Ischioceratops on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Ischioceratops'' () is an extinct
 In 2015, the
In 2015, the  The
The
 ''Ischioceratops'' was a relatively small ceratopsian, reaching in length. The describing authors indicated some distinguishing traits. The taxon has been referred to
''Ischioceratops'' was a relatively small ceratopsian, reaching in length. The describing authors indicated some distinguishing traits. The taxon has been referred to

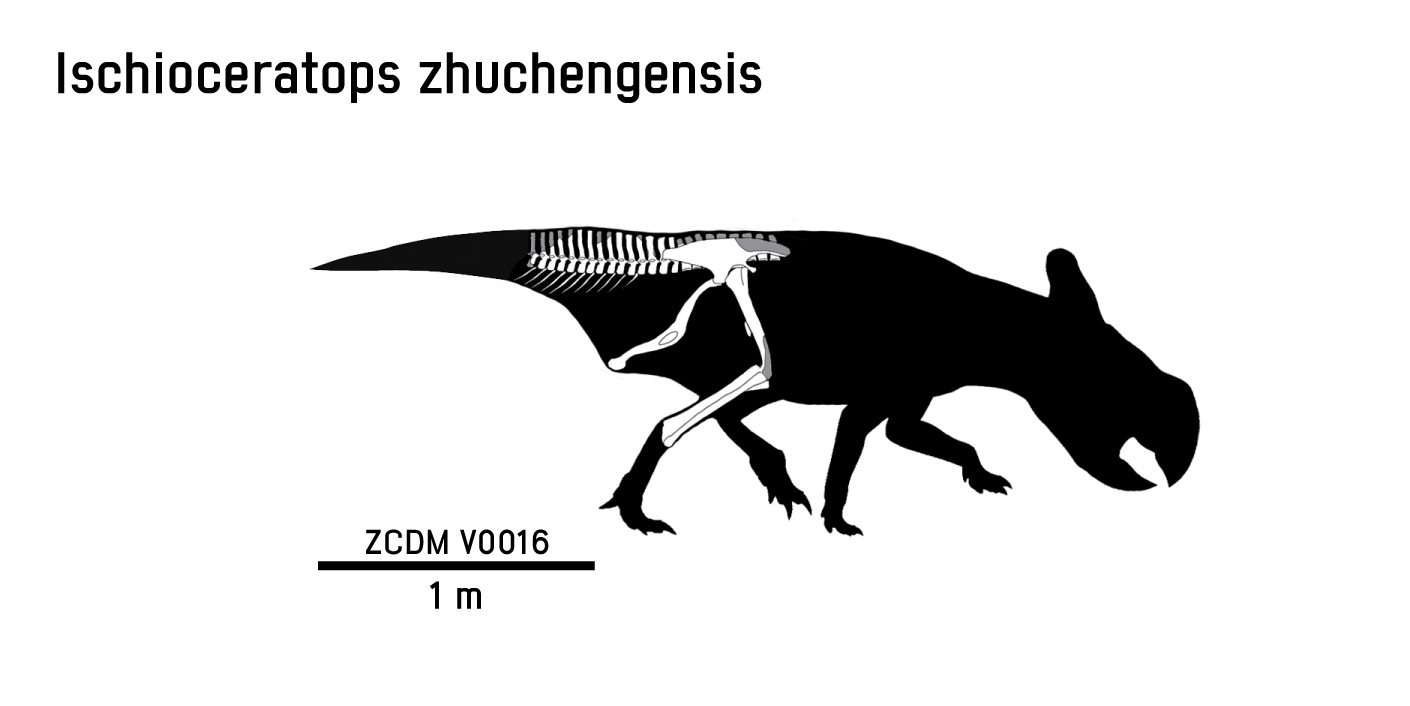
 ''Ischioceratops'' is one of the few ceratopsian dinosaurs which is not known by the skull. The most peculiar traits are located in the ischium. With most relatives the ischium shaft has a constant curvature to the rear. Another characteristic of ''Ischioceratops'' is the presence of an elevation in the proximal part of its tail, which is present also in ''
''Ischioceratops'' is one of the few ceratopsian dinosaurs which is not known by the skull. The most peculiar traits are located in the ischium. With most relatives the ischium shaft has a constant curvature to the rear. Another characteristic of ''Ischioceratops'' is the presence of an elevation in the proximal part of its tail, which is present also in ''

 Phylogenetic analyzes confirmed ''Ischioceratops'' as a leptoceratopsid. Its closest relative taxon or
Phylogenetic analyzes confirmed ''Ischioceratops'' as a leptoceratopsid. Its closest relative taxon or
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial n ...
of small herbivorous ceratopsian
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassi ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived approximately 69 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
during the latter part of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
in what is now China.
''Ischioceratops'' was a small sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuo ...
herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthp ...
, whose total body length has been estimated to be about . The ceratopsians were a group of dinosaurs with parrot
Parrots, also known as psittacines (), are birds of the roughly 398 species in 92 genera comprising the order Psittaciformes (), found mostly in tropical and subtropical regions. The order is subdivided into three superfamilies: the Psittaco ...
-like beaks which fed on vegetation and thrived in North America and Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an ...
during the Cretaceous Period, which ended approximately 66 million years ago, at which point they all became extinct. Its name means "ischium horned face", referring to the peculiar shape of the ischiatic bones.
''Ischioceratops'' existed in the Wangshi Group
The Wangshi Group () is a geological Group in Shandong, China whose strata date back to the Coniacian to Campanian stages of the Late Cretaceous.Sinoceratops
''Sinoceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 73 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Shandong province in China. It was named in 2010 by Xu Xing ''et al.'' ...
'' and ''Zhuchengtyrannus
''Zhuchengtyrannus'' (meaning "Zhucheng tyrant") is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous of Shandong Province, China. It belongs to the subfamily Tyrannosaurinae, and contains a singl ...
''.
Discovery and naming
 In 2015, the
In 2015, the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen( ...
''Ischioceratops zhuchengensis'' was named and described by He Yiming, Peter J. Makovicky, Wang Kebai, Chen Shuqing, Corwin Sullivan, Han Fenglu and Xu Xing. The generic name combines a reference to the ''os ischii'', its uniquely formed ischium
The ischium () form ...
, with ~ceratops, "horn face", a usual suffix in the names of Ceratopia. The suffix itself is derived from Greek ''keras'', "horn", and ''ops'', "face". The specific name Specific name may refer to:
* in Database management systems, a system-assigned name that is unique within a particular database
In taxonomy, either of these two meanings, each with its own set of rules:
* Specific name (botany), the two-part (bino ...
refers to the provenance from Zhucheng. Because the name was published in an electronic publication
Electronic publishing (also referred to as publishing, digital publishing, or online publishing) includes the digital publication of e-books, digital magazines, and the development of digital libraries and catalogues. It also includes the edit ...
, PLoS ONE, ''Life Science Identifiers
Life Science Identifiers are a way to name and locate pieces of information on the web. Essentially, an LSID is a unique identifier for some data, and the LSID protocol specifies a standard way to locate the data (as well as a standard way of descr ...
'' were required for its validity. These were 19A423ED-8EAA -4842-9ECF-695876EC5EC0 for the genus and 71CD0FAE-070C-4CC4-96CC-B37D5B1071CE for the species. ''Ischioceratops'' was one of eighteen dinosaur taxa from 2015 to be described in open access or free-to-read journals.
holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of seve ...
ZCDM V0O016 was discovered in Kugou, a locality in the Shandong Province of China which presents layers of the Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', ...
Wangshi Group, possibly dating from the late Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campani ...
or earliest Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interv ...
. It is part of the Zhucheng
Zhucheng () is a county-level city in the southeast of Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Weifang city and had at the 2010 census a population of 1,086,222 even though its built-up (''or metro'') area ...
Dinosaur Museum collection and it represents an incomplete, partially articulated specimen comprising the entire sacrum
The sacrum (plural: ''sacra'' or ''sacrums''), in human anatomy, is a large, triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30.
The sacrum situates at the upper, back part ...
, a few ossified tendons, both halves of the pelvis, the anteriormost fifteen caudal vertebrae
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates, Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristi ...
in an articulated series, and the right femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
, tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
and fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a human leg, leg bone on the Lateral (anatomy), lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long ...
.
Description
Size and distinguising traits
 ''Ischioceratops'' was a relatively small ceratopsian, reaching in length. The describing authors indicated some distinguishing traits. The taxon has been referred to
''Ischioceratops'' was a relatively small ceratopsian, reaching in length. The describing authors indicated some distinguishing traits. The taxon has been referred to Leptoceratopsidae
Leptoceratopsidae is an extinct family of neoceratopsian dinosaurs from Asia, North America and Europe. Leptoceratopsids resembled, and were closely related to, other neoceratopsians, such as the families Protoceratopsidae and Ceratopsidae, b ...
and is distinguished from other known leptoceratopsids based on the following combination of characters: nine sacral vertebrae, more than in any other known basal (non-ceratopsid) ceratopsian but fewer than in ceratopsids; the ischium has a robust shaft that resembles that of a recurved bow and flares gradually to form a subrectangular-shaped obturator process in its middle portion while an elliptical fenestra perforates the obturator process. This morphology, unique for the Dinosauria as a whole, was seen as a single autapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an autapomorphy is a distinctive feature, known as a derived trait, that is unique to a given taxon. That is, it is found only in one taxon, but not found in any others or outgroup taxa, not even those most closely related to t ...
, unique derived character.
Skeleton

 ''Ischioceratops'' is one of the few ceratopsian dinosaurs which is not known by the skull. The most peculiar traits are located in the ischium. With most relatives the ischium shaft has a constant curvature to the rear. Another characteristic of ''Ischioceratops'' is the presence of an elevation in the proximal part of its tail, which is present also in ''
''Ischioceratops'' is one of the few ceratopsian dinosaurs which is not known by the skull. The most peculiar traits are located in the ischium. With most relatives the ischium shaft has a constant curvature to the rear. Another characteristic of ''Ischioceratops'' is the presence of an elevation in the proximal part of its tail, which is present also in ''Protoceratops
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. helleni ...
'', ''Koreaceratops
''Koreaceratops'' () is a genus of basal ceratopsian dinosaur discovered in Albian-age Lower Cretaceous rocks of South Korea.
Discovery
It is based on KIGAM VP 200801, an articulated series of 36 caudal vertebrae associated with ...
'' and in a more similar way in ''Montanoceratops
''Montanoceratops'' is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. ''Montanoceratops'' was a small sized, mode ...
'' and ''Cerasinops
''Cerasinops'' (meaning 'cherry face') was a small ceratopsian dinosaur. It lived during the Campanian of the late Cretaceous Period.
''. The elevation forms a tail crest.
Classification


 Phylogenetic analyzes confirmed ''Ischioceratops'' as a leptoceratopsid. Its closest relative taxon or
Phylogenetic analyzes confirmed ''Ischioceratops'' as a leptoceratopsid. Its closest relative taxon or sister species
In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree.
Definition
The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram:
Taxon A and ...
was ''Montanoceratops
''Montanoceratops'' is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. ''Montanoceratops'' was a small sized, mode ...
''.
The following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
is based on an analysis in the describing paper of 2015.
See also
*Timeline of ceratopsian research
This timeline of ceratopsian research is a chronological listing of events in the History of paleontology, history of paleontology focused on the ceratopsians, a group of herbivorous marginocephalian dinosaurs that evolved parrot-like beaks, bon ...
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q21871534 Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia Leptoceratopsids Taxa named by Philip J. Currie Ornithischian genera