Inuit History on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar
 The exchanges that accompanied the arrival and colonization by the Europeans greatly damaged Inuit way of life. Mass death was caused by the new infectious diseases carried by whalers and explorers, to which the Indigenous peoples had no acquired immunity. The high mortality rate contributed to the enormous social disruptions caused by the distorting effect of Europeans' material wealth and the introduction of different materials. Nonetheless, Inuit society in the higher latitudes largely remained in isolation during the 19th century.
The
The exchanges that accompanied the arrival and colonization by the Europeans greatly damaged Inuit way of life. Mass death was caused by the new infectious diseases carried by whalers and explorers, to which the Indigenous peoples had no acquired immunity. The high mortality rate contributed to the enormous social disruptions caused by the distorting effect of Europeans' material wealth and the introduction of different materials. Nonetheless, Inuit society in the higher latitudes largely remained in isolation during the 19th century.
The
 In the 1960s, the Canadian government funded the establishment of
In the 1960s, the Canadian government funded the establishment of
 Inuit speak Inupiaq (Inupiatun),
Inuit speak Inupiaq (Inupiatun),
 Inuit hunted
Inuit hunted
 During the winter, certain Inuit lived in a temporary shelter made from snow called an ''
During the winter, certain Inuit lived in a temporary shelter made from snow called an ''
 The
The
 The environment in which Inuit lived inspired a
The environment in which Inuit lived inspired a
 The
The
 The
The
 Inuit art, carving, print making, textiles and
Inuit art, carving, print making, textiles and  Although Inuit life has changed significantly over the past century, many traditions continue. '' Inuit Qaujimajatuqangit'', or
Although Inuit life has changed significantly over the past century, many traditions continue. '' Inuit Qaujimajatuqangit'', or  Visual and performing arts are strong features of Inuit culture. In 2002 the first
Visual and performing arts are strong features of Inuit culture. In 2002 the first
Inuit Circumpolar Council
Inuit Circumpolar Council Greenland
Inuit Circumpolar Council Alaska
National Inuit Organization in Canada
Inuit Treaty Project
Inuit Atlas Project
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Canada History of Indigenous peoples of North America Hunter-gatherers of Canada Hunter-gatherers of the Arctic Hunter-gatherers of the United States Indigenous peoples in Atlantic Canada Indigenous peoples in Northern Canada
Indigenous peoples
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
traditionally inhabiting the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
and Subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cair ...
regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
, Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
, Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the Nunavut Land Claims Agr ...
, the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
, Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
(traditionally), Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, and the Chukotsky District
Chukotsky District (, ''Čukótskiy Raion, rayón''; Chukchi language, Chukchi: , ''Čukotkakèn rajon'') is an administrativeLaw #33-OZ and municipalLaw #47-OZ district (raion), one of the administrative divisions of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, six ...
of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug
Chukotka ( ; ), officially the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, is the easternmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Russia. It is an Autonomous okrugs of Russia, autonomous okrug situated in the Russian Far East, and shares a border wi ...
. The Inuit languages
The Inuit languages are a closely related group of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and the adjacent subarctic regions as far south as Labrador. The Inuit ...
are part of the Eskaleut languages
The Eskaleut ( ), Eskimo–Aleut or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan languages are a language family native to the northern portions of the North American continent, and a small part of northeastern Asia. Languages in the family are indigenous to parts of ...
, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskimo–Aleut.
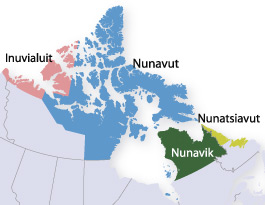
Canadian Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada
Northern Canada (), colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three Provinces_and_territories_of_Canada#Territories, terr ...
in the territory
A territory is an area of land, sea, or space, belonging or connected to a particular country, person, or animal.
In international politics, a territory is usually a geographic area which has not been granted the powers of self-government, ...
of Nunavut, Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; ) is an area in Canada which comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homelan ...
in the northern third of Quebec, the Nunatsiavut
Nunatsiavut (; ) is an autonomous area claimed by the Inuit in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement area includes territory in Labrador extending to the Quebec border. In 2002, the Labrador Inuit Association submitted a proposal for ...
in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories and Yukon (traditionally), particularly around the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region
The Inuvialuit Settlement Region, abbreviated as ISR (; ), located in Canada's western Arctic, was designated in 1984 in the Inuvialuit Final Agreement by the Government of Canada for the Inuvialuit (''the real people''). It spans , including ...
. These areas are known, by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (Inuktitut syllabics: , meaning "Inuit are united in Canada"), previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada (Eskimo Brotherhood of Canada), is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit acro ...
and the Government of Canada
The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federation, federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes Minister of t ...
, as Inuit Nunangat
Inuit Nunangat (; ), formerly Inuit Nunaat (), is the homeland of the Inuit in Canada. This Arctic homeland consists of four Northern Canada, northern Canadian regions called the Inuvialuit Settlement Region (, home of the Inuvialuit and th ...
. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982
The ''Constitution Act, 1982'' () is a part of the Constitution of Canada.Formally enacted as Schedule B of the ''Canada Act 1982'', enacted by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Section 60 of the ''Constitution Act, 1982'' states that the ...
classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Aboriginal Canadians who are not included under either the First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
or the Métis
The Métis ( , , , ) are a mixed-race Indigenous people whose historical homelands include Canada's three Prairie Provinces extending into parts of Ontario, British Columbia, the Northwest Territories and the northwest United States. They ha ...
.
Greenlandic Inuit
The Greenlandic Inuit or sometimes simply the Greenlandic are an ethnic group and nation Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous to Greenland, where they constitute the largest ethnic population. They share a common #History, ancestry, ...
, also known as Kalaallit, are descendants of Thule
Thule ( ; also spelled as ''Thylē'') is the most northerly location mentioned in ancient Greek and Roman literature and cartography. First written of by the Greek explorer Pytheas of Massalia (modern-day Marseille, France) in about 320 BC, i ...
migrations from Canada by 1100 CE. Although Greenland withdrew from the European Communities in 1985, Inuit of Greenland are Danish citizens and, as such, remain citizens of the European Union. In the United States, the Alaskan Iñupiat
The Inupiat (singular: Iñupiaq), also known as Alaskan Inuit, are a group of Alaska Natives whose traditional territory roughly spans northeast from Norton Sound on the Bering Sea to the northernmost part of the Canada–United States borde ...
are traditionally located in the Northwest Arctic Borough
Northwest Arctic Borough is a List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, borough located in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 7,793, up from 7,523 in 2010. The borough seat is Kotze ...
, on the Alaska North Slope
The Alaska North Slope is the region of the U.S. state of Alaska located on the northern slope of the Brooks Range along the coast of two marginal seas of the Arctic Ocean, the Chukchi Sea being on the western side of Point Barrow, and the Beau ...
, the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
and on Little Diomede Island
Little Diomede Island or Yesterday Island (, formerly known as Krusenstern Island, ) is an inhabited island of Alaska. It is the smaller of the two Diomede Islands located in the Bering Strait between the Alaskan mainland and Siberia. The islan ...
. In Russia, few pockets of diaspora
A diaspora ( ) is a population that is scattered across regions which are separate from its geographic place of birth, place of origin. The word is used in reference to people who identify with a specific geographic location, but currently resi ...
communities of Russian Iñupiat from Big Diomede Island
Big Diomede Island or Tomorrow Island (; Ratmanov Island, ; ) is the western island of the two Diomede Islands in the middle of the Bering Strait. The island is home to a Russian military base which is located midway along the island's North sho ...
, of which inhabitants were removed to Russian Mainland, remain in Bering Strait coast of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, particularly in Uelen
Uelen is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Chukotsky District, just south of the Arctic Circle in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug in the Russian Far East. As of the Russian Census (2010), 2010 C ...
, Lavrentiya
Lavrentiya (, Yupik language, Yupik: Ӄышы; Chukchi language, Chukchi: Ӄытрын, ''Ḳytryn''; Naukan language, Naukan: ''Qerre''; Iñupiaq language, Inupiaq: ''Kesrreq'' or ''Kisrriq'') is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural l ...
, and Lorino.
Many individuals who would have historically been referred to as ''Eskimo
''Eskimo'' () is a controversial Endonym and exonym, exonym that refers to two closely related Indigenous peoples: Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Canadian Inuit, and the Greenlandic Inuit) and the Yupik peoples, Yupik (or Sibe ...
'' find that term offensive or forced upon them in a colonial way, ''Inuit'' is now a common autonym
Autonym may refer to:
* Autonym, the name used by a person to refer to themselves or their language; see Exonym and endonym
* Autonym (botany), an automatically created infrageneric or infraspecific name
See also
* Nominotypical subspecies, in zo ...
for a large sub-group of these people. The word ''Inuit'' (varying forms Iñupiat, Inuvialuit
The Inuvialuit (sing. Inuvialuk; ''the real people'') or Western Canadian Inuit are Inuit who live in the western Canadian Arctic region. They, like all other Inuit, are descendants of the Thule who migrated eastward from Alaska. Their homelan ...
, Inughuit
The Inughuit (singular: Inughuaq), Inuhuit, or Smith Sound Inuit, historically called Arctic Highlanders or Polar Eskimos, are an ethnic subgroup of the Greenlandic Inuit. They are the northernmost group of Inuit and the northernmost people in No ...
, etc.), however, is an ancient self-referential to a group of peoples which includes at most the Iñupiat of Bering Strait coast of Chukotka and northern Alaska, the four broad groups of Inuit in Canada, and the Greenlandic Inuit. This usage has long been employed to the exclusion of other, closely related groups (e.g. Yupik, Aleut
Aleuts ( ; (west) or (east) ) are the Indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleuts and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska ...
). in Therefore, the Aleut (Unangan) and Yupik peoples (Alutiiq
The Alutiiq (pronounced in English; from Promyshlenniki Russian Алеутъ, "Aleut"; plural often "Alutiit"), also called by their ancestral name ( or ; plural often "Sugpiat"), as well as Pacific Eskimo or Pacific Yupik, are a Yupik ...
/Sugpiaq, Central Yup'ik, Siberian Yupik
Siberian Yupiks, or Yuits (), are a Yupik peoples, Yupik people who reside along the coast of the Chukchi Peninsula in the far Russian Far East, northeast of the Russia, Russian Federation and on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska. They speak Si ...
), who live in Alaska and Siberia, at least at an individual and local level, generally do not self-identify as Inuit.
History
Pre-contact history
Inuit are the descendants of whatanthropologists
An anthropologist is a scientist engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropologists study aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms, values ...
call the Thule people
The Thule ( , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by 1000 AD and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people of the ...
, who emerged from the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
and western Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
around 1000 CE. They had split from the related Aleut
Aleuts ( ; (west) or (east) ) are the Indigenous people of the Aleutian Islands, which are located between the North Pacific Ocean and the Bering Sea. Both the Aleuts and the islands are politically divided between the US state of Alaska ...
group about 4000 years ago and from northeastern Siberian migrants. They spread eastward across the Arctic. They displaced the related Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
, called the in Inuktitut
Inuktitut ( ; , Inuktitut syllabics, syllabics ), also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of ...
, which was the last major Paleo-Eskimo
The Paleo-Eskimo meaning ''"old Eskimos"'', also known as, pre-Thule people, Thule or pre-Inuit, were the peoples who inhabited the Arctic region from Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Chukotka (e.g., Chertov Ovrag) in present-day Russia across North Am ...
culture.
Inuit legends speak of the as "giants", people who were taller and stronger than Inuit. Less frequently, the legends refer to the Dorset as "dwarfs". Researchers believe that Inuit society had advantages by having adapted to using dogs as transport animals, and developing larger weapons and other technologies superior to those of the Dorset culture. By 1100 CE, Inuit migrants had reached west Greenland, where they settled. During the 12th century, they also settled in East Greenland.
Faced with population pressures from the Thule and other surrounding groups, such as the Algonquian and Siouan
Siouan ( ), also known as Siouan–Catawban ( ), is a language family of North America located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who ...
-speaking peoples to the south, the gradually receded. The were thought to have become completely extinct as a people by about 1400 or 1500. But in the mid-1950s, researcher Henry B. Collins determined that based on the ruins found at Native Point, on Southampton Island
Southampton Island (Inuktitut: ''Shugliaq'') is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of t ...
, the Sadlermiut
The Sadlermiut (also called Sagdlirmiut, or Sallirmiut in modern Inuktitut spelling, from ''Sadlerk'' now ''Salliq'', the Inuktitut name for the settlement of Coral Harbour, Nunavut) were an Inuit group living in near isolation mainly on and arou ...
were likely the last remnants of the Dorset culture, or . The Sadlermiut population survived up until winter 1902–1903 when exposure to new infectious disease
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
s brought by contact with Europeans led to their extinction as a people.
In the early 21st century, mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA and mDNA) is the DNA located in the mitochondrion, mitochondria organelles in a eukaryotic cell that converts chemical energy from food into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is a small portion of the D ...
research has supported the theory of continuity between the and the Sadlermiut peoples. It also provided evidence that a population displacement did not occur within the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; , "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before Alaska Purchase, 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain ...
between the Dorset and Thule transition. However a subsequent 2012 genetic analysis showed no genetic link between the Sadlermiut and the Dorset or people. In contrast to other populations, the Aleut and Sadlermiut benefited from both geographical isolation and their ability to adopt certain Thule technologies.
In Canada and Greenland, Inuit circulated almost exclusively north of the Arctic tree line, with the exception of Inuit in Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
where there are large swaths of coastal barrens. In Labrador there are two Inuit groups, one accepted by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (Inuktitut syllabics: , meaning "Inuit are united in Canada"), previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada (Eskimo Brotherhood of Canada), is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit acro ...
, Nunatsiavut
Nunatsiavut (; ) is an autonomous area claimed by the Inuit in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement area includes territory in Labrador extending to the Quebec border. In 2002, the Labrador Inuit Association submitted a proposal for ...
and one independent, NunatuKavut
NunatuKavut () is a proposed NunatuKavummiut territory in central and southern Labrador. The region proposed by the NunatuKavut Community Council (NCC) extends from north of the community of Makkovik in Nunatsiavut to south of the community of ...
. The most southern Inuit community in Nunatsiavut is Rigolet
Rigolet (Inuttitut: ''Tikigâksuagusik'') (population 327) is a remote, coastal Labrador community established in 1735 by French-Canadian trader Louis Fornel. The town is the southernmost officially recognized Inuit community in the world. Loca ...
while the most southern community within the traditional Inuit territory of NunatuKavut and in the world is L'anse au Clair, Labrador.
In other areas south of the tree line
The tree line is the edge of a habitat at which trees are capable of growing and beyond which they are not. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually low ...
, non-Inuit Indigenous cultures were well established. As a result, being challenged by the groups below the tree line including Chukchi and Siberian Yupik
Siberian Yupiks, or Yuits (), are a Yupik peoples, Yupik people who reside along the coast of the Chukchi Peninsula in the far Russian Far East, northeast of the Russia, Russian Federation and on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska. They speak Si ...
for Russian Iñupiat, Arctic Athabascan and Gwichʼin
The Gwichʼin (or Kutchin or Loucheux) are an Athabaskan languages, Athabaskan-speaking First Nations in Canada, First Nations people of Canada and an Alaskan Athabaskans, Alaska Native people. They live in the northwestern part of North America ...
for Alaskan Iñupiat and Inuvialuit, Cree
The Cree, or nehinaw (, ), are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people, numbering more than 350,000 in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada, First Nations. They live prim ...
for Nunavummiut (Nunavut Inuit) and Nunavimmiut (Northern Quebec Inuit), and Innu
The Innu/Ilnu ('man, person'), formerly called Montagnais (French for ' mountain people'; ), are the Indigenous Canadians who inhabit northeastern Labrador in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador and some portions of Quebec. They refer to ...
for Nunatsiavummiut (Labrador Inuit) and NunatuKavummiut (Southern Inuit or Inuit-metis), Inuit did not make significant progress South, or in the case of Labrador, East.
Inuit had trade relations with more southern cultures; boundary disputes were common and gave rise to aggressive actions. Warfare was not uncommon among those Inuit groups with sufficient population density. Inuit such as the Nunamiut
The Nunamiut or Nunatamiut (, , "People of the Land") are semi-nomadic inland Iñupiat located in the northern and northwestern Alaskan interior, mostly around Anaktuvuk Pass, Alaska.
History
Early Nunamiut lived by hunting caribou instead of th ...
(''Uummarmiut
The Uummarmiut or Uummaġmiut (, ''people of the green trees'') is the name given to the Inuvialuit who live predominantly in the Mackenzie Delta communities of Aklavik and Inuvik, Northwest Territories, Canada. Their language is known as Uumm ...
''), who inhabited the Mackenzie River
The Mackenzie River (French: ; Slavey language, Slavey: ' èh tʃʰò literally ''big river''; Inuvialuktun: ' uːkpɑk literally ''great river'') is a river in the Canadian Canadian boreal forest, boreal forest and tundra. It forms, ...
delta area, often engaged in warfare. The more sparsely settled Inuit in the Central Arctic, however, did so less often.
Their first European contact was with the Vikings
Vikings were seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway, and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded, and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9� ...
who had settled in Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
centuries prior. The saga
Sagas are prose stories and histories, composed in Iceland and to a lesser extent elsewhere in Scandinavia.
The most famous saga-genre is the (sagas concerning Icelanders), which feature Viking voyages, migration to Iceland, and feuds between ...
s recorded meeting ', probably an undifferentiated label for all the Indigenous peoples whom the Norse encountered, whether , Inuit, or Beothuk
The Beothuk ( or ; also spelled Beothuck) were a group of Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous people of Canada who lived on the island of Newfoundland (island), Newfoundland.
The Beothuk culture formed around 1500 CE. This may have been ...
.
After about 1350, the climate grew colder during the period known as the Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Mat ...
. During this period, Russian and Alaskan natives were able to continue their whaling
Whaling is the hunting of whales for their products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that was important in the Industrial Revolution. Whaling was practiced as an organized industry as early as 875 AD. By the 16t ...
activities. But, in the high Arctic, Inuit were forced to abandon their hunting and whaling sites as bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus''), sometimes called the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, and polar whale, is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena' ...
s disappeared from Canada and Greenland
Greenland is an autonomous territory in the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. It is by far the largest geographically of three constituent parts of the kingdom; the other two are metropolitan Denmark and the Faroe Islands. Citizens of Greenlan ...
. These Inuit had to subsist on a much poorer diet, and lost access to the essential raw materials for their tools and architecture which they had previously derived from whaling.
Post-contact history
Canada
=Early contact with Europeans
= The lives of Paleo-Eskimos of the far north were largely unaffected by the arrival of visiting Norsemen except for mutual trade. After the disappearance of the Norse colonies in Greenland, Inuit had no contact with Europeans for at least a century. By the mid-16th century,Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
whalers and fishermen were already working the Labrador coast and had established whaling stations on land, such as the one that has been excavated at Red Bay, Labrador. Inuit do not appear to have interfered with their operations, but raided the stations in winter, taking tools and items made of worked iron, which they adapted to their own needs.
Martin Frobisher
Sir Martin Frobisher (; – 22 November 1594) was an English sailor and privateer who made three voyages to the New World looking for the North-west Passage. He probably sighted Resolution Island near Labrador in north-eastern Canada, before ...
's 1576 search for the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic ...
was the first well-documented contact between Europeans and Inuit. Frobisher's expedition landed in Frobisher Bay
Frobisher Bay is an inlet of the Davis Strait in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the southeastern corner of Baffin Island. Its length is about and its width varies from about at its outlet into the Davis Strait ...
, Baffin Island
Baffin Island (formerly Baffin Land), in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second-largest island in the Americas (behind Greenland), and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is (slightly smal ...
, not far from the settlement now called Iqaluit
Iqaluit is the capital of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is the territory's largest community and its only city, and the northernmost city in Canada. It was known as Frobisher Bay from 1942 to 1987, after the large bay on the coast on ...
. Frobisher encountered Inuit on Resolution Island where five sailors left the ship, under orders from Frobisher, with instructions to stay clear of Inuit. They became part of Inuit mythology. Inuit oral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (19 ...
tells that the men lived among them for a few years of their own free will until they died attempting to leave Baffin Island in a self-made boat and vanished. Frobisher, in an attempt to find the men, captured three Inuit and brought them back to England. They were possibly the first Inuit ever to visit Europe.
The semi-nomadic Inuit were fishermen and hunters harvesting lakes, seas, ice platforms, and tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
. While there are some allegations that Inuit were hostile to early French and English explorers, fishermen, and whalers, more recent research suggests that the early relations with whaling stations along the Labrador coast and later James Bay
James Bay (, ; ) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. It borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario, and is politically part of Nunavut. Its largest island is Akimiski Island.
Numerous waterways of the ...
were based on a mutual interest in trade. In the final years of the 18th century, the Moravian Church
The Moravian Church, or the Moravian Brethren ( or ), formally the (Latin: "Unity of the Brethren"), is one of the oldest Protestant denominations in Christianity, dating back to the Bohemian Reformation of the 15th century and the original ...
began missionary activities in Labrador, supported by the British who were tired of the raids on their whaling stations. The Moravian missionaries could easily provide Inuit with the iron and basic materials they had been stealing from whaling outposts, materials whose real cost to Europeans was almost nothing, but whose value to Inuit was enormous. From then on, contacts between the national groups in Labrador were far more peaceful.
 The exchanges that accompanied the arrival and colonization by the Europeans greatly damaged Inuit way of life. Mass death was caused by the new infectious diseases carried by whalers and explorers, to which the Indigenous peoples had no acquired immunity. The high mortality rate contributed to the enormous social disruptions caused by the distorting effect of Europeans' material wealth and the introduction of different materials. Nonetheless, Inuit society in the higher latitudes largely remained in isolation during the 19th century.
The
The exchanges that accompanied the arrival and colonization by the Europeans greatly damaged Inuit way of life. Mass death was caused by the new infectious diseases carried by whalers and explorers, to which the Indigenous peoples had no acquired immunity. The high mortality rate contributed to the enormous social disruptions caused by the distorting effect of Europeans' material wealth and the introduction of different materials. Nonetheless, Inuit society in the higher latitudes largely remained in isolation during the 19th century.
The Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC), originally the Governor and Company of Adventurers of England Trading Into Hudson’s Bay, is a Canadian holding company of department stores, and the oldest corporation in North America. It was the owner of the ...
opened trading post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory in European and colonial contexts, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded.
Typically a trading post allows people from one geogr ...
s such as Great Whale River (1820), today the site of the twin villages of Whapmagoostui
Whapmagoostui (, "place of the beluga") is the northernmost Cree village in Quebec, Canada, located at the mouth of the Great Whale River () on the coast of Hudson Bay in Nunavik. About 906 Cree with about 650 Inuit, living in the neighbourin ...
(Cree-majority) and Kuujjuarapik
Kuujjuarapik (also spelled Kuujjuaraapik; ''little great river'') is the southernmost northern village (Inuit community) at the mouth of the Great Whale River () on the coast of Hudson Bay in Nunavik, Quebec, Canada. Almost 1,000 people, mos ...
(Inuit-majority), where whale products of the commercial whale hunt were processed and furs traded. The expedition of 1821–23 to the Northwest Passage led by Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank as well as a job title in many army, armies. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countri ...
William Edward Parry
Sir William Edward Parry (19 December 1790 – 8 July 1855) was a Royal Navy officer and explorer best known for his 1819–1820 expedition through the Parry Channel, probably the most successful in the long quest for the Northwest Passa ...
twice over-wintered in Foxe Basin
Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice (fast ice) and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.
Th ...
. It provided the first informed, sympathetic and well-documented account of the economic, social and religious life of Inuit. Parry stayed in what is now Igloolik
Igloolik ( Inuktitut syllabics: , ''Iglulik'', ) is an Inuit hamlet in Foxe Basin, Qikiqtaaluk Region in Nunavut, northern Canada. Because its location on Igloolik Island is close to Melville Peninsula, it is often mistakenly thought to be o ...
over the second winter. Parry's writings, with pen and ink illustrations of Inuit everyday life, and those of George Francis Lyon were widely read after they were both published in 1824. Captain George Comer
Captain George Comer (April 1858 – 1937) was considered the most famous American whaling captain of Hudson Bay, and the world's foremost authority on Hudson Bay Inuit in the early 20th century.
Comer was a polar explorer, whaler/ sealer, ethn ...
's Inuk wife Shoofly, known for her sewing skills and elegant attire, was influential in convincing him to acquire more sewing accessories and beads for trade with Inuit.
=Early 20th century
= During the early 20th century, a few traders and missionaries circulated among the more accessible bands. After 1904, they were accompanied by a handful ofNorth-West Mounted Police
The North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) was a Canadian paramilitary police force, established in 1873, to maintain order in the new Canadian North-West Territories (NWT) following the 1870 transfer of Rupert's Land and North-Western Territory to ...
(NWMP). Unlike most Aboriginal peoples in Canada, however, Inuit did not occupy lands that were coveted by European settlers. Used to more temperate climates and conditions, most Europeans considered the homeland of Inuit to be hostile hinterland
Hinterland is a German word meaning the 'land behind' a city, a port, or similar. Its use in English was first documented by the geographer George Chisholm in his ''Handbook of Commercial Geography'' (1888). Originally the term was associated wi ...
. Southerners enjoyed lucrative careers as bureaucrats and service providers to the people of the North, but very few ever chose to visit there.
Once its more hospitable lands were largely settled, the government of Canada and entrepreneurs began to take a greater interest in its more peripheral territories, especially the fur and mineral-rich hinterlands. By the late 1920s, there were no longer any Inuit who had not been contacted by traders, missionaries or government agents. In 1939, the Supreme Court of Canada
The Supreme Court of Canada (SCC; , ) is the highest court in the judicial system of Canada. It comprises nine justices, whose decisions are the ultimate application of Canadian law, and grants permission to between 40 and 75 litigants eac ...
found, in a decision known as ''Re Eskimos
is a decision by the Supreme Court of Canada regarding the constitutional status of Canada's Inuit, then called "Eskimos." The case concerned section 91(24) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', then the ''British North America Act, 1867'', which ass ...
'', that Inuit should be considered Indians and were thus under the jurisdiction of the federal government.
Native customs were worn down by the actions of the RCMP, who enforced Canadian criminal law
The criminal law of Canada is under the exclusive legislative jurisdiction of the Parliament of Canada. The power to enact criminal law is derived from section 91(27) of the ''Constitution Act, 1867''. Most criminal laws have been codified in ...
on Inuit. People such as Kikkik often did not understand the rules of the alien society with which they had to interact. In addition, the generally Protestant missionaries of the British preached a moral code
Morality () is the categorization of intentions, decisions and actions into those that are ''proper'', or ''right'', and those that are ''improper'', or ''wrong''. Morality can be a body of standards or principles derived from a code of conduc ...
very different from the one Inuit had as part of their tradition. Many Inuit were systematically converted to Christianity in the 19th and 20th centuries, through rituals such as the ''Siqqitiq
''Siqqitiq'' (meaning transforming one's life, more specifically adopting Christianity) is the ritual of converting Inuit with shamanist beliefs to Christianity. This is usually accompanied by ritualistic consumption of foods held taboo by shaman ...
''.
=The Second World War to the 1960s
= World War II and the Cold War made Arctic Canada strategically important to the great powers for the first time. Thanks to the development of modern long-distance aircraft, these areas became accessible year-round. The construction of air bases and theDistant Early Warning Line
The Distant Early Warning Line, also known as the DEW Line or Early Warning Line, was a system of radar stations in the northern Arctic region of Canada, with additional stations along the north coast and Aleutian Islands of Alaska (see List o ...
in the 1940s and 1950s brought more intensive contact with European society, particularly in the form of public education for children. The traditionalists complained that Canadian education promoted foreign values that were disdainful of the traditional structure and culture of Inuit society.
In the 1950s, the Government of Canada
The Government of Canada (), formally His Majesty's Government (), is the body responsible for the federation, federal administration of Canada. The term ''Government of Canada'' refers specifically to the executive, which includes Minister of t ...
undertook what was called the High Arctic relocation
The High Arctic relocation took place during the Cold War in the 1950s, when 92 Inuit, sometimes called High Arctic exiles, were moved by the Government of Canada under Liberal Prime Minister Louis St. Laurent to the High Arctic.
The forced mig ...
for several reasons. These were to include protecting Canada's sovereignty in the Arctic, alleviating hunger (as the area currently occupied had been over-hunted), and attempting to solve the "Eskimo problem", by seeking assimilation of the people and the end of their traditional Inuit culture. One of the more notable relocations was undertaken in 1953, when 17 families were moved from Port Harrison (now Inukjuak, Quebec) to Resolute and Grise Fiord
Grise Fiord (; ) is an Inuit hamlet on the southern tip of Ellesmere Island, in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is one of three populated places on the island; despite its low population (144 residents at the 2021 Canadian census), ...
. They were dropped off in early September when winter had already arrived. The land they were sent to was very different from that in the Inukjuak area; it was barren, with only a couple of months when the temperature rose above freezing, and several months of polar night
Polar night is a phenomenon that occurs in the polar regions of Earth, northernmost and southernmost regions of Earth when the Sun remains below the horizon for more than 24 hours. This only occurs inside the polar circles. The opposite phen ...
. The families were told by the RCMP they would be able to return to their home territory within two years if conditions were not right. However, two years later more Inuit families were relocated to the High Arctic. Thirty years passed before they were able to visit Inukjuak.
By 1953, Canada's prime minister Louis St. Laurent
Louis Stephen St. Laurent (; February 1, 1882 – July 25, 1973) was a Canadian lawyer and politician who served as the 12th prime minister of Canada from 1948 to 1957.
Born and raised in southeastern Quebec, St. Laurent was a leading la ...
publicly admitted, "Apparently we have administered the vast territories of the north in an almost continuing absence of mind." The government began to establish about forty permanent administrative centers to provide education, health, and economic development services. Inuit from hundreds of smaller camps scattered across the north began to congregate in these hamlets.
Regular visits from doctors and access to modern medical care raised the birth rate
Birth rate, also known as natality, is the total number of live childbirth, human births per 1,000 population for a given period divided by the length of the period in years. The number of live births is normally taken from a universal registr ...
and decreased the death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
, causing a marked natural increase
In demography and population dynamics, the rate of natural increase (RNI), also known as natural population change, is defined as the birth rate minus the death rate of a particular population, over a particular time period. It is typically expre ...
in the population that made it more difficult for them to survive by traditional means. In the 1950s, the Canadian government began to actively settle Inuit into permanent villages and cities, occasionally against their will (such as in Nuntak and Hebron). In 2005 the Canadian government acknowledged the abuses inherent in these forced resettlements. By the mid-1960s, encouraged first by missionaries, then by the prospect of paid jobs and government services, and finally forced by hunger and required by the police, most Canadian Inuit lived year-round in permanent settlements. The nomadic migrations that were the central feature of Arctic life had become a much smaller part of life in the North. Inuit, a once self-sufficient people in an extremely harsh environment were, in the span of perhaps two generations, transformed into a small, impoverished minority, lacking skills or resources to sell to the larger economy, but increasingly dependent on it for survival.
Although anthropologists like Diamond Jenness
Diamond Jenness, (February 10, 1886, Wellington, New Zealand – November 29, 1969, Chelsea, Quebec, Canada) was one of Canada's greatest early scientists and a pioneer of Canadian anthropology.
Early life (1886–1910)
Family and childho ...
(1964) were quick to predict that Inuit culture was facing extinction, Inuit political activism was already emerging.
=Cultural renewal
= In the 1960s, the Canadian government funded the establishment of
In the 1960s, the Canadian government funded the establishment of secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin , or or ), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. The origins of secularity can be traced to the Bible itself. The concept was fleshed out through Christian hi ...
, government-operated high school
A secondary school, high school, or senior school, is an institution that provides secondary education. Some secondary schools provide both ''lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper secondary education'' (ages 14 to 18), i.e., ...
s in the Northwest Territories (including what is now Nunavut) and Inuit areas in Quebec and Labrador along with the residential school system
The Canadian Indian residential school system was a network of boarding schools for Indigenous peoples. The network was funded by the Canadian government's Department of Indian Affairs and administered by various Christian churches. The scho ...
. Inuit population was not large enough to support a full high school in every community, so this meant only a few schools were built, and students from across the territories were boarded there. These schools, in Aklavik
Aklavik (Inuvialuktun: ''Akłarvik'') (from the Inuvialuktun meaning '' barrenground grizzly place'') is a hamlet located in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. Until 1961, with a population over 1,500, the community served ...
, Iqaluit, Yellowknife
Yellowknife is the capital, largest community, and the only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the outlet of t ...
, Inuvik
Inuvik (''place of man'') is the only town in the Inuvik Region, and the List of municipalities in the Northwest Territories, third largest community in Canada's Northwest Territories. Located in what is sometimes called the Beaufort Delta Re ...
and Kuujjuaq
Kuujjuaq (; or ), formerly known as (ᓲᐃᕙᐅᖃᔾ) and by #Names, other names, is a former Hudson's Bay Company outpost at the mouth of the Koksoak River on Ungava Bay that has become the largest northern village (Quebec), northern vil ...
, brought together young Inuit from across the Arctic in one place for the first time and exposed them to the rhetoric of civil
Civil may refer to:
*Civility, orderly behavior and politeness
*Civic virtue, the cultivation of habits important for the success of a society
*Civil (journalism)
''The Colorado Sun'' is an online news outlet based in Denver, Colorado. It lau ...
and human rights
Human rights are universally recognized Morality, moral principles or Social norm, norms that establish standards of human behavior and are often protected by both Municipal law, national and international laws. These rights are considered ...
that prevailed in Canada in the 1960s. This was a real wake-up call for Inuit, and it stimulated the emergence of a new generation of young Inuit activists in the late 1960s who came forward and pushed for respect for Inuit and their territories.
Inuit began to emerge as a political force in the late 1960s and early 1970s, shortly after the first graduates returned home. They formed new politically active associations in the early 1970s, starting with the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada (Inuit Brotherhood and today known as Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami), an outgrowth of the Indian and Eskimo Association of the '60s, in 1971, and more region-specific organizations shortly afterward, including the Committee for the Original People's Entitlement (representing the Inuvialuit), the Northern Quebec Inuit Association (Makivik Corporation
Makivvik (, ; ) (''formerly Makivik Corporation'') is the legal representative of Quebec's Inuit, established in 1978 under the terms of the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement, the agreement that established the institutions of Nunavik. As s ...
) and the Labrador Inuit Association (LIA) representing Northern Labrador Inuit. Since the mid-1980s the disputed Southern Labrador Inuit of NunatuKavut
NunatuKavut () is a proposed NunatuKavummiut territory in central and southern Labrador. The region proposed by the NunatuKavut Community Council (NCC) extends from north of the community of Makkovik in Nunatsiavut to south of the community of ...
began organizing politically after being geographically cut out of the LIA, because the organization called itself the Labrador Métis Nation just a few years before. Various activist movements began to change the direction of Inuit society in 1975 with the James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement
The James Bay and Northern Quebec Agreement () is an Aboriginal land claim settlement, approved in 1975 by the Cree and Inuit of northern Quebec, and later slightly modified in 1978 by the Northeastern Quebec Agreement (), through which Quebec's ...
. This comprehensive land claims settlement for Quebec Inuit, along with a large cash settlement and substantial administrative autonomy in the new region of Nunavik, set the precedent for the settlements to follow. The northern Labrador Inuit submitted their land claim in 1977, although they had to wait until 2005 to have a signed land settlement establishing Nunatsiavut
Nunatsiavut (; ) is an autonomous area claimed by the Inuit in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement area includes territory in Labrador extending to the Quebec border. In 2002, the Labrador Inuit Association submitted a proposal for ...
. Southern Labrador Inuit of NunatuKavut is currently in the process of establishing land claims and title rights that would allow them to negotiate with the Newfoundland Government.
Canada's 1982 Constitution Act recognized Inuit as Aboriginal peoples in Canada. In the same year, the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut The Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut (TFN, , ) was the organization officially recognized from 1982 to 1993 as representing the Inuit of what is now Nunavut, but was then part of the Northwest Territories, for the purpose of negotiating treaties and ...
(TFN) was incorporated, in order to take over negotiations for land claims on behalf of Inuit living in the eastern Northwest Territories, that would later become Nunavut, from Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, which became a joint association of Inuit of Quebec, Labrador, and the Northwest Territories.
=Inuit cabinet members at the federal level
= On October 30, 2008, Leona Aglukkaq was appointed asMinister of Health
A health minister is the member of a country's government typically responsible for protecting and promoting public health and providing welfare spending and other social security services.
Some governments have separate ministers for mental heal ...
, " ecomingthe first Inuk to hold a senior cabinet position, although she is not the first Inuk to be in cabinet altogether." Jack Anawak
Jack Iyerak Anawak (born September 26, 1950) is a Canadian politician. He represented the electoral district of Nunatsiaq in the House of Commons of Canada from 1988 to 1997. He sat in the house as a member of the Liberal Party of Canada. Foll ...
and Nancy Karetak-Lindell were both parliamentary secretaries respectively from 1993 to 1996 and in 2003.
Nomenclature
The term ''Eskimo'' is still used by people; however in the 21st century, usage in North America has declined. In the United States the term ''Eskimo
''Eskimo'' () is a controversial Endonym and exonym, exonym that refers to two closely related Indigenous peoples: Inuit (including the Alaska Native Iñupiat, the Canadian Inuit, and the Greenlandic Inuit) and the Yupik peoples, Yupik (or Sibe ...
'' was, as of 2016, commonly used to describe Inuit and the Siberian and Alaskan Yupik, and Iñupiat peoples. Eskimo is still used by some groups and organizations to encompass Inuit and Yupik, as well as other Indigenous Alaskan and Siberian peoples.
In 2011, Lawrence Kaplan of the Alaska Native Language Center
The Alaska Native Language Center, established in 1972 in Fairbanks, Alaska, is a research center focusing on the research and documentation of the Native languages of Alaska. It publishes grammars, dictionaries, folklore collections and research m ...
at the University of Alaska Fairbanks
The University of Alaska Fairbanks (UAF or Alaska) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-, National Sea Grant College Program, sea-, and National Space Grant College and Fellowship Program, space-grant research university in ...
wrote that ''Inuit'' was not generally accepted as a term for the Yupik, and ''Eskimo'' was often used as the term that applied to the Yupik, Iñupiat, and Inuit. Since then Kaplan has updated this to indicate that the term ''Inuit'' has gained acceptance in Alaska.
Though there is much debate, the word ''Eskimo'' likely derives from a Innu-aimun
Innu-aimun or Montagnais is an Algonquian language spoken by over 10,000 Innu in Labrador and Quebec in Eastern Canada. It is a member of the Cree–Montagnais–Naskapi dialect continuum and is spoken in various dialects depending on the com ...
(Montagnais) in exonym
An endonym (also known as autonym ) is a common, name for a group of people, individual person, geographical place, language, or dialect, meaning that it is used inside a particular group or linguistic community to identify or designate them ...
meaning 'a person who laces a snowshoe', but is also used in folk etymology
Folk etymology – also known as (generative) popular etymology, analogical reformation, (morphological) reanalysis and etymological reinterpretation – is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a mo ...
as meaning 'eater of raw meat' in the Cree language
Cree ( ; also known as Cree–Montagnais language, Montagnais–Naskapi language, Naskapi) is a dialect continuum of Algonquian languages spoken by approximately 86,475 people across Canada in 2021, from the Northwest Territories to Alberta to ...
. Though the Cree etymology has been discredited, "Eskimo" is considered pejorative by some Canadian and English-speaking Greenlandic Inuit.
In Canada and Greenland, ''Inuit'' is preferred. ''Inuit'' is the Eastern Canadian Inuit (Inuktitut) and West Greenlandic
(), also known as West Greenlandic (), is the primary language of Greenland and constitutes the Greenlandic language, spoken by the vast majority of the inhabitants of Greenland, as well as by thousands of Greenlandic Inuit in Denmark proper (i ...
(Kalaallisut) word for 'the people'. Since Inuktitut and Kalaallisut are the prestige dialect
Prestige in sociolinguistics is the level of regard normally accorded a specific language or dialect within a speech community, relative to other languages or dialects. Prestige varieties are language or dialect families which are generally c ...
s in Canada and Greenland, respectively, their version has become dominant, although every Inuit dialect uses cognates from the Proto-Eskimo ''*ińuɣ'' for example, "people" is ''inughuit'' in North Greenlandic
Inuktun (, , ) is the language of approximately 1,000 Indigenous Inughuit (Polar Inuit), inhabiting the world's northernmost settlements in Qaanaaq and the surrounding villages in northwestern Greenland.
Geographic distribution
Apart from the to ...
and ''iivit'' in East Greenlandic
(), also known as East Greenlandic (), is the language of the Tunumiit in East Greenland. It is generally categorised as a dialect of Greenlandic, but verges on being a distinct language.Nicole Tersis, in Variations on polysynthesis: the Eskal ...
.
Cultural history
Languages
Inuinnaqtun
Inuinnaqtun (, ; natively meaning 'like the real human beings/peoples') is an Inuit language. It is spoken in the central Canadian Arctic. It is related very closely to Inuktitut, and some scholars, such as Richard Condon, believe that Inuinna ...
, Inuktitut
Inuktitut ( ; , Inuktitut syllabics, syllabics ), also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of ...
, Inuvialuktun
Inuvialuktun (part of ''Western Canadian Inuit'' / ''Inuktitut'' / '' Inuktut'' / '' Inuktun'') comprises several Inuit language varieties spoken in the northern Northwest Territories by Canadian Inuit who call themselves ''Inuvialuit''. Some d ...
, and Greenlandic language
Greenlandic, also known by its Endonym and exonym, endonym Kalaallisut (, ), is an Inuit languages, Inuit language belonging to the Eskaleut languages#Internal classification, Eskimoan branch of the Eskaleut languages, Eskaleut language family. ...
s, which belong to the Inuit-Inupiaq branch of the Inuit-Yupik-Unangan language family.
Inupiaq (Inupiatun) is spoken in Russia (extinct) and Alaska, which is one of the 22 official languages of the State of Alaska. In Russia, due to the replacement from their traditional territory in Big Diomede Island to Mainland Russia, Inupiaq language has been nearly extinct with most of them speaking Central Siberian Yupik or Russian predominantly with some Inupiaq linguistic features.
In Canada, three Inuit languages (Inuvialuktun, Inuinnaqtun, Inuktitut) are spoken. Inuvialuktun is spoken in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region
The Inuvialuit Settlement Region, abbreviated as ISR (; ), located in Canada's western Arctic, was designated in 1984 in the Inuvialuit Final Agreement by the Government of Canada for the Inuvialuit (''the real people''). It spans , including ...
, Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
, with official language status from the territorial government. Inuinnaqtun is spoken across the Northwest Territories and the Kitikmeot Region
Kitikmeot Region (; Inuktitut: ''Qitirmiut'' ) is an List of regions of Nunavut, administrative region of Nunavut, Canada. It consists of the southern and eastern parts of Victoria Island with the adjacent part of the mainland as far as the Boo ...
of Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the Nunavut Land Claims Agr ...
with official language status from both territories. Inuktitut, the most widely spoken Inuit language in Canada, however, is an official, and one of two main languages, alongside English, of Nunavut and has its speakers throughout Nunavut, Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; ) is an area in Canada which comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homelan ...
(Northern Quebec), Nunatsiavut
Nunatsiavut (; ) is an autonomous area claimed by the Inuit in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement area includes territory in Labrador extending to the Quebec border. In 2002, the Labrador Inuit Association submitted a proposal for ...
(Labrador), and the Northwest Territories, where it is also an official language.
Kalaallisut is the official language of Greenland. The Greenlandic languages are divided into: Kalaallisut (Western), Inuktun
Inuktun (, , ) is the language of approximately 1,000 Indigenous Inughuit (Polar Inuit), inhabiting the world's northernmost settlements in Qaanaaq and the surrounding villages in northwestern Greenland.
Geographic distribution
Apart from the t ...
(Northern), and Tunumiit
Iivit or Tunumiit are Indigenous Greenlandic Inuit from Iivi Nunaa, Tunu in the area of Kangikajik and Ammassalik, the eastern part of Inuit Nunaat (East Greenland). The Iivit live now mainly in Tasiilaq and Ittoqqortoormiit and are a part o ...
(Eastern). As Inuktitut was the language of the Eastern Canadian Inuit and Kalaallisut is the language of the Western Greenlandic Inuit, they are related more closely than most other dialects.
Inuit in Alaska and Northern Canada also typically speak English. In Greenland, Inuit also speak Danish and learn English in school. Inuit in Russia mostly speak Russian and Central Siberian Yupik. Canadian Inuit, particularly those from Nunavik, may also speak Québécois French
Quebec French ( ), also known as Québécois French, is the predominant variety of the French language spoken in Canada. It is the dominant language of the province of Quebec, used in everyday communication, in education, the media, and governme ...
.
Finally, deaf Inuit use Inuit Sign Language
Inuit Sign Language (IUR; ) is one of the Inuit languages and the indigenous sign language of the Inuit people. It is a language isolate native to Inuit communities in the Canadian Arctic. It is currently only attested within certain communities ...
(ISL), which is a language isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi ...
and is almost extinct as only around 50 people still use it.
Diet
Inuit have traditionally been fishermen and hunters. They still huntwhale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s (esp. bowhead whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus''), sometimes called the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, and polar whale, is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena' ...
), seal
Seal may refer to any of the following:
Common uses
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, also called "true seal"
** Fur seal
** Eared seal
* Seal ( ...
, (esp. ringed seal, harp seal
The harp seal (''Pagophilus groenlandicus''), also known as the saddleback seal or Greenland seal, is a species of earless seal, or true seal, native to the northernmost Atlantic Ocean and Arctic Ocean. Originally in the genus '' Phoca'' with a ...
, common seal
The harbor (or harbour) seal (''Phoca vitulina''), also known as the common seal, is a true seal found along temperate and Arctic marine coastlines of the Northern Hemisphere. The most widely distributed species of pinniped (walruses, eared sea ...
, bearded seal
The bearded seal (''Erignathus barbatus''), also called the square flipper seal, is a medium-sized pinniped that is found in and near to the Arctic Ocean. It gets its Genus, generic name from two Greek language, Greek words (''eri'' and ''gnathos ...
), polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
s, muskox
The muskox (''Ovibos moschatus'') is a hoofed mammal of the family Bovidae. Native to the Arctic, it is noted for its thick coat and for the strong odor emitted by males during the seasonal rut, from which its name derives. This musky odor ha ...
en, caribou
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only represe ...
, birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
, and fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
and at times other less commonly eaten animals such as the Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small species of fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Tundra#Arctic tundra, Arctic tundra biome. I ...
. The typical Inuit diet is high in protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
and very high in fat
In nutrition science, nutrition, biology, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester of fatty acids, or a mixture of such chemical compound, compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food.
The term often refers specif ...
– in their traditional diets, Inuit consumed an average of 75 percent of their daily energy intake from fat. While it is not possible to cultivate plants for food in the Arctic, Inuit have traditionally gathered those that are naturally available. Grasses
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in ...
, tuber
Tubers are a type of enlarged structure that plants use as storage organs for nutrients, derived from stems or roots. Tubers help plants perennate (survive winter or dry months), provide energy and nutrients, and are a means of asexual reproduc ...
s, root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often bel ...
s, plant stems, berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone fruit, stone or pit (fruit), pit although many wikt:pip#Etymology 2, pips or seeds may be p ...
, and seaweed
Seaweed, or macroalgae, refers to thousands of species of macroscopic, multicellular, marine algae. The term includes some types of ''Rhodophyta'' (red), '' Phaeophyta'' (brown) and ''Chlorophyta'' (green) macroalgae. Seaweed species such as ...
(''kuanniq'' or edible seaweed) were collected and preserved depending on the season and the location. There is a vast array of different hunting technologies that Inuit used to gather their food.
In the 1920s, anthropologist Vilhjalmur Stefansson
Vilhjalmur Stefansson (November 3, 1879 – August 26, 1962) was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. He was born in Manitoba, Canada.
Early life and education
Stefansson, born William Stephenson, was born at Arnes, Manitoba, Canada, in 1879. ...
lived with and studied a group of Inuit. The study focused on Stefansson's observation that Inuit's low-carbohydrate diet
Low-carbohydrate diets restrict carbohydrate consumption relative to the average diet (nutrition), diet. Foods high in carbohydrates (e.g., sugar, bread, pasta) are limited, and replaced with foods containing a higher percentage of fat and pro ...
apparently had no adverse effects on their health, nor indeed, on his own health. Stefansson (1946) also observed that Inuit were able to get the necessary vitamins they needed from their traditional winter diet, which did not contain any plant matter. In particular, he found that adequate vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits, berries and vegetables. It is also a generic prescription medication and in some countries is sold as a non-prescription di ...
could be obtained from items in their traditional diet of raw meat
Raw meat generally refers to any type of uncooked muscle tissue of an animal used for food. In the meat production industry, the term "meat" refers specifically to mammalian flesh, while the words "poultry" and "seafood" are used to differentiate ...
such as ringed seal liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
and whale skin (muktuk
Muktuk (transliterated in various ways, see below) is a traditional food of Inuit and other circumpolar peoples, consisting of whale skin and blubber. A part of Inuit cuisine, it is most often made from the bowhead whale, although the belu ...
). While there was considerable skepticism when he reported these findings, the initial anecdotal reports were reaffirmed both in the 1970s, and more recently.
Modern Inuit have lifespans 12 to 15 years shorter than the average Canadian's, which is thought to be influenced by factors such as their diet and limited access to medical services. The life expectancy gap is not closing and remains stagnant.
Tattoos
The ancient art of face tattooing among Inuit women, which is called '' kakiniit'' or ''tunniit'' inInuktitut
Inuktitut ( ; , Inuktitut syllabics, syllabics ), also known as Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the North American tree line, including parts of the provinces of ...
, dates back nearly 4,000 years. The facial tattoos detailed aspects of the women's lives, such as where they were from, who their family was, their life achievements, and their position in the community. When Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
missionaries arrived in the area in the early 20th century they outlawed the practice, but it is now making a comeback thanks to some modern Inuit women who want to revive the practices of their ancestors and get in touch with their cultural roots. The traditional method of tattooing was done with needles made of sinew or bone soaked in suet and sewn into the skin, but today they use ink. The Inuit Tattoo Revitalization Project is a community that was created to highlight the revitalization of this ancient tradition.
Transport, navigation, and dogs

sea animals
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
from single-passenger, seal-skin covered boats called ''qajaq
Qajaq (, also Romanized as Qajāq) is a village in Mian Rokh Rural District, Jolgeh Rokh District, Torbat-e Heydarieh County, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persi ...
'' (Inuktitut syllabics: ''ᖃᔭᖅ'') which were extraordinarily buoyant, and could be righted by a seated person, even if completely overturned. Because of this property, the design was copied by Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
and Americans who still produce them under Inuit name kayak
]
A kayak is a small, narrow human-powered watercraft typically propelled by means of a long, double-bladed paddle. The word ''kayak'' originates from the Inuktitut word '' qajaq'' (). In British English, the kayak is also considered to be ...
.
Inuit also made '' Umiak, umiaq'' ("woman's boat"), larger open boats made of wood frames covered with animal skins, for transporting people, goods, and dogs. They were long and had a flat bottom so that the boats could come close to shore. In the winter, Inuit would also hunt sea mammals by patiently watching an ''aglu'' (breathing hole) in the ice and waiting for the air-breathing seals to use them. This technique is also used by the polar bear, who hunts by seeking holes in the ice and waiting nearby.
In winter, both on land and on sea ice, Inuit used dog sled
A dog sled or dog sleigh is a sled pulled by one or more sled dogs used to travel over ice and through snow, a practice known as mushing. Numerous types of sleds are used, depending on their function. They can be used for Sled dog racing, dog sl ...
s (''qamutik'') for transportation. The ''husky
Husky is a general term for a type of dog used in the polar regions, primarily and specifically for work as sled dogs. It refers to a traditional northern type, notable for its cold-weather tolerance and overall hardiness. Modern racing huskies ...
'' dog breed comes from the Siberian Husky
The Siberian Husky is a dog breed, breed of medium-sized Working dog, working sled dog. The breed belongs to the Spitz genetic family. It is recognizable by its thickly furred Coat (dog), double coat, erect triangular ears, and distinctive mark ...
. These dogs were bred from wolves, for transportation. A team of dogs in either a tandem/side-by-side or fan formation would pull a sled made of wood, animal bones, or the baleen
Baleen is a filter feeder, filter-feeding system inside the mouths of baleen whales. To use baleen, the whale first opens its mouth underwater to take in water. The whale then pushes the water out, and animals such as krill are filtered by th ...
from a whale's mouth and even frozen fish, over the snow and ice. Inuit used stars to navigate at sea and landmarks to navigate on land; they possessed a comprehensive native system of toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper na ...
. Where natural landmarks were insufficient, Inuit would erect an '' inukshuk''. Also, Greenland Inuit created Ammassalik wooden maps, which are tactile devices that represent the coastline.
Dogs played an integral role in the annual routine of Inuit. During the summer they became pack animals, sometimes dragging up to of baggage and in the winter they pulled the sled. Yearlong they assisted with hunting by sniffing out seals' holes and pestering polar bears. They also protected Inuit villages by barking at bears and strangers. Inuit generally favoured, and tried to breed, the most striking and handsome of dogs, especially ones with bright eyes and healthy coats. Common husky dog breeds used by Inuit were the Canadian Eskimo Dog
The Canadian Eskimo Dog or Canadian Inuit Dog is a breed of working dog from the Arctic. Other names include ''qimmiq''Greenland Dog
The Greenland Dog ( Greenlandic: ''Kalaallit Qimmiat'', Danish: ''Grønlandshund'') is a large breed of husky-type dog kept as a sled dog. They were brought from Siberia to North America by the Thule people 1,000 years ago, along with the Ca ...
, the Siberian Husky and the Alaskan Malamute
The Alaskan Malamute () is a large breed of dog that was originally bred for its strength and endurance, to haul heavy freight as a sled dog. It is similar to other arctic breeds such as the husky, the spitz, the Greenland Dog, Canadian Eski ...
.
Industry, art, and clothing
Inuit industry relied almost exclusively on animal hides,driftwood
Driftwood is a wood that has been washed onto a shore or beach of a sea, lake, or river by the action of winds, tides or waves. It is part of beach wrack.
In some waterfront areas, driftwood is a major nuisance. However, the driftwood provides ...
, and bones, although some tools were also made out of worked stones, particularly the readily worked soapstone
Soapstone (also known as steatite or soaprock) is a talc-schist, which is a type of metamorphic rock. It is composed largely of the magnesium-rich mineral talc. It is produced by dynamothermal metamorphism and metasomatism, which occur in sub ...
. Walrus ivory
Walrus ivory, also known as morse, comes from two modified upper canines of a walrus. The tusks grow throughout life and may, in the Pacific walrus, attain a length of one metre. Walrus teeth are commercially carved and traded; the average wa ...
was a particularly essential material, used to make knives. Art played a big part in Inuit society and continues to do so today. Small sculptures of animals and human figures, usually depicting everyday activities such as hunting
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
and whaling, were carved from ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
and bone. In modern times prints and figurative works carved in relatively soft stone such as soapstone, serpentinite
Serpentinite is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of serpentine group minerals formed by serpentinization of mafic or ultramafic rocks. The ancient origin of the name is uncertain; it may be from the similarity of its texture or color ...
, or argillite
Argillite () is a fine-grained sedimentary rock composed predominantly of Friability, indurated clay particles. Argillaceous rocks are basically lithified muds and Pelagic sediment, oozes. They contain variable amounts of silt-sized particles. T ...
have also become popular.
Traditional Inuit clothing
Traditional Inuit clothing is a complex system of Winter clothing, cold-weather garments historically made from animal hide and fur, worn by Inuit, a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples inhabitin ...
and footwear is made from animal skins, sewn together using needles made from animal bones and threads made from other animal products, such as sinew
A tendon or sinew is a tough band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It sends the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system, while withstanding tension.
Tendons, like ligaments, are made of ...
. The anorak
A parka, like the related anorak, is a type of coat with a hood, that may be lined with fur or fake fur. Parkas and anoraks are staples of Inuit clothing, traditionally made from caribou or seal skin, for hunting and kayaking in the frigid A ...
(parka) is made in a similar fashion by Arctic peoples from Europe through Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
and the Americas, including Inuit. The back part of an ''amauti
The amauti (also ''amaut'' or ''amautik'', plural ''amautiit'') is the parka worn by Inuit women of the eastern area of Northern Canada. Up until about two years of age, the child nestles against the mother's back in the amaut, the built-in baby ...
'' (women's parka) was traditionally made extra-large with a separate compartment below the hood to allow the mother to carry a baby against her back and protect it from the harsh wind. Styles vary from region to region, from the shape of the hood to the length of the tails. Boots (''mukluk
Mukluks or kamik ( ) (singular: , plural: ) are soft boots, traditionally made of reindeer (caribou) skin or sealskin, and worn by Indigenous Arctic peoples, including Inuit, Iñupiat, and Yup'ik.
Mukluks may be worn over an inner boot liner a ...
'' or ''kamik''), could be made of caribou or seal skin, and designed for men and women.
 During the winter, certain Inuit lived in a temporary shelter made from snow called an ''
During the winter, certain Inuit lived in a temporary shelter made from snow called an ''igloo
An igloo (Inuit languages: , Inuktitut syllabics (plural: )), also known as a snow house or snow hut, is a type of shelter built of suitable snow.
Although igloos are often associated with all Inuit, they were traditionally used only by the ...
'', and during the few months of the year when temperatures were above freezing, they lived in tents, known as ''tupiq
The tupiq (dual: ''tupiik,'' plural: ''tupiit'', Inuktitut syllabics: ᑐᐱᖅ) is a traditional Inuit tent made from seal or caribou skin. An Inuk was required to kill five to ten ''ugjuk'' (bearded seals) to make a sealskin tent. When a man we ...
'', made of animal skins supported by a frame of bones or wood. Some, such as the Siglit
The Sallirmiut (formerly Siglit) are an Inuit group residing in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region.
The Sallirmiut are regarded as part of the Inuvialuit, or western Canadian Inuit. Inuvialuit is a modern political identity that brings together S ...
, used driftwood, while others built sod
Sod is the upper layer of turf that is harvested for transplanting. Turf consists of a variable thickness of a soil medium that supports a community of turfgrasses.
In British and Australian English, sod is more commonly known as ''turf'', ...
houses.
Inuit also used the Cape York Meteorite
The Cape York meteorite, also known as the Innaanganeq meteorite, is one of the largest known iron meteorites, classified as a medium octahedrite in chemical group IIIAB meteorites, IIIAB. In addition to many small fragments, at least eight large ...
as a primary resource of Iron, using a technique called cold forging
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which ...
, which consisted in slicing a piece of the meteorite and giving it shape by smashing it with rocks until getting the desired shape, for example, tools for fishing. They used this meteorite for centuries until Robert E. Peary
Robert Edwin Peary Sr. (; May 6, 1856 – February 20, 1920) was an American explorer and officer in the United States Navy who made several expeditions to the Arctic in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He was long credited as being ...
sold it to the American Natural History Museum
The American Museum of Natural History (AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. Located in Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 21 interconn ...
in 1883.
Gender roles, marriage, birth, and community
 The
The division of labor
The division of labour is the separation of the tasks in any economic system or organisation so that participants may specialise (Departmentalization, specialisation). Individuals, organisations, and nations are endowed with or acquire specialis ...
in traditional Inuit society had a strong gender component, but it was not absolute. The men were traditionally hunters and fishermen, and the women took care of the children, cleaned the home, sewed, processed food, and cooked. However, there are numerous examples of women who hunted, out of necessity or as a personal choice. At the same time, men, who could be away from camp for several days at a time, would be expected to know how to sew and cook.
The marital customs among Inuit were not strictly monogamous
Monogamy ( ) is a relationship of two individuals in which they form a mutual and exclusive intimate partnership. Having only one partner at any one time, whether for life or serial monogamy, contrasts with various forms of non-monogamy (e.g. ...
: many Inuit relationships were implicitly or explicitly sexual. Open marriage
Open marriage is a form of non-monogamy in which the partners of a dyadic marriage agree that each may engage in extramarital sexual or romantic relationships, without this being regarded by them as infidelity, and consider or establish an ope ...
s, polygamy
Polygamy (from Late Greek , "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marriage, marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more tha ...
, divorce
Divorce (also known as dissolution of marriage) is the process of terminating a marriage or marital union. Divorce usually entails the canceling or reorganising of the legal duties and responsibilities of marriage, thus dissolving the M ...
, and remarriage were known. Among some Inuit groups, if there were children, divorce required the approval of the community and particularly the agreement of the elders. Marriages were often arranged
In music, an arrangement is a musical adaptation of an existing composition. Differences from the original composition may include reharmonization, melodic paraphrasing, orchestration, or formal development. Arranging differs from orchestratio ...
, sometimes in infancy, and occasionally forced on the couple by the community.
Marriage was common for women at puberty and for men when they became productive hunters. Family
Family (from ) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). It forms the basis for social order. Ideally, families offer predictabili ...
structure was flexible: a household might consist of a husband and wife (or wives) and children; it might include his parents or his wife's parents as well as adopted children; it might be a larger formation of several siblings with their parents, wives, and children; or even more than one family sharing dwellings and resources. Every household had its head, either an elder or a particularly respected man.
There was also a larger notion of community as, generally, several families shared a place where they wintered. Goods were shared within a household, and also, to a significant extent, within a whole community.
Inuit were hunter–gatherers, and have been referred to as nomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
ic.
One of the customs following the birth of an infant was for an ''Angakkuq
The Inuit angakkuq (plural: ''angakkuit'', Inuktitut syllabics ᐊᖓᑦᑯᖅ or ᐊᖓᒃᑯᖅ; Inuvialuktun: '; , pl. ''angakkut''; Iñupiaq: ''aŋatkuq'') is an intellectual and spiritual figure in Inuit culture who corresponds to a med ...
'' (shaman
Shamanism is a spiritual practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into ...
) to place a tiny ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
carving of a whale into the baby's mouth, in hopes this would make the child good at hunting. Loud singing and drumming were also customary at birth.
Raiding
Virtually all Inuit cultures haveoral tradition
Oral tradition, or oral lore, is a form of human communication in which knowledge, art, ideas and culture are received, preserved, and transmitted orally from one generation to another.Jan Vansina, Vansina, Jan: ''Oral Tradition as History'' (19 ...
s of raids by other Indigenous peoples, including fellow Inuit, and of taking vengeance on them in return, such as the Bloody Falls massacre
The Bloody Falls massacre was an incident that took place during Hudson's Bay Company employee Samuel Hearne's exploration of the Coppermine River for copper deposits near modern-day Kugluktuk, Nunavut, Canada on 17 July 1771. Hearne's origina ...
. Western observers often regarded these tales as generally not entirely accurate historical accounts, but more as self-serving myths. However, evidence shows that Inuit cultures had quite accurate methods of teaching historical accounts to each new generation. In northern Canada, historically there were ethnic feuds between the Dene
The Dene people () are an Indigenous group of First Nations who inhabit the northern boreal, subarctic and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages and it is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term ...
and Inuit, as witnessed by Samuel Hearne
Samuel Hearne (February 1745 – November 1792) was an English explorer, fur-trader, author and naturalist.
He was the first European to make an overland excursion across northern Canada to the Arctic Ocean, specifically to Coronation Gulf, vi ...
in 1771. In 1996, Dene and Inuit representatives participated in a healing ceremony to reconcile the centuries-old grievances.
The historic accounts of violence against outsiders make it clear that there was a history of hostile contact within Inuit cultures and with other cultures. It also makes it clear that Inuit nations existed through history, as well as confederations of such nations. The known confederations were usually formed to defend against a more prosperous, and thus stronger, nation. Alternately, people who lived in less productive geographical areas tended to be less warlike, as they had to spend more time producing food.
Justice within Inuit culture was moderated by the form of governance that gave significant power to the elders. As in most cultures around the world, justice could be harsh and often included capital punishment for serious crimes against the community or the individual. During raids against other peoples, Inuit, like their non-Inuit neighbors, tended to be merciless.
Suicide, murder, and death
A pervasive European myth about Inuit is that they killed elderly (senicide
Senicide, also known as geronticide or gerontocide, is the practice of killing the elderly. This killing of the elderly can be characterized by both active and passive methods as senio-euthanasia or altruistic self-sacrifice. The aim of activ ...
) and "unproductive people", but this is not generally true. In a culture with an oral history
Oral history is the collection and study of historical information from
people, families, important events, or everyday life using audiotapes, videotapes, or transcriptions of planned interviews. These interviews are conducted with people who pa ...
, elders are the keepers of communal knowledge, effectively the community library. Because they are of extreme value as the repository of knowledge, there are cultural taboo
A taboo is a social group's ban, prohibition or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, offensive, sacred or allowed only for certain people.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
s against sacrificing elders.
In Antoon A. Leenaars' book ''Suicide in Canada,'' he states that "Rasmussen
The surname Rasmussen () is a Danish and Norwegian surname, meaning ''Rasmus' son''. It is the ninth-most-common surname in Denmark, shared by about 1.9% of the population.Franz Boas
Franz Uri Boas (July 9, 1858 – December 21, 1942) was a German-American anthropologist and ethnomusicologist. He was a pioneer of modern anthropology who has been called the "Father of American Anthropology". His work is associated with the mov ...
, suicide was "not of rare occurrence" and was generally accomplished through hanging. Writing of the Labrador Inuit, Hawkes (1916) was considerably more explicit on the subject of suicide and the burden of the elderly:
When food is not sufficient, the elderly are the least likely to survive. In the extreme case of famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
, Inuit fully understood that, if there was to be any hope of obtaining more food, a hunter was necessarily the one to feed on whatever food was left. However, a common response to desperate conditions and the threat of starvation was infanticide
Infanticide (or infant homicide) is the intentional killing of infants or offspring. Infanticide was a widespread practice throughout human history that was mainly used to dispose of unwanted children, its main purpose being the prevention of re ...
. A mother abandoned an infant in hopes that someone less desperate might find and adopt the child before the cold or animals killed it. The belief that Inuit regularly resorted to infanticide may be due in part to studies done by Asen Balikci, Milton Freeman and David Riches among the Netsilik, along with the trial of Kikkik. Other recent research has noted that "While there is little disagreement that there were examples of infanticide in Inuit communities, it is presently not known the depth and breadth of these incidents. The research is neither complete nor conclusive to allow for a determination of whether infanticide was a rare or a widely practiced event." There is no agreement about the actual estimates of the frequency of newborn female infanticide in Inuit population. Carmel Schrire mentions diverse studies ranging from 15 to 80 percent.
Anthropologists believed that Inuit cultures routinely killed children born with physical defects because of the demands of the extreme climate. These views were changed by late 20th century discoveries of burials at an archaeological site. Between 1982 and 1994, a storm with high winds caused ocean waves to erode part of the bluffs near Utqiaġvik, Alaska
Utqiagvik ( ; , ), formerly known as Barrow ( ), is the borough seat and largest city of the North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located north of the Arctic Circle, it is one of the northernmost cities and towns in the world and th ...
, and a body was discovered to have been washed out of the mud. Unfortunately, the storm claimed the body, which was not recovered. But examination of the eroded bank indicated that an ancient house, perhaps with other remains, was likely to be claimed by the next storm. The site, known as the "Ukkuqsi archaeological site", was excavated. Several frozen bodies (now known as the "frozen family") were recovered, autopsies were performed, and they were re-interred as the first burials in the then-new Imaiqsaun Cemetery south of Barrow. Years later another body was washed out of the bluff. It was a female child, approximately nine years old, who had clearly been born with a congenital birth defect. This child had never been able to walk, but must have been cared for by family throughout her life. She was the best preserved body ever recovered in Alaska, and radiocarbon dating of grave goods and of a strand of her hair all place her back to about 1200 CE.
Health
During the 19th century, the Western Arctic suffered a population decline of close to 90 per cent, resulting from exposure to new diseases, includingtuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
, measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles v ...
, influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, and smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
. Autopsies near Greenland reveal that, more commonly pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, ches ...
, kidney diseases
Kidney disease, or renal disease, technically referred to as nephropathy, is damage to or disease of a kidney. Nephritis is an inflammatory kidney disease and has several types according to the location of the inflammation. Inflammation can ...
, trichinosis
Trichinosis, also known as trichinellosis, is a parasitic disease caused by roundworms of the '' Trichinella'' genus. During the initial infection, invasion of the intestines can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and vomiting. Migration of ...
, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, and degenerative disorders may have contributed to mass deaths among different Inuit tribes. Inuit believed that the causes of the disease were of a spiritual origin.
Canadian churches and, eventually, the federal government ran the earliest health facilities for Inuit population, whether fully segregated hospitals or "annexes" and wards attached to settler hospitals. These "Indian hospital
The Indian hospitals were racially segregated hospitals, originally serving as tuberculosis sanatoria but later operating as general hospitals for indigenous peoples in Canada which operated during the 20th century. The hospitals were origin ...
s" were focused on treating people for tuberculosis, though diagnosis was difficult and treatment involved forced removal of individuals from their communities for in-patient confinement in other parts of the country.
Dr. Kevin Patterson, a physician, wrote an op-ed in ''The Globe and Mail
''The Globe and Mail'' is a Newspapers in Canada, Canadian newspaper printed in five cities in Western Canada, western and central Canada. With a weekly readership of more than 6 million in 2024, it is Canada's most widely read newspaper on week ...
'': "In October (2017) the federal Minister of Indigenous Services, Jane Philpott, announced that in 2015 tuberculosis... Was 270 times... More common among the Canadian Inuit than it is among non-Indigenous southern Canadians." The Canadian Medical Association Journal published in 2013 that "tuberculosis among Canadian Inuit has dramatically increased since 1997. In 2010 the incidence in Nunavut... Was 304 per 100,000—more than 66 times the rate seen in the general population.
Traditional law
Inuit Qaujimajatuqangit or Inuit traditional laws are anthropologically different fromWestern law
Western law comprises the legal traditions of Western culture, with roots in Roman law and canon law. As Western culture shares a Graeco-Roman Classical and Renaissance cultural influence, so do its legal systems.
History
The rediscovery of ...
concepts. Customary law
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law".
Customary law (also, consuetudinary or unofficial law) exists wher ...
was thought non-existent in Inuit society before the introduction of the Canadian legal system
The legal system of Canada is Legal pluralism, pluralist: its foundations lie in the English common law system (inherited from its period as a colony of the British Empire), the Napoleonic Code, French civil law system (inherited from its New Fr ...
. In 1954, E. Adamson Hoebel concluded that only "rudimentary law" existed amongst Inuit. No known Western observer before 1970 was aware that any form of governance existed among any Inuit; however, there was a set way of doing things that had to be followed:
* ''maligait'' refers to what has to be followed
* ''piqujait'' refers to what has to be done
* ''tirigusuusiit'' refers to what has to be avoided
If an individual's actions went against the tirigusuusiit, maligait or piqujait, the angakkuq
The Inuit angakkuq (plural: ''angakkuit'', Inuktitut syllabics ᐊᖓᑦᑯᖅ or ᐊᖓᒃᑯᖅ; Inuvialuktun: '; , pl. ''angakkut''; Iñupiaq: ''aŋatkuq'') is an intellectual and spiritual figure in Inuit culture who corresponds to a med ...
(shaman) might have to intervene, lest the consequences be dire to the individual or the community.
Traditional beliefs
 The environment in which Inuit lived inspired a
The environment in which Inuit lived inspired a mythology
Myth is a genre of folklore consisting primarily of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society. For scholars, this is very different from the vernacular usage of the term "myth" that refers to a belief that is not true. Instead, the ...
filled with adventure tales of whale and walrus hunts. Long winter months of waiting for caribou herds or sitting near breathing holes hunting seals gave birth to stories of the mysterious and sudden appearance of ghosts and fantastic creatures. Some Inuit looked into the ''aurora borealis
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras),
also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arc ...
'', or northern lights, to find images of their family and friends dancing in the next life. However, some Inuit believed that the lights were more sinister and if you whistled
Whistling, without the use of an artificial whistle, is achieved by creating a small opening with one's lips, usually after applying moisture (licking one's lips or placing water upon them) and then blowing or sucking air through the space. Th ...
at them, they would come down and cut off your head. This tale is still told to children today. For others they were invisible giants, the souls of animals, a guide to hunting and as a spirit for the ''angakkuq'' to help with healing. They relied upon the ''angakkuq'' (shaman) for spiritual interpretation. The nearest thing to a central deity was the Old Woman ('' Sedna''), who lived beneath the sea. The waters, a central food source, were believed to contain great gods.
Inuit practiced a form of shamanism based on animist
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in ...
principles. They believed that all things had a form of spirit, including humans, and that to some extent these spirits could be influenced by a pantheon of supernatural entities that could be appeased when one required some animal or inanimate thing to act in a certain way. The ''angakkuq'' of a community of Inuit was not the leader, but rather a sort of healer and psychotherapist
Psychotherapy (also psychological therapy, talk therapy, or talking therapy) is the use of Psychology, psychological methods, particularly when based on regular Conversation, personal interaction, to help a person change behavior, increase hap ...
, who tended wounds and offered advice, as well as invoking the spirits to assist people in their lives. Their role was to see, interpret and exhort the subtle and unseen. ''Angakkuit'' were not trained; they were held to be born with the ability and recognized by the community as they approached adulthood.
Inuit religion
Inuit religion is the shared spiritual beliefs and practices of the Inuit, an indigenous people from Alaska, northern Canada, Greenland, and parts of Siberia. Their religion shares many similarities with some Alaska Native religions. Traditional ...
was closely tied to a system of rituals integrated into the daily life of the people. These rituals were simple but held to be necessary. According to a customary Inuit saying, "The great peril of our existence lies in the fact that our diet consists entirely of souls".
By believing that all things, including animals, have souls like those of humans, any hunt that failed to show appropriate respect and customary supplication would only give the liberated spirits cause to avenge themselves.
The harshness and unpredictability of life in the Arctic ensured that Inuit lived with concern for the uncontrollable, where a streak of bad luck could destroy an entire community. To offend a spirit was to risk its interference with an already marginal existence. Inuit understood that they had to work in harmony with supernatural powers to provide the necessities of day-to-day life.
Demographics
In total, there are about 155,000 Inuit living in four countries, Canada, Greenland, Denmark and the United States. * * * * * * * * * * * * *Canada
, there were 70,540 people identifying as Inuit living in Canada. This was up from the2016 Canadian census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial census. ...
count of 65,025 people. Over two thirds (48,695 people or ) of Inuit lived in one of the four regions comprising Inuit Nunangat
Inuit Nunangat (; ), formerly Inuit Nunaat (), is the homeland of the Inuit in Canada. This Arctic homeland consists of four Northern Canada, northern Canadian regions called the Inuvialuit Settlement Region (, home of the Inuvialuit and th ...
(Nunavut, Nunavik, Nunatsiavut, and the Inuvialuit Settlement Region) and 21,810 people or . From 2016 to 2021, the Inuit population grew by inside Inuit Nunangat and outside of the Inuit homelands.
The largest population of Inuit in Canada live in Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the Nunavut Land Claims Agr ...
with 30,865 Inuit out of a total population of 36,858 residents. In Nunavut, Inuit population forms a majority in all communities and is the only jurisdiction of Canada where Indigenous peoples form a majority. Between 2016 and 2021, the Inuit population of Nunavut grew by
, there were 15,800 Inuit living in Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
. The majority, about 12,595, live in Nunavik
Nunavik (; ; ) is an area in Canada which comprises the northern third of the province of Quebec, part of the Nord-du-Québec region and nearly coterminous with Kativik. Covering a land area of north of the 55th parallel, it is the homelan ...
. Inuit population of Nunavik grew between the 2016 and 2021 censuses. This was the fastest growth among all four regions of Inuit Nunangat.
Canadian census found there were 7,330 Inuit living in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
including 2,090 who live in Nunatsiavut
Nunatsiavut (; ) is an autonomous area claimed by the Inuit in Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. The settlement area includes territory in Labrador extending to the Quebec border. In 2002, the Labrador Inuit Association submitted a proposal for ...
. In Nunatsiavut, the Inuit population showed a decrease of between 2016 and 2021.
, there were 4,155 Inuit living in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
. The majority, 3,145, live in the six communities of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region
The Inuvialuit Settlement Region, abbreviated as ISR (; ), located in Canada's western Arctic, was designated in 1984 in the Inuvialuit Final Agreement by the Government of Canada for the Inuvialuit (''the real people''). It spans , including ...
. Inuit population growth in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region was between 2016 and 2021.
Outside of Inuit Nunangat, Inuit population was 21,810 . This was a growth of between the 2016 and 2021 censuses. Of those Inuit living outside of Inuit Nunangat lived in Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (), is the list of regions of Canada, region of Eastern Canada comprising four provinces: New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landma ...
( in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the populatio ...
), lived in Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, live in the Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provin ...
, lived in Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, lived in British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that ...
and in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
and Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
.
Included in the population of Newfoundland and Labrador outside of Inuit Nunangat is the unrecognized Inuit territory of NunatuKavut
NunatuKavut () is a proposed NunatuKavummiut territory in central and southern Labrador. The region proposed by the NunatuKavut Community Council (NCC) extends from north of the community of Makkovik in Nunatsiavut to south of the community of ...
where about 6,000 NunatuKavummiut
NunatuKavummiut (or People of NunatuKavut) are an Indigenous collective descended from Inuit and European people in central to southern Labrador. They have also been called the Southern Inuit, Inuit-Métis and Labrador Métis. While some Nunatu ...
(formerly known as "Labrador-metis") reside in southern Labrador
Labrador () is a geographic and cultural region within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is the primarily continental portion of the province and constitutes 71% of the province's area but is home to only 6% of its populatio ...
. The numbers are not projected to rise in any significant way because of the enrollment requirements, which require proof Inuit ancestry and demonstrated connection with NunatuKavut society.
Greenland
According to a 2024 estimate in the ''CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA; ) is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States tasked with advancing national security through collecting and analyzing intelligence from around the world and ...
World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the United States' Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print ver ...
'', Inuit population of Greenland is 88 per cent (50,878) out of a total of 57,751 people. Like Nunavut, the population lives throughout the habitable areas of the region.
Denmark
The population size ofGreenlandic people in Denmark
Greenlandic people in Denmark (; also known as Greenlandic Danes) are residents of Denmark with Greenlanders, Greenlandic or Greenlandic Inuit heritage. According to StatBank Greenland, as of 2020, there were 16,780 people born in Greenland livin ...
varies from source to source between 15,000 and 20,000. According to 2023 figures from Statistics Denmark
Statistics Denmark () is a Danish governmental organization under the Ministry of the Interior and Housing, reporting to the Minister of Economic and Internal Affairs. The organization is responsible for creating statistics on the Danish society ...
, there are 17,067 people residing in Denmark of Greenlandic Inuit ancestry. Most travel to Denmark for educational purposes, and many remain after finishing their education, which results in the population being mostly concentrated in the big four educational cities of Copenhagen
Copenhagen ( ) is the capital and most populous city of Denmark, with a population of 1.4 million in the Urban area of Copenhagen, urban area. The city is situated on the islands of Zealand and Amager, separated from Malmö, Sweden, by the ...
, Aarhus
Aarhus (, , ; officially spelled Århus from 1948 until 1 January 2011) is the second-largest city in Denmark and the seat of Aarhus municipality, Aarhus Municipality. It is located on the eastern shore of Jutland in the Kattegat sea and app ...
, Odense
Odense ( , , ) is the third largest city in Denmark (after Copenhagen and Aarhus) and the largest city on the island of Funen. As of 1 January 2025, the city proper had a population of 185,480 while Odense Municipality had a population of 210, ...
, and Aalborg
Aalborg or Ålborg ( , , ) is Denmark's List of cities and towns in Denmark, fourth largest urban settlement (behind Copenhagen, Aarhus, and Odense) with a population of 119,862 (1 July 2022) in the town proper and an Urban area, urban populati ...
, which all have vibrant Greenlandic communities and cultural centers (Kalaallit Illuutaat).
United States
According to the 2000 United States Census there were a total of 16,581 Inuit / Inupiat living throughout the country. The majority, about 14,718, live in the state ofAlaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
. According to 2019-based U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the U ...
data, there are 700 Alaskan Natives in Seattle
Seattle ( ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Washington and in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. With a population of 780,995 in 2024, it is the 18th-most populous city in the United States. The city is the cou ...
, many of whom are Inuit and Yupik, and almost 7,000 in Washington state
Washington, officially the State of Washington, is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is often referred to as Washington State to distinguish it from the national capital, both named after George Washington ...
.
Governance
 The
The Inuit Circumpolar Council
The Inuit Circumpolar Council (ICC; formerly the Inuit Circumpolar Conference) is a multinational non-governmental organization (NGO) and Indigenous Peoples' Organization (IPO) representing the 180,000 Inuit and Yupik (sometimes referred to a ...
is a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
-recognized non-governmental organization
A non-governmental organization (NGO) is an independent, typically nonprofit organization that operates outside government control, though it may get a significant percentage of its funding from government or corporate sources. NGOs often focus ...
(NGO), which defines its constituency as Canada's Inuit and Inuvialuit
The Inuvialuit (sing. Inuvialuk; ''the real people'') or Western Canadian Inuit are Inuit who live in the western Canadian Arctic region. They, like all other Inuit, are descendants of the Thule who migrated eastward from Alaska. Their homelan ...
, Greenland's Kalaallit Inuit, Alaska's Inupiat and Yup'ik
The Yupʼik or Yupiaq (sg & pl) and Yupiit or Yupiat (pl), also Central Alaskan Yupʼik, Central Yupʼik, Alaskan Yupʼik ( own name ''Yupʼik'' sg ''Yupiik'' dual ''Yupiit'' pl; Russian: Юпики центральной Аляски), are an ...
, and Russia's Siberian Yupik
Siberian Yupiks, or Yuits (), are a Yupik peoples, Yupik people who reside along the coast of the Chukchi Peninsula in the far Russian Far East, northeast of the Russia, Russian Federation and on St. Lawrence Island in Alaska. They speak Si ...
, despite the last two neither speaking an Inuit dialect or considering themselves "Inuit". Nonetheless, it has come together with other circumpolar cultural and political groups to promote Inuit and other northern people in their fight against ecological
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely re ...
problems such as climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
which disproportionately affects Inuit population. The Inuit Circumpolar Council is one of the six group of Arctic Indigenous peoples that have a seat as a so-called "Permanent Participant" on the Arctic Council
The Arctic Council is a high-level intergovernmental forum that addresses issues faced by the Arctic governments and the indigenous people of the Arctic region. At present, eight countries exercise sovereignty over the lands within the Arctic ...
, an international high level forum in which the eight Arctic Countries (United States, Canada, Russia, Denmark, Iceland, Norway, Sweden and Finland) discuss Arctic policy. On 12 May 2011, Greenland's Prime Minister Kuupik Kleist
Jakob Edvard Kuupik Kleist (born 31 March 1958) is a Greenlandic politician who served as the fourth prime minister of Greenland between 2009 and 2013. A member of the Inuit Ataqatigiit party, he was the first prime minister not affiliated with ...
hosted the ministerial meeting of the Arctic Council, an event for which the American Secretary of State Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, lawyer and diplomat. She was the 67th United States secretary of state in the administration of Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, a U.S. senator represent ...
came to Nuuk, as did many other high-ranking officials such as Russian Foreign Minister Sergei Lavrov
Sergey Viktorovich Lavrov (, ; born 21 March 1950) is a Russian diplomat who has served as Minister of Foreign Affairs since 2004. He is the longest-serving Russian foreign minister since Andrei Gromyko during the Soviet Union.
Lavrov was b ...
, Swedish Foreign Minister Carl Bildt
Nils Daniel Carl Bildt (born 15 July 1949) is a Swedish politician and diplomat who served as Prime Minister of Sweden from 1991 to 1994. He led the Moderate Party from 1986 to 1999, appearing as its lead candidate in four general elections, b ...
and Norwegian Foreign Minister Jonas Gahr Støre
Jonas Gahr Støre (; born 25 August 1960) is a Norwegian politician who has served as the prime minister of Norway since 2021.
He has been Leader of the Labour Party since 2014. He served under Prime Minister Jens Stoltenberg as Minister of ...
. At that event they signed the Nuuk Declaration.
Canada
WhileInuit Nunangat
Inuit Nunangat (; ), formerly Inuit Nunaat (), is the homeland of the Inuit in Canada. This Arctic homeland consists of four Northern Canada, northern Canadian regions called the Inuvialuit Settlement Region (, home of the Inuvialuit and th ...
is within Canada, and the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (Inuktitut syllabics: , meaning "Inuit are united in Canada"), previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada (Eskimo Brotherhood of Canada), is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit acro ...
oversees only the four official regions, there remains the unrecognized NunatuKavut
NunatuKavut () is a proposed NunatuKavummiut territory in central and southern Labrador. The region proposed by the NunatuKavut Community Council (NCC) extends from north of the community of Makkovik in Nunatsiavut to south of the community of ...
in southern Labrador.
 The
The Inuvialuit
The Inuvialuit (sing. Inuvialuk; ''the real people'') or Western Canadian Inuit are Inuit who live in the western Canadian Arctic region. They, like all other Inuit, are descendants of the Thule who migrated eastward from Alaska. Their homelan ...
are western Canadian Inuit who remained in the Northwest Territories when Nunavut split off. They live primarily in the Mackenzie River delta, on Banks Island
Banks Island is one of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago. Situated in the Inuvik Region, and part of the Inuvialuit Settlement Region, of the Northwest Territories, it is separated from Victoria Island to its east by the Prince of ...
, and parts of Victoria Island
Victoria Island () is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at in area, it is Canada's second-largest i ...
in the Northwest Territories. They are officially represented by the Inuvialuit Regional Corporation and, in 1984, received a comprehensive land claims settlement, the first in Northern Canada, with the signing of the Inuvialuit Final Agreement.
The TFN worked for ten years and, in September 1992, came to a final agreement with the Government of Canada. This agreement called for the separation of the Northwest Territories into an eastern territory whose Aboriginal population would be predominately Inuit, the future Nunavut, and a rump Northwest Territories in the west. It was the largest land claim
A land claim is "the pursuit of recognized territorial ownership by a group or individual". The phrase is usually only used with respect to disputed or unresolved land claims. Some types of land claims include Aboriginal title, aboriginal land cla ...
agreement in Canadian history. In November 1992, the ''Nunavut Final Agreement'' was approved by nearly 85 per cent of Inuit of what would become Nunavut. As the final step in this long process, the ''Nunavut Land Claims Agreement
The Nunavut Land Claims Agreement (NCLA, ) was signed on May 25, 1993, in Iqaluit, by representatives of the Tunngavik Federation of Nunavut (now Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated), the Government of Canada and the Government of the Northwest Terri ...
'' was signed on May 25, 1993, in Iqaluit by Prime Minister Brian Mulroney
Martin Brian Mulroney (March 20, 1939 – February 29, 2024) was a Canadian lawyer, businessman, and politician who served as the 18th prime minister of Canada from 1984 to 1993.
Born in the eastern Quebec city of Baie-Comeau, Mulroney studi ...
and by Paul Quassa, the president of Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated
Nunavut Tunngavik Incorporated (NTI; , ) is the legal representative of the Inuit of Nunavut for the purposes of native treaty rights and treaty negotiation. The presidents of NTI, Makivik Corporation, Nunatsiavut, and the Inuvialuit Regional Co ...
, which replaced the TFN with the ratification of the Nunavut Final Agreement. The Canadian Parliament
The Parliament of Canada () is the federal legislature of Canada. The Crown, along with two chambers: the Senate and the House of Commons, form the bicameral legislature.
The 343 members of the lower house, the House of Commons, are styled a ...
passed the supporting legislation in June of the same year, enabling the 1999 establishment of Nunavut as a territorial entity.
Greenland
In 1953, Denmark put an end to the colonial status of Greenland and grantedhome rule
Home rule is the government of a colony, dependent country, or region by its own citizens. It is thus the power of a part (administrative division) of a state or an external dependent country to exercise such of the state's powers of governan ...
in 1979 and in 2008 a self-government referendum was passed with 75 per cent approval. Although still a part of the Kingdom of Denmark
The Danish Realm, officially the Kingdom of Denmark, or simply Denmark, is a sovereign state consisting of a collection of constituent territories united by the Constitution of Denmark, Constitutional Act, which applies to the entire territor ...
(along with Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
proper and the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faroes) are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. Located between Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a populat ...
), Greenland, known as Kalaallit Nunaat in the Greenlandic language
Greenlandic, also known by its Endonym and exonym, endonym Kalaallisut (, ), is an Inuit languages, Inuit language belonging to the Eskaleut languages#Internal classification, Eskimoan branch of the Eskaleut languages, Eskaleut language family. ...
, maintains much autonomy today. Of a population of 56,000, 80 per cent of Greenlanders identify as Inuit. Their economy is based on fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
and shrimping.
The Thule people arrived in Greenland in the 13th century. There they encountered the Norsemen, who had established colonies there since the late 10th century, as well as a later wave of the Dorset people. Because most of Greenland is covered in ice, the Greenland Inuit (or Kalaallit) only live in coastal settlements, particularly the northern polar coast, the eastern Amassalik coast and the central coasts of western Greenland.
Alaska
Inuit of Alaska are theIñupiat
The Inupiat (singular: Iñupiaq), also known as Alaskan Inuit, are a group of Alaska Natives whose traditional territory roughly spans northeast from Norton Sound on the Bering Sea to the northernmost part of the Canada–United States borde ...
who live in the Northwest Arctic Borough
Northwest Arctic Borough is a List of boroughs and census areas in Alaska, borough located in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 7,793, up from 7,523 in 2010. The borough seat is Kotze ...
, the North Slope Borough
The North Slope Borough is the northernmost borough in the US state of Alaska and, thus, the northernmost county or equivalent of the United States as a whole. As of the 2020 census, the population was 11,031. The borough seat and largest cit ...
and the Bering Strait
The Bering Strait ( , ; ) is a strait between the Pacific and Arctic oceans, separating the Chukchi Peninsula of the Russian Far East from the Seward Peninsula of Alaska. The present Russia–United States maritime boundary is at 168° 58' ...
region. Utqiagvik, the northernmost city in the United States, is in the Inupiat region. Their language is Iñupiaq.
Genetics
A genetic study published in ''Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'' in August 2014 examined a large number of remains from the Dorset culture
The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from to between and , that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset (now Kinngait) in ...
, Birnirk culture
The Birnirk culture was a prehistoric Inuit culture dating from the 6th to 12th centuries of the Chukchi Peninsula of Russia and the Alaska North Slope. The Birnirk culture first appeared on the American side of the Bering Strait, descending from ...
and the Thule people
The Thule ( , ) or proto-Inuit were the ancestors of all modern Inuit. They developed in coastal Alaska by 1000 AD and expanded eastward across northern Canada, reaching Greenland by the 13th century. In the process, they replaced people of the ...
. Genetic continuity was observed between Inuit, Thule and Birnirk, who overwhelmingly carried the maternal haplogroup A2a
A2A S.p.A. is an Italian company, organised as a ''società per azioni'', that generates, distributes, and markets renewable energy, electricity, gas, integrated water supply, and waste management services. The company has significant presence i ...
and were genetically very different from the Dorset. The evidence suggested that Inuit descend from the Birnirk of Siberia, who through the Thule culture expanded into northern Canada and Greenland, where they genetically and culturally completely replaced the Indigenous Dorset people some time after 1300 AD.
Inuit people tend to have the dry variant of human earwax.
Modern culture
 Inuit art, carving, print making, textiles and
Inuit art, carving, print making, textiles and Inuit throat singing
Inuit throat singing, or ''katajjaq'' (), is a distinct type of throat singing uniquely found among the Inuit. It is a form of musical performance, traditionally consisting of two women who sing duets in a close face-to-face formation with no i ...
, are very popular, not only in Canada but globally, and Inuit artists are widely known. Canada has adopted some of Inuit culture as national symbols, using Inuit cultural icons like the inuksuk in unlikely places, such as its use as a symbol at the 2010 Winter Olympics
The 2010 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XXI Olympic Winter Games () and also known as Vancouver 2010 (), were an international winter multi-sport event held from February 12 to 28, 2010 in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, with ...
in Vancouver. Respected art galleries display Inuit art, the largest collection of which is at the Winnipeg Art Gallery
The Winnipeg Art Gallery (WAG) is an art museum in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. Its permanent collection includes over 24,000 works from Canadian, Indigenous Canadian, and international artists. The museum also holds the world's largest collect ...
. Their traditional New Year is called '' Quviasukvik''.
Some Inuit languages, such as Inuktitut, appear to have a more secure future in Quebec and Nunavut. There are a number of Inuit, even those who now live in urban centres such as Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital city of Canada. It is located in the southern Ontario, southern portion of the province of Ontario, at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the cor ...
, Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
and Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Manitoba. It is centred on the confluence of the Red River of the North, Red and Assiniboine River, Assiniboine rivers. , Winnipeg h ...
, who have experienced living on the land in the traditional life style. People such as Legislative Assembly of Nunavut
The Legislative Assembly of Nunavut is the legislative assembly for the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The seat of the Assembly is the Legislative Building of Nunavut in Iqaluit.
Prior to the creation of Nunavut as a Canadian territory on ...
member, Levinia Brown and former Commissioner of Nunavut
The commissioner of Nunavut (; Inuinnaqtun: ''Kamisinauyuq Nunavunmut''; ) is the Government of Canada's representative in the territory of Nunavut. The current commissioner since January 14, 2021 is Eva Aariak who served as Premier of Nunavut, Pre ...
and the NWT, Helen Maksagak were born and lived the early part of their life "on the land". Inuit culture is alive and vibrant today in spite of the negative impacts of recent history.
An important biennial event, the Arctic Winter Games, is held in communities across the northern regions of the world, featuring traditional Inuit and northern sports as part of the events. A cultural event is also held. The games were first held in 1970, and while rotated usually among Alaska, Yukon and the Northwest Territories, they have also been held in Schefferville
Schefferville () is a town in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. Schefferville is in the heart of the Naskapi and Innu territory in northern Quebec, less than 2 km (1¼ miles) from the border with Labrador o ...
, Quebec, in 1976, in Slave Lake
Slave Lake is a town in northern Alberta, Canada that is surrounded by the Municipal District of Lesser Slave River No. 124. It is approximately northwest of Edmonton. It is located on the southeast shore of Lesser Slave Lake at the junction ...
, Alberta, and a joint Iqaluit, Nunavut-Nuuk
Nuuk (; , formerly ) is the capital and most populous city of Greenland, an autonomous territory in the Kingdom of Denmark. Nuuk is the seat of government and the territory's largest cultural and economic center. It is also the seat of gove ...
, Greenland staging in 2002. In other sporting events, Jordin Tootoo
Jordin John Kudluk Tootoo (; born February 2, 1983) is a Canadian former professional hockey player, who played for the Nashville Predators, Detroit Red Wings, New Jersey Devils and Chicago Blackhawks. Of Inuit, Ukrainian and English descent, h ...
became the first Inuk to play in the National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; , ''LNH'') is a professional ice hockey league in North America composed of 32 teams25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. The NHL is one of the major professional sports leagues in the United States and Cana ...
in the 2003–2004 season, playing for the Nashville Predators
The Nashville Predators (colloquially referred to as the Preds) are a professional ice hockey team based in Nashville, Tennessee. The Predators compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Central Division (NHL), Central Divisio ...
.
 Although Inuit life has changed significantly over the past century, many traditions continue. '' Inuit Qaujimajatuqangit'', or
Although Inuit life has changed significantly over the past century, many traditions continue. '' Inuit Qaujimajatuqangit'', or traditional knowledge
Traditional knowledge (TK), indigenous knowledge (IK), folk knowledge, and local knowledge generally refers to knowledge systems embedded in the cultural traditions of regional, indigenous, or local communities.
Traditional knowledge includes ...
, such as storytelling, mythology, music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ...
, and dancing remain important parts of the culture. Family and community are very important. The Inuktitut language is still spoken in many areas of the Arctic and is common on radio and in television programming.
Well-known Inuit politicians include Premier of Nunavut
The premier of Nunavut (; Inuinnaqtun: ''Hivuliqti Nunavunmi''; ) is the first minister for the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The premier is the territory's head of government, although their powers are somewhat more limited than those of a pr ...
, P.J. Akeeagok, Lori Idlout
Lori Idlout () (born March 28, 1974) is a Canadian politician who has served as Member of Parliament (Canada), member of parliament for the riding of Nunavut (electoral district), Nunavut in the House of Commons of Canada since 2021. She is a m ...
, member of parliament for the riding of Nunavut, Eva Aariak
Eva Qamaniq Aariak (, ; born January 10, 1955) is a Canadian Inuit, Inuk politician, who was elected in the 2008 Nunavut general election, 2008 territorial election to represent the Electoral district (Canada), electoral district of Iqaluit Ea ...
, Commissioner of Nunavut
The commissioner of Nunavut (; Inuinnaqtun: ''Kamisinauyuq Nunavunmut''; ) is the Government of Canada's representative in the territory of Nunavut. The current commissioner since January 14, 2021 is Eva Aariak who served as Premier of Nunavut, Pre ...
and Múte Bourup Egede
Múte Inequnaaluk Bourup Egede (; born 11 March 1987) is a Greenlandic politician who served as the 7th Prime Minister of Greenland from 2021 to 2025. He has also served as Chairman of the Inuit Ataqatigiit since December 2018, and a Member of t ...
, Prime Minister of Greenland
The prime minister of Greenland (; ), also known as the premier of Greenland,Members of the Cabinet
G ...
. Leona Aglukkaq, former MP, was the first Inuk to be sworn into the Canadian Federal Cabinet as Health Minister in 2008. In May 2011 after being re-elected for her second term, Aglukkaq was given the additional portfolio of Minister of the Canadian Northern Economic Development Agency. In July 2013 she was sworn in as the minister of the environment.
G ...
 Visual and performing arts are strong features of Inuit culture. In 2002 the first
Visual and performing arts are strong features of Inuit culture. In 2002 the first feature film
A feature film or feature-length film (often abbreviated to feature), also called a theatrical film, is a film (Film, motion picture, "movie" or simply “picture”) with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole present ...
in Inuktitut, '' Atanarjuat: The Fast Runner'', was released worldwide to great critical and popular acclaim. It was directed by Zacharias Kunuk
Zacharias Kunuk (, born November 27, 1957) is a Canadian Inuk producer and director, most notable for his film '' Atanarjuat: The Fast Runner.'' It is the first Canadian dramatic feature film produced entirely in Inuktitut with an all Indige ...
, and written, filmed, produced, directed, and acted almost entirely by Inuit of Igloolik. In 2009, the film '' Le Voyage D'Inuk'', a Greenlandic-language feature film, was directed
Direct may refer to:
Mathematics
* Directed set, in order theory
* Direct limit of (pre), sheaves
* Direct sum of modules, a construction in abstract algebra which combines several vector spaces
Computing
* Direct access (disambiguation), a ...
by Mike Magidson and co-written by Magidson and French film producer Jean-Michel Huctin. One of the most famous Inuit artists is Pitseolak Ashoona. Susan Aglukark
Susan Aglukark, ( Inuktitut syllabics: ᓲᓴᓐ ᐊᒡᓘᒃᑲᖅ ''suusan agluukkaq''; born 27 January 1967) is a Canadian singer whose blend of Inuit folk music traditions with country and pop songwriting has made her a major recording st ...
is a popular singer. Mitiarjuk Attasie Nappaaluk worked at preserving Inuktitut and wrote one of the first novels ever published in that language. In 2006, Cape Dorset
Kinngait (Inuktitut meaning 'high mountain' or 'where the hills are'; Syllabics: ᑭᙵᐃᑦ), known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island ...
was hailed as Canada's most artistic city, with 23 per cent of the labor force employed in the arts. Inuit art such as soapstone carvings is one of Nunavut's most important industries. Ada Eyetoaq was an Inuk artist who made miniature sculptures out of soapstone.
Recently, there has been an identity struggle among the younger generations of Inuit, between their traditional heritage and the modern society which their cultures have been forced to assimilate into in order to maintain a livelihood. With current dependence on modern society for necessities, (including governmental jobs, food, aid, medicine, etc.), Inuit have had much interaction with and exposure to the societal norms
A social norm is a shared standard of acceptable behavior by a group. Social norms can both be informal understandings that govern the behavior of members of a society, as well as be codified into rules and laws. Social normative influences or s ...
outside their previous cultural boundaries. The stressors regarding the identity crisis
In psychology, identity crisis is a stage in Erik Erikson's theory of personality development. This stage happens during adolescence. It is a period of deep reflection and examination of various perspectives on oneself.
The Erikson's stages of ps ...
among teenagers have led to disturbingly high numbers of suicide.
A series of authors have focused upon the increasing myopia
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurry, while close objects appear normal. ...
in the youngest generations of Inuit. Myopia was almost unknown prior to Inuit adoption of Western culture
Western culture, also known as Western civilization, European civilization, Occidental culture, Western society, or simply the West, refers to the Cultural heritage, internally diverse culture of the Western world. The term "Western" encompas ...
. Principal theories are the change to a Western style diet with more refined foods, and extended education.
David Pisurayak Kootook was awarded the Meritorious Service Cross, posthumously, for his heroic efforts in a 1972 plane crash. Other notable Inuit include the freelance journalist Ossie Michelin, whose iconic photograph of the activist Amanda Polchies
Amanda Polchies is a Lakota Sioux and Mikmaq woman who lives in Elsipogtog First Nation. She became known for an iconic photograph of her, holding aloft an eagle feather while facing down a line of police, as she participated in an anti- frackin ...
went viral after the 2013 anti-fracking protests at Elsipogtog First Nation
Elsipogtog First Nation (), formerly called the Big Cove Band, is a Miꞌkmaq First Nations band government in New Brunswick, Canada. The First Nation's territory comprises Richibucto Reserve #15, lying southwest of Five Rivers, New Brunswic ...
.
Notes
References
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * Also at * * * * * * * *External links
Inuit Circumpolar Council
Inuit Circumpolar Council Greenland
Inuit Circumpolar Council Alaska
National Inuit Organization in Canada
Inuit Treaty Project
Inuit Atlas Project
{{Authority control Ethnic groups in Canada History of Indigenous peoples of North America Hunter-gatherers of Canada Hunter-gatherers of the Arctic Hunter-gatherers of the United States Indigenous peoples in Atlantic Canada Indigenous peoples in Northern Canada