Irkutsk Economics Academy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat and mn, Эрхүү, ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and
 In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a ''zimovye'' (winter quarters) near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for collecting fur taxes from the
In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a ''zimovye'' (winter quarters) near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for collecting fur taxes from the
/ref> In the "big city", as the posad was called, the commercial and economic life of Irkutsk was concentrated. It was inhabited mainly by people from the northern regions of Russia: In the early 19th century, many Russian artists, officers, and
In the early 19th century, many Russian artists, officers, and  By the end of the 19th century, the population consisted of one exiled man for every two locals. People of varying backgrounds, from members of the Decembrist uprising to
By the end of the 19th century, the population consisted of one exiled man for every two locals. People of varying backgrounds, from members of the Decembrist uprising to  The Epiphany Cathedral, the governor's palace, a school of medicine, a museum, a military hospital and the crown factories are among the public institutions and buildings. The
The Epiphany Cathedral, the governor's palace, a school of medicine, a museum, a military hospital and the crown factories are among the public institutions and buildings. The
 The center of the historical part of the city is Kirov Square. In that place on July 6, 1661, Yakov Pokhabov laid a prison for collecting
The center of the historical part of the city is Kirov Square. In that place on July 6, 1661, Yakov Pokhabov laid a prison for collecting
 The
The
" ''
administrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, L ...
of Irkutsk Oblast
Irkutsk Oblast (russian: Ирку́тская о́бласть, Irkutskaya oblast; bua, Эрхүү можо, Erkhüü mojo) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of the Angara, Lena, and ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
. With a population of 617,473 as of the 2010 Census, Irkutsk is the 25th-largest city in Russia by population, the fifth-largest in the Siberian Federal District
Siberian Federal District (russian: Сиби́рский федера́льный о́круг, ''Sibirsky federalny okrug'') is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 17,178,298 according to the 2010 Census, livi ...
, and one of the largest cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
.
Located in the south of the eponymous oblast, the city proper lies on the Angara River
The Angara ( Buryat and mn, Ангар, ''Angar'', "Cleft"; russian: Ангара́, ''Angará'') is a major river in Siberia, which traces a course through Russia's Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. It drains out of Lake Baikal and is ...
, a tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
of the Yenisei
The Yenisey (russian: Енисе́й, ''Yeniséy''; mn, Горлог мөрөн, ''Gorlog mörön''; Buryat: Горлог мүрэн, ''Gorlog müren''; Tuvan: Улуг-Хем, ''Uluğ-Hem''; Khakas: Ким суғ, ''Kim suğ''; Ket: Ӄук ...
, about 850 kilometres (530 mi) to the south-east of Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk ( ; rus, Красноя́рск, a=Ru-Красноярск2.ogg, p=krəsnɐˈjarsk) (in semantic translation - Red Ravine City) is the largest city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yen ...
and about 520 kilometres (320 mi) north of Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar (; mn, Улаанбаатар, , "Red Hero"), previously anglicized as Ulan Bator, is the capital and most populous city of Mongolia. It is the coldest capital city in the world, on average. The municipality is located in north c ...
. The Trans-Siberian Highway
The Trans-Siberian Highway is the unofficial name for a network of federal highways that span the width of Russia from the Baltic Sea of the Atlantic Ocean to the Sea of Japan. In the Asian Highway Network, the route is known as AH6. It stretche ...
(Federal M53 and M55 Highways) and Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the eas ...
connect Irkutsk to other regions in Russia and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
.
Many distinguished Russians were sent into exile in Irkutsk for their part in the Decembrist revolt
The Decembrist Revolt ( ru , Восстание декабристов, translit = Vosstaniye dekabristov , translation = Uprising of the Decembrists) took place in Russia on , during the interregnum following the sudden death of Emperor Al ...
of 1825, and the city became an exile-post for the rest of the century. Some historic wooden houses still survive. When the railway reached Irkutsk, it had earned the nickname of "The Paris of Siberia." The city was the center of bitter fighting in the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
of 1918–20. Afterward, in the Soviet period, its architecture was dominated by the mandatory squared-up style. The city became a major centre of aircraft manufacture. The historic centre of Irkutsk is located on UNESCO's tentative list of World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
s.
Etymology
Irkutsk was named after theIrkut River
The Irkut (russian: Ирку́т; Buryat and mn, Эрхүү гол, ''Erhüü go''l) is a river in the Buryat Republic and Irkutsk Oblast of Russia. It is a left tributary of the Angara. It flows out of lake Ilchir which is situated 50 km ...
. Its name was derived from the Buryat word for "spinning," and was used as an ethnonym among local tribes, who were known as ''Yrkhu'', ''Irkit'', ''Irgit'', and ''Irgyt''. The city was formerly known as ''Yandashsky'' after the local Tuvan chief Yandasha Gorogi.
The old spelling of the name of the city was «Иркуцкъ». Before the revolution, the city was called "East Paris", "Siberian Petersburg", "Siberian Athens".
History
 In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a ''zimovye'' (winter quarters) near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for collecting fur taxes from the
In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a ''zimovye'' (winter quarters) near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for collecting fur taxes from the Buryats
The Buryats ( bua, Буряад, Buryaad; mn, Буриад, Buriad) are a Mongolic ethnic group native to southeastern Siberia who speak the Buryat language. They are one of the two largest indigenous groups in Siberia, the other being the Ya ...
. In 1661, Yakov Pokhabov built an '' ostrog'' (a small fort) nearby. The ''ostrog'' gained official town rights from the government in 1686.
The Irkutsk prison, founded in 1661 as an outpost for the advancement of Russian explorers in the Angara region, soon ceased to be only a defensive structure due to the advantage of its geographical position. According to historical documents, 10 years later, in 1671, here, in addition to servicemen and yasak people, lived "plowed peasants with their wives and children." A posad
A posad (russian: посад, uk, посад) was a historical type of settlement in East Slavic lands since the Ancient Rus, often surrounded by ramparts and a moat, adjoining a town or a kremlin, but outside of it, or adjoining a monaster ...
appeared, which gave rise to residential quarters of the future city. As for the prison itself, as its influence in the region grew, it was completely rebuilt twice (in 1669 and 1693), expanding in size.
The fate of the prison was such that its military-defensive significance was less noticeable than other previously erected forts near the Angars, for example, Bratsk (1631) or Verkholensk (1644). However, its location at the crossroads of colonization, trade and industrial routes predetermined the role of Irkutsk in the history of Eastern Siberia. In 1682 it became the center of an independent region, and in 1686 it received the status of a city. Irkutsk at the beginning of the 18th century was divided into two parts: "small town", or the prison itself, and "big city". The first one started from the bank of the Angara and was a wooden fortress with adjacent buildings. These included the stone building of the provincial chancellery, the house of the vice-governor (former voivodship) with barns and cellars, the Church of the Savior. "Small town" was the administrative center of the vast Irkutsk province since 1731.Иркутский острог. Возникновение и основные этапы развития города Иркутска/ref> In the "big city", as the posad was called, the commercial and economic life of Irkutsk was concentrated. It was inhabited mainly by people from the northern regions of Russia:
Veliky Ustyug
Veliky Ustyug (russian: Вели́кий У́стюг) is a town in Vologda Oblast, Russia, located in the northeast of the oblast at the confluence of the Sukhona and Yug Rivers. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 31,665.
Veliky ...
, Yarensk
Yarensk (russian: Я́ренск) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') and the administrative center of Lensky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located on the bank of the Vychegda River near its confluence with the Yarenga. Population:
...
, Pinega
Pinega (russian: Пинега) is a rural locality (a settlement), formerly a town, in Pinezhsky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located on the right bank of the Pinega River (hence the name). It serves as the administrative center of P ...
, Solvychegodsk
Solvychegodsk (russian: Сольвычего́дск, lit. "salt on the Vychegda River") is a town in Kotlassky District of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located on the right-hand bank of the Vychegda River northeast of Kotlas, the admini ...
, Pereyaslavl-Zalessky
Pereslavl-Zalessky ( rus, Переславль-Залесский, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈslavlʲ zɐˈlʲɛskʲɪj, lit. ''Pereslavl beyond the woods''), also known as Pereyaslavl-Zalessky, is a town in Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located on the main Mosc ...
, who brought their traditions, customs, and culture to Siberia.
The first road connection between Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and Irkutsk, the Siberian Route
The Siberian Route (russian: Сибирский тракт; ''Sibirsky trakt''), also known as the Moscow Highway (, Московский тракт) and Great Highway (, Большой тракт), was a historic route that connected European Russ ...
, was built in 1760, and benefited the town economy. Many new products, often imported from China via Kyakhta
Kyakhta (russian: Кя́хта, ; bua, Хяагта, Khiaagta, ; mn, Хиагт, Hiagt, ) is a town and the administrative center of Kyakhtinsky District in the Republic of Buryatia, Russia, located on the Kyakhta River near the Mongolia–Rus ...
, became widely available in Irkutsk for the first time, including gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, ...
s, fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket ...
, wood
Wood is a porous and fibrous structural tissue found in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulose fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of ligni ...
, silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
, and tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by pouring hot or boiling water over cured or fresh leaves of '' Camellia sinensis'', an evergreen shrub native to East Asia which probably originated in the borderlands of southwestern China and north ...
. In 1821, as part of the Mikhail Speransky
Count Mikhail Mikhailovich Speransky (russian: Михаи́л Миха́йлович Спера́нский; 12 January 1772 – 23 February 1839) was a Russian reformist during the reign of Alexander I of Russia, to whom he was a close advisor. ...
's reforms, Siberia was administratively divided at the Yenisei River
The Yenisey (russian: Енисе́й, ''Yeniséy''; mn, Горлог мөрөн, ''Gorlog mörön''; Buryat: Горлог мүрэн, ''Gorlog müren''; Tuvan: Улуг-Хем, ''Uluğ-Hem''; Khakas: Ким суғ, ''Kim suğ''; Ket: Ӄук ...
. Irkutsk became the seat of the Governor-General of East Siberia.
 In the early 19th century, many Russian artists, officers, and
In the early 19th century, many Russian artists, officers, and nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteri ...
were sent into exile in Siberia for their part in the Decembrist revolt
The Decembrist Revolt ( ru , Восстание декабристов, translit = Vosstaniye dekabristov , translation = Uprising of the Decembrists) took place in Russia on , during the interregnum following the sudden death of Emperor Al ...
against Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the te ...
Nicholas I. Irkutsk became the major center of intellectual and social life for these exiles, and they developed much of the city's cultural heritage. They had wooden houses built that were adorned with ornate, hand-carved decorations. Many still survive today, in stark contrast with the standard Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
apartment blocks that surround them.
 By the end of the 19th century, the population consisted of one exiled man for every two locals. People of varying backgrounds, from members of the Decembrist uprising to
By the end of the 19th century, the population consisted of one exiled man for every two locals. People of varying backgrounds, from members of the Decembrist uprising to Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s, had been in Irkutsk for many years and had greatly influenced the culture and development of the city. As a result, Irkutsk became a prosperous cultural and educational center in Eastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
.
From 1848 to 1861 Count Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky
Count Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky (also spelled as Nikolai Nikolaevich Muraviev-Amurskiy; russian: link=no, Никола́й Никола́евич Муравьёв-Аму́рский; – ) was a Russian general, statesman and diplomat, ...
was the Governor-General. He annexed the Amur Territory to Russia, however, on the spot he showed unbridled despotism and extreme cruelty. Since the opening of communication along the Amur in 1854, on the way from St. Petersburg to the Pacific Ocean, the old Yakutsk tract began to decline. The population of the city is 28,000, of them there were 3,768 exiles.
In 1879, on July 4 and 6, a fire burned out of control, destroying the palace of the Governor General, and the principal administrative and municipal offices. Many of the other public buildings, including the government archives, the library, and the museum of the Siberian section of the Russian Geographical Society
The Russian Geographical Society (russian: Ру́сское географи́ческое о́бщество «РГО»), or RGO, is a learned society based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It promotes geography, exploration and nature protection wi ...
, were completely ruined. Three-quarters of the city was destroyed, including approximately 4,000 houses. The city quickly rebounded, installing electricity in 1896. The first theater was built in 1897 and a major train station opened in 1898. The first train arrived in Irkutsk on August 16 of that year. By 1900, the city had earned the nickname of "The Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. ...
of Siberia."
During the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, which broke out after the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
, Irkutsk became the site of many furious, bloody clashes between the " White movement" and the "Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
", known as the "Reds". In 1920, Aleksandr Kolchak
Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak (russian: link=no, Александр Васильевич Колчак; – 7 February 1920) was an Imperial Russian admiral, military leader and polar explorer who served in the Imperial Russian Navy and fough ...
, the once-feared commander of the largest contingent of anti-Bolshevik forces, was executed in Irkutsk. This effectively destroyed the anti-Bolshevik resistance.
Irkutsk was the administrative center of the short-lived East Siberian Oblast The East Siberian Oblast was an early oblast of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, which existed from December 5, 1936 to September 26, 1937. It was created when the East Siberian Krai was divided into the East Siberian Oblast and th ...
, from 1936 to 1937. The city subsequently became the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast
Irkutsk Oblast (russian: Ирку́тская о́бласть, Irkutskaya oblast; bua, Эрхүү можо, Erkhüü mojo) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast), located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of the Angara, Lena, and ...
, after East Siberian Oblast was divided into Chita Oblast
Chita Oblast ( rus, Чити́нская о́бласть, r=Čitínskaja óblastj, p=tɕɪˈtʲinskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) was a federal subject of Russia (an oblast) in southeast Siberia, Russia. Its administrative center was the city of Chita. ...
and Irkutsk Oblast.
During the communist years, the industrialization of Irkutsk and Siberia in general was strongly encouraged. The large Irkutsk Reservoir was built on the Angara River
The Angara ( Buryat and mn, Ангар, ''Angar'', "Cleft"; russian: Ангара́, ''Angará'') is a major river in Siberia, which traces a course through Russia's Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. It drains out of Lake Baikal and is ...
between 1950 and 1959 in order to generate hydroelectric power and facilitate industrial development.
 The Epiphany Cathedral, the governor's palace, a school of medicine, a museum, a military hospital and the crown factories are among the public institutions and buildings. The
The Epiphany Cathedral, the governor's palace, a school of medicine, a museum, a military hospital and the crown factories are among the public institutions and buildings. The Aleksandr Kolchak
Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak (russian: link=no, Александр Васильевич Колчак; – 7 February 1920) was an Imperial Russian admiral, military leader and polar explorer who served in the Imperial Russian Navy and fough ...
monument, designed by Vyacheslav Klykov
Vyacheslav Mikhailovich Klykov (russian: Вячесла́в Миха́йлович Клы́ков; 19 October 1939 — 2 June 2006) was a Russian sculptor who specialized in public monuments to key figures of national history and culture.
He was ...
, was unveiled in 2004. On July 27, 2004, the Irkutsk Synagogue (1881) was gutted by a fire.
In December 2016, 74 people in Irkutsk died in a mass methanol poisoning, after drinking this toxic alcohol substitute.
In 2018, the BBC reported that men in Irkutsk had an average life span of only 63. The society had declined and their health had suffered markedly
In October 2021, it was reported that armed Russian OMON (Special Purpose Mobile Unit of the Russian National Guard) officers physically assaulted and tortured two Jehovah’s Witness couples as part of a round up of Jehovah’s Witnesses in the city. Despite the persecution, the Jehovah's Witnesses continue their neutral stand on politics.
Geography
Irkutsk is located about to the south-east ofKrasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk ( ; rus, Красноя́рск, a=Ru-Красноярск2.ogg, p=krəsnɐˈjarsk) (in semantic translation - Red Ravine City) is the largest city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yen ...
, and about north of Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar (; mn, Улаанбаатар, , "Red Hero"), previously anglicized as Ulan Bator, is the capital and most populous city of Mongolia. It is the coldest capital city in the world, on average. The municipality is located in north c ...
, the capital of Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
. The city proper lies on the Angara River
The Angara ( Buryat and mn, Ангар, ''Angar'', "Cleft"; russian: Ангара́, ''Angará'') is a major river in Siberia, which traces a course through Russia's Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. It drains out of Lake Baikal and is ...
, a tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
of the Yenisei
The Yenisey (russian: Енисе́й, ''Yeniséy''; mn, Горлог мөрөн, ''Gorlog mörön''; Buryat: Горлог мүрэн, ''Gorlog müren''; Tuvan: Улуг-Хем, ''Uluğ-Hem''; Khakas: Ким суғ, ''Kim suğ''; Ket: Ӄук ...
, below its outflow from Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, I ...
and on the bank opposite the suburb of Glaskovsk. The river, wide, is crossed by the Irkutsk Hydroelectric Dam and three other bridges downstream.
The Irkut River
The Irkut (russian: Ирку́т; Buryat and mn, Эрхүү гол, ''Erhüü go''l) is a river in the Buryat Republic and Irkutsk Oblast of Russia. It is a left tributary of the Angara. It flows out of lake Ilchir which is situated 50 km ...
, from which the town takes its name, is a smaller river that joins the Angara directly opposite the city. The main portion of the city is separated from several landmarks—the monastery, the fort and the port, as well as its suburbs—by another tributary, the Ida (or Ushakovka) River. The two main parts of Irkutsk are customarily referred to as the "left bank" and the "right bank", with respect to the flow of the Angara River.
Irkutsk is situated in a landscape of rolling hills within the thick taiga
Taiga (; rus, тайга́, p=tɐjˈɡa; relates to Mongolic and Turkic languages), generally referred to in North America as a boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces ...
that is typical in Eastern Siberia.
The population has been shrinking since the late 1980s: . According to the regional plan, Irkutsk city will be combined with its neighboring industrial towns of Shelekhov
Shelekhov ( rus, Шелехов, p=ˈʂelʲɪxəf) is a town and the administrative center of Shelekhovsky District in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Irkutsk, the administrative center of the oblast. It is located on the plains bet ...
and Angarsk
Angarsk ( rus, Ангарск, p=ɐnˈgarsk) is a city and the administrative center of Angarsky District of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Kitoy River, from Irkutsk, the administrative center of the oblast. Population:
History
It ...
to form a metropolitan area with a total population of over a million.
Urban layout
Yasak
''Yasak'' or ''yasaq'', sometimes ''iasak'', (russian: ясак; akin to Yassa) is a Turkic word for "tribute" that was used in Imperial Russia to designate fur tribute exacted from the indigenous peoples of Siberia.
Origin
The origins of yasa ...
, a tax collected from the local population with fur. The architectural appearance of present-day Irkutsk has been born since the days of the wooden prison. The historic center of the city is now concentrated in its place. By the beginning of the 18th century, it had turned into a massive and developed wooden fortress, which protected the inhabitants from the raids of nomads. A major fire of 1716 almost completely destroyed the fortifications, but in just a year new ones were built, already made of stone. Of the buildings on the territory of the Irkutsk Kremlin of that time, the Savior Church has survived, the stone building of which was laid in 1706 in the north-western corner of the fort. Along with the Epiphany Cathedral, erected behind the eastern wall of the fortress and also preserved to this day, this is one of the oldest stone building in Siberia. The protective palisade and the moat, which once defended the Irkutsk fortress from the south, from the Angara bank to the Ushakovka River, existed until the middle of the 18th century. Arising in such a place, in the absence of administrative regulation, early Irkutsk was built up only for reasons of expediency determined by the homeowners. The courtyards were located in convenient areas, initially there were no streets at all, the buildings approached the driveways with random turns and only with subsequent alterations were turned around with front facades. The first settlers did not orientate their houses in relation to neighboring buildings either. When building a new house, the owners usually adhered only to the orientation of the windows to the south side. This is how the layout of the oldest part of the city took shape—from Angara to modern Karl Marx Street: the main directions of the streets repeat the outlines of the coastline, which, in turn, are crossed by transverse passages connecting the outskirts of the city with the center and overlooking the Angara bank. Until now, in the location of the central streets, the curvature, the disparity of the quarters formed by them, the semi-spontaneous process of their formation that once took place can be seen. This is especially noticeable in the example of Basninskaya Street (now Sverdlova Street), which they tried to straighten with each new attempt to streamline the development. And it simply repeated the outlines of the log that once was here, formed, possibly, by the old lady of the Gryaznushka river, which connected Ushakovka and Angara.
In 1726, defensive fortifications (palisade) were built in Irkutsk, behind which the barracks of the local garrison were taken out. The construction of the palisade changed the process of the spontaneous evolution of buildings and influenced the formation of the city's layout in the most significant way. After the fortification was dismantled in 1790, a complete mismatch of street directions in the old and new parts of the city was revealed.
The state of development of the "pre-palisade" period is reflected in the first of the known plans of Irkutsk in 1729. Its main advantage is the fixation of the city's borders, which ran along the line of the modern Karl Marx Street. Between 1729 and 1768 in the space between Angara and Ushakovka, the first "zapalisadny" row of blocks is formed. A spontaneous settlement appears near the soldiers' barracks, first along the roads that approached the Mill and Overseas gates, and then between them. The development proceeded unevenly, the closest to the current state at that time were the fragments of buildings located in the area of Zamorskaya (Lenin st.) And Institutskaya (Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsii st.) Streets. Now it is, roughly, quarters No. 90, 91, 92.
The last third of the 18th century was extremely significant both for the history of the city as a whole and for the formation of its buildings. With the formation of the Irkutsk province in 1764, Irkutsk became the center of the largest region in Russia—Eastern Siberia, which included Transbaikalia, Yakutia, the entire northeast to the Pacific Ocean. Irkutsk needed to expand, and by that time there were no enemies ready to lay claim to the city. The palisade was dismantled, and in its place appeared Bolshaya Preshpektnaya Street, now Karla Marxa Street, the only straight street in modern Irkutsk. The devastating fire of 1879 made its own adjustments to the construction laws as it was from here that the border began, beyond which it was forbidden to build from wood. This in fact has divided the old Irkutsk into two parts: closer to the Angara river, mainly stone buildings remained, and on the other side, where there were once outskirts, the wooden Irkutsk grew.
Climate
Irkutsk originally had a borderline subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
''Dwc''). Since 2000, the temperatures have resembled a humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Köppen climate classification ''Dwb''). Snow cover has disappeared earlier, from late April in the 1930s to late March in the 1980s. Discontinuous permafrost depth had decreased from 200 m to 100 m during the same period.
Irkutsk is characterized by an extreme variation of temperatures between seasons. It can be very warm in the summer, and very cold in the winter. However, Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, I ...
has a tempering effect, giving Irkutsk temperatures that are less extreme than elsewhere in Siberia. The warmest month of the year is July, when the average temperature is ; the highest temperature recorded being . The coldest month of the year is January, when the average temperature is , and record low of . Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
varies widely throughout the year, with July being the wettest month, when precipitation averages . The driest month is February, when precipitation averages only . Almost all precipitation during the Siberian winter falls as fluffy, dry snow.
Administrative and municipal status
Irkutsk is theadministrative center
An administrative center is a seat of regional administration or local government, or a county town, or the place where the central administration of a commune is located.
In countries with French as administrative language (such as Belgium, L ...
of the oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdom ...
and, within the framework of administrative divisions, it also serves as the administrative center of Irkutsky District
Irkutsky District (russian: Ирку́тский райо́н) is an administrative district, one of the thirty-three in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia.Charter of Irkutsk Oblast, Article 13 Municipally, it is incorporated as Irkutsky Municipal Dist ...
,Law #49-OZ even though it is not a part of it. As an administrative division, it is incorporated separately as the City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be de ...
of IrkutskCharter of Irkutsk Oblast—an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
. As a municipal division, the City of Irkutsk is incorporated as Irkutsk Urban Okrug.Law #88-oz
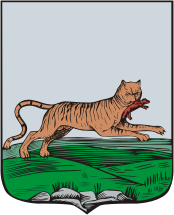
Coat of arms
 The
The coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in it ...
of Irkutsk features an old symbol of Dauria
Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia ( rus, Забайка́лье, r=Zabaykalye, p=zəbɐjˈkalʲjɪ), or Dauria (, ''Dauriya'') is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" (trans-) Lake Baikal in Far Eastern Russia.
The steppe and ...
: a Siberian tiger
The Siberian tiger or Amur tiger is a population of the tiger subspecies ''Panthera tigris tigris'' native to the Russian Far East, Northeast China and possibly North Korea. It once ranged throughout the Korean Peninsula, but currently inhabi ...
with a sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kaz ...
in his mouth. When the coat of arms was devised in 1690, the animal was described as a tiger ("babr", a bookish word of Persian derivation) with a sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kaz ...
in his mouth. This image had been used by the Yakutsk
Yakutsk (russian: Якутск, p=jɪˈkutsk; sah, Дьокуускай, translit=Djokuuskay, ) is the capital city of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located about south of the Arctic Circle. Fueled by the mining industry, Yakutsk has become one ...
customs office from about 1642. It has its origin in a seal of the Siberia Khanate
The Khanate of Sibir (also Khanate of Turan,
sty, Себер ханлыгы) was a Tatar Khanate located in southwestern Siberia with a Turco-Mongol ruling class. Throughout its history, members of the Shaybanid and Taibugid dynasties often co ...
representing a sable and showcasing the fact that Siberia (or rather Yugra
Yugra or Iuhra (Old Russian Югра ''Jugra''; Byzantine Greek Οὔγγροι ''Oὔggroi''; la, OngariaeMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. (Actually, the English word "sable" is derived from the Russian "sobol").
By the mid-19th century, the word "babr" had fallen out of common usage, but it was still recorded in the Armorial of the Russian Empire
A roll of arms (or armorial) is a collection of coats of arms, usually consisting of rows of painted pictures of shields, each shield accompanied by the name of the person bearing the arms.
The oldest extant armorials date to the mid-13th centur ...
. Furthermore, the tigers became extinct in this part of Siberia. In the 1870s, a high-placed French heraldist with a limited command of Russian assumed that "babr" was a misspelling of "bobr", the Russian word for "beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers a ...
", and changed the wording accordingly. This modification engendered a long dispute between the local authorities, who were so confused by the revised description that they started to depict the "babr" as a fabulous animal, half-tiger and half-beaver.
The Soviets abolished the image altogether, but it was restored following the dissolution of the Soviet Union.
Economy
Energy
The 662.4 MWIrkutsk Hydroelectric Power Station
The Irkutsk Hydroelectric Power Station (Irkutsk HPS) is a rock-fill dam on the Angara River with an adjacent hydroelectric power station. It is located adjacent to Irkutsk, Irkutsk Oblast in Russia and is the first dam on the Angara cascades. C ...
was the first cascade hydroelectric power station in the Irkutsk region. The construction of the dam started in 1950 and finished in 1958.
Industry
The largest industry in Irkutsk is Irkut, the Irkutsk Aviation Industrial Association, which was set up in 1932 in the Transbaykal region of theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
. It is best known as being the manufacturer of the Su-30
The Sukhoi Su-30 (russian: Сухой Су-30; NATO reporting name: Flanker-C/G/H) is a twin-engine, two-seat supermaneuverable fighter aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by Russia's Sukhoi Aviation Corporation. It is a multirole fighte ...
family of interceptor
Interceptor may refer to:
Vehicles
* Interceptor aircraft (or simply "interceptor"), a type of point defense fighter aircraft designed specifically to intercept and destroy enemy aircraft
* Ford Crown Victoria Police Interceptor, a police car
* ...
/ground-attack aircraft
An attack aircraft, strike aircraft, or attack bomber is a tactical military aircraft that has a primary role of carrying out airstrikes with greater precision than bombers, and is prepared to encounter strong low-level air defenses while pres ...
. The Russian government has merged Irkut with Ilyushin
The public joint stock company Ilyushin Aviation Complex, operating as Ilyushin (russian: Илью́шин) or as Ilyushin Design Bureau, is a former Soviet and now a Russian aircraft manufacturer and design bureau, founded in 1933 by Sergey V ...
, Mikoyan
Russian Aircraft Corporation "MiG" (russian: Российская самолётостроительная корпорация „МиГ“, Rossiyskaya samolyotostroitel'naya korporatsiya "MiG"), commonly known as Mikoyan and MiG, was a Russi ...
, Sukhoi
The JSC Sukhoi Company (russian: ПАО «Компания „Сухой“», ) is a Russian aircraft manufacturer (formerly Soviet Union, Soviet), headquartered in Begovoy District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow, that designs both civil ...
, Tupolev
Tupolev (russian: Ту́полев, ), officially Joint Stock Company Tupolev, is a Russian aerospace and defence company headquartered in Basmanny District, Moscow.
Tupolev is successor to the Soviet Tupolev Design Bureau ( OKB-156, design of ...
, and Yakovlev
The JSC A.S. Yakovlev Design Bureau (russian: ОАО Опытно-конструкторское бюро им. А.С. Яковлева) is a Russian aircraft designer and manufacturer (design office prefix Yak). Its head office is in Aeroport D ...
into a new company named United Aircraft Building Corporation
, former_name = OJSC United Aircraft Corporation (2006–2015)
, type = Public, PJSC
, traded_as =
, industry = Aerospace, defense
, predecessor = Ilyushin, Irkut, Mikoyan, Sukhoi, Tupolev, Yakovlev
, founded =
, founder = Vladimir P ...
.Russian Aircraft Industry Seeks Revival Through Merger" ''
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
.'' February 22, 2006
There is the Irkutsk Aluminium Smelter which belongs to the Rusal
United Company RUSAL, international public joint-stock company (russian: МКПАО «ОК РУСАЛ», MKPAO «ОК RUSAL») is the world's second largest aluminium company by primary production output (as of 2016). It was the largest until ov ...
Company.
Transportation
Important roads and railways like theTrans-Siberian Highway
The Trans-Siberian Highway is the unofficial name for a network of federal highways that span the width of Russia from the Baltic Sea of the Atlantic Ocean to the Sea of Japan. In the Asian Highway Network, the route is known as AH6. It stretche ...
(Federal M53 and M55 Highways) and Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the eas ...
connect Irkutsk to other regions in Russia and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
. The city is also served by the Irkutsk International Airport
Irkutsk International Airport ( Russian: Международный Аэропорт Иркутск) is an international airport on the outskirts of Irkutsk, Russia, at a distance of 60 kilometers (37 miles) from Lake Baikal.
Operations
The a ...
and the smaller Irkutsk Northwest Airport
Irkutsk Northwest Airport is an airport in Russia located 11 km northwest of Irkutsk. It is a flyaway airfield for the Irkutsk Aviation Plant, and has no parallel taxiways. It is also known as ''Irkutsk II'' airport, and occasionally serve ...
.
The Federal road and railway to Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea ...
pass through the other side of the Angara River from central Irkutsk.
Trams
A tram (called a streetcar or trolley in North America) is a rail vehicle that travels on tramway tracks on public urban streets; some include segments on segregated right-of-way. The tramlines or networks operated as public transport are ...
are one major mode of public transit in Irkutsk. Other modes are trolleybus, bus, fixed-route taxi (marshrutka
''Marshrutka''
File:Иркутск. Улица Ленина 2.JPG, Trolleybus
File:Иркутск. Улица Седова 1.JPG, Bus on Sedov Street
Irkutsk Institute of Rare and Precious Metals and Diamonds (Irgiredmet)
part of the Petropavlovsk Group of Companies., and the Vostoksibacademcenter of th
Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences
that publishes the Project Baikal journal.
 Irkutsk is a point of interest for tourists with its numerous museums and old architecture. The Taltsy Museum (russian: Тальцы), located on the Angara South of Irkutsk, is an open-air museum of Siberian
Irkutsk is a point of interest for tourists with its numerous museums and old architecture. The Taltsy Museum (russian: Тальцы), located on the Angara South of Irkutsk, is an open-air museum of Siberian

Official website of Irkutsk
Irkutsk Business Directory
Irkutsk city architecture views
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Governorate Populated lakeshore places in Russia Populated places established in 1686 World Heritage Tentative List 1686 establishments in Russia
Health
Despite its remoteness, Irkutsk was reported in 2004 to have the highestHIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
infection rate in Russia. Tens of thousands of drug addicts, mostly ethnic Russians in their mid to late teens are infected. The number of reported AIDS cases increased by more than 10,000% during the 1999–2000 period. Although the epidemic, which started in 1999, is reported to have slowed down, Irkutsk will lose tens of thousands of its working age population from 2010 onwards. This is one of the reasons Irkutsk's male life expectancy, at 53 years, is one of the lowest in all of Russia. Preventive measures are in place to prevent the spread of the epidemic to the generation which was born after the breakup of the USSR.
Culture
Television and mass media
There are many state-owned and privately owned television stations in Irkutsk, including state company IGTRK and private ones, such as AS Baikal TV, TV company AIST, TV company Gorod, and also other media outlets, like the VSP Newspaper Agency. There is also a live webcam broadcasting from the city center.Education
Irkutsk is home to the East Siberian Education Academy (since 1909),Irkutsk State University
Irkutsk State University (russian: Ирку́тский госуда́рственный университе́т) was founded in October 1918 in Irkutsk, Siberia. Nowadays Irkutsk State University is a large scientific and educational institut ...
(1918), Irkutsk State Medical University (1918), Baykalsky State University of Economics and Law
Baikal State University (BSU),
BSU) also known as Baikal National University of Economics and Law, is a Irkutsk State Technical University National Research Irkutsk State Technical University (full name in Russian: ''Иркутский национальный исследовательский технический университет''), formerly Irkutsk State Technical Uni ...
(since 1939), BSU) also known as Baikal National University of Economics and Law, is a Irkutsk State Technical University National Research Irkutsk State Technical University (full name in Russian: ''Иркутский национальный исследовательский технический университет''), formerly Irkutsk State Technical Uni ...
Irkutsk State Academy of Agriculture
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat and mn, Эрхүү, ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 617,473 as of the 2010 Census, Irkutsk is the 25th-larges ...
, Irkutsk State Linguistic University
Irkutsk State Linguistic University (russian: Иркутский государственный лингвистический университет (ИГЛУ)) was a university in Irkutsk, Siberia in eastern Russia founded in 1948.
In 2016, i ...
(1948), Irkutsk State Railway Transport University
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat and mn, Эрхүү, ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 617,473 as of the 2010 Census, Irkutsk is the 25th-larges ...
(since 1975), and a number of private colleges: Siberian Institute of Law, Economics and Management
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
(since 1993), Institute of Economics of ISTU
An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations ( research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body.
In some countries, institutes ca ...
(since 1996), and others.
Science
As Irkutsk is within the influence of the Siberian Division of theRussian Academy of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; russian: Росси́йская акаде́мия нау́к (РАН) ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across t ...
, there are nine research institutes located in the Irkutsk Academgorodok suburb: the Institute of Geography, the Energy System Institute
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
, the Institute of Geochemistry Institute of Geochemistry (), which is located in Guiyang, the capital of Guizhou Province of China, was founded in 1966 by the Beijing Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (now Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sc ...
, the Institute of System Dynamics and Control Theory
An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations ( research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body.
In some countries, institutes ca ...
, the Earth's Crust Institute, the Solar-Terrestrial Physics Institute, the Institute of Chemistry The Royal Institute of Chemistry was a British scientific organisation. Founded in 1877 as the Institute of Chemistry of Great Britain and Ireland (ICGBI), its role was to focus on qualifications and the professional status of chemists, and its aim ...
, the Limnological Institute
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems.
The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristic ...
(formerly located on Lake Baikal's shore), the Institute of Plant Physics
An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations ( research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body.
In some countries, institutes ca ...
, Laser Physics Institute
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The fir ...
(a Branch of the Institute of Laser Physics in Novosibirsk).
A number of institutes conduct research within Irkutsk State University
Irkutsk State University (russian: Ирку́тский госуда́рственный университе́т) was founded in October 1918 in Irkutsk, Siberia. Nowadays Irkutsk State University is a large scientific and educational institut ...
: the Institute of Biology, the Institute of Oil and Coal Chemistry and Synthesis, the Laboratory of Quantum Chemistry, the Institute of Applied Physics, the Interregional Institute of Social Studies, the Astronomical Observatory, and the Botanical Gardens.
The East-Siberian Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences is also located in Irkutsk and is represented by the following research organizations: the Scientific Center for Medical Ecology, the Institute for Paediatrics and Human Reproduction, the Institute for Microbiology and Epidemiology, the Institute for Medicine of the Workplace and Human Ecology, the Institute of Reconstructive and Restorative Surgery, the Institute of Surgery, and the Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics. Also, the Fyodorov Eye Microsurgery Scientific and Technical Center Fyodorov or Fedorov (russian: Фёдоров, masculine) and Fyodorova or Fedorova (Фёдорова, feminine) is a common Russian last name that is derived from the given name Fyodor and literally means ''Fyodor's''. It is transliterated in Polis ...
has a branch in Irkutsk. Additionally, there are R&D institutes including GAZPROM
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the largest ...
R&D Institute (a Branch of a Moscow-based institute), thIrkutsk Institute of Rare and Precious Metals and Diamonds (Irgiredmet)
part of the Petropavlovsk Group of Companies., and the Vostoksibacademcenter of th
Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences
that publishes the Project Baikal journal.
Literature
Irkutsk was home to the well-known Russian writerValentin Rasputin
Valentin Grigoriyevich Rasputin (; russian: Валентин Григорьевич Распутин; 15 March 193714 March 2015) was a Russian writer. He was born and lived much of his life in the Irkutsk Oblast in Eastern Siberia. Rasputin's w ...
; many of his novels and stories take place in the Angara
The Angara ( Buryat and mn, Ангар, ''Angar'', "Cleft"; russian: Ангара́, ''Angará'') is a major river in Siberia, which traces a course through Russia's Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. It drains out of Lake Baikal and is ...
Valley. An essay on the cultural history of Irkutsk (and another one about the nearby Lake Baikal) is included in Rasputin's non-fiction collection Siberia, Siberia
''Siberia, Siberia'' (russian: Сибирь, Сибирь...) is a non-fiction book by the Russian writer Valentin Rasputin. It was originally published in Russian in 1991 by Molodaya Gvardiya (Young Guard). The second and third editions appear ...
, which is also available in an English translation. Irkutsk also figures prominently in descriptions by foreign travelers, including the so-called British "Blind Traveler" James Holman
James Holman FRS (15 October 1786 – 29 July 1857), known as the "Blind Traveller," was a British adventurer, author and social observer, best known for his writings on his extensive travels. Completely blind and experiencing pain and limi ...
, who was suspected of spying and conducted back forcibly to the frontiers of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
.
Museums
 Irkutsk is a point of interest for tourists with its numerous museums and old architecture. The Taltsy Museum (russian: Тальцы), located on the Angara South of Irkutsk, is an open-air museum of Siberian
Irkutsk is a point of interest for tourists with its numerous museums and old architecture. The Taltsy Museum (russian: Тальцы), located on the Angara South of Irkutsk, is an open-air museum of Siberian traditional architecture
Vernacular architecture is building done outside any academic tradition, and without professional guidance. This category encompasses a wide range and variety of building types, with differing methods of construction, from around the world, bo ...
. Numerous old wooden buildings from villages in the Angara valley, which have been flooded after the construction of the Bratsk Dam
The Bratsk Hydroelectric Power Station (also referred to as The ''50 years of Great October'' Dam) is a concrete gravity dam on the Angara River and adjacent hydroelectric power station. It is the second level of the Angara River hydroelectric s ...
and Ust-Ilimsk Dam
The Ust-Ilimsk Hydroelectric Power Station (Ust-Ilimsk HPS) is a concrete gravity dam on the Angara River and adjacent hydroelectric power station. It is located near Ust-Ilimsk, Irkutsk Oblast in Russia and is the third dam on the Angara cascade ...
, have been transported to the museum and reassembled there. One of the centerpieces of the collection is a partial recreation of the 17th-century ''ostrog'' (fortress) of Ilimsk, which consists of the original Spasskaya Tower and the Church of Our Lady of Kazan transported from the flooded ''ostrog'' in the mid-1970s, to which an exact modern copy of another tower of the ''ostrog'' and the Southern wall of the fortress were added in the early 2000s.
The Botanic Garden of the Irkutsk State University
The Botanic Garden of the Irkutsk State University is a botanical garden, botanic garden in Irkutsk, Siberia, Russia.
It is the only botanic garden in Baikalian Siberia (the Lake Baikal region) and is known as the Irkutsk Botanic Garden. Its mis ...
known as the "Irkutsk Botanic Garden" is the only botanic garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
as a living museum
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical
History (derived ) is the systematic study and th ...
in Irkutsk Oblast and Baikalian Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
. Its mission is "to protect and enrich the flora of the Lake Baikal area and the world for people through public education, collection, propagation, research, and conservation of plants". The garden is mainly an educational and scientific tool for the Irkutsk State University
Irkutsk State University (russian: Ирку́тский госуда́рственный университе́т) was founded in October 1918 in Irkutsk, Siberia. Nowadays Irkutsk State University is a large scientific and educational institut ...
and maintains the largest plant collection of living plants in Eastern Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
(more than 5,000 plant taxa), a herbarium, and a seed bank. It occupies within Irkutsk city, West of Lake Baikal. It has a federal status of especially protected land and a nature memorial of Irkutsk.
Theaters
Irkutsk is also home to several theaters, including the Okhlopkov Drama Theater, one of Russia's oldest.Sports

Bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
is popular in the city. There are several clubs, most notably Baykal-Energiya
Baykal-Energiya (russian: Байкал-Энергия) is a bandy club from Irkutsk, Russia. The team plays in the Russian Bandy Super League, the highest level of Russian bandy.
It was founded in 1923 changing its name several times before beco ...
of the Russian Bandy Super League
The Russian Bandy Super League (russian: Чемпионат России по хоккею с мячом — Суперлига), is a men's professional bandy league in Russia, the top division of Russian bandy.
There is no definite rule which t ...
, which can draw spectator crowds of 30,000. It is also the centre of women's bandy in Russia with the club Rekord, which provides most players to the national team. In the national championship 2019, four teams were from Irkutsk and only two from the rest of the country.
In Irkutsk, there are 384 sports facilities, of which 200 are municipal ones. Among them there are 23 swimming pools, 14 ski bases, a sports palace, 154 courts, 165 gyms, an athletics arena, a racetrack, 7 stadiums— Trud, Rekord, Dynamo, Zenit, Aviator, Lokomotiv-2, sports complex of Irktusk and the main football arena—Lokomotiv.
2012 Women's Bandy World Championship
The Bandy World Championship for women 2012 was contested between 6 bandy playing countries. The championship was played in Irkutsk, Russia from 23 to 26 February. Sweden defeated Russia, 5-3, in the final-game.
Participating teams
*
*
*
*
*
*
V ...
was hosted in Irkutsk and received praise from Federation of International Bandy
The Federation of International Bandy (FIB; french: Fédération internationale de bandy, russian: Международная федерация хоккея с мячом, sv, Internationella Bandyförbundet) is the international governing bo ...
. 2014 Bandy World Championship
The 2014 Bandy World Championship was held between 26 January and 2 February 2014, in Irkutsk and Shelekhov, Russia. 17 nations participated in the tournament, playing in two divisions partitioned into two subdivisions. A team representing Somalia ...
was played in the city. The final of Russian Bandy Super League
The Russian Bandy Super League (russian: Чемпионат России по хоккею с мячом — Суперлига), is a men's professional bandy league in Russia, the top division of Russian bandy.
There is no definite rule which t ...
2016 was played at Rekord Stadium
Rekord Stadium is a sports venue in Irkutsk. It is the home of Baykal-Energiya.
References
Bandy venues in Russia
Sport in Irkutsk
{{Russia-sports-venue-stub ...
. The 2019 Bandy World Championship
2019 Bandy World Championship was held in Vänersborg, Sweden, between men's national teams among bandy playing nations. It was the XXXIXth Bandy World Championship.
Host selection
The tournament was supposed to be held in Irkutsk in Russia. How ...
was scheduled to also be hosted in Irkutsk. The decision was reconsidered, though. Then it was thought that Irkutsk might get the right to host the 2020 tournament instead, if FIB was given guarantees that the planned indoor arena would be ready for use in time. It will also be an indoor speed skating arena. Its construction started in October 2018 and is expected to be ready for use by March 2020, just in time for the Bandy World Championship.
Twin towns – sister cities
Irkutsk istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Częstochowa
Częstochowa ( , ; german: Tschenstochau, Czenstochau; la, Czanstochova) is a city in southern Poland on the Warta River with 214,342 inhabitants, making it the thirteenth-largest city in Poland. It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship (admi ...
, Poland
* Eugene
Eugene may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Eugene (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name
* Eugene (actress) (born 1981), Kim Yoo-jin, South Korean actress and former member of the sin ...
, United States
* Gangneung
Gangneung () is a municipal city in the province of Gangwon-do, on the east coast of South Korea. It has a population of 213,658 (as of 2017).Gangneung City (2003)Population & Households. Retrieved January 14, 2006. Gangneung is the economic ...
, South Korea
* Haute-Savoie
Haute-Savoie (; Arpitan: ''Savouè d'Amont'' or ''Hiôta-Savouè''; en, Upper Savoy) or '; it, Alta Savoia. is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region of Southeastern France, bordering both Switzerland and Italy. Its prefecture is ...
, France
* Kanazawa
is the capital city of Ishikawa Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 466,029 in 203,271 households, and a population density of 990 persons per km2. The total area of the city was .
Overview Cityscape
File:もてな ...
, Japan
* Karlovy Vary Region
The Karlovy Vary Region or Carlsbad Region ( cs, Karlovarský kraj, German: ''Karlsbader Region'') is an administrative unit ( cs, kraj) of the Czech Republic, located in the westernmost part of its historical region of Bohemia. It is named afte ...
, Czech Republic
* Pforzheim
Pforzheim () is a city of over 125,000 inhabitants in the federal state of Baden-Württemberg, in the southwest of Germany.
It is known for its jewelry and watch-making industry, and as such has gained the nickname "Goldstadt" ("Golden City") ...
, Germany
* Pordenone Province, Italy
* Prijedor
Prijedor ( sr-cyrl, Приједор, ) is a city and municipality located in the Republika Srpska entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. As of 2013, it has a population of 89,397 inhabitants within its administrative limits. Prijedor is situated in ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Primorje-Gorski Kotar County
Primorje-Gorski Kotar County ( hr, Primorsko-goranska županija, ) is a county in western Croatia that includes the Bay of Kvarner, the surrounding Northern Croatian Littoral, and the mountainous region of Gorski kotar. Its center is Rijeka. ...
, Croatia
* Shenyang, China
* Strömsund
Strömsund (; sma, Straejmie) is a locality and the seat of Strömsund Municipality in Jämtland County, Sweden with 3,589 inhabitants in 2010.
Stroms church (''Ströms kyrka'') was inaugurated in 1847.The Grand Hotel dates to 1909. The Court ...
, Sweden
* Ulaanbaatar
Ulaanbaatar (; mn, Улаанбаатар, , "Red Hero"), previously anglicized as Ulan Bator, is the capital and most populous city of Mongolia. It is the coldest capital city in the world, on average. The municipality is located in north c ...
, Mongolia
* Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest ci ...
, Belarus
Notable people
*Nikolai Polevoy
Nikolai Alekseevich Polevoy ( rus, Никола́й Алексе́евич Полево́й, r=Nikoláy Alekséevich Polevóy, ― ) was a controversial Russian editor, writer, translator, and historian; his brother was the critic and journalist ...
(1796–1846), editor, writer, translator and historian
*Innocent of Alaska
Saint Innocent of Alaska (August 26, 1797 – March 31, 1879, O.S.), also known as Saint Innocent Metropolitan of Moscow ( Russian: Святитель Иннокентий Митрополит Московский) was a Russian Orthodox mi ...
(1797-1879), archbishop, linguist, architect, missionary
*Vladimir Kornilov
Vice Admiral Vladimir Alexeyevich Kornilov (; 13 February 1806 – 17 October 1854) was a Russian naval officer who took part in the Crimean War and is known for his battle against the Pervaz-ı Bahrî in what is considered the first battle ...
(1806–1854), naval officer who took part in the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included t ...
*Alexei Pavlovich Fedchenko
Alexei Pavlovich Fedchenko (russian: Алексей Павлович Федченко;
31 August/15 September 1873), a.k.a. Alexei Pavlovich Fedtschenko, was a Russian naturalist and explorer well known for his travels in central Asia. Alterna ...
(1844–1873), naturalist and explorer
*Nikolay Vtorov
Nikolay Alexandrovich Vtorov (russian: Никола́й Алекса́ндрович Вто́ров; – 20 May 1918) was a Russian industrialist. According to a 2006 Forbes study, which excluded the ruling House of Romanov, he held the title ...
(1866–1918), industrialist
*Alexander Kolchak
Alexander Vasilyevich Kolchak (russian: link=no, Александр Васильевич Колчак; – 7 February 1920) was an Imperial Russian admiral, military leader and polar explorer who served in the Imperial Russian Navy and fough ...
(1874 -1920)) Russian Civil War leader, executed at Irkutsk
*Nikolay Okhlopkov
Nikolay Pavlovich Okhlopkov (russian: Никола́й Па́влович Охло́пков; 15 May 1900, in Irkutsk – 8 January 1967, in Moscow), was a Soviet and Russian actor and theatre director who patterned his work after Meyerhold. Pat ...
(1900–1967), Soviet actor and theatre director
* Mikhail Romm (1901–1971), Soviet film director
*Nikolay Kamov
Nikolai Ilyich Kamov (russian: Никола́й Ильи́ч Ка́мов; 24 November 1973) was a Soviet aerospace engineer, a pioneer in the design of helicopters, and founder of the Kamov helicopter design bureau.
Biography
Kamov was bor ...
(1902–1973), leading constructor of the Soviet-Russian Kamov helicopter design bureau
*Mikhail Mil
Mikhail Leontyevich Mil (russian: Михаи́л Лео́нтьевич Миль; 22 November 1909 – 31 January 1970) was a Russian aerospace engineer and scientist. He was the founder and general designer of the Mil Moscow Helicopter Plan ...
(1909–1970), Soviet aerospace engineer
* Konstantin Vyrupayev (1930–2012), Soviet wrestler and Olympic Champion
*Boris Volynov
Boris Valentinovich Volynov (russian: Бори́с Валенти́нович Волы́нов; born 18 December 1934) is a Soviet cosmonaut who flew two space missions of the Soyuz programme: Soyuz 5, and Soyuz 21. Following the death of Alexei ...
(born 1934), Soviet cosmonaut
*Alexander Vampilov
Alexander Valentinovich Vampilov (russian: Александр Валентинович Вампилов) (19 August 1937 – 17 August 1972) was a Soviet playwright. His play ''The Elder Son'' was first performed in 1969, and became a national succ ...
(1937–1972), Soviet playwright
*Rudolf Nureyev
Rudolf Khametovich Nureyev ( ; Tatar/ Bashkir: Рудольф Хәмит улы Нуриев; rus, Рудо́льф Хаме́тович Нуре́ев, p=rʊˈdolʲf xɐˈmʲetəvʲɪtɕ nʊˈrʲejɪf; 17 March 19386 January 1993) was a Soviet ...
(1938–1993), Soviet ballet and contemporary dancer and choreographer
*Olga Buyanova
Olga Vladimirovna Buyanova (russian: Ольга Владимировна Буянова; born March 27, 1954 in Irkutsk, RSFSR) is an Honored Master of Sports coach in Rhythmic gymnastics of the USSR and Russia.
Personal life
Olga Vladimirovn ...
(born 1954), Honored Master of Sports coach in Rhythmic gymnastics of the USSR and Russia
*Oleksandr Shlapak
Oleksandr Vіtaliyovych Shlapak ( uk, Олександр Віталійович Шлапак; born 1 January 1960) is a Ukrainian politician, bureaucrat, and former Minister of Finance of Ukraine.
Biography
He was born to Vitaliy Fedorovich ...
(born 1960), Ukrainian politician, bureaucrat, and former Minister of Finance of Ukraine
*Anatoli Ivanishin
Anatoli Alekseyevich Ivanishin (russian: link=no, Анатолий Алексеевич Иванишин; born 15 January 1969) is a former Russian cosmonaut. His first visit to space was to the International Space Station on board the Soyuz TMA ...
(born 1969), cosmonaut
*Oxana Kostina
Oksana Alexandrovna Kostina (russian: Оксана Александровна Костина; 15 April 1972 – 11 February 1993) was a Soviet and Russian individual rhythmic gymnast. She was the 1992 World All-around champion and 1992 Europ ...
(1972–1993), Soviet individual rhythmic gymnast
*Aleksandr Averbukh
Aleksandr "Alex" Valeryevich Averbukh ( he, אלכס אברבוך, russian: Александр Валерьевич Авербух; born October 1, 1974) is a retired Russian decathlete and Israeli Olympic athlete, who competed in the pole vault. ...
(born 1974), Israeli Olympic athlete who competed in the pole vault
*Denis Matsuev
Denis Leonidovich Matsuev ( rus, Дени́с Леони́дович Мацу́ев /ma'tsujef/; born June 11, 1975) is a Russian classical pianist and occasional jazz performer.
Biography
Born in Irkutsk, Soviet Union, Matsuev is the only child o ...
(born 1975), classical pianist
* Maria Bruntseva (born 1980), volleyball player
*Nina Kraviz
Nina Kraviz (russian: Нина Кравиц, Nina Kravits) is a Russian DJ, music producer and singer.
Early life and career
Kraviz was born and raised in Irkutsk, Siberia, Russia. She moved to Moscow to study dentistry where she later gained ...
(born 1982), dj, musician, producer
*Olga Zhitova
Olga Zhitova (born 25 July 1983) is a retired Russian volleyball player. She was a member of the Russian team that won the gold medal at the 2006 FIVB Women's World Championship
The 2006 FIVB Volleyball Women's World Championship, FIVB Women's ...
(born 1983), volleyball player
* Olga Kurban (born 1987), heptathlete
*Alexey Negodaylo
Alexey Aleksandrovich Negodaylo (russian: Алексей Александрович Негодайло; born 28 May 1989) is a Russian bobsledder who has competed since 2010.
Career
Negodaylo was part of a four-man Russian team who originally wo ...
(born 1989), bobsledder
*Angelina Zhuk-Krasnova
Angelina Zhuk-Krasnova ( rus, Ангели́на Серге́евна Жук-Красно́ва, , ɐnɡʲɪˈlʲinə sʲɪrˈɡʲe(j)ɪvnə ʐuk krɐsˈnovə; born 7 February 1991) is a Russian athlete specialising in the pole vault
Pole va ...
(born 1991), athlete specializing in the pole vault
*Darya Dmitriyeva
Darya Andreyevna Dmitriyeva ( rus, Дарья Андреевна Дмитриева, , ˈdarʲɪ̯ə ˈdmʲitrʲɪ(ɪ̯)ɪvə; born 22 June 1993) is a Russian rhythmic gymnast. She is the 2012 Olympic all-around silver medalist, the 2010 Worl ...
(born 1993), Russian rhythmic gymnast
*Nazí Paikidze
Nazí Paikidze, sometimes also referred to as Nazí Paikidze-Barnes ( ka, ნაზი პაიკიძე, ''Nazí Ṗaiḳiʒe'', ; russian: Нази Нодаровна Паикидзе-Барнс, , born 27 October 1993), is a Russian-born ...
(born 1993), Georgian-American chess player
See also
*Immaculate Heart of Mary Cathedral, Irkutsk
The Immaculate Conception is the belief that the Virgin Mary was free of original sin from the moment of her conception.
It is one of the four Marian dogmas of the Catholic Church, meaning that it is held to be a divinely revealed truth wh ...
*Irkutskoye Slovo
''Irkutskoye Slovo'' (Irkutsk Word; Иркутское слово) was a Menshevik-oriented weekly newspaper in Russia, published in Irkutsk from 1911 to 1912. Its publisher, Rozhkov, had joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party
The ...
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * *Brumfield, William. ''Irkutsk: Architectural Heritage in Photographs'' // Moscow: Tri Kvadrata Publishing, 2006. * Her Majesty — Queen of Siberia // Publishers Korobov. — Irkutsk, 2008.External links
*Official website of Irkutsk
Irkutsk Business Directory
Irkutsk city architecture views
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Governorate Populated lakeshore places in Russia Populated places established in 1686 World Heritage Tentative List 1686 establishments in Russia