|
Montanoceratops
''Montanoceratops'' is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. ''Montanoceratops'' was a small sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated in length and in body mass. Description ''Montanoceratops'' was a typical primitive ceratopsian in many respects, distinguished from the later species by the presence of claws, rather than hooves, and by having teeth in its upper jaw, rather than a toothless beak. It was once thought to have a horn on its nose but that was a misplaced cheek horn.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2008) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages'Supplementary Information/ref> According to Brown and Schlaikjer (1935), ''Montanoceratops'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics: * the nasal bone is proportionally l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
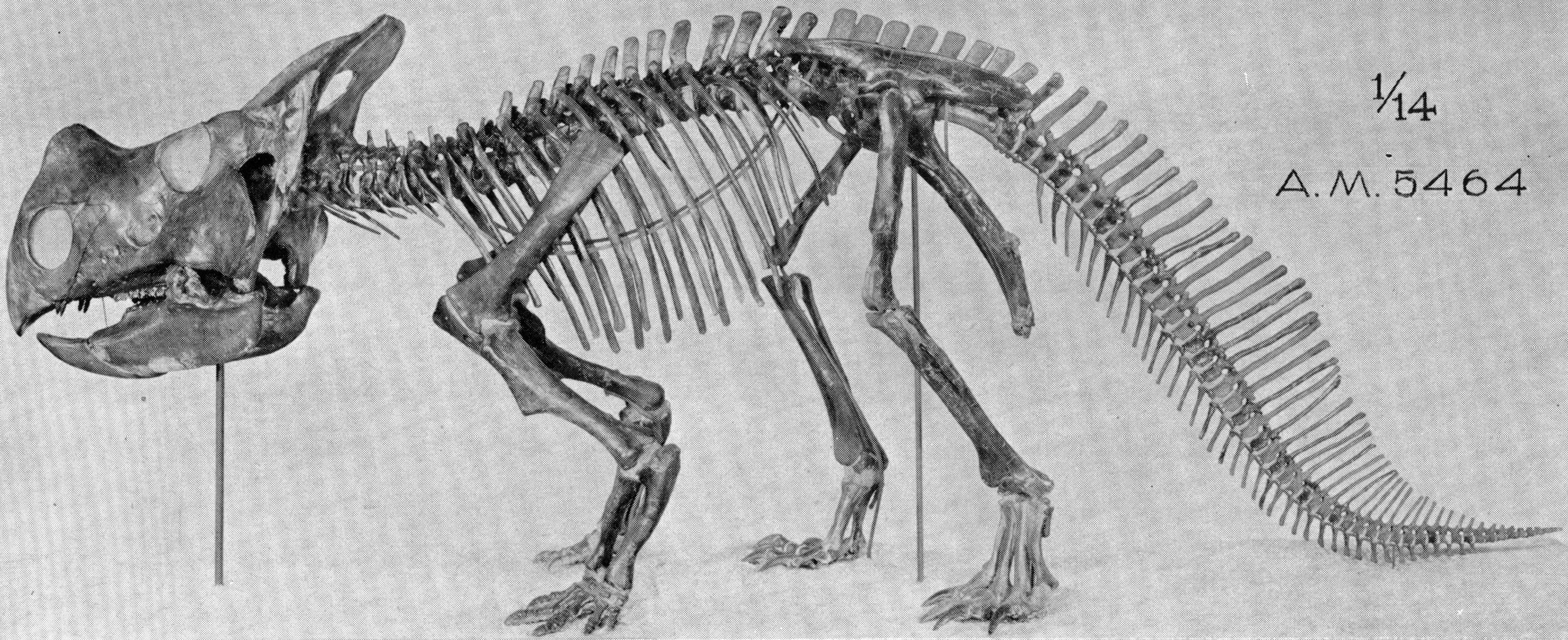
Montanoceratops Skeleton
''Montanoceratops'' is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. ''Montanoceratops'' was a small sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated in length and in body mass. Description ''Montanoceratops'' was a typical primitive ceratopsian in many respects, distinguished from the later species by the presence of claws, rather than hooves, and by having teeth in its upper jaw, rather than a toothless beak. It was once thought to have a horn on its nose but that was a misplaced cheek horn.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2008) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages'Supplementary Information/ref> According to Brown and Schlaikjer (1935), ''Montanoceratops'' can be distinguished based on the following characteristics: * the nasal bone is proportionally lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratopsian
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. The earliest known ceratopsian, '' Yinlong downsi'', lived between 161.2 and 155.7 million years ago.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2011) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages,'Winter 2010 Appendix./ref> The last ceratopsian species, '' Triceratops prorsus'', became extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, . ''Triceratops'' is by far the best-known ceratopsian to the general public. It is traditional for ceratopsian genus names to end in "''-ceratops''", although this is not always the case. One of the first named genera was ''Ceratops'' itself, which lent its name to the group, although it is considered a ''nomen dubium'' today as its fossil remains have no distinguishing char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Maren Schlaikjer
Erich Maren Schlaikjer (; November 22, 1905 in Newtown, Ohio – November 5, 1972) was an American geologist and dinosaur hunter. Assisting Barnum Brown, he co-described ''Pachycephalosaurus'' and what is now ''Montanoceratops''. Other discoveries include ''Miotapirus'' and a new species of ''Mesohippus''. Schlaikjer attended Harvard University, where he graduated with a bachelor's degree in 1929. He received master’s and doctoral degrees from Columbia University in 1931 and in 1935, respectively. Honors Selected highlights of honors: * Parmentier Scholar, Harvard University 1924 to 1925. * University Fellow, Columbia University, 1931 to 1932. * Cressy Morrison Prize, New York Academy of Science, 1939. * Fellow of The Geological Society of America, 1939. * Fellow of the Paleontological Society of America, 1940. * Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science. * Who’s Who in America Marquis Who's Who ( or ) is an American publisher of a number of directo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptoceratops
''Leptoceratops'' (meaning 'Thin-horned face' and derived from Greek ''lepto-/λεπτο-'' meaning 'small', 'insignificant', 'slender', 'meagre' or 'lean', ''kerat-/κερατ-'' meaning 'horn' and ''-ops/ωψ'' meaning face), is a genus of leptoceratopsid ceratopsian dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous Period (late Maastrichtian age, 68.8-66 Ma ago) of what is now Western North America. Their skulls have been found in Alberta, Canada and Wyoming. Description ''Leptoceratops'' could probably stand and run on their hind legs: analysis of forelimb function indicates that even though they could not pronate their hands, they could walk on four legs. Paul proposed that ''Leptoceratops'' was around long and could have weighed , but Tereschenko proposed a maximum length of . Discovery and species The first small ceratopsian named ''Leptoceratops'' was discovered in 1910 by Barnum Brown in the Red Deer Valley in Alberta, Canada. He described it four years later. The first speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen(s). Article 67.1 A similar concept is used for suprageneric groups and called a type genus. In botanical nomenclature, these terms have no formal standing under the code of nomenclature, but are sometimes borrowed from zoological nomenclature. In botany, the type of a genus name is a specimen (or, rarely, an illustration) which is also the type of a species name. The species name that has that type can also be referred to as the type of the genus name. Names of genus and family ranks, the various subdivisions of those ranks, and some higher-rank names based on genus names, have such types. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montana
Montana () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West List of regions of the United States#Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions, division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbia, and Saskatchewan to the north. It is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, fourth-largest state by area, the List of U.S. states and territories by population, eighth-least populous state, and the List of U.S. states and territories by population density, third-least densely populated state. Its state capital is Helena, Montana, Helena. The western half of Montana contains numerous mountain ranges, while the eastern half is characterized by western prairie terrain and badlands, with smaller mountain ranges found throughout the state. Montana has no official nickname but several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Museum Of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 interconnected buildings housing 45 permanent exhibition halls, in addition to a planetarium and a library. The museum collections contain over 34 million specimens of plants, animals, fossils, minerals, rocks, meteorites, human remains, and human cultural artifacts, as well as specialized collections for frozen tissue and genomic and astrophysical data, of which only a small fraction can be displayed at any given time. The museum occupies more than . AMNH has a full-time scientific staff of 225, sponsors over 120 special field expeditions each year, and averages about five million visits annually. The AMNH is a private 501(c)(3) organization. Its mission statement is: "To discover, interpret, and disseminate—through scientific research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stage (stratigraphy)
In chronostratigraphy, a stage is a succession of rock strata laid down in a single age on the geologic timescale, which usually represents millions of years of deposition. A given stage of rock and the corresponding age of time will by convention have the same name, and the same boundaries. Rock series are divided into stages, just as geological epochs are divided into ages. Stages can be divided into smaller stratigraphic units called chronozones. (See chart at right for full terminology hierarchy.) Stages may also be divided into substages or indeed grouped as superstages. The term faunal stage is sometimes used, referring to the fact that the same fauna (animals) are found throughout the layer (by definition). Definition Stages are primarily defined by a consistent set of fossils (biostratigraphy) or a consistent magnetic polarity (see paleomagnetism) in the rock. Usually one or more index fossils that are common, found worldwide, easily recognized, and limited to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Tyrrell Museum
The Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology (RTMP, and often referred to as the Royal Tyrrell Museum) is a palaeontology museum and research facility in Drumheller, Alberta, Canada. The museum was named in honour of Joseph Burr Tyrrell, and is situated within a designed by BCW Architects at Midland Provincial Park. Efforts to establish a palaeontology museum were announced by the provincial government in 1981, with the palaeontology program of the Provincial Museum of Alberta spun-off to help facilitate the creation of a palaeontology museum. After four years of preparation, the Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology was opened in September 1985. The museum was later renamed the Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology in June 1990, following its bestowal of the title "royal" from Queen Elizabeth II. The museum's building was expanded twice in the 21st century. The first expansion was designed by BCW Architects, and was completed in 2003; while the second expansion was designed by Kasian Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(2).jpg)


