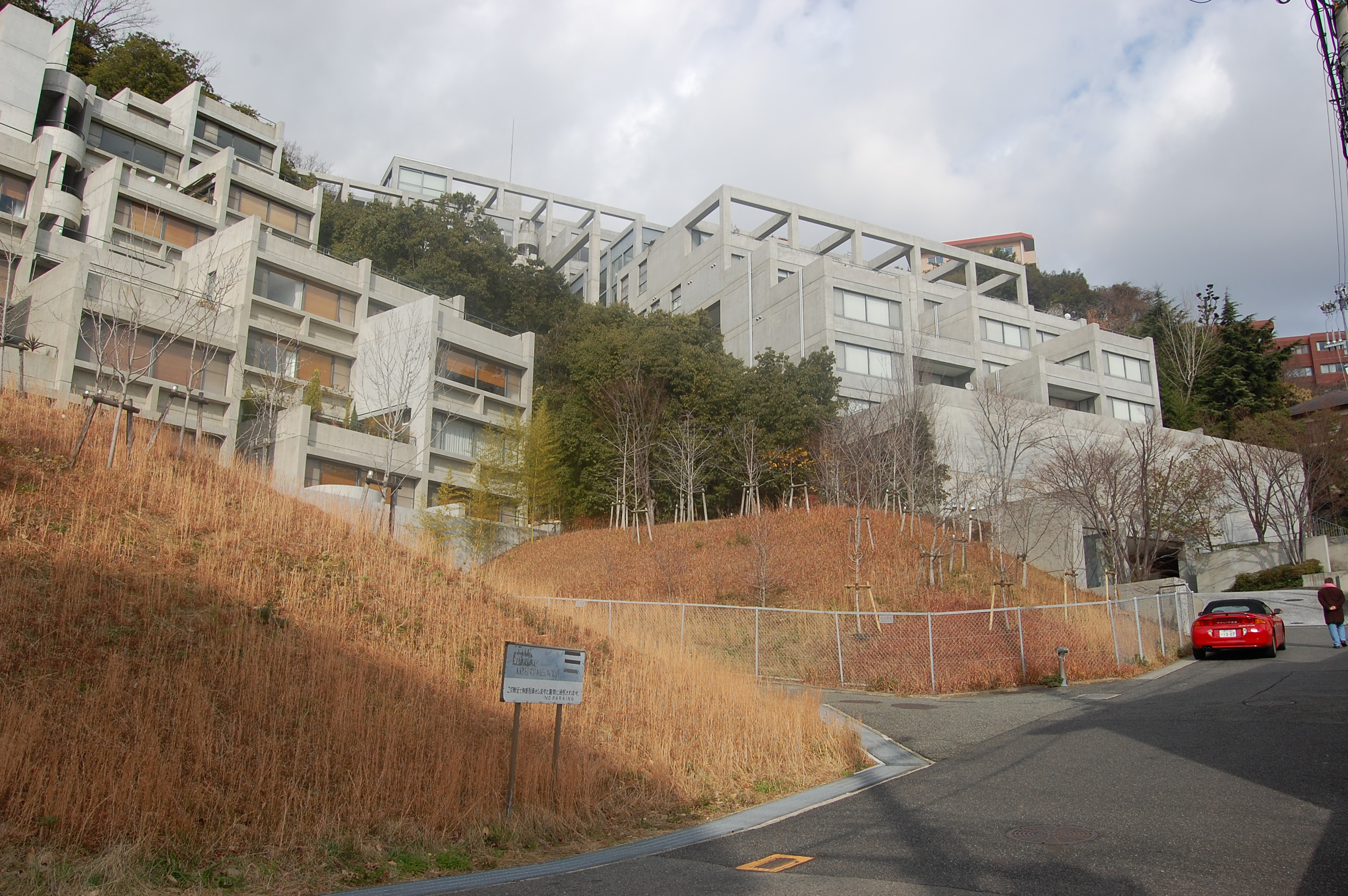  In the late seventies and early eighties Tadao Ando's architecture and theoretical writings explored the idea of Critical regionalism – the idea of promoting local or national culture within architecture. Ando's interpretation of this was demonstrated by his idea of reacquainting the Japanese house with nature, a relationship he thought had been lost with Modernist architecture. His first projects were for small urban houses with enclosed courtyards (such as the Azuma House in Ōsaka in 1976). His architecture is characterised by the use of concrete, but it has been important for him to use the interplay of light, through time, with this and other materials in his work. His ideas about the integration of nature converted well into larger projects such as the Rokkō Housing 1 (1983) (on a steep site on Mount Rokkō) and the Church on the Water (1988) in Tomamu, Hokkaidō.
The late eighties saw the first work by architects of the so-called "Shinohara" school. This included Toyō Itō and Itsuko Hasegawa who were both interested in urban life and the contemporary city. Itō concentrated on the dynamism and mobility of the city's "urban nomads" with projects like the Tower of Winds (1986) which integrated natural elements like light and wind with those of technology. Hasegawa concentrated on what she termed "architecture as another nature". Her Shōnandai Cultural Centre in Fujisawa (1991) combined the natural environment with new high-tech materials.
Highly individualist architects of the late eighties included the monumental buildings of Shin Takamatsu and the "cosmic" work of Masaharu Takasaki. Takasaki, who worked with the Austrian architect Günther Domenig in the 1970s shares Domenig's organic architecture. His Zero Cosmology House of 1991 in Kagoshima Prefecture constructed from concrete has a contemplative egg-shaped "zero space" at its centre.
In the late seventies and early eighties Tadao Ando's architecture and theoretical writings explored the idea of Critical regionalism – the idea of promoting local or national culture within architecture. Ando's interpretation of this was demonstrated by his idea of reacquainting the Japanese house with nature, a relationship he thought had been lost with Modernist architecture. His first projects were for small urban houses with enclosed courtyards (such as the Azuma House in Ōsaka in 1976). His architecture is characterised by the use of concrete, but it has been important for him to use the interplay of light, through time, with this and other materials in his work. His ideas about the integration of nature converted well into larger projects such as the Rokkō Housing 1 (1983) (on a steep site on Mount Rokkō) and the Church on the Water (1988) in Tomamu, Hokkaidō.
The late eighties saw the first work by architects of the so-called "Shinohara" school. This included Toyō Itō and Itsuko Hasegawa who were both interested in urban life and the contemporary city. Itō concentrated on the dynamism and mobility of the city's "urban nomads" with projects like the Tower of Winds (1986) which integrated natural elements like light and wind with those of technology. Hasegawa concentrated on what she termed "architecture as another nature". Her Shōnandai Cultural Centre in Fujisawa (1991) combined the natural environment with new high-tech materials.
Highly individualist architects of the late eighties included the monumental buildings of Shin Takamatsu and the "cosmic" work of Masaharu Takasaki. Takasaki, who worked with the Austrian architect Günther Domenig in the 1970s shares Domenig's organic architecture. His Zero Cosmology House of 1991 in Kagoshima Prefecture constructed from concrete has a contemplative egg-shaped "zero space" at its centre.
File:Kanagawa Concert Hall 2009.jpg, Kanagawa Prefectural Library and Music Hall, Yokohama, built in 1954
File:26 martyrs museum.jpg, Twenty-Six Martyrs Museum and Monument, Nagasaki, built in 1962
File:Kobe port tower11s3200.jpg, Kobe Port Tower, Kōbe, built in 1963
File:Azuma house.JPG, Azuma House, Ōsaka, built in 1976
File:Kirin Plaza.JPG, Kirin Plaza, Ōsaka, built in 1987 (now demolished)
File:ゼロのいえ - Zero House - ZERO COSMOLOGY.jpg, Zero House, Kagoshima, built in 1991
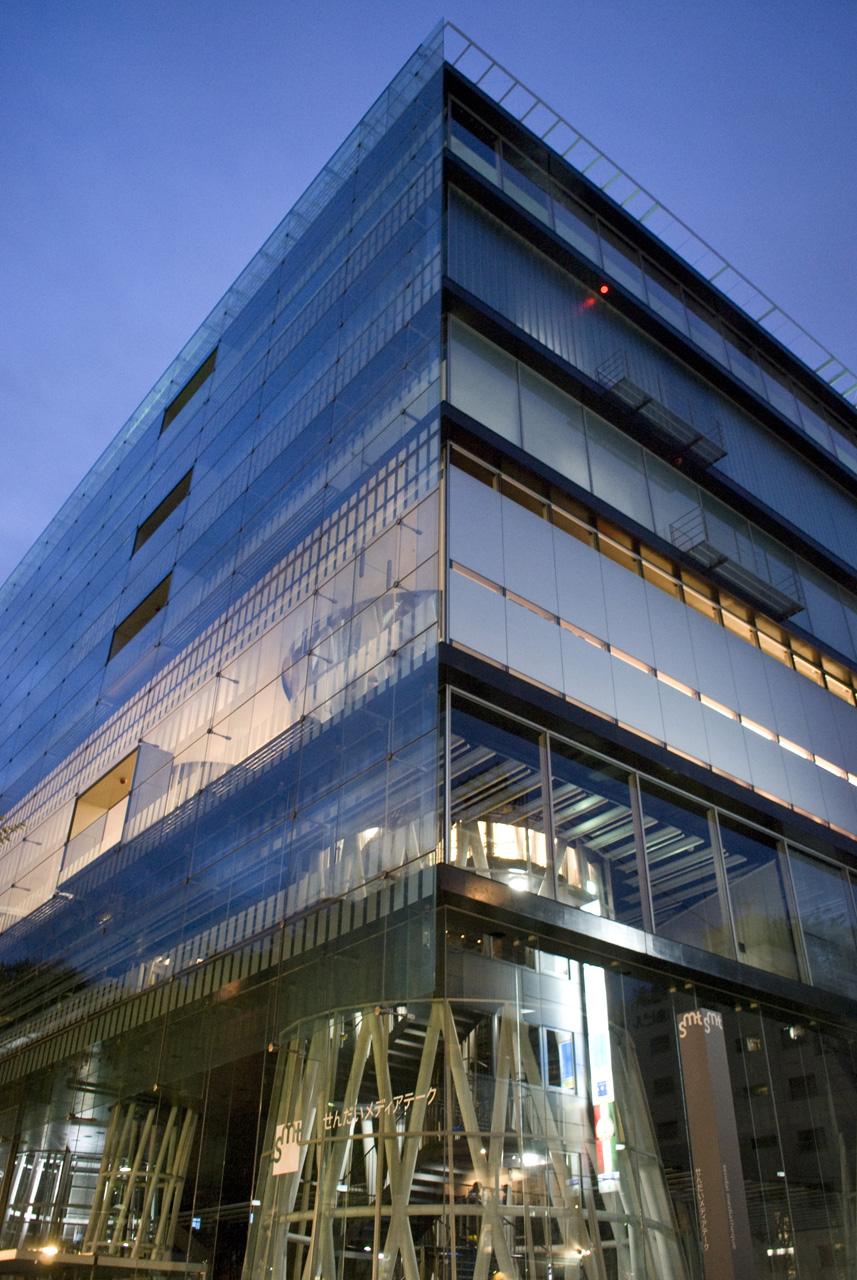

 The Heisei period began with the collapse of the so-called "bubble economy" that had previously boosted Japan's economy. Commissions for commercial works of architecture virtually dried up and architects relied upon government and prefectural organisations to provide projects.
Building on elements from the Shōnandai Culture Centre, Itsuko Hasegawa undertook a number cultural and community centres throughout Japan. These included the Sumida Cultural Centre (1995) and the Fukuroi Community Centre (2001) where she involved the public in the process of design whilst exploring her own ideas about the filtration of light through the external walls into the interior. In his 1995 competition win for
The Heisei period began with the collapse of the so-called "bubble economy" that had previously boosted Japan's economy. Commissions for commercial works of architecture virtually dried up and architects relied upon government and prefectural organisations to provide projects.
Building on elements from the Shōnandai Culture Centre, Itsuko Hasegawa undertook a number cultural and community centres throughout Japan. These included the Sumida Cultural Centre (1995) and the Fukuroi Community Centre (2001) where she involved the public in the process of design whilst exploring her own ideas about the filtration of light through the external walls into the interior. In his 1995 competition win for
File:Church of Light.JPG, The Church of the Light, Ibaraki, Ōsaka, built in 1989
File:Pabellon de japon expo 92.jpg, Japanese pavilion at the 1992 Seville Exposition
Built in 1992 File:Ki-no-dendo04s3200.jpg, Museum for Wood Culture, Kami, Hyogo Prefecture
Built in 1994 File:Osanbashi Pier2.jpg, Yokohama International Port Terminal
Built between 1994 and 2002 File:Takatori Catholic Church.JPG, Paper Church, Kōbe
Built in 1995 File:Within the dome structure, Yamanashi Fruit Museum and Garden, Japan.jpg, Yamanashi Fruit Museum
Built in 1996 File:Tama Art University Library.JPG, Tama Art University Library, Tōkyō
Built in 2007
 After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, Japan's relations to Euro-American powers became more prominent and involved. This spilled into a broader interacting with the modern world, which in terms of interior design, resulted in the introduction of western style interiors, while the vernacular style came to be more associated with tradition and the past. The typical interiors found in Japanese homes and western homes in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries were vastly different with almost opposing attitudes to furniture, versatility of space and materials.
Many public spaces had begun to incorporate chairs and desks by the late nineteenth century, department stores adopted western-style displays; a new "urban visual and consumer culture" was emerging. In the
After the Meiji Restoration of 1868, Japan's relations to Euro-American powers became more prominent and involved. This spilled into a broader interacting with the modern world, which in terms of interior design, resulted in the introduction of western style interiors, while the vernacular style came to be more associated with tradition and the past. The typical interiors found in Japanese homes and western homes in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries were vastly different with almost opposing attitudes to furniture, versatility of space and materials.
Many public spaces had begun to incorporate chairs and desks by the late nineteenth century, department stores adopted western-style displays; a new "urban visual and consumer culture" was emerging. In the
''Sir Banister Fletcher's a History of Architecture''
Architectural Press, 20th edition, 1996 (first published 1896). . Cf. Part Four, Chapter 25 * Koji Yagi (text), Ryo Hata (photos): ''A Japanese Touch For Your Home''. Kodansha International, Tokyo, New York, London 1999 (Pbck.),
mooponto — Portal for Japanese minimalist architecture
Explore the vision behind the modern Japanese minimalist architecture
JAANUS (Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System)
On-line dictionary of Japanese architectural and art historical terminology {{DEFAULTSORT:Japanese Architecture
 has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors ('' fusuma'') and other traditional partitions were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to be customized for different occasions. People usually sat on cushions or otherwise on the floor, traditionally; chairs and high tables were not widely used until the 20th century. Since the 19th century, however, Japan has incorporated much of Western, modern, and post-modern architecture into construction and design, and is today a leader in cutting-edge architectural design and technology.
The earliest Japanese architecture was seen in prehistoric times in simple pit-houses and stores adapted to the needs of a hunter-gatherer population. Influence from
has been typified by wooden structures, elevated slightly off the ground, with tiled or thatched roofs. Sliding doors ('' fusuma'') and other traditional partitions were used in place of walls, allowing the internal configuration of a space to be customized for different occasions. People usually sat on cushions or otherwise on the floor, traditionally; chairs and high tables were not widely used until the 20th century. Since the 19th century, however, Japan has incorporated much of Western, modern, and post-modern architecture into construction and design, and is today a leader in cutting-edge architectural design and technology.
The earliest Japanese architecture was seen in prehistoric times in simple pit-houses and stores adapted to the needs of a hunter-gatherer population. Influence from Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
China via Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republi ...
saw the introduction of more complex grain stores and ceremonial burial chambers.
The introduction of Buddhism in Japan
Buddhism has been practiced in Japan since about the 6th century CE. Japanese Buddhism () created many new Buddhist schools, and some schools are original to Japan and some are derived from Chinese Buddhist schools. Japanese Buddhism has had ...
during the sixth century was a catalyst for large-scale temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called church (building), churches), Hindui ...
building using complicated techniques in wood. Influence from the Chinese Sui and Tang dynasties led to the foundation of the first permanent capital in Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
. Its checkerboard street layout used the Chinese capital of Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
as a template for its design.
In 894 during the Heian period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese ...
(794–1185), Japan abolished ''kentōshi'' (Japanese missions to Tang China) and began to distance itself from Chinese culture, and a culture called ''Kokufu bunka'' (lit., Japanese culture) which was suited to the Japanese climate and aesthetic sense flourished. The '' shinden-zukuri'' style, which was the architectural style of the residences of nobles in this period, showed the distinct uniqueness of Japanese architecture and permanently determined the characteristics of later Japanese architecture. Its features are an open structure with few walls that can be opened and closed with doors, '' shitomi'' and '' sudare'', a structure in which shoes are taken off to enter the house on stilts, and sitting or sleeping directly on '' tatami'' mats without using chairs and beds.
As the samurai
were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of History of Japan#Medieval Japan (1185–1573/1600), medieval and Edo period, early-modern Japan from the late 12th century until their abolition in 1876. They were the well-paid retai ...
class gained power in the Kamakura period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first '' shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle bet ...
(1185–1333), the ''shinden-zukuri'' style changed, and in the Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by ...
(1333–1573), the '' shoin-zukuri'' style appeared. This style had a lasting influence on later Japanese architectural styles and became the basis of modern Japanese houses. Its characteristics were that sliding doors called '' fusuma'' and paper windows called '' shōji'' were fully adopted, and '' tatami'' mats were laid all over the room.
The introduction of the tea ceremony emphasised simplicity and modest design as a counterpoint to the excesses of the aristocracy. In the Azuchi–Momoyama period
The was the final phase of the in Japanese history from 1568 to 1600.
After the outbreak of the Ōnin War in 1467, the power of the Ashikaga Shogunate effectively collapsed, marking the start of the chaotic Sengoku period. In 1568, Oda Nobu ...
(1568–1600), sukiya-zukuri style villas appeared under the influence of a tea house called '' chashitsu''. At first it was an architectural style for the villas of '' daimyo'' (Japanese feudal lords) and court nobles, but in the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional ''daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
(1683–1807) it was applied to '' ryōtei'' (Japanese-style restaurants) and ''chashitsu'', and later it was also applied to residences.sukiya-zukuri.Kotobank. During the Meiji Restoration of 1868 the history of Japanese architecture was radically changed by two important events. The first was the Kami and Buddhas Separation Act of 1868, which formally separated Buddhism from
Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoist ...
and Buddhist temples from Shinto shrine
A is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more '' kami'', the deities of the Shinto religion.
Overview
Structurally, a Shinto shrine typically comprises several buildings.
The '' honden''Also called (本殿, mean ...
s, breaking an association between the two which had lasted well over a thousand years. Secondly, it was then that Japan underwent a period of intense Westernization in order to compete with other developed countries. Initially, architects and styles from abroad were imported to Japan, but gradually the country taught its own architects and began to express its own style. Architects returning from study with Western architects introduced the International Style International style may refer to:
* International Style (architecture), the early 20th century modern movement in architecture
*International style (art), the International Gothic style in medieval art
*International Style (dancing), a term used in ...
of modernism into Japan. However, it was not until after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
that Japanese architects made an impression on the international scene, firstly with the work of architects like Kenzo Tange and then with theoretical movements, like Metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
.
General features of Japanese traditional architecture
In traditional Japanese architecture, there are various styles, features and techniques unique to Japan in each period and use, such as residence,castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
, Buddhist temple and Shinto shrine
A is a structure whose main purpose is to house ("enshrine") one or more '' kami'', the deities of the Shinto religion.
Overview
Structurally, a Shinto shrine typically comprises several buildings.
The '' honden''Also called (本殿, mean ...
. On the other hand, especially in ancient times, it was strongly influenced by Chinese culture like other Asian countries, so it has characteristics common to architecture in Asian countries.(Hozumi (1996:9-11)
Partly due, also, to the variety of climates in Japan, and the millennium encompassed between the first cultural import and the last, the result is extremely heterogeneous, but several practically universal features can nonetheless be found. First of all is the choice of materials, always wood in various forms (planks, straw, tree bark, paper, etc.) for almost all structures. Unlike both Western and some Chinese architecture
Chinese architecture ( Chinese:中國建築) is the embodiment of an architectural style that has developed over millennia in China and it has influenced architecture throughout Eastern Asia. Since its emergence during the early ancient era, th ...
, the use of stone is avoided except for certain specific uses, for example temple podia
A podium (plural podiums or podia) is a platform used to raise something to a short distance above its surroundings. It derives from the Greek ''πόδι'' (foot). In architecture a building can rest on a large podium. Podiums can also be used ...
and pagoda foundations.
The general structure is almost always the same: posts and lintels support a large and gently curved roof, while the walls are paper-thin, often movable and never load-bearing. Arches and barrel roofs are completely absent. Gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aest ...
and eave curves are gentler than in China and columnar entasis (convexity at the center) limited.
The roof is the most visually impressive component, often constituting half the size of the whole edifice. The slightly curved eaves extend far beyond the walls, covering verandas, and their weight must therefore be supported by complex bracket systems called '' tokyō'', in the case of temples and shrines. Simpler solutions are adopted in domestic structures. The oversize eaves give the interior a characteristic dimness, which contributes to the building's atmosphere. The interior of the building normally consists of a single room at the center called ''moya'', from which depart any other less important spaces.
Inner space divisions are fluid, and room size can be modified through the use of screens or movable paper walls. The large, single space offered by the main hall can therefore be divided according to the need. For example, some walls can be removed and different rooms joined temporarily to make space for some more guests. The separation between inside and outside is itself in some measure not absolute as entire walls can be removed, opening a residence or temple to visitors. Verandas appear to be part of the building to an outsider, but part of the external world to those in the building. Structures are therefore made to a certain extent part of their environment. Care is taken to blend the edifice into the surrounding natural environment.
The use of construction modules keeps proportions between different parts of the edifice constant, preserving its overall harmony. (On the subject of building proportions, see also the article ''ken'').
Even in cases as that of Nikkō Tōshō-gū, where every available space is heavily decorated, ornamentation tends to follow, and therefore emphasize, rather than hide, basic structures.
Being shared by both sacred and profane architecture, these features made it easy converting a lay building into a temple or vice versa. This happened for example at Hōryū-ji, where a noblewoman's mansion was transformed into a religious building.
Prehistoric period
The prehistoric period includes the Jōmon, Yayoi and Kofun periods stretching from approximately 5000 BCE to the beginning of the eighth century CE. During the three phases of the Jōmon period the population was primarily hunter-gatherer with some primitive agriculture skills and their behaviour was predominantly determined by changes in climatic conditions and other natural stimulants. Early dwellings were pit houses consisting of shallow pits with tamped earth floors and grass roofs designed to collect rainwater with the aid of storage jars. Later in the period, a colder climate with greater rainfall led to a decline in population, which contributed to an interest in ritual. Concentric stone circles first appeared during this time. During the Yayoi period, the Japanese people began to interact with the ChineseHan dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
, whose knowledge and technical skills began to influence them. The Japanese began to build raised-floor storehouses as granaries, which were constructed using metal tools like saws and chisels that began to appear at this time. A reconstruction in Toro, Shizuoka is a wooden box made of thick boards joined in the corners in a log cabin
A log cabin is a small log house, especially a less finished or less architecturally sophisticated structure. Log cabins have an ancient history in Europe, and in America are often associated with first generation home building by settlers.
Eu ...
style and supported on eight pillars. The roof is thatched but, unlike the typically hipped roof of the pit dwellings, it is a simple V-shaped gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aest ...
. Some authors credit the raised structure designs of this period to contact with the rice-cultivating Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Au ...
from coastal eastern China or Taiwan, rather than the Han.
The Kofun period marked the appearance of many-chambered burial mounds or tumuli (''kofun'' literally means "old mounds"). Similar mounds in Korean Peninsula
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
are thought to have been influenced by Japan. Early in the period, the tombs, known as "keyhole ''kofun''" or , often made use of the existing topography, shaping it and adding man-made moats to form a distinctive keyhole shape, i.e. that of a circle interconnected with a triangle. Access was via a vertical shaft that was sealed off once the burial was completed. There was room inside the chamber for a coffin and grave goods. The mounds were often decorated with terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terracotta i ...
figures called '' haniwa''. Later in the period mounds began to be located on flat ground and their scale greatly increased. Among many examples in Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
and Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
, the most notable is the ''Daisen-kofun'', designated as the tomb of Emperor Nintoku. The tomb covers and it is thought to have been decorated with 20,000 ''haniwa'' figures.
Towards the end of the Kofun period, tomb burials faded out as Buddhist
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
cremation ceremonies gained popularity.
Yoshinogari Yoshinogari may refer to:
* Yoshinogari, Saga, Japan ( :ja:吉野ヶ里町).
* Yoshinogari site, a prehistoric site located in Yoshinogari, Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated o ...
, Saga Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located on the island of Kyushu. Saga Prefecture has a population of 809,248 (1 August 2020) and has a geographic area of 2,440 km2 (942 sq mi). Saga Prefecture borders Fukuoka Prefecture to the northeast and Nagasa ...
, 2nd or 3rd century
File:YoshinogariDwellings.jpg, Reconstructed pit dwelling houses in Yoshinogari Yoshinogari may refer to:
* Yoshinogari, Saga, Japan ( :ja:吉野ヶ里町).
* Yoshinogari site, a prehistoric site located in Yoshinogari, Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated o ...
File:Toro1.jpg, Reconstructed grain storehouse in Toro, Shizuoka
File:YoshinogariIseki.jpg, Reconstructed raised-floor building in Yoshinogari Yoshinogari may refer to:
* Yoshinogari, Saga, Japan ( :ja:吉野ヶ里町).
* Yoshinogari site, a prehistoric site located in Yoshinogari, Saga
is a series of science fantasy role-playing video games by Square Enix. The series originated o ...
File:NintokuTomb Aerial photograph 2007.jpg, Daisenryō Kofun, Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
, 5th century
Asuka and Nara architecture
The most significant contributor to architectural changes during theAsuka period
The was a period in the history of Japan lasting from 538 to 710 (or 592 to 645), although its beginning could be said to overlap with the preceding Kofun period. The Yamato polity evolved greatly during the Asuka period, which is named after t ...
was the introduction of Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
. New temples became centers of worship with tomb burial practices quickly became outlawed. Also, Buddhism brought to the idea of permanent shrines and gave to Shinto architecture much of its present vocabulary.
Some of the earliest structures still extant in Japan are Buddhist temples established at this time. The oldest surviving wooden buildings in the world are found at Hōryū-ji, northeast of Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
. First built in the early 7th century as the private temple of Crown Prince Shōtoku, it consists of 41 independent buildings; the most important ones, the main worship hall, or ''Kon-dō'' (金堂, Golden Hall), and the five-story pagoda), stand in the centre of an open area surrounded by a roofed cloister ('' kairō''). The Kon-dō, in the style of Chinese worship halls, is a two-story structure of post-and-beam construction, capped by an '' irimoya'', or hipped-gabled, roof of ceramic tiles.
Heijō-kyō
was the Capital of Japan during most of the Nara period, from 710 to 740 and again from 745 to 784. The imperial palace is a listed UNESCO World Heritage together with other places in the city of Nara (cf. Historic Monuments of Ancient ...
, modern day Nara, was founded in 708 as the first permanent capital of the state of Japan. The layout of its checkerboard streets and buildings were modeled after the Chinese capital of Chang'an
Chang'an (; ) is the traditional name of Xi'an. The site had been settled since Neolithic times, during which the Yangshao culture was established in Banpo, in the city's suburbs. Furthermore, in the northern vicinity of modern Xi'an, Qin ...
. The city soon became an important centre of Buddhist worship in Japan. The most grandiose of these temples was Tōdai-ji, built to rival temples of the Chinese T'ang and Sui dynasties. Appropriately, the 16.2-m (53-ft) Buddha or Daibutsu (completed in 752) enshrined in the main hall is a Rushana Buddha, the figure that represents the essence of Buddhahood
In Buddhism, Buddha (; Pali, Sanskrit: 𑀩𑀼𑀤𑁆𑀥, बुद्ध), "awakened one", is a title for those who are awake, and have attained nirvana and Buddhahood through their own efforts and insight, without a teacher to poin ...
, just as Tōdai-ji represented the centre for imperially sponsored Buddhism and its dissemination throughout Japan. Only a few fragments of the original statue survive, and the present hall and central Buddha are reconstructions from the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional ''daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
. Clustered around the main hall (the Daibutsuden) on a gently sloping hillside are a number of secondary halls: the Hokke-dō (Lotus Sutra Hall), and the storehouse, called the Shōsō-in, and the adjoining Kōfuku-ji. This last structure is of great importance as an art-historical cache, because in it are stored the utensils that were used in the temple's dedication ceremony in 752, as well as government documents and many secular objects owned by the imperial family.
Built in 7th century File:Hokiji03ds1536.jpg, Pagoda at Hokki-ji, Ikaruga, Nara
Built in 706 File:Yakushiji Toto.jpg, Pagoda at Yakushi-ji, Nara, Nara
Originally built in 730 File:Todaiji10s3200.jpg, Hokkedō at Tōdai-ji, Nara, Nara
Founded in 743 File:Shoso-in.jpg, Shōsō-in at Tōdai-ji, Nara, Nara
Built in 8th century File:Toshodaiji Nara Nara pref01s5s4290.jpg, Golden Temple at Tōshōdai-ji, Nara, Nara
Built in 8th century
Heian period
Although the network of Buddhist temples across the country acted as a catalyst for an exploration of architecture and culture, this also led to the clergy gaining increased power and influence. Emperor Kanmu decided to escape this influence by moving his capital first toNagaoka-kyō
was the capital of Japan from 784 to 794. Its location was reported as Otokuni District, Yamashiro Province, and Nagaokakyō, Kyoto, which took its name from the capital. Parts of the capital were in what is now the city of Nagaokakyō, while ...
and then to Heian-kyō
Heian-kyō was one of several former names for the city now known as Kyoto. It was the official capital of Japan for over one thousand years, from 794 to 1868 with an interruption in 1180.
Emperor Kanmu established it as the capital in 794, m ...
, known today as Kyōto. Although the layout of the city was similar to Nara's and inspired by Chinese precedents, the palaces, temples and dwellings began to show examples of local Japanese taste.
Heavy materials like stone, mortar and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
were abandoned as building elements, with simple wooden walls, floors and partitions becoming prevalent. Native species like cedar (''sugi'') were popular as an interior finish because of its prominent grain, while pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
(''matsu'') and larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to much of the cooler temperate northern hemisphere, on lowlands in the north and high on mountains furt ...
(''aka matsu'') were common for structural uses. Brick roofing tiles and a type of cypress called '' hinoki'' were used for roofs. It was sometime during this period that the hidden roof, a uniquely Japanese solution to roof drainage problems, was adopted.
The increasing size of buildings in the capital led to an architecture reliant on columns regularly spaced in accordance with the '' ken'', a traditional measure of both size and proportion. The imperial palace '' Shishinden'' demonstrated a style that was a precursor to the later aristocratic-style of building known as '' shinden-zukuri''. The style was characterised by symmetrical buildings placed as arms that defined an inner garden. This garden then used borrowed scenery to seemingly blend with the wider landscape. A gradual increase in the size of buildings led to standard units of measurement as well as refinements in layout and garden design.Bussagli (1989), p. 166
In 894, Japan abolished ''kentōshi'' (Japanese missions to Tang China) and began to distance itself from Chinese culture, and a culture called ''Kokufu bunka'' (lit., Japanese culture) which was suited to the Japanese climate and aesthetic sense flourished. The '' shinden-zukuri'' style, which was the architectural style of the residences of nobles in this period, showed the distinct uniqueness of Japanese architecture and permanently determined the characteristics of later Japanese architecture. Its features are an open structure with few walls that can be opened and closed with doors and '' shitomi'' and '' sudare'', a structure in which shoes are taken off to enter the house on stilts, sitting or sleeping directly on '' tatami'' mats without using chairs and beds, a roof made of laminated ''hinoki'' (Japanese cypress) bark instead of ceramic tiles, and a natural texture that is not painted on pillars.Kokufu bunka.Kotobank.Shinden-zukuri.
Kotobank.Seiroku Ota (1987) ''Study of Shinden-zukuri'' p.22. Yoshikawa Kōbunkan. A Buddhist architectural style called '' Wayō'', which developed in accordance with the Japanese climate and aesthetic sense, was established. The priest Kūkai (best known by the posthumous title Kōbō Daishi, 774–835) journeyed to China to study Shingon, a form of
Vajrayana
Vajrayāna ( sa, वज्रयान, "thunderbolt vehicle", "diamond vehicle", or "indestructible vehicle"), along with Mantrayāna, Guhyamantrayāna, Tantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Tantric Buddhism, and Esoteric Buddhism, are names referring t ...
Buddhism, which he introduced into Japan in 806. At the core of Shingon worship are the various mandalas, diagrams of the spiritual universe that influenced temple design. The temples erected for this new sect were built in the mountains, far away from the court and the laity in the capital. The irregular topography of these sites forced their designers to rethink the problems of temple construction, and in so doing to choose more indigenous elements of design.Bussagli (1989), p. 168
At this time the architectural style of Buddhist temples began to influence that of the Shintō shrines. For example, like their Buddhist counterparts the Shintō shrines began to paint the normally unfinished timbers with the characteristic red cinnabar
Cinnabar (), or cinnabarite (), from the grc, κιννάβαρι (), is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining elemental mercury and is the historic source for the bri ...
colour.
During the later part of the Heian Period there were the first documented appearances of vernacular houses in the '' minka'' style/form. These were characterized by the use local materials and labor, being primarily constructed of wood, having packed earth floors and thatched roofs.
Built in 1053 File:Ujigami jinja01 2816.jpg, Ujigami Shrine, Uji, Kyoto
Built in 1060 File:Itsukushima Honden Haiden.jpg, Itsukushima Shrine
Honden
In Shinto shrine architecture, the , also called , or sometimes as in Ise Shrine's case, is the most sacred building at a Shinto shrine, intended purely for the use of the enshrined '' kami'', usually symbolized by a mirror or sometimes by a s ...
, Hatsukaichi, HiroshimaBuilt in 1168 File:Ichijoji Kasai13bs4272.jpg, Pagoda of Ichijō-ji, Kasai, Hyōgo
Built in 1171 File:Japan Tottori MitokuSan Nageiredo DSC01248.jpg, Nageire-dō of Sanbutsu-ji, Misasa, Tottori File:Gassho-zukuri farmhouse-01.jpg, Typical minka-style ''
gasshō-zukuri
are vernacular houses constructed in any one of several traditional Japanese building styles.
In the context of the four divisions of society, were the dwellings of farmers, artisans, and merchants (i.e., the three non-samurai castes). This c ...
'' farmhouse
Kamakura and Muromachi periods
During theKamakura period
The is a period of Japanese history that marks the governance by the Kamakura shogunate, officially established in 1192 in Kamakura by the first '' shōgun'' Minamoto no Yoritomo after the conclusion of the Genpei War, which saw the struggle bet ...
(1185–1333) and the following Muromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by ...
(1336–1573), Japanese Buddhist architecture made technological advances that made it diverge from its Chinese counterpart. In response to native requirements such as earthquake resistance and shelter against heavy rainfall and the summer heat and sun, the master carpenters of this time responded with a unique type of architecture, creating the '' Daibutsuyō'' and ''Zenshūyō
is a Japanese Buddhist architectural style derived from Chinese Song Dynasty architecture. Named after the Zen sect of Buddhism which brought it to Japan, it emerged in the late 12th or early 13th century. Together with Wayō and Daibutsuyō, ...
'' styles. The '' Wayō'' style was combined with ''Daibutsuyō'' and the ''Zenshūyō'' to create the ''Shin-Wayō'' and the '' Setchūyō'' styles, and the number of temples in the pure ''Wayō'' style decreased after the 14th century.
The Kamakura period began with the transfer of power in Japan from the imperial court to the Kamakura shogunate
The was the feudal military government of Japan during the Kamakura period from 1185 to 1333. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Kamakura-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 459.
The Kamakura shogunate was established by Minamoto no Yo ...
. During the Genpei War (1180–1185), many traditional buildings in Nara and Kyoto were damaged. For example, Kōfuku-ji and Tōdai-ji were burned down by Taira no Shigehira of the Taira clan in 1180. Many of these temples and shrines were later rebuilt by the Kamakura shogunate to consolidate the ''shōgun
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of Japan during most of the period spanning from 1185 to 1868. Nominally appointed by the Emperor, shoguns were usually the de facto rulers of the country, though during part of the Kamakur ...
''s authority.
Although less elaborate than during the Heian period, architecture in the Kamakura period was informed by a simplicity due to its association with the military order. New residences used a ''buke-zukuri'' style that was associated with buildings surrounded by narrow moats or stockades. Defense became a priority, with buildings grouped under a single roof rather than around a garden. The gardens of the Heian period houses often became training grounds.Bussagli (1989), p. 172
After the fall of the Kamakura shogunate in 1333, the Ashikaga shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establis ...
was formed, having later its seat in the Kyoto district of Muromachi. The proximity of the shogunate to the imperial court led to a rivalry in the upper levels of society which caused tendencies toward luxurious goods and lifestyles. Aristocratic houses were adapted from the simple ''buke-zukuri'' style to resemble the earlier ''shinden-zukuri'' style. A good example of this ostentatious architecture is the Kinkaku-ji in Kyōto, which is decorated with lacquer and gold leaf, in contrast to its otherwise simple structure and plain bark roofs.
 During the Muromachi period, ''shinden-zukuri'' style, which was the mainstream of the residences of Japanese nobles, declined, and '' shoin-zukuri'', which developed from ''buke-zukuri'' of samurai class residences, became the mainstream. ''Shoin-zukuri'' had a lasting impact on later Japanese housing and is the basis of modern Japanese housing. In the old architectural style, '' tatami'' mats were laid only in a part of the room, but in the ''shoin-zukuri'' style, ''tatami'' mats were laid all over the room. In this style, sliding doors called '' fusuma'' were used to separate rooms, and an inner window called '' shoji'', which was made by pasting paper permeable to sunlight on a wooden frame, was installed inside the wooden shutters. In the room, '' tokonoma'' (alcove for the display of art objects) and ''
During the Muromachi period, ''shinden-zukuri'' style, which was the mainstream of the residences of Japanese nobles, declined, and '' shoin-zukuri'', which developed from ''buke-zukuri'' of samurai class residences, became the mainstream. ''Shoin-zukuri'' had a lasting impact on later Japanese housing and is the basis of modern Japanese housing. In the old architectural style, '' tatami'' mats were laid only in a part of the room, but in the ''shoin-zukuri'' style, ''tatami'' mats were laid all over the room. In this style, sliding doors called '' fusuma'' were used to separate rooms, and an inner window called '' shoji'', which was made by pasting paper permeable to sunlight on a wooden frame, was installed inside the wooden shutters. In the room, '' tokonoma'' (alcove for the display of art objects) and ''chigaidana
A , or simply , is a recessed space in a Japanese-style reception room, in which items for artistic appreciation are displayed. In English, a could be called an alcove.
History
There are two theories about the predecessor of : the first is ...
'' (shelves built into the wall) were set up to decorate various things.Shoin-zukuri.Kotobank.tatami.
Kotobank. In an attempt to rein in the excess of the upper classes, the Zen masters introduced the tea ceremony. In architecture this promoted the design of '' chashitsu'' (tea houses) to a modest size with simple detailing and materials. A typically sized ''Chashitsu'' is 4 1/2 ''tatami'' mats in size. In the garden, Zen principles replaced water with sand or gravel to produce the dry garden ('' karesansui'') like the one at
Ryōan-ji
Ryōan-ji ( ja, 竜安寺, label= Shinjitai, ja, 龍安寺, label= Kyūjitai, ''The Temple of the Dragon at Peace'') is a Zen temple located in northwest Kyoto, Japan. It belongs to the Myōshin-ji school of the Rinzai branch of Zen Buddhis ...
.Bussagli (1989), p. 177
Ono
ONO, Ono or Ōno may refer to:
Places Fiji
* Ono Island (Fiji)
Israel
* Kiryat Ono
* Ono, Benjamin, ancient site
Italy
* Ono San Pietro
Ivory Coast
* Ono, Ivory Coast, a village in Comoé District
Japan
* Ōno Castle, Fukuoka
* Ō ...
, HyōgoBuilt in 1194 File:Koyasan Danjogaran Fudodo.JPG, Danjogaran Fudo-dō in Mt. Kōya, Wakayama
Built in 1197. File:Sanjusangendo temple02s2040.jpg, Sanjūsangen-dō, Kyoto
Built in 1266 File:Kozanji Temple (Shimonoseki).JPG, ''Butsuden'' of Kōzan-ji, Shimonoseki, Yamaguchi
Built in 1320 File:Shofukuji Jizo Hall Left Front.JPG, Shōfuku-ji, Tokyo, Completed in 1407 File:GinkakujiTemple.jpg, Ginkaku-ji, Kyoto
Built in the 15th century File:Negoroji03s3200.jpg, Pagoda of
Negoro-ji
is a Buddhist temple located in the city of Iwade, Wakayama Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan. Surrounded by the sacred peaks of the Katsuragi Mountains, the temple grounds were designated as a National Historic Site and a National ...
in Iwade, WakayamaBuilt in 1547. File:RyoanJi-Dry garden.jpg,
Ryōan-ji
Ryōan-ji ( ja, 竜安寺, label= Shinjitai, ja, 龍安寺, label= Kyūjitai, ''The Temple of the Dragon at Peace'') is a Zen temple located in northwest Kyoto, Japan. It belongs to the Myōshin-ji school of the Rinzai branch of Zen Buddhis ...
dry garden in Kyoto
File:Tenryuji Kyoto41n4592.jpg, Garden of Tenryū-ji in Kyoto
Azuchi-Momoyama period
During theAzuchi–Momoyama period
The was the final phase of the in Japanese history from 1568 to 1600.
After the outbreak of the Ōnin War in 1467, the power of the Ashikaga Shogunate effectively collapsed, marking the start of the chaotic Sengoku period. In 1568, Oda Nobu ...
(1568–1600) Japan underwent a process of unification after a long period of civil war. It was marked by the rule of Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese '' daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period. He is regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan.
Nobunaga was head of the very powerful Oda clan, and launched a war against other ''daimyō'' to unif ...
and Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and '' daimyō'' ( feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the C ...
, men who built castles as symbols of their power; Nobunaga in Azuchi, the seat of his government, and Hideyoshi in Momoyama. The Ōnin War during the Muromachi period had led to rise of castle architecture in Japan. By the time of the Azuchi-Momoyama period each domain was allowed to have one castle of its own. Typically it consisted of a central tower or surrounded by gardens and fortified buildings. All of this was set within massive stone walls and surrounded by deep moats. The dark interiors of castles were often decorated by artists, the spaces were separated up using sliding ''fusuma'' panels and '' byōbu'' folding screens.
The '' Shoin-zukuri'' style in the Muromachi period continued to be refined. Verandas linked the interiors of residential buildings with highly cultivated exterior gardens. ''Fusuma'' and ''byōbu'' became highly decorated with paintings and often an interior room with shelving and alcove (''tokonoma'') were used to display art work (typically a hanging scroll).
During this period, sukiya-zukuri style villas appeared under the influence of a tea house called '' chashitsu'' (tea house).
Matsumoto, Kumamoto
is the capital city of Kumamoto Prefecture on the island of Kyushu, Japan. , the city has an estimated population of 738,907 and a population density of 1,893 people per km2. The total area is 390.32 km2.
had a population of 1,461,0 ...
and Himeji (popularly known as the White Heron castle) are excellent examples of the castles of the period, while Nijō Castle in Kyōto is an example of castle architecture blended with that of an imperial palace, to produce a style that is more in keeping with the Chinese influence of previous centuries.
Completed in 1618 File:Matsumoto Castle05s5s4592.jpg, Matsumoto Castle in Matsumoto, Nagano,
Completed in 1600. File:Kumamoto Castle 02n3200.jpg, Dry stone walls of Kumamoto Castle,
Completed in 1600. File:Nijo Castle.jpg, Ninomaru Palace within Nijō Castle, Kyoto File:Byobu.jpg, A six-panel byōbu from the 17th century
Edo period

 The
The Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in ...
took the city of Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
(later to become part of modern-day Tōkyō) as their capital. They built an imposing fortress around which buildings of the state administration and residences for the provincial ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominall ...
s'' were constructed. The city grew around these buildings connected by a network of roads and canals. By 1700 the population had swollen to one million inhabitants. The scarcity of space for residential architecture resulted in houses being built over two stories, often constructed on raised stone plinths.
Although '' machiya'' (townhouses) had been around since the Heian period they began to be refined during the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional ''daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
. ''Machiya'' typically occupied deep, narrow plots abutting the street (the width of the plot was usually indicative of the wealth of the owner), often with a workshop or shop on the ground floor. Tiles rather than thatch were used on the roof and exposed timbers were often plastered in an effort to protect the building against fire. Ostentatious buildings that demonstrated the wealth and power of the feudal lords were constructed, such as the Kamiyashiki of Matsudaira Tadamasa or the Ōzone Shimoyashiki.
Edo suffered badly from devastating fires and the 1657 Great Fire of Meireki was a turning point in urban design. Initially, as a method of reducing fire spread, the government built stone embankments in at least two locations along rivers in the city. Over time these were torn down and replaced with ''dōzō'' storehouses that were used both as fire breaks and to store goods unloaded from the canals. The ''dōzō'' were built with a structural frame made of timber coated with a number of layers of earthen plaster on the walls, door and roof. Above the earthen roofs was a timber framework supporting a tiled roof. Although Japanese who had studied with the Dutch at their settlement in Dejima advocated building with stone and brick this was not undertaken because of their vulnerability to earthquakes. ''Machiya'' and storehouses from the later part of the period are characterised by having a black coloration to the external plaster walls. This colour was made by adding India ink to burnt lime and crushed oyster shell.
The clean lines of the civil architecture in Edo influenced the '' sukiya'' style of residential architecture. Katsura Detached Palace and Shugaku-in Imperial Villa on the outskirts of Kyōto are good examples of this style. Their architecture has simple lines and decor and uses wood in its natural state. The ''sukiya'' style was applied not only to villas but also to '' ryōtei'' (Japanese-style restaurants) and ''chashitsu'', and later it was also applied to residences.
In the very late part of the period ''sankin-kōtai
''Sankin-kōtai'' ( ja, 参覲交代/参覲交替, now commonly written as ja, 参勤交代/参勤交替, lit=alternate attendance, label=none) was a policy of the Tokugawa shogunate during most of the Edo period of Japanese history.Jansen, M ...
'', the law requiring the ''daimyōs'' to maintain dwellings in the capital was repealed which resulted in a decrease in population in Edo and a commensurate reduction in income for the shogunate.
Built in 1607 File:Hirosakijo.jpg, Tenshu of Hirosaki Castle in Hirosaki, Aomori
Completed in 1611 File:Genkyuen03s3000.jpg, Hikone Castle in Hikone, Shiga
Completed in 1622 File:Kiyomizu-dera in Kyoto-r.jpg, Hondo of Kiyomizu-dera,
Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the ...
, Built in 1633
File:Enryakuji Konponchudo04n4272.jpg, Konponchudo of Enryaku-ji
is a Tendai monastery located on Mount Hiei in Ōtsu, overlooking Kyoto. It was first founded in 788 during the early Heian period (794–1185) by Saichō (767–822), also known as Dengyō Daishi, who introduced the Tendai sect of ...
in Ōtsu, ShigaBuilt in 1641 File:NikkoYomeimon5005.jpg, Yomeimon of Tōshō-gū, Nikkō, Tochigi File:Shokin-tei.jpg, Inside the Shokintei at Katsura Imperial Villa, Kyoto
Built in 17th century File:Kochi Castle04s3872.jpg, Tenshu of Kōchi Castle in
Kōchi
Kochi is a city in Kerala, India.
Kochi or Kōchi may also refer to:
People
* Kochi people, a predominantly Pashtun nomadic people of Afghanistan
* , a Japanese surname:
** Arata Kochi (born 1948 or 1949), Japanese physician and World Health Org ...
, Kōchi PrefectureBuilt in 1748 File:Engyoji05s4592.jpg, Three halls of Engyō-ji in Himeji, Hyōgo, Completed in 18th century File:Edogura.jpg, Townhouse with black (edoguro) colouring to upper floor
Meiji, Taishō, and early Shōwa periods
Towards the end of the Tokugawa shogunate, Western influence in architecture began to show in buildings associated with the military and trade, especially naval and industrial facilities. After theEmperor Meiji
, also called or , was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession. Reigning from 13 February 1867 to his death, he was the first monarch of the Empire of Japan and presided over the Meiji era. He was the figur ...
was restored to power (known as the Meiji Restoration) Japan began a rapid process of Westernization which led to the need for new building types such as schools, banks and hotels.
Early Meiji Architecture was initially influenced by colonial architecture in Chinese treaty ports such as Hong Kong. In Nagasaki, the British trader Thomas Glover built his own house in just such a style using the skill of local carpenters. His influence helped the career of architect who designed the Osaka Mint in 1868, a long, low building in brick and stone with a central pedimented portico. In Tōkyō, Waters designed the Commercial Museum, thought to have been the city's first brick building.
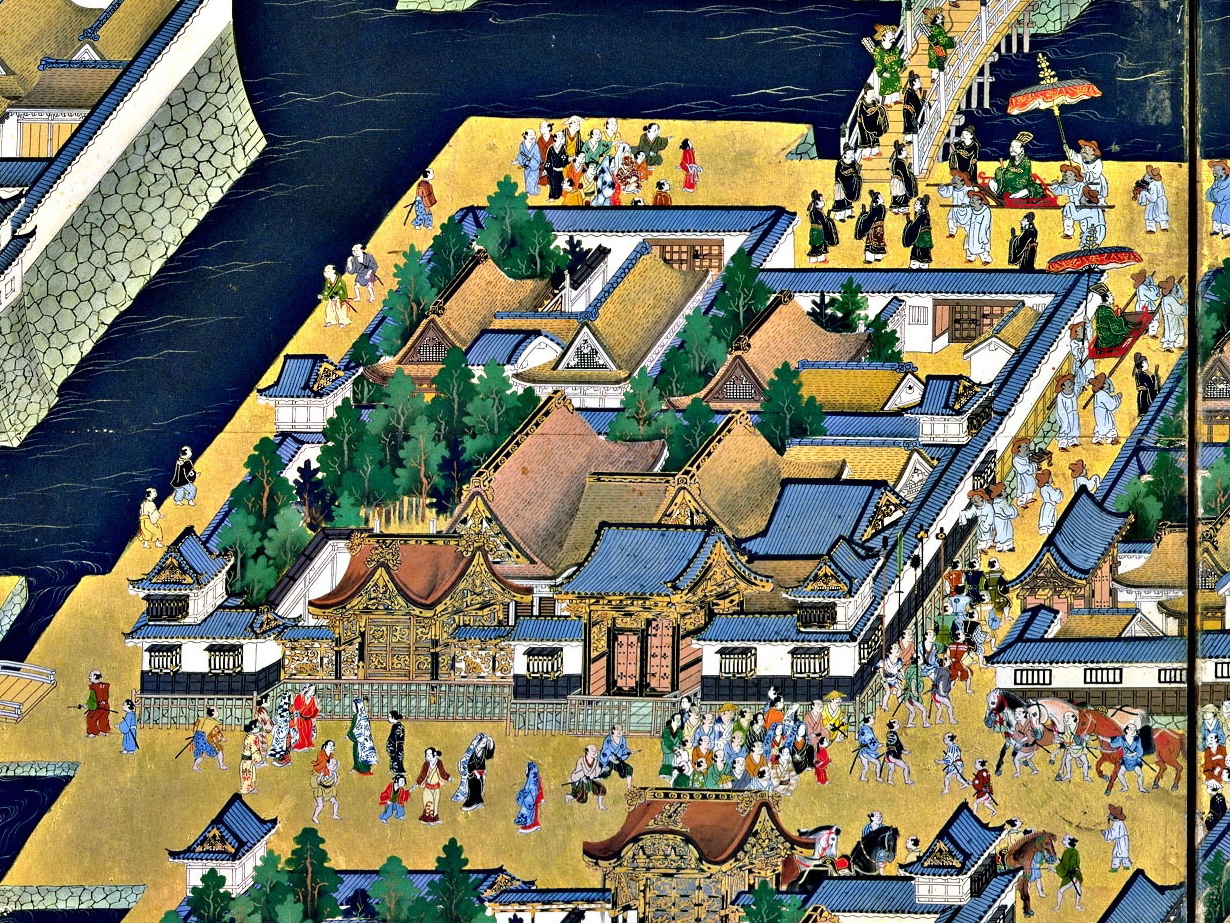
In Tokyo, after the Tsukiji area burnt to the ground in 1872, the government designated the Ginza area as model of modernization. The government planned the construction of fireproof brick buildings, and larger, better streets connecting the Shimbashi Station and the foreign concession in Tsukiji, as well as to important government buildings. Designs for the area were provided by the British architect Thomas James Waters; the Bureau of Construction of the Ministry of Finance was in charge of construction. In the following year, a Western-style Ginza was completed. "Bricktown" buildings were initially offered for sale, later they were leased, but the high rent meant that many remained unoccupied. Nevertheless, the area flourished as a symbol of "civilization and enlightenment", thanks to the presence of newspapers and magazine companies, who led the trends of the day. The area was also known for its window displays, an example of modern marketing techniques. The "Bricktown" of Ginza served as a model for many other modernization schemes in Japanese cities.
 One of the prime examples of early western architecture was the '' Rokumeikan'', a large two-story building in Tokyo, completed in 1883, which was to become a controversial symbol of Westernisation in the
One of the prime examples of early western architecture was the '' Rokumeikan'', a large two-story building in Tokyo, completed in 1883, which was to become a controversial symbol of Westernisation in the Meiji period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912.
The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ...
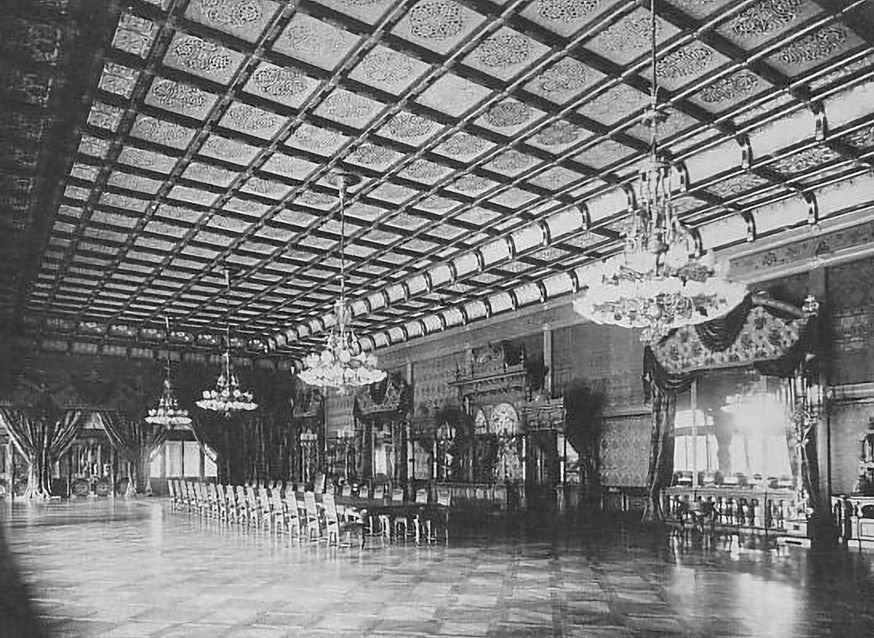
. Commissioned for the housing of foreign guests by the Foreign Minister Inoue Kaoru, it was designed by , a prominent foreign government advisors in Meiji Japan (''o-yatoi gaikokujin''). The '' Ryōunkaku'' was Japan's first western-style skyscraper, constructed in 1890 in Asakusa. However traditional architecture was still employed for new buildings, such as the ''Kyūden'' of Tokyo Imperial Palace, albeit with token western elements such as a spouting water fountain in the gardens.
 In contrast to Waters's neoclassical style building, Japanese carpenters developed a pseudo-Japanese style known as ''giyōfū'' chiefly using wood. A good example of which is Kaichi Primary School in Nagano Prefecture built in 1876. The master carpenter Tateishi Kiyoshige travelled to Tōkyō to see which Western building styles were popular and incorporated these in the school with traditional building methods. Constructed with a similar method to traditional () storehouses, the wooden building plastered inside and out incorporates an octagonal Chinese tower and has stone-like quoins to the corners. Traditional
In contrast to Waters's neoclassical style building, Japanese carpenters developed a pseudo-Japanese style known as ''giyōfū'' chiefly using wood. A good example of which is Kaichi Primary School in Nagano Prefecture built in 1876. The master carpenter Tateishi Kiyoshige travelled to Tōkyō to see which Western building styles were popular and incorporated these in the school with traditional building methods. Constructed with a similar method to traditional () storehouses, the wooden building plastered inside and out incorporates an octagonal Chinese tower and has stone-like quoins to the corners. Traditional namako
Sea cucumbers are marine animals of the class Holothuroidea. They can be used as food, in fresh or dried form, in various cuisines. In some cultural contexts the sea cucumber is thought to have medicinal value.
The creature and the food product ...
plasterwork was used at the base of the walls to give the impression that the building sits on a stone base. Another example was the First National Bank building in Tokyo, built in 1872.
 The Japanese government also invited foreign architects to both work in Japan and teach new Japanese architects. One of these, the British architect went on to train many of the most prominent of the Japanese Meiji era architects, including
The Japanese government also invited foreign architects to both work in Japan and teach new Japanese architects. One of these, the British architect went on to train many of the most prominent of the Japanese Meiji era architects, including Kingo Tatsuno
was a Japanese architect born in Karatsu, Saga Prefecture, Kyushu. Doctor of Engineering. Conferred Jusanmi (従三位, Junior Third Rank) and Kunsanto (勲三等, Order of Third Class). Former dean of Architecture Department at Tokyo Imperial ...
, Tatsuzō Sone and Tokuma Katayama. Tatsuno's early works had a Venetian style influenced by John Ruskin, but his later works such as the Bank of Japan
The is the central bank of Japan. Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric. (2005). "Nihon Ginkō" in The bank is often called for short. It has its headquarters in Chūō, Tokyo.
History
Like most modern Japanese institutions, the Bank of Japan was fou ...
(1896) and Tōkyō Station (1914) have a more Beaux-Arts feel. On the other hand, Katayama was more influenced by the French Second Empire style which can be seen in the Nara National Museum (1894) and the Kyōto National Museum (1895).
In 1920, a group of young architects formed the first organization of modernist architects. They were known as the ''Bunriha'', literally "Secessionist group", inspired in part by the Vienna Secessionists. These architects were worried about the reliance on historical styles and decoration and instead encouraged artistic expression. They drew their influence from European movements like Expressionism and the Bauhaus and helped pave the way towards the introduction of the International Style International style may refer to:
* International Style (architecture), the early 20th century modern movement in architecture
*International style (art), the International Gothic style in medieval art
*International Style (dancing), a term used in ...
of Modernism.Bognar (1995), p. 14
 In the Taishō and early Shōwa periods two influential American architects worked in Japan. The first was
In the Taishō and early Shōwa periods two influential American architects worked in Japan. The first was Frank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
who designed the Imperial Hotel, Tokyo (1913–1923) and the Yodokō Guest House (1924), both of which used locally quarried Ōya stone. Wright had a number of Japanese apprentices under his tutelage, such as Arata Endo
Arata Endo (Japanese: 遠藤 新) (January 1, 1889 - June 29, 1951) was a Japanese architect. He was a disciple of Frank Lloyd Wright. One of his most important works was the Kōshien Hotel, the architectural style being heavily influenced by Wri ...
, who constructed the Kōshien Hotel
The was a Mayan Revival-style hotel in Nishinomiya, Hyōgo, Japan, constructed by Arata Endo
Arata Endo (Japanese: 遠藤 新) (January 1, 1889 - June 29, 1951) was a Japanese architect. He was a disciple of Frank Lloyd Wright. One of his ...
in 1930.
The second was Antonin Raymond who worked for Wright on the Imperial Hotel before leaving to set up his own practice in Tōkyō. Although his early works like Tōkyō Women's Christian College show Wright's influence, he soon began to experiment with the use of in-situ reinforced concrete, detailing it in way that recalled traditional Japanese construction methods. Between 1933 and 1937 Bruno Taut
Bruno Julius Florian Taut (4 May 1880 – 24 December 1938) was a renowned German architect, urban planner and author of Prussian Lithuanian heritage ("taut" means "nation" in Lithuanian). He was active during the Weimar period and is kno ...
stayed in Japan. His writings, especially those on Katsura Imperial Villa reevaluated traditional Japanese architecture whilst bringing it to a wider audience.Bognar (1995), p. 15
As in the Meiji era experience from abroad was gained by Japanese architects working in Europe. Among these were Kunio Maekawa and Junzo Sakakura
was a Japanese architect and former president of the Architectural Association of Japan.
After graduating from university he worked in Le Corbusier's atelier in Paris. He rose to the position of studio chief during his seven-year stay in the s ...
who worked at Le Corbusier's atelier in Paris and Bunzō Yamaguchi and Chikatada Kurata who worked with Walter Gropius.
Some architects built their reputation upon works of public architecture. Togo Murano, a contemporary of Raymond, was influenced by Rationalism and designed the Morigo Shoten office building, Tōkyō (1931) and Ube Public Hall, Yamaguchi Prefecture (1937). Similarly, Tetsuro Yoshida's rationalist modern architecture included the Tōkyō Central Post Office (1931) and Ōsaka Central Post Office (1939).
 Running contrary to modernism in Japan was the so-called Imperial Crown style (''teikan yōshiki''). Buildings in this style were characterised by having a Japanese-style roof such as the Tōkyō Imperial Museum (1937) by Hitoshi Watanabe and Nagoya City Hall and the Aichi Prefectural Government Office. The increasingly militaristic government insisted that major buildings be designed in a "Japanese Style" limiting opportunities for modernist design to works of infrastructure such as Bunzō Yamaguchi's Number 2 Power Plant for the Kurobe Dam, (1938).
A large number of buildings from the Meiji, Taishō and Shōwa eras were lost during and after World War II, such as the Rokumeikan. Taniguchi Yoshirō (谷口 吉郎, 1904–79), an architect, and Moto Tsuchikawa established Meiji Mura in 1965, close to Nagoya, where a large number of rescued buildings are re-assembled. A similar museum is the Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum.
Running contrary to modernism in Japan was the so-called Imperial Crown style (''teikan yōshiki''). Buildings in this style were characterised by having a Japanese-style roof such as the Tōkyō Imperial Museum (1937) by Hitoshi Watanabe and Nagoya City Hall and the Aichi Prefectural Government Office. The increasingly militaristic government insisted that major buildings be designed in a "Japanese Style" limiting opportunities for modernist design to works of infrastructure such as Bunzō Yamaguchi's Number 2 Power Plant for the Kurobe Dam, (1938).
A large number of buildings from the Meiji, Taishō and Shōwa eras were lost during and after World War II, such as the Rokumeikan. Taniguchi Yoshirō (谷口 吉郎, 1904–79), an architect, and Moto Tsuchikawa established Meiji Mura in 1965, close to Nagoya, where a large number of rescued buildings are re-assembled. A similar museum is the Edo-Tokyo Open Air Architectural Museum.
Colonial architecture
 The colonial authorities constructed a large number of public buildings, many of which have survived. Examples include the large-scale concept of what is today
The colonial authorities constructed a large number of public buildings, many of which have survived. Examples include the large-scale concept of what is today Ketagalan Boulevard
Ketagalan Boulevard () is an arterial road in Zhongzheng District in Taipei, Taiwan, between the Presidential Office Building and the . It is long and has a total of ten lanes in each direction with no median.
History
The former name of t ...
in central Zhongzheng District of Taipei
Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Located in Northern Taiwan, Taipei City is an enclave of the municipality of New Taipei City that sits about southwest of the ...
that showcases the Office of the Governor-General, Taiwan Governor Museum, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei Guest House, Judicial Yuan, the Kangyo Bank and Mitsui Bussan Company buildings, as well as many examples of smaller houses found on Qidong Street.
In Korea under Japanese administration, public buildings such as train stations and city halls were also constructed in various styles. Although the largest Japanese colonial building, the immense Government-General Building, was demolished in 1995, many colonial buildings have been preserved. These include the former Keijo City Hall, today Seoul Metropolitan Library; the former Keijo station, today Old Seoul Station; the former Bank of Chosen, designed by Tatsuno Kingo, today the headquarters of the Bank of Korea; and the former branch of Mitsukoshi
is an international department store chain with headquarters in Tokyo, Japan. It is a subsidiary of Isetan Mitsukoshi Holdings, which also owns the Isetan department store chain.
History
It was founded in 1673 with the (shop name) , sel ...
department store, today the flagship of Shinsegae department store.
After winning Dalian as the result of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–05, Japan continued to build the Russian-built city with the modern buildings on "Large Square". With the conquest and establishment of the puppet state Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese in ...
, massive funds and efforts were invested into the master plan for the construction of the capital city of Shinkyō ( Hsinking). Many official buildings erected during the colonial period still stand today, including those of the Eight Grand Ministries of Manchukuo, the Imperial Palace, the headquarters of the Kwantung Army and Datong Avenue.
Seoul
Seoul (; ; ), officially known as the Seoul Special City, is the Capital city, capital and largest metropolis of South Korea.Before 1972, Seoul was the ''de jure'' capital of the North Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea (North Korea ...
Metropolitan Library, built in 1925
File:Manchukuo State Council Building cropped.jpg, Manchukuo
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese in ...
State Council building, Changchun
File:Краеведческий музей Южно-Сахалинска.jpg, The Museum of Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, completed in 1937
File:Yokohama Specie Bank Dalian.JPG, Bank of China Dalian branch, designed by Tsumaki Yorinaka in 1909
File:Taipei_Guest_House_Front_Near_View.jpg, Taipei Guest House in Taipei, built in 1901
File:Former Osaka Shosen Taipei Branch restoration 20190525b.jpg, Former Osaka Shosen (now Mitsui O.S.K. Lines) Office Building in Taipei, built in 1937
File:Kyoto National Museum 01.jpg, Kyoto National Museum
The is one of the major art museums in Japan. Located in Kyoto's Higashiyama ward, the museum focuses on pre-modern Japanese and Asian art.
History
The Kyoto National Museum, then the Imperial Museum of Kyoto, was proposed, along with the Imp ...
in Kyōto, , built in 1895
File:Bank of Japan headquarters in Tokyo, Japan.jpg, Bank of Japan, Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
, , built in 1896
File:Osaka prefectural nakanoshima library01 1920.jpg, Osaka Prefectural Nakanoshima Library, Osaka
is a designated city in the Kansai region of Honshu in Japan. It is the capital of and most populous city in Osaka Prefecture, and the third most populous city in Japan, following Special wards of Tokyo and Yokohama. With a population of ...
, , built in 1904
File:Imperial Hotel Wright House.jpg, Imperial Hotel, Tōkyō, , built between 1913 and 1924
File:Sumitomo bld02s3200.jpg, Sumitomo Building, Osaka, , built in 1924
File:Diet of Japan Kokkai 2009.jpg, National Diet Building in Tōkyō, , , built in 1936
File:090408 aichi kenchou.jpg, Main building of Aichi Prefectural Office, , Jin Watanabe, built in 1938
File:Kurobe Daini Hydropowerstation.jpg, Kurobe Dam No 2 Power Plant, , built in 1938
Late Showa period
 After the war and under the influence of the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers, General Douglas MacArthur, Japanese political and religious life was reformed to produce a demilitarised and democratic country. Although a new
After the war and under the influence of the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers, General Douglas MacArthur, Japanese political and religious life was reformed to produce a demilitarised and democratic country. Although a new constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
was established in 1947, it was not until the beginning of the Korean War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Korean War
, partof = the Cold War and the Korean conflict
, image = Korean War Montage 2.png
, image_size = 300px
, caption = Clockwise from top: ...
that Japan (as an ally of the United States) saw a growth in its economy brought about by the manufacture of industrial goods. In 1946 the Prefabricated Housing Association was formed to try and address the chronic shortage of housing, and architects like Kunio Maekawa submitted designs. However, it was not until the passing of the Public Housing Act in 1951 that housing built by the private sector was supported in law by the government. Also in 1946, the War Damage Rehabilitation Board put forward ideas for the reconstruction of thirteen Japanese cities. Architect Kenzō Tange submitted proposals for Hiroshima and Maebashi.
In 1949, Tange's winning competition entry to design the Hiroshima Peace Memorial Museum gave him international acclaim. The project (completed in 1955) led to a series of commissions including the Kagawa Prefectural Office Building in Takamatsu (1958) and Old Kurashiki City Hall (1960). At this time both Tange and Maekawa were interested in the tradition of Japanese architecture and the influence of local character. This was illustrated at Kagawa with elements of Heian period design fused with the International Style.
 In 1955, Le Corbusier was asked by the Japanese government to design the National Museum of Western Art in Tōkyō. He was assisted by his three former students: Maekawa, Sakakura and
In 1955, Le Corbusier was asked by the Japanese government to design the National Museum of Western Art in Tōkyō. He was assisted by his three former students: Maekawa, Sakakura and Takamasa Yoshizaka
, family name also romanized as Yosizaka, was a Japanese architect and former president of the Architectural Institute of Japan and a keen mountaineer.
After graduating from university, he worked at Le Corbusier's atelier in Paris for two years ...
. The design was based upon Le Corbusier's museum in Ahmedabad, and both of the museums are square and raised on piloti.
Due largely to the influence of Tange, the 1960 World Design Conference was held in Tōkyō. A small group of Japanese designers who came to represent the Metabolist Movement presented their manifesto and a series of projects. The group included the architects Kiyonori Kikutake, Masato Ōtaka, Kisho Kurokawa and Fumihiko Maki. Originally known as the Burnt Ash School, the Metabolists associated themselves with idea of renewal and regeneration, rejecting visual representations of the past and promoting the idea that the individual, the house and the city were all parts of a single organism. Although the individual members of the group went in their own directions after a few years the enduring nature of their publications meant that they had a longer presence overseas. The international symbol of the Metabolists, the capsule, emerged as an idea in the late 1960s and was demonstrated in Kurokawa's Nakagin Capsule Tower in Tōkyō in 1972.
In the 1960s Japan saw both the rise and the expansion of large construction firms, including the Shimizu Corporation and Kajima. Nikken Sekkei emerged as a comprehensive company that often included elements of Metabolist design in its buildings.
 The 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo saw a large boost to new design. Venues were constructed and the Yoyogi National Gymnasium, built between 1961 and 1964 by Kenzo Tange, became a landmark structure famous for its suspension roof design, recalling traditional elements of Shinto shrines. Other structures include the Nippon Budokan, the
The 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo saw a large boost to new design. Venues were constructed and the Yoyogi National Gymnasium, built between 1961 and 1964 by Kenzo Tange, became a landmark structure famous for its suspension roof design, recalling traditional elements of Shinto shrines. Other structures include the Nippon Budokan, the Komazawa Gymnasium
Komazawa Gymnasium is an indoor sporting arena located in Komazawa Olympic Park, Tokyo, Japan. The capacity of the arena is 3,875 spectators.
Designed by Japanese architect Yoshinobu Ashihara, along with the landmark Control Tower, that feature ...
and many others. The Olympic Games symbolised the re-emergence of Japan after the destruction of World War II, reflecting the new confidence in its architecture.
During the 1960s there were also architects who did not see the world of architecture in terms of Metabolism. For example, Kazuo Shinohara specialised in small residential projects in which he explored traditional architecture with simple elements in terms of space, abstraction and symbolism. In the Umbrella House (1961) he explored the spatial relationship between the '' doma'' (earth-paved internal floor) and the raised tatami floor in the living room and sleeping room. This relationship was explored further with the House with an Earthen floor (1963) where a tamped-down earthen floor was included in the kitchen area. His use of a roof to anchor his design for the House in White (1966) has been compared with Frank Lloyd Wright's Prairie Houses. Shinohara explored these abstractions as "Three Styles", which were periods of design that stretched from the early sixties to the mid seventies.
A former employee of Kenzo Tange was Arata Isozaki who was initially interested in the Metabolist Movement and produced innovative theoretical projects for the City in the Air (1961) and Future City (1962). However he soon moved away from this towards a more Mannerist approach similar to the work of James Stirling. This was particularly striking at the Oita Branch for Fukuoka Mutual (1967) with its mathematical grids, concrete construction and exposed services. In the Gunma Prefectural Museum (1971–74) he experimented with cubic elements (some of them twelve metres to a side) overlaid by a secondary grid expressed by the external wall panels and fenestration. This rhythm of panelling may have been influenced by Corbusier's detailing on the Museum of Western Art in Tōkyō.
Japanese cities where they lack European-like piazzas and squares often emphasise the relationship of people with the everyday workings of the street. Fumihiko Maki was one of a number of architects who were interested in the relationship of architecture and the city and this can be seen in works like Ōsaka Prefectural Sports Centre (1972) and Spiral in Tōkyō (1985). Likewise, Takefumi Aida :ja:相田武文 (member of the group known as ArchiteXt) rejected the ideas of the Metabolist Movement and explored urban semiology.
 In the late seventies and early eighties Tadao Ando's architecture and theoretical writings explored the idea of Critical regionalism – the idea of promoting local or national culture within architecture. Ando's interpretation of this was demonstrated by his idea of reacquainting the Japanese house with nature, a relationship he thought had been lost with Modernist architecture. His first projects were for small urban houses with enclosed courtyards (such as the Azuma House in Ōsaka in 1976). His architecture is characterised by the use of concrete, but it has been important for him to use the interplay of light, through time, with this and other materials in his work. His ideas about the integration of nature converted well into larger projects such as the Rokkō Housing 1 (1983) (on a steep site on Mount Rokkō) and the Church on the Water (1988) in Tomamu, Hokkaidō.
The late eighties saw the first work by architects of the so-called "Shinohara" school. This included Toyō Itō and Itsuko Hasegawa who were both interested in urban life and the contemporary city. Itō concentrated on the dynamism and mobility of the city's "urban nomads" with projects like the Tower of Winds (1986) which integrated natural elements like light and wind with those of technology. Hasegawa concentrated on what she termed "architecture as another nature". Her Shōnandai Cultural Centre in Fujisawa (1991) combined the natural environment with new high-tech materials.
Highly individualist architects of the late eighties included the monumental buildings of Shin Takamatsu and the "cosmic" work of Masaharu Takasaki. Takasaki, who worked with the Austrian architect Günther Domenig in the 1970s shares Domenig's organic architecture. His Zero Cosmology House of 1991 in Kagoshima Prefecture constructed from concrete has a contemplative egg-shaped "zero space" at its centre.
In the late seventies and early eighties Tadao Ando's architecture and theoretical writings explored the idea of Critical regionalism – the idea of promoting local or national culture within architecture. Ando's interpretation of this was demonstrated by his idea of reacquainting the Japanese house with nature, a relationship he thought had been lost with Modernist architecture. His first projects were for small urban houses with enclosed courtyards (such as the Azuma House in Ōsaka in 1976). His architecture is characterised by the use of concrete, but it has been important for him to use the interplay of light, through time, with this and other materials in his work. His ideas about the integration of nature converted well into larger projects such as the Rokkō Housing 1 (1983) (on a steep site on Mount Rokkō) and the Church on the Water (1988) in Tomamu, Hokkaidō.
The late eighties saw the first work by architects of the so-called "Shinohara" school. This included Toyō Itō and Itsuko Hasegawa who were both interested in urban life and the contemporary city. Itō concentrated on the dynamism and mobility of the city's "urban nomads" with projects like the Tower of Winds (1986) which integrated natural elements like light and wind with those of technology. Hasegawa concentrated on what she termed "architecture as another nature". Her Shōnandai Cultural Centre in Fujisawa (1991) combined the natural environment with new high-tech materials.
Highly individualist architects of the late eighties included the monumental buildings of Shin Takamatsu and the "cosmic" work of Masaharu Takasaki. Takasaki, who worked with the Austrian architect Günther Domenig in the 1970s shares Domenig's organic architecture. His Zero Cosmology House of 1991 in Kagoshima Prefecture constructed from concrete has a contemplative egg-shaped "zero space" at its centre.
Heisei period

 The Heisei period began with the collapse of the so-called "bubble economy" that had previously boosted Japan's economy. Commissions for commercial works of architecture virtually dried up and architects relied upon government and prefectural organisations to provide projects.
Building on elements from the Shōnandai Culture Centre, Itsuko Hasegawa undertook a number cultural and community centres throughout Japan. These included the Sumida Cultural Centre (1995) and the Fukuroi Community Centre (2001) where she involved the public in the process of design whilst exploring her own ideas about the filtration of light through the external walls into the interior. In his 1995 competition win for
The Heisei period began with the collapse of the so-called "bubble economy" that had previously boosted Japan's economy. Commissions for commercial works of architecture virtually dried up and architects relied upon government and prefectural organisations to provide projects.
Building on elements from the Shōnandai Culture Centre, Itsuko Hasegawa undertook a number cultural and community centres throughout Japan. These included the Sumida Cultural Centre (1995) and the Fukuroi Community Centre (2001) where she involved the public in the process of design whilst exploring her own ideas about the filtration of light through the external walls into the interior. In his 1995 competition win for Sendai Mediatheque
Sendai Mediatheque is a library in Sendai, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It was designed by Toyo Ito in 1995 and completed in 2001.
History
The Sendai Mediatheque held its official opening in January 2001.
Ito also refers to Mies' Barcelona Pavilio ...
, Toyō Itō continued his earlier thoughts about fluid dynamics within the modern city with "seaweed-like" columns supporting a seven-story building wrapped in glass. His work later in the period, for example, the library to Tama Art University in Tōkyō in 2007 demonstrates more expressive forms, rather than the engineered aesthetic of his earlier works.
Although Tadao Ando became well known for his use of concrete, he began the decade designing the Japanese pavilion at the Seville Exposition 1992, with a building that was hailed as "the largest wooden structure in the world". He continued with this medium in projects for the Museum of Wood Culture, Kami, Hyōgo Prefecture (1994) and the Komyo-ji Shrine in Saijo (2001).
The UK practice, Foreign Office Architects won an international competition in 1994 to design the Yokohama International Port Terminal. It is an undulating structure that emerges from the surrounding city and forms a building to walk over as well as into. Klein Dytham Architecture are one of a handful of foreign architects who managed to gain a strong foothold in Japan. Their design for Moku Moku Yu (literally "wood wood steam"), a communal bathhouse in Kobuchizawa, Yamanashi Prefecture in 2004 is a series of interconnected circular pools and changing rooms, flat-roofed and clad in coloured vertical timbers.
After the 1995 Kōbe earthquake, Shigeru Ban developed cardboard tubes that could be used to quickly construct refugee shelters that were dubbed "Paper Houses". Also as part of that relief effort he designed a church using 58 cardboard tubes that were 5m high and had a tensile roof that opened up like an umbrella. The church was erected by Roman Catholic volunteers in five weeks. For the Nomadic Museum, Ban used walls made of shipping containers, stacked four high and joined at the corners with twist connectors that produced a checkerboard effect of solid and void. The ancillary spaces were made with paper tubes and honeycomb panels. The museum was designed to be disassembled and it subsequently moved from New York, to Santa Monica, Tōkyō and Mexico.
Historian and architect Terunobu Fujimori's studies in the 1980s into so-called architectural curios found in the city inspired the work of a younger generation of architects such as the founders of Atelier Bow-Wow. Yoshiharu Tsukamoto and Momoyo Kajima surveyed the city for "no-good" architecture for their book ''Made in Tokyo'' in 2001. Their work in turn seeks to embrace its context rather than block it out. Although their office in Tōkyō is on a tight site they have welcomed the city in with huge windows and spacious porches.
Sou Fujimoto's architecture relies upon a manipulation of basic building blocks to produce a geometric primitivism. His buildings are very sensitive to the topographical form of their context and include a series of houses as well as a children's home in Hokkaidō.
Two former employees of Toyō Itō, Kazuyo Sejima and Ryue Nishizawa formed a collaborative partnership in 1995 called SANAA
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Go ...
. They are known for creating lightweight, transparent spaces that expose the fluidity and movement of their occupants. Their Dior
Christian Dior SE (), commonly known as Dior (stylized DIOR), is a French luxury fashion house controlled and chaired by French businessman Bernard Arnault, who also heads LVMH, the world's largest luxury group. Dior itself holds 42.36% shar ...
store in Shibuya, Tōkyō, in 2001 was reminiscent of Itō's Mediatheque, with cool white acrylic sheets on the external facade that filter the light and partially reveal the store's contents. Their dynamic of fluidity is demonstrated by the Rolex Learning Centre at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern Franc ...
, completed in 2010. This building has an undulating floor plane set under a continuous concrete shell roof that was poured in one go over two days. The plan is like a biological cell punctuated with tables and courtyards alike. In 2009 they designed the Serpentine Gallery Pavilion in London that comprised a reflective, floating aluminium roof supported by slender columns.
Built in 1992 File:Ki-no-dendo04s3200.jpg, Museum for Wood Culture, Kami, Hyogo Prefecture
Built in 1994 File:Osanbashi Pier2.jpg, Yokohama International Port Terminal
Built between 1994 and 2002 File:Takatori Catholic Church.JPG, Paper Church, Kōbe
Built in 1995 File:Within the dome structure, Yamanashi Fruit Museum and Garden, Japan.jpg, Yamanashi Fruit Museum
Built in 1996 File:Tama Art University Library.JPG, Tama Art University Library, Tōkyō
Built in 2007
Japanese interior design
Japanese interior design has a unique aesthetic derived fromShinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoist ...
, Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, Zen Buddhism
Zen ( zh, t=禪, p=Chán; ja, text= 禅, translit=zen; ko, text=선, translit=Seon; vi, text=Thiền) is a school of Mahayana Buddhism that originated in China during the Tang dynasty, known as the Chan School (''Chánzong'' 禪宗), and ...
, world view of '' wabi-sabi'', specific religious figures and the West. This aesthetic has in turn influenced Western style, particularly Modernism
Modernism is both a philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new forms of art, philosophy, ...
.
Traditional Japanese aesthetic
What is generally identified as the Japanese aesthetic stems from ideals of JapaneseShinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoist ...
and Chinese Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
. Japanese culture is extremely diverse; despite this, in terms of the interior, the aesthetic is one of simplicity and minimalism.
The specific idea that a room's true beauty is in the empty space within the roof and walls came from Laozi, a philosopher and the founder of Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
, who held to the "aesthetic ideal of emptiness", believing that the mood should be captured in the imagination, and not so heavily dictated by what is physically present. Japanese design is based strongly on craftsmanship, beauty, elaboration, and delicacy. The design of interiors is very simple but made with attention to detail and intricacy. This sense of intricacy and simplicity in Japanese designs is still valued in modern Japan as it was in traditional Japan.
Interiors are very simple, highlighting minimal and natural decoration. Traditional Japanese interiors, as well as modern, incorporate mainly natural materials including fine woods, bamboo, silk, rice straw mats, and paper '' shōji'' screens. Natural materials are used to keep simplicity in the space that connects to nature. Natural color schemes are used and neutral palettes including black, white, off-white, gray, and brown.
Impermanence is a strong theme in traditional Japanese dwellings. The size of rooms can be altered by interior sliding walls or screens, the already mentioned ''shōji''. Cupboards built smoothly into the wall hide futon, mattresses pulled out before going to bed, allowing more space to be available during the day. The versatility of these dwellings becomes more apparent with changes of seasons. In summer, for example, exterior walls can be opened to bring the garden and cooling breezes in. The minimal decoration also alters seasonally, with a different scroll hanging or new flower arrangement.
The Japanese aesthetic developed further with the celebration of imperfection and insufficiency, characteristics resulting from the natural ageing process or darkening effect. Shinto
Shinto () is a religion from Japan. Classified as an East Asian religion by scholars of religion, its practitioners often regard it as Japan's indigenous religion and as a nature religion. Scholars sometimes call its practitioners ''Shintoist ...
, the indigenous religious tradition of Japan, provides a basis for the appreciation of these qualities, holding to a philosophy of appreciation of life and the world. Sei Shōnagon was a trend-setting court lady of the tenth century who wrote in ‘The Pillow Book
is a book of observations and musings recorded by Sei Shōnagon during her time as court lady to Empress Consort Teishi during the 990s and early 1000s in Heian-period Japan. The book was completed in the year 1002.
The work is a collection ...
’ of her dislike for "a new cloth screen with a colourful and cluttered painting of many cherry blossoms", preferring instead to notice "that one's elegant Chinese mirror has become a little cloudy". Her taste was not out of place in the ancient Japanese court. In the twelfth century a Buddhist monk, Yoshida Kenkō, exerted his influence on Japanese aesthetic sensibility resulting from his philosophy of life. He asked, "Are we to look at cherry blossoms only in full bloom, the moon only when it is cloudless? ...Branches about to blossom or garden strewn with faded flowers are worthier of our admiration." The incomplete is also praised by Kenkō, "uniformity and completeness are undesirable". Underpinning or complementing these aesthetic ideals, is the valuing of contrast; when imperfection or the impoverished is contrasted with perfection or opulence, each is emphasised and thus better appreciated.
Traditional materials of the interior
Japanese interior design is very efficient in the use of resources. Traditional and modern Japanese interiors have been flexible in use and designed mostly with natural materials. The spaces are used as multifunctional rooms. The rooms can be opened to create more space for a particular occasion or for more privacy, or vice versa closed-off by pulling closed paper screens called '' shōji''. Japanese Zen interior designs draw inspiration from elements of nature as they have immense respect for nature. Their designs have a strong connection with natural elements such as wood, plants, natural lighting and more. A large portion of Japanese interior walls are often made of ''shōji'' screens that can be pushed open to join two rooms together, and then close them allowing more privacy. The ''shōji'' screens are made of paper attached to thin wooden frames that roll away on a track when they are pushed. Another important feature of the ''shōji'' screen, besides privacy and seclusion, is that they allow light through. This is an important aspect to Japanese design. Paper translucent walls allow light to be diffused through the space and create light shadows and patterns. '' Tatami'' mats are rice straw floor mats often used to cover the floor in Japan's interiors; in modern Japanese houses there are usually only one or two ''tatami'' rooms. Another way to connect rooms in Japan's interiors is through sliding panels made of wood and paper, like the ''shōji'' screens, or cloth. These panels are called '' fusuma'' and are used as an entire wall. They are traditionally hand painted. ''Tatami'' are the basis of traditional Japanese architecture, regulating a building's size and dimensions. They originated in ancient Japan when straw was laid on bare earth as a softener and warmer. In theHeian Period
The is the last division of classical Japanese history, running from 794 to 1185. It followed the Nara period, beginning when the 50th emperor, Emperor Kanmu, moved the capital of Japan to Heian-kyō (modern Kyoto). means "peace" in Japanese ...
(794–1185), this idea developed into moveable mats that could be laid anywhere in the house to sit or sleep on before becoming a permanent floor covering in the fifteenth century. ''Tatami'' are suitable for the Japanese climate because they let air circulate around the floor.
Bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
is prominently used and even expected in the Japanese house, used both for decorative and functional purposes. Bamboo blinds, '' sudare'', replace '' shoji'' in summer to prevent excess heat inside and also offer greater ventilation. Country dwellings and farmhouses often use it for ceilings and rafters. The natural properties of bamboo, its raw beauty with the knots and smooth surface, correspond to Japanese aesthetic ideals of imperfection, contrast and the natural.
The use of paper, or '' washi'', in Japanese buildings is a main component in the beauty and atmosphere of the Japanese interior, the way variation of shadow combines to create a "mystery of shadows". A range of papers are used for various purposes in the home.
Wood is generally used for the framework of the home, but its properties are valuable in the Japanese aesthetic, namely its warmth and irregularity.
A recessed space called '' tokonoma'' is often present in traditional as well as modern Japanese living rooms. This is the focus of the room and displays Japanese art, usually a painting or calligraphy.
Western influence
domestic sphere The private sphere is the complement or opposite to the public sphere. The private sphere is a certain sector of societal life in which an individual enjoys a degree of authority, unhampered by interventions from governmental or other institutions. ...
, the manner and dress of inhabitants were determined by the interior style, Japanese or Western. One of the examples is the ''Hōmei-Den'' of the Meiji era Tokyo Imperial Palace, which fused Japanese styles such as the coffered ceiling with western parquet floor and chandeliers.
There was a push by bureaucrats for Japan to develop into a more "modern" (Western) culture. The modernising of the home was considered the best way to change the daily life of the people. Much of the reason for modernisation was a desire to "present a ‘civilised’ face to the world, thus helping to secure Japan's position as a modern nation in the world order". Even with governmental encouragement to transform the home, the majority of Japanese people still lived in fairly traditional style dwellings well into the 1920s, partly due to economic situation in the early 1910s that meant western style was out of reach for the majority of people. It was also difficult to incorporate furniture into traditional dwellings due to their small size and intended flexible use of space, a flexibility made difficult to maintain when bulky furniture was involved; it was impractical, but aesthetically incongruent too.
Influence on the West
Some of the earliest influence on the West came in the form of Japanese art, which gained popularity in Europe in particular, in the latter part of the nineteenth century. In terms of architecture and interior design though, the influence on the West is much more centered on the United States of America. Before the twentieth century, very little of the West's knowledge of the Japanese building was gained in Japan. Instead it was gained through exhibitions the Japanese partook in such as the 1876 Centennial International Exhibition in Philadelphia. The early influence of such exhibitions was more in the creation of an enthusiasm for things Japanese instead of something more authentic. The result was exuberant Japanese decoration, the simplicity of Japanese design lost in the clutter of Victorian ostentation. During the twentieth century though, a number of now renowned architects visited Japan includingFrank Lloyd Wright
Frank Lloyd Wright (June 8, 1867 – April 9, 1959) was an American architect, designer, writer, and educator. He designed more than 1,000 structures over a creative period of 70 years. Wright played a key role in the architectural movements o ...
, Ralph Adams Cram, Richard Neutra and Antonin Raymond. These architects, among others, played significant roles in bringing the Japanese influence to Western modernism. Influence from the Far East was not new in America at this time. During the eighteenth and a large part of the nineteenth centuries, a taste for Chinese art and architecture existed and often resulted in a "superficial copying". The Japanese influence was different however. The modernist context, and the time leading up to it, meant that architects were more concerned with "the problem of building, rather than in the art of ornamenting". The simplicity of Japanese dwellings contrasted the oft-esteemed excessive decoration of the West. The influence of Japanese design was thus not so much that it was directly copied but rather, "the west discovered the quality of space in traditional Japanese architecture through a filter of western architectural values".
The culture that created traditional Japanese architecture is so far removed from Western values philosophies of life that it could not be directly applied in a design context.
See also
* Shinto architecture * Japanese Buddhist architecture *Japanese-Western Eclectic Architecture
is an architectural style that emerged from the Eclecticism in architecture movement of the late 19th and early 20th century, which intentionally incorporated Japanese architectural and Western architectural components into one building design. ...
* Japanese garden
* Architecture of Tokyo
* List of Japanese architects
The following is a chronological list of notable Japanese architects.
Pre Meiji period, Meiji period (1868–1911), Taishō Period (1912–1925), Shōwa Period (1926–1945)
Post World War II
See also
* Architecture of Japan
...
* Architectural forgery in Japan
* Housing in Japan
* Giboshi
Notes and references
Bibliography
* * * Bowring, R. and Kornicki, P. (1993), ''The Cambridge Encyclopedia of Japan'', pp. 201–208, Cambridge University Press, . * Coaldrake, William H. (1996) ''Architecture and Authority in Japan (Nissan Institute/Routledge Japanese Studies Series)'', Routledge, * Daniell, Thomas (2008) ''After the Crash: Architecture in Post-Bubble Japan'', Princeton Architectural Press, * * Fiévé, Nicolas (1996).''L'architecture et la ville du Japon ancien. Espace architectural de la ville de Kyôto et des résidences shôgunales aux XIVe et XVe siècles'', Bibliothèque de l'Institut des Hautes Études Japonaises, Collège de France, Paris, Maisonneuve & Larose, 358 pages + 102 illustrations. . * Fiévé, Nicolas (dir.) (2008).''Atlas historique de Kyôto. Analyse spatiale des systèmes de mémoire d’une ville, de son architecture et de ses paysages urbains''. Foreword Kôichirô Matsuura, Preface Jacques Gernet, Paris, Éditions de l’UNESCO / Éditions de l’Amateur, 528 pages, 207 maps et 210 ill. . * Fiévé, Nicolas and Waley, Paul. (2003). Japanese Capitals in Historical Perspective: Place, Power and Memory in Kyoto, Edo and Tokyo. London: Routledge. 417 pages + 75 ill. * * * Gregory, Rob, August 2007, "Reading Matter", ''Architectural Review'' * Gregory, Rob, August 2007, "Rock Solid", ''Architectural Review'' * * * * Payne, James, March 2010, "Lausanne", ''Architecture Today'' * * * Slessor, Catherine, October 2001, "Comment", ''Architectural Review'' * Slessor, Catherine, October 2001, "Common Ground", ''Architectural Review'' * * * * * * * Webb, Michael, October 2001, "Layered Media", ''Architectural Review'' * Webb, Michael, May 2006, "Container Art", ''Architectural Review'' * Spring 2005, "Do_co,mo.mo Japan: the 100 selection", ''The Japan Architect'', No. 57 *Fletcher, Banister
Sir Banister Flight Fletcher (15 February 1866 – 17 August 1953) was an English architect and architectural historian, as was his father, also named Banister Fletcher. They wrote the standard textbook ''A History of Architecture'', ...
; Cruickshank, Dan''Sir Banister Fletcher's a History of Architecture''
Architectural Press, 20th edition, 1996 (first published 1896). . Cf. Part Four, Chapter 25 * Koji Yagi (text), Ryo Hata (photos): ''A Japanese Touch For Your Home''. Kodansha International, Tokyo, New York, London 1999 (Pbck.),
External links
mooponto — Portal for Japanese minimalist architecture
Explore the vision behind the modern Japanese minimalist architecture
JAANUS (Japanese Architecture and Art Net Users System)
On-line dictionary of Japanese architectural and art historical terminology {{DEFAULTSORT:Japanese Architecture